Abstract
Background
Even force distribution would generate efficient external chest compression (ECC). Little research has been done to compare force distribution between one-hand (OH) and two-handed (TH) during child ECC. Therefore, this study was to investigate force distribution, rescuer perceived fatigue and discomfort/pain when applying OH and TH ECC in children.
Methods
Crossover manikin study. Thirty-five emergency department registered nurses performed lone rescuer ECC using TH and OH techniques, each for 2 min at a rate of at least 100 compressions/min. A Resusci Junior Basic manikin equipped with a MatScan pressure measurement system was used to collect data. The perceived exertion scale (modified Borg scale) and numerical rating scale (NRS) was applied to evaluate the fatigue and physical pain of delivering chest compressions.
Results
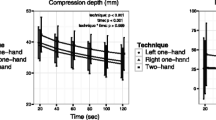
The maximum compression force (kg) delivered was 56.58 ± 13.67 for TH and 45.12 ± 7.90 for OH ECC (p < 0.001). The maximum-minimum force difference force delivered by TH and OH ECC was 52.24 ± 13.43 and 41.36 ± 7.57, respectively (p < 0.001). The mean caudal force delivered by TH and OH ECC was 29.45 ± 16.70 and 34.03 ± 12.01, respectively (p = 0.198). The mean cranial force delivered by TH and OH ECC was 27.13 ± 11.30 and 11.09 ± 9.72, respectively (p < 0.001). The caudal–cranial pressure difference delivered by TH and OH ECC was 19.14 ± 15.96 and 26.94 ± 14.48, respectively (p = 0.016). The perceived exertion and NRS for OH ECC was higher than that of the TH method (p < 0.001, p = 0.004, respectively).
Conclusions
The TH method produced greater compression force, had more efficient compression, and delivered a more even force distribution, and produced less fatigue and physical pain in the rescuer than the OH method.
Trial registration
The Cheng Kung University Institutional Review Board A-ER-103-387. http://nckuhirb.med.ncku.edu.tw/sitemap.php
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Child basic life support (BLS) guidelines are applicable to children from the age of approximately 1 year until puberty. When performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) on most children, either one or two hands can be used to compress the chest [1,2,3,4,5].
In pediatric manikin studies, two-handed (TH) external chest compression (ECC) will produce a greater compression depth, [6] larger intrathoracic pressure, [7] and less rescuer fatigue, [8] and insufficient recoil than one-handed (OH) ECC [6]. Peska et al. suggested TH has a better balance control [6]. A better balance control could be related to more even force distribution during ECC. Although even force distribution would produce effective resultant force, labor-saving, and to be easier and comfort for ECC, little research has been done to compare force distribution between OH and TH ECC.
ECC is a cyclic movement of compression and decompression. Different forces distribution across the rescuers’ hands were produced according to the different methods of chest compression [7]. This differences could further affect the performance of CPR. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to investigate force distribution, rescuer perceived fatigue and discomfort/pain when applying OH and TH ECC in children.
Methods
Study design
A randomized crossover study.
Participants
Thirty-five emergency department CPR-certified and registered nurses voluntarily participated in this study. Participants was professionals in first aid related work and had CPR certification. No participant had any muscular skeletal injury, sprain, or pain. Participants were not allowed to eat within 30 min of the tests. Consuming alcohol, tea, or coffee was prohibited on the days of the test. This simulation study was approved by the Cheng Kung University Institutional Review Board. All subjects provided written informed consent.
Equipment
A Resusci Junior Basic and SkillGuide manikin (Laerdal, Stavanger, Norway) was equipped with a MatScan pressure measurement system (Tekscan Inc., South Boston, USA), which was applied to a Junior Basic manikin and used to record the delivered force at a sampling frequency of 30 Hz. The MatScan consists of 2288 pressure sensors aligned in 44 rows and 52 columns, with a spatial resolution of 1.4 sensors/cm2. The sensors are paper thin, lightweight, and flexible. The system has displayed high accuracy and moderate to good reliability [8, 9].
The perceived exertion scale and numerical rating scale
Two subjective scales, the perceived exertion scale (modified Borg scale) and the numerical rating scale (NRS), were applied for rating the perceived fatigability of chest compression delivery and physical pain or discomfort, respectively.
The ratings of perceived exertion (RPE) were given using a modified Borg scale which had been validated to estimate the instantaneous fatigue status of the muscle in tasks [10]. It with scores ranging from 0 to 10, where, for example, 0 represents no fatigue at all, 3 represents moderate fatigued, 5 represents very fatigued, 7 represents nearly exhausted and 10 represents absolutely exhausted [10].
