Abstract
Background
The resistance of Plasmodium falciparum to artemisinin has been identified in Asia and some parts of Africa. The drug resistance of P. falciparum will be an obstacle to the successful elimination of malaria by 2025. Whole-genome sequencing of the artemisinin-resistant parasite line revealed mutations on the k13 gene associated with drug resistance in P. falciparum. To understand the artemisinin resistance of the imported P. falciparum cases from Africa, the mutations in the k13 gene in parasites from imported malaria cases in Guangxi Province were detected and the treatment efficiency of artesunate monotherapy was observed.
Methods
DNA was extracted from 319 blood samples from migrant workers with P. falciparum infection who returned to their hometown in Guangxi Province from Africa between 2014 and 2017. The k13-propeller gene was amplified by nested PCR, and sequencing, gene mutation frequency and geographic difference of imported P. falciparum cases were analysed by comparison with the wild-type strain. Of 319 patients, 158 were P. falciparum-infected and were treated with intravenous injection of artesunate and were observed, including the time of asexual stage clearance and the dose of artesunate used.
Results
Of the 319 P. falciparum samples, 12 samples had the k13-propeller mutation, and 11 point mutations were detected; 5 were non-synonymous mutations (T474I, A481T, A578S, V603E, G665S) and were not associated with artemisinin resistance. The clinical treatment observation showed that the median (IQR) dose of artesunate for peripheral blood parasite asexual stage clearance was 407.55 (360–510) mg, and the D3 parasite clearance rate was 70.25%, including the five k13-propeller mutations of P. falciparum. After 7 days of treatment, 98.73% of cases were cleared. Two cases were treated with artemisinin for 8 days with a 960-mg dose to completely clear the asexual parasite, but they did not have a mutation in the k13 gene.
Conclusions
Five mutations of the k13-propeller gene in 319 P. falciparum samples from patients returning from Africa were identified. The frequency of the k13-propeller mutants was low, and the mutations were not strongly associated with artemisinin resistance. The median (IQR) dose of artesunate monotherapy in actual clinical treatment to remove asexual parasite stages was 407.55 (360–510) mg, equivalent to D3–D4. Some P. falciparum cases without a k13-propeller mutation showed obvious delayed clearance of the parasite from peripheral blood.
Trial registration The diagnosis of malaria and the treatment of malaria-infected patients are the routine work of Centres for Disease Control and Prevention. Information on the patients was conveyed with the patient’s approval, and the research aim, methods, risks and benefits of the study were explained in detail to the patients
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The resistance of Plasmodium falciparum to artemisinin and its derivatives has attracted worldwide attention. The WHO reported a decreased sensitivity of P. falciparum to artemisinin and warned of the possibility and danger of its resistance in 2005 [1]. The resistance of P. falciparum to artemisinin was first reported in Thailand and the Cambodian border area of the Greater Mekong River Basin in Southeast Asia [2, 3], and within 10 years, the epidemic of artemisinin-resistant strains spread rapidly to the whole Mekong River Basin, resulting in great challenges to the prevention and treatment of malaria [4, 5].
Recent studies have confirmed that chromosome 13 is associated with P. falciparum drug resistance [6,7,8]. Studies found that the C580Y, R539T, Y493H, M476I, and F446I mutations of the k13 gene are closely related to the resistance of artemisinin [9, 10]. However, the mutations of the k13 gene vary in different regions. For example, in Cambodia, Vietnam, Laos, the C580Y mutation is the dominant mutation (has the highest prevalence at 50%); at the Thailand/Myanmar/China border, F446I is dominant, and there are a small number of C580Y mutations; and the most common mutation in Africa is A578S [11,12,13]. Although there is not sufficient evidence to suggest that resistance to artemisinin derivatives of P. falciparum originating in the Mekong River Basin has spread to Africa, South America, Oceania and East and Central Asia [14,15,16], the decrease in sensitivity to artemisinin in several cases recorded in Africa is not related to the mutation of k13 but to the severe infection in children [17,18,19]. However, P. falciparum imported into China from Equatorial Guinea in Africa has been found to be resistant to artemisinin [20] in vitro.
