Abstract
Background
Breast cancer patients in sub-Saharan Africa experience long time intervals between their first presentation to a health care facility and the start of cancer treatment. The role of the health system in the increasing treatment time intervals has not been widely investigated. This review aimed to identify existing information on health system factors that influence diagnostic and treatment intervals in women with breast cancer in sub-Saharan Africa to contribute to the reorientation of health policies in the region.
Methods
PubMed, ScienceDirect, African Journals Online, Mendeley, ResearchGate and Google Scholar were searched to identify relevant studies published between 2010 and July 2020. We performed a qualitative synthesis in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement. Related health system factors were extracted and classified according to the World Health Organization’s six health system building blocks. The quality of qualitative and quantitative studies was assessed by using the Critical Appraisal Skills Program Quality-Assessment Tool and the National Institute of Health Quality Assessment Tool, respectively. In addition, we used the Confidence in the Evidence from Reviews of Qualitative Research tool to assess the evidence for each qualitative finding.
Results
From 14,184 identified studies, this systematic review included 28 articles. We identified a total of 36 barriers and 8 facilitators that may influence diagnostic and treatment intervals in women with breast cancer. The principal health system factors identified were mainly related to human resources and service delivery, particularly difficulty accessing health care, diagnostic errors, poor management, and treatment cost.
Conclusion
The present review shows that diagnostic and treatment intervals among women with breast cancer in sub-Saharan Africa are influenced by many related health system factors. Policy makers in sub-Saharan Africa need to tackle the financial accessibility to breast cancer treatment by adequate universal health coverage policies and reinforce the clinical competencies for health workers to ensure timely diagnosis and appropriate care for women with breast cancer in this region.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women worldwide, with an estimated 6,875,099 five-year prevalent cases between 2013 and 2018 [1]. Breast cancer accounted for 24.2% of all new cancer cases among females in 2018 [1]. Despite advances in cancer therapy, there are significant differences in survival rates between developing and developed countries [2, 3]. More than 67% of breast cancer deaths worldwide occur in low-and middle-income countries (LMICs), including sub-Saharan Africa [1]. With 55,938 estimated deaths in 2018, breast cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer death among women in sub-Saharan Africa after cervical cancer [4].
Breast cancer can be preventable and curable with early and adequate screening and management, but it is a fact that, in most developing countries, women with breast cancer are diagnosed very late, mainly due to a lack of information on early detection and insufficient access to health services [5,6,7].
By 2019, more than 90% of high-income countries reported that their public health systems had comprehensive cancer treatment services, while less than 15% of low-income countries reported comprehensive cancer treatment services [8]. Many studies from LMICs have reported an association between an advanced clinical stage of breast cancer at treatment onset and time intervals of more than three months between symptom discovery and treatment start [9]. The evidence shows that the median of this interval is 30–48 days in high-income countries but 3–8 months in LMICs [9].
In sub-Saharan Africa, delays in diagnosis and treatment and barriers to care experienced by breast cancer patients have been previously explored [6, 10], and many findings show that patients experienced long time intervals between initial symptoms and presentation to a health care facility (patient interval) and between first presentation and definitive diagnosis or treatment (provider interval) [6, 10].
Most studies conducted among sub-Saharan African women were focused mainly on patient interval factors (sociodemographic, cultural and economic related factors), early detection [11, 12], and knowledge, attitudes, and practices of women regarding breast cancer and self-examination [13, 14].
In addition, most of the review studies conducted in the sub-Saharan Africa region were focused on time to presentation, diagnosis and related factors and stages of diagnosis [11, 12]. However, the role of health system-related factors delaying diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer (from presentation to first treatment) has not been well investigated. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first systematic review to focus on health system factors that may explain delay in diagnosis and treatment in women with breast cancer in sub-Saharan Africa. The results from this study will contribute to the improvement of breast cancer health policies in this region.
Methods
This systematic review was conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement by Moher et al. [15].
Protocol and registration
The review protocol was registered in the database of the international prospective register of systematic reviews “PROSPERO” on April 28, 2020, under the number CRD42020182585 and is available at the following link: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42020182585
Data sources and search strategy
We developed a comprehensive search strategy and conducted an exhaustive search for studies in different databases: Medline (PubMed), ScienceDirect, African Journals Online, Mendeley, ResearchGate and Google Scholar. To make the search exhaustive and identify additional articles, we looked for other sources and carried out country-by-country (48 sub-Saharan African countries) searches. Reference lists of relevant articles were also hand-searched.
The following keywords were combined by Boolean operators “AND”, “OR” and “Not” to obtain several search equations according to the databases:
“Breast cancer”; “Breast carcinoma”; “Breast neoplasm”; “Breast Tumor”; “Factors”; “Determinants”; “Barriers”; “Challenges”; “Facilitators”; “Opportunities”; “Delayed treatment”; “Time-to-Treatment”; “Provider delay”; “Doctor delay”; “Treatment delay”; “Health system delay”; “Healthcare delivery”; “healthcare access”; “health service accessibility”; “Africa”; “sub-Saharan Africa”; and the names of each of the 48 sub-Saharan African countries (details are provided in supplementary data: Table S4).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Articles were eligible for inclusion in this systematic review if they reported findings from primary research studies conducted among women with breast cancer in sub-Saharan Africa, addressed health system factors influencing the time-to-treatment of women with breast cancer, and were published between January 2010 and 2020. There were no language restrictions, and there were no prior restrictions regarding the study design (qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods). Studies without abstracts or for which the full text was not available were excluded. Additionally, we excluded studies that mixed female and male breast cancer in their results. No studies were excluded after quality assessment.
