Abstract
Background
One of the main elements of patient-centered care is an enhancement of patient preparedness. Thus, pre-visit planning assessment tools was emerged to prepare and involve patients in their treatment process.
Objective
The main objective of this article was to review the applied tools and techniques for consideration of putting pre-visit planning into practice.
Methods
Web of Science, Scopus, IEEE, and PubMed databases were searched using keywords from January 2001 to November 2020. The review was completed according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses checklist. Then, qualitative analysis was done to suggest an appropriate framework by mapping the main concepts.
Results
Out of 385 citations were retrieved in initial database searches, 49 studies from ten countries were included. Applied pre-visit techniques can be classified into eight categories. Our results showed that almost 81% of studies were related to procedures that were done between each visit, while 42% of articles were related to before visits. Accordingly, the main approach of included articles was patient preparedness. While 38 studies reported this approach is effective, three studies reported the effectiveness of such tools as moderate, only two articles believed it had a low effect on improving patient-centered care.
Conclusion
This survey summarized the characteristics of published studies on pre-visit planning in the proposed framework. This approach could enhance the quality of patient care alongside enhancement patient-provider communication. However, such an approach can also be helpful to control pandemic diseases by reducing unnecessary referrals.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
In the information-driven care era, although the ultimate goal of health systems is still improving the quality of patient care, the patient care model has shifted from personal responsibility to participatory medical decision-making [1]. Thus, the responsibility of the patient’s health is no longer solely with the physician. On the other hand, the role of the patient in promoting his health status cannot be denied [2]. Hence, the patient-centered care (PCC) model was introduced to show the participatory role of the patient and other health care providers in the process of treatment and patient care [3,4,5,6]. Since the PCC idea was introduced, various definitions and models have been proposed to distinguish the main elements of this model [5, 7,8,9,10,11,12]. Up to now, the best model that has been able to explain the main components of such a care model is the model presented by the Picker Institute [13]. This model consists of eight parts that outline the factors affecting the achievement of an optimal patient-centered care model [5, 12, 14].
One of the main elements of the PCC approach is respect for patients’ value by preparation of patients for each visit [6]. Sometimes patients have to spend more time in the waiting room than in a physician’s office [15, 16]. Also, in each appointment, especially in the first visit, more than 5 min should be devoted to determining who the patient is, what is his problems, which drugs she/he used, what is his/her medical history, and so on [17]. This process is so complex in patients who have a chronic condition or patients with multiple chronic conditions with multiple medications [18, 19]. It can be useful to prevent the spread of the disease. Limited time for each visit and patient complexity might have a negative impact on the patient-physician relationship.
In this context, pre-visit planning and visit preparation concepts have been suggested by American Medical Association (AMA) as a solution to address these challenges. It can help physicians when the patient checks in for the first time, he is already behind [20]. This term (pre-visit planning) was introduced by Sinsky et al. in 2014 to collect and organize patient data before a patient visit [21].
The purpose of pre-visit planning is to help the patient and physician to save time and improve care by gathering and organizing information in a structured way. Therefore, a health care provider can pay more attention to interpretation, discussion, and response to a patient during the visit. This idea is not just to plan ahead before each visit. Dr. Sinsky explains that pre-visit planning could include a broader concept that could generally refer to preparing the patient for a face-to-face visit more effectively [21]. The pre-visit planning concept is described in Fig. 1 as a conceptual model.
However, there are various methods to apply this new approach into practice, it usually includes scheduling future appointments and preparing patients before the visit [22]. These techniques are known as pre-visit assessment tools. The use of pre-visit assessment tools focuses on involving the patient and the physician through the patient care process [23]. As it is apparent in Fig. 1, it can occur at end of each visit, arranging for the next visit, programming for the next clinical and paraclinical testing, gathering the necessary information for the subsequent visits, and take steps regarding the handoff of patients [24].
With pre-visit planning, patients and physicians are prepared to make meaningful use of their time during each visit. Furthermore, patients could have an impressive role in clinical decision-making regarding their treatment process [25]. Hence, several studies have focused on the power of patient-centered care to improve patient care, but no studies have been published to examine the applying pre-visit planning techniques in the context of patient-centered care. The main objective of this study is to review the consideration of pre-visit planning used in patient-centered care. Throughout this paper, the term pre-visit planning will refer to any intervention, care program, patient-centered planning, or even educational plan that is considered to prepare the patient for a face-to-face visit or improve the patient-provider relationship. Specific aims of this survey are as follows: 1) representing an overview of applied methods regarding pre-visit planning with their characteristics in published studies, 2) to investigate the published studies on applying pre-visit planning regarding clinical aspects such as type of disease, 3) to determine the effectiveness of putting pre-visit planning into routine practice, 3) providing an overview of the sample size, approaches, and collected information concerning applied methods and techniques, 4) suggesting a framework in this context.
Method
A systematic search of four databases (Web of Science, Scopus, IEEE, and PubMed) was conducted from January 2001 to November 2020 using keywords alongside Mesh terms. These databases were selected for their inclusion of qualitative studies and health research. The keywords used in the search strategy were drawn from preliminary searches according to our study goals. Those keywords were validated and additional keywords added by checking the terms used in articles identified in preliminary searches. Boolean search strategies were described in Additional file 1: Table A-1. Since no result was found in the IEEE database, it was removed from source databases in Table A-1. This systematic review was completed according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) checklist to ensure the inclusion of relevant studies [26].
