Abstract
Background
Anti-malarial drug resistance is still a major threat to malaria elimination in the Great Mekong Sub-region. Plasmodium vivax parasites resistant to anti-malarial drugs are now found in Myanmar. Molecular surveillance on drug resistance genes in P. vivax parasites from northeastern Myanmar was aimed at estimating the underlying drug resistance in this region.
Methods
Blood samples from patients with vivax malaria were collected from Laiza city in northeastern Myanmar in 2020. Drug resistance genes including Pvcrt-o, Pvmdr1, Pvdhfr and Pvdhps were amplified and sequenced. Genetic polymorphisms and haplotypes were analysed to evaluate the prevalence of mutant alleles associated with drug resistance.
Results
A total of 149 blood samples from P. vivax patients were collected. The prevalence of Pvmdr1 mutations at codons 958 and 1076 was 100.0% and 52.0%, respectively, whereas no single nucleotide polymorphism was present at codon 976. The proportions of single and double mutant types were 48.0% and 52.0%, respectively. A K10 “AAG” insertion in the Pvcrt-o gene was not detected. Mutations in Pvdhfr at codons 57, 58, 61, 99 and 117 were detected in 29.9%, 54.3%, 27.6%, 44.9% and 55.1% of the samples, respectively. Wild type was predominant (46.3%), followed by quadruple and double mutant haplotypes. Of three types of tandem repeat variations of Pvdhfr, Type B, with three copies of GGDN repeats, was the most common. Pvdhps mutations were only detected at codons 383 and 553 and the wild type Pvdhps was dominant (78.0%). Eleven haplotypes were identified when combining the mutations of Pvdhfr and Pvdhps, among which the predominant one was the wild type (33.9%), followed by double mutant alleles S58R/S117N /WT (24.6%).
Conclusions
This study demonstrated resistant P. vivax phenotypes exists in northeastern Myanmar. Continued surveillance of drug resistance markers is needed to update treatment guidelines in this region.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Plasmodium vivax, the most geographically widespread human malaria parasite, causes significant morbidity in Southeast Asia, the Western Pacific, Central and South America, and parts of Africa [1]. There were an estimated 2.5 billion people at risk of P. vivax infection worldwide and 6.4 million clinical vivax malaria cases in 2019, mainly distributed in Southeast Asia [2]. In the past 20 years, the burden of P. vivax malaria has decreased dramatically, with many countries in the Asia-Pacific and the Americas reporting reductions of 90% in the number of clinical cases [2]. As a consequence, 34 countries are actively attempting to eliminate malaria, and countries in Central America and East Asia have declared their intention to eliminate malaria from their regions by 2025 and 2030, respectively [3, 4].
Myanmar, formerly Burma, has the heaviest malaria burden in the Greater Mekong Sub-region (GMS), with more cases and deaths than the rest of the region combined [2]. In recent years, Myanmar has made significant progress in reducing malaria morbidity and mortality [5,6,7]. Driven by the emergence and spread of artemisinin resistance in the GMS, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared their goal to eliminate malaria in the GMS by 2030 [8]. The National Plan for Malaria Elimination in Myanmar 2016–2030 was developed with the goal of decreasing the annual parasite index (API) to < 1 in all states/regions by 2020, interrupting the transmission of falciparum malaria in all states/regions by 2025 and eliminating malaria nationwide by 2030 [5]. However, conflict-affected settings and regions with high population mobility have posed challenges to malaria elimination [9].
Plasmodium vivax resistance to different anti-malarial drugs, including chloroquine (CQ), mefloquine, sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine (SP), has been reported in many countries or regions [10,11,12,13,14,15]. Molecular surveillance of drug resistance markers, as one of the tools in malaria surveillance, has been widely performed throughout the world [16]. Several candidate drug resistance genes in P. vivax parasites have been identified [17]. Plasmodium vivax chloroquine resistance transporter (Pvcrt) and the P. vivax multidrug resistance transporter (Pvmdr1) have been confirmed to be the Plasmodium falciparum orthologs involving CQ resistance genes [18, 19]. The Pvcrt-o gene was characterized nearly two decades ago [19]; it is similar to its P. falciparum orthologue and has an intron-rich gene structure with 14 exons that encodes a protein with 451 amino acids and 10 membrane domains [20]. Sequence polymorphism is relatively limited in the Pvcrt-o locus but a lysine (AAG) insertion at amino acid position 10 (K10), which was initially discovered in Southeast Asian strains, has been suggested to be associated with CQ resistance [21]. Since then, this polymorphism has been observed in both Southeast Asian and South American parasites [17, 22, 23]. The Pvmdr1 gene encodes a transmembrane protein of the parasite’s digestive vacuole with 12 transmembrane domains and 1464 amino acids, and was characterized in 2005 [24].
