Abstract
Background
Although many patients still have anxiety about upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy, there have been few reports on the influence of distractions for a person who is going to undergo upper GI endoscopy soon. This study was a prospective randomized controlled study investigating the influence of distractions, such as auditive and visual distractions using subjective and objective assessments including autonomic nervous function prior to upper GI endoscopy.
Methods
206 subjects who underwent upper GI endoscopy as regular health check-ups were divided randomly into 4 groups prior to upper GI endoscopy; group 1 (control group), group 2 (auditive group), group 3 (visual group), and group 4 (combination group). We measured vital signs, autonomic nervous function, profile of mood state (POMS), and the impression for upper GI endoscopy pre- and post-distraction in the 4 groups.
Results
There was no significant difference in vital signs between 5 and 15 min after sitting in group 1, however, several vital signs in all distraction groups improved significantly after distraction (Pulse rate (P): p < 0.001 in group 4; blood pressure: p < 0.05 in group 2, 3, 4) and the rate of decrease in P and diastolic blood pressure was highest in group 4 (p < 0.001). Several scores of POMS and the impression for upper GI endoscopy post-distraction improved significantly compared to pre-distraction between distraction groups and the satisfaction for distraction was highest in group 4 (p < 0.01). Regarding autonomic nerve function, the low- frequency power/ high- frequency power ratio post-distraction was significantly lower than that pre-distraction in all distraction groups (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
Although auditive distraction alone and visual distraction alone were effective, a combination distraction was more effective than any other distraction by subjective and objective assessments. These distractions, which were simple and safe, may play an assistive role in the stability of physical and psychological conditions prior to upper GI endoscopy.
Trial registration
This trial was registered in the University Hospital Medical Information Network (UMIN) Clinical Trials Registry as UMIN000022801. Registered on 10 July 2016.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy has become an indispensable examination to discover upper GI lesion. However, many patients still have feelings of vulnerability, fear, and embarrassment regarding upper GI endoscopy [1, 2]. Strong anxiety before upper GI endoscopy may be a reason why some patients avoid undergoing upper GI endoscopy. Additionally, high levels of anxiety may induce displeasure and lead to incomplete procedures. Although the use of medication for sedation is known to reduce anxiety and pain in patients undergoing endoscopy examination or endoscopic procedures, sedation may increase the likelihood of complications such as hypotension and depression of respiration [3,4,5]. Therefore, various noninvasive interventions, such as listening to music, have been used to attempt to improve patients’ anxiety during endoscopic examination. Although there are several reports that have examined the effect of listening to music or watching images during various endoscopic procedures, the majority of these reports were concerned with decreasing the dose of sedation and improving tolerance for pain and anxiety [1, 6,7,8]. Additionally, there have been few reports on the influence of distractions for a subject who is going to undergo upper GI endoscopy soon using subjective and objective assessments including vital signs, autonomic nerve function, and psychological questionnaires. In this study, we performed a prospective randomized controlled trial to assess the influence of distractions, such as auditive and visual distractions, prior to upper GI endoscopy.
Methods
Subjects and study design
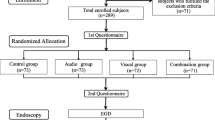
A flow chart of the enrollment and procedures of this study is shown in Fig. 1. Subjects included 250 individuals who underwent a regular health check-up including upper GI endoscopy at our hospital. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) attending a sedated upper GI endoscopy; (2) taking medicine; and (3) auditive and visual disability. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects prior to their participation by a representative of this study. The endoscopy nurse who assisted at upper GI endoscopy performed the randomization divide into 4 groups by selecting sealed, opaque envelopes. We conducted a prospective randomized controlled trial from August 2016 to March 2017 at Shikoku Central Hospital of the Mutual Aid Association of Public School teachers. The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee in Shikoku Central Hospital of the Mutual Aid Association of Public School teachers and this study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. This trial was registered in the University Hospital Medical Information Network (UMIN) Clinical Trials Registry as UMIN000022801.