Inclusion and exclusion criteria for study selection
Articles were included if they met the following criteria: 1) The focus of the study was on applying the pre-visit approach through the patient care process. 2) Population includes all of the patients with any type of disease, 3) This study covered all phases of the patient care process, 4) Published in recent 10 years and matched with the search query, 5) Limited to those published in the English language, 6) Only published articles and reviews in peer-reviewed journals were included, 7) All type of study designs, 8) Improve patient-centered care, 9) Studies that received an acceptable score in terms of quality based on the checklist. Articles excluded if they met the following criteria: 1) The title, abstract, or full text of the article did not relate to pre-visit planning, 2) Thesis, book chapters, letters to editors, short briefs, reports, technical reports, book reviews, review, or meta-analysis, 3) Non-English papers, 4) Publication that their full-text is not available.
Data screening phase
Based on our search strategy; articles were retrieved from databases. Additionally, related studies were added manually by a simple search in Google Scholar and reference checking. All of the citations were imported to EndNote software for better resource management. Then, duplicated articles were removed. In the first phase, all titles and abstracts of articles were examined based on our main objective to select relevant studies by one author (MG). A second reviewer (MGH) reviewed a sample of studies randomly. After that, the full texts of relevant studies were screened thoroughly by two reviewers (MG and MGH). If there was a disagreement between the authors in the selection of relevant studies, the final decision was made by HA. Lastly, some studies remained as eligible articles for qualitative analysis. The extraction forms were designed by researchers to manage and investigate the obtained information. To diminish bias, key subjects of articles summarized and entered into customized extraction forms based on specific classifications. Two authors (MG and MGH) independently extracted the study characteristics based on the classification. The information extracted by the researchers was re-examined to reach an agreement. The next reviewer (HA) assessed and verified the extracted information.
Critical quality appraisal
The methodological quality of the included articles was evaluated using the Qualitative research Critical Appraisal Program (CASP) tool by two authors. This instrument was used in systematic reviews frequently for qualitative synthesis [27]. It was employed for appraising the strengths and limitations of any qualitative research methodology. It was recommended for health-related researches and it is appropriate for novice researchers [28]. Critical appraisal was performed independently by two researchers.
Analysis
To extract some necessary information, specific categories were considered to classify and analyze relevant articles. All of the articles were synthesized regarding general and specific domains. The general domain comprises the title, author, year of publication, journal name, type of study, the main objectives. Accordingly, the specific domain comprises applied pre-visit techniques, disease, clinic, sample size, country, outcome measures, effectiveness, and collected data. Analysis of the extracted information from eligible articles and framework suggestions were conducted based on these predefined categories.
Results
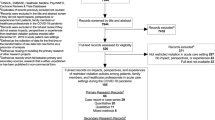
In total, systematic literature searching of databases yielded 385 citations. Of which 99 articles were removed due to duplication. Next, one hundred and sixty-six papers were excluded after screening titles and abstracts. In the following, 72 papers were excluded after full-text reading. Finally, 49 papers are identified as an eligible article which met our inclusion criteria. The screening process for articles based on the PRISMA checklist is shown in Fig. 2. All included papers had the minimum score (10 from 20) of quality assessment using the CASP tool. Only four papers were excluded based on quality appraisal assessment. Therefore, forty-nine articles were identified as eligible studies for qualitative analysis.
General characteristics
All included studies are published in journals from 2001 to 2020. The trend of publishing articles in this field was following an upward trend. In terms of the type of study, studies were conducted in different designs. Most of which were clinical trial studies. The descriptive analysis regarding the type of study in the included articles is represented in Table 1. In the following, the results of the review of studies by author, year of publication, the main objectives, the sample size, type of pre-visit planning, clinic, the effectiveness of the applied method, and outcome of using the pre-visit planning are summarized in Table 2.
Analysis of studies showed that the application of pre-visit planning is the most favorite of developed countries. Of them, the USA has the most contribution among other studies. After that Canada ranks second in the deployment plan is allocated to pre-visit intervention. The distribution of studies concerning the country is shown in Fig. 3.
Different techniques for putting pre-visit into practice
The investigation showed that pre-visit can apply in different ways regarding timing, main approaches, and types. The analysis showed that different types of pre-visit techniques have been employed by authors to facilitate office visits and patient care. All of these plans can be categorized into eight different categories, utilizing an electronic pre-office checklist with 12 studies (24.5%) [25, 29,30,31,32,33,34,35, 48, 58, 59, 68], educating patients and support them before each visit in form of online and offline source of information with 12 studies (24.5%) [23, 36,37,38,39,40,41,42, 60,61,62, 66, 74], applying an EHR-linked care program with different checklists and assessment tools with nine studies (18.4%) [22, 43, 44, 49, 63, 67, 70, 71, 73], using paper-based checklists with nine studies (18.4%) [45, 46, 50,51,52, 64, 65, 69, 72], preparing and assess patient with the pre-visit phone-based intervention with two studies (4.1%) [24, 53], using self-triage or self-assessment tools with two studies (4.1%) [54, 55], using automatic reminders and sheets with one article (2%) [56], and using pre-clinic consultation by other health care team member with one article (2%) to prepare the patient for each visit [57].
According to findings, the most favorite types of pre-visit model were related to using electronic pre-office visit checklists and supporting patients by providing them with the necessary information in the form of online and offline training. In three articles, this information was provided to patients in the form of educational websites [37, 39, 40, 60], while in the other six articles, the information was provided to patients in the form of training sessions before the patient’s visit and referring to the clinic [23, 36, 38, 41, 42, 61, 62, 66].