Sequencing of Pvmdr1 genes from several regions of the world has revealed more than fifty polymorphisms, as well as copy number variants (CNVs). Six SNPs have been reported at high frequency in multiple studies in regions with reported drug resistance: S513R, G698S, M908L, T958M, Y976F and F1076L. Among these, the two most common mutations were Y976F and F1076L. The essential enzymes dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS) and dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase (DHFR-TS) are involved in folate synthesis and are targets of sulfadoxine and pyrimethamine, respectively [14, 25]. SP has been used to treat P. falciparum for a long time, but it is primarily used for intermittent preventive treatment in pregnancy (IPTp) and IPT for infants (IPTi), and seasonal malaria chemoprevention combining with amodiaquine in some regions of Africa owing to its widespread resistance [26,27,28].
CQ is also used to treat vivax malaria in Southeast Asia, the prevalence of high CQ-resistant falciparum malaria resulted for a time in the widespread use of SP, which was available widely in areas where malaria was endemic and was still a first-line treatment in the adjacent countries Laos and Myanmar [29]. However, CQ and SP resistant P. falciparum and P. vivax were reported in Myanmar several decades ago, especially in southern Myanmar and at the border between Myanmar and Thailand [29,30,31,32,33,34,35]. Recently, increasing clinical failures after CQ treatment have been reported in multiple regions of Myanmar [36, 37]. Currently, the first-line treatment for P. vivax in Myanmar is CQ combined with primaquine (PQ) [5]. In northeastern Myanmar, the treatment efficacy of CQ was found to be relatively high, with a cumulative rate of parasite recurrence less than 3% [35]. The northernmost state in Myanmar, with a long border of almost 2000 km with Tibet and Yunnan Province in China, mainly in Kachin State, also called Jinghpaw Mung, where malaria has a relatively high rate of transmission [6], resulting from relatively low access to health services and difficulties in deploying interventions to hard-to-reach communities [38, 39]. Limited data have defined the molecular epidemiology of P. vivax resistance markers in northeastern Myanmar. In this study, genetic polymorphisms in genes potentially associated with drug resistance in P. vivax parasites from northeastern Myanmar were analysed to estimate the underlying drug resistance, with the aim of implementing an appropriate drug policy in this region.
Methods
Study site
Samples were collected from central hospitals and community clinics in Laiza (24° 45′ 36″ N, 97° 33′ 48″ E), a remote city in Kachin State in northeastern Myanmar, along the China-Myanmar border. This region is mountainous and its climate is defined as subtropical, with a dry season from October to April and a rainy season from May to September. In recent years, malaria cases have declined dramatically owing to cooperation between China and Myanmar towards malaria elimination [38, 40]. Local malaria transmission displayed a distinct seasonality with two peaks, a large peak in April-August and a small peak in November, except 2020 with a mall peak in September (Fig. 1). Four human malaria parasites including P. falciparum, P. vivax, Plasmodium ovale and Plasmodium malariae have been detected, and P. vivax is the predominant species, accounting for more than 90% [41]. On the other side of Laiza city is Nabang township, Yunnan, China, and there is no barrier along the border. A large number of immigrants from both countries cross the border frequently through Nabang port, one of the provincial ports along the border. Anopheles minimus is reported to be the dominant mosquito species in this area and most malaria infection occurred in population with subsistence activities associated with forest areas, such as logging, banana or rubber planting, and living in planting areas during the farming season or entire year [42].
Sample collection and DNA extraction
Blood samples were collected from P. vivax-infected patients prior to anti-malarial drug treatment in the central hospitals and community clinics in Laiza city from July to October 2020. Blood samples were spotted on filter paper (Whatman™ 903, GE Healthcare, USA), air dried, and then stored at − 20 °C before DNA extraction. Parasite DNA was extracted from the dried blood spots using a QIAamp DNA Mini Kit (Valencia, CA, USA) following the protocol. A polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplifying the small-subunit rRNA gene of Plasmodium spp. [43] was performed to confirm the positive samples and identify the species before the four genes were sequenced.
PCR amplification and sequencing
The Pvcrt-o gene was amplified by a single-round PCR and Pvmdr1, Pvdhps and Pvdhfr were amplified by nested PCR, as previously described [21, 34, 44,45,46]. The primers, cycling conditions and sizes of the PCR products are shown in Additional file 1. PCR reactions were performed in a 25 µL reaction mixture that contained 1 µL of genomic DNA, 12.5 µL 2×Taq Master Mix (TIANGEN, Beijing, China), 9.5 µL ddH2O and 10 µM primers. The amplification products were analysed by 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis and directly sequenced. The PCR products were purified using filter plates (Edge Biosystems, Gaithersburg, MD, USA) and sequenced on an ABI 3730XL automatic sequencer. Bidirectional sequencing was performed, and all the products were sequenced twice using independently amplified PCR products.