Procedures of inspection
Participating subjects who were scheduled to receive upper GI endoscopy went to the endoscope floor after a more than 12 h fasting period, and were randomly divided into 4 groups. First, all subjects sat on a sofa and rested quietly for 5 min in a private room which was close to the endoscope room. Then, subjects in group 1 (control group) continued to sit on the sofa and rested quietly for 10 min prior to an upper GI endoscopy. Subjects in group 2 (auditive group) sat on the sofa while listening to music for 10 min. Subjects in group 3 (visual group) sat on the sofa while watching a silent natural image for 10 min. Subjects in group 4 (combination group) sat on the sofa and watched a natural image while listening to music for 10 min. The music used in this study was healing music such as country and classical based on the tone of a music box, and was chosen as good by 20 volunteers in the pre-meeting before the start of this study. The moving images used in this study were various natural images including a mountain, forest, river, waterfall, lake, and sunset. Music and natural images were supplied by using a wall-type Hi-vision liquid crystal television (TH-42AS650; Panasonic Corporation, Osaka Japan). And then, 3 endoscopy specialists who performed more than 180 upper GI endoscopy per month performed the endoscopic procedures after pharyngeal anesthesia with lidocaine pump spray (Xylocaine Pump Spray8%; AstraZeneca, Osaka, Japan) without any sedative agents.
Measurement of cardiovascular and respiratory responses
Pulse rate (P), systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), and peripheral blood oxygen saturation (SpO2) were measured using a monitor unit (BSM-7100 Life Scope; NIHON KOHDEN CORPORATION, Tokyo, Japan). P and blood pressure were measured at the right upper arm. SpO2 was measured at the left finger. The parameters were determined at 5 and 15 min after sitting on the sofa. Changes in each parameter were calculated using the following equation: (values after sitting on the sofa for 5 min) - (values after sitting on the sofa for 15 min).
Analysis of heart-rate variations
We measured heart rate variability (HRV) with a Heart Rhythm Scanner (HRV analysis system from Biocom Technologies, Ark Trading Pacific, Inc.) equipped with software that performs algorithms for short-term HRV analysis. Measurements were taken from subjects sitting on a sofa for 15 min in a private quiet room. A Biocom HRS − 08 Blue Tooth Wireless Pulse Wave Sensor, the photoplethysmography monitor used in this study, was clipped to the right earlobe to measure HRV for 15 min. We assessed autonomic nervous function while sitting on the sofa for 15 min by power spectral analysis (PSA). Data regarding the average R-R intervals for 5 min after sitting for 5 min and after sitting for 15 min were subjected to PSA using a software HRV analysis system. The amplitudes of the low-frequency range (LF, 0.04–0.15 Hz) and the high-frequency range (HF, 0.15–0.40 Hz) were analyzed by complex demodulation. The former was designated the low-frequency power (LF power), and the latter was designated the high-frequency power (HF power). The HF power represents the fluctuation in the heart rate caused by respiration, which is mediated by cardiac parasympathetic nervous activity [9, 10]. The ratio of LF power to HF power has been reported as an index of sympathetic nervous activity [9, 11, 12]. We converted HF power data to a logarithmic scale to make it possible to analyze with linear regression.
Profile of mood states (POMS) questionnaire
A shortened Japanese version of POMS (POMS2), adapted from the original POMS standard version, was used in this study. POMS is known to be a self-report measure that allows for quick assessment of transient, fluctuating feelings and enduring affect states [13, 14]. The POMS2 is composed of 35 items rated on a scale from 0 to 4, namely 0) “not at all,” 1) “a little,” 2) “moderately,” 3) “quite a bit,” and 4) “extremely”. The checklist items are comprised of 8 subscale scores: anger-hostility (A-H), confusion-bewilderment (C-B), depression-dejection (D-D), fatigue-languid (F-I), tension-anxiety (T-A), total mood distress (TMD), vigor-vitality (V-V), and friendship (F). All subjects completed the POMS scale to measure psychological well-being at baseline conditions (immediately after sitting on the sofa) and 15 min after sitting on the sofa.