The next widely applied method was the EHR-linked care program that put pre-visit planning into practice. Ten articles used pre-visit solutions such as electronic checklists, automated reminders, decision-making tools, and reviewable forms that could be implemented by connecting to electronic medical records. In third place, there are paper-based checklists used for patient preparation with nine papers. These checklists included questions about demographic information, the main problems, medical history, general symptoms, illness history, hospitalizations, medications, family history of a specific illness, level of education, location, and questions about the patient’s lifestyle. Other solutions were used in a smaller number of articles. Regarding pre-visit counseling, only one article applied the consultation of clinical pharmacists before the office visit. This approach leads to providing the physician with better information after the initial completion of the medical record.
In terms of timing, pre-visit intervention could be conducted at a different time in the patient care process. Taken together, all of these possibilities could be categorized into four situations. It can be occurred before each visit, between visits, at the end of each visit on the current visit, and in a combination of the previous three models. Our results showed that almost 81% of studies were related to procedures that were done between each visit, while 42% of articles were related to procedures that were done before each visit. Only 10 % of studies were conducted at end of the current visit.
In terms of main approaches, the analysis of studies showed that all studies can be divided into three main categories based on the main approaches. These three approaches comprise, improving the current visit and preparing the patient for the next visit, perform some procedures for patient preparedness such as sending reminders or filling pre-visit checklists, and providing more inclusively insight about the patient for the physician before they come in for an office visit. The final analysis of the studies based on the main objectives and the timing is summarized in Table 3. Out of 49 studies, the main approach forty-eight of articles were related to patient preparedness and enhance patient adherence to their treatment.
Out of 49 studies, only one study did not report the sample size of their study. In total, the sample size ranged from 15 to 12,228 with a mean sample size of 1160.3877 (SD = ± 2613.799). In Fig. 4, the distribution of studies based on sample size, year, and different techniques are represented.
The effectiveness of pre-visit planning
Articles were also reviewed regarding the effectiveness of the applied methods. Out of 49 studies, the authors of 41 articles (83.67%) considered pre-visit planning to be effective in clinical practice. While six studies (12.24%) reported the effectiveness of these tools as moderate, only two articles (4.08%) believed that using this method had very little effect on improving patient-centered care. The effectiveness of studies concerning applied methods is shown in Fig. 5.
The effectiveness has been reported by researchers using various outcome measures in studies. These outcome measures reported in reviewed articles, along with their frequency and their effectiveness, are shown in Table 4.
Different diseases and the main reason for referral
Through this survey, the referred clinic and the main reasons for the referral were also examined in reviewed articles. In terms of the reason for referral and diseases, the most common reason for referral was related to chronic disease and general problems. The frequency of disease regarding applied methods and their effectiveness are represented in Fig. 6. Regarding the type of clinic that was considered for implementing pre-visit planning, the highest frequency was related to primary care clinics. Next, surgical clinics had the largest number of pre-visit programs.
Information and collected data
To implement pre-visit planning, various types of data and information have been collected in studies. These collected data were very diverse. Hence, these different types of information can be divided into nine categories concerning their application. The different types of information regarding applied techniques are shown in Fig. 7.
Determining the main categories of applied techniques regarding medical informatics
Coding of all research studies and extracted themes using thematic analysis leads to discover the main sub-themes in terms of medical informatics. Therefore, all of the employed techniques can be divided into four categories, pre-assessment forms, educational resources, decision aid tools, and reminders as the main themes. The main themes and sub-themed are shown in Fig. 8. Different aspects of such a model were shaped by mapping the main concepts obtained through this survey. The details of applied techniques in terms of the medical informatics view are described in Table 2.
Framework suggestion and IT-based solution
After a qualitative analysis of the results based on predetermined categories, the main ideas can be summarized in a proposed framework as an electronic-based advanced care program. Based on the results, this model is divided into four main parts in terms of time. This model is represented in Fig. 9. In this model, the main focus is on the patient. The workflow is designed to improve the relationship between physician and patient in the simplest way. It is done by involving the patient in their care, which is one of the main purposes of using pre-visits in studies.
In this model, it is assumed that an electronic system is available to manage patient information. To implement a pre-visit-based program, a section is also considered for patient access to his care plan in the proposed model. Based on this model, the patient can pursue the main goals of pre-visit planning through suggested workflow, such as disease management, treatment adherence, receiving the necessary advice and training, and preparing for each visit. To increase the effectiveness of the devised model, it is suggested that the proposed system should have interacted with existing databases and electronic health systems.
Discussion
Summary of findings
This survey summarized the characteristics of published studies on pre-visit planning and its application in various health domains. To our knowledge, this study represents the first overview of the existing evidence about the different pre-visit planning techniques in clinical practice. Forty-nine articles from ten countries were included in this survey. As mentioned in the results, these techniques can classify into eight categories. Among them, the most widely used methods are related to using electronic pre-office visit checklists and supporting patients by providing them with the necessary information in the form of online and offline educational resources.
Consistent with the present findings, our results showed that applying pre-visit techniques was not restricted to office visits [75]. So, pre-consultation planning can employ before each patient’s consultation, between the patient’s visits, and during the current visit to facilitate complicated patient care process.
One of the remarkable results of this study is that this approach has been used more in developed countries. It may be because it is easier to take a participatory approach to patient care in developed countries due to a high level of patient literacy.
Results in the context of other researches
Our results showed that most studies have been conducted with the main goal of preparing the patient by involving them in their treatment process. Patient preparedness had the most impact on the patient’s perceptions of his disease and overall patient satisfaction [76]. Similarly, Ringdal et al. [77] indicated through their survey that patients were satisfied with their active role as a partner on the healthcare team. Also, this is exactly in line with the main goal of the patient-centered care paradigm regarding the individualized approach to the patient’s treatment [78,79,80].
