Abstract
Background
Ephedra chilensis K Presl, known locally as pingo–pingo, is a Chilean endemic plant used in traditional medicine as an anti-inflammatory and used in other treatments. However, unlike for the other Ephedra species, there have been no reports on the antioxidant and cytotoxic effects of this plant. The present study aims to explore the potential applications of E. chilensis extract as a cytotoxic agent against in vitro cancer cell lines and to explore the relationship between this extract and antioxidant activity.
Methods
Total anthraquinone, flavonoid, and phenolic contents, as well as antioxidant activity (DPPH, FRAP, and TRAP assays) and cytotoxic effect on several cancer cell lines (MCF-7, PC-3, DU-145, and HT-29) were measured for the hexane, dichloromethane and ethanol extracts of E. chilensis. In addition, several correlations among the phytochemical content, antioxidant activity, and cytotoxic effect were evaluated. Finally, GC-MS analyses of the most active extracts were carried out to identify their major components and to relate these components to the cytotoxic effect.
Results
Antioxidant activity was found in the EtOH extracts of Ephedra, and the results were correlated with the phenolic content. For the cytotoxic activity, the non-polar extracts of E. chilensis had the highest antiproliferative effect for the MCF-7 and PC-3 cancer lines; the extract was shown to be up to three times more selective than doxorubicin. However, the cytotoxic effect was not correlated with the antioxidant activity. Lastly, the GC-MS analysis showed a high concentration of saturated fatty acids (mainly n-hexadecanoic acid) and terpenoids (mainly 4-(hydroxy-ethyl)-γ-butanolactone).
Conclusion
The cytotoxic activity and selectivity of the non-polar extracts of E. chilensis for the MCF-7 and PC-3 cell lines could be related to the terpenic compounds and fatty acids of the extracts or to the synergistic effect of all of the compounds in the extracts. These non-polar extracts can be used for the development of new drugs against breast and prostate cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
There has been an ongoing increase in the incidence of chronic non-communicable diseases (CNCDs) worldwide, with cancer as one example of such diseases [1]. In fact, the World Health Organization estimated that in the year 2030, 11 million people will die due to cancer [2]. The traditional chemotherapy treatment against cancer causes undesirable side effects, and complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) has thus emerged as a possible solution. Among CAM treatments, phytotherapy is currently the most commonly used [3]. Several studies have focused on the natural antioxidant intake because oxidation is closely related to cancer development [4].
The genus Ephedra is the only genus in the Ephedraceae family (which contains 35 to 45 species in total, commonly found worldwide) [5]. This genus has been studied due its high contents of ephedrine alkaloids [6]. However, several secondary metabolites as alkaloids (amphetamine-type, imidazole, quinoline, pyrrolidine, and others), flavonoids (flavonols, dihydroflavonol, flavanone, flavanols, flavones, anthocyanin), tannins (dimmer, trimmer and tetramer of proanthocyanidins), lignans, naphthalenes, esters, terpenoids, phenolic acids, and quinones have been reported in the Ephedra genus plants [7]. In addition, some Ephedra species have anti-inflammatory, antiviral, hepatoprotective, antibacterial and antifungal activities, as well as anticancer activities [7]. In fact, E. foeminea and E. alata are used in CAM for cancer treatment in south-eastern Europe [8]. By contrast, Chile has one such species, namely Ephedra chilensis K Presl, commonly known as pingo-pingo [9]. It is particularly abundant in the central zone and has a pink fruit that is fleshy and edible [10]. The ethnopharmacological information showed that E. chilensis is used for treating ulcers, abscesses, and clearing pus, as an astringent, anti-inflammatory, diuretic, and tonic, and for treatment of colds, and stomach and bladder pain, and is beneficial in the treatment of asthma, gonorrhoea, and syphilis [10]. Additionally, potential bioactive applications of E. chilensis have been explored. Examples of such applications are sun protection properties and growth-inhibitory activity against some bacterial cultures [11, 12].
Despite the previous ethnopharmacological applications of E. chilensis, no studies have been reported on its effect on cancer or on the antioxidant capacity of this species. Therefore, the goals of this work are to measure the phytochemical content (anthraquinones, phenols, and flavonoids), to evaluate the antioxidant activity and the cytotoxicity against cancer cells (MCF-7, HT-29, PC-3, and DU-145) and non-tumour (CoN) lines for different E. chilensis extracts, and to identify the chemical composition (GC-MS analysis) of the extracts that present the greatest activity against the cancer cell lines.
Methods
Plant material
The plant was collected at the coordinates 33° 05′ 50″ S – 71° 35′ 27″ W at 460 m.a.s.l. in April 2016. A voucher specimen is kept in the Herbarium of Natural Products Laboratory of Universidad de Playa Ancha, Valparaíso, Chile (ECKP-2016). The plant was recognized by Rodrigo Villaseñor, Biology professor and expert in botany. He considered the plant’s morphological properties.
Extraction procedure
The portion of the plant selected (aerial parts) was dried at room temperature and then subjected to successive extractions using different solvents of increasing polarity, similar to a procedure reported in a previous study [13]. Using dried plant (310 g) and 1 L of each solvent (n-hexane (Hex), dichloromethane (CH2Cl2) and ethanol (EtOH)), the extraction of E. chilensis was completed in 48 h, and replicated three times. All of the obtained extracts were concentrated in a rotary evaporator at 40 °C, and then each extract was stored at room temperature in the dark.
Phytochemical determination
Total anthraquinones content estimation
This estimation was carried out using the protocol of Arvouet-Grand et al. adapted by Mellado et al [14]. One mL of 2% w/v aluminium trichloride (AlCl3) in ethanol was mixed with the same volume of the extract solution in ethanol (1.0 mg/mL). The mix was incubated for 10 min at room temperature, and absorbance was measured at 486 nm against a blank sample consisting of 1.0 mL extract solution with 1.0 mL of methanol without AlCl3. The absorbance values were interpolated using an emodin calibration curve (0–70 mg / L). The total anthraquinones content was expressed as μg of emodin equivalents (EE) / g of dry extract. All of the determinations were performed in triplicate.