Assessment of the impression for upper GI endoscopy
We investigated the impression for upper GI endoscopy at baseline conditions (immediately after sitting on the sofa) and 15 min after sitting on the sofa with distraction. We used questionnaires of the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) consisting of a 100-mm horizontal line that was scored from 0 (none) to 100 (strong) for the degree of strain, anxiety, and fear for upper GI endoscopy.
Impression of distraction after upper GI endoscopy
After upper GI endoscopy examination, we investigated the impression of distraction using the questionnaire about the satisfaction for distraction and the willing for the use of distraction at next upper GI endoscopy examination. We used questionnaires of VAS consisting of a 100-mm horizontal line that was scored from 0 (none) to 100 (strong satisfaction or willing).
Statistical analysis
We determined that the appropriate sample size for the randomized subjects was over 180 subjects. This was based on the requirement of a significant difference between 4 groups with a significance level of 0.05, power of 80%, and, effect size of 0.25. Additionally, we estimated that the required number of subject who receive upper GI endoscopy was over 250 in consideration of the exclusion criteria. This was based on the assumption of 25% that was the rate of subjects who fill exclusion criteria by referring to our previous prospective randomized trial on endoscopy. Baseline data, including subject characteristics such as age, number of upper GI endoscopy, POMS, VAS, P, blood pressure, and SpO2, are expressed as the means ± standard deviation (SD). Also, parameters of autonomic nervous function are expressed as the means ± standard error of the mean (SEM). All statistical differences at a p value less of than 0.05 were considered significant. The χ2-test or the Mann-Whitney U-test was used to compare between 2 groups or pre- and post-distraction in same group. The Kruskal Wallis-test or m × n χ2-test was used to compare among 3 or 4 groups. If the Kruskal Wallis-test show the difference in the groups, post-hoc pairwise comparisons were made using the Mann-Whitney U test with Bonferroni correction. All analyses were performed using Med Calc Software (Broekstraat, Mariakerke, Belgium).
Results
Characteristics of subjects
Subject characteristics are shown in Table 1. The proportion of males and females were 58.3% and 41.7%, respectively. The mean age was 51.8 ± 6.6 years. The mean number of upper GI endoscopy was 4.0 ± 3.4. The mean of P, SBP, DBP, and SpO2 was 65.2 ± 9.2 /min, 124.0 ± 15.9 mmHg, 80.1 ± 12.0 mmHg, and 98.2 ± 1.3%, respectively.
Comparison of baseline characteristics among the four groups
A comparison of the baseline characteristics among the 4 groups is shown in Table 2. There was no significant difference in gender, age, the frequency, and the duration of upper GI endoscopy among the 4 groups. There was no significant difference in the baseline score of POMS and the impression for upper GI endoscopy among the 4 groups.
Influence of distraction on vital signs
The comparison of vital signs between pre- and post-distraction among the 4 groups is shown in Fig. 2. P post-distraction was significantly lower than that pre-distraction in group 4 (p < 0.001). SBP and DBP post-distraction was significantly lower than that pre-distraction in group 2, group 3, and group 4 (p < 0.05, p < 0.05, and p < 0.005). There was no significant difference in SpO2 between pre- and post-distraction among the 4 groups. A comparison of the rate of decrease in vital signs between pre- and post-distraction among the 4 groups is shown in Table 3. There was a significant difference in the rate of decrease in P, SBP, and DBP among the 4 groups on the Kruskal Wallis-test (< 0.001). In post-hoc pairwise comparisons, the rate of decrease in P and DBP in group 4 was significantly higher than that in other 3 groups.
Comparison of vital signs between pre- and post-distractions in the 4 groups. a Comparison of P between pre- and post-distraction. b Comparison of SpO2 between pre- and post-distraction. c Comparison of SBP between pre- and post-distraction. d Comparison of DBP between pre- and post-distraction. The white bar indicates the value at pre-distraction. The gray bar indicates value at post-distraction. DBP, diastolic blood pressure; P, pulse; SBP, systolic blood pressure; SpO2, peripheral blood oxygen saturation; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.005; ***p < 0.001
Influence of distraction on autonomic nerve function
The comparison of autonomic nerve function between pre- and post-distraction among the 4 groups is shown in Fig. 3. There was no significant difference in Log HF power between pre- and post-distraction among the 4 groups. The LF power/ HF power ratio post-distraction was significantly lower than that pre-distraction in group 2, group 3, and group 4 (p < 0.001).
