Abstract
Background
Previous studies indicate that psychological, social, and organizational factors at work contribute to health, motivation, absence from work, and functional ability.
The objective of the study was to assess the current state of knowledge of the contribution of psychological, social, and organizational factors to disability retirement by a systematic review and meta-analyses.
Methods
Data sources: A systematic literature search for studies of retirement due to disability in Medline, Embase, and PsychINFO was performed. Reference lists of relevant articles were hand-searched for additional studies. Data extraction: Internal validity was assessed independently by two referees with a detailed checklist for sources of bias. Conclusions were drawn based on studies with acceptable quality. Data synthesis: We calculated combined effect estimates by means of averaged associations (Risk ratios) across samples, weighting observed associations by the study’s sample size. Thirty-nine studies of accepted quality were found, 37 of which from the Nordic countries.
Results
There was moderate evidence for the role of low control (supported by weighted average RR = 1.40; 95% CI = 1.21-1.61) and moderate evidence for the combination of high demands and low control (although weighted average was RR = 1.45; 95% CI = 0.96-2.19) as predictors of disability retirement. There were no major systematic differences in findings between the highest rated and the lowest rated studies that passed the criterion for adequate quality. There was limited evidence for downsizing, organizational change, lack of employee development and supplementary training, repetitive work tasks, effort-reward imbalance to increase risk of disability pension. Very limited evidence was found for job demands, evening or night work, and low social support from ones superior.
Conclusions
Psychological and organizational factors at work contribute to disability retirement with the most robust evidence for the role of work control. We recommend the measurement of specific exposure factors in future studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
With the unprecedented global population ageing, extending the working life is becoming increasingly important for sustaining welfare for all citizens [1]. Early exit from working life due to disability incurs large production losses and compensations costs for societies as well as challenges to the quality of life to the individuals. The objective of the present systematic review was to assess the state of knowledge of the contribution of psychological, social, and organizational factors at work to retirement due to disability.
Disability is defined as the general inability to perform ones job, either due to (i) a problem in body function or structure (impairment), (ii) difficulties in executing tasks (activity limitation), or (iii) problems experienced in participating in tasks or social relations at the workplace (participation restriction), cfr The International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health (ICF; http://www.who.int/classifications/icf/en/) developed by the WHO. While job disability is a condition or state at which one decides that a job cannot be performed, the level of ‘work ability’ may vary over time. Work ability is a central concept in social security and rehabilitation medicine referring to abilities necessary to perform and hold a job. Competence is a central concept in management and employment referring to knowledge and skills and relevant abilities. Hence, these concepts overlap (Tengland [2]) and both are either defined relative to demands posed by one specific job (e.g., the job held by an individual) or relative to demands of holding a job in general [2].
A large body of studies have shown that psychological and social factors at work may contribute to health and disease. Most of these studies have tested predictions of the demand-control model (Karasek [3]). Originally this “model predicts that mental strain results from the interaction of job demands and decision latitude” [3]. This model has been paramount in advancing research from the ambiguous and circular concept “work stress” to elucidation of the exposure dimensions demands and control that relate to basic research on responding to challenge (e.g., Weiss [4]). An instrument developed to measure these factors, the Job Content Questionnaire (JCQ) has been widely used in research of work and health [5]. The combination of high level of demand and low levels of control seems to contribute to cardiovascular disease (e.g., Kivimäki et al [6]) and several other health problems (e.g., Kraatz et al [7]).
The demand-control model addresses broad dimensions, but still only represents few aspects of exposures at work. Recent research of work and health has provided knowledge of other factors; for example effort-reward imbalance [5], organizational justice (e.g., Kivimäki et al [8]) and Ylipaavalniemi et al [9]), team climate (e.g., Ylipaavalniemi et al. [9]) [10], interpersonal conflict [11]”[12], and role conflict (Christensen & Knardahl [13, 14]).
Of many organizational factors, downsizing, organization of work schedules (shift work, and long working hours) have been reported to contribute to health and disease (e.g., heart disease [15–17] and musculoskeletal pain disorders [18]. Rapid rates of upsizing may also contribute to health problems [19].
The combination of illness perceptions, illness beliefs, and the appraisal of demands posed by the work tasks influence an individual’s appraisal of work ability. Subjective appraisal of work ability may influence attitudes to work. The workplace is an arena where individuals face challenges from work tasks and social interactions. Work also provides opportunities for positive achievement, fulfilment, and friendship. For many people the job is a major source of feedback on attitudes and behaviour. Studies of organizational psychology have revealed psychological factors of significance to work motivation (e.g., Hackman & Oldham [20]) and Adams [21] and global satisfaction with ones job (e.g., Spector [22]). Hypothetically, psychological, social, and organizational factors at work may contribute to early retirement with disability pension by influencing several of the processes leading from a state of good health and work ability to a state of reduced health and disability.
Ilmarinen, Tuomi, and Seitsamo [23] proposed that several dimensions of health resources, competence, values, and factors at work contributes to work ability and modelled this like a house of four floors (“the house model of work ability”). The theoretical basis of the present study was three assumptions. (I) retirement due to disability is a result of a series of processes, each with multifactorial causation. (II) Both biological/medical, psychological, and social factors contribute in these processes: clinical medical condition, physiological and cognitive function, competence, job demand characteristics, individual appraisal of work ability, physician’s assessment of work ability, job motivation, and attitudes to one’s job may contribute in the processes leading from high work ability, and adequate competence to disability resulting in exit from working life (e.g., de Wind et al. [24]; Volanen et al. [25]). (III) Psychological, social, and organizational factors at work influence several of these factors and processes and henceforth may contribute to retirement due to disability. Society-level factors influence exit from working life and retirement compensation, but are outside the scope of the present study.
The present systematic review aimed to answer the following research questions: Which psychological task-level work factors contribute to retirement due to disability? Which social interaction factors at work contribute to retirement due to disability? Which organizational work factors contribute to retirement due to disability? We did not limit the review to models, theories, or to specific factors and sought to grade the level of evidence for each factor studied.
Methods
With the aim to examine whether psychological, social, or organizational factors at work contribute to retirement due to disability, we performed systematic literature searches plus an extensive evaluation of the methodological quality of the retrieved articles. Retirement was defined as permanently not performing paid work. In order to include any relevant work factor and allow variations in wording of factors (constructs), searches did not specify work factors. We also performed meta-analyses when applicable.
Methods of inclusion criteria, analyses, and eligibility were specified in an unpublished protocol (developed by the research group to ensure that all procedures were standardized and adhered to throughout the study). Minor modifications of protocols were performed during the study. All modifications were documented and all conclusions were based on the final version of the methods.
Eligibility criteria and search strategy
Disability retirement was defined as permanently not performing paid work due to disability. Psychological factors were defined as variables pertaining to the contents of a job and work tasks. Social factors were defined as interactions with other people, either co-workers, superiors/leaders, or clients, customers, or patients. We defined organizational factors as ways work is organized, e.g., working hours and shift-work systems, downsizing, upsizing, reorganization e.g., merging of units.
For inclusion, studies had to meet all the following criteria:
-
1.
Outcome measures: addressed registry-based disability pension awards or self-reported retirement from work due to ill health or disease;
-
2.
Types of exposures: measured any organizational, psychological, and social exposure pertaining to work in subjects that were employed and working.;
-
3.
Types of studies: designed as a prospective cohort study, case control study (longitudinal), or intervention study;
-
4.
Types of participants: employees, reported analyses estimating effects of work factors.
The review was limited to publications written in English, German, Danish, Finnish, Norwegian, or Swedish.
Information sources
We searched systematically Medline, Embase and PsycInfo up to April 23rd, 2015 to identify primary studies that addressed the risk of retirement due to disability in relation to any organizational, psychological, and social exposure pertaining to work.
An additional table A (see Additional file 1, Table A: Search strategy) shows the search strategy that was developed and adapted for each database with a combination of free text terms and controlled, hierarchical vocabulary (e.g., Medical Subject Heading terms for Medline). No limits and a search strategy with a high sensitivity were selected. The search terms were constructed to identify articles that addressed the risk of disability pension awards or related outcomes pertaining to retirement, independent of work-related exposures. We tested the specificity and sensitivity of each eligible search term before inclusion in the search string. Pilot searches showed that search profiles with exposures terms (psychosocial, demands, control, etc) did not result in more relevant sets of studies and often excluded relevant studies.
Screening
Two reviewers retrieved and screened the 19545 abstracts produced by the searches. When in doubt, the study was read in full text. The full-text versions of all potentially relevant articles were independently reviewed for inclusion by two of the authors. If disagreement or doubt, the article was subjected to formal assessment of methodological quality.
In addition to database searches, the reference lists of all articles of acceptable quality were inspected (“hand-searched”). We found one additional article on factors determining remaining at work [26], but decided that the definition of “remaining at work” did not meet our inclusion criteria of retirement due to disability.
The current review defined psychological, social, and organizational factors at work as exposures that individuals are subjected to during work. Studies of personality traits were not relevant for the present review. It may be argued that job dissatisfaction, low commitment, low job involvement may be proxies of poor work environments. However, these factors are mediators between exposures and outcomes, not exposures. Therefore, a study which investigated effects of job satisfaction and job enjoyment [27] and a study of organizational commitment and meaning of work [28] were excluded from the systematic review.
Data on health status at baseline was scored as a potential confounder in the quality check list (positive if measured and adjusted or stratified in analyses). Some studies of prognostic factors in specific diseases like insomnia, obesity, rheumatoid arthritis or coronary heart disease have measured work factors as predictors of disability retirement [29–33]. However, many of these studies have treated work factors as covariates only [29–31].
Data extraction
We extracted data from each included study using the following variables: study characteristics (Authors’ of the study, date of the study, and study location), exposures investigated (instruments used to measure factors at work), employee groups/types of work and number of subjects studied, outcomes/definition of disability pension and number of cases, effect estimates (the most completely adjusted estimates reported), and confounders controlled for.
Risk of bias: The assessment of validity of findings (study quality)
The present systematic critical review defined the quality of primary studies as internal validity, the extent to which the effects reported in a study are truly caused by the treatment or exposure in the study sample (rather than being due to other biasing effects of extraneous variables). External validity (generalizability) determines which (specific) populations the conclusions apply to.
Systematic reviews have assessed methodological quality of primary studies by several systems. The Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation Working Group (GRADE) system for the evaluation of treatment trials grade evidence as high (GRADE 4), moderate (3), limited (2), and very limited (1) [34]. In studies of treatments the serious threats to internal validity of conclusions are selection bias and information bias due to inadequate blinding. There is no consensus or gold standard for assessing the quality of observational epidemiological studies (e.g., Sanderson et al. [35]; Shamliyan et al. [36]). Recommendations for reporting or evaluating observational studies (e.g., the STROBE statement) [37] address variables in general terms: “give sources of data and details of methods of assessment (measurement)”. The GRADE system categorizes observational studies as limited evidence (GRADE 2) even if conducted with prospective design and no known selection bias because of high risk of bias [36, 38]. However, the evidence may be upgraded to moderate (GRADE 3) if several studies show the same result or if a limited number of studies are unequivocal.