Study selection and data collection process
Zotero reference manager software [16] was used to organize and detect duplicate references. We identified eligible articles by using the PRISMA flow diagram. The first and second authors independently screened all titles and abstracts identified by the search, and those clearly irrelevant to the topic were excluded. The full texts of all potentially eligible papers were retrieved and reviewed for inclusion in this review according to the inclusion criteria. All included studies were independently reviewed by two authors to confirm eligibility (GG and MB).
Data extraction and items
For the included studies, two authors (GG and MB) independently extracted information such as the characteristics of the study (title, authors, year of publication, country, study design, research method, age group, participants, and sample size), health system factors (barriers and facilitators), and the time to treatment (if available).
All health system factors were classified according to the World Health Organization (WHO) Health Systems Framework’s six building blocks [17], namely: 1) health service delivery, 2) health workforce, 3) heath information systems, 4) access to essential medicines and technologies, 5) health system financing, and 6) leadership and governance. Any discrepancies in the process of selection and extraction were resolved through discussion, if necessary, with two other authors (MK and IH).
As reported in the Aarhus statement’s Guidelines [18], we define “diagnostic interval” as the time between first presentation and diagnosis, and “treatment interval” as the time between diagnosis and treatment start.
Quality assessment
The quality of the qualitative studies was assessed by using the Critical Appraisal Skills Program (CASP) Quality-Assessment Tool (http://www.casp-uk.net) [19]. The quality of the quantitative studies was assessed using the National Institute of Health (NIH) Quality Assessment Tool for Observational Cohort and Cross-Sectional Studies [20]. Study quality was assessed according to the following criteria: research question, study population, eligibility criteria of the population, sample size justification, outcome measures, response and follow-up rates, statistical analyses, and ethical issues. In addition, we used the Confidence in the Evidence from Reviews of Qualitative Research (CERQual) Tool to assess the evidence for each qualitative finding. Based on the assessment of four components (methodological limitations, relevance, adequacy, and coherence), all qualitative findings were classified into three categories: high confidence, moderate confidence, or low confidence [21].
Results
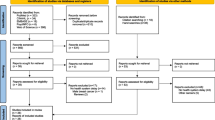
A total of 14,184 studies were identified by the literature search. After exclusion of duplicate studies and studies outside the scope of our review, only 67 studies were retrieved for full-text review. A total of 28 studies were eligible for inclusion in the review (Fig. 1).
Study characteristics
The main characteristics of the included studies are summarized in Table 1. Among the 28 studies included in the review, 11 were quantitative, 12 were qualitative, and five were studies with mixed methods (quantitative and qualitative approaches). They were conducted across 13 countries in sub-Saharan Africa. Thirteen (46%) studies were conducted in East Africa, 10 (35%) in West Africa, 3 (10%) were conducted in Southern Africa and 2 (7%) were multi-country studies mixing countries from three parts of sub-Saharan Africa (East, West and Southern Africa). The study publication dates ranged from 2013 to 2020. The sample sizes of the studies ranged from 64 to 1429 for the quantitative and mixed studies. Eleven (69%) quantitative and mixed studies were cross-sectional surveys, while three were cohort studies. The qualitative articles used focus group discussions and in-depth interviews to explore different factors influencing diagnostic and treatment intervals in breast cancer patients. In 21 (75%) studies, their study populations exclusively included women with breast cancer, whether newly diagnosed or not, whereas the seven other studies included physicians, health care workers, family members and women without breast cancer. In the large majority of included studies, women with breast cancer were aged 40 years and over.
Factors influencing diagnostic and treatment intervals in breast cancer patients
There was a total of 36 barriers and eight facilitators identified across all studies. Factors identified in each study and classified according to the WHO Health Systems Framework’s six building blocks are summarized in Tables 2 and 3, respectively. Among the barriers, misdiagnosis was the most common (16 studies), followed by provider attitude (11 studies) and the high cost of investigation and treatment (11 studies). The appearances of other barriers and facilitators ranged from one to seven times.
Health service delivery
Health service delivery was addressed by 23 of the studies included in the review, and the factors identified can be grouped into two major themes: logistics and infrastructure.
Logistical difficulties included different waiting times for an appointment (medical or specialist consultation), investigations (imaging, biopsy), test results, referral or treatment (surgery, radiotherapy) [22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30]. A long waiting time for test results, more specifically for the biopsy results, was a factor influencing diagnostic and treatment intervals in 11 included studies [23, 25,26,27,28,29, 31,32,33,34,35]. In seven studies included in this review, visiting other health facilities (1 to 4 times or more) before attending the breast cancer diagnostic center was identified as one of the reasons for longer diagnostic intervals [22, 23, 29, 35,36,37,38]. Studies have also shown that the type of healthcare facility and the type of health worker visited at the first consultation had an impact on diagnostic and treatment intervals [38, 39], and women who first visited a community health centre or general practitioner experienced longer time intervals than those who first saw a specialist (surgeon or oncologist) [38, 39]. Being referred by an oncologist or surgeon or having received the first consult evaluation in a public hospital have been identified as factors facilitating diagnosis and access to treatment [38, 39]. Being referred directly to tertiary care hospital with specialized services after the first visit to the primary care clinic or general practitioner while bypassing a secondary care hospital (without specialized services) was identified as a factor facilitating women’s access to diagnosis and treatment. Indeed, women who went through the secondary care hospital or other health facilities were more likely to experience long diagnostic intervals [23, 40]. Logistic problems also included poor organization and unavailability or shortage of breast cancer services [29, 30, 41].
