Abstract
Background
A small proportion of patients use an excessively large amount of emergency care resources which often results in emergency department (ED) overcrowding, decreased quality of care and efficiency. There is a need to better identify these patients in order to target those who will benefit most from interventions adapted to their specific needs. We aimed to identify the predictive factors of short-term frequent use of ED (over a 1-year period) and chronic frequent use of ED (over a multiple-year period) and to highlight recurring characteristics in patients.
Methods
A scoping review was performed of all relevant articles found in Medline published between 1979 and 2015 (Ovid). This scoping review included a total of 20 studies, of these, 16 articles focussed on frequent ED users and four others on chronic frequent ED users.
Results
A majority of articles confirm that patients who frequently visit the ED are persons of low socioeconomic status. Both frequent and chronic frequent ED users show high levels of health care use (other than the ED) and suffer from multiple physical and mental conditions.
Conclusions
This research highlights which individual factors predict frequent emergency department use. Further research is needed to better characterize and understand chronic frequent users as well as the health issues and unmet medical needs that lead to chronic frequent ED use.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
A small proportion of patients utilize a disproportionately large amount of acute emergency care resources [1]. They represent as little as 2.7 % [2] of patients attending the emergency department (ED), but make up to 67 % [3] of all ED visits over a given period of time (usually 1 year). Many studies have discussed the concept of frequent users and their multiple characteristics. A recurring definition is four ED visits or more during a 12-month period [4–11].
Frequent ED visits represent substantial costs to the health care system [12–14]. They also decrease ED efficiency [15], contribute to ED overcrowding [16, 17] and can potentially impact services by redirecting them away from urgent cases [13]. Quality of care received may be suboptimal for frequent ED users, as care can be fragmented, episodic and poorly coordinated [18–21]. Physicians could also hold biases and feel less empathy for frequent ED patients [22]. Hence, the use of ED services by frequent users can often be perceived as inappropriate and nonurgent [3, 23]. As a result, the uncoordinated acute care received in the ED by these patients can be less effective compared to what they receive or would receive in primary care [24–26].
Previous studies have shown that frequent ED users are more likely to have chronic diseases, suffer from mental illnesses or have substance use disorders [4, 5, 27–32]. It has also been observed that from 1 year to the next, there is a natural decline of ED use by frequent users. However, the attrition rates of those who remained frequent ED users over the years decreased [30], making them an ideal group for targeted interventions. Very few studies have examined predictors of chronic frequent ED use, whereas frequent ED use is regarded as an excessive number of visits during a single year, chronic frequent ED use is defined as frequently visiting the ED for multiple years in a row. Improving our understanding of the needs of frequent and chronic frequent ED users and defining a new approach to correctly identify these patients would allow healthcare professionals to intervene before frequent use occurs and redirect them to more appropriate health services [33].
The main objective of this scoping review was to identify predictive factors of frequent use found in the literature and to highlight trends. A secondary objective was to underline the factors that are predictive of chronic frequent use over a multiple-year period.
Methods
We used the methodological framework for conducting a scoping review developed by Arksey and O’Malley [34]. Scoping review is recognized as a process of mapping the main concepts of a research area to its source and evidence available in the literature. The five key phases the authors developed were followed in order to maintain a rigorous and transparent method for data collection, analysis and interpretation: 1) identifying the research question; 2) identifying relevant studies; 3) selecting studies; 4) charting the data; and 5) collating, summarizing, and reporting the results.
Scoping review
-
1.
Identifying the research question
Based on current knowledge found in an initial review of the literature, our primary research question was defined as follows:
-
Which factors are predictive of frequent emergency department use?
A secondary question was also explored:
-
Which factors predict chronic frequent emergency department use over a multiple-year period?
-
-
2.
Identifying relevant studies
An electronic literature search of Medline (Ovid) for English and French articles published between 1979 and May 2015 was conducted. No articles discussing frequent or chronic frequent ED use were found prior to 1979. The following key words were used: Frequent user, Frequent attender, Heavy user, Super user, Repeat user and Emergency department. One hundred and forty articles were found. In addition to the primary search, an examination of the reference list of two systematic reviews, one literature review (found during the primary search) and the articles included in the review was done (hand searching). The latest systematic review published focused on frequent users and callers to emergency medical services [15]. Most of the studies also focused on case management, analyzed specific populations such as elderly people, mentally ill patients or 911 callers, or used descriptive statistics to define frequent ED users. Only one of the studies found in this paper was used in our scoping review. The second systematic review, which was published 5 years ago, only included American studies [35]. Finally, the literature review examined gaps in current knowledge and stated efforts needed in order to identify factors predictive of future frequent ED use before it occurs. Our scoping review adds new information as it provides an international perspective of all studies that have rigorously analysed predictive factors of heavy ED use.