Most studies of psychological and social work exposures are based on self-reported data which present challenges to validity of measurement methods. The individual’s reporting is influenced by psychological mechanisms like perception, cognitive appraisal, expectancies, attitudes, etc, which in turn are influenced by personality traits and culture (e.g., Watson et al. [39]; Chen & Spector. [40]; Oliver et al. [41]). Recommendations for reporting or evaluating observational studies (Sanderson et al, 2007; the STROBE statement) [35, 37] do not address evaluating psychometrics of variables [42].
The present systematic review evaluated primary articles with a detailed check list (see Additional file 1, Table B: Quality assessment check list) which included items for grading quality of subjective-report methods. There were separate check lists for each study design type since some items are design specific (e.g., blinding and randomization in experimental designs). Since work exposure variables may vary considerably over time, single-point measurements may be unreliable estimates of exposure. Hence, an item addressing repeated measurements of exposures was included.
The main arguments for applying a detailed check list for observational studies were to ensure that (i) reviewers actively search out all information relevant to internal validity in each article, (ii) the two reviewers put equal weights on sources of bias, (iii) to provide a standard for grading methods based on different self-report instruments, observations, or registries, and to (iv) to provide full transparency of assessments. In addition to assessing internal validity (recruitment of study population/subjects; methods for exposure measurements; methods for outcome measurements; analysis and data presentation; and inclusion of confounders), we scored external validity (generalizability, the representativeness of the study population), and moderators (other types of exposures at work (e.g., physical, chemical) and leisure-time exposures). The two latter aspects are not taken into account in the present review. Before the scoring of articles took place, a pilot test of the check list was conducted by all reviewers to test the system.
Each study was first assessed independently by two reviewers. After assessing quality, the two referees compared and scored the study. If there was disagreement on checklist item scores, the referees discussed the reason for disagreement and agreed upon the score of the item. All authors participated in the assessment of quality.
The 27 different items of the checklist for internal validity of prospective studies were weighted for their potential significance for methodological quality (0-3 points). Factors of potential serious bias were assessed by more than one check-list item and higher obtainable scores. The grading of subjective-report methods for measuring exposures contained items pertaining to psychometric quality of instruments (explicit documentation of validity and reliability, repeated measurements) and reporting behavior (analysis of data at organizational unit-level), and reporting historical exposures. These are methodological measures that improve quality, but have not been considered necessary for accepting studies in epidemiology journals.
The scores were summed and a total score for internal validity was the basis for the conclusion of quality. To be given a maximum score (100%) a study must exhibit no discernible selection bias, attrition to follow-up lower than 15%, all measurements performed with objective (neutral) methods using interval or ratio scales, include three or more measurements of exposure factors (high reliability), include analyses which control confounders age, gender, education, socioeconomic gradients, and perform comprehensive statistical analyses. After having scored all articles published until 2012 the research group concluded that studies meeting customary criteria for acceptable methods exhibited scores exceeding 50% of maximum. The criterion for accepting methodological quality of a study was set to internal validity score of 50% or more. This level eliminated studies with “(1) failure to develop and apply appropriate eligibility criteria (inclusion of control population), (2) flawed measurement of both exposure and outcome (3) failure to adequately control confounding, and (4) incomplete follow-up” (GRADE guidelines) [38]. The highest score was 81% [43]. The study group agreed that studies that scored 66% or higher could be defined as high-quality studies. We have not found previous studies differentiating between acceptable and high quality base on detailed check list of all factors listed above.
Conclusions were based on studies with acceptable quality only. The conclusion “high evidence for an effect” required that randomized control studies of interventions targeted at a specific exposure factor (a change of exposure) showed that this exposure was significant. The conclusion “moderate evidence” required that there was sufficient reason to upgrade evidence from observational studies from the normal level of limited evidence: either (i) two or more observational studies of acceptable quality showed the same effect with no studies showing nonsignificant or opposite effects, or (ii) many observational studies of accepted quality showed an effect and in addition, a significant combined effect estimate in meta-analyses. The conclusion “limited evidence” was made if (i) there was only one study of acceptable quality of the factor in question (no replication) and this study showed a significant effect, or (ii) there were studies showing significant and a small number showing nonsignificant effects, but none showing significant opposite effects. The conclusion “very limited evidence” was drawn if there were several studies with nonsignificant findings and meta-analyses did not produce unequivocal results.
Meta-analyses
Combined effect estimates were calculated by means of averaged associations across samples, weighting each observed association by the study’s sample size [44]. Eligible studies for inclusion in the meta-analyses reported categorical exposure variables with the unexposed employees (or employees with the lowest exposure category) as reference category. We synthesized studies reporting both Odds ratios and Hazard ratios and computed means of average associations as approximations of Relative risk ratios. This approximation is valid if the incidence rate of a study outcome is rare. The most completely adjusted risk estimates from each study and their corresponding confidence intervals or standard errors were used to compute combined effect estimates. When applicable, we computed additional subgroup analysis of the most comparable studies, i.e., studies that used the same exposure instrument measures, e.g., the Job content questionnaire (JCQ).
We computed random-effects models which estimate the mean of a distribution of true effects. The random effects model is recommended when there is reason to assume that the true effect vary from one study to the next [44]. The Q statistic was computed to assess the heterogeneity of studies (p < 0.05 rejects the null hypothesis of homogeneity). The I2 statistic shows the heterogeneity in percentages. To address the potential problem of publication bias, we computed the fail-safe N statistic which indicates the number of studies reporting null results that would be required to reduce the overall effect to non-significant [45]. All of the computed statistics were carried out by the Comprehensive Meta-Analysis (version 2) software, Biostat, Englewood, USA [46].
Results
Identified studies
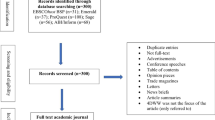
Of the 19545 abstracts, we identified 39 studies that fulfilled the inclusion criteria and satisfied the criteria for quality [12, 32, 43, 47–82]. Figure 1 depicts the identification, screening, eligibility, and inclusion processes. Studies excluded in the initial screening did not fulfill any of the inclusion criteria, or were duplicates (identified by Endnote reference library program, n = 3705). In all, 184 studies were considered as potentially relevant in the initial screening process. Of these 184 studies, 63 were excluded because of cross-sectional design or irrelevant outcome measures. In total, 121 [12, 24, 27–33, 43, 47–157] studies were independently reviewed in full text by two of the authors. Among these studies, 19 studies did not have a relevant exposure measure [33, 84, 90, 97, 105, 115–117, 119–121, 124, 131, 137, 141, 143, 147–149], seven studies did not report relevant outcome measures [87, 93, 103, 106, 110, 113, 129], five studies were not written in English, German, or a Nordic language [114, 125, 128, 136, 140], three studies were only reported as congress abstracts [92, 139, 144], and one study had a cross sectional design [130].
In total, 86 studies were included for assessment of quality [12, 24, 27–32, 43, 47–83, 85, 86, 88, 89, 91, 94–96, 98–102, 104, 107–109, 111, 112, 118, 122, 123, 126, 127, 132–135, 138, 142, 145, 146, 150–157]. Two referees independently assessed full-text articles from each study. Of these 86 studies, 23 were excluded because no relevant exposure full-filling the criteria was reported [27, 28, 95, 96, 146, 152, 154, 155], no relevant outcome was reported [24, 99, 109, 118, 127, 132, 138, 156, 157], and cross-sectional design [108, 126, 133, 134, 151, 153]. Of the remaining 63 studies [12, 29–32, 43, 47–75, 83, 85, 86, 88, 89, 91, 94, 98, 100–102, 104, 107, 111, 112, 122, 123, 135, 142, 145, 150], 24 studies with lower than 50% quality score [29–31, 83, 85, 86, 88, 89, 91, 94, 98, 100–102, 104, 107, 111, 112, 122, 135, 142, 145, 150] [123]: eleven did not report work-related risk estimates [29–31, 85, 88, 89, 91, 94, 111, 122, 142], twelve studies reported crude estimates only [83, 86, 98, 100–102, 104, 107, 112, 123, 135, 145, 150].
The table C of Additional file 1 presents characteristics and findings of the studies that did not meet the criterion quality score. The table D of Additional file 1 shows the scores of internal validity for accepted studies. The table E of Additional file 1 depicts the scores of internal validity for studies that were excluded by quality criteria.
Overview of included studies
Of the 39 studies finally included, 19 studies were of high quality (internal validity of 66% or more) [12, 32, 43, 47–55, 76–82]. The highest score was 81% [43]. Table 1 presents a detailed overview of these 39 studies.
Fourteen studies were based on a Finnish population [12, 32, 43, 47, 48, 51, 53, 59, 60, 62, 65, 67, 72, 78], nine studies on a Norwegian population [50, 56–58, 61, 74, 75, 80, 81], nine studies on a Danish population [52, 55, 63, 64, 68, 70, 71, 76, 82], five studies on a Swedish population [49, 54, 66, 77, 79]. One study was based on a population from the UK [69], and one study used data from several European countries [73]. Twenty-five studies were based on general working population samples (ns range: 3164 – 69842), five studies on public-sector employees, three studies on municipal employees, four studies on specific occupations, and two studies based on twins. Thirty-three studies identified disability retirement by registries while six studies depended on self-report questionnaire.
Studies reporting several work factors are presented in two or more sections in this article.
Overall appraisal of the work environment
One representative general-population study by Støver and coworkers [81] found that overall poor psychosocial work environment predicted disability retirement, based on the number of “poor psychosocial work exposures” out of 11 questions encompassing variation, feedback, support, influence (control), demands, reorganization, and bullying.
Studies of psychological factors
Job demands
Twenty studies addressed aspects of job demands [49, 50, 52, 54, 55, 58, 60, 62, 63, 66–68, 71, 73–76, 79, 80, 82] (Table 1). The study populations were: all Danish nurses [52], nurses’ aides [55], male waste collectors & municipal employees [68], rural male farmers and non-farmers [66], Finnish public sector employees [67], employees of the city of Helsinki [60], and in fourteen studies data from the general working population [49, 50, 54, 58, 62, 63, 71, 73–76, 79, 80, 82]. Except for five studies [62, 67, 68, 73, 80], all used registry data to assess disability retirement.
Ten studies assessed job demands with measures from, or derived from the Job Content Questionnaire (JCQ) [49, 54, 55, 60, 63, 66–68, 71, 79], whereas one study assessed “amount of work” with the Copenhagen Psychosocial Questionnaire (COPSOQ) [82]. In Eight of the remaining nine studies, aspects of job demands were assessed with single item measures [50, 52, 58, 62, 73, 74, 76, 80]. Finally, one study assessed aspects of job demands with a non-validated two item scale [75].