Comparison of autonomic nerve function between pre- and post-distraction among the 4 groups. a Comparison of Log HF power between pre- and post-distraction among the 4 groups. b Comparison of LF power/ HF power ratio between pre- and post-distraction among the 4 groups. The white bar indicates the value at pre-distraction. The gray bar indicates value at post-distraction. HF, high frequency; LF low frequency; *p < 0.001
Influence of distraction on POMS and the impression for upper GI endoscopy
The comparison of POMS and the impression for upper GI endoscopy between pre- and post-distraction among the 3 groups is shown in Table 4. The score of A-H, F-I, T-A, and TMD post-distraction was significantly lower than that pre-distraction in group 2 (p < 0.05, p < 0.05, p < 0.01, and p < 0.05). The score of C-B, D-D, F-I, T-A, and TMD post-distraction was significantly lower than that pre-distraction in group 3 (p < 0.05, p < 0.01, p < 0.05, p < 0.01, and p < 0.01). The score of C-B, D-D, F-I, T-A, and TMD post-distraction was significantly lower than that pre-distraction in group 4 (p < 0.05, p < 0.01, p < 0.01, p < 0.01, and p < 0.01). However, there was no significant difference in the score of positive mood between pre- and post-distraction among group 2, group 3, and group 4.
The VAS of anxiety for upper GI endoscopy post-distraction was significantly lower than that pre-distraction in group 2 (p < 0.05). The VAS of strain for upper GI endoscopy post-distraction was significantly lower than that pre-distraction in group 3 (p < 0.01). The VAS of strain, anxiety, and fear for upper GI endoscopy post-distraction was significantly lower than that pre-distraction in group 4 (p < 0.001, p < 0.05, and p < 0.05).
Impression of distraction after upper GI endoscopy
The comparison of the impression of distraction after upper GI endoscopy among the 3 distraction groups is shown in Table 5. The VAS of satisfaction for distraction in group 2, group 3, and group 4 was 62.7 ± 17.7, 63.4 ± 16.9, and 72.6 ± 19.1, respectively. There was a significant difference in the satisfaction for distraction among the 3 distraction groups on the Kruskal Wallis-test (< 0.01). In post-hoc pairwise comparisons, the satisfaction for distraction in group 4 was significantly higher than that in group 2 and group 3. The VAS of willingness for the use of distraction at next examination in group 2, group 3, and group 4 was 71.9 ± 16.6, 72.4 ± 20.2, and 76.4 ± 18.3, respectively, and although there was no significant difference among the 3 distraction groups, the VAS in all distraction groups was excellent in comparison.
Discussion
The aim of the present study was to investigate the influence of interventions using audio distractions, visual distractions, and the combination of auditive and visual distractions for a person who is going to undergo upper GI endoscopy soon. Although there have been several studies on auditive and visual effects using subjective assessments such as anxiety and satisfaction during various endoscopies [1, 3, 15,16,17,18,19,20,21], there have been few reports on the influence of distraction for a person who is going to undergo upper GI endoscopy soon using objective assessments such as autonomic nervous function. The present study demonstrated that, although auditive distraction alone and visual distraction alone improved psychological evaluation, cardiovascular responses, and some autonomic nervous function parameters prior to upper GI endoscopy, the combination of auditive and visual distractions may be more effective.
