Abstract
Background
Fertilization failure after intracytoplasmic sperm injection continues to affect couples and the etiology is not well-understood.
Case presentation
We characterized a couple with 2-year history of primary unexplained infertility. Three different assisted reproduction attempts (IVF + rescue ICSI, ICSI and ICSI-AOA) showed repeated fertilization failure for MII oocyte retrieval after controlled ovarian hyperstimulation. After whole-exome sequencing and sanger sequencing of the couple and their family members, variant pathogenicity was assessed using SIFT, PolyPhen2, Mutation Taster, and Human Splicing Finder software. We identified novel compound heterozygous mutations, c.1535 + 3A > G and c.946C > T (p. Leu316Phe), in WEE2 in the female proband. Trios analysis of the variations revealed an autosomal recessive pattern. c.1535 + 3A > G in WEE2 was predicted to break the wild-type donor site and affect splicing, and the missense mutation c.946C > T (p. Leu316Phe) of WEE2 was predicted to be pathogenic.
Conclusion
A novel compound heterozygous mutation in WEE2 was identified in an infertile female who experienced repeated fertilization failure even after ICSI-AOA. These novel mutations in WEE2 provided genetic evidence for fertilization failure.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Total fertilization failure (TFF) occurs in 5–10% of total in vitro fertilization (IVF) cycles [1]. TFF is a mentally and financially devasting event for infertile couples. Since 1992, intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) has been widely used to improve fertilization rates in couples with male factor infertility. However, TFF still occurs in 1–3% of ICSI cycles [2].
The etiology underlying TFF remains unclear. Several studies have shown that oocyte activation defects are the main cause of fertilization failure after ICSI. Oocyte activation is a complex process initiated by intracellular calcium oscillations after sperm enter the ooplasm. Artificial oocyte activation (AOA) is a technique that triggers an artificial increase in intracellular calcium. ICSI followed by AOA (ICSI-AOA) is typically used to improve the fertilization rate of patients with male factor-related oocyte activation defects [3]. Genetic factors play important roles in oocyte activation defects and likely result in repeated human fertilization failure even after ICSI-AOA. Given the importance of oocyte- and sperm-related factors in oocyte activation, deleterious mutations in oocyte-specific genes and sperm-specific genes can result in TFF in humans. A mutation in the sperm-specific gene PLCZ1 was showed to cause abnormal calcium oscillations and TFF in two infertile brothers with normal sperm morphology [4]. A mutation in the maternal effect gene TLE6 impaired oocyte meiosis and led to a low fertilization rate and early cleavage failure in two families with female infertility [5]. Recently, Sang et al. [6] identified a mutation in the oocyte-specific gene WEE2 which resulted in the failure of pronuclei formation and human fertilization in four independent infertile women.
WEE2 (WEE1 homolog 2, also known as WEE1B) belongs to the WEE kinase family and is conserved from yeast to humans [7]. A previous study indicated that in mouse oocytes at the germinal vesicle stage, Wee2 acted as a key maturation-promoting factor inhibitory kinase and is involved in maintaining meiotic arrest [8]. In mouse oocytes at metaphase II stage, Wee2 inhibited the phosphorylation of Cdc2, which was required for metaphase II exit. As a result, downregulation of Wee2 during egg activation leads to failure of pronucleus formation even after calcium oscillations [9]. Recently, mutations in WEE2 were found to be associated with human pronucleus formation and repeated fertilization failure [6, 10,11,12,13,14]. In this study, whole-exome sequencing was performed to clarify the genetic cause of repeated fertilization failure after ICSI-AOA in a non-consanguineous family. Additionally, a novel compound heterozygous mutation in WEE2 was identified.