Aspects of job demands were reported to predict subsequent disability retirement in four out of total twenty studies. Job demands were positively related to subsequent disability retirement in two [54, 79] of the eleven studies that measured demands by validated instruments, one of which pertained to retirement due to mental diagnoses [48]. However Ropponen et al. [79] reported that low demands was associated with an increased risk of disability awards with musculoskeletal diagnoses and Clausen et al. [76] found that medium-level of demands reduced risk of disability pension awards compared to low demands.
Specific aspects of job demands were significantly related to subsequent disability retirement in two of the eight studies that were based on single item demand measures [50, 74]. Krokstad et al [50] found significant associations between high levels of “concentration and attention” and subsequent disability retirement among women in the general working population, but not among men. Based on the same population and measurements as Krokstad et al, Hagen et al [74] found a significant sex and age-adjusted increased risk.
Thirteen of the twenty studies were suitable for meta-analysis [50, 52, 54, 55, 60, 67, 71, 73–75, 80–82]. Figure 2 shows the forest plot and the results from the meta-analysis. The combined relative risk estimate of the thirteen studies did not show an association (RR = 1.12; 95% CI = 0.98-1.28). The Q statistics showed substantially heterogeneity between studies (Table 2). The reason may be that the different studies measured different exposures (e.g., job stress, busy at work, high time pressure, demands in concentration and attention, JCQ-job demands). In addition, some studies measured the outcome by questionnaire whereas other studies reported registry data. The subgroup analysis of the four comparable studies which measured job demands with JCQ and based information on disability pension on registries [54, 55, 60, 71], showed no significant association (RR = 1.14; 95% CI = 0.80-1.62). The heterogeneity between these studies was substantial (p < 0.01).
Stratified analyses for studies with single item (n = 7) and multiple item (n = 6) measurements of demands showed a RR of 1.08 (95% CI: 0.90-1.30) for single item and an RR of 1.16 (95% CI: 0.92-1.47) for multiple item measures.
Stratified analyses for studies with high quality (n = 8) and acceptable quality (n = 5) did not reveal a difference in results of the effects of demands on disability pension (high quality studies RR = 1.06; 95% CI = 0.89-1.27 vs acceptable quality studies RR = 1.26; 95% CI = 0.96-1.65).
Repetitive work tasks (monotonous work)
One representative general-population study by Sterud [80] found that reporting having repetitive work tasks three quarters of the work day or more predicted disability pension. Repetitive work tasks was measured with a single item: Does your job consist of constantly repeated tasks, meaning that you do the same thing hour after hour?”
Control
The control dimension pertains to freedom to choose between alternatives. Twenty-four studies addressed aspects of job control [49–52, 54–60, 63, 66–68, 70, 71, 73–77, 79, 80]. The study populations were: all Danish nurses [52], nurses’ aides [55], employees of the city of Helsinki [60], Finnish civil service employees [59], rural male farmers and non-farmers [66], Finnish public sector employees [51, 67], male waste collectors and municipal workers [68], and in sixteen studies data from the general working population [49, 50, 54, 56–58, 63, 70, 71, 73–77, 79, 80]. In nineteen studies, disability retirement was extracted from registry data, whereas five studies were based on a questionnaire [62, 67, 68, 73, 80].
Twelve studies used measures from or derived from the JCQ [49, 54, 55, 60, 63, 66–68, 71, 73, 77, 79]. This instrument defines the control dimension as job-decision latitude consisting of two factors: decision authority and skill discretion (required skills for the job). Nine of the twelve studies reported decision latitude [49, 54, 55, 60, 66, 67, 73, 77, 79], whereas two studies assessed decision authority and skill discretion separately, [68, 71] and one study assessed decision authority only [63]. Of the remaining twelve studies, one study measured influence at work with a four item scale from COPSOQ [76], one study assessed work-time control by a validated instrument (self-reported and co-worker-reported) [51], one study assessed job control with a three item scale [80], while one study measured decision authority-like aspects of control with a non-validated two item scale [75], and eight studies measured decision-authority like aspects of job control with single items [50, 52, 56–59, 70, 74].
Aspects of job control were significantly associated with subsequent disability retirement in 18 [49–52, 54, 56, 57, 59, 60, 67, 68, 70, 73, 75] of 24 studies. Seven [49, 54, 60, 67, 73, 77, 79] of the nine studies that assessed decision latitude with measures from the JCQ found a significant association with subsequent disability retirement [49, 54, 55, 60, 66, 67, 73]. None of the three studies that assessed decision authority with measures from JCQ found significant associations [63, 68, 71]. One of the two studies [68, 71] that assessed skill discretion with measures from JCQ found increased risk [68].
Aspects of job control were significantly associated with disability retirement in three [51, 75, 76] of the four studies that used other psychometric scales than the JCQ [51, 75, 76, 80]. Aspects of job control were significantly associated with subsequent disability retirement in seven [50, 52, 56, 57, 59, 70, 74] of the eight studies that used single-item measures [50, 52, 56–59, 70, 74].
Sixteen of the 24 studies were suitable for meta-analysis [50, 52, 54–57, 60, 67, 68, 70, 71, 73, 75–77, 80]. The combined relative risk estimate of the six teen studies also showed a significant association (RR = 1.40; 95% CI = 1.21-1.61; Fig. 3). The fail-safe N estimates indicate that the observed effect estimates were robust (Table 2). Nevertheless, the Q-statistics indicated substantial heterogeneity between the included studies. A plausible reason is that different exposure and outcome measures have been investigated. The subgroup analysis between the most comparable studies [54, 55, 60, 67, 73], in which all studies measured decision latitude with the JCQ, showed a significant association (RR = 1.33; 95%CI = 1.04-1.69). Nevertheless, the Q-statistic (p < 0.01) showed substantial heterogeneity between these studies as well.
Job strain
Six studies addressed job strain [47–49, 54, 67, 79] referring to the combination of high level of demands and low level of control (the job–strain model; Karasek [3]) (Table 1). All of these assessed job strain with measures from or derived from the Job Content Questionnaire (JCQ) [5]. Mantyniemi et al [47] and Samuelsson et al [49] used aggregated scores (work unit/job title and Job Exposure Matrix, respectively) to determine strain. The studies by Ahola et al [48], Ropponen et al [79], Samuelsson et al [49] and Canivet et al [54] were based on data from the general working population, whereas the studies by Mantyniemi et et al [47] and Laine et al [67] pertained to Finnish public-sector employees. With the exception of the study by Ahola et al [48] that measured disability retirement by a questionnaire, all studies assessed disability retirement by registries.
Job strain was a significant predictor of subsequent disability retirement in four out of six studies [47, 48, 54, 67]. The studies with nonsignificant results for job strain showed an increased risk of disability for the combination of low job demands and low job control (passive jobs) [49, 79], hence control may be the decisive factor.
Of the six studies, five were suitable for meta-analysis [48, 49, 54, 67, 79]. Figure 4 and Table 2 shows that high job strain was borderline significantly associated with increased risk of disability pension (RR = 1.45; 95% CI = 0.96-2.19). The two studies with nonsignificant results for job strain were based on two samples drawn from the same population [48, 78], but were both included in this analysis. The Q-statistic indicates substantial heterogeneity between studies (p < 0.01).
Effort-reward imbalance (ERI)
High effort-reward imbalance and low rewards were found to predict disability pension due to depression, both in analyses of individual level and work-unit level of ERI scores in one study [78]. The population was Finnish public sector employees. Effort-reward imbalance was measured with a four-item questionnaire, one item measuring effort and three measuring rewards. Individual level scores of ERI also predicted disability retirement due to musculoskeletal disorders.
Development and training
One study of the Danish general working population study found significant effects of both low employee development and low supplementary training on the risk of registry based disability-pension awards [63].
Studies of social factors
Social support
Social support refers to assistance, information, feedback, and emotional support. Nine studies addressed aspects of social support [49, 53, 54, 59, 60, 63, 68, 71, 79]. Data were extracted from the general working population in six of these studies [49, 53, 54, 63, 71, 79], whereas two studies were based on civil service employees [59] and employees of the city of Helsinki [60], respectively. In all of these studies, disability retirement was assessed by registry data. In the remaining study, the population was waste collectors and municipal workers, and disability retirement was assessed by questionnaire [68]. Seven studies assessed support with measures from the JCQ [49, 53, 54, 63, 68, 71, 79]. Of the remaining two studies, Hinkka et al [59] assessed support with a single item, whereas Lahelma et al [60] used another validated instrument.
Social support was related to subsequent disability retirement in three out of nine studies. Low supervisor support was found to increase the risk of subsequent disability retirement in the study by Sinokki et al [53] and Canivet et al [54]; whereas high social support was found to increase the risk in the study by Samuelsson et al [49]. In all these three studies, aspects of social support were assessed with measures from the JCQ.
Of the nine studies three were suitable for meta-analysis [53, 54, 71]. Figure 5 and Table 2 shows that aspects of low social support were nonsignificantly associated with subsequent disability retirement (RR = 1.17; 95% CI = 0.86-1.61).
Conflicts
Three studies examined the effect of conflicts on subsequent disability retirement (Table 1). Appelberg et al [12] assessed interpersonal conflicts with a single item, whereas Lund et al [63] and Labriola et al [71] assessed conflicts at work with measures derived from the JCQ. All three studies were based on the general working populations of Finland [12] and Denmark [63, 71], and all used registry data to assess disability retirement. Appelberg et al [12] found an increased risk for women, whereas Labriola et al [71] and Lund et al [63] did not find any significant associations between conflicts at work and disability retirement.
Harassment
One study of harassment based on the general working population found that harassment did not significantly predict disability retirement when controlling for distress, gender, age, and work exposure factors [80].
Team climate
Two studies examined the effect of team climate on disability retirement (Table 1). Hinkka et al [59] studied civil-service employees, and assessed team climate based on five items, whereas Ahola et al [48] used data from the general working population, and items from the Healthy Organization Questionnaire. Both studies assessed disability retirement by registries. Hinkka et al found a protective effect of good team climate, whereas no effect was found in the study by Ahola et al.
Studies of organizational factors
Working hours, shift work
Twelve studies addressed work-time schedules [32, 48, 52, 55–57, 59, 60, 62, 64, 65, 72]. Six of these studies compared permanent day workers with shift workers not specifying time of day [56, 57, 59, 60, 62, 64], whereas five studies compared day workers with shift workers specifying evening- or night-shifts [32, 52, 55, 65, 72]. In total, three studies examined the effect of hours worked per week [48, 60, 62].
Three [59, 62, 64] of six [56, 57, 59, 60, 62, 64] studies found significant associations between shift work and subsequent disability retirement. One of these studies reported a protective effect of regular shift work compared to day work in the general male working population [62]. Three [52, 55, 65] out of five studies found significant associations for evening and/or night work.
Of the three studies that examined the effect of hours worked per week [48, 60, 62], the study by Krause et al [62] [48, 60, 62] compared those who worked 60 h or more per week, 45 to 49 h per week, and 40-44 h per week with those who worked less than 40 h per week, respectively. There was a significant increased risk of working 60 h or more per week [62]. Ahola et al [48] and Lahelma et al [60] found no effects of working more than 40 h per week compared to working less.
