Abstract
Background
Depression is an important public health problem and is closely associated with suicidal behavior in the population. Although the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) is widely used for assessment of depression, the psychometric characteristics of this scale have not been explored in studies of suicide attempters and local residents in rural areas.
Methods
In this study, reliability and validity of CES-D were assessed in 409 suicide attempters and 409 comparison residents from rural China and through internal consistency analysis and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA).
Results
Cronbach’s alpha values of the CES-D were 0.940 and 0.895 in, respectively, suicide attempters and comparison residents. CES-D scores were significantly correlated with the scores of Trait Anxiety Inventory (TAI) and Beck Hopelessness Scale (BHS) in both the suicide attempters and the comparison residents. Confirmatory factor analyses indicated that 3-factor structure (positive affect, interpersonal problems, depressive mood and somatic symptoms combined) with 14 items (excluding items 9, 10, 13, 15, 17, and 19) had the best fit in these two populations.
Conclusions
The CES-D scale has satisfactory reliability and validity when used for assessing depression in suicide attempters and comparison residents in rural China.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Depression is an important public health problem and confers one of the most important risk factors for suicidal behavior in the general population regardless of sex and age groups [1,2]. Serious bouts of depression in individuals with a history of suicidal behavior could influence their capacity for normal life in the future [3,4]. Therefore, accurate diagnosis of depression in patients who attempted suicide is crucial for clinical treatment and for follow-up care of the patients [5,6]. The accuracy of depression assessment, however, highly relies on the validity of the tools that can be used for the assessment.
The Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D), a self-report questionnaire, was developed to screen for depression, to assess depressive symptoms and to detect risks of having depressive disorder of a person [7]. The CES-D has shown to have generally good reliability and validity for depression assessment in various populations [8-10]. For instance, the CES-D was a useful tool in identifying clinical depression in Chinese American women and exhibited good construct validity and satisfactory internal consistency, albeit a cultural response bias was also detectable [11]. In spite of the popularity of the CES-D, there are areas of concern in terms of its factor structure and detail items [12-15]. Comparing with the original model, which is a four-factor model (depressed, somatic, interpersonal, and positive) and comprises 20 items [7], there have been various recommendations in studies validating this scale in specific populations. In a study of Chinese adolescents, the CES-D gave consistent results across the genders on the assessment of specific depressive symptom manifestations (i.e., depressed affect, positive affect, and somatic complaints) [13]. A few other studies from China have demonstrated that the four-factor model (depressed, somatic, interpersonal, and positive) fitted very well [14,15].
When applying the CES-D for research, it is important to examine whether the scale is reliable and valid for the study population, because, as indicated in the CES-D instruction, different ethnic and socio-demographic groups may have different factor structures [16]. Table 1 lists the original model and the factor models recommended in the recent literature. There have been obvious variations in the most suitable factor model when applying the CES-D in various populations. Aside from the original four-factor model, two-factor and three-factor models have also been recommended for specific groups of populations. In this study, we want to evaluate the psychometric characteristics of the CES-D in two sample populations comprising 409 suicide attempters and 409 paired comparison residents from rural China. We also want to examine which of the CES-D structure models recommended in the literature is most applicable to our study populations.
Method
Study population
Six disease surveillance counties in Shandong Province (i.e., Jyu’nan, Lijin, Ningyang, Penglai, Tengzhou, and Zoucheng) were selected as study sites for data collection. Consecutive cases of rural residents aged 15–70 years old who attempted to kill themselves and therefore were sent for emergent treatment at one central general hospital of these Counties during the period from October 1, 2009 to March 31, 2011, were recruited as the cases of this study. The CDC (Centers for Disease Prevention and Control) of each County, as a routine, collected new incident cases from the hospital on a daily basis and provided us the information of the suicide attempters. In total, 1070 suicide attempters were reported during the study period. Of these individuals, 248 provided a made-up name or imprecise living address at the time of hospital treatment for suicide attempt, 369 were not at home during the follow-up surveys, and 44 refused to participate in the study. Therefore, 409 suicide attempters were finally included in this study, corresponding to a participation rate of 38.2%. There were no significant differences in the age (t = 1.088, P = 0.277) or gender (χ2 = 0.060, P = 0.807) of the interviewed cases versus those not interviewed.
In order to facilitate a comparison, 409 comparison residents were recruited into the study, on the basis that these individuals had no history of suicide attempts, and were 1:1 matched to the suicide attempters on gender, age (within 3 years) and village of residence.
