Abstract
Methods
Twenty-seven clinical isolates of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae with MICs ≥4 mg/L for imipenem or meropenem were obtained from inpatients in a hospital in Vietnam. Antimicrobial susceptibility tests and whole genome sequencing were performed. Multilocus sequence typing and the presence of drug resistant genes were determined and a maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree was constructed by SNP alignment of whole genome sequencing data.
Results
All the isolates harbored one of genes encoding carbapenemases, including KPC-2, NDM-1, NDM-4 and OXA-48. Of the isolates, 13 were resistant to arbekacin with MICs ≥256 mg/L and to amikacin with MICs ≥512 mg/L. These isolates harbored a gene encoding a 16S rRNA methylase, either RmtB or RmtC. Eighteen and 4 isolates belonged to international clones, ST15 and ST16, respectively. None of the isolates had colistin-resistant factors.
Conclusion
Carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae isolates belonged to international clones spread in a medical setting in Vietnam, and that these isolates harbored genes encoding various combinations of carbapenemases and 16S rRNA methylases. This is the first report of KPC-2, NDM-4 and OXA-48 producers in a medical setting in Vietnam.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Emergence of carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates has become serious problems worldwide [1]. These isolates produce several carbapenemases belonging to class A, B, and D, including KPCs, NDMs and OXA-48, respectively [2]. KPC-1 was initially found in a carbapenem-resistant strain K. pneumoniae 1534, which was collected in a surveillance during 1996 to 1997 in the United States hospitals [3]. NDM-1 was initially identified in K. pneumoniae and Escherichia coli in 2009 in Sweden [4]. Since then, NDM-1-producing Enterobacteriaceae have been reported worldwide [5]. OXA-48 was first identified in K. pneumoniae 11,978, which was isolated in 2001 in Turkey [6].
K. pneumoniae producing 16S rRNA methylase genes responsible for an extremely high level of resistance to various aminoglycosides have been increasingly reported [7]. To date, 10 types of 16S rRNA methylases, including ArmA, RmtA, RmtB, RmtC, RmtD, RmtE, RmtF, RmtG, RmtH and NpmA, have been found in clinical isolates. Of them, RmtB spread widely among various bacterial species, including Acinetobacter baumannii, Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and RmtC spread among Enterobacteriaceae [7].
Methods
Bacterial strains and antimicrobial susceptibility
Twenty-seven K. pneumoniae isolates with minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) ≥4 mg/L for imipenem or meropenem were obtained from 27 inpatients treated at a hospital, Vietnam, from from February 2014 to April 2015. Of them, 22 isolates were from respiratory tracts, 3 from pus samples, 1 from a bile sample, and 1 from a urine sample. The isolates were phenotypically identified and species identification was confirmed by 16S rRNA sequencing. MICs were determined using the microdilution method, according to the guidelines of the Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (M100-S25). The colistin MICs were also determined by Etest in colistin-resistant isolates evaluated by broth microdilution method.
Detection of antibiotic-resistance genes and their genetic environments
The entire genome of each isolate was extracted by DNeasy Blood & Tissue kit (QIAGEN, Tokyo, Japan) and sequenced by MiSeq (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Sequences of drug-resistance genes, including β-lactamase encoding genes at the website (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pathogens/beta-lactamase-data-resources/), aminoglycoside resistance genes (aminoglycoside-acetyltransferase, −adenylyltransferase and -phosphotransferase encoding genes), colistin resistance genes (mcr-1, mcr-2 and mgrB), registered in GenBank (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/) and quinolone resistance genes gyrA and parC, were determined using CLC genomics workbench version 9.0.1. Genetic environments surrounding bla KPC-2, bla NDMs and bla OXA-48 and the genes encoding the 16S rRNA methylases were determined.
MLST and phylogenetic analysis
Multilocus sequence types (MLSTs) were deduced as described in the protocols of the Institut Pasteur MLST (IP-MLST) (http://bigsdb.pasteur.fr/klebsiella/klebsiella.html) databases. Clonal complexes (CC) were determined by eBURST version 3 (http://eburst.mlst.net). Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of the genome sequences of all carbapenem-resistant isolates tested were identified by comparisons with the sequence of NDM-1 producing ST15 K. pneumoniae PMK1, (Gen Bank accession no. CP008929), with all the reads of each isolate aligned against the PMK1 sequence using CLC Genomic Workbench version 9.0.1. SNP concatenated sequences were aligned using MAFFT (http:/mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/server/). Phylogenetic trees were constructed from the SNP concatemers. Models and parameters used for the phylogenetic analyses were computed using j-Model Test-2.1.4. A maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree was constructed from SNP alignment with PhyML 3.0.
Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and southern hybridization
The plasmids in each ST strain were extracted and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis was performed as describing previously [8]. Probes for bla KPC-2, bla NDMs and bla OXA-48 were amplified by PCR using the primer sets as follows; KPC-F-TCGCTAAACTCGAACAGG and KPC-R-TTACTGCCCGTTGACGCCCAATCC for bla KPC-2, NDM-F- TTGGCCTTGCTGTCCTTG and NDM-R- ACACCAGTGACAATATCACCG for bla NDMs and OXA-48-F-TGTTTTTGGTGGCATCGAT and OXA-48-R-GTAAMRATGCTTGGTTCGC for bla OXA-48, respectively. Signal detection was carried out using DIG High Prime DNA Labeling and Detection Starter Kit II (Roche Applied Science, Indianapolis, IN).
Nucleotide sequence accession numbers
The whole genome sequences of all 27 isolates have been deposited at GenBank as accession numbers DRA005275.
Results
Antimicrobial susceptibility
MICs of 27 carbapenem-resistant isolates were shown in Table 1. All the isolates had MIC50 8 mg/L and MIC90 64 mg/L for imipenem, and MIC50 8 mg/L and MIC90 128 mg/L for meropenem. They were resistant to ampicillin with MICs ≥1024 mg/L, to aztreonam with MIC50 512 mg/L and MIC90 1024 mg/L, to ceftazidime with MIC50 256 mg/L and MIC90 > 1024 mg/L, and to ciprofloxacin with MIC50 256 mg/L and MIC90 512 mg/L. Of all the isolates, 19 isolates (70%) were resistant to amikacin with MIC50 1024 mg/L and MIC90 > 1024 mg/L. They had MIC50 256 mg/L and MIC90 > 1024 mg/L for arbekacin, MIC50 0.25 mg/L and MIC90 32 mg/L to colistin, and MIC50 2 mg/L and MIC90 2 mg/L to tigecycline. The colistin MICs of K. pneumoniae isolates were significantly higher by the microdilution method than by Etest. MICs of colistin using Etest were from 0.75 to 2 mg/L (Table 1).
Drug resistant genes
All isolates tested had a carbapenemase encoding gene, such as bla KPC-2, bla NDM-1, bla NDM-4 and bla OXA-48; and the majority had a 16S rRNA methylase encoding gene, such as rmtB and rmtC (Table 1). Of the all isolates, 19 had bla OXA-48, 5 had bla NDM-4, 2 had bla NDM-1, and 1 had bla KPC-2. Seventeen had rmtB and 2 had rmtC. These isolates also had (an) extended spectrum β-lactamase encoding gene(s), including bla CTX-M-14, bla CTX-M-15, bla CTX-M-27, bla SHV-1, bla SHV-11, bla SHV-12, bla SHV-28, bla SHV-55, and/or bla TEM-1; and aminoglycoside modification enzymes, including aac(6′)-Ib-cr and/or aadA1 (Table 1). All isolates had 2 or 3 point mutations in the quinolone-resistance-determining regions of gyrA and parC (Table 1). None of the isolates harbor mcr-1 or mcr-2, and our analysis did not reveal any isolates with disruption in the mrgB gene.
Genetic environments surrounding genes encoding carbapenemases
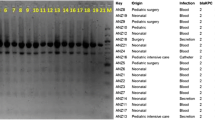
The genetic structure surrounding bla KPC-2, bla NDM-1, bla NDM-4 and bla OXA-48 were shown in Fig. 1. The genomic structure surrounding bla KPC-2 was identical with that of Aeromonas hydrophila strain WCHAH01 plasmid pKPC2 (GenBank accession no. KR014106), which was isolated in China.
All isolates harboring bla NDM-1 tested had the same genetic structure surrounding bla NDM-1 (Fig. 1), which was identical with that of plasmid pRIH26 in NDM-1 producing K. pneumoniae isolated from a patient in 2012 in Rhode Island, the United States [9]. This patient had returned to the United States after a hospitalization in Vietnam [9].