-
3.
Selecting studies (Fig. 1)
In order to be included in the review, studies had to 1) report frequent ED use in adult populations, 2) define frequent use as a minimum of 3 or more ED visits per year and 3) use regression methods to define predictive factors of frequent ED use. Studies limited to a specific population like psychiatric, geriatric, homeless or addicted patients were excluded.
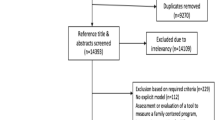
Fig. 1 Flow chart of literature search indicating exclusion criteria and the number of included articles. Figure 1 provides the literature search process and exclusion criteria established to select final articles included for data extraction.
The first step was to read the titles and abstracts of all potential articles and to exclude non-eligible articles based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria. This part was accomplished by one team member (CK). In case of uncertainty, the full articles were retrieved and also read by a second team member (CH). During this first step, a total of 59 articles were excluded as they had no connection with frequent ED use. Eighty-one articles from the primary search were retained for detailed evaluation. These articles were reviewed by two team members (CK and CH). Of these 81 articles, 68 were excluded: six were limited to a specific population; 35 focused on case management, primary care or patient satisfaction; four were either systematic reviews or qualitative interviews; and 23 of them used descriptive statistics to present the characteristics of frequent ED users. Another seven articles, which were all thoroughly examined by both team members (CK and CH), were retrieved by hand searching and added to the list of included articles. A total of 20 articles were included in this scoping review.
-
4.
Charting the data
The charting involved the extraction of information from individual articles. We collected descriptive characteristics such as authors, year of publication, study period, country where the study was held, study design, study population, sample size, definition of frequent use and predictive factors of frequent ED use.
-
5.
Collating, summarizing, and reporting the results
Results
Study designs and definitions (Table 1)
Out of the 20 articles that fulfilled the inclusion criteria, five were published between 2010 and 2014 [6, 11, 28, 36, 37]. All the other studies were published between 1998 and 2009 [3–5, 8–10, 23, 30, 33, 38–42] with the exception of one that was published in 1987 [31].
Twelve studies were from the USA [3, 4, 8, 9, 23, 33, 38–41], two were from Canada [11, 27], two were from Sweden [5, 7] and the four other studies were from Singapore [37], Switzerland [6], Taiwan [10] and Australia [42].
There was no standard definition of a frequent user, although the majority of the included studies (8) defined frequent use as 4 or more ED visits during a 12-month period [4–11]. Other definitions varied between 3 [39] and 17 [27] or more ED visits per year. A total of eight studies analyzed frequent ED use during a multiple-year period [7, 9, 30, 36, 38–40, 42]. However, only four [7, 36, 38, 39] of these studies used regression modeling to identify factors predicting chronic frequent ED use. Of the observed populations, frequent ED users represented between 3.5 % [10] and 29 % [36] of all patients attending the ED but accounted for 12.1 % [30] to 67 % [3] of all ED visits made.
Characteristics of frequent ED use (Table 2)
Gender
Three studies [27, 30, 37] found that males were more likely to be frequent users. Another study [11] found that being a female was predictive of frequent ED attendance and that male patients had a lower likelihood of being frequent attenders. A total of four other studies [3, 9, 33, 42] also analyzed gender as a potential independent factor but found that it was not a significant predictor of frequent ED use.
Age
In a population of 59,803 patients, patients in the geriatric age group (75 and older) were more likely to be frequent ED users compared to younger adults (20 to 49 years old). They also found that, compared to young adults, the odds of frequent use were lower for older adults (50 to 74 years old) [11]. Another study [37] also found that being 75 years old or more was a predictive factor of frequent ED use. However, two other studies stated otherwise as they found that frequent ED users were more likely to be between 30 and 59 years old and significantly younger than the non-ED users [30, 41]. Conversely, six studies stated that patient age was not a significant risk factor of frequent ED use [3, 9, 10, 27, 33, 42].