Procedure of data collection
The staff members of local CDCs were responsible for collecting information on suicide attempters treated in hospitals at the county level. Following the reported information from the CDC, interviews to the study cases were arranged with the help of the local CDC. The interviews were generally held one month after the attempted suicide in order to prevent undermining of the emotional stability of suicide attempters. Village doctors assisted the trained interviewers to find the homes of suicide attempters and comparison residents. Written informant consent was obtained from each subject prior to the interview. The interviews were undertaken face-to-face and tape-recorded upon the consent of the participants at the participants’ homes or the village clinics and without a third person present. Each interview lasted approximately 1.5 hours in duration.
Instruments
Besides personal socio-demographic information such as gender, age, education level, marital status, occupation, and religious status, the following instruments were used for the data collection.
The CES-D comprises 20 items, and employs four-point Likert scales, ranging from “rarely or none of the time” (0 point) to “most or all of the times” (3 points). The total score ranges from 0 to 60, in which a higher score indicates more severe depressive symptoms [7]. Generally, a total CES-D score of 16 or greater can be considered indicative of depression [17]. But the validity and psychometric properties of several items (e.g., Items 7, 15,17, 19 ) on the CES-D have been questioned by the researchers [18].
The Trait Anxiety Inventory (TAI) of the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) (Spielberger, 1983) consists of 20 statements and is usually used to evaluate respondents’ general tendency to perceive situations as threatening [19]. The total score on the TAI ranges from 20 to 80 [20]. In the present study, the Cronbach’s alpha values for the TAI in suicide attempters and comparison residents were 0.903 and 0.852, respectively.
The Beck Hopelessness Scale (BHS) [21,22] is a 20-item tool designed to measure three major aspects of hopelessness: feelings about the future, loss of motivation, and expectations. The BHS is a 5-point Likert scale, with answers from 1 (complete match) to 5 (in complete opposition), and a total score between 20 and 100. The Cronbach’s alpha values for the BHS were 0.954 and 0.883, respectively, for suicide attempters and comparison residents in this study.
Data analysis
Data were analyzed via SPSS 16.0 (IBM SPSS, Inc. in Chicago, Illinois, USA) and Student version of LISREL 8.7 (Scientific Software International, Inc., Lincolnwood, IL, USA). A multivariate conditional logistic regression analysis was used to evaluate association between depression and attempted suicide. Reliability was assessed via assessment of internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha). The scores of TAI and BHS were included in the analysis in order to evaluate the criterion validity of the CES-D via calculation of their correlation coefficients. Factor structures of the CES-D in the two study populations were examined through confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). Each model was evaluated by the following indices for fitness: 1) chi-square (values should not be significant); 2) chi-square/df ratio (values should be less than 5.0); 3) Comparative Fit Index (CFI) must be greater than 0.90; 4) the Standardized Root Mean Square Residual (SRMR) must be less than 0.10;5) Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) must be less than 0.08 with 90% confidence interval values below 0.10; and 6) lower values of Expected Cross-Validation Index (ECVI) indicate a closer fit across different models [18].
Ethics statement
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Shandong University School of Public Health. All subjects signed the informed consent form. For subjects under 18 years of age, their parents also signed on the informed consent form.
Results
Demographic characteristics of the study samples
The population of 409 suicide attempters comprised 132 (32.3%) males and 277 (67.7%) females. The male to female ratio was 1:1.72. Because of the use of a paired case–control design, suicide attempters and comparison residents had virtually the same age and gender distribution.
As illustrated in Table 2, there were no significant differences in marital and religious status between the two study populations. However, suicide attempters were more often to be peasants and had a relatively lower level of education and higher scores of the CES-D as compared with the comparison residents (Ps < 0.001). Therefore, the suicide attempters and the comparison residents could be regarded as different groups and should not be integrated into one sample when assessing the psychometric characteristics of the CES-D.
Multivariate conditional logistic regression analysis was performed to assess the relative influence of the variables in the panel on risk for attempted suicide (Table 2). Depression was significantly associated with attempted suicide with an odds ratio (OR) of 33.140 (95% CI: 15.212-72.198) after the adjustment of the effects of other factors.
