Abstract
Background
Large scale association studies have found a significant association between type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) polymorphism rs7903146. However, the quality of data varies greatly, as the studies report inconsistent results in different populations. Hence, we perform this meta-analysis to give a more convincing result.
Methods
The articles, published from January 1st, 2000 to April 1st, 2017, were identified by searching in PubMed and Google Scholar. A total of 56628 participants (34232 cases and 22396 controls) were included in the meta-analysis. A total of 28 studies were divided into 4 subgroups: Caucasian (10 studies), East Asian (5 studies), South Asian (5 studies) and Others (8 studies). All the data analyses were analyzed by the R package meta.
Results
The significant association was observed by using the dominant model (OR = 1.41, CI = 1.36 - 1.47, p < 0.0001), recessive model (OR = 1.58, CI = 1.48 - 1.69, p < 0.0001), additive model(CT vs CC) (OR = 1.34, CI = 1.28-1.39, p < 0.0001), additive model(TT vs CC) (OR = 1.81, CI = 1.69-1.94, p < 0.0001)and allele model (OR = 1.35, CI = 1.31-1.39, p < 0.0001).
Conclusion
The meta-analysis suggested that rs7903146 was significantly associated with T2DM in Caucasian, East Asian, South Asian and other ethnicities.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Diabetes is one of the largest global health emergencies in the twenty-first century. According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) [1], 46.5% of the adults with diabetes are undiagnosed, and 1 in 11 adults, about 415 million people, have diabetes. Every 6 s a person dies of diabetes (5.0 million deaths per year). By 2040, 1 in 10 adults, approximately 642 million people, will have diabetes. Notably, 12% of the global health expenditure, up to $673 billion, is dedicated to diabetes treatments, and the related take up most of the total expenditure.
The most prevalent form of diabetes is type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and in the developed countries up to 91% of the adults, who are being troubled by the diabetes, have T2DM. Excess body weight, physical inactivity, poor nutrition, genetics, family history of diabetes, past history of gestational diabetes and older age are risk factors that increase the rate of T2DM. Besides, T2DM is a complex disease, and and the function of the glycosylation plays a significant role [2, 3].
The SNP rs7903146(C/T) is a common variant in the gene TCF7L2, and allele T is the risk allele related to T2DM. The gene TCF7L2 is a transcription factor involved in the Wnt signaling pathway, and acts as a critical component of Wnt signalling and action [4–6]. The TCF7L2 gene product, a high mobility group box-containing transcription factor previously implicated in blood glucose homeostasis, is considered to act through the regulation of proglucagon gene expression in enteroendocrine cells via the Wnt signaling pathway [7]. In human islets, TCF7L2 expression associates positively with insulin gene expression [8, 9].
To address the genetic variations of T2DM, many scholars devoted themselves to the related research [10–16]. The common Pro12Ala polymorphism rs1801282 in PPAR γ, the E23K variant rs5219 in KCNJ11, the polymorphism of the 5-HT2C receptor rs3813929 and the VKORC1 polymorphism rs9923231 were found to be associated with T2DM [17–20]. In 2006, Grant SF, et al. [7] confirmed a strongly significant association between susceptibility related to T2DM and common variants in transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) in Icelandic subjects, and the result was the same with case-control method in Danish cohort and U.S. cohort. In 2006, Cauchi et al. [21] reported that the T-allele of the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs7903146 increased the risk of T2DM in the French population with 2367 cases and 2499 controls.The same results were shown by Horikoshi, Yu and Barra in case of the Japanese population, African American population and Brasilia [22–24]. However, Zheng et al. [25] found no association between rs7903146 and T2DM in the Chinese population.
The quality of the data varies greatly, is one of the reasons that the studies report inconsistent results, and the small sample size is another reason. The statistical efficiency can be improved after combining some samples together. The collected data in the control group was tested by the Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium (HWE) in view of the quality of data. Therefore, we conducted a meta-analysis of published studies involving rs7903146 and T2DM to achieve a more comprehensive result. Finally, a total of 28 studies from 26 single studies [4, 22–46] were collected to reevaluate the association between rs7903146 and T2DM.