Location
One American and two Canadian studies suggested that hospital location could be a predictive factor of frequent ED use. One study concluded that frequent ED use was predicted by attending a rural ED [11] whereas the two other studies stated that patients living in urban areas were at higher risk of becoming frequent ED users [27, 33]. One study showed that living close to the ED (less than 10 km away) increased the risk of frequent ED use [6], while another one found that traveling more than 2 km in order to get to the ED significantly increased the odds of frequent ED attendance [37].
Education and socioeconomic factors
Two studies stated that lower-level education was predictive of frequent ED use [8, 33] and one study suggested that those with at least a college degree were less likely to be heavy ED users [40]. Two other studies found that patient education was not a significant factor [3, 10].
Many studies concluded that patients who had a low income [4, 8, 27, 40], were unemployed [6] or received a government pension [6, 42] were more likely to be frequent ED users. A few studies, however, found that monthly household income, financial barriers [10] and poverty [33] were not significant predictors of frequent ED use. Six different studies found that the type of health insurance a patient had would potentially predict ED use [3, 4, 23, 30, 33, 40]. Three studies also noted that without health insurance patients were also more likely to fall into this category [3, 4, 6].
Factors associated with current healthcare use
Frequent ED users tended to heavily use other medical services; some of the variables used to describe their health care use included multiple visits to a specialist physician [9, 27, 41] multiple visits to a primary care provider [5, 8, 27, 40], calling health helplines, [27] being previously hospitalized [3, 6, 8, 10, 41], having outpatient visits [4, 10], visiting a clinic [6, 10], having a history of past ED use [39], identifying an ED or hospital clinic as primary care site [8] and finally, using prescription medication [3, 9, 33]. Accessibility to primary healthcare was also discussed in a few studies. Two studies found that frequent ED users were significantly more likely to have listed primary care providers [8, 11].
Medical factors
Multiple studies stated that physical diseases were an important contributing factor in heavy ED use [3, 4, 8, 10, 27, 30, 37, 40]. Frequent ED users suffered from various medical conditions which included chronic diseases [10, 27], pulmonary diseases [3, 8, 10, 37] such as asthma [8, 27], chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [37] and acute respiratory infection [37], cardiovascular diseases [10] such as heart failure [41] and stroke [27], gastrointestinal diseases [10], diabetes [27], cancer [10], and exacerbation of chronic conditions including sickle cell anemia, renal failure and COPD [30]. Poor physical health was also a predictor of ED use in two studies which measured physical health with the SF-12 Health survey [4] and with self-reported statements [10].
ED patients with mental illnesses were also at higher risk of becoming frequent ED users [4, 6, 8–10, 27, 30, 42]. The relative risk of frequent use was higher in patients who were seen for substance abuse problems such as alcohol withdrawal, alcohol dependence and alcohol intoxication [30] or abuse problems [4]. Other studies also found that patients with poor mental health [4], high ratings of psychological distress [8] and depression [9] had greater odds of being frequent ED users.
Characteristics of chronic frequent ED use (Table 3)
Four studies examined factors that could predict frequent ED use over a multiple-year period. A first study found that previous ED visits was a predictive factor of chronic ED use. More so, they found other predictive factors such as having contact with psychiatric care, living alone and perceived loneliness [7]. In the second study, the authors used predictive modeling using standard regression techniques to predict which patients were most likely to become frequent ED users. Amongst the patients selected in the model, 77.9 % of chronic frequent users had higher levels of chronic illness and one half had multiple chronic conditions. A majority of this population also had behavioural health problems with 58.8 % of them having a history of substance abuse, 72.3 % a history of mental illness and 48.9 % having a history of both these conditions. Finally, those identified by this model had more ambulatory visits and were also at higher risk of becoming chronic users or “serial users” [36]. The third study found that patients who had at least one previous hospitalisation and at least one primary care visit were more likely to present frequent chronic use of the ED [38]. In the fourth and last study, the authors concluded that being a frequent user over the previous year was the only independent predictor of the level of ED use the following year [39].
Discussion
This scoping review aimed to conduct a scan of the current knowledge on predictive characteristics of both frequent and chronic frequent ED use. In general, patients frequently visiting the ED had a low socioeconomic status, high levels of health care use (other than the ED) and suffered from multiple physical and mental conditions. Although, to date, only a few studies have analyzed chronic frequent ED use, most predictive factors found for this population are similar to those found in frequent ED users.