Comparing scores of men and women by t-tests indicated that there were not statistically significant differences by gender (P > 0.05) on most CES-D items except on CES-D items (17,19) in suicide attempters and CES-D items (4, 5, 10, 17, 18, 20) in comparison residents. Meanwhile, the sizes of gender effect were negligible (r2 < 0.01) for all items in both study populations.
Internal consistency
Internal consistency was of an acceptable level for suicide attempters and comparison residents, with Cronbach’s coefficient alphas of 0.940 and 0.895, respectively, for the two populations. As depicted in Table 3, the item-correlation coefficient values were also significant (Ps < 0.01). Pearson coefficient values produced from an item-if-deleted analysis ranged from 0.298 to 0.839, and 0.259 to 0.728, respectively, for suicide attempters and comparison residents.
Criterion validity
Mean values of CES-D, BHS, and TAI scores were, respectively, 23.59 (SD = 1.69), 57.49 (SD = 2.07), and 38.59 (SD = 1.03) for suicide attempters, and respectively, 3.04 (SD = 0.63), 32.46 (SD = 0.99), and 30.47 (SD = 0.69) for the comparison residents.
CES-D scores were significantly correlated with BHS scores in both suicide attempters (r = 0.72) and comparison residents (r = 0.44) (Ps < 0.001). Similarly, CES-D scores were also significantly correlated with TAI scores in suicide attempters (r = 0.46) and comparison residents (r = 0.58) (Ps < 0.001).
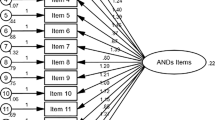
Factor structure of the CES-D
The original model and 5 currently recommended models were assessed in the sample populations of suicide attempters and comparison residents using the confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). Detailed results are listed in Table 4. The results showed that the ECVI of both groups were lowest in the 3-factor model comprising 14-item derived by Carleton and his colleagues [18]. This means that this model has the best fit for the factorial structure in the two study populations. In suicide attempters, χ2/df was less than 5. The RMSEA was less than 0.10. The CFI was over 0.90, and the SRMR was less than 0.05. In the sample of comparison residents, χ2/df was close to 5. The RMSEA was close to 0.10. The CFI was over 0.90, and the SRMR was close to 0.05.
Discussion
This study sought to assess the reliability and validity of the CES-D in the assessment of depression in Chinese rural suicide attempters and community comparison residents. The findings indicate that the CES-D has satisfactory reliability in depression assessment situated within the Chinese culture and that the three-factor model with 14 items of the CES-D [18] has an acceptable goodness of fit in the two sample populations of suicide attempters and comparison residents in rural China. Such results were consistent with previous validation of this scale in the populations of suicide completers and comparison residents from rural China [8,17].
The CES-D has exhibited a satisfactory reliability in a number of studies of the general population, with a high Cronbach’s alpha value, for instance, in Armenian (0.89 for women and 0.83 for men), Dutch (0.93), and English and the Spanish people (0.91 and 0.92 respectively) [23-25]. The CES-D has also showed a satisfactory reliability in specific groups of populations. For example, a Canadian study reported a Cronbach’s alpha of 0.88 for the overall CES-D in patients with systemic sclerosis [26]. The Cronbach’s alpha was also high (0.84) in a sample of Dutch elderly [27]. In this study, the Cronbach’s alpha was above 0.80 for both suicide attempters and comparison residents, indicating a good internal consistency and a high reliability of the CES-D when used in these populations.
The present study shows that CES-D scores were significantly higher in suicide attempters than that in comparison residents, and that depression was significantly associated with attempted suicide. These results are highly in line with the literature that depression is an important risk factor for suicidal behavior [28,29]. Such findings underscore the need and importance of depression assessment in suicide prevention practices.
In this study, the TAI and BHS were used to evaluate the criterion validity of the CES-D. The TAI is designed to assess trait anxiety personality, which embodies stable individual differences in tendency toward anxiety and general proneness to respond with anxiety to perceived threats in the environment [19]. This inventory has adequate psychometrics for measuring trait anxiety in suicide victims and living controls in rural China [30]. Although anxiety is not a necessary syndrome of pre-suicide, more than 70% of suicide attempters have an anxiety disorder [31] and the disorder shares some clinical characteristics with depression and confers an important risk factor for suicide attempt and completion [32]. On the basis of the cognitive theory of depression, hopelessness increases the risk of depression, because it gives rise to negative feelings including worthlessness, loss, and expected failure in response to a stressor [33]. Previous studies have shown that, the BHS has a high degree of internal consistency and validity in the context of Chinese culture [34-36] and that hopelessness is strongly related to suicide attempt [11,37]. In this study, the CES-D scores were significantly and positively correlated with the scores of both TAI and BHS, which indicate that the CES-D has good criterion validity in the two study populations.