Methods
Search strategy
The articles, published from January 1st, 2000 to April 1st, 2017, were identified by searching the keywords “rs7903146” and “type 2 diabetes mellitus” in PubMed and Google Scholar. The selected articles were written in English.
Study selection criteria
We selected studies according to the following criteria: (1) The study was designed based on the case-control method. (2) The study evaluated the association between rs7903146 and T2DM. (3) The number of genotypes in case-controls groups was provided for calculating Odds Ratios (ORs). (4) The control group meets HWE. Besides, the p value of HWE was calculated by R program HWE version 1.2 [47]. If p < 0.05, the article was preserved, otherwise the article was removed.
Data extraction
We extracted the following information from each study: (1) the first author of each article; (2) the publication year of each article; (3) the population of the study; (4) the ethnicity of individuals in each study; (5) the number of the rs7903146 genotypes both in cases and controls; (6) p value of HWE in the control group. We used R package meta to analyze the data. We also referred to some other methods [48–51] to conduct the meta-analysis.
Choice of genetic model
The rs7903146 has two alleles: C and T. We analyzed the association between rs7903146 and T2DM by using the dominant model (TT+CT versus CC), recessive model (TT versus CC+CT), additive model (CT versus CC), additive model(TT versus CC) and allele model (T versus C), respectively [52].
Heterogeneity test
Odds Ratios and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated to assess the association between rs7903146 and T2DM. The two quantities, Cochran’s Q and I2, were adopted to evaluate the heterogeneity in different kinds of ethnic groups. Q approximately follows a chi square distribution with k-1 degrees of freedom (where k is the number of studies), and the p value can be used to measure the significance level of the heterogeneity. The value of I2, ranging from 0 to 100%, is calculated according to the formula, which is I 2 = (Q-(K-1))/Q*100%. The low, moderate, and high heterogeneity were labelled by I2 levels of 25%, 50% and 75%, respectively. If I2 is less than 50%, or p is more than 0.10, the fixed effect model is used, otherwise the random effect model is adopted.
Meta-analysis and subgroup analysis
After the heterogeneity test, we used the R package meta to perform the experiment with the fixed effect model [53].
Publication bias analysis and sensitivity analysis
Begg’s test [54] and Egger’s test [55] were selected for testing the publication bias. When a two-tailed value is less than 0.05, the publication bias is significant.
Results
Literature search
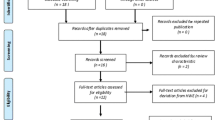
A flow diagram for the study selection process was shown in Fig. 1. A total of 355 articles were identified by the search strategy, abd 28 studies from 26 articles were left. The detailed information about the search strategy was displayed in Additional file 1: Table S1.
The flow chart of collecting articles for analyzing the association. And a total of 355 articles were identified by the search strategy. Firstly, a total of 230 articles were removed according to the title and abstract, and 45 articles were removed as the studies did not use case-control method, and 26 articles were removed as the studies did not have sufficient data to calculate OR, and 10 articles were excluded as they did not evaluate the association between rs7903146 and T2DM. After that 44 articles remained. Then, 5 articles were excluded as the control groups didn’t meet the Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium (HWE), 9 articles were excluded when we made subgroup analyses and reduced the heterogeneity, and 4 articles were excluded as some LADA or type 1 diabetes patients were included in the case groups. Finally 28 studies from 26 articles were left
Study characteristics
As shown in Table 1, a total of 56628 participants (34232 cases and 22396 controls) of 28 studies from 26 articles were included in this meta-analysis. The studies were divided into Caucasian (10 studies) [4, 22, 29–36], East Asian (5 studies) [23, 25, 37–39], South Asian (5 studies) [42–46] and Others (Arab (2 studies) [26, 27], Black African (3 studies) [22, 28, 29] and Brazilian (3 studies) [24, 40, 41]) subgroups. The collected data, performed with the R package meta in this meta-analysis, was displayed in Additional file 1: Table S2.