Data analysis
The output sequence data were assembled, edited and aligned using Geneious (version 2021.0.3) software, comparing the samples with the reference sequences of Pvmdr1 (accession number: AY618622), Pvdhps (accession number: XM001617159) and Pvdhfr (accession number: XM001615032) from GenBank. The known polymorphisms relating to drug resistance at codons 958, 976, 1076 of the Pvmdr1 gene and codons 57, 58, 61, 117, 173 of the Pvdhfr gene, and codons 382, 383, 553, 580 and 558 of Pvdhps gene, were evaluated for haplotype. The wild-type haplotypes of Pvmdr1, Pvdhfr and Pvdhps genes were T958/Y976/F1076, F57/S58/T61/R76/S117/I173 and S382/A383/A553/R580/V585, respectively. The mixed alleles were determined according to the emergence of two chromatogram peaks at one nucleotide site through Mutation Surveyor (Soft Genetics LLC., version 5.1, State College, PA, USA). The K10 “AAG” insertion in Pvcrt-o gene was determined by comparing with the reference strain of Sal-1 retrieved from Plasmodium data base [47]. The nucleotide sequences were submitted to GenBank under accession numbers MZ819186-MZ819695. SAS software (SAS Institute Inc, Version 9.2, Cary, NC, USA) was used for data processing and statistical analysis. The chi-squared test and Fisher’s exact test were used to evaluate differences among the different subgroups. P value < 0.05 were used to identify significant differences.
Results
Demographics of patients
A total of 149 blood samples from patients with P. vivax infections were collected before treatment from hospitals and clinics in Laiza city in 2020. All the patients were confirmed to be infected with P. vivax by microscopic examination of Giemsa-stained thick smears through passive case detection. They were treated for 3 days with CQ plus 14 days with PQ according to the anti-malarial drug policy in Myanmar. The majority of the patients were male (70.5%, 105/149) and aged 21–30 years (61.7%, 92/149). The median (range) age of the 149 patients was 22 years (ranges: 6–79) (Additional file 2).
Prevalence of Pvmdr1 mutations and K10-insertion in Pvcrt-o
Among the 149 samples, 82.6% (123/149) samples showed successful amplification of Pvmdr1. Mutations in codons 958 and 1076 were identified, with a prevalence of 100% and 52.0% (Fig. 2), respectively. No single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) was present in codon 976. Analysis of the Pvmdr1 haplotype prevalence showed that all the isolates were of the mutant type. Appropriately half of them carried a single T958M mutation or a double T958M/F1076L mutation, with a prevalence of 48.0% and 52.0%, respectively (Table 1). The percentage of 88.6% (132/149) samples were successfully sequenced in Pvcrt-o gene, and K10 “AAG” insertion was not detected in any of the 132 successfully sequenced samples (Table 1).
Polymorphisms in the Pvdhfr gene
The Pvdhfr amplicon was successfully sequenced for 85.2% (127/149) P. vivax isolates. Amino acid changes in Pvdhfr due to mutations in codons 57, 58, 61, 99 and 117 were detected in 29.9%, 54.3%, 27.6%, 44.9% and 55.1% of the samples, respectively. In addition, the I13L and I173L was not detected in present study. The wild type was predominant (46.3%, 57/127). The two most common point mutations were S58R (54.3%) and S117T/N (55.1%), followed by H99S (44.9%), F57L/I (29.9%), and T61M (27.6%). Among 70 isolates that carried a point mutation in codon 117, 38 carried 117T whereas 32 carrying 117 N. Moreover, 38 samples with a point mutation in codon 57 included 34 isolates carrying 57I and 4 carrying 57 L. A single mutation in codon 117 was identified in only one isolate. In addition, one synonymous mutation in codon 69, TAT to TAC (Y), was detected in two isolates.
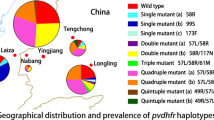
The haplotype analysis revealed seven distinct allelic forms of the Pvdhfr gene (Table 1); among them, the wild type was predominant. A quadruple-mutant haplotype, F57I/S58R/T61M/S117T (26.8%) and a double-mutant haplotype S58R/S117N (24.4%) were the two most common mutant types (Fig. 2). The single-mutant haplotype S117T, triple mutant types S58R/T61M/S117N and S58R/T61M/S117T and quadruple-mutant haplotype F57I/S58R/T61M/S117N were rare, being identified in only one, two, one, and one isolate, respectively.
Variations were identified in the central tandem repeat region between amino acid positions 88 and 103 of Pvdhfr (Fig. 2). Three types of tandem repeat variation were observed: Type A contained three copies of GGDN repeats, which was the same as the reference strain (accession number: X98123.1) designated as the wild type [48]; Type B also had three copies of GGDN repeats but showed a mutant allele in codon 99; Type C lacked six amino acids from positions 98 to 103.
