Abstract
Background
Recent large trials have shown the survival benefits of 10-year use of tamoxifen by reducing late recurrence compared with 5-year therapy in estrogen receptor(ER)-positive breast cancer. We tried to identify clinical factors associated with the late recurrence.
Methods
We reviewed our database of ER-positive patients who had received operations between 1996 and 2006 in two institutions. We selected 444 who had completed 5-year tamoxifen and were disease-free up to 10 years after the operation. Patients who had received aromatase inhibitors with any regimens were excluded. As a late recurrence group, 139 patients were identified who had completed 5-year tamoxifen, but had recurrence afterwards. Among them, 61 had local/contralateral breast recurrence and 78 had distant metastasis. The median follow-up was 9.7 years. Clinicopathological factors at the time of initial operation, such as age, menopausal status, progesterone receptor expression, HER2 status, tumor grade and Ki-67, were compared between the disease-free group and the late recurrence group.
Results
In a univariate analysis, tumor size (>2 cm), lymph node metastasis and high histologic grade were significantly associated with late recurrences (p < 0.05). In a multivariate analysis, only axillary lymph node metastasis was significant (p < 0.001). Late distant metastasis was significantly associated with tumor size and axillary lymph node metastasis (p = 0.038, p < 0.001,respectively). Late local/contralateral breast recurrence was associated with axillary lymph node metastasis (p = 0.042).
Conclusions
Our data showed axillary lymph node metastasis at initial operation was the only risk factor of late recurrence after completion of tamoxifen for 5 years. Our results can be helpful in making decisions to use extended tamoxifen beyond 5 years.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The treatment of breast cancer has developed remarkably in recent decades, especially in hormone receptor-positive subtype breast cancer [1–7]. Although adjuvant endocrine therapy was highly effective and could reduce recurrence and the mortality of hormone receptor-positive patients, the long-term follow-up data showed that there was a sustained hazard of recurrence even after the completion of 5 years of adjuvant endocrine therapy [2, 6, 8–10]. Therefore, strategies to reduce late recurrence in this subtype of breast cancer have been intensively studied [11–15].
For the past few decades, 5-year use of tamoxifen has been a standard adjuvant endocrine therapy with a large survival gain and minimal adverse effects [8, 16–19]. Studies have shown that tamoxifen therapy has a carryover effect, which results in the reduction in recurrence well after treatment has stopped [9, 17, 20]. Some earlier studies suggested that use of tamoxifen for more than 5 years has few benefits and increases side effects [17, 19, 21]. However, two recent large clinical trials, ATLAS (Adjuvant Tamoxifen: Longer Against Shorter) and aTTom (adjuvant Tamoxifen–To Offer More?) have shown that continuing tamoxifen therapy beyond 5 years reduces recurrence and death from breast cancer over the following years [22, 23]. Accordingly, the new ASCO guidelines recommend a adjuvant hormonal therapy of women who have hormone receptor–positive breast cancer for a duration of up to 10 years rather than 5 years [24]. The next challenge is to determine which patients will benefit from this long-term treatment, because its side effects, such as menopausal symptoms and the risk of endometrial cancer, are considerable [11, 21].
We analyzed the clinicopathological features at the time of surgery of patients who had late recurrence compared with those of patients who were long-term disease-free. We found predictive factors, which will help clinics to select patients who will benefit more from extended adjuvant tamoxifen use for more than 5 years.
Methods
Study subjects
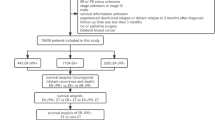
We reviewed the data of 3920 patients with estrogen receptor (ER)-positive primary invasive breast cancer who underwent curative surgery in both Seoul National University Hospital and National cancer center from January 1996 to September 2006. We identified 2154 patients who were disease-free when they had finished 5-year adjuvant tamoxifen therapy. Patients who had received aromatase inhibitors at any time during tamoxifen therapy were excluded. Additionally, patients who had received extended endocrine therapy with tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors for a total duration of more than 5 years were excluded. For the disease-free group, patients who were lost before 10 years of follow-up from the initial surgery were excluded. Late recurrence was defined as any locoregional (in the ipsilateral/contralateral breast, chest wall, or regional lymph nodes including micro-, macro-metastasis and isolated tumor cells in axilla) or distant relapse on the image study or pathologic confirmation occurring after the completion of 5-year adjuvant tamoxifen therapy. Finally, a total of 583 patients were enrolled in this study. A total of 444 were placed in the disease-free group, and 139 were placed in the late recurrence group (Fig. 1). This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Hospital (IRB number: 1409-155-616).