Heterogeneity test
According to the genotypes shown in Table1, a total of 28 studies were analyzed by the dominant model, recessive model, additive model and allele model, respectively. The heterogeneity of all subgroups was shown in Table 2. According to the data displayed in Table 2, we didn’t get the significant heterogeneity in the dominant model (p = 0.39 and I2 = 5.00%), recessive model (p = 0.33 and I2 = 9%), additive model (CT vs CC: p = 0.76 and I2 = 0.00%), additive model (TT vs CC: p = 0.15 and I2 = 22%) and allele model (p = 0.08 and I2 = 29%). As the p value was more than 0.1, we selected the fixed effect model.
Publication bias analysis and sensitivity analysis
The publication bias was not found in all models below. The p values of Begg’s test and Egger’s test for the dominant, recessive, additive (CT vs CC), additive (TT vs CC) and allele model are 0.7821 and 0.7352, 0.3635 and 0.441, 0.6354 and 0.711, 0.4528 and 0.5199, 0.6927 and 0.5673, respectively. The results were reflected in the funnel plots Fig. 2(a-e) directly.
The funnel plots of publication bias in different models. The funnel plots showed the results of the publication bias analyses between rs7903146 and T2DM by using a Dominant Model, b Recessive Model, c Additive Model (CT vs CC), d Allele Model and e Additive Model (TT vs CC). The Y-axis indicated the standard error of each study, and the standard error was smaller, the effect of the meta-analysis would be better
Association between rs7903146 and type 2 diabetes mellitus
The association between rs7903146 and T2DM was shown in the forest plots: Figs. 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 were the forest plots of the dominant model (TT+CT versus CC), recessive model (TT versus CC+CT), additive model (CT versus CC), allele model (T versus C) and additive model(TT versus CC), respectively. We made the Z test, and the result was displayed in the Table 3.
In Caucasian subgroup, the results were shown as follows: dominant model (TT + CT vs CC): (OR = 1.45, CI = 1.38 - 1.52, p < 0.0001); recessive model (TT vs CC + CT): (OR = 1.66, CI = 1.53 - 1.79, p < 0.0001); additive model (CT vs CC): (OR = 1.36, CI = 1.29 - 1.43, p < 0.0001); additive model(TT vs CC): (OR = 1.91, CI = 1.76 - 2.08), p < 0.0001); allele model (T vs C): (OR = 1.37, CI = 1.32 - 1.43, p < 0.0001).
In East Asian subgroup, the results were shown as follows: dominant model (TT + CT vs CC): (OR = 1.44, CI = 1.24 - 1.68, p < 0.0001); recessive model (TT vs CC + CT): (OR = 2.82, CI = 1.00 - 7.98, p = 0.0509); additive model (CT vs CC): (OR = 1.42, CI = 1.21 - 1.65, p<0.0001); additive model(TT vs CC): (OR = 1.81, CI = 1.69 - 1.94, p < 0.0001); additive model(TT vs CC): (OR = 2.90, CI = 1.03 - 8.22, p = 0.0446); allele model (T vs C): (OR = 1.37, CI = 1.32 - 1.43, p < 0.0001).
In South Asian subgroup, the results were shown as follows: dominant model (TT + CT vs CC): (OR = 1.41, CI = 1.31 - 1.64, p < 0.0001); recessive model (TT vs CC + CT): (OR = 1.52, CI = 1.26 - 1.83, p < 0.0001); additive model (CT vs CC): (OR = 1.42, CI = 1.29 - 1.43, p < 0.0001); additive model(TT vs CC): (OR = 1.81, CI = 1.69 - 1.94, p < 0.0001); additive model(TT vs CC): (OR = 1.77, CI = 1.46 - 2.15, p < 0.0001) allele model (T vs C): (OR = 1.44, CI = 1.24 - 1.67, p < 0.0001).