Case presentation
Clinical characteristics of female proband
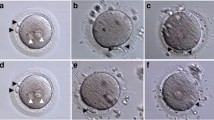
The infertile couple is from a non-consanguineous family. The proband is a 36-year-old woman, Chinese, Han ethnic with a 2-year history of primary infertility of unknown cause. Her husband is a 38-year-old Chinese man with a 2-year history of primary infertility; his seminal parameters showed 49% sperm motility and 4% normal sperm morphology per ejaculate. A total of three ART cycles was conducted (Table 1). During the patient’s first IVF cycle, 15 oocytes were collected; however, pronucleus formation was not observed. Late rescue ICSI was performed for 8 MII oocytes; 2 two-pronuclei-fertilized oocytes and 1 three-pronuclei-fertilized oocyte were obtained. Unfortunately, the zygote stopped developing at the 2-cell stage. During the second ICSI cycle, 12 oocytes (9 MII oocytes) were collected but none was fertilized. During the third ICSI-AOA cycle, the oocytes were dispersed in a calcium ionophore solution containing 10 μmol/L of A23187 (I9657, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) for 10 min at 37 °C with 6% CO2. Totally 15 oocytes (11 MII oocytes) were collected followed by ICSI-AOA but PN formation was not observed.
Sequencing analysis
Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood samples of the couple and their parents. Whole-exome capture and sequencing were performed following the standard protocols provided by BGI Genomics (BGI, Shenzhen, China) and Tianjin Medical Laboratory BGI (Tianjin, China). The genomic DNA library was subjected to Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer and BMG and sequenced with MGISEQ-2000. The sequencing depth of WES was 100×. For Sanger sequencing, the primers and conditions used for PCR are listed in Additional file 1: Table S1. The PCR product was sequenced on an ABI 3100 DNA analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) and the data were analyzed with Sequencer 4.9 software.
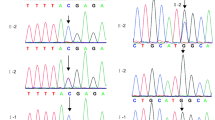
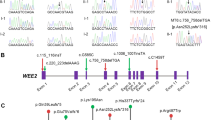
Aneuploidy or pathogenic microdeletion/microduplication (> 100 Kb) was not detected in the infertile couple by low-coverage whole-genome sequencing. A novel compound heterozygous mutation c.1535 + 3A > G and c.946C > T (p. Leu316Phe) in WEE2 was found in the infertile female proband by whole-exome sequencing. The allele frequencies of variations c.1535 + 3A > G and c.946C > T were not listed in Exome Aggregation Consortium (ExAC; exac.broadinstitute.org) or the 1000Genomes Project Database (browser.1000genomes.org) (see Table 2). The identified missense mutation c.946C > T (p. Leu316Phe) was conserved among different species assessed with Clustal Omega software (Science Foundation Ireland) (Fig. 2a). Sanger sequencing validated that variation c.1535 + 3A > G was inherited from her father and variation c.946C > T (p. Leu316Phe) was inherited from her mother. As shown in Fig. 1, Trios analysis revealed an autosomal recessive mode of the detected variations in WEE2.
Function prediction of the mutations
The locations of the mutations in WEE2 and WEE2 protein are shown in Table 2 and Fig. 2b. Variation c.1535 + 3A > G was at an intervening sequence 3 base pairs away from the edge of exon 10. Variation c.946C > T was in exon 6 and caused an amino acid substitution at position 316 in WEE2 protein. This missense mutation was in both the PKinase domain and putative nuclear export sequence (NES) of WEE2.
The pathogenicity of the variants was assessed using four software programs: SIFT (sift.jcvi.org), PolyPhen2 (www.genetics.bwh.harvard.edu/pph2/), Mutation Taster (www.mutationtaster.org/), and Human Splicing Finder (www.umd.be/HSF3/). As shown in Table 2, variation c.1535 + 3A > G in WEE2 was predicted to break the wild-type donor site and affect splicing. For the cryptic site used, the exon length alteration was expected to be 152 base pairs according to Human Splicing Finder software. The missense mutation p.Leu316Phe of WEE2 was predicted to be pathogenic by SIFT, PolyPhen-2, and Mutation Taster software.
Discussion and conclusion
In this study, through whole-exome sequencing, a novel compound heterozygous mutation in WEE2 was identified in an infertile female who experienced repeated fertilization failure even after ICSI-AOA.