IHC staining and interpretation
This method was previously used in a published study [25]. The samples were immunostained with the following antibodies according to the manufacturers' instructions: Anti-ER (1:100; 1D5; Dako, Glostrup, Denmark), anti-progesterone receptor (PgR) (1:100; 636; Dako), and anti-HER2 (1:200; A0485; Dako). The IHC staining was scored and confirmed by two pathologists who were blinded to the clinical information. Positive ER and PgR expression were defined as nuclear staining in 10 % or more of tumor cells. The HER2 membranous staining was scored on a scale of 0 to 3+ according to the HercepTest protocol. For tissue samples with a HER2 staining score of 2+, additional HER2 FISH testing was performed. HER2 status was considered positive when the IHC score was 3+ or the gene copy ratio of HER2/CEP17 by FISH was 2.0 or higher.
Statistical analysis
Disease-free survival (DFS) was defined as the length of time after surgery for primary breast cancer to the earliest report of any locoregional or distant recurrence. Pearson’s chi-square test was used to analyze the association between clinicopathological factors and late recurrence. Logistic regression analysis was used for the multivariate analysis of significant variables in the univariate chi-square tests, such as age, menopausal status, tumor size (e.g., ≤2 cm or >2 cm), metastatic axillary lymph nodes (positive or negative), tumor grade (Nottingham Histologic Score 1, 2, or 3), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) status (positive or negative), progesterone receptor expression (positive or negative), and Ki67 level (high (≥10 % in SNUH, ≥14 % in NCC) or low (<10 % in SNUH, <14 % in NCC)) [26]. Kaplan–Meier plots were used to show the survival results and comparison between the groups. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS Version 19.0 software. All p values were two-sided, and p < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Table 1 summarizes the clinicopathologic characteristics of this study population. The mean age of patients was 45.5 years old. The mean follow-up period was 10.6 years in disease-free patients, and the mean disease-free time was 8.0 years (ranging from 5.1 to 14.3 years) in the late recurrence group. A total of 444 patients of 583 (76.2 %) had disease-free status by the end of the follow-up date, at least 10 years after diagnosis. A total of 139 patients (23.8 %) experienced local or distant recurrences after completion of adjuvant tamoxifen therapy for 5 years. Recurrences occurred between 5 to 10 years after the operation in 118 (84.9 %) women and after 10 years in 21(15.1 %) patients. A total of 61 patients experienced locoregional or contralateral breast recurrence, and 78 experienced distant metastasis (Table 2).
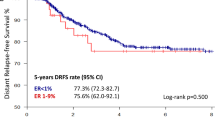
In the univariate analysis, large tumor size (>2 cm), positive axillary lymph node metastasis, and high histologic grade were significantly related to late recurrence (p = 0.002, p < 0.001, and p = 0.018, respectively). In the multivariate logistic regression analysis, only axillary lymph node metastasis at the time of initial operation was significantly associated with late recurrence compared with the disease-free group (p < 0.001) (Table 3). In the subgroup analysis, distant metastasis in the late recurrence group was significantly associated with axillary lymph node metastasis and large tumor size (p < 0.001, p = 0.038, respectively), and local recurrence or contralateral breast recurrence was associated with only axillary lymph node metastasis (p = 0.042) (Table 4). Figure 2 shows Kaplan–Meier curves for DFS according to lymph node status. Patients who were lymph node-positive at the time of initial operation had significantly worse survival rates after the completion of 5-year adjuvant tamoxifen therapy (log rank p-value <0.001).
Discussion
Although there have been great advances in the survival outcomes of patients with ER-positive breast cancer, many patients still experience late recurrence [1, 2]. The use of extended endocrine therapy for more than 5 years in order to reduce late recurrence is controversial [11, 27]. Due to the publication of positive results from large randomized trials that have shown the benefits of 10-year tamoxifen therapy, new ASCO guidelines recommend a total of 10 years of adjuvant hormonal therapy for all ER-positive patients [22, 24]. However, it is not clear whether all ER-positive breast cancer patients should be offered extended endocrine treatment. The important question is which patients would be at a higher risk of recurrence after 5 years of endocrine therapy and which would benefit from extended therapy.