Polymorphisms in the Pvdhps gene
A percentage of 88.6% (132/149) samples were successfully assessed for the Pvdhps gene. Pvdhps displayed limited polymorphisms and a relatively low prevalence of mutations. Nonsynonymous mutations were detected only in codons 383 and 553, with a prevalence of 20.5% (27/132) and 22.0% (29/132), respectively. The wild-type Pvdhps was dominant (78.0%) (Table 1; Fig. 2). Among the mutant types, the single-mutant A553G was rare and only detected in two isolates, whereas the double-mutant A383G/A553G was more frequent (20.5%, 27/132) (Table 1). Point mutations in codons 382, 580 and 585 were not observed in this study.
Analysis of allelic combinations of Pvdhfr and Pvdhps
Allelic combinations of the Pvdhfr and Pvdhps enzymes are responsible for the biosynthesis of folate and are potentially under similar drug pressure. A total of 118 isolates were sequenced successfully for both genes. The combinations of point mutations in the Pvdhfr and Pvdhps genes were analyzed in codons 57, 58, 61, and 117, and codons 383 and 553, respectively (Table 2). Eleven haplotypes were identified, and 33.9% (40/118) harboured the wild type, as the predominant allele. The double Pvdhfr mutant S58R/S117N and wild-type Pvdhps was the most common mutant haplotype, with a frequency of 24.6% (29/118). The quadruple-mutant F57I/S58R/T61M/S117T/WT, quadruple Pvdhfr mutant F57I/S58R/T61M/S117T and wild-type Pvdhps alleles or double Pvdhps mutant A383G/A553G were present at intermediate frequencies of 16.1%, 11.0% and 9.3%, respectively. Rare haplotypes including single-, triple-, quadruple-, and quintuple-mutant alleles, were detected in one isolate each (Table 2).
Discussion
Myanmar has the heaviest malaria burden in the GMS [49], and its geographical location between Southeast Asia and South Asia makes it a strategically important point for the potential spread of resistant parasites. In the present study, genetic polymorphisms in the Pvdhps and Pvdhfr genes associated with SP resistance and Pvcrt-o and Pvmdr1, two putative molecular markers of resistance to CQ, were analysed to evaluate the level of drug resistance in northeastern Myanmar.
Previous studies have shown that 48.3–72.7% of isolates carried Pvcrt-o K10 insertions in Myanmar between 2009 and 2016 [21, 34], and approximately 19% of the samples from Yunnan Province bordering Myanmar harbored this insertion [50]. In the present study, among all the tested samples, the K10 “AAG” insertion in the Pvcrt-o gene was not identified, in contrast to the results of previous studies. However, these results are validated to some extent with the high CQ cure rate for P. vivax along the China-Myanmar border [37, 51]. Interestingly, the K10 insertion is rarely observed in Thailand, the border region between Thailand and Myanmar, and the border region between Thailand and Cambodia [44, 52]. Other studies have reported no association between the K10 insertion and in vitro or ex vivo P. vivax CQ resistance [22, 53, 54]. Given the geographical genetic differences among parasite populations, the prevalence of the Pvcrt-o K10 insertion shows significant temporal and spatial heterogeneity [55] and the discrepancy may have resulted from differences in geography, population movement or sample size issues. Moreover, the role of the Pvcrt-o K10 insertion in CQ resistance in the parasite remains unknown.
Pvmdr1 T958M mutation is present in isolates from different countries having low to high levels of CQ resistance, thus T958M appears to be an allelic variant of the wild type and is most likely not associated with CQ resistance [24, 56]. In this study, Pvmdr1 T958M was present in all the tested samples, whereas F1076L occurred at an intermediate frequency, with a prevalence of 52.0%. However, Y976F was not detected in this study, although it has been frequently reported in other regions with a high prevalence [18, 21,22,23, 53, 57]. Another study also found that Y976F was rare in Myanmar [34], which supports the findings of this study. In addition, the association of the Pvmdr1 substitution Y976F with CQ-resistant P. vivax in vitro was confirmed in Papua, Indonesia [53], while other studies did not find such an association [24].