The geographical inaccessibility of healthcare facilities and the insufficiency of diagnostic centres are part of the infrastructure problems [27,28,29,30, 41]. In Uganda, for instance, one patient interviewed said, ‘The health centre nearby the community does not offer screening services, and someone may find it hard to leave this place [Ssisa sub-county] to go to Kampala; but if they bring the services closer to the community, some will find it easier to visit them.’ [Semi-structured #2] [41].
Health workforce
Misdiagnosis, misinterpretation and mismanagement
Among health workforce factors, misdiagnosis was the most common and appeared in 16 studies [23, 24, 28, 29, 31, 33,34,35, 37,38,39, 42,43,44,45,46]. Patients reported being inappropriately reassured by health workers that their breast lump was benign without a biopsy or with an incorrect biopsy interpretation.
“… I noticed something, a small lump on my breast … I woke up in the morning and went to my doctor. He told me it could be a tumour. I asked him if it could be a cancer because I heard about it on TV. He told me it is not a cancer.” (P07) [28].
Symptom misinterpretation and misdiagnosis were the most frequent reasons for prolongation of the primary care interval. In six studies, caregivers mismanaged breast cancer patients by giving incorrect medical prescriptions or incorrect advice [26, 27, 29, 35, 43, 44]. For instance, Pruitt et al. reported that the majority of women described receiving oral medication or injections, usually antibiotics, sometimes for months or years before being referred or making an independent decision to seek care elsewhere [26].
‘I went to the Referral Hospital in XXX. They gave me drugs which I took for 3 months. During that period, I did not see any amelioration … 3 months later I went back to my doctor and he gave me other prescriptions for blood analyses … ‘(Patient 7) [44].
Olayide Agodirin et al. found that the rate of long primary care intervals was higher among patients who received incorrect advice (81%, 44 of 54) than among those who received correct advice (67%, 100 of 148) (OR 2.1, 95% CI 1.0–4.6) [35].
Poor knowledge and skills
Misdiagnosis is often attributed to poor knowledge and lack of health workers training about breast cancer; most health workers provided incorrect information to patients [24, 29, 31, 34, 41]. For instance, in one study, women reported that some of the health workers were unable to examine them appropriately [24]. As an illustration, in one focus group, a health worker said: ‘For me, I have never gotten training on breast cancer detection but I just hear that breast cancer is very dangerous and it is good for someone to go for check-ups but I have never received training on breast cancer examination.’ [FGD CHWs #7] [41].
Attitude of health workers
The attitude of providers was also an important factor influencing women’s access to treatment. Some studies reported that poor attitudes and corruption among health workers were factors that accounted for delays in the start of definitive treatment [27]. Sanuade et al. reported that women in Ghana experienced longer treatment intervals due to corrupt practices of health workers favoring patients they knew personally. Other women said they used bribery to alleviate delays in accessing treatment [27]. Patients also said some health workers disrespect them, refused to answer their questions or did not treat them well, which forced them to delay the start of treatment [27], while others had good communication with health care providers, which made it easier for them to manage their breast cancer [46].
Strikes and shortage of caregivers
The shortage of health workers and strikes were also identified as factors delaying women’s access to breast cancer treatment [24, 26, 27, 31, 35, 42, 44]. Studies have reported that various hospital departments turned women away because a doctor was not available [31]. Women faced a long time intervals in receiving their test results and had difficulty accessing care due to strikes by various members of the healthcare team, including consultants and residents [26].
Health financing
Six key elements were identified among financing-related factors: high costs of treatment and investigations, lack of insurance or limited insurance coverage, expensive private insurance and discrimination by private insurance. For instance, some of the breast cancer patients were often not eligible for private health insurance [47]. The high cost of treatment was reported as an important factor influencing women’s access to breast cancer treatment in 11 studies [26,27,28,29,30, 37, 46,47,48,49,50]. One woman in the study reported by Sanuade et al. said, “The chemo is expensive. The trauma and money you spend is a problem too. If you do not have at least 200 Ghana cedis, you cannot buy the drugs. When someone hears all this, the individual would opt for herbal medicine or prayer. So, as for me, I think that lack of money is a factor. I paid 1000 Ghana cedis to use the chemo machine. If you do not have money, you would go home. So, money is a serious factor.” (FGD 4-R1) [27].
Lack of or limited insurance coverage was also mentioned as a barrier to care. In the study conducted by Subramanian et al. in Kenya, 78% out of 400 women with breast cancer reported borrowing money from family or friends to cover out-of-pocket medical and related expenses [47]. In another study conducted in the Ivory Coast, 36% out of 126 patients declared having had a delayed diagnosis due to lack of financial resources [33]. Many women reported having no insurance coverage [47,48,49]. For instance, Okoronkwo et al. found that 71.8% out of 194 patients studied in Nigeria did not have health insurance coverage [48].
Medication access and technologies
Unavailability of drugs and equipment failure were the most common factors among those related to medication access and technologies [27, 29, 31, 44, 46, 47]. Diagnostic assessments were not available in small health centres, and multiple visits were required for X-rays or blood tests or to obtain a biopsy sample, according to interviewees. Various hospital departments turned women away because the computer was broken or the X-ray machine was not working [27, 29, 31]. Study results also identified drug shortages as an important factor in lengthening the treatment time interval [31, 44, 46].