All isolates harboring bla NDM-4 tested had the same genetic structure surrounding bla NDM-4 (Fig. 1), which was identical to that of NDM-1 producing K. pneumoniae strain KP4 plasmid pKP04NDM isolated in China (GenBank accession no. KU314941).
OXA-48 producers had either one of two genetic structures surrounding bla OXA-48 (Fig. 1). Of them, one was not reported (the second structure from the bottom in Fig. 1), whereas the other was identical with plasmids in OXA-48 producing K. pneumoniae strains 153,877–1 in Netherlands (GenBank accession no. KP659188), KP112 in France (GenBank accession no. LN864819), Kpn-E1.Nr7 in Switzerland (GenBank accession no. KM406491), E71T in Ireland (GenBank accession no. KC335143), KP1 and KP2 in France (GenBank accession no. KC757416 and KC757417, respectively), and 23 plasmid pIncL_M_DHQP1400954 in the USA (GenBank accession no CP016927).
The bla KPC-2, bla NDM-1, bla NDM-4 and bla OXA-48 in each ST strain will be all located on plasmids and the sizes of the plasmids were shown in Table 1.
MLST and molecular phylogenetic analysis
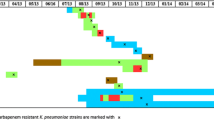
The clinical isolates of K. pneumoniae tested belonged to either one of ST15, ST16, ST147, ST307, ST395 and ST2353 (Table 1). Of these isolates, 18 belonged to ST15 and 4 belonged to ST16 (Table 1). The new sequence type, ST2353, belonged to CC147. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that the isolates belonging to ST15 formed the largest clade among the 27 isolates (Fig. 2a). The 18 isolates belonging to ST15 harbored either one of two genes encoding carbapenemases, including bla OXA-48 and bla NDM-4; and genes encoding aminoglycoside resistance factors, including aac(6′)-Ib-cr and rmtB (Table 1). The phylogenetic tree among 18 ST15 isolates showed two subclades, A and B (Fig. 1b). Of them, 16 belonging to subclade A harbored bla OXA-48 and 2 belonging to subclade B harbored bla NDM-4 (Fig. 2b).
a Molecular phylogeny of the 27 K. pneumoniae strains. A maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree was constructed from the 27 carbapenem-resistant isolates. The isolates belonging to ST15 formed the largest clade among the 27 isolates. b Molecular phylogeny of the 18 K. pneumoniae strains belonging to ST15. A maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree was constructed from the 18 carbapenem-resistant isolates. Of them, 16 belonging to subclade A harbored bla OXA-48 and 2 belonging to subclade B harbored bla NDM-4
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first report of the whole genome based molecular epidemiological analysis of carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae in Vietnam. Our study suggests that carbapenem-producing ST15 K. pneumoniae have been spreading in medical settings in Vietnam. A NDM-1 producing K. pneumoniae clinical isolate in Vietnam was firstly obtained from a urinary tract of a 62-year-old man in 2010 [10].
This is the first report of NDM-4 or OXA-48 producing K. pneumoniae in Vietnam. NDM-4 was firstly detected in E. coli I5, which was recovered from a urine sample of a patient hospitalized in 2010 in India [11]. Since then, NDM-4 producers were reported in Enterobacter cloacae in Sri Lanka [12], E. coli in India [13], Italy [14] and Vietnam [15], and K. pneumoniae in Japan [16]. NDM-4 possessed increased hydrolytic activity toward carbapenems and several cephalosporins compared to NDM-1 [11]. NDM-4 with an amino acid substitution at position 130 (Met to Leu) showed increased hydrolytic activity toward carbapenems and several cephalosporins compared to NDM-1 [11].