As a province of China, Guangxi has had no local cases of malaria reported since 2003 and is now in the early stage of malaria elimination [21]. In recent years, a large number of workers in Guangxi have travelled to Africa, mostly to engage in gold washing; the returning workers can bring malaria back to China [22]. Approximately 300 imported malaria cases are reported annually in Guangxi; more than 90% were imported from the African continent, and more than 60% were P. falciparum. Therefore, monitoring of the imported malaria, identification of anti-malaria drug resistance and case management are the main challenges in the present stage of malaria control, especially the monitoring and identification of drug resistance, which plays an important role in elimination. In this study, the P. falciparum k13 gene mutation characteristics of Chinese migrants from Africa and the effects of artesunate in practical clinical treatment were studied and observed, exploring the drug resistance of imported malaria from Africa and providing useful guidance for actual clinical treatment.
Methods
Sample collection and Plasmodium falciparum detection
Blood samples were obtained from 319 migrant workers with uncomplicated P. falciparum infection who returned from Africa to Guangxi Province between 2014 and 2017. Blood was collected before treatment, and thick and thin blood smear films were prepared and stained with 3% Giemsa for 40 min. The diagnosis of the microscopic examination was conducted by an experienced technician. The DNA was extracted from the blood samples using the QIAamp DNA Mini Kit (QIAGEN Inc., Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions and stored at − 20 °C for use in PCR assays. The diagnosis of P. falciparum was performed by nested PCR according to the Chinese industry standards (WS259-2015). Briefly, the first round amplified the Plasmodium spp. genus with the universal primers rPLU5/rPLU6 (rPLU5 5′-CCTGTTGTTGCCTTAAACTTC-3′ rPLU6 5′-TTAAAATTGTTGCAGTTAAAACG-3′). Then, nested PCR was performed with the P. falciparum specific primers rFAL1/rFAL2 (rFAL15′-TTAAACTGGTTTGGGAAAACCAAATATATT-3′ rFAL2 5′-ACACAATGAACTCAATCATGACTACCCGTC-3′).
k13-propeller gene amplification and sequencing
The k13-propeller gene of P. falciparum was amplified by the nested PCR method as previously described [23]. Briefly, first-round PCR was performed in a 20 μl reaction volume containing 1.0 μl each of the forward and reverse primers AF (GCCTTGTTGAAAGAAGCAGAA) and AR (CGCCATTTTCTCCTCCTGTA) (10 μmol/l) and 17 μl of KAPA 2G Robust Mix (JianLian Gene Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) and 1.0 μl of DNA template. Nested PCR was performed using a DNA Applied Biosystems 9700 thermal cycler (Life Technologies, Singapore). The PCR conditions were 95 °C for 15 min, followed by 30 cycles at 94 °C for 1 min, 59 °C for 1.5 min, and 72 °C for 2 min, and a final extension at 72 °C for 10 min. One microliter of the first-round product was used as the template in the second-round amplification, with the same cycling conditions as the first round. The amplified products were sent to XiangYin Biotechnology Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China) and sequenced using an ABI platform (3730XL).
Sequencing alignments and data analysis
The sequences were analysed by Mutation Surveyor 4.1 to remove the false positive and (or) false negative mutant sites and aligned to reference Pf3D7_1343700 (http://www.plasmodb.org) using Mega7 [24]. The k13-propeller allele frequency was also calculated.
Clinical observations
To observe the clearance of P. falciparum treatment with artesunate monotherapy, 158 of the 319 P. falciparum-infected patients in Shanglin County People’s Hospital between 2014 and 2017 were enrolled and analysed. The axillary temperature in these patients was more than 37.5 °C, the parasitaemia was between 1000 and 200,000/μl, and anti-malarial drugs were not taken at least 3 months before hospitalization. The asexual parasite clearance time and the dosage of artesunate were observed.
Artesunate (Gulin Pharmaceutical Co., China) at 2.4 mg/kg body weight was injected intravenously (IV bolus). Since all the patients were adults, they were given 120 mg daily according to the drug instructions. Thick and thin smears were taken on day 0 (before treatment) and during subsequent prescribed follow-up on days 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 until asexual parasite clearance was achieved. Patients were treated with oral dihydroartemisinin piperaquine (KBN, Zhejiang Pharmaceutical Co., China) for 2 days after the asexual parasite was undetectable and discharged from the hospital. Blood films were made using 3% Giemsa staining for 40 min and were independently read by two experienced microscopists to identify and calculate the number of parasites. The average of the two counts was taken as the parasite density. If the results of examination of malaria parasites between the two microscopists were inconsistent, nested PCR was used for final determination.