We demonstrated an association between axillary lymph node metastasis at the time of initial operation and late recurrence in patients who completed 5-year tamoxifen therapy. This result can be helpful for clinics when considering the extended use of tamoxifen beyond 5 years. Doctors might be able to strongly recommend this therapy when the patient is lymph node-positive at the time of initial surgery. Several previous reports have shown similar results [12, 28, 29]. A meta-analysis conducted by Al-Mubarak et al. on extended adjuvant endocrine therapy for early breast cancer showed that the apparent benefits were observed only among patients with lymph node-positive disease, and the absolute risk reduction during 10 years of follow-up was almost doubled in lymph node-positive patients [30].
In this study, it is notable that tumor biological factors known as predictors of early recurrence, such as Ki67 or HER2, were not predictors of late recurrence. This suggests the necessity of developing a new biomarker with good prediction accuracy for late recurrence in ER-positive disease. Recently, multigene assays have shown promising results in the prediction of late recurrence [29, 31–34]. Sgroi et al. compared the prognostic efficacies of the breast-cancer index (BCI) assay, 21-gene recurrence score (Oncotype DX), and an immunohistochemical prognostic model (IHC4). As a result, BCI assay provided significant prognostic information for both early and late distant recurrence [31]. Another multigene-based assay, the EndoPredict test combined with nodal status and tumor size (EPclin), reliably identified a subgroup of patients who showed excellent long-term prognoses after 5 years of endocrine therapy [32]. In a recent large combined analysis of TranATAC and ABCSG8 studies, the risk of recurrence(ROR) score of the PAM50 added clinically meaningful prognostic information to the Clinical Treatment Score in all patients and subgroups in the late follow-up period. They suggested that the ROR score could be helpful for separating into risk groups patients who could be spared or potentially benefit from extended hormonal therapy beyond 5 years of treatment [35].
In our study, the small number of late recurrence events was a weakness. This limitation is due to the fact that the study was performed in just two institution. It was also because we excluded patients whose follow-up duration was not sufficient and who took aromatase inhibitors in any sequence with adjuvant tamoxifen. Another limitation of our study was considerable missing data on HER2 status. Before the adjuvant trastuzumab era, HER2 status was determined by IHC alone. We regarded HER2 as unknown when the HER2 IHC score was 2+ and HER2 FISH data was not available for the patient. Moreover, the absence of information on the degree of ER expression known to be directly associated with the benefits of tamoxifen [8] was another limitation of our study.
Conclusions
Our data showed that axillary lymph node metastasis at the time of initial operation was significantly associated with late recurrence after completion of 5-year tamoxifen therapy. This result would be useful for making decisions regarding using extended tamoxifen therapy for more than 5 years and when multi-gene assays are not available.
Abbreviations
AI, anastrozole inhibitor; ALN, axillary lymph node; ALND, axillary lymph node dissection; BCI, breast-cancer index; DFS, disease-free survival; ER, estrogen receptor; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; IHC, immunohistochemistry; LN, lymph node; PgR, progesterone receptor; ROR, risk of recurrence; SLNBx., sentinel lymph node biopsy; TMX, tamoxifen
References
Cossetti RJ, Tyldesley SK, Speers CH, Zheng Y, Gelmon KA. Comparison of breast cancer recurrence and outcome patterns between patients treated from 1986 to 1992 and from 2004 to 2008. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(1):65–73.
Saphner T, Tormey DC, Gray R. Annual hazard rates of recurrence for breast cancer after primary therapy. J Clin Oncol. 1996;14(10):2738–46.
Polychemotherapy for early breast cancer: an overview of the randomised trials. Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group. Lancet (London, England). 1998, 352(9132):930–42.
Voduc KD, Cheang MC, Tyldesley S, Gelmon K, Nielsen TO, Kennecke H. Breast cancer subtypes and the risk of local and regional relapse. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(10):1684–91.
Park S, Koo JS, Kim MS, Park HS, Lee JS, Lee JS, Kim SI, Park BW. Characteristics and outcomes according to molecular subtypes of breast cancer as classified by a panel of four biomarkers using immunohistochemistry. Breast (Edinburgh, Scotland). 2012;21(1):50–7.
Ribelles N, Perez-Villa L, Jerez JM, Pajares B, Vicioso L, Jimenez B, de Luque V, Franco L, Gallego E, Marquez A, et al. Pattern of recurrence of early breast cancer is different according to intrinsic subtype and proliferation index. Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15(5):R98.