However, Geraghty et al. [81] showed through their study that there is a linear relationship between patient satisfaction and visit length. Unfortunately, long waits are common at outpatient clinics [82]. Hence, our results illustrated that using a pre-visit assessment tool such as a simple checklist or questionnaire is almost effective to maximize the available time during a consultation for making the best decisions by physicians. Also, it can provide better insight for physicians to better communicate with the patient by knowing the patient’s background during the consultation [22, 33, 35, 47, 54, 60, 64, 67, 69, 70, 83,84,85,86,87,88].
Analysis of results revealed that most studies considered the pre-visit assessment tool as an independent solution that was not connected to existing electronic systems. However, in some studies, a comprehensive care plan has been taken. A pre-visit planning program could be linked to a patient’s electronic medical record as used in some reviewed studies. This approach is similar to the motivational interviewing (MI) technique that is applied to improve patient-centeredness in other studies. Motivational interviewing is a technique to help patients address their chief problems and increase their understanding of their participatory role in the treatment process [89].
Implications for research and practice
Planned and targeted care is one of the main components of the patient-centered care model [79]. Hence, implementing pre-visit tools within an advanced planned care program might be more effective in moving towards effective patient-centered care. However, pre-visit planning care is a new approach, no framework or conceptual model was introduced according to this subject. Only a planned care model was introduced by the Health Research and Quality Agency as a comprehensive patient-centered medical home (PCMH) approach in which one of its main components is pre-visit planning [90, 91]. Hence, our findings are summarized in a conceptual model regarding applying the pre-visit assessment tool in electronic-based planned patient care (Fig. 9). However, the EHR-linked pre-visit type was used only in the nine studies, the suggested model is not devised in a stand-alone model. Nowadays, with the advent of the digital age, applying integrative electronic systems and medical informatics-based solutions are inevitable [92].
One of the significant gaps that were mentioned in the studies is the unnecessary referrals of patients to outpatient offices [93, 94]. These unnecessary visits in the event of pandemics can also lead to the spread of disease [95, 96]. In such a framework, avoiding unnecessary referrals was considered to fight the pandemic. Such an approach can be useful to prevent the spread of the COVID-19 disease too.
Limitations
Since this study is the first attempt to review and analyze the published articles regarding pre-visit planning, it encounters some limitations. The results of some studies might be published in the form of reports, letters to the editor, or other types of study. Thus, we might not have considered them based on our exclusion criteria. The results showed that most studies point out pre-visit planning conducted by large institutions and reputable organizations; their data are absurdly confounded by the fact that better-funded institutions probably produce better outcomes. Also, some researchers might put pre-visit into practice but they did not publish their attempts in form of any research article or conference paper. It could cause publication bias. Thus, further researches for specific domains in clinical practices might be done in the future.
Conclusion
Using a systematic review approach leads to get a comprehensive overview of literature conducted in the use of various pre-visit approaches. Our results revealed that the direct outcome of planning a pre-visit care program was enhancing the quality of patient care alongside enhancement patient-provider communication. Improving the patient-physician relationship is a key factor in moving towards a patient-centered care paradigm. The qualitative and thematic analysis of the articles also showed that pre-visit planning has the greatest impact on the relationship between physician and patient. It can account for such a useful tool to move toward patient-centered care. However, such an approach can also be helpful to control pandemic diseases by reducing unnecessary referrals. Thus, the application of pre-visit tools can be considered as one of the key components of designing a patient-centered care system. In this survey, we tried to summarize our findings and our suggestions in a complete patient care framework based on pre-visit planning techniques.
Availability of data and materials
The study involves only a review of the literature without involving any data.
Abbreviations
- PRISMA:
-
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
- PCC:
-
Patient-centered care
References
Thompson AGH. The meaning of patient involvement and participation in health care consultations: a taxonomy. Soc Sci Med. 2007;64(6):1297–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2006.11.002.
Castro EM, Van Regenmortel T, Vanhaecht K, Sermeus W, Van Hecke A. Patient empowerment, patient participation and patient-centeredness in hospital care: a concept analysis based on a literature review. Patient Educ Couns. 2016;99(12):1923–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pec.2016.07.026.
Halabi IO, Scholtes B, Voz B, Gillain N, Durieux N, Odero A, et al. “Patient participation” and related concepts: a scoping review on their dimensional composition. Patient Educ Couns. 2020;103(1):5–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pec.2019.08.001.
Coulter A, Oldham J. Person-centred care: what is it and how do we get there? Future Hosp J. 2016;3(2):114–6. https://doi.org/10.7861/futurehosp.3-2-114.
Davis K, Schoenbaum SC, Audet A-M. A 2020 vision of patient-centered primary care. J Gen Intern Med. 2005;20(10):953–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1497.2005.0178.x.
Naughton CA. Patient-centered communication. Pharmacy (Basel). 2018;6(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy6010018.
Braddock CH, Snyder L, Neubauer RL, Fischer GS. For the American College of Physicians Ethics P, human rights C, the Society of General Internal Medicine ethics C: the patient-centered medical home: an ethical analysis of principles and practice. J Gen Intern Med. 2013;28(1):141–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-012-2170-x.
Cowie MR. Person-centred care: more than just improving patient satisfaction? Eur Heart J. 2011;33(9):1037–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehr354.
Epstein RM, Street RL Jr. The values and value of patient-centered care. Ann Fam Med. 2011;9(2):100–3. https://doi.org/10.1370/afm.1239.