Total flavonoid content estimation
The total flavonoid content was determined using the Dowd method, as adapted by Arvouet-Grand et al. [15]. One mL of 2% w/v aluminium trichloride (AlCl3) in ethanol was mixed with the same volume of the extract solution in ethanol (1.0 mg/mL). The mix was incubated for 10 min at room temperature, and absorbance was measured at 415 nm against a blank sample consisting of a 1.0 mL extract solution with 1.0 mL of methanol without AlCl3. The absorbance values were interpolated using a quercetin calibrate curve (0–100 mg / L). The total flavonoid content was expressed as μg of quercetin equivalents (QE) / per g of dry extract. All of the measurements were replicated three times.
Total phenolic content determination
The amount of total phenolic compounds in the extracts was determined using the method reported by Waterman et al. with small modifications determined by our research team [13]. Each extract sample (2.0 mg) was diluted to 2.0 mL with ethanol. Five hundred microliters were mixed with a Folin-Ciocalteau reagent (2.5 mL, 0.2 N) and incubated for 5 min. Then, a 7.5% w/v Na2CO3 solution (2.0 mL) was added and the mix was incubated in the dark at room temperature for 2 h. The absorbance of the solution was measured at 700 nm using ethanol as the blank. The obtained absorbance values were interpolated using a Gallic acid standard curve (0–200 mg / L) and the total phenolic content was expressed as mg of Gallic acid equivalents (GAE) per g of dried extract. All of the measurements were replicated three times.
Antioxidant capacity
Radical scavenging assays using DPPH
The DPPH assay was performed as described by Brand-Williams et al, with modifications [16]. The sample (100 μL, extracts at 0–10 mg / mL) was mixed with a 50 μM DPPH● solution (2.9 mL) freshly prepared in ethanol. A 50 μM DPPH● solution (2.9 mL) with ethanol (0.1 mL) was used as the control. The sample and control solutions were incubated for 15 min at room temperature, and the absorbance was measured at 517 nm. The inhibition (%) was calculated by the following equation:
From the obtained Inhibition (%) values, the IC50 value was determined by linear regression analysis.
Ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) assay (III)
The ferric reducing power was measured as described by Dudonné et al. with modifications [17]. Freshly prepared (10 volumes of 300 mM acetate buffer, pH 3.6, with 1.0 volume of 10 mM TPTZ (2,4,6-tri(2-pyridyl)-s-triazine) in 40 mM hydrochloric acid, and 1.0 volume of 20 mM ferric chloride) FRAP reagent (3.0 mL) was mixed with deionized water (300 μL) and the sample (100 μL, 1.0 mg/mL of each extract). The mix was incubated for 30 min at 37 °C in a water bath and the absorbance was measured at 593 nm using ethanol as the blank solution. The obtained absorbance values were interpolated in a Trolox calibrate curve (0–200 mg / L) and the FRAP values were expressed in mM Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (mM TEAC). All of the measurements were performed in triplicate.
Total reactive antioxidant power (TRAP) assay
The method developed by Romay et al. was slightly modified for this experiment [18]. One volume of 10 mM solution of ABAP (2,2′-azo-bis(2-amidino propane) was mixed with the same volume of 150 μM solution of ABTS (2,2′-azinobi(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) using PBS 100 mM at pH of 7.4 (TRAP solution). The mixture was incubated at 45 °C for 30 min and then cooled to room temperature for use. Sample solution (10 μL, 1.0 mg / mL of each extract) was mixed with the TRAP solution (990 μL), and the absorbance was measured after 50 s at 734 nm against the ABTS solution as the blank. The absorbance values were interpolated in a Trolox standard curve (0–120 mg / L). All of the measurements were replicated three times.
Cell lines
The following experimental cell cultures were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (Rockville, MD, USA): MCF-7 (human breast cancer), HT-29 (human colon cancer), PC-3 and DU-145 (human prostate cancer) and CoN (human colon epithelial cells CCD 841). All of the cell lines were grown in a DMEM-F12 medium containing 10% FCS, 100 U/mL penicillin, 100 μg/mL streptomycin and 1 mM glutamine. The cells were seeded into 96 well microliter plates at 100 μL, with a plating density of 3 × 103 cells/well. After a 24 h incubation at 37 °C (under a 5% humidified carbon dioxide ambient to allow cell attachment), the cells were treated with different concentrations of drugs and incubated for 72 h under the same conditions. A stock solution of extracts was prepared in ethanol, and the final concentration of this solvent was kept constant at 0.1%. Control cultures received only 0.1% ethanol.
In vitro growth inhibition assay
Following the method of Skehan et al., the sulforhodamine B assay was used with modifications [19, 20]. Briefly, the cells were seeded at 3 × 103 cells per well of a 96-well, flat-bottomed 200 μL microplate. The cells were incubated at 37 °C in a 5% humidified CO2 ambient plus 95% air mixture and were treated with the extracts at different concentrations for 72 h. At the end of the drug exposure, the cells were fixed with 50% trichloroacetic acid at 4 °C (TCA final concentration 10%). After washing with distilled water, the cells were stained with 0.1% sulphorhodamine B (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), dissolved in 1% acetic acid (50 μL/well) for 30 min, and then washed with 1% acetic acid to remove the unbound stain. The protein-bound stain was solubilized with a 10 mM unbuffered Tris base (100 μL). The cell density was determined using a fluorescence plate reader (wavelength 540 nm). Untreated cells were used as the negative control while cells treated with doxorubicin (Doxo.) were used as the positive control. In addition, all of the samples were tested from 0 to 10 μg/mL (concentration of extracts) using ethanol as the carrier solvent. All of the measurements were replicated three times. Finally, Sigma Plot software was used to calculate the IC50 value.