WEE2 was previously identified as a testis-abundant gene [7] but has not been demonstrated to be associated with male infertility in humans. Since 2011, Wee2 has been considered as a crucial factor contributing to oocyte activation and pronucleus formation. In 2018, causative WEE2 mutations of human fertilization failure were first identified in humans. Jing et al. detected mutations in WEE2 in 20.8% (5/24) of women with TFF or poor fertilization, whereas Shuai et al. identified WEE2 mutations in nearly 6% (5/90) women with TFF, indicating that WEE2 mutations play important role in TFF cases. Nineteen genetic mutations have been detected in WEE2 in women who experienced fertilization failure. We summarized all previously reported variations of WEE2 in affected cases with total fertilization failure/poor fertilization in Table 3. Nearly all the patients with WEE2 mutations presented with complete obstacles in PN formation on day 1 (D1) from MII oocytes despite the use of ICSI or the calcium ionophore A23187 for activation. However, cases with mutation c.1228C > T, c.1576T > G and c.293_294ins presented with low fertilization rate and none normal cleavage embryos [11, 12, 14]. In our study, we identified a novel compound heterozygous mutation in WEE2, expanding the mutation spectrum of this gene in fertilization failure.
The compound heterozygous mutation c.1535 + 3A > G and c.946C > T (p. Leu316Phe) follow an autosomal recessive pattern and may contribute to the loss of WEE2 protein function. Variant p. Leu316Phe is in the PKinase domain of WEE2 protein, which has protein kinase activity [15]. A mutation in the PKinase domain may affect the serine phosphorylation of WEE2, resulting in impairment of Cdc2 phosphorylation and leading to the failure of fertilization [6]. In addition, variant p. Leu316Phe is in the NES of WEE2. Jeong et al. found that nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of Wee2 in mouse was mediated by NES sequences [16]. Thus, mutation in this region may disrupt the nuclear localization of WEE2.Variation c.1535 + 3A > G is likely affects splicing. This splicing mutation may result in a 152-base pair alteration in exon length and generate a truncated protein.
In this study, ICSI-AOA via chemical activation of A23187 was performed in a patient after two failed IVF/ICSI cycle. Unfortunately, fertilization failure was encountered in ICSI-AOA cycle. Consistent with our observations, early Ca2+ signaling during egg activation was previously found to be normal in Wee2 knockdown mouse [9]. We predicted that Ca2+ release from the oocyte endoplasmic reticulum and calcium-calmodulin–dependent kinase II (CaMKII) activation occurred normally in this patient. However, CaMKII-triggered WEE2 phosphorylation, inhibitory CDC2 phosphorylation, and maturation-promoting factor destruction were impaired [17]. Receiving the donated egg is an option for patients with defective WEE2. In addition, Sang et al. injected WEE2 complementary RNA into the oocyte of a patient with defective WEE2 and found that fertilization failure was rescued and blastocysts were formed in vitro. Further studies are required to develop treatments for patients with WEE2 defects.
In conclusion, we identified a novel compound heterozygous mutation in WEE2 responsible for fertilization failure. Our results expand the spectrum of WEE2 mutations and provide genetic evidence for fertilization failure.
Availability of data and materials
All datasets generated for this study are included in the article.
Abbreviations
- TFF:
-
Total fertilization failure
- IVF:
-
In vitro fertilization
- ICSI:
-
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection
- AOA:
-
Artificial oocyte activation
- ICSI-AOA:
-
ICSI followed by AOA
References
Mahutte NG, Arici A. Failed fertilization: is it predictable? Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2003;15(3):211–8.
Esfandiari N, Javed MH, Gotlieb L, Casper RF. Complete failed fertilization after intracytoplasmic sperm injection–analysis of 10 years’ data. Int J Fertil Womens Med. 2005;50(4):187–92.
Vanden Meerschaut F, Nikiforaki D, Heindryckx B, De Sutter P. Assisted oocyte activation following ICSI fertilization failure. Reprod Biomed Online. 2014;28(5):560–71.
Escoffier J, Lee HC, Yassine S, Zouari R, Martinez G, Karaouzene T, Coutton C, Kherraf ZE, Halouani L, Triki C, et al. Homozygous mutation of PLCZ1 leads to defective human oocyte activation and infertility that is not rescued by the WW-binding protein PAWP. Hum Mol Genet. 2016;25(5):878–91.