In Others subgroup, the results were shown as follows: dominant model (TT + CT vs CC): (OR = 1.24, CI = 1.12 - 1.36, p < 0.0001); recessive model (TT vs CC + CT): (OR = 1.35, CI = 1.15 - 1.58, p = 0.0002); additive model (CT vs CC): (OR = 1.4, CI = 1.24 - 1.58, p = 0.0019); additive model(TT vs CC): (OR = 1.48, CI = 1.26 - 1.75, p < 0.0001); allele model (T vs C): (OR = 1.37, CI = 1.25 - 1.49, p < 0.0001).
In total groups, the results were shown as follows: dominant model (TT + CT vs CC): (OR = 1.41, CI = 1.36 - 1.47, p < 0.0001); recessive model (TT vs CC + CT): (OR = 1.58, CI = 1.48 - 1.69, p < 0.0001); additive model (CT vs CC): (OR = 1.34, CI = 1.28 - 1.39, P < 0.0001); additive model(TT vs CC): (OR = 1.81, CI = 1.69 - 1.94, p < 0.0001); allele model (T vs C): (OR = 1.35, CI = 1.31 - 1.39, p < 0.0001).
Discussion
In the meta-analysis, 56628 participants (34232 cases and 22396 controls) of 28 studies from 26 articles were included. The result of the four subgroups (Caucasian, East Asian, South Asian and Others) suggested that rs7903146 was significantly associated with T2DM in all subgroups and the total groups.
We removed each one of the studies in the groups or any subgroups in the dominant, recessive, additive and allele model for testing the robustness of results, respectively. The results did not change significantly, which displayed that the conclusion was robust. The heterogeneity and publication bias were not found in our meta-analysis.
We used the keywords “rs7903146”, “type 2 diabetes” and “meta-analysis” to search in PubMed, and got nine articles [46, 56–63]. Our work was different from others. We analyzed the association between rs7903146 and T2DM in Caucasian, East Asian, South Asian and Others groups. We did not find a significant heterogeneity in all subgroup analyses, so the fixed effect model was used. We found that rs7903146 was associated with T2DM in Caucasian, East Asian, South Asian and other ethnicities significantly.
Some limitations existed in this meta-analysis. Firstly, considering the heterogeneity in all subgroup analyses, we excluded 9 articles. More articles should be added into the meta-analysis. Secondly, some of the same cases or controls may be used in different studies.
Conclusion
The meta-analysis suggested that rs7903146 was significantly associated with T2DM in Caucasian, East Asian, South Asian and other ethnicities.
Abbreviations
- CIs:
-
Confidence intervals
- HWE:
-
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
- ORs:
-
Odds ratio
- SNP:
-
Single necluotide polymorphism
- T2DM:
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- TCF7L2:
-
Transcription factor 7-like 2
References
Cho NH, Whiting D, Forouhi N, Guariguata L, Hambleton I, Li R, Majeed A, Mbanya JC. Idf diabetes atlas. 7th edition. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation; 2015.
Yu X, Wang Y, Kristic J, Dong J, Chu X, Ge S, Wang H, Fang H, Gao Q, Liu D, et al. Profiling igg n-glycans as potential biomarker of chronological and biological ages: A community-based study in a han chinese population. Medicine. 2016;95(28).
Meng Q, Ge S, Yan W, Li R, Dou J, Wang H, Wang B, Ma Q, Zhou Y, Song M. Screening for potential serum-based proteomic biomarkers for human type 2 diabetes mellitus using maldi-tof ms PROTEOMICS-Clinical Applications. 2017;11(3-4).
Vcelak J, Vejrakova D, Vaňkova M, Lukasova P, Bradnova O, Halkova T, Bestak J, Andělova K, Kvasnickova H, Hoskovcova P, et al. T2d risk haplotypes of the tcf7l2 gene in the czech population sample: the association with free fatty acids composition. Physiol Psychol. 2012; 61(3):229.
Smith U. Tcf7l2 and type 2 diabetes—we wnt to know. Diabetologia. 2007; 50(1):5–7.
Ross SE, Hemati N, Longo KA, Bennett CN, Lucas PC, Erickson RL, Macdougald OA. Inhibition of adipogenesis by wnt signaling. Science. 2000; 289(5481):950–953.