Results
Patient information
A total of 319 samples were collected from migrant workers from 23 countries in Africa during 2014–2017. Most of the patients suffered from fever, chills, sweating, headache, and diarrhoea, and few had serious complications. Of them, 42 were collected in 2014, 120 were obtained in 2015, 89 were taken in 2016, and 68 were collected in 2017. Of the 319 patients, the majority had returned from West Africa (46.71%, 149/319) and Central Africa (40.44%, 129/319), and the percentages of workers from South Africa and East Africa were only 10.66% and 2.19%, respectively (Table 1).
K13-propeller point mutations and distribution
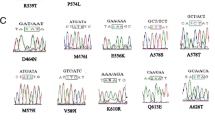
A 744 bp fragment was amplified from all the samples by nested PCR, and sequencing was successfully performed using 319 P. falciparum samples collected from 23 countries in Africa during 2014–2017 in Guangxi. Except a sequence from Democratic Republic of the Congo found two mutated points (1/319), the other 11 sequences were single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) 3.45% (11/319), 11 point mutations were identified, and the 12 mutated samples were distributed in 7 countries including Ghana, the Republic of Guinea, Uganda, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Chad, Sierra Leone, and Cameroon; with the exception of Ghana, the other countries had only one mutated sample (Table 2). In the 11 mutated points, only two point mutations were identified as two sequence mutations, whereas the other mutations were single sequence mutations. In the 12 samples, only a sequence from the Congo had two point mutations, and the others were a single point mutation. In the 11 point mutations, 6 were synonymous, and 5 were non-synonymous mutations (T474I, A481T, A578S, V603E, G665S). Of these, the mutated sequences were from Ghana (T474I, A481T, A578S, G665S), Cameroon (A578S), and Sierra Leone (V603E) (Table 2).
Of 12 mutated samples, 8 were from West Africa (Ghana, Sierra Leone, Guinea) and 3 were from Central Africa (Chad, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Cameroon), one was from East Africa (Uganda), and no mutations were detected in the 34 samples from South Africa. Most of the returning workers were from Ghana (95) and Cameroon (87) (Table 1). In Ghana, 6 DNA mutated samples were detected, with a mutation prevalence of up to 6.32% (6/95), while in Cameroon, only one mutant sequence was detected, with a mutation prevalence of 1.15% (1/87). Two mutated sequences from the Democratic Republic of the Congo were detected. One DNA mutation was detected in the K13-propeller gene in Uganda, Chad, the Republic of Guinea, Uganda, and Sierra Leone (Table 2).
Observations regarding clearance delay
The median (IQR) dose of intravenous artesunate to remove asexual blood parasites from the peripheral was 407.55 (360–510) mg in 158 cases. Artesunate dosage and efficacy were D1 (120 mg), 0 cases of clearance; D2 (240 mg, n = 58), 36.71%; D3 (360 mg, n = 111), 70.25%; D4 (480 mg, n = 141), 89.24%; D5 (600 mg, n = 151), 95.57%; D6 (720 mg, n = 154), 97.47%; D7 (840 mg, n = 156), 98.73%; and D8 (960 mg, n = 158), 100% (Fig. 1). The sequenced T474I (n = 1), A481T (n = 1), A578S (n = 1), V603E (n = 1), and G665S (n = 1) mutations were all cleared within D3, with no delay observed. Nine (C-87, B114, A-9, C-53, C-87, B-107, C-28, E8, C-37, B-22 Table 2) of the 158 patients who were observed the artesunate treatment detected the mutation of P. falciparum k13 gene, of the nine mutated samples, 8 point mutations were identified, 3 points are non-synonymous and the other 5 are synonymous. In 9 mutated P. falciparum had not found the delayed clearance, the parasite were cleared by artesunate within day 4.