For instance, key informants in one study conducted in Uganda reported that the existing health system is not equipped to manage breast cancer [41].
Leadership and governance
Lack of cancer policies and low prioritization of non-communicable diseases, were the common factors identified in the included studies [41]. Key informants in one study conducted in Uganda highlighted the lack of cancer policy-providing guidelines for cancer management across each spectrum of the cancer care continuum [41].
‘There is no such policy on cancer screening or cancer prevention; there’s nothing like that.’ [key Informant #6] [41].
Information system
The information system was addressed by only one study among those included in the review [36]. The key factor identified was the delay in administrative procedures. In this study, conducted in Rwanda, 27% out of 113 women interviewed said that, to receive public insurance coverage for care provided at a district hospital, a referral form needs to be signed by the referring health center. Many patients described the need for a transfer form as a reason for the delay.
Quality appraisal of the included studies
The majority of the quantitative studies were rated as good quality based on the NIH study quality assessment tools for Observational Cohort and Cross-Sectional Studies (Supplementary data, Table S1). Most qualitative studies were of high quality based on the CASP checklists (Supplementary data, Table S2). There was no low quality among studies according to the individual assessment of studies based on the NIH Study Quality Assessment Tools and CASP Checklists.
Based on the four components (methodological limitations, relevance, adequacy, and coherence) of the CERQual approach, the confidence in the majority of the qualitative evidence summated (16 of 21) was rated as low. (Supplementary data, Table S3).
Discussion
This review aimed to identify the health system factors that influence diagnostic and treatment intervals in women with breast cancer in sub-Saharan Africa. The qualitative synthesis of studies identified 44 factors, including 36 barriers and 8 facilitators. These factors are mainly related to health service delivery, health workforce and financing, followed by factors related to medication access and technologies, governance and leadership, and the information system.
Poor organization of health service delivery was responsible for increasing the waiting times for different investigations (often the biopsy, consultation or surgery appointment, and referrals). This was mainly attributed to misdiagnosis, mismanagement or misinterpretation and a long primary care interval. The geographical inaccessibility of different services was also found to be an important barrier to care. These results may be a reasonable representation of the phenomenon of interest according to the level of confidence in the qualitative evidence, as assessed by the CERQual tool. However, they are supported by quantitative and mixed studies that were mostly assessed as good quality studies. These results are consistent with those reported in a recently published systematic review by Nathan R. Brand et al. in LMICs. In their review, 92 studies looked at breast cancer, 10 identified reduced access to primary care, 6 identified limited access to diagnostic services, and 14 identified geographic inaccessibility as factors related to health system [51]. Similar results were reported in studies conducted in Morocco [52,53,54], Palestine [55] and Brazil [56]. These findings suggest the need for efforts to be deployed by decision-makers to ensure the availability and quality of screening services and specialized and comprehensive care for breast cancer in sub-Saharan Africa.
The factors related to the health workforce have been identified as a major handicap to women’s access to treatment in our review. These are mainly diagnostic errors and inadequate care, especially at first contact with the health system, followed by the attitude of providers and the lack of human resources. According to the CERQual assessment tool, these data provide a moderate level of confidence in the synthesis of the qualitative findings, and they are also found in quantitative and mixed studies of good methodological quality according to the NIH Assessment Tool. In addition, it is important to note the variations in some attitudes of health professionals that were identified by these studies, particularly in terms of communication, trust, patient information and corruption. These variations would be related to the differences in contexts and experiences lived and reported by women. However, inappropriate diagnosis remains the most common factor in our studies and is also found in other settings. In their critical review, Unger-Saldaña K. identified medical errors in initial diagnosis, screening interpretation and pathology review as factors related to access or quality of care deficiencies that have been associated with diagnostic and treatment intervals in different countries, such as the United States, England Thailand, Scotland, Netherlands, Canada and Mexico [9]. Our results are also in line with those of the review conducted in Africa by Espina et al. [11] These very alarming findings should arouse enormous interest among professionals in health care and health policies to give importance to initial and continuing medical training in breast cancer.
As a factor related to financing, this review identified the probable influence of treatment costs. Lack of health insurance or limited health insurance coverage forces women to pay for services out of pocket, which is not always easy for the most vulnerable individuals. These results are consistent with those of a review conducted in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region [57] and with a similar study conducted in India [58]. The financing-related factors identified in our review have been reported by mostly high-quality qualitative studies according to the CASP Assessment Tool and good-quality quantitative studies according to the NIH Assessment Tool. It is therefore necessary to accelerate the race for medical coverage to ensure adequate and timely care for patients, as stipulated in the sustainable development goals (SDGs) adopted by the United Nations General Assembly [59].
The remaining three health system building blocks (medication access and technologies, governance and leadership, and information systems) were weakly represented. This is likely the influence of the lack of health policies and the possible influence of other factors, such as the lack or shortage of drugs, care equipment failure and the low prioritization of non-communicable diseases. The only factor related to the information system is the difficulty of administrative procedures. This factor was reported in one mixed study of good methodological quality. The relevance of factors related to medication access and technologies, governance and the information system remains limited. Therefore, more primary studies on these factors and, above all, adapting health policies to local specificities should be recommended.