Selectivity index
The selectivity of each extract in each cell line was analysed by calculating the selectivity index (SI) as IC50 CoN / IC50 cancer cell line. If the values of SI were equal or greater than 3, it is said that the extract is selective. If the value exceeds 10, the selectivity was assumed to be very high [21].
GC-MS analysis
All extracts of E. chilensis were analysed by GC-MS (Shimadzu GC-17 A, mass detector GC-MS-QP5050, Shimadzu Corp, Kioto, Japan). The extracts (1.0 μL) were injected in the splitless mode (5 min) into a BPX-5MS column (30 m, 0.25 mm diameter, SGE) with helium as the carrier gas at a constant flow of 1.5 mL min− 1 and a column pressure of 92.3 KPa. The Injector temperature was 260 °C. The thermal profile was as follows: the temperature was held for 2 min at 80 °C and then increased at a rate of 8 °C /min− 1 to 270 °C, and then that temperature was maintained for 15 min. The mass scan was set between 35 and 500 a.m.u. The mass spectra were compared with the internal spectra database. A match below 90% confidence was considered as “unknown compounds”. Compounds in the chromatograms were identified by comparison of their mass spectra with those in the NIST/EPA/NIH Mass spectral Library [22]. Chromatographic peaks were considered “unknown” when their similarity index (MATCH) and reverse similarity index (RMATCH) were less than 850 and were discarded [23]. These parameters refer to the matching capability of the target spectrum with the standard spectrum in the NIST Library (a value of 1000 indicates a perfect fit). Additionally, a comparison of the retention index was made with values reported in the literature for the same type of column, or with commercial standards when available [24]. The retention indexes were determined under the same operating conditions in relation to a homologous n-alkanes series (C8–C36) by the equation:
where n is the number of carbon atoms in the smaller n-alkane, N is the number of carbon atoms in the larger n-alkane, and Tr was the retention time. The relative concentrations of the components were obtained by peak area normalization.
Statistical analysis
The data were reported as the mean values ± standard deviation (SD). Due to non-parametric data, a Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA was used with a confidence level of 95% with STATISTICA 7.0 program.
Results
Phytochemical content
After E. chilensis extracts were obtained, their phytochemical content (total anthraquinone, flavonoid, and phenolic contents) was measured using colorimetric assays as summarized in Table 1. For the total anthraquinones and flavonoids content, there are significant differences in the CH2Cl2 extracts (p < 0.05) compared to the other extracts. The total phenolic content in both CH2Cl2 extract and EtOH extract shows significant differences (p < 0.05) with the Hex extract.
Antioxidant activity
The antioxidant activity of E. chilensis extracts was evaluated in a series of in vitro tests using the DPPH, FRAP and TRAP assays (see Table 2). The DPPH assay showed that the Hex extract had poor activity (p < 0.05) compared with the positive controls (Trolox and Gallic acid). CH2Cl2 and EtOH extracts show similar activities, and these activities are different from the activities of Trolox and Gallic acid (p < 0.05). For the FRAP assay, the CH2Cl2 and EtOH extracts show better antioxidant activity than the positive controls (p < 0.05). Finally, the TRAP assay showed that the Hex extract was the least active of all of the tested extracts compared with the positive controls (Gallic acid and BHT) with significant differences (p < 0.05).
Phytochemical content - antioxidant activity relationship
The correlation between the phytochemical content and antioxidant activity was evaluated using Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient (r). All of the obtained correlations are summarized in Table 3. In this case, all of the antioxidant assays were closely related to the total phenolic content (r > 0.9 and p < 0.05), while anthraquinones and flavonoids were not related to this property (r < 0.9 and p > 0.05).
Cytotoxic activity
The cytotoxic activity of E. chilensis extracts was evaluated using a colorimetric assay, in vitro against different cancer cell lines, namely MCF-7 breast cancer, HT-29 colon cancer, DU-145 and PC-3 prostate cancer, and one non-tumour cell line of human colon epithelial cells CCD 841 (CoN). IC50 values were obtained from this assay and are summarized in Table 4. For the MCF-7 and PC-3 cancer cell lines, Hex and CH2Cl2 showed more activity than Doxorubicin (p < 0.05), while for the HT-29 and DU-145 cell lines, all of extracts were less active than Doxorubicin (p < 0.05). Finally, for the non-cancer cell line (CoN), CH2Cl2 had the most active extract.
Phytochemical content - antioxidant activity – cytotoxic effect relationships
The correlations between the cytotoxic effects on the MCF-7 and PC-3 cancer cell lines, phytochemical content, and antioxidant activity were evaluated out using Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient (r). The results are shown in Table 5. It was found that in this assay, the phytochemical content and antioxidant activity are not correlated with the cytotoxic effect on both cancer cell lines (r < 0.9 and p > 0.05).
Selectivity of cytotoxic effect
The selectivity measurement was carried out using a ratio between the non-cancer cell line and the cancer cell line (IC50CoN / IC50 cancer cell line). The results of the selectivity for E. chilensis extracts are presented in Table 6. For the MCF-7 and PC-3 cancer cell lines, the n-hexane extract showed more selectivity than Doxorubicin (1.8 times in MCF-7 and 3.3 times in PC-3). However, no extracts were selective against HT-29 and DU-145 (selectivity ≤1.0).