The NRS is an 11-point scale comprising a number from 0 through 10; 0 indicates “no pain”, and 10 indicates the “worst imaginable pain”. Patients were instructed to choose a single number from the scale that best indicates their level of pain [11].
In studies, the NRS and Borg scale have exhibited good validity and reliability [11,12,13,14].
Procedure
The participants practiced on manikins before they began the tests to familiar with CPR skill.
Each participant performed child BLS using both TH and OH ECC in random order using a computer-generated random table [15]. A lone rescuer administered compressions and ventilations at a ratio of 30:2, delivering compressions at a rate of at least 100 compressions/min. An audio prompt was used to keep participants on pace to deliver an adequate rate of compression, namely 110/min, and a visual prompt was used to keep participants on target to deliver a suitable compression depth [2]. To ensure the quality of chest compressions and mitigate the stress of coordinating ventilation and compression efforts, specific breaks were provided for performing ventilation [16]. A 4-s pause was added to replace ventilation between each set of 30 chest compressions to simulate the actual practice of CPR. Participants performed each technique of ECC for 2 min, with a rest period of 30 min between sessions [16]. The delivered force was recorded during 2 min ECC. Physiological parameters, including heart rate and blood pressure, of each participant were measured before and after each ECC session. At the end of every test of ECC delivery, the participants were asked to rate the RPE and NRS immediately.
Data analysis
During the 2-min CPR sessions, compression pressure was recorded. The maximum pressure, maximum and minimum force over the entire compression area, the cranial area, and the caudal area were calculated. The nipple line of the manikin separated the entire compression area into the cranial and caudal areas [7].
A sample size calculation was performed using G*Power [17] based on the results of a pilot study comprising eight subjects. We used the mean and SD of difference (3.25 ± 7.11 kg) of the primary outcome variable corresponding to the caudal-cranial force difference. A total sample size of 31 is required to achieve 80% power and the calculated effect size of 0.46 at an alpha level of 0.05. Considering a potential attrition rate of 10%, we concluded that 35 participants were necessary.
We used descriptive statistics to present outcome variables. The difference between the TH and OH techniques were analyzed using paired t-tests for continuous variables, or Wilcoxon signed rank test for continuous variables without normal distribution and ordinal variables. The significance level was set at p < 0.05. The data were analyzed using SPSS version 17 (SPSS Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
Results
Thirty-five CPR-certified RNs voluntarily participated in the study. Among them, 28 were women. The mean age of the rescuers was 27.8 ± 4.0 years, the mean height was 163.0 ± 7.4 cm, the mean weight was 61.4 ± 14.0 kg, and the mean CPR related work experience was 3.8 ± 3.5 years.
Pressure distribution
Figure 1 illustrates the hand position placement and pressure mapping of the palm in a sample of one person. Table 1 presents a summary of palm caudal pressure, cranial pressure, and the caudal–cranial pressure gradient exerted in the two methods. Significant differences between the two compression methods were evident in the pressure delivered to the cranial and caudal areas. The mean caudal pressure was 1.78 ± 0.64 kg/cm2 in TH ECC and 2.13 ± 0.56 kg/cm2 in OH ECC, with a mean difference (95% confidence interval [CI] of difference) of − 0.35 (− 0.59 to − 0.11), p = 0.006. The mean cranial pressure was 1.56 ± 0.65 kg/cm2 in TH ECC and 1.23 ± 0.77 kg/cm2 in OH ECC, with a mean difference (95% CI of difference) of 0.33 (0.33–0.64), p = 0.031. The paired comparison revealed that while the maximum pressure and caudal–cranial pressure differences were not significant, p = 0.227 and p = 0.083, respectively.
Force distribution
Table 2 presents the compression force delivered by the TH and OH methods. A paired comparison of maximum force indicates that the compression force delivered by the TH method was significantly higher than that delivered by the OH method (p < 0.001) and minimum (residual) force was not significant difference (p = 0.970). The Maximum-Minimum force difference presented the efficient compression force was the TH method was significantly higher than the OH method (p < 0.001). The caudal side force delivered in TH ECC was similar to that delivered in OH ECC (p = 0.198). The cranial side force delivered in TH ECC was greater than that in OH ECC (p < 0.001). TH ECC delivered a smaller caudal–cranial force than did OH ECC (p = 0.016). The results indicated that the compression method affects the force delivered and force distribution. The TH method produced more force, whereas the OH method produced a greater caudal–cranial force difference. This causes force to be distributed more toward the manikin’s head.