Kennecke H, Yerushalmi R, Woods R, Cheang MC, Voduc D, Speers CH, Nielsen TO, Gelmon K. Metastatic behavior of breast cancer subtypes. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(20):3271–7.
Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet (London, England). 2005, 365(9472):1687–1717.
Davies C, Godwin J, Gray R, Clarke M, Cutter D, Darby S, McGale P, Pan HC, Taylor C, Wang YC, et al. Relevance of breast cancer hormone receptors and other factors to the efficacy of adjuvant tamoxifen: patient-level meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet (London, England). 2011;378(9793):771–84.
Rosen PP, Groshen S, Kinne DW. Prognosis in T2N0M0 stage I breast carcinoma: a 20-year follow-up study. J Clin Oncol. 1991;9(9):1650–61.
Strasser-Weippl K, Badovinac-Crnjevic T, Fan L, Goss PE. Extended adjuvant endocrine therapy in hormone-receptor positive breast cancer. Breast (Edinburgh, Scotland). 2013;22 Suppl 2:S171–5.
Kennecke HF, Olivotto IA, Speers C, Norris B, Chia SK, Bryce C, Gelmon KA. Late risk of relapse and mortality among postmenopausal women with estrogen responsive early breast cancer after 5 years of tamoxifen. Ann Oncol. 2007;18(1):45–51.
Goss PE, Ingle JN, Martino S, Robert NJ, Muss HB, Piccart MJ, Castiglione M, Tu D, Shepherd LE, Pritchard KI, et al. A randomized trial of letrozole in postmenopausal women after five years of tamoxifen therapy for early-stage breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(19):1793–802.
Mamounas EP, Jeong JH, Wickerham DL, Smith RE, Ganz PA, Land SR, Eisen A, Fehrenbacher L, Farrar WB, Atkins JN, et al. Benefit from exemestane as extended adjuvant therapy after 5 years of adjuvant tamoxifen: intention-to-treat analysis of the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast And Bowel Project B-33 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(12):1965–71.
Goss PE, Ingle JN, Pater JL, Martino S, Robert NJ, Muss HB, Piccart MJ, Castiglione M, Shepherd LE, Pritchard KI, et al. Late extended adjuvant treatment with letrozole improves outcome in women with early-stage breast cancer who complete 5 years of tamoxifen. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(12):1948–55.
Tamoxifen for early breast cancer: an overview of the randomised trials. Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group. Lancet (London, England). 1998, 351(9114):1451–1467.
Fisher B, Dignam J, Bryant J, DeCillis A, Wickerham DL, Wolmark N, Costantino J, Redmond C, Fisher ER, Bowman DM, et al. Five versus more than five years of tamoxifen therapy for breast cancer patients with negative lymph nodes and estrogen receptor-positive tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996;88(21):1529–42.
Fisher B, Dignam J, Bryant J, Wolmark N. Five versus more than five years of tamoxifen for lymph node-negative breast cancer: updated findings from the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project B-14 randomized trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93(9):684–90.
Stewart HJ, Prescott RJ, Forrest AP. Scottish adjuvant tamoxifen trial: a randomized study updated to 15 years. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93(6):456–62.
Bliss JM, Kilburn LS, Coleman RE, Forbes JF, Coates AS, Jones SE, Jassem J, Delozier T, Andersen J, Paridaens R, et al. Disease-related outcomes with long-term follow-up: an updated analysis of the intergroup exemestane study. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2012;30(7):709–17.
Tormey DC, Gray R, Falkson HC. Postchemotherapy adjuvant tamoxifen therapy beyond five years in patients with lymph node-positive breast cancer. Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996;88(24):1828–33.
Davies C, Pan H, Godwin J, Gray R, Arriagada R, Raina V, Abraham M, Medeiros Alencar VH, Badran A, Bonfill X, et al. Long-term effects of continuing adjuvant tamoxifen to 10 years versus stopping at 5 years after diagnosis of oestrogen receptor-positive breast cancer: ATLAS, a randomised trial. Lancet (London, England). 2013;381(9869):805–16.
Azim HA, Saadeldeen A. Commentary on "aTTom": long-term effects of continuing adjuvant Tamoxifen to 10 years. Chin Clin Oncol. 2014;3(1):7.