Grant SF, Thorleifsson G, Reynisdottir I, Benediktsson R, Manolescu A, Sainz J, Helgason A, Stefansson H, Emilsson V, Helgadottir A, et al. Variant of transcription factor 7-like 2 (tcf7l2) gene confers risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet. 2006; 38(3):320–3.
Lyssenko V, Lupi R, Marchetti P, Guerra SD, Orhomelander M, Almgren P, Sjogren M, Ling C, Eriksson K, Lethagen S, et al. Mechanisms by which common variants in the tcf7l2 gene increase risk of type 2 diabetes. J Clin Investig. 2007; 117(8):2155–63.
Osmark P, Hansson O, Jonsson AM, Ronn T, Groop L, Renstrom E. Unique splicing pattern of the tcf7l2 gene in human pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 2009; 52(5):850–4.
Orahilly S, Barroso I, Wareham NJ. Genetic factors in type 2 diabetes: The end of the beginning?Science. 2005; 307(5708):370–3.
Manolopoulos VG, Ragia G, Tavridou A. Pharmacogenomics of oral antidiabetic medications: current data and pharmacoepigenomic perspective. Pharmacogenomics. 2011; 12(8):1161–91.
Iordanidou M, Tavridou A, Petridis I, Arvanitidis KI, Christakidis D, Vargemezis V, Manolopoulos VG. The serotonin transporter promoter polymorphism (5-httlpr) is associated with type 2 diabetes. Clinica Chimica Acta. 2010; 411(3):167–71.
Ragia G, Petridis I, Tavridou A, Christakidis D, Manolopoulos VG. Presence of cyp2c9* 3 allele increases risk for hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetic patients treated with sulfonylureas. Pharmacogenomics. 2009; 10(11):1781–87.
Ragia G, Tavridou A, Petridis I, Manolopoulos VG. Association of kcnj11 e23k gene polymorphism with hypoglycemia in sulfonylurea-treated type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2012; 98(1):119–24.
Zhao F, Mamatyusupu D, Wang Y, Fang H, Wang H, Gao Q, Dong H, Ge S, Yu X, Zhang J, et al. The uyghur population and genetic susceptibility to type 2 diabetes: potential role for variants in capn10, apm1 and fut6 genes. J Cell Mol Med. 2016; 20(11):2138–47.
Adua E, Roberts P, Sakyi SA, Yeboah FA, Dompreh A, Frimpong K, Anto EO, Wang W. Profiling of cardio-metabolic risk factors and medication utilisation among type ii diabetes patients in ghana: a prospective cohort study. Clin Transl Med. 2017; 6(1):32.
Altshuler D, Hirschhorn JN, Klannemark M, Lindgren CM, Vohl M, Nemesh J, Lane CR, Schaffner SF, Bolk S, Brewer C, et al. The common ppar|[gamma]| pro12ala polymorphism is associated with decreased risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet. 2000; 26(1):76–80.
Gloyn AL, Weedon MN, Owen KR, Turner MJ, Knight BA, Hitman G, Walker M, Levy JC, Sampson M, Halford S, et al. Large-scale association studies of variants in genes encoding the pancreatic β-cell katp channel subunits kir6. 2 (kcnj11) and sur1 (abcc8) confirm that the kcnj11 e23k variant is associated with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2003; 52(2):568–72.
Iordanidou M, Tavridou A, Vasiliadis MV, Arvanitidis KI, Petridis J, Christakidis D, Vargemezis V, Bougioukas G, Manolopoulos VG. The-759c/t polymorphism of the 5-ht2c receptor is associated with type 2 diabetes in male and female caucasians. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2008; 18(2):153–9.
Tavridou A, Petridis I, Vasileiadis M, Ragia G, Heliopoulos I, Vargemezis V, Manolopoulos VG. Association of vkorc1- 1639 g/a polymorphism with carotid intima–media thickness in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011; 94(2):236–41.
Cauchi S, Meyre D, Dina C, Choquet H, Samson C, Gallina S, Balkau B, Charpentier G, Pattou F, Stetsyuk V, et al. Transcription factor tcf7l2 genetic study in the french population. Diabetes. 2006; 55(10):2903–8.