Pvdhfr and Pvdhps, the targets of SP drugs, disrupt folate synthesis in P. vivax [12, 14, 25]. Compared with Pfdhfr and Pfdhps in P. falciparum, Pvdhfr and Pvdhps are highly conserved in P. vivax [58]. The prevalence of the Pvdhfr mutation (53.7%) was lower in this study than in other studies from the China-Myanmar border, southern Thailand and western Myanmar [23, 44, 50, 52]. Moreover, amino acid changes in PvDHFR were detected in 27.6–55.1% of the isolates, which was also lower than the values in other studies [34, 44, 52]. With respect to Pvdhfr haplotypes, the double-mutant S58R/S117N and quadruple-mutant F57I/S58R/T61M/S117T were dominant in northeastern Myanmar and were also the most common types in Myanmar, Thailand and southern Yunnan Province, China [50, 52]. A previous study on the expression of mutant PvDHFR-TS in a yeast system demonstrated that these mutations confer high levels of pyrimethamine resistance, and the quadruple mutation resulted in a thousand-fold increase in resistance to pyrimethamine [17]. Interestingly, some researchers have hypothesized that the T61M mutation may be a compensatory mutation to offset possible fitness costs resulting from the carriage of other resistance mutations, because a triple Pvdhfr mutant (58R/61M/117T) resulted in susceptibilities similar to those of the wild-type to all drugs with the exception of pyrimethamine, for which this haplotype conferred a 58-fold increase in resistance. In this study, single mutations at residues 58 and 117 were rare, as was the triple mutation, but the double mutation S58R/S117N was more common. These results suggest that vivax parasites in northeastern Myanmar may be under low to medium drug pressure. In addition, the majority (74.8%) had three copies of tandem repeats in Pvdhfr gene and Type B was predominant (44.9%, 57/127), followed by Type A (29.9%) and Type C (25.2%). This pattern was different from that reported from southern China [50], which showed Type C as the main type (40.5%, 118/291), followed by Type B and Type A. However, the mechanism of action of the tandem repeat variants in pyrimethamine resistance remains unclear [44], as these variants are not present in the Pfdhfr gene in P. falciparum [59, 60].
Similar to SP resistance in P. falciparum, mutations in Pvdhps alone are thought to be insufficient to confer resistance to SP. Strains containing both the Pvdhps A383G and A553G mutations and mutant Pvdhfr alleles have been implicated in SP treatment failure [61]. The Pvdhps mutations exhibited much less diversity and lower prevalence in this study than in previous studies, which reported a high mutation prevalence (80–90%) in Pvdhps in Malaysia, Thailand, India, Indonesia, and China and high failure rates of SP treatment [14, 52, 62,63,64]. Additionally, the prevalence of Pvdhfr mutations in regions where P. vivax is the dominant parasite is lower than that in regions where P. falciparum and P. vivax are co-endemic; the reason for this may be that the pressure of SP treatment of P. falciparum can lead to co-selection of Pvdhfr mutant alleles, which could also occur for other drugs, including artemisinin partner drugs [63].
Recently, high treatment efficacy of CQ was found in Bangladesh, Bhutan, India and Nepal, but high failure rates of treatment with CQ were confirmed in some sites in Myanmar and Timor-Leste [65]. However, this study demonstrated that the frequency of mutant haplotypes in northeastern Myanmar was relatively low, whereas the frequency of the wild type was increasing. In addition, genetic polymorphisms were rarer than in other regions of Myanmar, as shown in previous reports as well. This result is consistent with the treatment efficacy of CQ reported from northeast Myanmar [35] and the China-Myanmar border [51]. These variations in drug resistance genes may suggest different drug selection pressures imposed on local P. vivax populations. The factors that influence the evaluation of drug resistance are not completely known, but drug pressure is probably a key element for the selection of resistant parasite mutants.
This study had limitations. First, Pvcrt-o and Pvmdr1 are only putative markers of CQ resistance and the Pvmdr1 copy number was not evaluated in this study. There was limited evidence for CQ resistance without in vitro susceptibility test of P. vivax isolates and in vivo therapeutic efficacy study to highlight therapeutic failure. Second, samples were collected only from Laiza city through passive case detection, which may not describe the whole picture of drug resistance in this region.
Conclusions
GMS has become a focus in the war against malaria after the emergence of artemisinin-resistant falciparum malaria, especially in remote areas along the Myanmar border. This study identified genetic polymorphisms in genes associated with drug resistance in P. vivax parasites in northeastern Myanmar, which indicated the risks associated with drug resistant P. vivax phenotypes, especially antifolate resistance. Therefore, continued surveillance of anti-malarial drug resistance markers is needed in northeastern Myanmar to inform case management and update treatment guidelines.
Availability of data and materials
The nucleotide sequences were submitted to GenBank under accession numbers MZ819186-MZ819695. The datasets analysed in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Price RN, Commons RJ, Battle KE, Thriemer K, Mendis K. Plasmodium vivax in the era of the shrinking P. falciparum map. Trends Parasitol. 2020;36:560–70.
WHO. World malaria report 2020. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2020.
Citizen News Service. East Asia Summit adopts unprecedented regional malaria goal. https://www.citizen-news.org/2014/11/east-asia-summit-adopts-unprecedented.html. 2014.
PAHO. Central America and Hispaniola seek to eliminate malaria by 2025. https://www3.paho.org/hq/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=8700:2013-paises-mesoamerica-espanola-analizan-iniciativa-alcanzar-eliminacion-malaria-2025&Itemid=40313&lang=en. 2013.
Myanmar National Malaria Control Programme (NMCP). Ministry of Health and Sports. National Strategic Plan 2016–2020 for intensifying malaria control and accelerating progress towards malaria elimination. https://apmen.org/sites/default/files/all_resources/National%20Strategic%20Plan_Myanmar_2016-2020.pdf. 2017.