Dose of artesunate use and the disappearance of the parasite ring. Cumulative artesunate use: D1 (120 mg) had 0 cases of clearance; D2 (240 mg, n = 58) had 36.71% clearance; D3 (360 mg, n = 111) had 70.25% clearance; D4 (480 mg, n = 141) had 89.24% clearance; D5 (600 mg, n = 151) had 95.57% clearance; D6 (720 mg, n = 154) had 97.46% clearance; D7 (840 mg, n = 156) had 98.73% clearance; and D8 (960 mg, n = 158) had 100% clearance
Discussion
In this study, 5 amino acid mutations of the k13-propeller genes from 319 P. falciparum were found, of which 4 mutations (T474I, A481T, A578S) had been reported previously [9, 13, 22, 25,26,27] and had been detected in Africa [14, 25,26,27]. The A578S mutation has been commonly observed in Africa [14,15,16, 19, 23, 26, 28, 29] but was also detected in Myanmar, Thailand, India, and Bangladesh. Notably, the C580Y, R539T and Y493H substitutions that were associated with delayed parasite clearance in Southeast Asia were not observed, nor was the M476I mutation that was selected in vitro in a Tanzanian parasite [9] or the M579I mutant that was first reported in Africa artemisinin-resistant P. falciparum in a Chinese worker returning from Equatorial Guinea [20]. Ariey et al. [9] reported the 2 polymorphism sites T474I and A481A from Ghana. In the present study, 2 mutant sites, V603E and G665S, were detected, which had not yet been described. According to the clinical observations, these 2 mutants were not related to the clearance delay.
In the 319 cases of P. falciparum, 6 mutations were synonymous, of which C469C, T478T, A557A, V589V, and K610K had been reported in African countries, but through the review of other research studies, revealing that some of these mutations are non-synonymous mutations. For example, the amino acid 478 in Cameroon [23, 26] and in the present study (from Ghana) was a synonymous mutation (T478T), whereas in Mali, it was non-synonymous (T478P) [26]; amino acid 589 from the Democratic Republic of Congo [14] and from Chad (in this study) was a synonymous mutation (V589 V) but was non-synonymous in Mali and Equatorial Guinea (V589I) [25, 26]; amino acid 610 from Ghana (in this study) was a synonymous mutation (K610 K), but the mutation from Nigeria was non-synonymous K610R [27]; and amino acid 557 from Ghana (in this study) was a synonymous mutation, but the mutation from the Democratic Republic of Congo was non-synonymous (A557S) [14, 23, 25]. All of these findings indicated that the mutations in different African countries vary, and the mutations are diverse, even when the prevalence of the mutation is very low.
In the present study, the clinical data of the enrolled patients and all the P. falciparum patient data and treatment information were recorded and analysed, and the mutant P. falciparum cases were confirmed, but the clearance delay of the parasite was not detected. The WHO’s Global Plan for Artemisinin Resistance Containment prioritizes the monitoring of artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) efficacy to detect resistance, and this is most credibly quantified using clinical efficacy data. The k13-propeller gene amplification associated with the clinical data analysis could better determine the ACT efficacy and the artemisinin or artemisinin-derivative resistance. Artemisinin resistance has not yet been clearly defined. The slow clearance of malaria in patients treated with artemisinin or ACT is considered to be an external manifestation of resistance [30]. Plasmodium falciparum ring-stage susceptibility assay (RSA) in vitro [31] and half-life counts in vivo [32, 33] have been widely used to monitor the resistance of P. falciparum to artemisinin. Plasmodium still exists in the peripheral blood after treatment with the recommended dosage for 3 days, which is considered drug resistance.
In the clinical observation, the median dose of artesunate needed to remove the parasite was 407.55 mg (D3–D4). This result was similar to that of work by Dondorp et al. [3] conducted in Pailin, Cambodia, but significantly different from the results that Byakika-Kibwika et al. [34] observed in children in Uganda. Among 158 patients, 29.7% (n = 47) of blood smear asexual parasites were still positive after 3 days of treatment, and 2 even needed 960 mg (D8) to completely clear the parasite. Although many factors could affect the drug efficacy without K13 gene mutations, including host immunity, biological characteristics of P. falciparum and drug factors [35], the positive rate is significantly higher after D3. According to epidemiological investigations, migrant workers who travel to remote regions in Africa and return to Guangxi and are repeatedly infected with malaria cannot undergo standardized treatment. This is a potential explanation for the higher positive rate after D3. Therefore, the observation implied that the efficacy of artesunate against P. falciparum imported from regions in Africa is at risk of decline.