In many cases, frequent use of ED is considered inappropriate [3, 4, 23]. As a result, the uncoordinated acute care received in the ED by these patients is potentially less effective compared to what they would receive in primary care. Frequent ED users also seek a lot of medical help outside of the ED, suggesting that they may have unmet healthcare and medical needs [8]. Most of these frequent users suffer from chronic conditions, many of which are ambulatory care sensitive conditions (ACSC), such as asthma [8, 27] COPD [37], and cardiovascular diseases like diabetes [29] and heart failure [37]. These are chronic diseases for which adequate ambulatory primary care could prevent deterioration or complications requiring ED visits or hospitalizations [43]. For some patients suffering from ACSC, the interaction with psychological and/or social problems could add a level of complexity that would interfere with usual care and lead to unmet healthcare needs [44, 45]. These predictive factors portray the complexity and multifaceted needs of frequent ED users. In order to provide adequate new strategies to better meet these patients’ healthcare needs, all of these factors must be taken into account.
The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Multiple Chronic Conditions Research Network defines complexity as the gap between an individual’s needs and the capacity of health services to answer those needs [46]. The implicit objective of the healthcare system is to identify these individuals’ needs and to treat them accordingly. The more complicated their needs get, the harder it is for healthcare services to provide the appropriate treatment. However, these patients often try in vain to handle their unmet healthcare needs by using multiple medical services such as the ED. Inevitably, this results in considerable costs to the healthcare system. Even though these patients try to handle their conditions, they still present low health indicators such as high mortality rates [47].
Hence, frequent ED users rely heavily on the ED for ambulatory care; however they could greatly benefit from timely access to preventive and continuous care in a primary care setting. Case management is recognized internationally as an appropriate intervention strategy for complex health situations and to improve the capacity of healthcare services to answer these patients’ particular needs [48, 49].
Due to the small number of studies analysing factors predictive of chronic frequent ED use, it is a challenge to properly portray these ED patients and to distinguish them from frequent ED users. Chronic frequent users share similar traits with frequent ED users, such as heavy use of health care services other than the ED. They also suffer from similar physical and mental diseases. However, more research is needed to better understand the underlying reasons leading to frequent users becoming chronic frequent users over time.
Strengths and limitations
To our knowledge, this is the first paper to review and summarise predictive factors of frequent and chronic ED use analyzed by regression modelling. Two independent authors reviewed all articles. However, only English and French articles were included, which may lead to selection bias. Furthermore, a majority of articles were based in American settings, limiting the comparability of results to other countries around the world. The lack of consistent definition of frequent ED use does not allow strong comparisons among studies. Only one database (Medline) was used in order to find relevant articles and this study did not include a quantitative summary of the results found. A meta-analysis could be the next step in research on predictive characteristics of frequent and chronic frequent ED users. The influence of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA) on frequent ED use is yet to be known.
Conclusions
Many frequent ED users have high levels of health care use (other than the ED), a lower socioeconomic status, and suffer often from concomitant multiple physical and mental conditions. More research is needed in order to better understand factors leading to chronic ED use and to develop effective strategies to better meet their complex health care needs.
Abbreviations
- ACSC:
-
Ambulatory care sensitive conditions
- COPD:
-
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- DRG:
-
Diagnosis-related group
- ED:
-
Emergency department
- MIDAS:
-
Migraine disability instrument
- PPACA:
-
The patient protection and affordable care act
References
Gawande A. The hot spotters: can we lower medical costs by giving the neediest patients better care? New Yorker; 2011. p. 40–51.
Murphy AW, Leonard C, Plunkett PK, Brazier H, Conroy R, Lynam F, Bury G. Characteristics of attenders and their attendances at an urban accident and emergency department over a one year period. J Accid Emerg Med. 1999;16(6):425–7.
Griswold SK, Nordstrom CR, Clark S, Gaeta TJ, Price ML, Camargo Jr CA. Asthma exacerbations in North American adults: who are the “frequent fliers” in the emergency department? Chest. 2005;127(5):1579–86.
Hunt KA, Weber EJ, Showstack JA, Colby DC, Callaham ML. Characteristics of frequent users of emergency departments. Ann Emerg Med. 2006;48(1):1–8.
Hansagi H, Olsson M, Sjoberg S, Tomson Y, Goransson S. Frequent use of the hospital emergency department is indicative of high use of other health care services. Ann Emerg Med. 2001;37:561–7.