GC-MS analysis
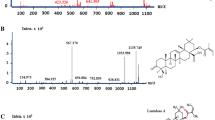
The most active and selective E. chilensis extracts against breast and prostate cancer cell lines (Hex and CH2Cl2) were analysed by GC-MS. The results of this analysis are shown in Tables 7 and 8. In the Hex extract, high amounts of fatty acids and derivatives were found. Among these, we found n-tetradecanoic, n-pentadecanoic, n-hexadecanoic, and n-octadecanoic acid (44.37% of the total extract composition, see Table 7). In the CH2Cl2 extract, we found n-tetradecanoic and n-hexadecanoic acid ethyl ester with 2.4% of the total composition (see Table 8). Alcohol derivatives of fatty acids were found in both extracts (trans-9-hexadecen-1-ol and 1-Eicosanol). For the ethanol extract, compounds with match quality higher than 65% could not be identified.
In addition, terpenic compounds were identified in the CH2Cl2 extract. Among these, we found phytol, loliolide, and 4-(Hydroxy-ethyl)-γ-butanolactone (29.43% of the total extract composition, see Table 8). Furthermore, the long-chain alkanes family was another compound family identified in GC-MS analysis. Among these compounds, we found n-heptadecane, n-triacontane and n-hexatriacontane (see Tables 7 and 8) with 5.75% of the Hex extract composition and 1.89% of the CH2Cl2 extract composition.
Other families of compounds identified in GC-MS were phenolic compounds that were found only in the CH2Cl2 extract, namely isovanillin and (E)- Coniferyl alcohol with 3.76% of the extract composition (see Table 8).
Discussion
The anthraquinone and flavonoid contents are concentrated in the CH2Cl2 extracts (p < 0.05, see Table 1), and comparing these results with other Ephedra species, we found that there are no reports of anthraquinones in any Ephedra species. However, flavonoids and related compounds have been reported in E. aphylla, E. sinica, E. campylopoda, and E. alata [7]. Furthermore, the obtained flavonoid content showed a three-fold decrease compared to that of E. major [25]. In addition, phenolic compounds were mainly found in the CH2Cl2 and EtOH extracts (see Table 1), and our results for both of these extracts have similar values to those of E. major, [25] and a higher phenolic content than E. sinica [26]. These compound types have not been reported in E. chilensis (except ephedrine). However, other Ephedra species have been isolated and some of these compounds have been identified [25, 27].
The antioxidant activity of E. chilensis extracts was evaluated in a series of in vitro tests (see Table 2). The DPPH assay showed that EtOH extracts of E. chilensis have the highest antioxidant activity, and present better activity than E. laristanica and E. Sarcocarpa (IC50 = 4.6 and IC50 = 5.3 mg / mL, respectively) [28, 29]. Despite these results, all extracts have lower antioxidant activity than the positive controls. The FRAP and TRAP assays showed that the Hex extract has less antioxidant activity than the CH2Cl2 and the EtOH extracts. However, FRAP assay showed that all extracts are more active than the positive control (between 2.1 and 17.3 times more active than Gallic acid). TRAP assay showed that the extracts have similar activity to the positive controls. In addition, phytochemical content has been associated with the antioxidant activity [30, 31]. The DPPH scavenging activity found in the present work is consistent with the total phenolic content (r = − 0.942, see Table 3), which is similar to the previous reports on E. sinica [32]. For the FRAP and TRAP assays, we found correlations between the total phenolic content (r > 0.9, p < 0.05, see Table 3). Based on the results obtained in the FRAP assay, the E. chilensis extracts manifest their antioxidant effect as reductive substances acting as single electron transferrers [33]. The TRAP assay on E. chilensis extracts showed great affinity of the extract with the peroxyl radical [34].
The cytotoxic effect of E. chilensis extracts was evaluated in vitro against several cell lines (see Table 4). The E. chilensis extracts present higher activity for the MCF-7 and PC-3 cell lines (IC50 < 1.0 μg / mL), while the HT-29 and DU-145 cell lines are resistant to the same treatment (IC50 > Doxo in each cell line, see Table 4). The cytotoxic effect is related to several factors among which we can mention the solvent used for the extraction and the species; e.g., decoctions of E. foeminea and E. alata are used for breast cancer treatment in south-eastern Europe [8]. E. alata extract has no cytotoxic effect against human liver cancer or against the leukaemia cell line, [35] E. sinica alcoholic extracts has a low cytotoxic effect against melanoma and non-cancer, [36] and the CHCl3 extract of E. viridis does show cytotoxic action against leukaemia cells [37]. The values obtained for MCF-7 and PC-3 cancer cell lines show promising anticancer properties for possible drug discovery and development according to the American National Center Institute [21]. In fact, the non-polar extracts possess more activity than the antineoplastic drug for the MCF-7 and PC-3 cancer cell lines (as much as 3.9 times higher activity for MCF-7 and up to 7.2 times higher for PC-3, see Table 4). Exogenous antioxidant intake could be associated with chemoprevention of chronic diseases such as cancer, together with the presented correlation between phytochemical content and the antioxidant activity [31, 38]. The correlation between the phytochemical content of E. chilensis extracts and the cytotoxic effect was evaluated, but it was found that there was no relationship between the antiproliferative effect and the phytochemical content or antioxidant activity (r < 0.5, see Table 5). In addition to the cytotoxic effect, the selectivity for the cancer cell lines as a possible drug development pathway is a very relevant feature that must be evaluated considering the undesirable side effects of traditional chemotherapy [39]. In this regard, the Hex and CH2Cl2 extracts of E. chilensis have better selectivity index values than doxorubicin (up to 1.8 times more selective for MCF-7 and 3.3 times more selective for PC-3, see Table 6).