Yan Y, North KE, Ballantyne CM, Brancati FL, Chambless LE, Franceschini N, Heiss G, Kottgen A, Pankow JS, Selvin E, et al. Transcription factor 7-like 2 (tcf7l2) polymorphism and context-specific risk of type 2 diabetes in african american and caucasian adults the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Diabetes. 2009; 58(1):285–9.
Horikoshi M, Hara K, Ito C, Nagai R, Froguel P, Kadowaki T. A genetic variation of the transcription factor 7-like 2 gene is associated with risk of type 2 diabetes in the japanese population. Diabetologia. 2007; 50(4):747–51.
Barra GB, Dutra LAS, Watanabe S, Costa PGG, Cruz PSMD, Azevedo MF, Amato AA. Association of the rs7903146 single nucleotide polymorphism at the transcription factor 7-like 2 (tcf7l2) locus with type 2 diabetes in brazilian subjects. Arq Bras Endocrinol E Metabologia. 2012; 56(8):479–84.
Zheng X, Ren W, Zhang S, Liu J, Li S, Li J, Yang P, He J, Su S, Li P. Association of type 2 diabetes susceptibility genes (tcf7l2, slc30a8, pcsk1 and pcsk2) and proinsulin conversion in a chinese population. Mol Biol Rep. 2011; 39(1):17–23.
Saadi H, Nagelkerke N, Carruthers SG. Association of tcf7l2 polymorphism with diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, and markers of beta cell function and insulin resistance in a population-based sample of emirati subjects. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2008; 80(3):392–398.
Ezzidi I, Mtiraoui N, Cauchi S, Vaillant E, Dechaume A, Chaieb M, Kacem M, Almawi WY, Froguel P, Mahjoub T, et al. Contribution of type 2 diabetes associated loci in the arabic population from tunisia: a case-control study. BMC Med Genet. 2009; 10(1):33–33.
Danquah I, Othmer T, Frank LK, Beduaddo G, Schulze MB, Mockenhaupt FP. The tcf7l2 rs7903146 (t) allele is associated with type 2 diabetes in urban ghana: a hospital-based case–control study. BMC Med Genet. 2013; 14(1):96–96.
Humphries SE, Gable DR, Cooper JA, Ireland H, Stephens JW, Hurel SJ, Li KW, Palmen J, Miller MA, Cappuccio FP, et al. Common variants in the tcf7l2 gene and predisposition to type 2 diabetes in uk european whites, indian asians and afro-caribbean men and women. J Mol Med. 2006; 84(12):1005–1014.
Groves CJ, Zeggini E, Minton JAL, Frayling TM, Weedon MN, Rayner NW, Hitman GA, Walker M, Wiltshire S, Hattersley AT, et al. Association analysis of 6,736 u.k. subjects provides replication and confirms tcf7l2 as a type 2 diabetes susceptibility gene with a substantial effect on individual risk. Diabetes. 2006; 55(9):2640–44.
Cauchi S, Achhab YE, Choquet H, Dina C, Krempler F, Weitgasser R, Nejjari C, Patsch W, Chikri M, Meyre D, et al. Tcf7l2 is reproducibly associated with type 2 diabetes in various ethnic groups: a global meta-analysis. J Mol Med. 2007; 85(7):777–82.
Van Vlietostaptchouk JV, Shirisverdlov R, Zhernakova A, Strengman E, Van Haeften TW, Hofker MH, Wijmenga C. Association of variants of transcription factor 7-like 2 (tcf7l2) with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in the dutch breda cohort. Diabetologia. 2007; 50(1):59–62.
Mayans S, Lackovic K, Lindgren P, Ruikka K, Agren A, Eliasson M, Holmberg D. Tcf7l2 polymorphisms are associated with type 2 diabetes in northern sweden. Eur J Hum Genet. 2007; 15(3):342–6.
Kimber CH, Doney AS, Pearson ER, Mccarthy MI, Hattersley AT, Leese GP, Morris AD, Palmer CNA. Tcf7l2 in the go-darts study: evidence for a gene dose effect on both diabetes susceptibility and control of glucose levels. Diabetologia. 2007; 50(6):1186–91.