Eleven studies compared day workers with evening-, night-, and/or shift workers, eight of which were eligible for meta-analysis [32, 52, 55, 59, 60, 64, 65, 72]. Figure 6 shows nonsignificant effects of shift-work on the risk of subsequent disability retirement (HR = 1.08; 95% CI = 0.92-1.28).
Contract type
One study examined the effect of temporary work contracts versus permanent contracts, and reported nonsignificant results [60].
Organizational change
Of the 32 studies, just one study addressed organizational change [69]. Based on office staff aged 35-55 working in 20 civil service departments in London, Virtanen et al found that the employees who were transferred to executive agencies compared to those who remained in the Civil Service exhibited increased risk of disability retirement.
Downsizing
Only one study addressed downsizing. Vahtera [43] et al found that a reduction in personnel of 18% or more was significantly related to subsequent disability retirement in both male and female municipal employees.
Discussion
Summary of evidence
The present systematic critical review found 19 articles of high [12, 32, 43, 47–55, 76–82] and 20 articles of acceptable [56–75] methodological quality. There was moderate evidence for the role of low control of work situation: low level of control was rather consistently associated with subsequent disability [49–52, 54, 56, 57, 59, 60, 67, 68, 70, 73–75], although five of the 20 studies reported nonsignificant results [55, 63, 66, 71, 74]. Moreover, there was moderate evidence for an effect of the combination of high quantitative demands and low control (job strain) (Karasek [3]) predicted subsequent disability [47, 48, 54, 67], although there were two studies (based on one population) with nonsignificant results [49, 79]. These two studies reported significant effectgs of the comniation of low demands and low control, hence control seems to be a decisive factor. There was no major systematic differences in findings between the highest rated and the lowest rated studies that met the criterion for adequate quality.
High job demands assessed with validated instruments was reported to predict disability in two studies [54], but nine studies reported nonsignificant findings [49, 55, 60, 63, 66–68, 71]. Low demands was found to predict disability awards in two studies [75, 78]. Of the eight studies that measured demands with single items [50, 52, 58, 62, 73–75], two studies [50, 74] reported that “concentration and attention” predicted disability. The meta-analysis did not show evidence of effects of high demands on subsequent disability retirement. Hence, with the large number of studies it seems merited to conclude that there is very limited evidence that general job demands predicts disability retirement, while there is limited evidence that the specific factor “concentration and attention” does contribute to disability.
There was limited evidence for the association between repetitive work tasks (monotonous work) and disability retirement (one study; Sterud [80]). There was limited evidence for a role of effort reward imbalance and low rewards as predictors of disability pension due to depression (one study; Juvani et al [78]).
Two studies reported that low support from the superior predicted disability pension awards [53, 54], while one [49] study reported that high social support predicted disability with mental diagnoses. Five other studies reported no effect of support [59, 60, 63, 68, 71]. Theoretically, one may argue that supportive superiors may facilitate retirement if in the best interest of the employee, or contribute to adjustments of work tasks (demands) to compensate for lower work ability. Hence, social support may affect retirement decisions through several mediation processes.
Interpersonal conflict was associated with disability pension awards in women [12], while two other studies did not find any association between conflicts and disability [63, 71].
Of organizational factors, downsizing [43] and organizational change [69] predicted subsequent disability retirement. The specific factors “employee development” and “supplementary training” have been reported by one study. These factors may be of significance, but the findings need to be confirmed by other studies and are therefore graded as limited evidence.
There is very limited evidence for evening and night work, shift or period work, working hours >60 per week. While three studies found effects of evening and night work [52, 55, 65], two did not [32, 72]. Two studies reported effects of shift or period –based work [59, 64], but four studies did not [56, 57, 60, 62]. The meta-analysis of the effects of shift work on subsequent disability retirement showed nonsignificant results.
While one study found effects of working hours >60 per week [62], two did not find effects of working hours >40 per week [48, 60].
Job dissatisfaction and low levels of meaning at work have been reported to predict higher risk of disability retirement ([11]; Clausen et al. [28]) indicating that some of the effects reported here may be mediated through emotional and cognitive factors like attitudes to work and the workplace.
On a theoretical level, we found that task-level, individual-level factors associated with control of one’s work situation was the most consistent significant work factor in processes leading to disability retirement. The level of control depends on the nature of work tasks and how work is organized. Disability is defined as the general inability to perform ones job and one would expect that the demands posed by the work tasks would be paramount in determining retirement due to disability. Surprisingly, psychological job demands was not a consistent predictor of disability awards. Theoretically, high levels of psychological demands may be associated with jobs held by employees with high levels of education and high job involvement [158], hence the appraisal of demands may vary between occupations resulting in inconsistent effect of demands.
Limitations: Methodological considerations pertaining to primary articles
Validity and specificity of exposure variables
The study of psychological and social factors is generally limited to methods based on self-report. Direct observations of working conditions by trained observers are usually not possible as they are very time-consuming. Moreover, the presence of an observer may influence the behavior of those observed.
Many articles presented minimal descriptions of the methods employed to measure psychological and social factors, referring to an instrument, but not specifying which items were used, response scales, or the properties of these.
Of psychological and social factors at work, most studies measured demands, control, and “job-strain”. The demands dimension includes several types of demands: Quantitative demands (amount of work, working hours, time pressure) differ from qualitative demands (complexity, standards for quality, problem solving) and emotional demands of dealing with clients, etc. Single-item assessment of demands can only tap into one (narrow) aspect of the many types of demands posed to the employee. Hence, it seems reasonable to recommend restricting conclusions to the specific factor measured rather than making statements pertaining to general job demands. Moreover, findings pertaining to specific factors may direct interventions. The finding that repetitive work tasks may predict disability retirement (Sterud, 2013) indicates that rather concrete organizational interventions may be beneficial.
Similarly, Control is a broad dimension that may be defined as the possibility or freedom to choose between alternatives. Control may pertain to control of decisions, breaks, work procedures, working hours (e.g., flexi-time), social interactions with clients or colleagues, etc. Hence, the control dimension incorporates several factors.
Most studies of demands, control, and job strain, were based on the Job Content Questionnaire instrument (JCQ; Karasek et al. [5]), which measures demands by questions pertaining to time pressure, amount of work, and role conflicts. Role conflicts may produce effects on health that differ from those of demands (e.g., Christensen & Knardahl [14, 159]). The control dimension (“decision latitude”) of the JCQ includes both “skill discretion” (variety of work and opportunity to use skills) and “decision authority” (control over decisions that influence work) which may affect health differentially [160]. High levels of skill discretion may imply more interesting work tasks and more responsibility (which may be related to demands). Furthermore, one [42] of two studies that reported skill discretion separately [42, 45] found a significant effect on disability [71]. Neither of these nor a third study from the same research group [37] found significant effects of low decision authority. Control of work time seems to be an important aspect of control [51].
The exposure assessment of studies on shift work was mostly based on dichotomous classification of data ("shift work" compared to "day work"). There is considerable variation in shift-schedule characteristics (e.g., the number of night shifts a year, the speed of shift rotation, regular vs. irregular shift systems, etc.) which may result in misclassification.
Therefore, although some of the most robust findings of the present systematic review pertain to broad dimensions each consisting of several factors; it is possible that applying instruments that measure specific factors would uncover stronger associations with subsequent disability. Some aspects of control may be more important with regard to disability pensioning than others, but this has not been sufficiently examined yet. Moreover, there is a need for studies of more specific exposure factors to allow practical application in interventions or prevention of disability retirement.
Exposure factors may be correlated. Shift-work schedules are most common in occupations in the manufacturing industry and in health-care and nursing where employees are sometimes also exposed to mechanical exposures (like lifting and pushing/pulling objects/patients), chemical exposures, and noise. Hence, many shift-work jobs present a combination of exposures making it difficult to assess the contribution of the shift work schedule per se. On the other hand, some organizations with continuous operations carry out most work-intensive procedures during daytime. Hence, some night shift jobs may present low job demands and working with a small group of coworkers. Therefore, drawing general conclusions of effects of shift work based on data from shift schedule with no information of type of work tasks or psychological and social factors is problematic. Conclusions probably only apply to the specific working population investigated and should not be generalized. This was a reason for not including external validity in the assessment of bias in this review. There is a need for studies of effects of interactions of shift characteristics and exposures during work.
Validity and specificity of the outcome variable retirement due to disability
The decision to award disability benefit may be based on both assessments of function and on availability of a suitable job. Criteria may vary in emphasis on medical diagnosis or tests of function. Even the support status of the claimant’s partner may be taken into account. To complicate things further, criteria for disability benefits may change over time as a consequence of political decisions. Some countries have introduced temporary disability pension in order to stimulate efforts for rehabilitation/return to work. Moreover, some insurance funds use the label disability compensation for payments of lost wages due to being unable to work due to injury or disease (e.g.,) [161], i.e., synonymously with sickness-absence compensation.
Countries vary in systems and criteria for assigning benefits and compensation to individuals who are no longer able to work. The Nordic countries all provide disability pension based on prolonged sickness absence and failure of retraining (http://www.nordsoc.org/en/) [162], while the Employment and Support Allowance (ESA) of the United Kingdom (UK) and the Social Security Disability Insurance of the United States (US) are based on medical assessments and general function tests [163, 164].
Of the present 39 studies with adequate quality rating, only two investigated non-Nordic populations. This may be a consequence of the differences in public pension systems. The normative age for receiving full pension is higher in the Nordic countries resulting in higher prevalence of disability retirees. Moreover, the public pension systems provide public registries available for scientific study. The age to receive full age pension in Norway is 67 years, 65 in Denmark and Sweden, and 68 in Finland. The state pension age in the UK and Austria is 60 years for women and 65 for men. The standard retirement age is 60 in Italy and until recently, 62 in France. Hence, several factors motivate research on factors determining disability retirement in the Nordic countries. A potential problem with this geographical bias of studies may be that the external validity of conclusions may be limited.
Influence of work ability on the perception and reporting of work exposures
Since work ability is a function of the ability of the individual and demands posed by the job, one should expect that individuals with lower work ability may perceive work tasks more demanding. Hence, reporting high levels of job demands may be a consequence of lower work ability, in which case one should expect high job demands to predict disability as a precursor (mediator) rather than as a pathogenic exposure factor.
Therefore, it seems surprising that job demands was not a consistent predictor of disability retirement across studies. Possibly, moderate or high job demands may be associated with interesting and motivating job tasks (and/or higher socioeconomic status), hence high job involvement may buffer effects of high demands in some jobs. Indeed, Blekesaune and Solem [75] reported that “People working in stressful jobs delay nondisability retirement compared with those in less stressful occupations.” An alternative explanation may be that employees with poor health may already have reduced their workload at the time of measuring their work exposures. It should be noted that Samuelsson et al. [48] found that higher levels of job demands was a risk factor of disability pension due to mental diagnoses, hence there may be specific associations between high demands and psychological health problems.