The few facilitators identified in this review reflect a variation and inequity in women’s access to care between some health structures but also between countries in sub-Saharan Africa. These facilitators were related to free health care, sufficient health coverage and the availability of resources. In a review conducted in the MENA region, having a health insurance facilitated access to mammography [57].
Studies that reported these same factors in high-income countries are mostly more than 10 years old [60, 61]. This would indicate two major conclusions: first, our phenomenon of interest is no longer a real problem for them, and second, there has been a clear advancement in the management of women with breast cancer in high-income countries compared to low- and middle-income countries. However, recent studies conducted in these countries have shown inequalities in access to breast cancer diagnosis and care for vulnerable populations such as immigrant women, residents of rural areas and black individuals [62,63,64].
Strengths and limitations of this review
To our knowledge, this is the first systematic review focused on health system factors that influence diagnostic and treatment intervals in women with breast cancer in sub-Saharan Africa. The majority of the included studies were of good methodological quality. Our review also has several limitations. First, the non-inclusion of grey literature does not exclude the risk of publication bias. Second, the review included studies from only 13 of the 48 sub-Saharan African countries, and the phenomenon studied could be worse or better for countries in which there are no data available. This reveals the paucity of published data on this topic, limits the relevance of our results and suggests the need for more primary research on the topic in the region. Third, most included studies explored more than 5000 women with breast cancer at the hospital level, which could constitute a selection bias. In fact, only women who succeeded in accessing healthcare facilities and obtaining a diagnosis were enrolled in the included studies, further limiting the representativeness or generalizability of the data. This limitation has been underlined by several of the included studies. The heterogeneity noted in the definition and quantification of the different time intervals did not affect the importance of the factors identified or hinder our initial objective, which was to identify any factor that could influence women’s access to diagnosis and treatment.
Implications for health policies and health system research
Despite the methodological limitations identified in some studies, our review findings suggest the need for developing appropriate breast cancer policies that take into account the reduction of financial and geographical accessibility barriers, the strengthening of the management of health service delivery to ensure the availability, the quality of timely screening services, specialized and comprehensive care for breast cancer in sub-Saharan Africa. Attention should also be paid to the continuing education, formative supervision for frontline health workers.
Evidence from LMICs suggests that there is no single best way to improve timely access for women to breast cancer diagnosis and treatment. In line with Haford et al. and Horton et al. [65,66,67], we suggest that effective reforms need to be comprehensive and context specific. These reforms need to include the development of National health insurance schemes, National breast cancer control plans (Zambia, Ghana), integration of breast cancer programs within existing health system platforms (Zambia and Tanzania) to benefit from pooled resources.
We also stress the importance of continuing education, formative supervision for frontline and community health workers in line with Pace et al. [68], community participation and the development of patient navigation programs coupled with public advocacy to improve early detection of breast cancer [65, 67].
Our review has also indicated some research gaps such as the importance of exploring the role of medication access and technologies, governance and leadership, and information systems facilitating women’s access to appropriate and timely breast cancer treatment in sub-Saharan Africa.
Conclusion
Our review indicates that diagnostic and treatment intervals among women with breast cancer in sub-Saharan Africa are influenced by many health system related factors. When women manage to overcome their fear, lack of knowledge, socioeconomic and cultural conditions, they also end up being challenged by overwhelming health system factors that they cannot cope with. Our review sheds light on the underlying factors that explain the longer time intervals and health system challenges women face in terms of financial and geographical access to care, diagnostic errors, inappropriate management and lack of an adequate cancer health policies.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this review are included in this document and its supplementary data.
Abbreviations
- PRISMA:
-
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
- PROSPERO:
-
International prospective register of systematic reviews
- CASP:
-
Critical Appraisal Skills Program
- NIH:
-
National Institute of Health
- CERQual:
-
Confidence in the Evidence from Reviews of Qualitative Research
- LMICs:
-
Low-and middle-income countries
- MENA:
-
Middle East and North Africa
- FGD:
-
Focus group discussion
- CHWs:
-
Community health workers
- SDGs:
-
Sustainable development goals
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492.
Farmer P, Frenk J, Knaul FM, Shulman LN, Alleyne G, Armstrong L, et al. Expansion of cancer care and control in countries of low and middle income: a call to action. Lancet. 2010;376(9747):1186–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61152-X.
Anyanwu SNC, Egwuonwu OA, Ihekwoaba EC. Acceptance and adherence to treatment among breast cancer patients in Eastern Nigeria. Breast (Edinburgh, Scotland). 2011;20(Suppl 2):S51–3.
Global Cancer Observatory. https://gco.iarc.fr/. Accessed 28 Aug 2020.
OMS | Octobre, un mois pour sensibiliser au cancer du sein. WHO. https://www.who.int/cancer/events/breast_cancer_month/fr/. Accessed 31 Jul 2020.
Galukande M, Mirembe F, Wabinga H. Patient delay in accessing breast Cancer Care in a sub Saharan African Country: Uganda. Br J Med Medical Res. 2014;4(13):2599–610. https://doi.org/10.9734/BJMMR/2014/7293.
Pace LE, Shulman LN. Breast Cancer in sub-Saharan Africa: challenges and opportunities to reduce mortality. Oncologist. 2016;21(6):739–44. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0429.
L’OMS présente des mesures de lutte contre le cancer qui pourraient sauver 7 millions de vies. https://www.who.int/fr/news-room/detail/04-02-2020-who-outlines-steps-to-save-7-million-lives-from-cancer. Accessed 1 Aug 2020.