Huang F, Zhang L, Xue JB, Zhou HN, Thi A, Zhang J, et al. From control to elimination: a spatial-temporal analysis of malaria along the China-Myanmar border. Infect Dis Poverty. 2020;9:158.
Aung PP, Thein ZW, Hein ZNM, Aung KT, Mon NO, Linn NYY, et al. Challenges in early phase of implementing the 1-3-7 surveillance and response approach in malaria elimination setting: a field study from Myanmar. Infect Dis Poverty. 2020;9:18.
WHO. Strategy for malaria elimination in the GMS (2015–2030). Geneva: World Health Organization; 2015. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/208203.
Win AYN, Maung TM, Wai KT, Oo T, Thi A, Tipmontree R, et al. Understanding malaria treatment-seeking preferences within the public sector amongst mobile/migrant workers in a malaria elimination scenario: a mixed-methods study. Malar J. 2017;16:462.
Amor D, Richards M. Mefloquine resistant P. vivax malaria in PNG. Med J Aust. 1992;156:883.
Baird JK, Wiady I, Fryauff DJ, Sutanihardja MA, Leksana B, Widjaya H, et al. In vivo resistance to chloroquine by Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium falciparum at Nabire, Irian Jaya, Indonesia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1997;56:627–31.
Hastings MD, Sibley CH. Pyrimethamine and WR99210 exert opposing selection on dihydrofolate reductase from Plasmodium vivax. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:13137–41.
Korsinczky M, Fischer K, Chen N, Baker J, Rieckmann K, Cheng Q. Sulfadoxine resistance in Plasmodium vivax is associated with a specific amino acid in dihydropteroate synthase at the putative sulfadoxine-binding site. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48:2214–22.
Hastings MD, Maguire JD, Bangs MJ, Zimmerman PA, Reeder JC, Baird JK, et al. Novel Plasmodium vivax dhfr alleles from the Indonesian Archipelago and Papua New Guinea: association with pyrimethamine resistance determined by a Saccharomyces cerevisiae expression system. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005;49:733–40.
Price RN, von Seidlein L, Valecha N, Nosten F, Baird JK, White NJ. Global extent of chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium vivax: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14:982–91.
WHO. Methods for surveillance of antimalarial drug efficacy. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2009.
Buyon LE, Elsworth B, Duraisingh MT. The molecular basis of antimalarial drug resistance in Plasmodium vivax. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2021;16:23–37.
Brega S, Meslin B, de Monbrison F, Severini C, Gradoni L, Udomsangpetch R, et al. Identification of the Plasmodium vivax mdr-like gene (pvmdr1) and analysis of single-nucleotide polymorphisms among isolates from different areas of endemicity. J Infect Dis. 2005;191:272–7.
Nomura T, Carlton JM, Baird JK, del Portillo HA, Fryauff DJ, Rathore D, et al. Evidence for different mechanisms of chloroquine resistance in 2 Plasmodium species that cause human malaria. J Infect Dis. 2001;183:1653–61.
Ferreira MU, Nobrega de Sousa T, Rangel GW, Johansen IC, Corder RM, Ladeia-Andrade S, et al. Monitoring Plasmodium vivax resistance to antimalarials: persisting challenges and future directions. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2021;15:9–24.
Lu F, Lim CS, Nam DH, Kim K, Lin K, Kim TS, et al. Genetic polymorphism in pvmdr1 and pvcrt-o genes in relation to in vitro drug susceptibility of Plasmodium vivax isolates from malaria-endemic countries. Acta Trop. 2011;117:69–75.
Noisang C, Meyer W, Sawangjaroen N, Ellis J, Lee R. Molecular detection of antimalarial drug resistance in Plasmodium vivax from returned travellers to NSW, Australia during 2008–2018. Pathogens. 2020;9:101.
Zhao Y, Wang L, Soe MT, Aung PL, Wei H, Liu Z, et al. Molecular surveillance for drug resistance markers in Plasmodium vivax isolates from symptomatic and asymptomatic infections at the China-Myanmar border. Malar J. 2020;19:281.
Sa JM, Nomura T, Neves J, Baird JK, Wellems TE, del Portillo HA. Plasmodium vivax: allele variants of the mdr1 gene do not associate with chloroquine resistance among isolates from Brazil, Papua, and monkey-adapted strains. Exp Parasitol. 2005;109:256–9.
Barnadas C, Tichit M, Bouchier C, Ratsimbasoa A, Randrianasolo L, Raherinjafy R, et al. Plasmodium vivax dhfr and dhps mutations in isolates from Madagascar and therapeutic response to sulphadoxine-pyrimethamine. Malar J. 2008;7:35.
WHO. Intermittent preventive treatment for infants using sulfadoxinepyrimethamine (SP-IPTi) for malaria control in Africa: Implementation field guide. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2011. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-IVB-11.07.
WHO. Seasonal malaria chemoprevention with sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine plus amodiaquine in children. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013.