The length of a study follow-up period may influence results. Theoretically, if the follow-up period is short, individuals receiving disability retirement may primarily be employees with somewhat reduced work ability at baseline when the exposure measurements were performed. The present review did not find a systematic tendency of significant results among the studies with the shortest follow-up period. For the control dimension, studies that reported significant effects (control p < 0.05; n = 18 studies) had a mean follow-up time of 7.6 years (median = 7 years), while studies reporting nonsignificant results (p > 0.05; n = 6 studies) had a mean follow-up time of 7.8 years (median = 7 years). Studies reporting significant effects of the demand dimension (p < 0.05; n = 4 studies) had a mean follow-up time of 7 years (median = 6.5 years), while studies reporting nonsignificant results (p > 0.05; n = 16 studies) had a mean follow-up time of 7.9 years (median = 7.5 years).
Limitations and strengths of the current review
A major strength of this review was the comprehensive systematic search. Pilot searches showed that it was not possible to cover all psychological, social, organizational exposures by search terms. Therefore, articles were searched based on outcome search terms and all articles investigating/containing organizational, psychological, and social exposures (including moderating factors) were reviewed in full-text. We are therefore reasonably confident that this systematic literature review includes all relevant studies within the time span.
Several studies were identified that measured psychological and social factors, but only entered these data as confounders or moderators in their final analyses. These studies did not allow any conclusions of the contribution of psychological and social factors and consequently failed to reach an acceptable-quality score in this review.
Assessment of methodological quality
A second strength of the present review was the specific evaluation of subjective report methods for assessing bias. Most measurements of psychological and social work exposures are based on self-reported data. Many studies only report internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha) and some measure exposures with scaled-down versions of commonly used instruments or with single items with unknown psychometric properties.
There is no universal agreement of criteria for “flawed measurement” of psychological and social factors at work. While many epidemiological studies have measured work exposures with single questions or scales with unknown psychometric properties, experts in psychometrics generally call for the use of multi-question scales that are extensively tested for several aspects of validity, reliability, and item bias in order to conclude that a method is adequate [165]. The present systematic review evaluated bias by a detailed checklist of sources of bias that might originate from subjective-report methods: psychometric quality of instruments (explicit documentation of validity and reliability), analysis of data at organizational unit-level, assessment of traits associated with reporting bias, design with repeated measurements of exposures, and reporting historical exposures. These are methodological issues that influence validity of data, but have not traditionally been considered necessary for publishing epidemiological studies. For the present review, we decided that meeting basic criteria of selection bias and adequate exposure and outcome measurement constituted adequate quality. We found that this corresponded to a quality score of 50%. However, a consequence of including the above-mentioned factors which raises the standards for “perfect methods”, was the broader range of scores (highest score was 81%).
All reviewers noted that some issues were difficult to assess due to inadequate reporting of procedures methods in the primary articles. The checklist was found to be effective in making sure all essential issues were checked in all included primary articles.
There were no major systematic differences in findings between the highest rated and the lowest rated studies that passed the criterion for adequate quality (50%), e.g., the mean internal validity score of the six studies that reported no effects of control was 61%, whereas the mean score of the 18 studies that reported significant effects was 63%. Regarding demands, the mean internal validity score of the 17 studies that reported no increased risk was 62%, whereas the mean score was 63% for the three studies that reported an increased risk.
A third strength of the present review was that the decision to accept methodological quality of a primary study was based on evaluation of its internal validity. External validity determines whom conclusions pertain to, and should not direct conclusions of methodological quality.
The decision of level of evidence was based on GRADE guidelines supplemented with meta analyses. The most completely adjusted effect estimates reported in each individual primary study was entered into the meta analyses, since conclusions of primary articles generally are based on adjusted estimates. It is possible that some studies adjust for factors that are mediators rather than confounders or moderators, e.g., health status. Correcting for mediators may lead to underestimation of the effects of the work related factors. However, it is often not possible to determine if a variable is a mediator with only one or two measurement points. In our opinion, it was not reasonable to compute the combined effect estimates based on the crude effects, given that the outcome is highly related to age.
External validity
The aim of the present review was elucidating predictors of permanent disability retirement, thus we did not include studies of employees already on sickness absence or temporary disability. Several countries do not have public systems of disability compensation and several countries do not have registries allowing scientific study of disability benefits. Therefore, one may question the general external validity of the current primary studies. One has to read each study to determine to whom the conclusions apply.
The findings of a study of one type or work or one occupation may not be generalized to other occupations, but may still be of great value. Even findings from a random representative sample in one country may not be generalized to another country with different laws, culture, or compensation systems. The large increase in unemployment in many European countries since 2008 may contribute to differences between countries.
Publication bias
The selective publication of studies based on the magnitude and direction of their findings constitute a threat to the validity of meta-analysis [166]. The most consistent finding in the present study was the association between low control and excess risk of subsequent disability retirement. The fail-safe N statistic showed that 623 studies reporting null effects would be needed to attenuate the findings in the present study to non-significant. Hence, the combined effects of control were robust.
Comparison of findings with previous systematic reviews
We have only found one systematic critical review of psychosocial factors at work as predictors of disability benefits, authored by Dragano and Schneider [167]. With search terms “early retirement”, “premature retirement”, “work disability”, “early pensioning”, “disability pension”, and “disability retirement” their search seems to be somewhat wider than the present review since “work disability” may denote temporary disability. They excluded studies of shift work, their only specified quality criterion was prospective study design, and they did not perform meta-analyses. They concluded that 20 studies met their criteria for inclusion and quality. Six studies in their review did not meet the quality criteria of the present review [95, 98, 99, 101, 104, 111]. Two of these studies reported significant effects of control, demands [99] and job strain [104]. One study [98] reported no effects of control, demands, or opportunities for development. The present review included 25 studies [32, 47–49, 52, 54, 55, 57, 59–61, 64–66, 69, 72–74, 76–82] that were not identified by Dragano and Schneider or that were published after July 31st, 2010, the time frame of their search. They reported “Important single factors were low control, monotonous work”, “job strain, effort-reward imbalance”, “lack of social support”, “problems related to the organization of work and to leadership behaviors”.
Conclusions
The present systematic review showed that psychological and organizational factors at work contribute to early retirement due to disability benefits. There was moderate evidence (i.e., several observational studies of high quality with coherent results) for the role of low control of work situation and for the combination of high quantitative demands and low control (job strain). There was limited evidence for downsizing, organizational change, work demanding attention and concentration, lack of employee development and supplementary training, repetitive work tasks, low rewards, and effort-reward imbalance as predictors of disability, but these findings need replication. There was very limited evidence that general job demands, evening or night work, and low social support from ones superior as predictors of disability retirement.
It seems justified to recommend that managers and leaders intensify their efforts to increase employees’ control of their work situation (decision authority, autonomy), in particular for employees with high levels of job strain. During periods of downsizing and organizational change, managers should pay attention to processes that may facilitate disability. Employee development and supplementary training may be particularly important measures to maintain competence/work ability in a working life with rapidly changing technology and demands.
Research needs
Most of the reviewed studies applied measurement instruments that measure broad dimensions combining factors that may have different effects on health-related outcomes. Most studies of job demands, control, and the combination of demands and control (job strain), have applied the JCQ [5]. This instrument includes role conflict in job demands and both decision authority and skill discretion under the control dimension. Therefore, studies conducted by the JCQ may underestimate effects if only one of these factors contribute to disability retirement. There is a need for studies based on measurements of specific work exposures. Furthermore, knowledge of risks (or protective factors) must be specific in order to direct design of interventions or prevention. It seems merited to recommend measurement of specific exposure factors in future studies of disability.
Almost all studies found were conducted with Nordic populations. In order to take cultural, political, and economic aspects into account, there is a need for studies of employees from non-Nordic countries. The challenges posed by the combination of current high rates of unemployment in young Europeans and the demographic shift to aging populations, raises the need for knowledge of trajectories of competence/work ability and exit from working life, and the influence of work factors on these trajectories.
Abbreviations
- COPSOQ:
-
The Copenhagen Psychosocial Questionnaire
- ERI:
-
Effort-reward imbalance model
- GRADE:
-
The Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation Working Group
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- JCQ:
-
The Job content questionnaire
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- RR:
-
Risk ratio
References
United Nations. Department of Economics and Social Affairs. http://www.un.org/esa/population/publications/worldageing19502050. Accessed 15 Dec 2014.
Tengland PA. The concept of work ability. J Occup Rehabil. 2011;21(2):275–85.
Karasek Jr RA. Job demands, job decision latitude, and mental strain: Implications for job redesign. Adm Sci Q. 1979;28:285-308.
Weiss JM. Effects of punishing the coping response (conflict) on stress pathology in rats. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1971;77(1):14.
Karasek R, Brisson C, Kawakami N, Houtman I, Bongers P, Amick B. The Job Content Questionnaire (JCQ): an instrument for internationally comparative assessments of psychosocial job characteristics. J Occup Health Psychol. 1998;3:322–55.
Kivimäki M, Nyberg ST, Batty GD, Fransson EI, Heikkilä K, Alfredsson L, Bjorner JB, Borritz M, Burr H, Casini A. Job strain as a risk factor for coronary heart disease: a collaborative meta-analysis of individual participant data. Lancet. 2012;380:1491-97.
Kraatz S, Lang J, Kraus T, Münster E, Ochsmann E. The incremental effect of psychosocial workplace factors on the development of neck and shoulder disorders: a systematic review of longitudinal studies. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health. 2013;86:1-21.
Kivimaki M, Ferrie JE, Brunner E, Head J, Shipley MJ, Vahtera J, Marmot MG. Justice at work and reduced risk of coronary heart disease among employees: the Whitehall II Study. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165(19):2245.
Ylipaavalniemi J, Kivimäki M, Elovainio M, Virtanen M, Keltikangas-Järvinen L, Vahtera J. Psychosocial work characteristics and incidence of newly diagnosed depression: a prospective cohort study of three different models. Soc Sci Med. 2005;61(1):111–22.
Moran ET, Volkwein JF. The cultural approach to the formation of organizational climate. Human relations. 1992;45(1):19–47.
Borg V, Kristensen TS, Burr H. Work environment and changes in self-rated health: a five year follow-up study. Stress Health. 2000;16(1):37–47.
Appelberg K, Romanov K, Heikkila K, Honkasalo ML, Koskenvuo M. Interpersonal conflict as a predictor of work disability: a follow-up study of 15,348 Finnish employees. J Psychosom Res. 1996;40(2):157–67.
Christensen JO, Knardahl S. Work and back pain: A prospective study of psychological, social and mechanical predictors of back pain severity. Eur J Pain. 2012;16(6):921–33.
Christensen JO, Knardahl S. Work and neck pain: a prospective study of psychological, social, and mechanical risk factors. Pain. 2010;151(1):162–73.