Based on the above discussion, the Hex and CH2Cl2 extracts were analysed by GC-MS (see Table 7 and Table 8). The analysis did not identify ephedrine, which is a typical compound of this species. The ephedrine concentration in Ephedra species is variable; e.g., E. major, E. fragilis, E. distachya, and E. monosperma have different ephedrine concentrations, while this alkaloid was not identified in E. tweediana and E. foeminica [40, 41]. Nevertheless, the effect of ephedrine as a cytotoxic compound is not important because comparing both extracts (those free of ephedrine and those that do have ephedrine), similar activity is observed for non-small cell lung cancer [42]. For breast cancer cells, ephedrine has a poor cytotoxic activity [43]. Moreover, the GC-MS of both E. chilensis non-polar extracts (Hex and CH2Cl2) showed high concentrations of long-chain fatty acids, and some of these have been identified in other Ephedra species, e.g., n-tetradecanoic, n-pentadecanoic, n-hexadecanoic, and n-octadecanoic acids were found in seeds of E. nevadensis, E. viridis, E. przewalskii, E. geradiana, E. campylopoda, and E. sinica, and in the leaves of E. equizetina [44,45,46]. Regarding the cytotoxic effect, these fatty acids can inhibit abnormal breast cancer cells [47]. In fact, n-tetradecanoic acid, n-dodecanoic acid, and n-octadecanoic acid have differentiation and/or cytotoxic and/or apoptotic effects on breast cancer cells [48,49,50]. n-octadecanoic acid has cytotoxic effects for prostate carcinoma [51, 52]. For n-hexadecanoic acid, there have been no reports of cytotoxic activity on breast or prostate cancer cells. However, n-hexadecanoic acid affects colon cancer cell growth, while its ethyl ester derivative can inhibit the DNA topoisomerase I and is an apoptosis inductor in leukaemia and neuroblastoma cells [53,54,55]. Furthermore, alcohol derivatives of fatty acids such as trans-9-hexadecen-1-olare only present in the CH2Cl2 E. chilensis extract. This compound has a growth inhibition effect on breast cancer [56]. Other fatty alcohol derivatives such as 1-Eicosanol and lignoceric alcohol have not been reported to show cytotoxic effects on breast or prostate cancer. Nevertheless, they show antiproliferative activity for other cancer cell lines [57, 58]. Regarding the fatty acids and their derivative content in non-polar Ephedra extract, they could be related with activity and selectivity due to the n-tetra, n-penta, n-hexa, and n-octadecanoic acids present in the hexane extract corresponding to 41.37% of the total extract (see Table 7). The dichloromethane extract has fewer n-tetra and n-octadecanoic acids (2.40% of total extract, see Table 8). However, the synergistic effect between the fatty acids and other secondary metabolites cannot be ruled out.
Terpenoid derivatives were also identified, mainly in the dichloromethane extract of E. chilensis (see Table 8). Among these, we found phytol which was also found in E. campylopoda [59]. This compound showed cytotoxic activity for a wide range of cancer cell lines, and particularly for the MCF-7 and PC-3 cancer cell lines [60]. Others terpenic derivatives such as 4-(hydroxy-ethyl)-γ-butanolactone and loliolide were identified in the same extract (CH2Cl2, see Table 8). These compounds have highly similar structures. The extracts that present loliolide have high activity for the breast cancer MCF-7 cell line [61]. Moreover, in the same extract, phenolic compounds such as isovanillin and (E)-coniferyl alcohol were identified (see Table 8). Similar compounds (vanillin, ferulic acid, and lignin) have been found in E. breana and E. alata [62, 63]. These compounds have a common core (benzene-3,4-OR) which is a fragment present in several molecules with antiproliferative activity such as lignins and benzaldehydes [64,65,66].
On the other hand, in both non-polar extracts, we identified long-chain alkanes such as n-heptadecane, n-triacontane, and n-hexatriacontane (see Table 7 and Table 8), of which n-heptadecane and n-triacontane had cytotoxic effects on several cancer cell lines, with a particularly pronounced effect on breast cancer observed for n-triacontane [67, 68].
Other compounds present in the Hex extract such as 6,10-dimethyl-2-undecanone and 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propionitrile were identified (see Table 7). The first compound has a cytotoxic effect on the breast cancer cell lines [69]. A compound similar to 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propionitrile presents β-oestrogen receptor-selective inhibition which is important for breast cancer cells [70, 71].
Finally, despite the above discussion of the cytotoxic effect of the principal components identified in the non-polar extracts, the synergic effect between them is not ruled out.
Conclusions
In conclusion, hexane and dichloromethane extracts of E. chilensis showed low antioxidant activity but high activity for MCF-7 and PC-3 cancer cell lines. However, there was no correlation between the antioxidant activity and the anticancer activity. In both extracts, we found significant amounts of fatty acids and derivatives, and terpenic and phenolic compounds were identified by the GC-MS technique. All of the compounds presented a cytotoxic effect on many cancer cell lines, mainly breast and prostate cancer lines. Nevertheless, the synergic effect between these compounds is not ruled out.
These promising results suggest that non-polar E. chilensis extracts could be a source for new drug discoveries against breast and prostate cancers. These new drugs could have significantly milder secondary effects compared to chemotherapy.
Abbreviations
- Ant:
-
Anthraquinones content
- CAM:
-
Complementary and alternative medicine
- CH2Cl2 :
-
Dichloromethane extract
- CNCDs:
-
Chronic non-communicable diseases
- CoN:
-
Human colon normal cell line
- Doxo:
-
Doxorubicin drug
- DPPH:
-
2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl free radical assay
- DU-145:
-
Human prostate carcinoma cell line
- EtOH:
-
Ethanol extract
- Flav:
-
Flavonoid content
- FRAP:
-
Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power assay
- GC-MS:
-
Gas chromatography – Mass Spectrometry coupled assay
- Hex:
-
n-Hexane extract
- HT-29:
-
Human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line
- IC50 :
-
Half Inhibition concentration
- MCF-7:
-
Human breast adenocarcinoma cell line
- PC-3:
-
Human prostate adenocarcinoma cell line
- Phen:
-
Phenolic content
- TRAP:
-
Total Reactive Antioxidant Power assay
References
Unwin N, Alberti KGMM. Chronic non-communicable diseases. Ann Trop Med Parasit. 2006;100(5–6):455–64.