De Silva NMG, Steele AM, Shields BM, Knight B, Parnell K, Weedon MN, Hattersley AT, Frayling TM. The transcription factor 7-like 2 (tcf7l2) gene is associated with type 2 diabetes in uk community-based cases, but the risk allele frequency is reduced compared with uk cases selected for genetic studies. Diabet Med. 2007; 24(10):1067–72.
Dahlgren A, Zethelius B, Jensevik K., Syvänen A-C, Berne C. Variants of the tcf7l2 gene are associated with beta cell dysfunction and confer an increased risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in the ulsam cohort of swedish elderly men. Diabetologia. 2007; 50(9):1852.
Hayashi T, Iwamoto Y, Kaku K, Hirose H, Maeda S. Replication study for the association of tcf7l2 with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in a japanese population. Diabetologia. 2007; 50(5):980–4.
Miyake K, Horikawa Y, Hara K, Yasuda K, Osawa H, Furuta H, Hirota Y, Yamagata K, Hinokio Y, Oka Y, et al. Association of tcf7l2 polymorphisms with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in 4,087 japanese subjects. J Hum Genet. 2007; 53(2):174–180.
Tabara Y, Osawa H, Kawamoto R. Replication study of candidate genes associated with type 2 diabetes based on genome-wide screening. Diabetes. 2009; 58(2):493–498.
Marquezine GF, Pereira AC, Sousa AB, Mill JG, Hueb W, Krieger JE. Tcf7l2 variant genotypes and type 2 diabetes risk in brazil: significant association, but not a significant tool for risk stratification in the general population. BMC Med Genet. 2008; 9(1):106–106.
Assmann TS, Duarte GCK, Rheinheimer J, Cruz LA, Canani LH, Crispim D. The tcf7l2 rs7903146 (c/t) polymorphism is associated with risk to type 2 diabetes mellitus in southern-brazil. Arq Bras Endocrinol E Metabologia. 2014; 58(9):918–25.
Chandak GR, Janipalli CS, Bhaskar S, Kulkarni SR, Mohankrishna P, Hattersley AT, Frayling TM, Yajnik CS. Common variants in the tcf7l2 gene are strongly associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus in the indian population. Diabetologia. 2007; 50(1):63–67.
Bodhini D, Radha V, Dhar M, Narayani N, Mohan V. The rs12255372(g/t) and rs7903146(c/t) polymorphisms of the tcf7l2 gene are associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus in asian indians. Metab Clin Exp. 2007; 56(9):1174–8.
Rees SD, Bellary S, Britten AC, Ohare JP, Kumar S, Barnett AH, Kelly MA. Common variants of the tcf7l2 gene are associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in a uk-resident south asian population. BMC Med Genet. 2008; 9(1):8–8.
Gupta V, Khadgawat R, Ng HKT, Kumar S, Aggarwal A, Rao VR, Sachdeva MP. A validation study of type 2 diabetes-related variants of the tcf7l2, hhex, kcnj11, and adipoq genes in one endogamous ethnic group of north india. Ann Hum Genet. 2010; 74(4):361–8.
Hussain H, Ramachandran V, Ravi S. Tcf7l2 rs7903146 polymorphism and diabetic nephropathy association is not independent of type 2 diabetes—a study in a south indian population and meta-analysis. Endokrynologia Polska. 2014; 65(4):298–305.
Guo SW, Thompson EA. Performing the exact test of hardy-weinberg proportion for multiple alleles. Biometrics. 1992:361–372.
Han Z, Jiang Q, Zhang T, Wu X, Ma R, Wang J, Bai Y, Wang R, Tan R, Wang Y. Analyzing large-scale samples confirms the association between the rs1051730 polymorphism and lung cancer susceptibility. Sci Rep. 2015; 5:15642.
Yang Y, Wang W, Liu G, Yu Y, Liao M. Association of single nucleotide polymorphism rs3803662 with the risk of breast cancer. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:29008.