Vahtera J, Kivimäki M, Pentti J, Linna A, Virtanen M, Virtanen P, Ferrie JE. Organisational downsizing, sickness absence, and mortality: 10-town prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2004;328(7439):555.
Vyas MV, Garg AX, Iansavichus AV, Costella J, Donner A, Laugsand LE, Janszky I, Mrkobrada M, Parraga G, Hackam DG. Shift work and vascular events: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ [Br Med J]. 2012;345:e4800.
Liu Y, Tanaka H. Overtime work, insufficient sleep, and risk of non-fatal acute myocardial infarction in Japanese men. Occup Environ Med. 2002;59(7):447–51.
Caruso CC, Waters TR. A review of work schedule issues and musculoskeletal disorders with an emphasis on the healthcare sector. Ind Health. 2008;46(6):523–34.
Westerlund H, Ferrie J, Hagberg J, Jeding K, Oxenstierna G, Theorell T. Workplace expansion, long-term sickness absence, and hospital admission. Lancet. 2004;363(9416):1193–7.
Hackman JR, Oldham GR. Motivation through the design of work: Test of a theory. Organ Behav Hum Perform. 1976;16(2):250–79.
Adams JS. Towards an understanding of inequity. J Abnorm Soc Psychol. 1963;67(5):422.
Spector PE. Job satisfaction: Application, assessment, causes, and consequences, vol. 3: Sage; 1997.
Ilmarinen J, Tuomi K, Seitsamo J. New dimensions of work ability. International congress series: 2005: Elsevier; 2005. p. 3-7.
de Wind A, Geuskens GA, Ybema JF, Blatter BM, Burdorf A, Bongers PM, van der Beek AJ. Health, job characteristics, skills, and social and financial factors in relation to early retirement--results from a longitudinal study in the Netherlands. Scand J Work Environ Health. 2014;40(2):186–94.
Volanen S-M, Suominen S, Lahelma E, Koskenvuo K, Koskenvuo M, Silventoinen K. Sense of coherence and intentions to retire early among Finnish women and men. BMC Public Health. 2010;10(1):22.
Borg TL, Vilhelm. Work environment and self-rated health as predictors of remaining in work 5 years later among Danish employees 35-59 years of age. Exp Aging Res. 1999;25(4):429–34.
Kuoppala J, Lamminpaa A, Vaananen-Tomppo I, Hinkka K. Employee well-being and sick leave, occupational accident, and disability pension: a cohort study of civil servants. J Occup Environ Med. 2011;53(6):633–40.
Clausen T, Burr H, Borg V. Does affective organizational commitment and experience of meaning at work predict risk of disability pensioning? An analysis of register-based outcomes using pooled data on 40,554 observations in four occupational groups. Am J Ind Med. 2014;57(6):709–17.
Haaramo P, Rahkonen O, Lahelma E, Lallukka T. The joint association of sleep duration and sleep problems with disability retirement: A longitudinal registerlinked study. Sleep and Biological Rhythms. 2011;9(4):405.
Lallukka T, Haaramo P, Lahelma E, Rahkonen O. Sleep problems and disability retirement: a register-based follow-up study. Am J Epidemiol. 2011;173(8):871–81.
Pietilainen O, Laaksonen M, Rahkonen O, Lahelma E. Self-rated health as a predictor of disability retirement - the contribution of ill-health and working conditions. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(9):e25004.
Hublin C, Partinen M, Koskenvuo K, Silventoinen K, Koskenvuo M, Kaprio J. Shift-work and cardiovascular disease: a population-based 22-year follow-up study. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25(5):315–23.
Eberhardt K, Larsson B-M, Nived K, Lindqvist E. Work disability in rheumatoid arthritis--development over 15 years and evaluation of predictive factors over time. J Rheumatol. 2007;34(3):481–7.
Atlanta: Grade Working Group. http://www.gradeworkinggroup.org/. Accessed Dec 15 2014.
Sanderson S, Tatt ID, Higgins JP. Tools for assessing quality and susceptibility to bias in observational studies in epidemiology: a systematic review and annotated bibliography. Int J Epidemiol. 2007;36(3):666–76.
Shamliyan T, Kane RL, Jansen S. Peer Reviewed: Quality of Systematic Reviews of Observational Nontherapeutic Studies. Prev Chronic Dis. 2010; 7(6):A133.
Von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gøtzsche PC, Vandenbroucke JP. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. Prev Med. 2007;45(4):247–51.
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist G, Kunz R, Brozek J, Alonso-Coello P, Montori V, Akl EA, Djulbegovic B, Falck-Ytter Y. GRADE guidelines: 4. Rating the quality of evidence—study limitations (risk of bias). J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64(4):407–15.
Watson D, Pennebaker JW, Folger R. Beyond negative affectivity: Measuring stress and satisfaction in the workplace. J Organ Behav Manag. 1987;8(2):141–58.
Chen PY, Spector PE. Negative affectivity as the underlying cause of correlations between stressors and strains. J Appl Psychol. 1991;76(3):398.
Oliver JE, Mansell A, Jose PE. A longitudinal study of the role of negative affectivity on the work stressor–strain process. Int J Stress Manag. 2010;17(1):56.
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, Moher D, Becker BJ, Sipe TA, Thacker SB. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. JAMA. 2000;283(15):2008–12.
Vahtera J, Kivimaki M, Forma P, Wikstrom J, Halmeenmaki T, Linna A, Pentti J. Organisational downsizing as a predictor of disability pension: the 10-town prospective cohort study. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2005;59(3):238–42.
Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins J, Rothstein HR. A basic introduction to fixed‐effect and random‐effects models for meta‐analysis. Res Synthesis Methods. 2010;1(2):97–111.
Rosenthal R. The file drawer problem and tolerance for null results. Psychol Bull. 1979;86(3):638.
Comprehensive Meta-Analysis (version 2) software, Biostat, Englewood, USA.
Mantyniemi A, Oksanen T, Salo P, Virtanen M, Sjosten N, Pentti J, Kivimaki M, Vahtera J. Job strain and the risk of disability pension due to musculoskeletal disorders, depression or coronary heart disease: a prospective cohort study of 69 842 employees. Occup Environ Med. 2012;69(8):574–81.
Ahola K, Virtanen M, Honkonen T, Isometsa E, Aromaa A, Lonnqvist J. Common mental disorders and subsequent work disability: a population-based Health 2000 Study. J Affect Disord. 2011;134(1-3):365–72.
Samuelsson A, Ropponen A, Alexanderson K, Svedberg P. Psychosocial working conditions, occupational groups, and risk of disability pension due to mental diagnoses: a cohort study of 43 000 Swedish twins. Scand J Work Environ Health. 2013;39:351-360.
Krokstad S, Johnsen R, Westin S. Social determinants of disability pension: a 10-year follow-up of 62 000 people in a Norwegian county population. Int J Epidemiol. 2002;31(6):1183–91.
Vahtera J, Laine S, Virtanen M, Oksanen T, Koskinen A, Pentti J, Kivimaki M. Employee control over working times and risk of cause-specific disability pension: the Finnish Public Sector Study. Occup Environ Med. 2010;67(7):479–85.
Friis K, Ekholm O, Hundrup YA. The relationship between lifestyle, working environment, socio-demographic factors and expulsion from the labour market due to disability pension among nurses. Scand J Caring Sci. 2008;22(2):241–8.
Sinokki M, Hinkka K, Ahola K, Gould R, Puukka P, Lonnqvist J, Virtanen M. Social support as a predictor of disability pension: the Finnish Health 2000 study. J Occup Environ Med. 2010;52(7):733–9.
Canivet C, Choi B, Karasek R, Moghaddassi M, Staland-Nyman C, Ostergren PO. Can high psychological job demands, low decision latitude, and high job strain predict disability pensions? A 12-year follow-up of middle-aged Swedish workers. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2013;86:307-319.
Jensen LD, Ryom PK, Christensen MV, Andersen JH. Differences in risk factors for voluntary early retirement and disability pension: a 15-year follow-up in a cohort of nurses' aides. BMJ Open. 2012;2(6):e000991.
Claussen B, Dalgard OS. Disability pensioning: the gender divide can be explained by occupation, income, mental distress and health. Scand J Public Health. 2009;37(6):590–7.
Claussen B, Dalgard OS, Bruusgaard D. Disability pensioning: Can ethnic divides be explained by occupation, income, mental distress, or health? Scand J Public Health. 2009;37(4):395–400.
Hagen KB, Tambs K, Bjerkedal T. A prospective cohort study of risk factors for disability retirement because of back pain in the general working population. Spine. 2002;27(16):1790–6.
Hinkka K, Kuoppala J, Vaananen-Tomppo I, Lamminpaa A. Psychosocial work factors and sick leave, occupational accident, and disability pension: a cohort study of civil servants. J Occup Environ Med. 2013;55(2):191–7.
Lahelma E, Laaksonen M, Lallukka T, Martikainen P, Pietilainen O, Saastamoinen P, Gould R, Rahkonen O. Working conditions as risk factors for disability retirement: a longitudinal register linkage study. BMC Public Health. 2012;12:309.
Brage S, Sandanger I, Nygard JF. Emotional distress as a predictor for low back disability: a prospective 12-year population-based study. Spine. 2007;32(2):269–74.
Krause N, Lynch J, Kaplan GA, Cohen RD, Goldberg DE, Salonen JT. Predictors of disability retirement. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1997;23(6):403–13.
Lund T, Csonka A. Risk factors in health, work environment, smoking status, and organizational context for work disability. Am J Ind Med. 2003;44(5):492–501.
Tuchsen F, Christensen KB, Lund T, Feveile H. A 15-year prospective study of shift work and disability pension. Occup Environ Med. 2008;65(4):283–5.
Karkkainen S, Pitkaniemi J, Silventoinen K, Svedberg P, Huunan-Seppala A, Koskenvuo K, Koskenvuo M, Alexanderson K, Kaprio J, Ropponen A. Disability pension due to musculoskeletal diagnoses: importance of work-related factors in a prospective cohort study of Finnish twins. Scand J Work Environ Health. 2013;39:343-50.
Holmberg SAC, Thelin AG. Primary care consultation, hospital admission, sick leave and disability pension owing to neck and low back pain: a 12-year prospective cohort study in a rural population. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2006;7:66.
Laine S, Gimeno D, Virtanen M, Oksanen T, Vahtera J, Elovainio M, Koskinen A, Pentti J, Kivimaki M. Job strain as a predictor of disability pension: the Finnish Public Sector Study. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2009;63(1):24–30.
Lund T, Iversen L, Poulsen KB. Work environment factors, health, lifestyle and marital status as predictors of job change and early retirement in physically heavy occupations. Am J Ind Med. 2001;40(2):161–9.
Virtanen M, Kivimaki M, Singh-Manoux A, Gimeno D, Shipley M, Vahtera J, Akbaraly T, Marmot M, Ferrie J. Work disability following major organisational change: The Whitehall II study. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2010;64(5):461–4.