Burstein HJ, Temin S, Anderson H, Buchholz TA, Davidson NE, Gelmon KE, Giordano SH, Hudis CA, Rowden D, Solky AJ, et al. Adjuvant endocrine therapy for women with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: american society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline focused update. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(21):2255–69.
Cha Y, Han SW, Seol H, Oh DY, Im SA, Bang YJ, Park IA, Han W, Noh DY, Kim TY. Immunohistochemical features associated with sensitivity to lapatinib-plus-capecitabine and resistance to trastuzumab in HER2-positive breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2014;34(8):4275–80.
Jung SY, Han W, Lee JW, Ko E, Kim E, Yu JH, Moon HG, Park IA, Oh DY, Im SA, et al. Ki-67 expression gives additional prognostic information on St. Gallen 2007 and Adjuvant! Online risk categories in early breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16(5):1112–21.
Goldhirsch A, Winer EP, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thurlimann B, Senn HJ. Personalizing the treatment of women with early breast cancer: highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2013. Ann Oncol. 2013;24(9):2206–23.
Goss PE, Ingle JN, Martino S, Robert NJ, Muss HB, Piccart MJ, Castiglione M, Tu D, Shepherd LE, Pritchard KI, et al. Randomized trial of letrozole following tamoxifen as extended adjuvant therapy in receptor-positive breast cancer: updated findings from NCIC CTG MA.17. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97(17):1262–71.
Sestak I, Dowsett M, Zabaglo L, Lopez-Knowles E, Ferree S, Cowens JW, Cuzick J. Factors predicting late recurrence for estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013;105(19):1504–11.
Al-Mubarak M, Tibau A, Templeton AJ, Cescon DW, Ocana A, Seruga B, Amir E. Extended adjuvant tamoxifen for early breast cancer: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2014;9(2), e88238.
Sgroi DC, Sestak I, Cuzick J, Zhang Y, Schnabel CA, Schroeder B, Erlander MG, Dunbier A, Sidhu K, Lopez-Knowles E, et al. Prediction of late distant recurrence in patients with oestrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer: a prospective comparison of the breast-cancer index (BCI) assay, 21-gene recurrence score, and IHC4 in the TransATAC study population. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14(11):1067–76.
Dubsky P, Brase JC, Jakesz R, Rudas M, Singer CF, Greil R, Dietze O, Luisser I, Klug E, Sedivy R, et al. The EndoPredict score provides prognostic information on late distant metastases in ER+/HER2- breast cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 2013;109(12):2959–64.
Ward S, Scope A, Rafia R, Pandor A, Harnan S, Evans P, Wyld L. Gene expression profiling and expanded immunohistochemistry tests to guide the use of adjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer management: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis. Health Technology Assessment (Winchester, England). 2013;17(44):1–302.
Dowsett M, Sestak I, Lopez-Knowles E, Sidhu K, Dunbier AK, Cowens JW, Ferree S, Storhoff J, Schaper C, Cuzick J. Comparison of PAM50 risk of recurrence score with oncotype DX and IHC4 for predicting risk of distant recurrence after endocrine therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(22):2783–90.
Sestak I, Cuzick J, Dowsett M, Lopez-Knowles E, Filipits M, Dubsky P, Cowens JW, Ferree S, Schaper C, Fesl Cet al. Prediction of late distant recurrence after 5 years of endocrine treatment: a combined analysis of patients from the Austrian breast and colorectal cancer study group 8 and arimidex, tamoxifen alone or in combination randomized trials using the PAM50 risk of recurrence score. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(8):916–22.
Funding
This research was supported by a grant of the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (grant number : HI14C3405, HI14C1277).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article and its Additional file 1.
Authors’ contributions
Conception and design: E-SL, WH and ESL. Collection of data: E-SL, MKK, JK, TY, MHL and KHL. Analysis and interpretation of data: E-SL, TYK, H-GM and SAI. Writing, review, and/or revision of the manuscript: E-SL and WH. Study supervision : WH, D-YN and ESL. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
No informed consent was needed for this study. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Hospital (IRB number: 1409-155-616).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional file
Additional file 1:
This file includes raw-data of 583 patients’ characteristics and survival. (XLSX 40 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, ES., Han, W., Kim, M.K. et al. Factors associated with late recurrence after completion of 5-year adjuvant tamoxifen in estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. BMC Cancer 16, 430 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-016-2423-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-016-2423-x