In utilization of the CES-D theory-driven confirmatory analyses may benefit more than do exploratory analyses. The present study is the first one that used the same study populations to examine the fit indices of the CES-D factor structure of the original model and the models recommended in previous studies. The factor structure proposed by Carleton et al. [18] produced the best fit indices in our study populations and was consistent with current DSM IV-TR conceptualization of depression. This factor structure eliminates the items of 9, 10, 13, 15, 17, and 19, and includes 3 structural factors of negative affect (items 3, 6, 14, 18), anhedonia (items 4, 8, 12, 16), and somatic complaints (items 1, 2, 5, 7, 11, 20).
It is not easy to explain why the three-factor model with 14 items proposed by Carleton et al. [18] shows the best fit in our study populations. Several studies have questioned the validity and psychometric properties of the scale items of 15, 17 and 19 [18] as well as the items of 9, 10 and 13 [7]. It is also possible that variations of socio-demographic characteristics of study populations as well as culture differences contribute to the observed differences of results from the present study to other studies in the literature. For instance, in stroke patients in Korea [38], the 5-factor structure was supported (loss of vitality, positive affect, psychomotor retardation, negative affect, and interpersonal problems) and could explain 61.25% of the variance. In a Hong Kong study of Chinese married couples [39], only two factors were derived (depressive symptom factor and interpersonal problem factor). In contrast to the depressed English-speaking smokers, a different pattern of three factors has emerged in the depressed Spanish -speaking smokers [25]. Zhang et al. proposed a three-factor model with 20 items in the samples of suicide informants and controls in rural China [8]. In Chinese adolescents, 3 factors explaining 48.58% of the total variance were produced to cover “depressed affect”, “somatic complaints”, and “positive affect” [32]. The slight difference of depression structure in suicide attempters from the structure in the comparison residents might to some extent be induced by differences in education level, occupation and scores of CES-D between the two populations. Further studies with larger samples are certainly needed for confirmation of the observations from the present study.
Some shortcomings of this study should be noted. The bias of most concern in this study is the recall bias because the data were collected through interview. The use of the TAI and the BHS to assess the criterion validity of the CES-D may not be as ideal as the use of, for instance, the HAMD [40], and Zung Self-Rating Depression Scale [41]. Other limitations include not using diagnostic interview, the absence of behavioral correlates, and an absent experimental design, relative small populations of study, etc.
Conclusions
The current study provides preliminary evidence on the reliability and validity of the CES-D in suicide attempters and comparison residents from rural China. It is the first study examining the fit indices of all suggested factor structure models of this scale in the two study populations simultaneously. The results indicate that the CES-D has satisfactory reliability and validity for the assessment of depression or depressive symptoms in suicide attempters and comparison residents in rural areas of China.
References
Li Y, Cao J. Factors associated with suicidal behaviors in mainland China: a meta-analysis. BMC Public Health. 2012;12:524.
Yi S, Yi Y, Jung HS. Factors on the suicidal attempt by gender of middle and high school student. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2011;41(5):652–62.
Vishnuvardhan G, Saddichha S. Psychiatric comorbidity and gender differences among suicide attempters in Bangalore, India. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2012;34(4):410–4.
Elisei S, Verdolini N, Anastasi S. Suicidal attempts among Emergency Department patients: one-year of clinical experience. Psychiatr Danub. 2012;24 Suppl 1:S140–2.
Cuijpers P, Beekman AT, Reynolds III CF. Preventing depression a global priority. JAMA. 2012;307(10):1033–4.
Runeson B, Tidemalm D, Dahlin M, Lichtenstein P, Långström N. Method of attempted suicide as predictor of subsequent successful suicide: national long term cohort study. BMJ. 2010;341. doi: 10.1136/bmj.c3222.
Radloff LS. The CES-D scale a self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Appl Psychol Meas. 1977;1(3):385–401.
Zhang J, Sun W, Kong Y, Wang C. Reliability and validity of the Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale in 2 special adult samples from rural China. Compr Psychiatry. 2012;53(8):1243–51.