Conclusions
Plasmodium falciparum resistance to ACT was not found through the observed clinical treatment, but the efficacy of artesunate is at risk of decline, and the k13-propeller gene amplification and analysis of 319 samples of P. falciparum from workers returning from Africa detected 11 mutation sites, including 6 synonymous mutations and 5 non-synonymous mutations. No mutation sites were associated with delayed parasite clearance.
Availability of data and materials
The data from this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
- ACT:
-
artemisinin-based combination therapy
- RSA:
-
ring-stage susceptibility assay
References
WHO. Global report on antimalarial drug efficacy and drug resistance: 2000–2010. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2010.
Noedl H, Se Y, Schaecher K, Smith BL, Socheat D, Fukuda MM. Evidence of artemisinin-resistant malaria in western Cambodia. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2619–20.
Dondorp AM, Nosten F, Yi P, Das D, Phyo AP, Tarning J, et al. Artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:455–67.
Dondorp AM, Fairhurst RM, Slutsker L, Macarthur JR, Breman JG, Guerin PJ, et al. The threat of artemisinin-resistant malaria. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:1073–5.
Enserink M. Malaria’s drug miracle in danger. Science. 2010;328:844–6.
Cheeseman IH, Miller BA, Nair S, Nkhoma S, Tan A, Tan JC, et al. A major genome region underlying artemisinin resistance in malaria. Science. 2012;336:79–82.
Takala-Harrison S, Clark TG, Jacob CG, Cummings MP, Miotto O, Dondorp AM, et al. Genetic loci associated with delayed clearance of Plasmodium falciparum following artemisinin treatment in Southeast Asia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:240–5.
Miotto O, Almagro-Garcia J, Manske M, Macinnis B, Campino S, Rockett KA, et al. Multiple populations of artemisinin-resistant Plasmodium falciparum in Cambodia. Nat Genet. 2013;45:648–55.
Ariey F, Witkowski B, Amaratunga C, Beghain J, Langlois AC, Khim N, et al. A molecular marker of artemisinin-resistant Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Nature. 2014;505:50–5.
Wang J, Huang Y, Zhao Y, Ye R, Zhang D, Pan W. Introduction of F446I mutation in the K13 propeller gene leads to increased ring survival rates in Plasmodium falciparum isolates. Malar J. 2018;17:248.
Talundzic E, Okoth SA, Congpuong K, Plucinski MM, Morton L, Goldman IF, et al. Selection and spread of artemisinin-resistant alleles in Thailand prior to the global artemisinin resistance containment campaign. PLoS Pathog. 2015;11:e1004789.
Wang Z, Shrestha S, Li X, Miao J, Yuan L, Cabrera M, et al. Prevalence of K13-propeller polymorphisms in Plasmodium falciparum from China-Myanmar border in 2007–2012. Malar J. 2015;14:168.
Huang F, Takala-Harrison S, Jacob CG, Liu H, Sun X, Yang H, et al. A single mutation in K13 predominates in southern China and is associated with delayed clearance of Plasmodium falciparum following artemisinin treatment. J Infect Dis. 2015;212:1629–35.
Taylor SM, Parobek CM, DeConti DK, Kayentao K, Coulibaly SO, Greenwood BM, et al. Absence of putative artemisinin resistance mutations among Plasmodium falciparum in sub-Saharan Africa: a molecular epidemiologic study. J Infect Dis. 2015;211:680–8.
Conrad MD, Bigira V, Kapisi J, Muhindo M, Kamya MR, Havlir DV, et al. Polymorphisms in K13 and falcipain-2 associated with artemisinin resistance are not prevalent in Plasmodium falciparum isolated from Ugandan children. PLoS One. 2014;9:e105690.
Zaw MT, Emran NA, Lin Z. Updates on k13 mutant alleles for artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium falciparum. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2018;51:159–65.
Borrmann S, Straimer J, Mwai L, Abdi A, Rippert A, Okombo J, et al. Genome-wide screen identifies new candidate genes associated with artemisinin susceptibility in Plasmodium falciparum in Kenya. Sci Rep. 2013;3:3318.
Henriques G, Hallett RL, Beshir KB, Gadalla NB, Johnson RE, Burrow R, et al. Directional selection at the Pfmdr1, Pfcrt, Pfubp1, and Pfap2mu loci of Plasmodium falciparum in Kenyan children treated with ACT. J Infect Dis. 2014;210:2001–8.