WHO. Implementing malaria in pregnancy programs in the context of World Health Organization recommendations on antenatal care for a positive pregnancy experience. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018. https://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/implementing-malaria-pregnancy-programmes-brief/en/.
Luxemburger C, van Vugt M, Jonathan S, McGready R, Looareesuwan S, White NJ, et al. Treatment of vivax malaria on the western border of Thailand. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1999;93:433–8.
Myat Phone K, Myint O, Myint L, Thaw Z, Kyin Hla A, Nwe Nwe Y. Emergence of chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium vivax in Myanmar (Burma). Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1993;87:687.
Marlar T, Myat Phone K, Aye Yu S, Khaing Khaing G, Ma S, Myint O. Development of resistance to chloroquine by Plasmodium vivax in Myanmar. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1995;89:307–8.
Smithuis F, Shahmanesh M, Kyaw MK, Savran O, Lwin S, White NJ. Comparison of chloroquine, sulfadoxine/pyrimethamine, mefloquine and mefloquine-artesunate for the treatment of falciparum malaria in Kachin State, North Myanmar. Trop Med Int Health. 2004;9:1184–90.
Guthmann JP, Pittet A, Lesage A, Imwong M, Lindegardh N, Min Lwin M, et al. Plasmodium vivax resistance to chloroquine in Dawei, southern Myanmar. Trop Med Int Health. 2008;13:91–8.
Nyunt MH, Han JH, Wang B, Aye KM, Aye KH, Lee SK, et al. Clinical and molecular surveillance of drug resistant vivax malaria in Myanmar (2009–2016). Malar J. 2017;16:117.
Xu S, Zeng W, Ngassa Mbenda HG, Liu H, Chen X, Xiang Z, et al. Efficacy of directly-observed chloroquine-primaquine treatment for uncomplicated acute Plasmodium vivax malaria in northeast Myanmar: a prospective open-label efficacy trial. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2020;6:101499.
Htun MW, Mon NCN, Aye KM, Hlaing CM, Kyaw MP, Handayuni I, et al. Chloroquine efficacy for Plasmodium vivax in Myanmar in populations with high genetic diversity and moderate parasite gene flow. Malar J. 2017;16:281.
Yuan L, Wang Y, Parker DM, Gupta B, Yang Z, Liu H, et al. Therapeutic responses of Plasmodium vivax malaria to chloroquine and primaquine treatment in northeastern Myanmar. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59:1230–5.
Wang RB, Dong JQ, Xia ZG, Cai T, Zhang QF, Zhang Y, et al. Lessons on malaria control in the ethnic minority regions in Northern Myanmar along the China border, 2007–2014. Infect Dis Poverty. 2016;5:95.
Huang F, Takala-Harrison S, Liu H, Xu JW, Yang HL, Adams M, et al. Prevalence of clinical and subclinical Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax malaria in two remote rural communities on the Myanmar-China border. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2017;97:1524–31.
Lin ZR, Li SG, Sun XD, Guo XR, Zheng Z, Yang J, et al. Effectiveness of joint 3 + 1 malaria strategy along China-Myanmar cross border areas. BMC Infect Dis. 2021;21:1246.
Li P, Zhao Z, Xing H, Li W, Zhu X, Cao Y, et al. Plasmodium malariae and Plasmodium ovale infections in the China-Myanmar border area. Malar J. 2016;15:557.
Yu G, Yan G, Zhang N, Zhong D, Wang Y, He Z, et al. The Anopheles community and the role of Anopheles minimus on malaria transmission on the China-Myanmar border. Parasit Vectors. 2013;6:264.
Snounou G, Viriyakosol S, Zhu XP, Jarra W, Pinheiro L, do Rosario VE, et al. High sensitivity of detection of human malaria parasites by the use of nested polymerase chain reaction. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993;61:315–20.
Tantiamornkul K, Pumpaibool T, Piriyapongsa J, Culleton R, Lek-Uthai U. The prevalence of molecular markers of drug resistance in Plasmodium vivax from the border regions of Thailand in 2008 and 2014. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2018;8:229–37.
Barnadas C, Kent D, Timinao L, Iga J, Gray LR, Siba P, et al. A new high-throughput method for simultaneous detection of drug resistance associated mutations in Plasmodium vivax dhfr, dhps and mdr1 genes. Malar J. 2011;10:282.
Ding S, Ye R, Zhang D, Sun X, Zhou H, McCutchan TF, et al. Anti-folate combination therapies and their effect on the development of drug resistance in Plasmodium vivax. Sci Rep. 2013;3:1008.
PlasmoDB. Plasmodium genomics resource. http://plasmodb.org. Accessed 10 Jan 2022.
Eldin de Pecoulas P, Basco LK, Tahar R, Ouatas T, Mazabraud A. Analysis of the Plasmodium vivax dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase gene sequence. Gene. 1998;211:177–85.
WHO. World Malaria Report 2018. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018.
