Abstract
Background
Evidence-based mailed educational brochures about the harms of sedative-hypnotic use lead to discontinuation of chronic benzodiazepine use in older adults. It remains unknown whether patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) are able to understand the information in the EMPOWER brochures, and whether they achieve similar rates of benzodiazepine discontinuation.
Methods
Post-hoc analysis of the EMPOWER randomized, double-blind, wait-list controlled trial that assessed the effect of a direct-to-consumer educational intervention on benzodiazepine discontinuation. 303 community-dwelling chronic users of benzodiazepine medication aged 65–95 years were recruited from general community pharmacies in the original trial, 261 (86%) of which completed the trial extension phase. All participants of the control arm received the EMPOWER brochure during the trial extension. Normal cognition (n = 139) or MCI (n = 122) was determined during baseline cognitive testing using the Montreal Cognitive Assessment questionnaire. Changes in knowledge pre- and post-intervention were assessed with a knowledge questionnaire and changes in beliefs were calculated using the Beliefs about Medicines Questionnaire. Logistic regression was used to compare knowledge gained, change in beliefs and benzodiazepine cessation rates between participants with and without MCI.
Results
Complete discontinuation of benzodiazepines was achieved in 39 (32.0% [24.4,40.7]) participants with MCI and in 53 (38.1% [30.5,46.4]) with normal cognition (adjusted OR 0.79, 95% CI [0.45–1.38]). Compared to individuals with normal cognition, MCI had no effect on the acquisition of new knowledge, change in beliefs about benzodiazepines or elicitation of cognitive dissonance.
Conclusions
The EMPOWER brochure is effective for reducing benzodiazepines in community-dwelling older adults with mild cognitive impairment.
Trial registration
Our ClinicalTrials.gov identifier is NCT01148186, June 21st 2010.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Sedative-hypnotic use is associated with cognitive impairment, and may contribute to mild neurocognitive disorders in older adults [1–3]. For this reason, both long and short-acting benzodiazepines are listed in the 2015 Beers criteria of medications to avoid in older adults [3]. A mild neurocognitive disorder is defined in the DSM-5 as a noticeable decrement in cognitive function beyond that of normal aging, which requires individuals to engage in compensatory strategies to maintain independence [4]. The term is meant to replace the previously used diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Over 1-in-5 community dwelling older adults have MCI at any given time, although the exact prevalence is difficult to estimate due to the variability in the criteria used, the source of subjects, the fluctuating nature of the condition and the reference standards [5, 6]. Individuals with MCI may demonstrate significant impairments in their ability to understand, reason and participate in health related decisions [7]. Longitudinal data suggest that medical decision-making capacity in patients with MCI tends to decline over time [8].
The majority of long-term benzodiazepine users aged 65 years of age and older report not being concerned about side effects, mainly because they have never been alerted to the risks [9]. However, when provided with evidence-based information about harm in the form of a mailed educational brochure, 27% of chronic users discontinued benzodiazepines within 6 months in the EMPOWER trial [10]. It remains unknown whether patients with MCI retain capacity to understand the material in the brochure, and whether they respond equally well to the educational intervention. The objective of this report is to examine whether cognitive status affected the comprehension and success rates of the EMPOWER patient-centered educational approach to the deprescribing of benzodiazepines.
Design & methods
Study population
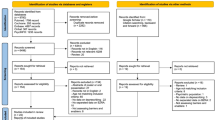
Participants in the EMPOWER trial were adults aged 65 years and older with polypharmacy (≥5 medications), taking at least one chronic benzodiazepine prescription (≥3 months). Participants with self-reported epilepsy, a diagnosis of established dementia, or a mental health disorder requiring treatment with antipsychotic medication, were deemed ineligible. In order to exclude patients with undiagnosed dementia from the study, the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) was administered at an in-home baseline screening interview. The MoCA was chosen due to its high sensitivity and specificity for distinguishing normal individuals from those with MCI [11]. Participants with a MoCA score of 26 and over were qualified as having normal cognition, while those with scores of 21 to 25 were classified as having mild cognitive impairment (MCI) [11]. Participants with scores under 21 were excluded in order to eliminate all potential cases of dementia [11]. In the original EMPOWER trial, participants randomized to the control group were wait-listed to receive the EMPOWER brochure at the end of the 6-month study period. In an extension to the trial, participants in the control arm were followed for an additional 6 months after study completion in order to evaluate their response to the EMPOWER brochure. This paper analyses all EMPOWER participants (from the intervention and control arm) having received the EMPOWER brochure and having completed the post-intervention EMPOWER assessment by 1-year (n = 261) [10].