WHO: World Health Organization: Media Centre: Cancer. In.; 2015.
Horneber M, Bueschel G, Dennert G, Less D, Ritter E, Zwahlen M. How many Cancer patients use complementary and alternative medicine: a systematic review and Metaanalysis. Integr Cancer Ther. 2012;11(3):187–203.
Mut-Salud N, Alvarez PJ, Garrido JM, Carrasco E, Aranega A, Rodriguez-Serrano F. Antioxidant intake and antitumor therapy: toward nutritional recommendations for optimal results. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:6719534.
Caveney S, Charlet DA, Freitag H, Maier-Stolte M, Starratt AN. New observations on the secondary chemistry of world Ephedra (Ephedraceae). Am J Bot. 2001;88(7):1199–208.
Ibragic S, Sofic E. Chemical composition of various Ephedra species. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2015;15(3):21–7.
Zhang BM, Wang ZB, Xin P, Wang QH, Bu H, Kuang HX. Phytochemistry and pharmacology of genus Ephedra. Chin J Nat Med. 2018;16(11):811–28.
Jaradat NA, Al-Ramahi R, Zaid AN, Ayesh OI, Eid AM. Ethnopharmacological survey of herbal remedies used for treatment of various types of cancer and their methods of preparations in the West Bank-Palestine. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016;16:93.
Hoffman A: Flora Silvestre de Chile Zona Central 2da Edicion edn. Chile: Fundación Claudio Gay; 1978.
Sánchez G. Los mapuchismos en el DRAE. Bol Filologia. 2010;45(2):149–256.
Gajardo S, Aguilar M, Stowhas T, Salas F, López J, Quispe C, Buc-Calderon P, Benites J. Determinaion of sun protection factor of six Chilean Altiplano plants. BLACPMA. 2016;15(5):352–63.
Morales G, Sierra P, Mancilla A, Paredes A, Loyola L, Gallardo O, Borquez J. Secondary metabolites from four medicinal plants from Northen Chile: antimicrobial activity and biotoxicity against Artemia Salina. J Chil Chem Soc. 2003;48(2):13–8.
Jara C, Leyton M, Osorio M, Silva V, Fleming F, Paz M, Madrid A, Mellado M. Antioxidant, phenolic and antifungal profiles of Acanthus mollis (Acanthaceae). Nat Prod Res. 2017;31(19):2325–8.
Mellado M, Madrid A, Jara C, Espinoza L. Antioxidant effects of Muehlenbeckia hastulata J. (Polygonaceae) extracts. J Chil Chem Soc. 2012;57(2):1301–4.
Arvouet-Grand A, Vennat B, Pourrat A, Legret P. Standardization d’une extrait de propolis et identification des principaux constituents. Pharm Belg. 1994;49:462–8.
Brand-Williams W, Cuvelier M, Berset C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT Food Sci Technol. 1995;28:25–30.
Dudonné S, Vitrac X, Coutière P, Woillez M, Mérillon J. Comparative study of antioxidant properties and total phenolic content of 30 plant extracts of industrial interest using DPPH, ABTS, FRAP, SOD, and ORAC assays. J Agric Food Chem. 2009;57:1768–74.
Romay C, Pascual C. E. L: the reaction between ABTS radical cation and antioxidants and it’s use to evaluate the antioxidant status of serum samples. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1996;29(2):175–83.
Skehan P, Storeng R, Scudiero D, Monks A, McMahon J, Vistica D, Warren J, Bokesch H, Kenney S, Boyd M. New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990;82:1107.
Vichai V, Kirtikara K. Sulforhodamine B colorimetric assay for cytotoxicity screening. Nat Protoc. 2006;1(3):1112–6.
de Oliveira PF, Alves JM, Damasceno JL, Oliveira RAM, Dias HJ, Crotti AEM, Tavares DC: Cytotoxicity screening of essential oils in cancer cell lines. Rev Bras Farmacogn 2015, 25(2):183–188.
NIST/EPA/NIH: Mass Spectral Library with Search Program In.; 2016.
Santander R, Creixell W, Sanchez E, Tomic G, Silva JR, Acevedo CA. Recognizing age at slaughter of cattle from beef samples using GC/MS-SPME chromatographic method. Food Bioprocess Tech. 2013;6(12):3345–52.
Adams RP. Identification of essential oil components by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. 4th ed. IL, USA: Allured Publishing Corporation; 2007.
Aghdasi M, Bojnoordi MM, Mianabadi M, Nadaf M. Chemical components of the Ephedra major from Iran. Nat Prod Res. 2016;30(3):369–71.
Song FL, Gan RY, Zhang YA, Xiao Q, Kuang L, Li HB. Total phenolic contents and antioxidant capacities of selected Chinese medicinal plants. Int J Mol Sci. 2010;11(6):2362–72.
Cottiglia F, Bonsignore L, Casu L, Deidda D, Pompei R, Casu M, Floris C. Phenolic constituents from Ephedra nebrodensis. Nat Prod Res. 2005;19(2):117–23.
Rustaiyan A, Javidnia K, Farjam H, Mohammadi M, Mohammadi N. Total phenols, antioxidant potential and antimicrobial activity of the methanolic extracts of Ephedra laristanica. J Med Plant Res. 2011;5(24):5713–7.
Rustaiyan A, Javidnia K, Farjam M, Aboee-Mehrizi F, Ezzatzadeh E. Antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of the Ephedra sarcocarpa growing in Iran. J Med Plant Res. 2011;5(17):4251–5.