Bieler G, Paroz S, Faouzi M, Trueb L, Vaucher P, Althaus F, Daeppen JB, Bodenmann P. Social and medical vulnerability factors of emergency department frequent users in a universal health insurance system. Acad Emerg Med. 2012;19(1):63–8.
Andrén KG, Rosenqvist U. Heavy users of an emergency department—A two year follow-up study. Soc Sci Med. 1987;25(7):825–31.
Sun BC, Burstin HR, Brennan TA. Predictors and outcomes of frequent emergency department users. Acad Emerg Med. 2003;10(4):320–8.
Friedman BW, Serrano D, Reed M, Diamond M, Lipton RB. Use of the emergency department for severe headache. A population-based study. Headache. 2009;49(1):21–30.
Huang JA, Tsai WC, Chen YC, Hu WH, Yang DY. Factors associated with frequent use of emergency services in a medical center. J Formos Med Assoc. 2003;102(4):222–8.
Palmer E, Leblanc-Duchin D, Murray J, Atkinson P. Emergency department use: is frequent use associated with a lack of primary care provider? Can Fam Physician. 2014;60(4):e223–9.
Cook LJ, Knight S, Junkins Jr EP, Mann NC, Dean JM, Olson LM. Repeat patients to the emergency department in a statewide database. Acad Emerg Med. 2004;11(3):256–63.
Lee A, Lau FL, Hazlett CB, Kam CW, Wong P, Wong TW, Chow S. Measuring the inappropriate utilization of accident and emergency services? Int J Health Care Qual Assur Inc Leadersh Health Serv. 1999;12(6–7):287–92.
Sandoval E, Smith S, Walter J, Schuman SA, Olson MP, Striefler R, Brown S, Hickner J. A comparison of frequent and infrequent visitors to an urban emergency department. J Emerg Med. 2010;38(2):115–21.
LaCalle E, Rabin E. Frequent users of emergency departments: the myths, the data, and the policy implications. Ann Emerg Med. 2010;56(1):42–8.
Trzeciak S, Rivers EP. Emergency department overcrowding in the United States: an emerging threat to patient safety and public health. Emerg Med J. 2003;20(5):402–5.
Cowan RM, Trzeciak S. Clinical review: Emergency department overcrowding and the potential impact on the critically ill. Crit Care. 2005;9(3):291–5.
Ettinger WH, Casani JA, Coon PJ, Muller DC, Piazza-Appel K. Patterns of use of the emergency department by elderly patients. J Gerontol. 1987;42(6):638–42.
Skinner J, Carter L, Haxton C. Case management of patients who frequently present to a Scottish emergency department. Emerg Med J. 2009;26(2):103–5.
Dale J, Green J, Reid F, Glucksman E. Primary care in the accident and emergency department: I. Prospective identification of patients. BMJ. 1995;311(7002):423–6.
Shumway M, Boccellari A, O’Brien K, Okin RL. Cost-effectiveness of clinical case management for ED frequent users: results of a randomized trial. Am J Emerg Med. 2008;26(2):155–64.
Survey: ED physicians report burnout, desire help for dealing with frequent users. ED Manag. 2011;23(9):104–05.
Ruger JP, Richter CJ, Spitznagel EL, Lewis LM. Analysis of costs, length of stay, and utilization of emergency department services by frequent users: implications for health policy. Acad Emerg Med. 2004;11(12):1311–7.
Salit SA, Kuhn EM, Hartz AJ, Vu JM, Mosso AL. Hospitalization costs associated with homelessness in New York City. N Engl J Med. 1998;338(24):1734–40.
Hwang SW. Homelessness and health. Can Med Assoc J. 2001;164(2):229–33.
Pearson DA, Bruggman AR, Haukoos JS. Out-of-hospital and emergency department utilization by adult homeless patients. Ann Emerg Med. 2007;50(6):646–52.
Doupe MB, Palatnick W, Day S, Chateau D, Soodeen RA, Burchill C, Derksen S. Frequent users of emergency departments: developing standard definitions and defining prominent risk factors. Ann Emerg Med. 2012;60(1):24–32.
Fuda KK, Immekus R. Frequent users of Massachusetts emergency departments: a statewide analysis. Ann Emerg Med. 2006;48(1):9–16.