Rescuer physiological parameters before and after performing ECC
A comparison of physiological variables (Table 3) before and after administering ECC indicates that heart rate (HR) and systolic blood pressure (SBP) increased significantly in response to administering both ECC techniques. Diastolic blood pressure (DBP) and mean arterial pressure (MAP), however, did not change significantly within-group for either technique. Between-group differences in the changes in SBP, DBP, MAP, and HR were not significant (p = 0.385, p = 0.102, p = 0.576, and p = 0.653, respectively).
Subjective RPE, level of fatigue, and discomfort
Table 4 indicates that perceived exertion of administering TH ECC was lower than that of administering OH ECC. The median perceived exertion score for both TH and OH was 4.5 and 5. Two min of child ECC was considered a “heavy” exercise. The overall discomfort of performing TH and OH ECC, measured using the NRS, was 4 and 5, respectively (p = 0.008). Participants experienced pain or discomfort during the test, which was most frequently localized in the wrist. The incidence of wrist pain when performing TH and OH ECC was 58 and 80%, respectively. The intensity of wrist pain in TH and OH ECC, measured using the NRS, was 3 and 5, respectively (p = 0.004). The compression discomfort when performing TH and OH ECC, measured using the NRS, was 4 and 5, respectively (p = 0.003). No significant difference in decompression discomfort, measured using the NRS, was identified between the two groups (p = 0.680). In OH ECC, the hand used is prone to tiring, and thus, a rescuer is more likely to have hand and body discomfort.
Discussion
This study assessing the difference in OH and TH ECC as related to pressure generated and performer perception. Study participants performed child BLS by using TH and OH ECC at a standard compression rate and depth with audio and visual prompts. The results indicated that the compression method affects the force delivered and force distribution. The TH method produced more force, whereas the OH method produced a greater caudal–cranial force difference. This causes the force to be distributed more toward the manikin’s head, which might increase the risk of fractures during ECC [7, 18]. From the evaluation of the two methods of ECC currently recommended under BLS guidelines, When the providers performed high quality ECCs i.e. adequate ECC in rate, depth, and recoil based on audiovisual feedback, TH compression is superior to OH in delivering force and distributing pressure evenly over the Resusci Junior Basic manikin and also induces less fatigue and physical discomfort in rescuers. The results can be used as a reference for subsequent child ECC quality improvement and training.
Previous child manikin ECC studies have determined that participants appreciated the higher chest compression performance obtained and the lessened rescuer fatigue that result from applying the TH technique [6, 19]. Biomechanical studies further supports that ECC cyclic movement produces force distribution across the heel, and different chest interface contact approaches may influence compression force transmission during ECC [18, 20]., Another study indicated that TH ECC produces significantly higher mean and peak intrathoracic pressures than does OH ECC [19]. No significant difference in peak pressure was identified between the TH and OH methods in our study, but significant differences were apparent in the maximum force, maximum–minimum force difference, caudal pressure, cranial pressure, and caudal–cranial force differences between TH and OH ECC. A more ergonomic type of exertion can help to prevent fatigue and discomfort. That the even force distribution resulted in less fatigue might explain why the majority of participants preferred the TH compression technique [6, 19]. Several researchers have reported that TH ECC was considered to have incomplete chest recoil when compared to OH ECC [1, 21]. In our study, although the difference was not statistically significant, there was a trend that TH has greater residual force than OH. Nevertheless, greater efficient compression force (maximum-minimum force difference) indicated TH had larger compression force than OH. It suggests that TH has a superior efficient compression, which might be able to compensate the incomplete recoil.
The joint most commonly affected by pain among rescuers performing ECC was the wrist. This finding is consistent with previous studies [22,23,24]. Curran and colleagues determined that the wrist being cyclically in positions of hyperextension, ulnar deviation, and intercarpal supination during ECC may cause damage to the scapholunate ligament of a rescuer’s wrist [25]. Here, OH generated a lower maximum force but caused more wrist pain. Wrist pain may influence force of delivery of ECC or its quality; Peska et al. found that the compression rate decreases more quickly when the rescuer uses the OH technique [6]. Compared with TH ECC, we determined that OH ECC produces more uneven force and force distribution, which may also be a risk factor for wrist pain.