Luxford K, Safran DG, Delbanco T. Promoting patient-centered care: a qualitative study of facilitators and barriers in healthcare organizations with a reputation for improving the patient experience. Int J Qual Health Care. 2011;23(5):510–5. https://doi.org/10.1093/intqhc/mzr024.
Ogden K, Barr J, Greenfield D. Determining requirements for patient-centred care: a participatory concept mapping study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17(1):780. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-017-2741-y.
Shaller D. Patient-centered care: what does it take?: Commonwealth Fund New York; 2007.
Gerteis M. Through the patient’s eyes: understanding and promoting patient-centered care; 1993.
Mead N, Bower P. Patient-centred consultations and outcomes in primary care: a review of the literature. Patient Educ Couns. 2002;48(1):51–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0738-3991(02)00099-X.
Zakare-Fagbamila RT, Park C, Dickson W, Cheng TZ, Gottfried ON. The true penalty of the waiting room: the role of wait time in patient satisfaction in a busy spine practice. J Neurosurg. 2020;1(aop):1–11.
Anderson RT, Camacho FT, Balkrishnan R. Willing to wait?: the influence of patient wait time on satisfaction with primary care. BMC Health Serv Res. 2007;7(1):31. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6963-7-31.
Oostrom T, Einav L, Finkelstein A. Outpatient office wait times and quality of care for Medicaid patients. Health Aff. 2017;36(5):826–32. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2016.1478.
Hewner S, Casucci S, Castner J. The roles of chronic disease complexity, health system integration, and Care Management in Post-Discharge Healthcare Utilization in a Low-income population. Res Nurs Health. 2016;39(4):215–28. https://doi.org/10.1002/nur.21731.
Østbye T, Yarnall KS, Krause KM, Pollak KI, Gradison M, Michener JL. Is there time for management of patients with chronic diseases in primary care? Ann Family Med. 2005;3(3):209–14. https://doi.org/10.1370/afm.310.
Grant RW, Altschuler A, Uratsu CS, Sanchez G, Schmittdiel JA, Adams AS, et al. Primary care visit preparation and communication for patients with poorly controlled diabetes: a qualitative study of patients and physicians. Prim Care Diabetes. 2017;11(2):148–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcd.2016.11.003.
Sinsky CA, Sinsky TA, Rajcevich E. Putting pre-visit planning into practice. Fam Pract Manag. 2015;22(6):34–8.
Grant RW, Uratsu CS, Estacio KR, Altschuler A, Kim E, Fireman B, et al. Pre-visit prioritization for complex patients with diabetes: randomized trial design and implementation within an integrated health care system. Contemp Clin Trials. 2016;47:196–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cct.2016.01.012.
Sleath B, Carpenter DM, Davis SA, Watson CH, Lee C, Loughlin CE, et al. Acceptance of a pre-visit intervention to engage teens in pediatric asthma visits. Patient Educ Couns. 2017;100(11):2005–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pec.2017.05.013.
Rivo J, Page TF, Arrieta A, Amofah SA, McCann S, Kassaye H, et al. The impact of comprehensive pre-visit preparation on patient engagement and quality of Care in a Population of underserved patients with diabetes: evidence from the care management medical home center model. Popul Health Manag. 2016;19(3):171–7. https://doi.org/10.1089/pop.2015.0063.
Liu TC, Ohueri CW, Schryver EM, Bozic KJ, Koenig KM. Patient-Identified Barriers and Facilitators to Pre-Visit Patient-Reported Outcomes Measures Completion in Patients With Hip and Knee Pain. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(3):643–649.e641.
Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: elaboration and explanation. BMJ. 2015;349(jan02 1):g7647. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.g7647.
Long HA, French DP, Brooks JM. Optimising the value of the critical appraisal skills programme (CASP) tool for quality appraisal in qualitative evidence synthesis. Res Methods Med Health Sci. 2020;1(1):31–42. https://doi.org/10.1177/2632084320947559.
Hannes K, Lockwood C, Pearson A. A comparative analysis of three online appraisal instruments’ ability to assess validity in qualitative research. Qual Health Res. 2010;20(12):1736–43. https://doi.org/10.1177/1049732310378656.
Albada A, van Dulmen S, Spreeuwenberg P, Ausems MG. Follow-up effects of a tailored pre-counseling website with question prompt in breast cancer genetic counseling. Patient Educ Couns. 2015;98(1):69–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pec.2014.10.005.
Albada A, van Dulmen S, Ausems MG, Bensing JM. A pre-visit website with question prompt sheet for counselees facilitates communication in the first consultation for breast cancer genetic counseling: findings from a randomized controlled trial. Genet Med. 2012;14(5):535–42. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2011.42.
Frost J, Gibson A, Ukoumunne O, Vaidya B, Britten N. Does a simple web-based intervention facilitate the articulation of patients’ unvoiced agenda for a consultation with their diabetologists? A qualitative study. BMJ Open. 2019;9(6):e026588. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2018-026588.
O'Brien MA, Sullivan F, Carson A, Siddiqui R, Syed S, Paszat L. Piloting electronic screening forms in primary care: findings from a mixed methods study to identify patients eligible for low dose CT lung cancer screening. BMC Fam Pract. 2017;18(1):95. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12875-017-0666-5.
Meropol NJ, Egleston BL, Buzaglo JS, Balshem A, Benson AB 3rd, Cegala DJ, et al. A web-based communication aid for patients with cancer: the CONNECT study. Cancer. 2013;119(7):1437–45. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.27874.
Vo MT, Uratsu CS, Estacio KR, Altschuler A, Kim E, Alexeeff SE, et al. Prompting patients with poorly controlled diabetes to identify visit priorities before primary care visits: a pragmatic cluster randomized trial. J Gen Intern Med. 2019;34(6):831–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-018-4756-4.