Intervention
The EMPOWER brochure consists of an 8-page paper-based benzodiazepine deprescribing tool embedded with program theories which participants received by mail. Development of the intervention has previously been described in detail [10, 12]. A generic version of the EMPOWER tool is available at http://www.criugm.qc.ca/fichier/pdf/BENZOeng.pdf. The deprescribing tool was individualized with the name of the participant’s benzodiazepine on the front page. It included true and false questions about the harms of benzodiazepines, a short paragraph describing changes in drug metabolism with age, suggestions for alternate non-drug therapies for anxiety and insomnia, a peer champion story, and a standard 21-week tapering protocol showing a picture-based diminishing schedule of full-pill, half-pill, and quarter-pill consumption. The pictogram was proposed by consumers during the development of the intervention and allows participants to apply the benzodiazepine tapering protocol regardless of the type or dose of sedative-hypnotic consumed.
Data collection
Baseline data, including demographic characteristics and prescription details were recorded during the initial in-person interview. Follow-up data was collected by phone 1 week, 6 weeks and 6 months after each participant received the EMPOWER brochure by mail. Benzodiazepine cessation or dose reduction was ascertained using pharmacy renewal profiles, which contained information on drugs purchased, dates of purchase, dose, and quantity served. Cessation was defined as an absence of any benzodiazepine prescription renewal, sustained for a minimum of 3 months during the follow-up period. A significant dose reduction consisted of a >25% dose reduction, sustained over a minimum of 3 months when compared to baseline use. Withdrawal symptoms were measured using the benzodiazepine withdrawal symptom questionnaire 6 weeks and 6 months post-intervention. Participants reporting any withdrawal symptoms at either time point were qualified as having experienced withdrawal symptoms [13].
Change in knowledge, beliefs and self-efficacy to taper benzodiazepines
In order to evaluate whether MCI participants understood and reacted similarly to the content of the deprescribing intervention, we measured knowledge gained, change in beliefs, improvements in self-efficacy and frequency of outreach to a healthcare professional. Change was calculated by comparing responses on the pre and post-intervention questionnaires. For knowledge, this consisted of scores on four true or false questions [12]. Beliefs about the necessity of taking benzodiazepines versus associated harms were measured by comparing the total scores on the specific section of the beliefs about medicines questionnaire [14]. Change in self-efficacy was evaluated with the Medication Reduction Self-efficacy scale [12]. Outreach to a healthcare professional was measured by self-report.
Analysis
Participant characteristics were described using means with standard deviations for continuous data and percentages for categorical data. A chi-square test was used when comparing baseline characteristics of MCI vs non-MCI participants. Univariable logistic regression was used to determine the odds of all reported outcomes comparing participants with normal cognitive function to those with MCI. Multivariate analyses were adjusted for variables that were significantly associated with MCI at baseline, namely living arrangement, education, baseline self-efficacy and anxiety as an indication for therapy (Table 1). The results are reported as proportions with 95% confidence intervals (CI), and odds ratios (OR) with 95% CI, as appropriate. By combining participants who were randomized to the intervention, as well as the wait-list control group who received the brochure during the trial extension, the sample was powered to detect a 15% difference in proportions of individuals with and without MCI who discontinued benzodiazepines, based on an alpha of 0.05 and 80% power. The statistical significance for all analyses was set at p < 0.05 (two-sided). SPSS Version 20.0 (SPSS Inc. Chicago, IL, USA) was used for all analyses.
Results
Participants in the post-hoc analysis consisted of older adults aged 74.4 years (6.3 year standard deviation) (Table 1). Participants were taking an average of 10 different medications and reported a mean of 7 comorbidities, with almost one third classifying their health status as unfavorable. The mean duration of benzodiazepine use was 10.7 years, indicated for insomnia and/or anxiety. Almost half (45.6%) of patients reported a previous attempt to taper their benzodiazepine. One third of the latter (15.7%) succeeded in the attempt, prior to re-initiating the drug at a later date.