ST15 will be an emerging high-risk multidrug-resistant clone with carbapenem-encoding genes, including bla KPCs, bla NDMs and bla OXAs. Outbreaks caused by ST15 OXA-48 produces were reported in France and Spain [2]. When Diancourt et al. [17] developed a MLST for K. pneumoniae in 2005, they already detected ST15 isolates from several countries in Europe, such as Austria, France, Portugal and Poland, and the most of the isolates were resistant to ceftazidime and ciprofloxacin. ST15 K. pneumoniae isolates were reported to spread in medical settings in 2005 in Hungary [2]. ST15 K. pneumoniae isolates were detected in other European countries, including Bulgaria, Croatia, Czech Republic, Denmark, Hungary, Italy, Netherlands, and Spain [2]; they were also detected in Asian countries, including China, South Korea, Malaysia, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam [2]; in African countries, including Côte d’Ivoire, Madagascar, Morocco, and Senegal [18]. These ST15 isolates frequently produced ESBL, including CTX-M, SHV-28 and TEM variants [19], and moreover, they became to produce various carbapenemases, including KPCs, OXA-48, NDMs and VIM-4 [19]. One of the well-recognized high-risk clones is CC258 which is frequently associated with KPCs-producing K. pneumoniae known as a high-risk clone [19], and these isolates were reported many countries, such as the United States, Greek, Norway, Sweden, Italy, Poland, Canada, Brazil and Korea [19]. ST11, a related clone ST258, was reported in KPCs-producing isolates mainly in China, but also in NDMs-producers from Czech Republic, Switzerland, Thailand, Australia, the United States, the United Arab Emirates and Greece [19].
Etest seems a more reliable method to measure colistin MICs than broth microdilution method [20, 21]. In the present study, 11 isolates were resistant to colistin with MICs 4–32 mg/L by broth microdilution method, although none of the isolates had colistin-resistant factors. Our previous study indicated that Enterobacteriacae isolates showed lower colistin MICs by Etest than by broth microdilution method [20]. It is necessary to find feasible susceptibility testing methods of determining the MICs of polymyxins for clinical laboratories.
Conclusions
This study showed that carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae isolates belonged to international clones spread, and that these isolates harbored genes encoding various combinations of carbapenemases and 16S rRNA methylases, in a medical setting in Vietnam.
Abbreviations
- ESBLs:
-
extended-spectrum β-lactamases
- MBLs:
-
Metallo-β-lactamases
- MICs:
-
minimal inhibition concentration
- MLST:
-
Multilocus sequence typing
References
Nordmann P, Cuzon G, Naas T. The real threat of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase-producing bacteria. Lancet Infect Dis. 2009 Apr;9(4):228–36.
Lee CR, Lee JH, Park KS, Kim YB, Jeong BC, Lee SH. Global dissemination of carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae: epidemiology, genetic context, treatment options, and detection methods. Front Microbiol. 2016 Jun 13;7:895.
Yigit H, Queenan AM, Anderson GJ, Domenech-Sanchez A, Biddle JW, Steward CD, et al. Novel carbapenem-hydrolyzing beta-lactamase, KPC-1, from a carbapenem-resistant strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001 Apr;45(4):1151–61.
Yong D, Toleman MA, Giske CG, Cho HS, Sundman K, Lee K, et al. Characterization of a new metallo-β-lactamase gene, bla NDM-1, and a novel erythromycin esterase gene carried on a unique genetic structure in Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 14 from India. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009 Dec;53(12):5046–54.
Cornaglia G, Giamarellou H, Rossolini GM. Metallo-beta-lactamases: a last frontier for beta-lactams? Lancet Infect Dis. 2011 May;11(5):381–93.
Poirel L, Heritier C, Tolun V, Nordmann P. Emergence of oxacillinase-mediated resistance to imipenem in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004 Jan;48(1):15–22.
Wachino J, Yamane K, Shibayama K, Kurokawa H, Shibata N, Suzuki S, et al. Novel plasmid-mediated 16S rRNA methylase, RmtC, found in a Proteus mirabilis isolate demonstrating extraordinary high-level resistance against various aminoglycosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Jan;50(1):178–84.
Tada T, Miyoshi-Akiyama T, Shimada K, Kirikae T. Biochemical analysis of the metallo-beta-lactamase NDM-3 from a multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli strain isolated in Japan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014 Mar;31
Rice LB, Tait-Kamradt A. A novel genetic region flanks the plasmid-carried bla NDM-1 isolated from a patient in Rhode Island in 2012. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Aug;57(8):4084–5.
Hoang TH, Wertheim H, Minh NB, Duong TN, Anh DD, Phuong TT, et al. Carbapenem-resistant Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae strains containing New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase isolated from two patients in Vietnam. J Clin Microbiol. 2013 Jan;51(1):373–4.