Grant RW, Lyles C, Uratsu CS, Vo MT, Bayliss EA, Heisler M. Visit planning using a waiting room health IT tool: the aligning patients and providers randomized controlled trial. The Annals of Family Medicine. 2019;17(2):141–9. https://doi.org/10.1370/afm.2352.
Myers PL, Park RH, Sherina V, Bossert RP. Knowledge is power: providing previsit insurance coverage information of body contouring procedures to improve understanding and satisfaction in the massive weight loss patient. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2020;73(3):571–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2019.09.052.
Stankowski-Drengler TJ, Tucholka JL, Bruce JG, Steffens NM, Schumacher JR, Greenberg CC, et al. A randomized controlled trial evaluating the impact of pre-consultation information on Patients’ perception of information conveyed and satisfaction with the decision-making process. Ann Surg Oncol. 2019;26(10):3275–81. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-019-07535-0.
Rodenbach RA, Brandes K, Fiscella K, Kravitz RL, Butow PN, Walczak A, et al. Promoting end-of-life discussions in advanced Cancer: effects of patient coaching and question prompt lists. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(8):842–51. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2016.68.5651.
Tucholka JL, Yang DY, Bruce JG, Steffens NM, Schumacher JR, Greenberg CC, et al. A randomized controlled trial evaluating the impact of web-based information on breast Cancer Patients’ knowledge of surgical treatment options. J Am Coll Surg. 2018;226(2):126–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2017.10.024.
Krist AH, Woolf SH, Johnson RE, Kerns JW. Patient education on prostate cancer screening and involvement in decision making. Ann Fam Med. 2007;5(2):112–9. https://doi.org/10.1370/afm.623.
Causarano N, Platt J, Baxter NN, Bagher S, Jones JM, Metcalfe KA, et al. Pre-consultation educational group intervention to improve shared decision-making for postmastectomy breast reconstruction: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Support Care Cancer. 2015;23(5):1365–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-014-2479-6.
Albada A, van Dulmen S, Lindhout D, Bensing JM, Ausems MG. A pre-visit tailored website enhances counselees’ realistic expectations and knowledge and fulfils information needs for breast cancer genetic counselling. Familial Cancer. 2012;11(1):85–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10689-011-9479-1.
Wald JS, Grant RW, Schnipper JL, Gandhi TK, Poon EG, Businger AC, et al. Survey analysis of patient experience using a practice-linked PHR for type 2 diabetes mellitus. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2009;2009:678–82.
Grant RW, Wald JS, Schnipper JL, Gandhi TK, Poon EG, Orav EJ, et al. Practice-linked online personal health records for type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Intern Med. 2008;168(16):1776–82. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.168.16.1776.
Purkaple BA, Mold JW, Chen S. Encouraging patient-centered care by including quality-of-life questions on pre-encounter forms. Ann Fam Med. 2016;14(3):221–6. https://doi.org/10.1370/afm.1905.
Wolff JL, Roter DL, Barron J, Boyd CM, Leff B, Finucane TE, et al. A tool to strengthen the older patient-companion partnership in primary care: results from a pilot study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014;62(2):312–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.12639.
Wald JS, Businger A, Gandhi TK, Grant RW, Poon EG, Schnipper JL, et al. Implementing practice-linked pre-visit electronic journals in primary care: patient and physician use and satisfaction. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2010;17(5):502–6. https://doi.org/10.1136/jamia.2009.001362.
Riese A, Mello MJ, Baird J, Steele DW, Ranney ML. Prompting discussions of youth violence using electronic previsit questionnaires in primary care: a cluster randomized trial. Acad Pediatr. 2015;15(3):345–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acap.2015.01.005.
Kim-Hwang JE, Chen AH, Bell DS, Guzman D, Yee HF Jr, Kushel MB. Evaluating electronic referrals for specialty care at a public hospital. J Gen Intern Med. 2010;25(10):1123–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-010-1402-1.
Frank O, Aylward P, Stocks N. Development of pre-consultation prevention summary and reminder sheets for patients: preliminary study of acceptability and sustainability. Aust Fam Physician. 2014;43(5):310–4.
Lewin W, Knäuper B, Roseman M, Adler P, Malus M. Detecting and addressing adolescent issues and concerns: evaluating the efficacy of a primary care previsit questionnaire. Can Fam Physician. 2009;55(7):742–3.
Walker ME, Chuang C, Moores CR, Webb ML, Buonocore SD, Grant Thomson J. The hand surgeon consultation improves patient knowledge in a hand surgery Mission to Honduras. J Hand Surg Asian Pac Vol. 2018;23(1):11–7. https://doi.org/10.1142/S2424835518500017.
Page TF, Amofah SA, McCann S, Rivo J, Varghese A, James T, et al. Care management medical home center model: preliminary results of a patient-centered approach to improving care quality for diabetic patients. Health Promot Pract. 2015;16(4):609–16. https://doi.org/10.1177/1524839914565021.
Hitchings S, Barter J. Effect of self-triage on waiting times at a walk-in sexual health clinic. J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care. 2009;35(4):227–31. https://doi.org/10.1783/147118909789587439.
Judson TJ, Odisho AY, Neinstein AB, Chao J, Williams A, Miller C, et al. Rapid design and implementation of an integrated patient self-triage and self-scheduling tool for COVID-19. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2020;27(6):860–6. https://doi.org/10.1093/jamia/ocaa051.
Frank OR, Stocks NP, Aylward P. Patient acceptance and perceived utility of pre-consultation prevention summaries and reminders in general practice: pilot study. BMC Fam Pract. 2011;12(1):40. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2296-12-40.