Unger-Saldaña K. Challenges to the early diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer in developing countries. World J Clin Oncol. 2014;5(3):465–77. https://doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v5.i3.465.
Ayoade BA, Salami BA, Agboola AJ, Tade AO, Adekoya AO, Olatunji AA, et al. Beliefs and practices associated with late presentation in patients with breast cancer; an observational study of patient presenting in a tertiary care facility in Southwest Nigeria. J Afr Cancer. 2015;7(4):178–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12558-015-0404-7.
Espina C, McKenzie F, Dos-Santos-Silva I. Delayed presentation and diagnosis of breast cancer in African women: a systematic review. Ann Epidemiol. 2017;27:659–671.e7.
Jedy-Agba E, McCormack V, Adebamowo C, dos-Santos-Silva I. Stage at diagnosis of breast cancer in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Global Health. 2016;4 undefined-undefined.
Makurirofa L, Mangwiro P, James V, Milanzi A, Mavu J, Nyamuranga M, et al. Women’s knowledge, attitudes and practices (KAP) relating to breast and cervical cancers in rural Zimbabwe: a cross sectional study in Mudzi District, Mashonaland East Province. BMC Public Health. 2019;19(1):109. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-018-6333-5.
Asobayire A, Barley R. Women’s cultural perceptions and attitudes towards breast cancer: northern Ghana. Health Promot Int. 2015;30(3):647–57. https://doi.org/10.1093/heapro/dat087.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097.
fr:creating bibliographies [Zotero Documentation]. https://www.zotero.org/support/fr/creating_bibliographies. Accessed 6 Nov 2020.
World Health Organization. Monitoring the building blocks of health systems: a handbook of indicators and their measurement strategies. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2010.
Weller D, Vedsted P, Rubin G, Walter FM, Emery J, Scott S, et al. The Aarhus statement: improving design and reporting of studies on early cancer diagnosis. Br J Cancer. 2012;106(7):1262–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2012.68.
casp. CASP Checklists. CASP - Critical Appraisal Skills Programme. https://casp-uk.net/casp-tools-checklists/. Accessed 29 Aug 2020.
Study Quality Assessment Tools | NHLBI, NIH. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/study-quality-assessment-tools. Accessed 18 Aug 2020.
Lewin S, Glenton C, Munthe-Kaas H, Carlsen B, Colvin CJ, Gülmezoglu M, et al. Using qualitative evidence in decision making for health and social interventions: an approach to assess confidence in findings from qualitative evidence syntheses (GRADE-CERQual). PLoS Med. 2015;12(10):e1001895. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001895.
Moodley J, Cairncross L, Naiker T, Constant D. From symptom discovery to treatment - women’s pathways to breast cancer care: a cross-sectional study. BMC Cancer. 2018;18(1):312. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-4219-7.
Joffe M, Ayeni O, Norris SA, McCormack VA, Ruff P, Das I, et al. Barriers to early presentation of breast cancer among women in Soweto, South Africa. PloS One. 2018;13(2):e0192071. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0192071.
Bedada T, Teshale H, Hailu A, Mulugeta T. Prevalence and factors contributing to late diagnosis of breast Cancer among women attending Tikur Anbessa specialized hospital, oncology unit, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2017. J Integrative Oncol. 2018;07(03). https://doi.org/10.4172/2329-6771.1000214.
Ntirenganya F, Hirwa A, Banguti P, Ainhoa CC, Rulisa S. Barriers to timely surgery and early surgical outcomes for breast cancer patients in a setting with limited resources. Rwanda Med J. 2019;76:1–5.
Pruitt L, Mumuni T, Raikhel E, Ademola A, Ogundiran T, Adenipekun A, et al. Social barriers to diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer in patients presenting at a teaching hospital in Ibadan. Nigeria Global Public Health. 2015;10(3):331–44. https://doi.org/10.1080/17441692.2014.974649.
Sanuade OA, Ayettey H, Hewlett S, Dedey F, Wu L, Akingbola T, Ogedegbe G, de-Graft Aikins A. Understanding the causes of breast cancer treatment delays at a teaching hospital in Ghana. J Health Psychol. 2021;26(3):357–66. https://doi.org/10.1177/1359105318814152. Epub 2018 Nov 30.
Gebremariam A, Addissie A, Worku A, Assefa M, Kantelhardt EJ, Jemal A. Perspectives of patients, family members, and health care providers on late diagnosis of breast cancer in Ethiopia: A qualitative study. PLoS One. 2019;14(8):e0220769. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0220769.
Getachew S, Tesfaw A, Kaba M, Wienke A, Taylor L, Kantelhardt EJ, et al. Perceived barriers to early diagnosis of breast Cancer in south and southwestern Ethiopia: a qualitative study. BMC Womens Health. 2020;20(1):38. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-020-00909-7.
Sherman S, Okungu V. Access to breast Cancer treatment Services in Mombasa County, Kenya: A quality of care analysis of patient and survivor experiences. Am J Public Health Res. 2018;6(4):189–94. https://doi.org/10.12691/ajphr-6-4-3.
Kohler RE, Gopal S, Miller AR, Lee CN, Reeve BB, Weiner BJ, et al. A framework for improving early detection of breast cancer in sub-Saharan Africa: A qualitative study of help-seeking behaviors among Malawian women. Patient Educ Couns. 2017;100(1):167–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pec.2016.08.012.