Limitations
This study has limitations. This is a manikin study, which may not reflect actual patients. The amount of force needed to move a fixed mannequin’s chest seems a great deal more than for an actual child so that the increased force able to be generated in this model may be too much and cause more fatigue than an actual patient. The choice of OH vs. TH is something ECC provider must consider in the 1–8 year old. This age gap represents a huge variation in chest wall size and recoil yet the measurements are done on one mannequin whose size likely more resembles the older child and so may not reflect the age group we often do one handed ECCs on—the younger child.
The authors compared measuring forces and pressures between two different methods of chest compression. However, there were no data on the performance of CPR such as average chest compression depth and rate, average ventilation volume and hands-off time (or chest compression fraction). Although comparisons of force or pressure between two different methods of chest compression are important, we should know whether the differences of pressure or force could affect the performance of CPR or not. As a result, we cannot determine whether the differences in the forces or pressures could affect the quality of CPR. We did not measure the performance of CPR. However, to ensure that the pressure distribution is observed under comparable condition and qualities, we provided visual and auditory feedbacks during ECC. Previous studies found real-time feedbacks may serve as a useful adjunct to guide the compression depth for rescuers during ECC [7, 26]. Our results may not be generalizable to other ECC providers especially given the small number of participants, mostly female which would make it hard to assess for confounders like gender, size, height.
Conclusions
Our biomechanical analysis indicated that TH ECC delivers a smoother force, more even pressure distribution and more efficient compression while inducing less fatigue and discomfort/pain in the rescuer than does OH child ECC. If possible, TH should be applied rather than OH for child ECC during CPR to optimize biomechanical efficiency and rescuer comfort.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Change history
01 September 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12873-022-00702-9
Abbreviations
- BLS:
-
Basic life support
- CPR:
-
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
- OH:
-
One-handed
- TH:
-
Two-handed
- ECC:
-
External chest compression
- NRS:
-
Numerical rating scale
- RPR:
-
Ratings of perceived exertion
- HR:
-
Heart rate
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- DBP:
-
Diastolic blood pressure
- MAP:
-
Mean arterial pressure
References
Atkins DL, Berger S, Duff JP, Gonzales JC, Hunt EA, Joyner BL, et al. Part 11: pediatric basic life support and cardiopulmonary resuscitation quality: 2015 American Heart Association guidelines update for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Circulation. 2015;132(18 Suppl 2):S519–25. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000265.
Berg MD, Schexnayder SM, Chameides L, Terry M, Donoghue A, Hickey RW, et al. Part 13: pediatric basic life support: 2010 American Heart Association guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Circulation. 2010;122(18 Suppl 3):S862–75. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.971085.
Maconochie IK, de Caen AR, Aickin R, Atkins DL, Biarent D, Guerguerian AM, et al. Part 6: Pediatric basic life support and pediatric advanced life support: 2015 International consensus on cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care science with treatment recommendations. Resuscitation. 2015(95):e147–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resuscitation.2015.07.044.
American Heart Association: Part 5. BLS for Infants and Children. . In: Basic Life Support (BLS) Provider Manual 1 Rfc Pap/ edition edn.: Amer Heart Assoc; ; 2016: 45–56.
Topjian AA, Raymond TT, Atkins D, Chan M, Duff JP, Joyner BL Jr, et al. Part 4: Pediatric Basic and Advanced Life Support: 2020 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Circulation. 2020;142(16_suppl_2):469–523. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000901.
Peska EKA, Kerr D, Green D. One-handed versus two-handed chest compressions in paediatric cardio-pulmonary resuscitation. Resuscitation. 2006;71(1):65–9 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0300957206000876.
Tsou JY, Kao CL, Hong MY, Chang CJ, Su FC, Chi CH. How does the side of approach impact the force delivered during external chest compression? Am J Emerg Med. 2021;48:67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2021.03.085.
Giacomozzi C. Appropriateness of plantar pressure measurement devices: a comparative technical assessment. Gait Posture. 2010;32(1):141–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2010.03.014.
Zammit GV, Menz HB, Munteanu SE. Reliability of the TekScan MatScan(R) system for the measurement of plantar forces and pressures during barefoot level walking in healthy adults. J Foot Ankle Res. 2010;3(3):11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1757-1146-3-11.
Whittaker RL, Sonne MW, Potvin JR. Ratings of perceived fatigue predict fatigue induced declines in muscle strength during tasks with different distributions of effort and recovery. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2019;47:88–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelekin.2019.05.012.
Bijur PE, Latimer CT, Gallagher EJ. Validation of a verbally administered numerical rating scale of acute pain for use in the emergency department. Acad Emerg Med. 2003;10(4):390–2. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1553-2712.2003.tb01355.x.