It has been reported that several distraction techniques based on visual, auditory, and olfactory stimulation were effective for the reduction of pain and anxiety during various medical inspections, care procedures, and treatments. In particular, music therapy has been used in a range of healthcare settings, including oncology, dementia, palliative care, and hospices [22, 23]. Recently, the positive effect of music for various different endoscopic procedures has been reported in several studies [1, 15, 24,25,26,27,28,29]. Kotwal MR et al. reported that there was a statistically significant effect of music on blood pressure and respiratory rate during gastroscopy between patients with and without music [24]. Bampton et al. reported that there was no significant difference in the overall tolerance score between the music group and the no-music group; however, a significantly higher proportion of patients described the experience of the GI endoscopic procedure as being at least moderately unpleasant in the no-music group [25]. The number of positive effect articles of music on anxiety levels for upper GI endoscopy may be slightly more than that of negative effect articles. The present study showed that the score in 4 items of POMS, blood pressure, and the LF power/HF power ratio immediately pre-upper GI endoscopy were significantly lower than that at baseline conditions in the music group.
Distraction due to visual stimulation has been used for various medical procedures [8, 30,31,32]. For example, visual stimulation using video glasses showed a hypoalgesic effect for experimental pain in a cold pressor test [30]. Also, there have been several studies on the influence of visual stimulation on colonoscopy. Umezawa et al. showed that there was no significant difference in the median anxiety score, median pain score, and SBP before, during, and after colonoscopy between the 2 groups watching a silent movie using a head-mounted display or only wearing the display; however, the median post-procedural satisfaction levels and the rate of wishing to use the same method for the next procedures in the subjects watching the silent movie was significantly higher than that in the subjects only wearing the display [32]. On the other hand, Lee DW et al. demonstrated that there was no significant difference in the dose of propofol for sedation and pain scores between 52 subjects with visual distraction and 53 subjects without visual distraction during colonoscopy [8]. The influence of visual distraction on colonoscopy has remained controversial, and to our knowledge, there has been no study of the influence of visual distraction for upper GI endoscopy. The present study showed that the scores of 5 items of POMS and strain level for upper GI endoscopy immediately pre-upper GI endoscopy were significantly lower than that at baseline conditions in the visual group. Additionally, blood pressure and the LF power/HF power ratio immediately pre-upper GI endoscopy were significantly lower than that at baseline conditions in the visual group.
To our knowledge, there have been 2 prospective randomized controlled trial studies investigating the influence of the combination of auditive and visual distractions on intestinal endoscopy examination [7, 8]. Lee DW et al. compared the influence of the combination of auditive and visual distractions with the influence of a visual distraction alone for sigmoidoscopy [8]. This study showed that the dose of propofol for sedation of sigmoidoscopy in 52 subjects with a combination of auditive and visual distractions was significantly lower than for 52 subjects with a visual distraction alone. However, there was no significant difference in the pain score, the satisfaction score, and the rate of willingness to repeat the same procedure for next examination between the 2 groups. On the other hand, Lembo et al. showed that the level of discomfort and anxiety during a flexible sigmoidoscopy in subjects with the combination of auditive and visual distractions group was lower than in the other 2 groups (no intervention group and audio distraction group) [7]. The present study showed that the score in 5 items of POMS, the impression for upper GI endoscopy, vital signs, and the LF power/HF power ratio immediately pre-upper GI endoscopy were significantly lower than that at baseline conditions in the combination group. Additionally, the decrease in the rate of P and DBP was significantly higher than in the other 3 groups. Also, the satisfaction for the distraction after upper GI endoscopy was highest in all distraction groups. The present study showed that the combination of auditive and visual distractions creates the most positive effect of all the distractions. Distraction may reduce anxiety by limiting attentional capacity, namely drawing attention away from upper GI endoscopy and induce an improvement of vital signs and psychological factors by stabilization of the balance of autonomic nervous function.
The present study had some limitations that should be noted. First, there was a possibility of different results between persons that undergo upper GI endoscopy for the first time and those repeating the upper GI endoscopy because the mean number of upper GI endoscopy in all subjects of the present study was 4 times. Further investigation of subjects who undergo upper GI endoscopy for the first time or comparison between persons who undergo upper GI endoscopy for the first time and repeat patients will be required. Second, there was the possibility of a selection bias, because all of the participants in the present study were healthy individuals who hoped to undergo a medical check-up. It is unclear whether results in sick persons or an elderly population would produce similar results to the present study. Further studies will be necessary to resolve these limitations.