Alazami AM, Awad SM, Coskun S, Al-Hassan S, Hijazi H, Abdulwahab FM, Poizat C, Alkuraya FS. TLE6 mutation causes the earliest known human embryonic lethality. Genome Biol. 2015;16:240.
Sang Q, Li B, Kuang Y, Wang X, Zhang Z, Chen B, Wu L, Lyu Q, Fu Y, Yan Z, et al. Homozygous mutations in WEE2 cause fertilization failure and female infertility. Am J Hum Genet. 2018;102(4):649–57.
Nakanishi M, Ando H, Watanabe N, Kitamura K, Ito K, Okayama H, Miyamoto T, Agui T, Sasaki M. Identification and characterization of human Wee1B, a new member of the Wee1 family of Cdk-inhibitory kinases. Genes Cells. 2000;5(10):839–47.
Han SJ, Chen R, Paronetto MP, Conti M. Wee1B is an oocyte-specific kinase involved in the control of meiotic arrest in the mouse. Curr Biol. 2005;15(18):1670–6.
Oh JS, Susor A, Conti M. Protein tyrosine kinase Wee1B is essential for metaphase II exit in mouse oocytes. Science. 2011;332(6028):462–5.
Yang X, Shu L, Cai L, Sun X, Cui Y, Liu J. Homozygous missense mutation Arg207Cys in the WEE2 gene causes female infertility and fertilization failure. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2019;36(5):965–71.
Zhang Z, Mu J, Zhao J, Zhou Z, Chen B, Wu L, Yan Z, Wang W, Zhao L, Dong J, et al. Novel mutations in WEE2: expanding the spectrum of mutations responsible for human fertilization failure. Clin Genet. 2019;95(4):520–4.
Zhao S, Chen T, Yu M, Bian Y, Cao Y, Ning Y, Su S, Zhang J, Zhao S. Novel WEE2 gene variants identified in patients with fertilization failure and female infertility. Fertil Steril. 2019;111(3):519–26.
Zhou X, Zhu L, Hou M, Wu Y, Li Z, Wang J, Liu Z, Zhang D, Jin L, Zhang X. Novel compound heterozygous mutations in WEE2 causes female infertility and fertilization failure. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2019;36(9):1957–62.
Dai J, Zheng W, Dai C, Guo J, Lu C, Gong F, Li Y, Zhou Q, Lu G, Lin G. New biallelic mutations in WEE2: expanding the spectrum of mutations that cause fertilization failure or poor fertilization. Fertil Steril. 2019;111(3):510–8.
Zhu JY, Cuellar RA, Berndt N, Lee HE, Olesen SH, Martin MP, Jensen JT, Georg GI, Schonbrunn E. Structural basis of wee kinases functionality and inactivation by diverse small molecule inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2017;60(18):7863–75.
Oh JS, Han SJ, Conti M. Wee1B, Myt1, and Cdc25 function in distinct compartments of the mouse oocyte to control meiotic resumption. J Cell Biol. 2010;188(2):199–207.
Sanders JR, Swann K. Molecular triggers of egg activation at fertilization in mammals. Reproduction. 2016;152(2):R41-50.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. XiaoZhou Li and Dr. Fei Teng of Tianjin Medical University General Hospital for critical review. The authors thank Editage for English language editing.
Funding
This research was supported by research grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81701410, 81901502), Beijing-Tianjin-HeBei Project (19JCZDJC65000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G.W. and J.W. collected all the clinical data and blood samples; Y.T. and X.B. wrote the manuscript; X.M., H.C., X.S. revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Tianjin Medical University General Hospital (Ethical No. IRB2019-WZ-164). Written informed consent was obtained from the couple in this study.
Consent for publication
Written consent for publication was obtained from the couple in this study.
Competing interests
All authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1: Table S1.
PCR primers and conditions used for Sanger sequencing. Primer pairs and the size of PCR products were shown. F, forward; R, reverse.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, Y., Wang, G., Wang, J. et al. Novel compound heterozygous mutation in WEE2 is associated with fertilization failure: case report of an infertile woman and literature review. BMC Women's Health 20, 246 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-020-01111-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-020-01111-5