Surh YJ. Cancer chemoprevention with dietary phytochemicals. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3(10):768–80.
Khlifi D, Sghaier RM, Amouri S, Laouini D, Hamdi M, Bouajila J. Composition and anti-oxidant, anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory activities of Artemisia herba-alba, Ruta chalpensis L and Peganum harmala L. Food and chemical toxicology : an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association. 2013;55:202–8.
Song FL, Gan RY, Zhang Y, Xiao Q, Kuang L, Li HB. Total phenolic contents and antioxidant capacities of selected chinese medicinal plants. Int J Mol Sci. 2010;11(6):2362–72.
Apak R, Gorinstein S, Böhm V, Schaich KM, Özyürek M, Güçlü K. Methods of measurement and evaluation of natural antioxidant capacity/activity. Pure Appl Chem. 2013;85(5):957–98.
Dresch MT, Rossato SB, Kappel VD, Biegelmeyer R, Hoff ML, Mayorga P, Zuanazzi JA, Henriques AT, Moreira JC. Optimization and validation of an alternative method to evaluate total reactive antioxidant potential. Anal Biochem. 2009;385(1):107–14.
Kmail A, Lyoussy B, Zaid H, Saad B. In vitro assessments of cytotoxic and cytostatic effects of Asparagus aphyllus, Crataegus aronia, and Ephedra alata in monocultures and co-cultures of Hepg2 and THP-1-derived macrophages. Pharmacog Comm. 2015;5(3):165–72.
Nam NH, Lee CW, Hong DH, Kim HM, Bae KH, Ahn BZ: Antiinvasive, antiangiogenic and antitumour activity of Ephedra sinica extract. Phytother Res : PTR 2003, 17(1):70–76.
Pullela SV, Takamatsu S, Khan SI, Khan IA. Isolation of lignans and biological activity studies of Ephedra viridis. Planta Med. 2005;71(8):789–91.
Kumar S. The importance of antioxidant and their role in pharmaceutical science - a review. Asian Journal of Research in Chemistry and Pharmaceutical. Sciences. 2014;1(1):27–44.
Ramalho SD, Bernades A, Demetrius G, Noda-Perez C, Vieira PC, Dos Santos CY, da Silva JA, de Moraes MO, Mousinho KC. Synthetic chalcone derivatives as inhibitors of cathepsins K and B, and their cytotoxic evaluation. Chem Biodivers. 2013;10(11):1999–2006.
Bach HG, Iturbe N, Agudelo IJ, Wagner ML, Ricco RA. Polyphenol dinamics in Ephedra tweediana Fisch & C. A. Mey. Emend. J. H. Hunz. (Ephedraceae). Boletin Latinoamericano y del Caribe de Plantas Medicinales y Aromaticas. 2017;16(1):1–13.
Ibragic S, Sofic E. Chemical composition of various Ephedra species. Bosnian J Basic Med. 2015;15(3):21–7.
Oshima N, Yamashita T, Hyuga S, Hyuga M, Kamakura H, Yoshimura M, Maruyama T, Hakamatsuka T, Amakura Y, Hanawa T, et al. Efficiently prepared ephedrine alkaloids-free Ephedra herb extract: a putative marker and antiproliferative effects. J Nat Med. 2016;70(3):554–62.
Chen D, Ma F, Liu XH, Cao R, Wu XZ. Anti-tumor effects of ephedrine and Anisodamine on Skbr3 human breast Cancer cell line. Afr J Tradit Complem. 2016;13(1):25–32.
Wolff RL, Christie WW, Pedrono F, Marpeau AM, Tsevegsuren N, Aitzetmuller K, Gunstone FD. Delta 5-olefinic acids in the seed lipids from four Ephedra species and their distribution between the alpha and beta positions of triacylglycerols. Characteristics common to Coniferophytes and Cycadophytes. Lipids. 1999;34(8):855–64.
Khasbagan, Soyolt. Ephedra sinica Stapf (Ephedraceae): the fleshy bracts of seed cones used in Mongolian food and its nutritional components. Econ Bot. 2007;61(2):192–7.
Mirzaazimova KT, Gusakova SD, Glushenkova AI. Lipids from leaves of Ephedra equizetina. Chem Nat Compd. 1999;35(6):616–8.
Golini J, Jones W. Buffered vs non-buffered aliphatic fatty acids and their antiproliferative effects in human tmor cell lines. Single Cell Biol. 2014;4(1):107–13.
Milner JA, Fomagnolo DF. Saturated fatty acids and cancer in: Bioactive compounds and cancer. Edn. Edited by Forman RL, Mahabir S. New York: Humana Press; 2010. p. 213–34.
Lappano R, Sebastiani A, Cirillo F, Rigiracciolo DC, Galli GR, Curcio R, Malaguarnera R, Belfiore A, Cappello AR, Maggiolini M. The lauric acid-activated signaling prompts apoptosis in cancer cells. Cell death discovery. 2017;3:17063.
Khan AA, Alanazi AM, Jabeen M, Chauhan A, Abdelhameed AS. Design, synthesis and in vitro anticancer evaluation of a stearic acid-based ester conjugate. Anticancer Res. 2013;33(6):2517–24.
Liu J, Shimizu K, Kondo R. Anti-androgenic activity of fatty acids. Chem Biodivers. 2009;6(4):503–12.
Hughes-Fulford M, Chen Y, Tjandrawinata RR. Fatty acid regulates gene expression and growth of human prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Carcinogenesis. 2001;22(5):701–7.
Engelbrecht AM, Toit-Kohn JL, Ellis B, Thomas M, Nell T, Smith R. Differential induction of apoptosis and inhibition of the PI3-kinase pathway by saturated, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids in a colon cancer cell model. Apoptosis : an international journal on programmed cell death. 2008;13(11):1368–77.