Aziato L, Clegg-Lamptey JNA. Breast cancer diagnosis and factors influencing treatment decisions in Ghana. Health Care Women Int. 2015;36(5):543–57. https://doi.org/10.1080/07399332.2014.911299.
Toure M, Nguessan E, Bambara AT, Kouassi YKK, Dia JML, Adoubi I. Factors linked to late diagnosis in breast cancer in Sub-Saharan Africa: case of Côte d’Ivoire. Gynecologie Obstetrique Fertilite. 2013;41:696–700.
Yang K, Msami K, Calixte R, Mwaiselage J, Dorn J, Soliman AS. Educational opportunities for Down-staging breast Cancer in low-income countries: an example from Tanzania. J Cancer Educ. 2019;34(6):1225–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13187-019-01587-2.
Agodirin O, Olatoke S, Rahman G, Olaogun J, Kolawole O, Agboola J, et al. Impact of primary care delay on progression of breast Cancer in a black African population: A multicentered survey. J Cancer Epidemiol. 2019;2019:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2407138.
Pace LE, Mpunga T, Hategekimana V, Dusengimana J-MV. Delays in breast Cancer presentation and diagnosis at two rural Cancer referral centers in Rwanda. Oncologist. 2015;20(7):780–8. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2014-0493.
Foerster M, McKenzie F, Zietsman A, Galukande M, Anele A, Adisa C, et al. Dissecting the journey to breast cancer diagnosis in sub-Saharan Africa: Findings from the multicountry ABC-DO cohort study. Int J Cancer. 2020:ijc.33209. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.33209.
Gebremariam A, Addissie A, Worku A, Assefa M, Pace LE, Kantelhardt EJ, et al. Time intervals experienced between first symptom recognition and pathologic diagnosis of breast cancer in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2019;9(11):e032228. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2019-032228.
Grosse Frie K, Kamaté B, Traoré CB, Ly M, Mallé B, Coulibaly B, et al. Factors associated with time to first healthcare visit, diagnosis and treatment, and their impact on survival among breast cancer patients in Mali. PLoS One. 2018;13(11):e0207928. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0207928.
Pace LE, Mpunga T, Hategekimana V, Dusengimana J-MV, Habineza H, Bigirimana JB, et al. Delays in breast Cancer presentation and diagnosis at two rural Cancer referral centers in Rwanda. Oncologist. 2015;20(7):780–8. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2014-0493.
Ilaboya D, Gibson L, Musoke D. Perceived barriers to early detection of breast cancer in Wakiso District, Uganda using a socioecological approach. Glob Health. 2018;14:9.
Agodirin O, Olatoke S, Rahman G, Olaogun J, Olasehinde O, Katung A, et al. Presentation intervals and the impact of delay on breast cancer progression in a black African population. BMC Public Health. 2020;20(1):962. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-020-09074-w.
Maree JE, Mulonda J. “My experience has been a terrible one, something I could not run away from”: Zambian women’s experiences of advanced breast cancer. Int J Africa Nurs Sci. 2015;3:24–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijans.2015.07.001.
Frie KG, Samoura H, Diop S, Kamate B, Traore CB, Malle B, et al. Why do women with breast Cancer get diagnosed and treated late in sub-Saharan Africa? Perspectives from women and patients in Bamako, Mali. Breast Care. 2018;13(1):39–43. https://doi.org/10.1159/000481087.
Moodley J, Cairncross L, Naiker T, Momberg M. Understanding pathways to breast cancer diagnosis among women in the Western Cape Province, South Africa: a qualitative study. BMJ Open. 2016;6(1):e009905. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2015-009905.
Gakunga R, Kinyanjui A, Ali Z, Ochieng’ E, Gikaara N, Maluni F, et al. Identifying barriers and facilitators to breast Cancer early detection and subsequent treatment engagement in Kenya: A qualitative approach. Oncologist. 2019;24(12):1549–56. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0257.
Subramanian S, Gakunga R, Jones M, Kinyanjui A, Ochieng’ E, Gikaara N, et al. Financial barriers related to breast cancer screening and treatment: A cross-sectional survey of women in Kenya. J Cancer Policy. 2019;22:100206.
Okoronkwo IL, Ejike-Okoye P, Chinweuba AU, Nwaneri AC. Financial barriers to utilization of screening and treatment services for breast cancer: an equity analysis in Nigeria. Niger J Clin Pract. 2015;18(2):287–91. https://doi.org/10.4103/1119-3077.151070.
Foerster M, Anderson BO, McKenzie F, Galukande M, Anele A, Adisa C, et al. Inequities in breast cancer treatment in sub-Saharan Africa: findings from a prospective multi-country observational study. Breast Cancer Res. 2019;21(1):93. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-019-1174-4.
Martei YM, Vanderpuye V, Jones BA. Fear of mastectomy associated with delayed breast Cancer presentation among Ghanaian women. Oncologist. 2018;23(12):1446–52. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0409.
Brand NR, Qu LG, Chao A, Ilbawi AM. Delays and barriers to Cancer Care in low- and Middle-Income Countries: A systematic review. Oncologist. 2019;24(12):e1371–80. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0057.
Maghous A, Rais F, Ahid S, Benhmidou N, Bellahamou K, Loughlimi H, et al. Factors influencing diagnosis delay of advanced breast cancer in Moroccan women. BMC Cancer. 2016;16(1):356. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-016-2394-y.