One hundred twenty-two (46.7%) participants were classified as having MCI at baseline. Participants with MCI were less well educated, more likely to live alone, more likely to be taking their benzodiazepine to treat anxiety, and expressed a lower level of confidence for successful tapering than their counterparts with normal cognitive function (Table 1).
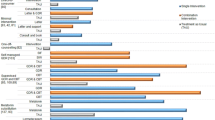
Complete discontinuation of benzodiazepines was achieved in 92 participants, with 39 (32.0% [24.4,40.7]) meeting MOCA criteria for mild cognitive impairment and 53 (38.1% [30.5,46.4]) having normal cognition (Adjusted OR = 0.79, 95% CI 0.45 to 1.38). An additional 28 participants significantly reduced their benzodiazepine dose during the same time period (12 in the normal group and 16 MCI participants). In total, 65 (46.8% [38.7–55.0]) participants with normal cognition and 55 (45.1% [36.5,53.9] MCI participants achieved dose reduction or complete discontinuation (Adjusted OR = 1.07, 95% CI 0.62 to 1.83) (Table 2).
Compared to participants with normal cognition, those with MCI exhibited the same ability to acquire new knowledge and change their beliefs following the intervention. Self-efficacy to taper and experience of withdrawal symptoms was the same in both groups. Additionally, cognitive status did not affect the participants’ decision to partake in a discussion about the intervention with their healthcare provider (Table 2).
Discussion
Although previous research indicates that individuals with MCI perform significantly worse than controls in multiple aspects of medical decision-making [7, 8, 15], we did not detect any difference in response to the EMPOWER deprescribing brochure among older adults who met MOCA criteria for MCI. Participants with MCI demonstrated improvements in knowledge and self-efficacy, were able to change their beliefs about benzodiazepines, and initiated discussions about deprescribing with a health care provider. Clinicians should be encouraged to distribute the EMPOWER brochure to their MCI patients in order to engage patients in conversations about deprescribing sedative hypnotics, leading to shared decision-making despite declining cognitive status.
Strengths and limitations
This is the first study of its kind to explore the association between MCI and the success rates of a patient-centered educational deprescribing intervention in a community-based clinical trial of older, community-dwelling adults. As the mild neurocognitive disorder diagnosis was not yet developed at the time of the study and the MoCA’s usefulness in detecting mild neurocognitive disorder is modest [16], we categorized participants according to the older MCI diagnosis. Our results are only generalizable to patients with mild-to-moderate MCI since we used a MoCA cut-off score of 21, thus excluding the lower spectrum of MCI (19–20), which overlaps with early dementia. Additionally, as we did not re-measure scores on the MOCA at study endpoint, and were unable to ascertain whether cognition improved after discontinuation. The mean lorazepam equivalent dose was only 1.25 mg/day in both groups of participants, which may have facilitated tapering.
Conclusions
This report illustrates that the EMPOWER brochure can be distributed to community-dwelling older adults with MCI and still work, whether directly through patient comprehension of the material or through the support of caregivers or family. The EMPOWER tool can and should be used in primary care or memory clinics for chronic benzodiazepine users who are candidates for deprescribing sedative-hypnotic medication.
References
Tannenbaum C, Paquette A, Hilmer S, Holroyd-Leduc J, Carnahan R. A systematic review of amnestic and non-amnestic mild cognitive impairment induced by anticholinergic, antihistamine, GABAergic and opioid drugs. Drugs Aging. 2012;29(8):639–58.
Billioti de Gage S, Moride Y, Ducruet T, Kurth T, Verdoux H, Tournier M, et al. Benzodiazepine use and risk of Alzheimer’s disease: case–control study. BMJ. 2014;349:g5205. Pubmed Central PMCID: PMC4159609. Epub 2014/09/12. eng.
AGS 2015 Beers Criteria Update Expert Panel. American geriatrics society 2015 updated beers criteria for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015;63(11):2227–46. Epub 2015/10/09. eng.
Sachs-Ericsson N, Blazer DG. The new DSM-5 diagnosis of mild neurocognitive disorder and its relation to research in mild cognitive impairment. Aging Ment Health. 2015;19(1):2–12.
Ward A, Arrighi HM, Michels S, Cedarbaum JM. Mild cognitive impairment: disparity of incidence and prevalence estimates. Alzheimers Dement. 2012;8(1):14–21.