Harada H, Yamashita U, Kurihara H, Fukushi E, Kawabata J, Kamei Y. Antitumor activity of palmitic acid found as a selective cytotoxic substance in a marine red alga. Anticancer Res. 2002;22(5):2587–90.
Pereira DM, Correia-da-Silva G, Valentao P, Teixeira N, Andrade PB. Palmitic acid and ergosta-7,22-dien-3-ol contribute to the apoptotic effect and cell cycle arrest of an extract from Marthasterias glacialis L. in neuroblastoma cells. Marine drugs. 2013;12(1):54–68.
Ghate NB, Das A, Chaudhuri D, Panja S, Mandal N. Sundew plant, a potential source of anti-inflammatory agents, selectively induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis in MCF-7 cells through upregulation of p53 and Bax/Bcl-2 ratio. Cell death discovery. 2016;2:15062.
Figueiredo CR, Matsuo AL, Massaoka MH, Girola N, Azevedo RA, Rabaca AN, Farias CF, Pereira FV, Matias NS, Silva LP, et al. Antitumor activity of kielmeyera coriacea leaf constituents in experimental melanoma, tested in vitro and in vivo in syngeneic mice. Advanced pharmaceutical bulletin. 2014;4(Suppl 1):429–36.
Vergara M, Olivares A, Altamirano C. Antiproliferative evaluation of tall-oil docosanol and tetracosanol over CHO-K1 and human melanoma cells. Electron J Biotechnol. 2015;18(4):291–4.
Kallassy H, Fayyad-Kazan M, Makki R, EL-Makhour Y, Rammal H, Leger DY, Sol V, Fayyad-Kazan H, Liagre B, Badran B. Chemical composition and antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and Antiproliferative activities of Lebanese &ITEphedra Campylopoda&IT plant. Med Sci Monit Basic. 2017;23:313–25.
Pejin B, Kojic V, Bogdanovic G. An insight into the cytotoxic activity of phytol at in vitro conditions. Nat Prod Res. 2014;28(22):2053–6.
Wei LS, Wee W, Siong JY, Syamsumir DF. Characterization of anticancer, antimicrobial, antioxidant properties and chemical compositions of Peperomia pellucida leaf extract. Acta medica Iranica. 2011;49(10):670–4.
Vio-Michaelis S, Apablaza-Hidalgo G, Gomez M, Pena-Vera R, Montenegro G. Antifungal activity of three Chilean plant extracts on Botrytis Cinerea. Bot Sci. 2012;90(2):179–83.
Nawwar MAM, Barakat HH, Buddrus J, Linscheid M. Alkaloidal, Lignan and phenolic constituents of Ephedra-Alata. Phytochemistry. 1985;24(4):878–9.
Medarde M, Maya ABS, Perez-Melero C. Naphthalene combretastatin analogues: synthesis, cytotoxicity and antitubulin activity. J Enzym Inhib Med Ch. 2004;19(6):521–40.
Lopez-Biedma A, Sanchez-Quesada C, Beltran G, Delgado-Rodriguez M, Gaforio JJ. Phytoestrogen (+)-pinoresinol exerts antitumor activity in breast cancer cells with different oestrogen receptor statuses. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016;16.
Madrid A, Espinoza L, Catalan K, Gonzalez C, Montenegro I, Mellado M, Werner E, Cuellar M, Villena J. Preliminary Antiproliferative evaluation of natural,-synthetic benzaldehydes and benzyl alcohols. J Chil Chem Soc. 2013;58(3):1814–6.
Kim DH, Park MH, Choi YJ, Chung KW, Park CH, Jang EJ, An HJ, Yu BP, Chung HY. Molecular study of dietary heptadecane for the anti-inflammatory modulation of NF-kB in the aged kidney. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59316.
Deepalakshmi K, Mirunalini S. Antiproliferative and apoptotic effect of Pleurotus ostreatus on human mammary carcinoma cell line (Michigan cancer foundation-7). Cancer Trans Med. 2016;2(4):95–104.
Bakr RO, El Bishbishy ME. Profile of bioactive compounds of Capparis spinosa var. aegyptiaca growing in Egypt. Rev Bras Farmacogn. 2016;26(4):514–20.
Mancuso M, Leonardi S, Giardullo P, Pasquali E, Borra F, Stefano ID, Prisco MG, Tanori M, Scambia G, Majo VD, et al. The estrogen receptor beta agonist diarylpropionitrile (DPN) inhibits medulloblastoma development via anti-proliferative and pro-apototic pathways. Cancer Lett. 2011;308(2):197–202.
Pettersson K, Gustafsson JA. Role of estrogen receptor beta in estrogen action. Annu Rev Physiol. 2001;63:165–92.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Vicerrectoría de Investigación y Estudios Avanzados (VRIEA) of Pontificia Universidad Católica de Valparaíso, and Miss Rafaela Sariego-Kluge for their technical support.
Funding
This work was financial supported by CONICYT Programa Formación de Capital Humano Avanzado 21130456, Fondecyt Postdoctorado grant 3180408 and Proyecto VRIEA-PUCV 37.0 / 2017.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed for this study are included in this publish article. However, raw data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MM. supervised the entire study. MS. collected E. chilensis and made all of the extracts. CJ. performed the study of antioxidant activity. FA. performed the GC-MS analysis. JV. conceived and designed the biological experiments; PG. and EW. performed the biological experiments. MM, AM. and IM. collaborated in the discussion and interpretation of the results. MM., AM. and IM. wrote the manuscript. All of the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not Applicable.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Mellado, M., Soto, M., Madrid, A. et al. In vitro antioxidant and antiproliferative effect of the extracts of Ephedra chilensis K Presl aerial parts. BMC Complement Altern Med 19, 53 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-019-2462-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-019-2462-3