Wang X, Ruan W, Zhou S, Feng X, Yan H, Huang F. Prevalence of molecular markers associated with drug resistance of Plasmodium vivax isolates in Western Yunnan Province, China. BMC Infect Dis. 2020;20:307.
Liu H, Yang HL, Tang LH, Li XL, Huang F, Wang JZ, et al. Monitoring Plasmodium vivax chloroquine sensitivity along China-Myanmar border of Yunnan Province, China during 2008–2013. Malar J. 2014;13:364.
Noisang C, Prosser C, Meyer W, Chemoh W, Ellis J, Sawangjaroen N, et al. Molecular detection of drug resistant malaria in Southern Thailand. Malar J. 2019;18:275.
Suwanarusk R, Russell B, Chavchich M, Chalfein F, Kenangalem E, Kosaisavee V, et al. Chloroquine resistant Plasmodium vivax: in vitro characterisation and association with molecular polymorphisms. PLoS ONE. 2007;2:e1089.
Silva SR, Almeida ACG, da Silva GAV, Ramasawmy R, Lopes SCP, Siqueira AM, et al. Chloroquine resistance is associated to multi-copy pvcrt-o gene in Plasmodium vivax malaria in the Brazilian Amazon. Malar J. 2018;17:267.
Zhou X, Tambo E, Su J, Fang Q, Ruan W, Chen JH, et al. Genetic diversity and natural selection in 42 kDa region of Plasmodium vivax merozoite surface protein-1 from China-Myanmar endemic border. Korean J Parasitol. 2017;55:473–80.
Schousboe ML, Ranjitkar S, Rajakaruna RS, Amerasinghe PH, Morales F, Pearce R, et al. Multiple origins of mutations in the mdr1 gene-A putative marker of chloroquine resistance in P. vivax. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015;9:e0004196.
Kosaisavee V, Hastings I, Craig A, Lek-Uthai U. The genetic polymorphism of Plasmodium vivax genes in endemic regions of Thailand. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2011;4:931–6.
Hawkins VN, Joshi H, Rungsihirunrat K, Na-Bangchang K, Sibley CH. Antifolates can have a role in the treatment of Plasmodium vivax. Trends Parasitol. 2007;23:213–22.
de Pecoulas PE, Tahar R, Ouatas T, Mazabraud A, Basco LK. Sequence variations in the Plasmodium vivax dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase gene and their relationship with pyrimethamine resistance. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1998;92:265–73.
Lu F, Lim CS, Nam DH, Kim K, Lin K, Kim TS, et al. Mutations in the antifolate-resistance-associated genes dihydrofolate reductase and dihydropteroate synthase in Plasmodium vivax isolates from malaria-endemic countries. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2010;83:474–9.
Imwong M, Pukrittayakamee S, Cheng Q, Moore C, Looareesuwan S, Snounou G, et al. Limited polymorphism in the dihydropteroate synthetase gene (dhps) of Plasmodium vivax isolates from Thailand. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005;49:4393–5.
Huang B, Huang S, Su XZ, Tong X, Yan J, Li H, et al. Molecular surveillance of pvdhfr, pvdhps, and pvmdr-1 mutations in Plasmodium vivax isolates from Yunnan and Anhui provinces of China. Malar J. 2014;13:346.
Alam MT, Bora H, Bharti PK, Saifi MA, Das MK, Dev V, et al. Similar trends of pyrimethamine resistance-associated mutations in Plasmodium vivax and P. falciparum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007;51:857–63.
Imwong M, Pukrittakayamee S, Looareesuwan S, Pasvol G, Poirreiz J, White NJ, et al. Association of genetic mutations in Plasmodium vivax dhfr with resistance to sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine: geographical and clinical correlates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001;45:3122–7.
WHO. Artemisinin resistance and artemisinin-based combination therapy efficacy. Status report. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2019.
Acknowledgements
We thank all the participants who provided blood samples for this study.
Funding
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (No. 18ZR1443400), the National Important Scientific & Technological Project (2018ZX10101002–002), and the Fifth Round of Three-Year Public Health Action Plan of Shanghai (No. GWV-10.1-XK13).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FH conceived and designed the study. FH and YC conducted the laboratory work and data analysis. SL, PT, LJSP and LY collected the blood samples. HL and DYB provided technique support for the data collection and analysis. FH drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ethical Review Committee of National Institute of Parasitic Diseases, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention and the Ethics Committee of Laiza Central Ministry of Public Health.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1.
Primers and cycling conditions for amplification of Pvcrt-o, Pvmdr1, Pvdhps and Pvdhfr by a PCR assay.
Additional file 2: Table S2.
Demographics of patients included in this study.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, F., Li, S., Tian, P. et al. Genetic polymorphisms in genes associated with drug resistance in Plasmodium vivax parasites from northeastern Myanmar. Malar J 21, 66 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-022-04084-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-022-04084-y