Christensen KB, Feveile H, Labriola M, Lund T. The impact of psychosocial work environment factors on the risk of disability pension in Denmark. Eur J Public Health. 2008;18(3):235–7.
Labriola M, Lund T. Self-reported sickness absence as a risk marker of future disability pension. Prospective findings from the DWECS/DREAM study 1990-2004. Int J Med Sci. 2007;4(3):153–8.
Ropponen A, Silventoinen K, Svedberg P, Alexanderson K, Huunan-Seppala A, Koskenvuo K, Koskenvuo M, Kaprio J. Effects of work and lifestyle on risk for future disability pension due to low back diagnoses: a 30-year prospective study of Finnish twins. J Occup Environ Med. 2012;54(11):1330–6.
Robroek SJ, Schuring M, Croezen S, Stattin M, Burdorf A. Poor health, unhealthy behaviors, and unfavorable work characteristics influence pathways of exit from paid employment among older workers in Europe: a four year follow-up study. Scand J Work Environ Health. 2013;39(2):125–33.
Hagen KB, Tambs K, Bjerkedal T. What mediates the inverse association between education and occupational disability from back pain?--A prospective cohort study from the Nord-Trondelag health study in Norway. Soc Sci Med. 2006;63(5):1267–75.
Blekesaune M, Solem PE. Working conditions and early retirement: A prospective study of retirement behavior. Res Aging. 2005;27(1):3–30.
Clausen T, Burr H, Borg V. Do psychosocial work conditions predict risk of disability pensioning? An analysis of register-based outcomes using pooled data on 40,554 observations. Scand J Public Health. 2014;42(4):377–84.
Falkstedt D, Backhans M, Lundin A, Allebeck P, Hemmingsson T. Do working conditions explain the increased risks of disability pension among men and women with low education? A follow-up of Swedish cohorts. Scand J Work Environ Health. 2014;40(5):483–92.
Juvani A, Oksanen T, Salo P, Virtanen M, Kivimaki M, Pentti J, Vahtera J. Effort-reward imbalance as a risk factor for disability pension: the Finnish Public Sector Study. Scand J Work Environ Health. 2014;40(3):266–77.
Ropponen A, Samuelsson A, Alexanderson K, Svedberg P. Register-based data of psychosocial working conditions and occupational groups as predictors of disability pension due to musculoskeletal diagnoses: a prospective cohort study of 24,543 Swedish twins. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013;14:268.
Sterud T. Work-related psychosocial and mechanical risk factors for work disability: a 3-year follow-up study of the general working population in Norway. Scand J Work Environ Health. 2013;39(5):468–76.
Stover M, Pape K, Johnsen R, Fleten N, Sund ER, Ose SO, Bjorngaard JH. Work environment and disability pension-- an 18-year follow-up study in a Norwegian working population. Scand J Public Health. 2013;41(6):587–96.
Thielen K, Nygaard E, Andersen I, Diderichsen F. Employment consequences of depressive symptoms and work demands individually and combined. Eur J Pub Health. 2014;24(1):34–9.
Johansson E, Leijon O, Falkstedt D, Farah A, Hemmingsson T. Educational differences in disability pension among Swedish middle-aged men: role of factors in late adolescence and work characteristics in adulthood. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2012;66(10):901–7.
Raymo JM, Warren JR, Sweeney MM, Hauser RM, Ho J-H. Precarious employment, bad jobs, labor unions, and early retirement. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 2011;66(2):249–59.
Leinonen T, Pietilainen O, Laaksonen M, Rahkonen O, Lahelma E, Martikainen P. Occupational social class and disability retirement among municipal employees - the contribution of health behaviors and working conditions. Scand J Work Environ Health. 2011;37(6):464–72.
Haukenes I, Mykletun A, Knudsen AK, Hansen H-T, Maeland JG. Disability pension by occupational class--the impact of work-related factors: the Hordaland Health Study Cohort. BMC Public Health. 2011;11:406.
von Bonsdorff ME, Huuhtanen P, Tuomi K, Seitsamo J. Predictors of employees' early retirement intentions: an 11-year longitudinal study. Occupational Med(Oxford). 2010;60(2):94–100.
van den Berg T, Schuring M, Avendano M, Mackenbach J, Burdorf A. The impact of ill health on exit from paid employment in Europe among older workers. Occup Environ Med. 2010;67(12):845–52.
Salo P, Oksanen T, Sivertsen B, Hall M, Pentti J, Virtanen M, Vahtera J, Kivimaki M. Sleep disturbances as a predictor of cause-specific work disability and delayed return to work. Sleep. 2010;33(10):1323–31.
Reinholdt S, Upmark M, Alexanderson K. Health-selection mechanisms in the pathway towards a disability pension. Work. 2010;37(1):41–51.
Lund T, Labriola M, Feveile H, Christensen KB. The fraction of disability pensions attributable to smoking and obesity. Results from a 15-year follow-up study. J Public Health. 2010;18(3):251–4.
Lallukka T, Haaramo P, Lahelma E, Rahkonen O. Insomnia complaints and disability pensions: A register-based follow-up study of public sector employees. J Sleep Res. 2010;19:161–2.
Omachi TA, Claman DM, Blanc PD, Eisner MD. Obstructive sleep apnea: a risk factor for work disability. Sleep. 2009;32(6):791–8.
Labriola M, Feveile H, Christensen KB, Stroyer J, Lund T. The impact of ergonomic work environment exposures on the risk of disability pension: Prospective results from DWECS/DREAM. Ergonomics. 2009;52(11):1419–22.
Labriola M, Feveile H, Christensen KB, Bultmann U, Lund T. The impact of job satisfaction on the risk of disability pension. A 15-year prospective study. Scand J Public Health. 2009;37(7):778–80.
Kamaleri Y, Natvig B, Ihlebaek CM, Bruusgaard D. Does the number of musculoskeletal pain sites predict work disability? A 14-year prospective study. European J Pain: Ejp. 2009;13(4):426–30.
Feveile H, Christensen KB, Flyvholm M-A. Self-reported occupational skin contact with cleaning agents and the risk of disability pension. Contact Dermatitis. 2009;60(3):131–5.
Alavinia SM, de Boer AGEM, van Duivenbooden JC, Frings-Dresen MHW, Burdorf A. Determinants of work ability and its predictive value for disability. Occup Med (Oxford). 2009;59(1):32–7.
Boedeker W, Friedel H, Friedrichs M, Rottger C. The impact of work on morbidity-related early retirement. J Public Health. 2008;16(2):97–105.
Turner JA, Franklin G, Fulton-Kehoe D, Sheppard L, Wickizer TM, Wu R, Gluck JV, Egan K, Stover B. Early predictors of chronic work disability associated with carpal tunnel syndrome: a longitudinal workers' compensation cohort study. Am J Ind Med. 2007;50(7):489–500.
Albertsen K, Lund T, Christensen KB, Kristensen TS, Villadsen E. Predictors of disability pension over a 10-year period for men and women. Scand J Public Health. 2007;35(1):78–85.
Sivertsen B, Overland S, Neckelmann D, Glozier N, Krokstad S, Pallesen S, Nordhus IH, Bjorvatn B, Mykletun A. The long-term effect of insomnia on work disability: the HUNT-2 historical cohort study. Am J Epidemiol. 2006;163(11):1018–24.
Burdorf A, Jansen JP. Predicting the long term course of low back pain and its consequences for sickness absence and associated work disability. Occup Environ Med. 2006;63(8):522–9.
Stattin M, Jarvholm B. Occupation, work environment, and disability pension: a prospective study of construction workers. Scand J Public Health. 2005;33(2):84–90.
Hannerz H, Tuchsen F, Spangenberg S, Albertsen K. Industrial differences in disability retirement rates in Denmark, 1996-2000. Int J Occup Med Environ Health. 2004;17(4):465–71.
Crimmins EM, Hayward MD. Workplace characteristics and work disability onset for men and women. Soz Praventivmed. 2004;49(2):122–31.
Salonen P, Arola H, Nygard CH, Huhtala H, Koivisto AM. Factors associated with premature departure from working life among ageing food industry employees. Occup Med. 2003;53(1):65–8.
Dellve L, Lagerstrom M, Hagberg M. Work-system risk factors for permanent work disability among home-care workers: a case-control study. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2003;76(3):216–24.
Mein G, Martikainen P, Stansfeld SA, Brunner EJ, Fuhrer R, Marmot MG. Predictors of early retirement in British civil servants. Age Ageing. 2000;29(6):529–36.
Friedrich M, Cermak T, Heiller I. Spinal troubles in sewage workers: epidemiological data and work disability due to low back pain. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2000;73(4):245–54.
Biering-Sorensen F, Lund J, Hoydalsmo OJ, Darre EM, Deis A, Kryger P, Muller CF. Risk indicators of disability pension. A 15 year follow-up study. Dan Med Bull. 1999;46(3):258–62.
Mansson NO, Rastam L, Eriksson KF, Israelsson B. Socioeconomic inequalities and disability pension in middle-aged men. Int J Epidemiol. 1998;27(6):1019–25.
Pope DP, Croft PR, Pritchard CM, Silman AJ, Macfarlane GJ. Occupational factors related to shoulder pain and disability. Occup Environ Med. 1997;54(5):316–21.
Izmerov NF, Molodkina NN. Early retirement in relation to work conditions (substantiation of medical-biological criteria). Med Tr Prom Ekol. 1997;7:19–23.
Mau W, Bornmann M, Weber H, Weidemann HF, Hecker H, Raspe HH. Prediction of permanent work disability in a follow-up study of early rheumatoid arthritis: Results of a tree structured analysis using RECPAM. Br J Rheumatol. 1996;35(7):652–9.
Blanc PD, Faucett J, Kennedy JJ, Cisternas M, Yelin E. Self-reported carpal tunnel syndrome: predictors of work disability from the National Health Interview Survey Occupational Health Supplement. Am J Ind Med. 1996;30(3):362–8.
Arndt V, Rothenbacher D, Brenner H, Fraisse E, Zschenderlein B, Daniel U, Schuberth S, Fliedner TM. Older workers in the construction industry: results of a routine health examination and a five year follow up. Occup Environ Med . 1996;53(10):686–91.
Reisine S, McQuillan J, Fifield J. Predictors of work disability in rheumatoid arthritis patients: A five- year followup. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38(11):1630–7.
Crook J, Moldofsky H. Prognostic indicators of disability after a work-related musculoskeletal injury. J Musculoskeletal Pain. 1995;3(2):155–9.
Vingard E, Alfredsson L, Fellenius E, Hogstedt C. Disability pensions due to musculo-skeletal disorders among men in heavy occupations. A case-control study. Scand J Soc Med. 1992;20(1):31–6.
Eva V, Lars A, Evy F, Christer H. Disability pensions due to musculo-skeletal disorders among men in heavy occupations. A case-control study. Scand J Soc Med. 1992;20(1):31–6.