Cox N, Tak CR, Cochella SE, Leishman E, Gunning K. Impact of pharmacist Previsit input to providers on chronic opioid prescribing safety. J Am Board Fam Med. 2018;31(1):105–12. https://doi.org/10.3122/jabfm.2018.01.170210.
Lee YK, Ng CJ, Low WY. Addressing unmet needs of patients with chronic diseases: impact of the VISIT website during consultations. J Eval Clin Pract. 2017;23(6):1281–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/jep.12777.
Johansen MA, Berntsen G, Shrestha N, Bellika JG, Johnsen JA. An exploratory study of patient attitudes towards symptom reporting in a primary care setting. Benefits for medical consultation and syndromic surveillance? Methods Inf Med. 2011;50(5):479–86. https://doi.org/10.3414/ME11-02-0005.
Bruce JG, Tucholka JL, Steffens NM, Mahoney JE, Neuman HB. Feasibility of providing web-based information to breast Cancer patients prior to a surgical consult. J Cancer Educ. 2018;33(5):1069–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13187-017-1207-6.
Hu X, Bell RA, Kravitz RL, Orrange S. The prepared patient: information seeking of online support group members before their medical appointments. J Health Commun. 2012;17(8):960–78. https://doi.org/10.1080/10810730.2011.650828.
Brackett CD, Kearing S. Use of a web-based survey to facilitate shared decision making for patients eligible for cancer screening. Patient. 2015;8(2):171–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40271-014-0079-7.
Muraywid B, Butkievich LE, Myers B. Effect of a virtual pharmacy review program: a population health case study. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2020;26(1):24–9. https://doi.org/10.18553/jmcp.2020.26.1.24.
Allende-Richter SH, Johnson ST, Maloyan M, Glidden P, Rice K, Epee-Bounya A. A Previsit screening checklist improves teamwork and access to preventive services in a medical home serving Low-income adolescent and young adult patients. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2018;57(7):835–43. https://doi.org/10.1177/0009922817733698.
Zanini C, Maino P, Möller JC, Gobbi C, Raimondi M, Rubinelli S. Enhancing clinical decisions about care through a pre-consultation sheet that captures patients’ views on their health conditions and treatments: a qualitative study in the field of chronic pain. Patient Educ Couns. 2016;99(5):747–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pec.2015.11.029.
Aboumatar HJ, Carson KA, Beach MC, Roter DL, Cooper LA. The impact of health literacy on desire for participation in healthcare, medical visit communication, and patient reported outcomes among patients with hypertension. J Gen Intern Med. 2013;28(11):1469–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-013-2466-5.
Harrington JT, Walsh MB. Pre-appointment management of new patient referrals in rheumatology: a key strategy for improving health care delivery. Arthritis Care Res. 2001;45(3):295–300. https://doi.org/10.1002/1529-0131(200106)45:3<295::AID-ART263>3.0.CO;2-3.
Fothergill KE, Gadomski A, Solomon BS, Olson AL, Gaffney CA, Dosreis S, et al. Assessing the impact of a web-based comprehensive somatic and mental health screening tool in pediatric primary care. Acad Pediatr. 2013;13(4):340–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acap.2013.04.005.
Savage C, Bjessmo S, Borisenko O, Larsson H, Karlsson J, Mazzocato P. Translating ‘See-and-Treat’ to primary care: opening the gates does not cause a flood. Int J Qual Health Care. 2019;31(7):30–6. https://doi.org/10.1093/intqhc/mzy244.
Bose-Brill S, Feeney M, Prater L, Miles L, Corbett A, Koesters S. Validation of a novel electronic health record patient portal advance care planning delivery system. J Med Internet Res. 2018;20(6):e208. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.9203.
Gadomski AM, Fothergill KE, Larson S, Wissow LS, Winegrad H, Nagykaldi ZJ, et al. Integrating mental health into adolescent annual visits: impact of previsit comprehensive screening on within-visit processes. J Adolesc Health. 2015;56(3):267–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2014.11.011.
Albertson G, Lin CT, Schilling L, Cyran E, Anderson S, Anderson RJ. Impact of a simple intervention to increase primary care provider recognition of patient referral concerns. Am J Manag Care. 2002;8(4):375–81.
Baker DW, Persell SD, Kho AN, Thompson JA, Kaiser D. The marginal value of pre-visit paper reminders when added to a multifaceted electronic health record based quality improvement system. J Am Med Informatics Assoc. 2011;18(6):805–11. https://doi.org/10.1136/amiajnl-2011-000169.
Albada A, van Dulmen S, Bensing JM, Ausems MG. Effects of a pre-visit educational website on information recall and needs fulfilment in breast cancer genetic counselling, a randomized controlled trial. Breast Cancer Res. 2012;14(2):R37. https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr3133.
Chwistek M. “Are you wearing your white coat?”: telemedicine in the time of pandemic. JAMA. 2020;324(2):149–50. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.10619.
Kenton K, Pham T, Mueller E, Brubaker L. Patient preparedness: an important predictor of surgical outcome. Am J Obstetr Gynecol. 2007;197(6):654.e651–6.
Ringdal M, Chaboyer W, Ulin K, Bucknall T, Oxelmark L. Patient preferences for participation in patient care and safety activities in hospitals. BMC Nurs. 2017;16(1):69. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-017-0266-7.
Niibo P, Pruunsild C, Voog-Oras Ü, Nikopensius T, Jagomägi T, Saag M. Contemporary management of TMJ involvement in JIA patients and its orofacial consequences. EPMA J. 2016;7(1):12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13167-016-0061-7.