Morin AJ, Moullec G, Maiano C, Layet L, Just JL, Ninot G. Psychometric properties of the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) in French clinical and nonclinical adults. Rev Epidemiol Sante Publique. 2011;59(5):327–40.
Chen Y-Y, Wu KC-C, Yousuf S, Yip PS. Suicide in Asia: opportunities and challenges. Epidemiol Rev. 2012;34(1):129–44.
Troister T, Holden RR. Comparing psychache, depression, and hopelessness in their associations with suicidality: a test of Shneidman’s theory of suicide. Pers Individ Differ. 2010;49(7):689–93.
Zhang B, Fokkema M, Cuijpers P, Li J, Smits N, Beekman A. Measurement invariance of the center for epidemiological studies depression scale (CES-D) among chinese and dutch elderly. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2011;11(1):74.
Wang M, Armour C, Wu Y, Ren F, Zhu X, Yao S. Factor structure of the CES-D and measurement invariance across gender in Mainland Chinese adolescents. J Clin Psychol. 2013;69(9):966–79.
Cheng CP, Yen CF, Ko CH, Yen JY. Factor structure of the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale in Taiwanese adolescents. Compr Psychiatry. 2012;53(3):299–307.
Li HC, Chung OK, Ho KY. Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale for Children: psychometric testing of the Chinese version. J Adv Nurs. 2010;66(11):2582–91.
Coman EN, Iordache E, Schensul JJ, Coiculescu I. Comparisons of CES-D depression scoring methods in two older adults ethnic groups. The emergence of an ethnic-specific brief three-item CES-D scale. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2013;28(4):424–32.
Han M, Jia CX. Reliability and validity of Center for Epidemiological Survey, Depression Scale in different rural populations. Chin J Public Health. 2012;28(10):1265–7.
Carleton RN, Thibodeau MA, Teale MJ, Welch PG, Abrams MP, Robinson T, et al. The Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale: a review with a theoretical and empirical examination of item content and factor structure. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58067.
Speilberger CD, Gorsuch R, Lushene R, Vagg P, Jacobs G. Manual for the state-trait anxiety inventory. Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologists; 1983.
Shek DTL. The Chinese version of the state-trait anxiety inventory: its relationship to different measures of psychological well-being. J Clin Psychol. 2006;49(3):349–58.
Beck A, Steer R. Beck hopelessness scale. San Antonio: The Psychological Corporation; 1988.
Beck AT, Weissman A, Lester D, Trexler L. The measurement of pessimism: the hopelessness scale. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1974;42(6):861.
Demirchyan A, Petrosyan V, Thompson M. Psychometric value of the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression (CES-D) scale for screening of depressive symptoms in Armenian population. J Affect Disord. 2011;133(3):489–98.
Cuijpers P, Boluijt P, van Straten A. Screening of depression in adolescents through the Internet. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2008;17(1):32–8.
Leykin Y, Torres LD, Aguilera A, Muñoz RF. Factor structure of the CES-D in a sample of Spanish-and English-speaking smokers on the Internet. Psychiatry Res. 2011;185(1):269–74.
Thombs BD, Hudson M, Schieir O, Taillefer SS, Baron M. Reliability and validity of the center for epidemiologic studies depression scale in patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59(3):438–43.
van de Rest O, van der Zwaluw N, Beekman AT, de Groot LC, Geleijnse JM. The reliability of three depression rating scales in a general population of Dutch older persons. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2010;25(10):998–1005.
Silver MA, Bohnert M, Beck AT, Marcus D. Relation of depression of attempted suicide and seriousness of intent. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1971;25(6):573.
Hawton K, Casanas ICC, Haw C, Saunders K. Risk factors for suicide in individuals with depression: a systematic review. J Affect Disord. 2013;147(1–3):17–28.
Zhang J, Gao Q. Validation of the trait anxiety scale for state-trait anxiety inventory in suicide victims and living controls of Chinese Rural Youths. Arch Suicide Res. 2012;16(1):85–94.
Nepon J, Belik SL, Bolton J, Sareen J. The relationship between anxiety disorders and suicide attempts: findings from the National Epidemiologic Survey on alcohol and related conditions. Depress Anxiety. 2010;27(9):791–8.
Kanwar A, Malik S, Prokop LJ, Sim LA, Feldstein D, Wang Z, et al. The association between anxiety disorders and suicidal behaviors: a systematic review and meta analysis. Depress Anxiety. 2013;30(10):917–29.