Conclusions
The present study demonstrated that auditive distraction and visual distraction were effective, however, a combination of auditive and visual distraction was more effective than any other group according to subjective and objective appropriate evaluations. Although it is important for persons receiving upper GI endoscopy to discover GI lesions, it should be considered necessary to improve various physical and psychological conditions before upper GI endoscopy. The distractions in the present study, which were simple, safe, and low-cost, may play an important role in improving physical and psychological factors before upper GI endoscopy.
Abbreviations
- DBP:
-
Diastolic blood pressure
- GI:
-
Gastrointestinal
- HF:
-
High-frequency
- HRV:
-
Heart rate variability
- LF:
-
Low-frequency
- P:
-
Pulse
- POMS:
-
Profile of mood states
- PSA:
-
Power spectral analysis
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- SpO2 :
-
Peripheral blood oxygen saturation
- VAS:
-
Visual analog scale
References
El-Hassan H, McKeown K, Muller AF. Clinical trial: music reduces anxiety levels in patients attending for endoscopy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2009;30:718–24.
Brandt L. Patients’ attitudes and apprehensions about endoscopy: how to calm troubled waters. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96:280–4.
Froehlich F, Gonvers JJ, Fried M. Conscious sedation, clinically relevant complications and monitoring of endoscopy: results of a nationwide survey in Switzerland. Endoscopy. 1994;26:231–4.
Holm C, Christensen M, Rasmussen V, Schulze S, Rosenberg J. Hypoxaemia and myocardial ischaemia during colonoscopy. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1998;33:769–72.
Ko CW, Riffle S, Michaels L, Morris C, Holub J, Shapiro JA, et al. Serious complications within 30 days of screening and surveillance colonoscopy are uncommon. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;8:166–73.
Lee DW, Chan KW, Poon CM, Ko CW, Chan KH, Sin KS, et al. relaxation music decreases the dose of patient-controlled sedation during colonoscopy: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002;55:33–6.
Lembo T, Fitzgerald L, Matin K, Woo K, Mayer EA, Naliboff BD. Audio and visual stimulation reduces patient discomfort during screening flexible sigmoidoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93:1113–6.
Lee DW, Chan AC, Wong SK, Fung TM, Li AC, Chan SK, et al. Can visual distraction decrease the dose of patient-controlled sedation required during colonoscopy? A prospective randomized controlled trial. Endoscopy. 2004;36:197–201.
Pagani M, Lombardi F, Guzzetti S, Rimoldi O, Furlan R, Pizzinelli P, et al. Power spectral analysis of heart rate and arterial pressure variabilities as a marker of sympatho-vagal interaction in man and conscious dog. Circ Res. 1986;59:178–93.
Hayano J, Sakakibara Y, Yamada A, Yamada M, Mukai S, Fujinami T, et al. Accuracy of assessment of cardiac vagal tone by heart rate variability in normal subjects. Am J Cardiol. 1991;67:199–204.
Malliani A, Pagani M, Lombardi F, Cerutti S. Cardiovascular neural regulation explored in the frequency domain. Circulation. 1991;84:482–92.
Task force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Heart rate variability. Standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. Circulation. 1996;93:1043–65.
Kanbara K, Fukunaga M, Mutsuura H, Takeuchi H, Kitamura K, Nakai Y. An exploratory study of subgrouping of patients with functional somatic syndrome based on the psychophysiological stress response: its relationship with moods and subjective variables. Psychosom Med. 2007;69:158–65.
Terry PC, Lane AM, Lane HJ, Keohane L. Development and validation of a mood measure for adolescents. J Sports Sci. 1999;17:861–72.
Ovayolu N, Ucan O, Pehlivan S, Pehlivan Y, Buyukhatipoglu H, Savas MC, et al. Listening to Turkish classical music decreases patients’ anxiety, pain, dissatisfaction and the dose of sedative and analgesic drugs during colonoscopy: a prospective randomized controlled trial. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:7532–6.
López-Cepero Andrada JM, Amaya Vidal A, Castro Aguilar-Tablada T, García Reina I, Silva L, Ruiz Guinaldo A, et al. Anxiety during the performance of colonoscopies: modification using music therapy. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004;16:1381–6.