Grant S, Aitchison T, Henderson E, Christie J, Zare S, McMurray J, et al. A comparison of the reproducibility and the sensitivity to change of visual analogue scales, Borg scales, and Likert scales in normal subjects during submaximal exercise. Chest. 1999;116(5):1208–17. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.116.5.1208.
Ferreira-Valente MA, Pais-Ribeiro JL, Jensen MP. Validity of four pain intensity rating scales. Pain. 2011;152(10):2399–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2011.07.005.
Dedering A, Hjelmsater MRA, Elfving B, Harms-Ringdahl K, Nemeth G. Between-days reliability of subjective and objective assessments of back extensor muscle fatigue in subjects without lower-back pain. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2000;10(3):151–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1050-6411(00)00009-2.
Kim J, Shin W. How to do random allocation (randomization). Clin Orthop Surg. 2014;6(1):103–9. https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.1.103.
Tsou JY, Kao CL, Chang CJ, Tu YF, Su FC, Chi CH. Biomechanics of two-thumb versus two-finger chest compression for cardiopulmonary resuscitation in an infant manikin model. Eur J Emerg Med. 2020;27(2):132–6. https://doi.org/10.1097/MEJ.0000000000000631.
Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang AG, Buchner A. G*power 3: a flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav Res Methods. 2007;39(2):175–91. https://doi.org/10.3758/bf03193146.
Baubin M, Kollmitzer J, Pomaroli A, Kraincuk P, Kranzl A, Sumann G, et al. Force distribution across the heel of the hand during simulated manual chest compression. Resuscitation. 1997;35(3):259–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0300-9572(97)00040-3.
Stevenson AG, McGowan J, Evans AL, Graham CA. CPR for children: one hand or two? Resuscitation. 2005;64(2):205–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resuscitation.2004.07.012.
Haid C, Rabl W, Baubin M. Active compression-decompression resuscitation: the influence of different chest geometries on the force transmission. Resuscitation. 1997;35(1):83–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0300-9572(97)01104-0.
Kim MJ, Lee HS, Kim S, Park YS. Optimal chest compression technique for paediatric cardiac arrest victims. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2015;23(1):36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13049-015-0118-y.
Chi CH, Tsou JY, Su FC. Effects of rescuer position on the kinematics of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and the force of delivered compressions. Resuscitation. 2008;76(1):69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resuscitation.2007.06.007.
Trowbridge C, Parekh JN, Ricard MD, Potts J, Patrickson WC, Cason CL. A randomized cross-over study of the quality of cardiopulmonary resuscitation among females performing 30: 2 and hands-only cardiopulmonary resuscitation. BMC Nurs. 2009;8(1):6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6955-8-6.
Neset A, Birkenes TS, Myklebust H, Mykletun RJ, Odegaard S, Kramer-Johansen J. A randomized trial of the capability of elderly lay persons to perform chest compression only CPR versus standard 30:2 CPR. Resuscitation. 2010;81(7):887–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resuscitation.2010.03.028.
Curran R, Sorr S, Aquino E. Potential wrist ligament injury in rescuers performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation. J Emerg Trauma Shock. 2013;6(2):123–5. https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-2700.110776.
Abella BS, Edelson DP, Kim S, Retzer E, Myklebust H, Barry AM, et al. CPR quality improvement during in-hospital cardiac arrest using a real-time audiovisual feedback system. Resuscitation. 2007;73(1):54–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resuscitation.2006.10.027.
Acknowledgments
This manuscript was edited by Wallace Academic Editing. In addition, the authors would like to thank Huan-Ling Hsu and Yi-Chen Li for their research assistance.
Funding
Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan for financially supporting this research under contract No. MOST 104–2314-B-006-010-.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JYT and CLK contributed equally to the work. JYT: Methodology, data curation, formal analysis, writing original draft, review & editing. CLK: Investigation, data curation, writing - review & editing. YFT and MYH: Writing - review & editing. FCS: Project administration, writing - review & editing. CHC: Conceptualization, methodology, supervision, writing original draft, review & editing, funding acquisition. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This simulation study was approved by the Cheng Kung University Institutional Review Board (IRB No. A-ER-103-387). All subjects provided written informed consent.
Consent for publication
All authors agreed to the publication of this manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors have no Competing interest relevant to this article to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Tsou, JY., Kao, CL., Tu, YF. et al. Biomechanical analysis of force distribution in one-handed and two-handed child chest compression- a randomized crossover observational study. BMC Emerg Med 22, 13 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12873-022-00566-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12873-022-00566-z