Beck AT. Cognitive therapy of depression. New York: Guilford Press; 1979.
Qian W, Liu B, Huang Y, Ba T, Wang P. Reliability and validity of Beck Hopelessness Scale and its application among medical students. Chin J School Health. 2008;29:612–4.
Kao YC, Liu YP, Lu CW. Beck hopelessness scale: exploring its dimensionality in patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatr Q. 2012:1-15. doi:10.1007/s11126-011-9196-9.
Liu Hui JC-X, Xu A-Q, Qiu H-M, Lu C-F, Wang L-l. Reliability and validity of the Beck Hopelessness Scale in rural suicide study. Chin Mental Health J. 2011;25(11):867–71.
David Klonsky E, Kotov R, Bakst S, Rabinowitz J, Bromet EJ. Hopelessness as a predictor of attempted suicide among first admission patients with psychosis: a 10-year cohort study. Suicide Life Threat Behav. 2012;42(1):1–10.
Kim JH, Park EY. The factor structure of the center for epidemiologic studies depression scale in stroke patients. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2012;19(1):54–62.
Cheung CK, Bagley C. Validating an American scale in Hong Kong: the Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale (CES-D). J Psychol. 1998;132(2):169–86.
Bech P, Allerup P, Gram L, Reisby N, Rosenberg R, Jacobsen O, et al. The Hamilton depression scale. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1981;63(3):290–9.
Zung WW, Richards CB, Short MJ. Self-rating depression scale in an outpatient clinic: further validation of the SDS. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1965;13(6):508.
Shafer AB. Meta-analysis of the factor structures of four depression questionnaires: Beck, CES-D, Hamilton, and Zung. J Clin Psychol. 2006;62(1):123–46.
Williams CD, Taylor TR, Makambi K, Harrell J, Palmer JR, Rosenberg L, et al. CES-D four-factor structure is confirmed, but not invariant, in a large cohort of African American women. Psychiatry Res. 2007;150(2):173–80.
Kohout FJ, Berkman LF, Evans DA, Cornoni-Huntley J. Two shorter forms of the CES-D depression symptoms index. J Aging Health. 1993;5(2):179–93.
Carpenter JS, Andrykowski MA, Wilson J, Hall LA, Rayens MK, Sachs B, et al. Psychometrics for two short forms of the Center for Epidemiologic Studies-Depression Scale. Issues Ment Health Nurs. 1998;19(5):481–94.
Irwin M, Artin KH, Oxman MN. Screening for depression in the older adult: criterion validity of the 10-item Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale (CES-D). Arch Intern Med. 1999;159(15):1701–4.
Schroevers MJ, Sanderman R, Van Sonderen E, Ranchor AV. The evaluation of the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression (CES-D) scale: Depressed and Positive Affect in cancer patients and healthy reference subjects. Qual Life Res. 2000;9(9):1015–29.
Rivera-Medina CL, Caraballo JN, Rodríguez-Cordero ER, Bernal G, Dávila-Marrero E. Factor structure of the CES-D and measurement invariance across gender for low-income Puerto Ricans in a probability sample. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2010;78(3):398.
Bush BA, Novack TA, Schneider JJ, Madan A. Depression following traumatic brain injury: the validity of the CES-D as a brief screening device. J Clin Psychol Med Settings. 2004;11(3):195–201.
Ying YW. Depressive symptomatology among Chinese-Americans as measured by the CESD. J Clin Psychol. 1988;44(5):739–46.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) [30972527], the Fundamental Research Funds of Shandong University [2014JC043], and the Distinguished Scholar Cultivating Program Fund from Shandong University School of Public Health [JC201301]. The authors would like to thank all persons who contributed to the data collection. The authors also want to acknowledge the valuable support from the CDC of Shandong Province and the CDCs of Jyu’nan, Lijin, Ningyang, Penglai, Tengzhou, and Zoucheng Counties.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
YL contributed to study design, data collection, statistical analysis and manuscript preparation. JCX contributed to study design, data collection, statistical analysis, result interpretation and revision of the manuscript. QP contributed to the discussions on study design and data analysis and made critical revision of the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Jia, CX. & Qin, P. Reliability and validity of the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) among suicide attempters and comparison residents in rural China. BMC Psychiatry 15, 76 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-015-0458-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-015-0458-1