Little J, Higgins JP, Ioannidis JP, Moher D, Gagnon F, Von Elm E, Khoury MJ, Cohen B, Davey-Smith G, Grimshaw J, et al. Strengthening the reporting of genetic association studies (strega): an extension of the strobe statement. Hum Genet. 2009; 125(2):131–51.
Lewis CM. Genetic association studies: design, analysis and interpretation. Brief Bioinform. 2002; 3(2):146–53.
Zhao F, Song M, Wang Y, Wang W. Genetic model. J Cell Mol Med. 2016; 20(4):765–765.
Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003; 327(7414):557–60.
Begg CB, Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics. 1994; 50(4):1088–101.
Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, Minder CE. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997; 315(7109):629–34.
Guan Y, Yan L, Liu XY, Zhu X, Wang S, Chen L. Correlation of the tcf7l2 (rs7903146) polymorphism with an enhanced risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. Genet Mol Res. 2016;15(3).
Peng S, Zhu Y, Lu B, Xu F, Li X, Lai M. Tcf7l2 gene polymorphisms and type 2 diabetes risk: a comprehensive and updated meta-analysis involving 121 174 subjects. Mutagenesis. 2013; 28(1):25–37.
Liu X, Xie CG, An Y, Zhang XX, Wu W. Meta-analysis of the association between the rs7903146 polymorphism at the tcf7l2 locus and type 2 diabetes mellitus susceptibility. Genet Mol Res. 2015; 14(4):16856.
Ding Y, Hu Z, Yuan S, Xie P, Liu Q. Association between transcription factor 7-like 2 rs7903146 polymorphism and diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Vasc Dis Res. 2015; 12(6):436–444.
Lin Y, Li P, Cai L, Zhang B, Tang X, Zhang X, Li Y, Xian Y, Yang Y, Wang L, et al. Association study of genetic variants in eight genes/loci with type 2 diabetes in a han chinese population. BMC Med Genet. 2010; 11(1):97–97.
Dou H, Ma E, Yin L, Jin Y, Wang H. The association between gene polymorphism of tcf7l2 and type 2 diabetes in chinese han population: a meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(3).
Zhang B, Li W, Zhu M, Xu Y. Association of tcf7l2 gene polymorphisms with type 2 diabetes mellitus in han chinese population: a meta-analysis. Gene. 2013; 512(1):76–81.
Wang J, Hu F, Feng T, Zhao J, Yin L, Li L, Wang Y, Wang Q, Hu D. Meta-analysis of associations between tcf7l2 polymorphisms and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in the chinese population. BMC Med Genet. 2013; 14(1):8–8.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully thanked the editors and reviewers to help improve the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by China Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 11301110), Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province of China (Grant No. QC2015076, No. A2015001 and No. LC2016024), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2015T80326 and No. 2013M541346), Heilongjiang Postdoctoral Fund (Grant No. LBH-TZ0504, No. LBH-Z13058 and No. LBH-Q13072), Open Project Program of Key Laboratory of Symbolic Computation and Knowledge Engineering of Ministry of Education of Jilin University (Grant No. 93K172016K16), Open Project of State Key Laboratory of Urban Water Resource and Environment of Harbin Institute of Technology (Grant No. ES201602) and National High-Tech Research and Development Program (863) of China (No: 2015AA020101, 2015AA020108, 2014AA021505).
Availability of data and materials
All the data generated or analyzed in this study was included in this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WYD wrote the paper. SLJ and LX revised the paper. WYD, ZJH, LJZ and SLJ collected and selected the data, designed and performed the experiment. QHJ and ZW conducted the project. ZJH and SLJ helped interpret the results. WYD and LX developed analytical tools. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declared that they had no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Additional file
Additional file 1
Table S1. The detailed information about the search strategy. Table S2. The collected data in the meta-analysis. (XLSX 13 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, W., Xu, L., Zhang, L. et al. Meta-analysis of association between TCF7L2 polymorphism rs7903146 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Med Genet 19, 38 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12881-018-0553-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12881-018-0553-5