Benbakhta B, Tazi M, Benjaafar N, Khattabi A, Maaroufi A. Determinants of patient and health system delays for women with breast cancer in Morocco, 2013. Rev Epidemiol Sante Publique. 2015;63(3):191–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respe.2015.03.121.
Nadam A, Belrhiti Z. NADAM, A. & BELRHITI, Z. Barrières et facilitateurs de la coordination des soins des cancers du sein et du col de l’utérus à la préfecture El Fida Mers Sultan – Casablanca : une évaluation réaliste; 2020. p. 2020.
Abo Al-Shiekh SS, Alajerami YS, Etewa BB, Elsous AM. System delay in breast Cancer diagnosis in Gaza strip. Palestine J Oncol. 2019;2019:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5690938.
Alves Soares Ferreira N, Melo Figueiredo de Carvalho S, Engrácia Valenti V, Pinheiro Bezerra IM, Melo Teixeira Batista H, de Abreu LC, et al. Treatment delays among women with breast cancer in a low socio-economic status region in Brazil. BMC Womens Health. 2017;17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-016-0359-6.
Bowser D, Marqusee H, El Koussa M, Atun R. Health system barriers and enablers to early access to breast cancer screening, detection, and diagnosis: a global analysis applied to the MENA region. Public Health. 2017;152:58–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.puhe.2017.07.020.
Kumar A, Bhagabaty SM, Tripathy JP, Selvaraj K, Purkayastha J, Singh R. Delays in diagnosis and treatment of breast Cancer and the pathways of care: A mixed methods study from a tertiary Cancer Centre in North East India. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2019;20(12):3711–21. https://doi.org/10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.12.3711.
dpicampaigns. About the Sustainable Development Goals. United Nations Sustainable Development. https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/sustainable-development-goals/. Accessed 28 Aug 2020.
Jenner DC, Middleton A, Webb WM, Oommen R, Bates T. In-hospital delay in the diagnosis of breast cancer. BJS (British Journal of Surgery). 2000;87:914–9.
Caplan LS, May DS, Richardson LC. Time to diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer: results from the National Breast and cervical Cancer early detection program, 1991-1995. Am J Public Health. 2000;90(1):130–4. https://doi.org/10.2105/ajph.90.1.130.
Lin Y, Wimberly MC, Da Rosa P, Hoover J, Athas WF. Geographic access to radiation therapy facilities and disparities of early-stage breast cancer treatment. Geospat Health. 2018;13:622.
Reeder-Hayes KE, Mayer SE, Olshan AF, Wheeler SB, Carey LA, Tse C-K, et al. Race and delays in breast cancer treatment across the care continuum in the Carolina breast Cancer study. Cancer. 2019;125(22):3985–92. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.32378.
Sheppard VB, Oppong BA, Hampton R, Snead F, Horton S, Hirpa F, et al. Disparities in breast cancer surgery delay: the lingering effect of race. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22(9):2902–11. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-015-4397-3.
Harford JB, Otero IV, Anderson BO, Cazap E, Gradishar WJ, Gralow JR, et al. Problem solving for breast health care delivery in low and middle resource countries (LMCs): Consensus statement from the Breast Health Global Initiative. Breast (Edinburgh, Scotland). 2011;20(SUPPL. 2):S20–9.
Harford J, Azavedo E, Fischietto M. Breast Health Global Initiative Healthcare Systems Panel. Guideline implementation for breast healthcare in low- and middle-income countries: breast healthcare program resource allocation. Cancer. 2008;113(8 Suppl):2282–96.
Horton S, Rodriguez RC, Anderson BO, Aung S, Awuah B, Pebé LD, et al. Health system strengthening: integration of breast cancer care for improved outcomes. Cancer. 2020;126(S10):2353–64. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.32871.
Pace LE, Dusengimana JMV, Shulman LN, Schleimer LE, Shyirambere C, Rusangwa C, et al. Cluster randomized trial to facilitate breast Cancer early diagnosis in a Rural District of Rwanda. J Glob Oncol. 2019;5(5):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1200/JGO.19.00209.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Mohammed VI University of Health Sciences of Casablanca for financial assistance in receiving English editing services. We thank Pr Radouane Belouali and all the members of the International School of Public Health for supporting this work. We thank Pr Fadila Guessous and Dr. Issam Bennis for proofreading this document.
IARC disclaimer:
Where authors are identified as personnel of the International Agency for Research on Cancer / World Health Organization, the authors alone are responsible for the views expressed in this article and they do not necessarily represent the decisions, policy or views of the International Agency for Research on Cancer / World Health Organization.
Funding
No funding was received for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Each author has made an important contribution to the realization of this review. GG, MB, IH and MK, conceptualised and designed the research study. GG and MB did the electronic database search, article screening, data extraction, quality assessment, synthesis and wrote the first draft of the manuscript with input from IH and MK. ZB and CN contributed significantly to all drafts of the manuscript and its final version. All authors read, revised and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This was a systematic review of publicly available studies. No ethical approval was required.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1.
NIH Quality Assessment Tool for observational cohort and cross-sectional studies. Table S2. Critical Appraisal Skills Program (CASP) Quality-Assessment Tool for qualitative studies. Table S3. CERQual assessment of confidence of qualitative findings. Table S4. Searches strategies. Table S5. List of full-text articles excluded and reasons for exclusion.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Gbenonsi, G., Boucham, M., Belrhiti, Z. et al. Health system factors that influence diagnostic and treatment intervals in women with breast cancer in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review. BMC Public Health 21, 1325 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-11296-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-11296-5