Hawkes M, Conroy AL, Opoka RO, Namasopo S, Zhong K, Liles WC, et al. Slow clearance of Plasmodium falciparum in severe pediatric malaria, Uganda, 2011–2013. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015;21:1237–9.
Lu F, Culleton R, Zhang M, Ramaprasad A, von Seidlein L, Zhou H, et al. Emergence of indigenous artemisinin-resistant Plasmodium falciparum in Africa. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:991–3.
Xia Z, Feng J, Zhou S. Malaria situation in the People’s Republic of China in 2012 (in Chinese). Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis. 2013;31:413–8.
Zhang L, Zhou S, Feng J, Fang W, Xia Z. Malaria situation in the People’ s Republic of China in 2014 (in Chinese). Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis. 2015;33:321–6.
Kamau E, Campino S, Amenga-Etego L, Drury E, Ishengoma D, Johnson K, et al. K13-propeller polymorphisms in Plasmodium falciparum parasites from sub-Saharan Africa. J Infect Dis. 2015;211:1352–5.
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol. 2016;33:1870-4.
MalariaGEN Plasmodium falciparum Community Project. Genomic epidemiology of artemisinin resistant malaria. eLife. 2016;5:e08714.
Ouattara A, Kone A, Adams M, Fofana B, Maiga AW, Hampton S, et al. Polymorphisms in the K13-propeller gene in artemisinin-susceptible Plasmodium falciparum parasites from Bougoula-Hameau and Bandiagara, Mali. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2015;92:1202–6.
Yang C, Zhang H, Zhou R, Qian D, Liu Y, Zhao Y, et al. Polymorphisms of Plasmodium falciparum k13-propeller gene among migrant workers returning to Henan Province, China from Africa. BMC Infect Dis. 2017;17:560.
Cooper RA, Conrad MD, Watson QD, Huezo SJ, Ninsiima H, Tumwebaze P, et al. Lack of artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium falciparum in Uganda based on parasitological and molecular assays. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59:5061–4.
Isozumi R, Uemura H, Kimata I, Ichinose Y, Logedi J, Omar AH, et al. Novel mutations in K13 propeller gene of artemisinin-resistant Plasmodium falciparum. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015;21:490–2.
White NJ. The parasite clearance curve. Malar J. 2011;10:278.
Witkowski B, Khim N, Chim P, Kim S, Ke S, Kloeung N, et al. Reduced artemisinin susceptibility of Plasmodium falciparum ring stages in western Cambodia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57:914–23.
Flegg JA, Guerin PJ, White NJ, Stepniewska K. Standardizing the measurement of parasite clearance in falciparum malaria: the parasite clearance estimator. Malar J. 2011;10:339.
WHO. Global plan for artemisinin resistance containment (GPARC). Geneva: World Health Organization; 2011.
Byakika-Kibwika P, Nyakato P, Lamorde M, Kiragga AN. Assessment of parasite clearance following treatment of severe malaria with intravenous artesunate in Ugandan children enrolled in a randomized controlled clinical trial. Malar J. 2018;17:400.
Hastings IM, Kay K, Hodel EM. How robust are malaria parasite clearance rates as indicators of drug effectiveness and resistance? Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59:6428–36.
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank the people who participated in the research study, including the patients returning from Africa and the doctors and nurses at Shanglin County People’s Hospital.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant Nos. 2016YFC1200500, 2016YFC1200503; 2016YFC1202000, 2016YFC1202001, 2016YFC1202004) and the Scientific Research Project of Guangxi Health and Family Planning Commission (220170131).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL and YLS developed the study protocol, and JL, YLS, WWZ, HY, KML, SJW, HYW, YCY, SPH, YXL, AXM, and JQ performed the sample collection, PCR amplification, and drug treatment and contributed to the data analysis. LJ and YLS performed the final analysis and wrote the first manuscript version. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Center for Disease Control and Prevention Ethics Committee. Information on the bitten patients was conveyed with the patient’s approval, and the research aim, methods, risks and benefits of the study were explained in detail to the patients.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Shi, Y., Zhang, W. et al. K13-propeller gene polymorphisms of Plasmodium falciparum and the therapeutic effect of artesunate among migrant workers returning to Guangxi, China (2014–2017). Malar J 18, 349 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-019-2984-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-019-2984-7