Greene SM, Tuzzio L, Cherkin D. A framework for making patient-centered care front and center. Permanente J. 2012;16(3):49–53.
Vahdat S, Hamzehgardeshi L, Hessam S, Hamzehgardeshi Z. Patient involvement in health care decision making: a review. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2014;16(1):e12454. https://doi.org/10.5812/ircmj.12454.
Geraghty EM, Franks P, Kravitz RL. Primary care visit length, quality, and satisfaction for standardized patients with depression. J Gen Intern Med. 2007;22(12):1641–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-007-0371-5.
Xie Z, Or C. Associations Between Waiting Times, Service Times, and Patient Satisfaction in an Endocrinology Outpatient Department: A Time Study and Questionnaire Survey. Inquiry. 2017;54:0046958017739527.
Eijk ES, Bettink-Remeijer MW, Timman R, Busschbach JJ. From pen-and-paper questionnaire to a computer-assisted instrument for self-triage in the ophthalmic emergency department: process and validation. Comput Biol Med. 2015;66:258–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2015.09.014.
Kripalani S, Hart K, Schaninger C, Bracken S, Lindsell C, Boyington DR. Use of a tablet computer application to engage patients in updating their medication list. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2019;76(5):293–300. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajhp/zxy047.
Morreel S, Philips H, Verhoeven V. Self-triage at an urgent care collaboration with and without information campaign. J Emerg Manag. 2019;17(6):511–6. https://doi.org/10.5055/jem.2019.0443.
Opel DJ, Henrikson N, Lepere K, Hawkes R, Zhou C, Dunn J, et al. Previsit Screening for Parental Vaccine Hesitancy: A Cluster Randomized Trial. Pediatrics. 2019;144(5):e20190802.
Sarkar U, Schillinger D, Bibbins-Domingo K, Nápoles A, Karliner L, Pérez-Stable EJ. Patient-physicians’ information exchange in outpatient cardiac care: time for a heart to heart? Patient Educ Couns. 2011;85(2):173–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pec.2010.09.017.
Sepucha K, Bedair H, Yu L, Dorrwachter JM, Dwyer M, Talmo CT, et al. Decision support strategies for hip and knee osteoarthritis: less is more: a randomized comparative effectiveness trial (DECIDE-OA study). J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019;101(18):1645–53. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.19.00004.
Bosworth HB, Fortmann SP, Kuntz J, Zullig LL, Mendys P, Safford M, et al. Recommendations for providers on person-centered approaches to assess and improve medication adherence. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32(1):93–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-016-3851-7.
The Annals of Family Medicine, AHRQ updates on primary care research: the AHRQ Patient-Centered Medical Home Resource Center. Ann Fam Med. 2014;12(6):586. https://doi.org/10.1370/afm.1728.
Almalki ZS, Karami NA, Almsoudi IA, Alhasoun RK, Mahdi AT, Alabsi EA, et al. Patient-centered medical home care access among adults with chronic conditions: National Estimates from the medical expenditure panel survey. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018;18(1):744. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-018-3554-3.
Gholamzadeh M, Abtahi H, Safdari R. Suggesting a framework for preparedness against the pandemic outbreak based on medical informatics solutions: a thematic analysis [published online ahead of print, 2021 Jan 27]. Int J Health Plann Manage. 2021;10.1002/hpm.3106. https://doi.org/10.1002/hpm.3106.
Ahmed S, Kelly YP, Behera TR, Zelen MH, Kuye I, Blakey R, et al. Utility, appropriateness, and content of electronic consultations across medical subspecialties: a cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172(10):641–7. https://doi.org/10.7326/M19-3852.
Hällfors E, Saku SA, Mäkinen TJ, Madanat R. A consultation phone service for patients with total joint Arthroplasty May reduce unnecessary emergency department visits. J Arthroplast. 2018;33(3):650–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2017.10.040.
Willan J, King A J, Jeffery K, Bienz N. Challenges for NHS hospitals during covid-19 epidemic. BMJ. 2020;368:m1117. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.m1117.
Ross SW, Lauer CW, Miles WS, Green JM, Christmas AB, May AK, et al. Maximizing the calm before the storm: tiered surgical response plan for novel coronavirus (COVID-19). J Am Coll Surg. 2020;230(6):1080–1091.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2020.03.019.
Acknowledgments
We would also like to express our gratitude to Farideh Namazi for their support with us during this research.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception idea of study: Marjan Ghazisaeeidi, Hamidreza Abtahi, Marsa Gholamzadeh; Acquisition of data: Marjan Ghazisaeeidi, Hamidreza Abtahi, Marsa Gholamzadeh. Analysis and/or interpretation of data: Marsa Gholamzadeh, Marjan Ghazisaeeidi. Drafting the manuscript: Marjan Ghazisaeeidi, Marsa Gholamzadeh. Revising the manuscript critically for important intellectual content: Marjan Ghazisaeeidi, Marsa Gholamzadeh, Hamidreza Abtahi. Approval of the version of the manuscript to be published: Marjan Ghazisaeeidi, Hamidreza Abtahi, Marsa Gholamzadeh. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study involves only a review of literature without involving humans and/or animals. The authors have no ethical conflicts to disclose.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table A-1.
Applied search strategies and their results.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Gholamzadeh, M., Abtahi, H. & Ghazisaeeidi, M. Applied techniques for putting pre-visit planning in clinical practice to empower patient-centered care in the pandemic era: a systematic review and framework suggestion. BMC Health Serv Res 21, 458 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-021-06456-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-021-06456-7