Nordmann P, Boulanger AE, Poirel L. NDM-4 metallo-beta-lactamase with increased carbapenemase activity from Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Apr;56(4):2184–6.
Papagiannitsis CC, Studentova V, Chudackova E, Bergerova T, Hrabak J, Radej J, et al. Identification of a New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase-4 (NDM-4)-producing Enterobacter cloacae from a Czech patient previously hospitalized in Sri Lanka. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2013 Nov;58(6):547–9.
Khan AU, Parvez S. Detection of bla NDM-4 in Escherichia coli from hospital sewage. J Med Microbiol. 2014 Oct;63(Pt 10):1404–6.
Coppo E, Del Bono V, Ventura F, Camera M, Orengo G, Viscoli C, et al. Identification of a New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase-4 (NDM-4)-producing Escherichia coli in Italy. BMC Microbiol. 2014 Jun 7;14:148,2180–14-148.
Jakobsen L, Hammerum AM, Hansen F, Fuglsang-Damgaard D. An ST405 NDM-4-producing Escherichia coli isolated from a Danish patient previously hospitalized in Vietnam. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014 Feb;69(2):559–60.
Khalifa HO, Soliman AM, Ahmed AM, Shimamoto T, Shimamoto T. NDM-4- and NDM-5-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae coinfection in a 6-month-old infant. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Jun 20;60(7):4416–7.
Diancourt L, Passet V, Verhoef J, Grimont PA, Brisse S. Multilocus sequence typing of Klebsiella pneumoniae nosocomial isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Aug;43(8):4178–82.
Breurec S, Guessennd N, Timinouni M, Le TA, Cao V, Ngandjio A, et al. Klebsiella pneumoniae Resistant to third-generation cephalosporins in five African and two Vietnamese major towns: Multiclonal population structure with two major international clonal groups, CG15 and CG258. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2013 Apr;19(4):349–55.
Pitout JD, Nordmann P, Poirel L. Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae, a key pathogen set for global nosocomial dominance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Oct;59(10):5873–84.
Nhung PH, Miyoshi-Akiyama T, Phuong DM, Shimada K, Anh NQ, Binh NG. Thanh do V, Ohmagari N, Kirikae T: evaluation of the Etest method for detecting colistin susceptibility of multidrug-resistant gram-negative isolates in Vietnam. J Infect Chemother. 2015;21(8):617–9.
Rojas LJ, Salim M, Cober E, Richter SS, Perez F, Salata RA, Kalayjian RC, Watkins RR, Marshall S, Rudin SD, Domitrovic TN, Hujer AM, Hujer KM, Doi Y, Kaye KS, Evans S, Fowler VG Jr, Bonomo RA, van Duin D. Antibacterial resistance leadership group: Colistin resistance in Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: laboratory detection and impact on mortality. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;64(6):711–8.
Acknowledgments
Biosafety Committee of the National Center for Global Health and Medicine (approval number: 27-M-52).
Funding
This study was supported by Japan Initiative for Global Research Network on Infectious Diseases (J-GRID), and a grant of the Research Program on Emerging and Re-emerging Infectious Diseases from Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED), a grant (27-A-1102) from International Health Cooperation Research, and JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 16 K19133.
Availability of data and materials
Nucleotide sequence accession numbers of the whole genome sequences of all 27 isolates have been deposited at GenBank as accession numbers DRA005275.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TT and MT: Performed whole genome sequencing, analyzed data and drafted the manuscript. KS: Performed drug-susceptibility tests. TTTN: Performed clinical bacterial analyses. LTAT and TTP: Designed protocols and supervised this study at CRH. NO and TK: Designed protocols and supervised this study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
The study protocol was carefully reviewed and approved by the ethics committee of Cho Ray Hospital (approval number: 1644/QD-BVCR), the ethics committee of the National Center for Global Health and Medicine (No. 1268), respectively. Respectively. Individual informed consent was waived by the ethics committee listed above because this study used currently existing sample collected during the course of routine medical care and did not pose any additional risks to the patients.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Tada, T., Tsuchiya, M., Shimada, K. et al. Dissemination of Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates with various combinations of Carbapenemases (KPC-2, NDM-1, NDM-4, and OXA-48) and 16S rRNA Methylases (RmtB and RmtC) in Vietnam. BMC Infect Dis 17, 467 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-017-2570-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-017-2570-y