Mancuso D, Nordlund DJ, Felver B. Frequent emergency room visits signal substance abuse and mental illness. Seattle: Washington State DSHS Research and Data Analysis Division; 2004.
Mandelberg JH, Kuhn RE, Kohn MA. Epidemiologic analysis of an urban, public emergency department’s frequent users. Acad Emerg Med. 2000;7(6):637–46.
Andren KG, Rosenqvist U. Heavy users of an emergency department: psycho-social and medical characteristics, other health care contacts and the effect of a hospital social worker intervention. Soc Sci Med. 1985;21(7):761–70.
Lowe RA, Young GP, Reinke B, White JD, Auerbach PS. Indigent health care in emergency medicine: an academic perspective. Ann Emerg Med. 1991;20(7):790–4.
Pines JM, Buford K. Predictors of frequent emergency department utilization in Southeastern Pennsylvania. J Asthma. 2006;43(3):219–23.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Scott J, Strickland AP, Warner K, Dawson P. Frequent callers to and users of emergency medical systems: a systematic review. Emerg Med J. 2014;31(8):684–91.
Billings J, Raven MC. Dispelling an urban legend: frequent emergency department users have substantial burden of disease. Health Aff. 2013;32(12):2099–108.
Paul P, Heng BH, Seow E, Molina J, Tay SY. Predictors of frequent attenders of emergency department at an acute general hospital in Singapore. Emerg Med J. 2010;27(11):843–8.
Rask KJ, Williams MV, McNagny SE, Parker RM, Baker DW. Ambulatory health care use by patients in a public hospital emergency department. J Gen Intern Med. 1998;13(9):614–20.
Okuyemi KS, Frey B. Describing and predicting frequent users of an emergency department. J Assoc Acad Minor Phys. 2001;12(1–2):119–23.
Zuckerman S, Shen YC. Characteristics of occasional and frequent emergency department users: do insurance coverage and access to care matter? Med Care. 2004;42(2):176–82.
Freitag FG, Kozma CM, Slaton T, Osterhaus JT, Barron R. Characterization and prediction of emergency department use in chronic daily headache patients. Headache. 2005;45(7):891–8.
Moore G, Gerdtz M, Manias E, Hepworth G, Dent A. Socio-demographic and clinical characteristics of re-presentation to an Australian inner-city emergency department: implications for service delivery. BMC Public Health. 2007;7:320.
Caminal J, Starfield B, Sanchez E, Casanova C, Morales M. The role of primary care in preventing ambulatory care sensitive conditions. Eur J Pub Health. 2004;14(3):246–51.
Matzer F, Wisiak UV, Graninger M, Sollner W, Stilling HP, Glawischnig-Goschnik M, Lueger A, Fazekas C. Biopsychosocial health care needs at the emergency room: challenge of complexity. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e41775.
de Jonge P, Huyse FJ, Stiefel FC. Case and care complexity in the medically ill. Med Clin North Am. 2006;90(4):679–92.
Grembowski D, Schaefer J, Johnson KE, Fischer H, Moore SL, Tai-Seale M, Ricciardi R, Fraser JR, Miller D, LeRoy L. A conceptual model of the role of complexity in the care of patients with multiple chronic conditions. Med Care. 2014;52 Suppl 3:S7–14.
Schoen C, Osborn R, Squires D, Doty M, Pierson R, Applebaum S. New 2011 survey of patients with complex care needs in eleven countries finds that care is often poorly coordinated. Health Aff. 2011;30(12):2437–48.
Berry-Millett R, Bodenheimer TS. Care management of patients with complex health care needs. Synth Proj Res Synth Rep. 2009;(19).
Van Mierlo LD, Meiland FJ, Van Hout HP, Droes RM. Towards personalized integrated dementia care: a qualitative study into the implementation of different models of case management. BMC Geriatr. 2014;14:84.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Fatoumata Diadiou and Susie Bernier for their precious help and constructive feedback on the final drafts of the manuscript.
Funding
Grant from the Université de Sherbrooke Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Authors’ contributions
CK and CH conceived and designed the study. CK and CH collected and analysed the data. CK and CH wrote the first draft of the manuscript. MCC and ID contributed to the writing of the manuscript. All authors agree with manuscript results and conclusions.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Krieg, C., Hudon, C., Chouinard, MC. et al. Individual predictors of frequent emergency department use: a scoping review. BMC Health Serv Res 16, 594 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-016-1852-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-016-1852-1