Panza F, D’Introno A, Colacicco AM, Capurso C, Del Parigi A, Caselli RJ, et al. Current epidemiology of mild cognitive impairment and other predementia syndromes. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2005;13(8):633–44.
Okonkwo O, Griffith H, Belue K, Lanza S, Zamrini E, Harrell L, et al. Medical decision-making capacity in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Neurology. 2007;69(15):1528–35.
Okonkwo OC, Griffith HR, Copeland JN, Belue K, Lanza S, Zamrini E, et al. Medical decision-making capacity in mild cognitive impairment a 3-year longitudinal study. Neurology. 2008;71(19):1474–80.
Iliffe S, Curran HV, Collins R, Yuen Kee SC, Fletcher S, Woods B. Attitudes to long-term use of benzodiazepine hypnotics by older people in general practice: findings from interviews with service users and providers. Aging Ment Health. 2004;8(3):242–8. Epub 2004/06/19. eng.
Tannenbaum C, Martin P, Tamblyn R, Benedetti A, Ahmed S. Reduction of inappropriate benzodiazepine prescriptions among older adults through direct patient education: the EMPOWER cluster randomized trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2014;174(6):890–8.
Nasreddine ZS, Phillips NA, Bedirian V, Charbonneau S, Whitehead V, Collin I, et al. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005;53(4):695–9.
Martin P, Tamblyn R, Ahmed S, Tannenbaum C. A drug education tool developed for older adults changes knowledge, beliefs and risk perceptions about inappropriate benzodiazepine prescriptions in the elderly. Patient education and counseling. 2013. Epub 2013/04/02. Eng.
Couvee JE, Zitman FG. The benzodiazepine withdrawal symptom questionnaire: psychometric evaluation during a discontinuation program in depressed chronic benzodiazepine users in general practice. Addiction. 2002;97(3):337–45.
Horne R, Weinman J, Hankins M. The beliefs about medicines questionnaire: the development and evaluation of a new method for assessing the cognitive representation of medication. Psychol Health. 1999;14(1):1–24. PubMed PMID: Peer Reviewed Journal: 1999-05846-001. English.
Boyle PA, Yu L, Wilson RS, Gamble K, Buchman AS, Bennett DA. Poor decision making is a consequence of cognitive decline among older persons without Alzheimer’s disease or mild cognitive impairment. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43647.
Liew TM, Feng L, Gao Q, Ng TP, Yap P. Diagnostic utility of Montreal cognitive assessment in the fifth edition of diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: major and mild neurocognitive disorders. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2015;16(2):144–8.
Acknowledgments
We express gratitude to all the participants and pharmacists who took part in this trial. Particular thanks are offered to the Pharmacy Services Department of the Jean Coutu Group (PJC) Inc. for their collaboration and support.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the Canadian Health Research Institutes: CIHR grant id: CIHR-2009MOP-201314-KTE. The authors retained full independence from the study sponsors in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, and approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Availability of data and materials
Philippe Martin (Faculty of Pharmacy – University of Montreal & Centre de recherche de l’Institut universitaire de gériatrie) had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Patient level data and the full dataset are available upon reasonable request from the authors. Consent or data sharing was not obtained but the presented data are anonymised and the risk of identification is low.
Authors’ contribution
PM participated in the data analysis and interpretation and wrote the manuscript. CT designed the study, participated in the data interpretation and manuscript revision. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
Both authors declare: no support from any organisation for the submitted work; no financial relationships with any organisations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous 3 years, and no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work. Philippe Martin received a bursary from the Michel Saucier Endowed Chair in Pharmacology, Health and Aging of the Faculty of Pharmacy of the Université de Montréal and Cara Tannenbaum is a clinician scientist funded by the Fonds de Recherche en Santé de Quebec. Cara Tannenbaum has on occasion been an advisory board member and received speaker honoraria from Pfizer, Astellas, Allergen and Ferring pharmaceuticals in the past 5 years.
Consent for publication
Consent or data sharing was not obtained but the presented data are anonymised and the risk of identification is low.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Signed informed consent was obtained from all participants. The Research Ethics Board of the Centre de Recherche de l’Institut Universitaire de Gériatrie de Montreal approved the study protocol on July 26, 2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Martin, P., Tannenbaum, C. Use of the EMPOWER brochure to deprescribe sedative-hypnotic drugs in older adults with mild cognitive impairment. BMC Geriatr 17, 37 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-017-0432-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-017-0432-5