Chlan L, Evans D, Greenleaf M, Walker J. Effects of a single music therapy intervention on anxiety, discomfort, satisfaction, and compliance with screening guidelines in outpatients undergoing flexible sigmoidoscopy. Gastroenterol Nurs. 2000;23:148–56.
Palakanis KC, DeNobile JW, Sweeney WB, Blankenship CL. Effect of music therapy on state anxiety in patients undergoing flexible sigmoidoscopy. Dis Colon Rectum. 1994;37:478–81.
Hayes A, Buffum M, Lanier E, Rodahl E, Sasso C. A music intervention to reduce anxiety prior to gastrointestinal procedures. Gastroenterol Nurs. 2003;26:145–9.
Danhauer SC, Marler B, Rutherford CA, Lovato JF, Asbury DY, McQuellon RP, et al. Music or guided imagery for women undergoing colposcopy: A randomized controlled study of effects on anxiety, perceivedpain, and patient satisfaction. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2007;11:39–45.
Colt HG, Powers A, Shanks TG. Effect of music on state anxiety scores in patients undergoing fiberoptic bronchoscopy. Chest. 1999;116:819–24.
Ueda T, Suzukamo Y, Sato M, Izumi S. Effects of music therapy on behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res Rev. 2013;12:628–41.
Demmer C. A survey of complementary therapy services provided by hospices. J Palliative Medicine. 2004;7:510–6.
Kotwal MR, Rinchhen CZ, Ringe VV. Stress reduction through listening to Indian classical music during gastroscopy. Diagn Ther Endosc. 1998;4:191–7.
Bampton P, Draper B. Effect of relaxation music on patient tolerance of gastrointestinal endoscopic procedures. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1997;25:343–5.
Wang MC, Zhang LY, Zhang YL, Zhang YW, Xu XD, Zhang YC. Effect of music in endoscopy procedures: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pain Med. 2014;15:1786–94.
Costa A, Montalbano LM, Orlando A, Ingoglia C, Linea C, Giunta M, et al. Music for colonoscopy: a single-blind randomized controlled trial. Dig Liver Dis. 2010;42:871–6.
Uedo N, Ishikawa H, Morimoto K, Ishihara R, Narahara H, Akedo I, et al. Reduction in salivary cortisol level by music therapy during colonoscopic examination. Hepato-Gastroenterology. 2004;51:451–3.
Rudin D, Kiss A, Wetz RV, Sottile VM. Music in the endoscopy suite: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies. Endoscopy. 2007;39:507–10.
Bentsen B, Svensson P, Wezel A. The effect of a new type of video glasses on the perceived intensity of pain and unpleasantness evoked by a cold test. Anesth Prog. 1999;46:113–7.
van den Berg MM, Maas J, Muller R, Braun A, Kaandorp W, van Lien R, et al. Autonomic Nervous System Responses to Viewing Green and Built Settings: Differentiating Between Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Activity. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015;12:15860–74.
Umezawa S, Higurashi T, Uchiyama S, Sakai E, Ohkubo H, Endo H, et al. Visual distraction alone for the improvement of colonoscopy-related pain and satisfaction. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:4707–14.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all subjects in our study.
Funding
This work was supported by Japan Mutual Aid Association of Public School Teachers Grant-in-Aid for Occupational Research on Healthcare and Medical Treatment.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study will be available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MS study concept and design, data collection, statistical analysis, and writing of the draft manuscript, TO and MN study co-design, YA, JO, and KO: endoscopy, MT, SH, YF, AH, and KK data collection and data analysis, AF data collection and visualization, TT study co-design and review of the manuscript. All authors have approved the final version of the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects. The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee in Shikoku Central Hospital of the Mutual Aid Association of Public School teachers and this study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. This trial was registered in the University Hospital Medical Information Network (UMIN) Clinical Trials Registry as UMIN000022801.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Sogabe, M., Okahisa, T., Adachi, Y. et al. The influence of various distractions prior to upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: a prospective randomized controlled study. BMC Gastroenterol 18, 132 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-018-0859-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-018-0859-y