Tuomi K, Luostarinen T, Ilmarinen J, Klockars M. Work load and individual factors affecting work disability among aging municipal employees. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1991;17 Suppl 1:94–8.
Hasle H, Jeune B. The significance of working conditions with regard to disability pensions. A case-controlled study among unskilled workers. Ugeskr Laeger. 1989;151(30):1929–31.
Sonnenberg A, Sonnenberg GS. Occupational factors in disability pensions for gastric and duodenal ulcer. J Occup Med. 1986;28(2):87–90.
Gluszczowa M. Causes of early retirement of workers chronically exposed to carbon disulfide. Med Pr. 1983;34(2):183–9.
Yelin E, Meenan R, Nevitt M, Epstein W. Work disability in rheumatoid arthritis: effects of disease, social, and work factors. Ann Intern Med. 1980;93(4):551–6.
Turner JA, Franklin G, Fulton-Kehoe D, Sheppard L, Stover B, Wu R, Gluck JV, Wickizer TM. ISSLS prize winner: early predictors of chronic work disability: a prospective, population-based study of workers with back injuries. Spine. 2008;33(25):2809–18.
Szubert Z, Sobala W. Some job factors associated with departure from working life before retirement age. Med Pr. 2006;57(4):325–34.
Soucy I, Truchon M, Cote D. Work-related factors contributing to chronic disability in low back pain. Work. 2006;26(3):313–26.
Lacaille D, Sheps S, Spinelli JJ, Chalmers A, Esdaile JM. Identification of modifiable work-related factors that influence the risk of work disability in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2004;51(5):843–52.
Partridge AJ, Karlson EW, Daltroy LH, Lew RA, Wright EA, Fossel AH, Straaton KV, Stern SH, Kavanaugh AF, Roberts WN, et al. Risk factors for early work disability in systemic lupus erythematosus: Results from a multicenter study. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40(12):2199–206.
Mark DB, Lai Choi L, Lee KL, Clapp-Channing NE, Williams RB, Pryor DB, Califf RM, Hlatky MA. Identification of patients with coronary disease at high risk for loss of employment: A prospective validation study. Circulation. 1992;86(5):1485–94.
Feuerstein M, Thebarge RW. Perceptions of disability and occupational stress as discriminators of work disability in patients with chronic pain. J Occup Rehabil. 1991;1(3):185–95.
Yelin EH, Henke CJ, Epstein WV. Work disability among persons with musculoskeletal conditions. Arthritis Rheum. 1986;29(11):1322–33.
Saastamoinen P, Laaksonen M, Kaaria S-M, Lallukka T, Leino-Arjas P, Rahkonen O, Lahelma E. Pain and disability retirement: A prospective cohort study. Pain. 2012;153(3):526–31.
Sole M, Rodriguez M. Disparities in the effect of working conditions on health between immigrant and native-born populations in Spain. Gac Sanit. 2010;24(2):145–50.
Dyreborg J, Hannerz H, Tuchsen F, Spangenberg S. Disability retirement among workers involved in large construction projects. Am J Ind Med. 2010;53(6):596–600.
Szubert Z, Sobala W. Current determinants of early retirement among blue collar workers in Poland. Int J Occup Med Environ Health. 2005;18(2):177–84.
Krokstad S, Johnsen R, Westin S. Medical and non-medical determinants for disability pension. [Norwegian] Medisinske og ikke-medisinske risikofaktorer for uforepensjon. Tidsskrift for Den Norske Laegeforening. 2002;122(15):1479–85.
David H, Bigaouette M. Disability and retirement patterns among blue-collar workers of a large municipality. [French] Inaptitude Au Travail Et Prises De Retraite Chez Les Ouvriers D'une Grande Municipalite. Travail Humain. 1989;52(2):131–46.
Palmore EB, George LK, Fillenbaum GG. Predictors of retirement. J Gerontol. 1982;37(6):733–42.
Nilsen SM, Ernstsen L, Krokstad S, Westin S. Educational inequalities in disability pensioning - the impact of illness and occupational, psychosocial, and behavioural factors: The Nord-Trondelag Health Study (HUNT). Scand J Public Health. 2012;40(2):133–41.
Saastamoinen P, Kaaria SM, Laaksonen M, Lallukka T, Leino-Arjas P, Rahkonen O, Lahelma E. Pain and disability retirement: A follow-up study. Eur J Pain Suppl. 2011;5(1):76–7.
Salaffi F, Ferraccioli G, Carotti M, Ciapetti A, Gasparini S, Grassi W. Work disability in early rheumatoid arthritis: Prognostic factors after two years of follow-up. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:1787.
Allaire S, Wolfe F, Jingbo NIU, Lavalley MP, Zhang BIN, Reisine S. Current risk factors for work disability associated with rheumatoid arthritis: Recent data from a US national cohort. Arthritis Care Res. 2009;61(3):321–8.
Enthoven P, Skargren E, Carstensen J, Oberg B. Predictive factors for 1-year and 5-year outcome for disability in a working population of patients with low back pain treated in primary care. Pain. 2006;122(1-2):137–44.
Hannerz H, Spangenberg S, Tuchsen F, Albertsen K. Disability retirement among former employees at the construction of the Great Belt Link. Public Health. 2005;119(4):301–4.
Wolfe F, Hawley DJ. The longterm outcomes of rheumatoid arthritis: Work disability: a prospective 18 year study of 823 patients. J Rheumatol. 1998;25(11):2108–17.
Bjerkedal T, Wergeland E. Disability pensions because of musculoskeletal diseases among women of different occupations. Tidsskrift for Den Norske Laegeforening. 1995;115(28):3522–7.
Tuomi K, Toikkanen J, Eskelinen L, Backman A-L, et al. Mortality, disability and changes in occupations among aging municipal employees. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1991;17 Suppl 1:58–66.
Reisine ST, Grady KE, Goodenow C, Fifield J. Work disability among women with rheumatoid arthritis. The relative importance of disease, social, work, and family factors. Arthritis Rheumatol. 1989;32(5):538–43.
Hayward MD, Grady WR, Hardy MA, Sommers D. Occupational influences on retirement, disability, and death. Demography. 1989;26(3):393–409.
Greenwald HP, Dirks SJ, Borgatta EF, McCorkle R, Nevitt MC, Yelin EH. Work disability among cancer patients. Soc Sci Med. 1989;29(11):1253–9.
Bergstrom G, Hagberg J, Busch H, Jensen I, Bjorklund C. Prediction of sickness absenteeism, disability pension and sickness presenteeism among employees with back pain. J Occup Rehabil. 2014;24(2):278–86.
Laaksonen M, Gould R. Regional differences in disability retirement: explaining between-county differences in Finland. Scand J Work Environ Health. 2013;39(6):609–17.
Landsbergis PA, Janevic T, Rothenberg L, Adamu MT, Johnson S, Mirer FE. Disability rates for cardiovascular and psychological disorders among autoworkers by job category, facility type, and facility overtime hours. Am J Ind Med. 2013;56(7):755–64.
Reinhardt JD, Wahrendorf M, Siegrist J. Socioeconomic position, psychosocial work environment and disability in an ageing workforce: a longitudinal analysis of SHARE data from 11 European countries. Occup Environ Med. 2013;70(3):156–63.
Lodahl TM, Kejner M. The Definition and Measurement of Job Involvement. J Appl Psychol. 1965;49:24–33.
Christensen JO, Knardahl S. Work and headache: A prospective study of psychological, social, and mechanical predictors of headache severity. Pain. 2012.
Joensuu M, Kivimäki M, Koskinen A, Kouvonen A, Pulkki-Råback L, Vahtera J, Virtanen M, Väänänen A. Differential associations of job control components with mortality: a cohort study, 1986–2005. Am J Epidemiol. 2012;175(7):609–19.
State Compensation Insurance Fund. http://www.statefundca.com/employees/TD.asp. Accessed Dec 15 2014.
Nordic Social Insurance Portal. http://www.nordsoc.org/en/. Accessed 15 Dec 2014.
The Academic Network of European Disability experts (ANED). http://www.disability-europe.net/. Accessed 15 Dec 2014.
Nidirect Government Services. http://www.nidirect.gov.uk/index/information-and-services/money-tax-and-benefits/benefits-and-financial-support/disability-1.htm. Accessed 15 Dec 2014.
Furr M. Scale construction and psychometrics for social and personality psychology: SAGE Publications Ltd; 2011. ISBN1446244903, 9781446244906.
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, Moher D, Becker BJ, Sipe TA, Thacker SB. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology. JAMA. 2000;283(15):2008–12.
Dragano N, Schneider L. (Work related psychosocial factors and the risk of early disability pensioning: a contribution to assessing the need for rehabilitation). Psychosoziale Arbeitsbelastungen als Prädiktoren der krankheitsbedingten Frühberentung: Ein Beitrag zur Beurteilung des Rehabilitationsbedarfs. Rehabilitation. 2011;50(1):28–36.
Acknowledgement
The authors thank Line Arneberg for advice on literature search strategies and Jani Ruotsalainen, Finnish Institute of Occupational Health, Helsinki, Finland, for valuable discussions.
Funding
The present systematic review was supported by the Nordic Council of Ministers grant # 11119. Salaries for the authors were contributed by their respective institutions.
Availability of data and materials
Criteria for inclusion and exclusion of studies are presented in the manuscript.
The search strategy (which when applied results in the initial dataset of articles) is available in Additional file 1.
The processes of including and excluding articles according to criteria (defined in the introduction and methods section of the manuscript) and the numbers of articles excluded for the various criteria are depicted in Fig. 1 Flow chart for selection of studies.
References for all primary articles of potential relevance are included in the manuscript.
All primary articles evaluated are presented in Table 1 of the manuscript (primary articles of adequate quality) and Additional file 1 Table C (studies that did not meet our quality criteria).
The check list for the evaluation of quality is presented in Additional file 1 Table B.
Check-list scores for individual articles are presented in Additional file 1 Tables D and E.
Authors’ contributions
SK took the initiative to the study, developed the first draft of the quality check list, and coordinated the study. HAJ handled primary study articles, made the tables, and conducted the meta-analyses. SK, HAJ, TS, MH, RR, JS, VB contributed in the processes of defining criteria for inclusion and exclusion of studies, reviewing and assessing the primary studies, discussing findings, drawing conclusions, as well as the completion of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
All primary articles incorporated in the present systematic review reported adequate -consent procedures.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable (all primary articles incorporated in the present systematic review reported adequate ethics approval procedures).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional file
Additional file 1:
Table A: Search strategy; Table B: Quality assessment check list; Table C: Excluded studies - characteristics and findings; Table D: Scores of internal validity for accepted studies; Table E: Scores of internal validity for studies that were excluded by quality criteria. (DOCX 97 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Knardahl, S., Johannessen, H.A., Sterud, T. et al. The contribution from psychological, social, and organizational work factors to risk of disability retirement: a systematic review with meta-analyses. BMC Public Health 17, 176 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-017-4059-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-017-4059-4