Abstract
Background
Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR), such as Bradyrhizobium japonicum IRAT FA3, are able to improve seed germination and plant growth under various biotic and abiotic stress conditions, including high salinity stress. PGPR can affect plants’ responses to stress via multiple pathways which are often interconnected but were previously thought to be distinct. Although the overall impacts of PGPR on plant growth and stress tolerance have been well documented, the underlying mechanisms are not fully elucidated. This work contributes to understanding how PGPR promote abiotic stress by revealing major plant pathways triggered by B. japonicum under salt stress.
Results
The plant growth-promoting rhizobacterial (PGPR) strain Bradyrhizobium japonicum IRAT FA3 reduced the levels of sodium in Arabidopsis thaliana by 37.7%. B. japonicum primed plants as it stimulated an increase in jasmonates (JA) and modulated hydrogen peroxide production shortly after inoculation. B. japonicum-primed plants displayed enhanced shoot biomass, reduced lipid peroxidation and limited sodium accumulation under salt stress conditions. Q(RT)-PCR analysis of JA and abiotic stress-related gene expression in Arabidopsis plants pretreated with B. japonicum and followed by six hours of salt stress revealed differential gene expression compared to non-inoculated plants. Response to Desiccation (RD) gene RD20 and reactive oxygen species scavenging genes CAT3 and MDAR2 were up-regulated in shoots while CAT3 and RD22 were increased in roots by B. japonicum, suggesting roles for these genes in B. japonicum-mediated salt tolerance. B. japonicum also influenced reductions of RD22, MSD1, DHAR and MYC2 in shoots and DHAR, ADC2, RD20, RD29B, GTR1, ANAC055, VSP1 and VSP2 gene expression in roots under salt stress.
Conclusion
Our data showed that MYC2 and JAR1 are required for B. japonicum-induced shoot growth in both salt stressed and non-stressed plants. The observed microbially influenced reactions to salinity stress in inoculated plants underscore the complexity of the B. japonicum jasmonic acid-mediated plant response salt tolerance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The impacts of abiotic stress factors, e.g. salt, are far-reaching with respect to crop production [1]. Excessive salt causes oxidative and osmotic stress, induces production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), reduces the photosynthetic rate, affects normal plant development, interferes with ionic balances and nutrient availability and alters soil pH, water availability and microbial diversity [2]. Methods employed to reduce soil salinity include soil flushing, liming, plant breeding and genetic engineering of salt tolerant crops [3]. Such methods have had limited success, are time consuming, expensive and can cause genetic erosion of indigenous crops species [3].
In order to cope with abiotic stress, plants employ several physical structures, e.g., a cuticle layer to reduce moisture loss and shield against incoming stressors [1] and regulatory molecular mechanisms [2, 4]. Abiotic stress alters cell homeostasis and increases production of ROS [5, 6]. Plants counter the increase in ROS through their defense mechanisms, which involve antioxidants and ROS-scavenging enzymes [4,5,6]. These enzymes include superoxide dismutase (SOD), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPX) and peroxiredoxin (PrxR) [7, 8]. The Salt Overly Sensitive (SOS) pathway has also been shown to play a role in mediating ionic homeostasis at the cellular level in Arabidopsis [7].
Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) are known to alleviate various abiotic and biotic stresses that plants may encounter [9, 10]. Some PGPR have been reported to increase the expression of antioxidant enzymes in plants under salt stress, e.g. Dietzia natronolimnaea STR1 in wheat [9]. Bradyrhizobium japonicum strains and other PGPR have been reported to enhance plant growth and productivity [8, 11], to induce production of phytohormones such as indole-3-acetic acid, zeatin, gibberellic acid, ethylene and abscisic acid [12], and to promote tolerance to drought [8] and salinity [9].
PGPR microbe-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs), and their specific cognate plant receptors, have evolved to elicit a more transient and less robust plant response than that provoked by pathogenic microbial MAMPs [13]. The plant response to PGPR MAMPs has been shown to include extracellular alkalinization, a cellular Ca2+ increase, oxidative burst and up-regulation of pathogenesis-related genes [13, 14]. Oxidative burst is the rapid production of ROS, i.e., molecules such as superoxide (O2−) or hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), that can react with a wide range of biomolecules resulting in signal transduction or cellular damage [15]. ROS-mediated signaling is associated with the regulation of various biological processes, including biotic and abiotic stress responses [4, 6, 13]. In Vinus vinifera cells treated with a PGPR MAMP, the oxidative burst and typical defense marker gene induction were observed to be weaker and more transient than those elicited by pathogen MAMPs [13]. These plant responses to a PGPR MAMP were indicative of the onset of priming, as further evidenced by a significant reduction in disease when leaves were subsequently challenged with a necrotrophic fungus [13, 16].
Inoculation of plants by PGPR induces a physiological state in which plants are potentiated for defense responses and have an enhanced resistance to abiotic stress [6]. Several PGPR have been assessed with regard to salt stress amelioration and have been found to help plants overcome mild salt stress [9, 17]. Inoculating wheat crops with Arthrobacter protophormiae and D. natronolimnaea resulted in increased shoot and root weight and length under salt stress [9]. Treatment of plants with PGPR has been shown to increase salt tolerance through the SOS pathway [9, 17]. Several factors have been shown to prime plants e.g. salicylic acid (SA), SA synthetic analogs, abscisic acid (ABA), pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), PGPR, plant growth promoting fungi (PGPF), and certain chemicals [18, 19]. Priming by PGPR has been extensively studied in association with induced systemic resistance (ISR), where pretreatment of plants with PGPR reduces disease in the plant [16]. ISR induction in Arabidopsis by the PGPR Pseudomonas fluorescens WCS417r has been shown to act through the jasmonic acid (JA) and ethylene (ET) signaling pathways [20]. However, this induced systemic resistance was not accompanied by induction of JA or ET production in the primed plants [21]. ISR induced by the PGPR Bacillus subtilis GB03 is independent of SA, JA pathways, but requires ET signaling [22]. Nevertheless, B. subtilis GB03 significantly up-regulated defense mechanisms mediated by SA and JA, indicating that the mechanism of ISR can vary among different PGPR.
Limited information is available on the genetic mechanisms through which PGPR stimulate salt tolerance. In our previous studies we observed that B. japonicum altered root architecture by regulating auxin transporters [23] and improved drought stress tolerance [8] and therefore we decided to investigate its role in salt stress tolerance. The objective of this study was to determine how B. japonicum affects the salt stress response of Arabidopsis and to uncover the molecular mechanism involved. Our results indicate that B. japonicum IRAT FA3 improves tolerance to salt stress by impacting biomass, root architecture, oxidative stress, and transcriptional regulation of stress response pathways. We found that B. japonicum induced tolerance against salt stress through modulation of jasmonic acid production and JA responsive genes, ROS, and upregulation of salt stress-related Responsive to Desiccation (RD) genes.
Results
Bradyrhizobium japonicum IRAT FA3 affects Arabidopsis shoot and root growth under salt stress
Experimental parameters were determined using wild type, Col-0, Arabidopsis seedlings grown on agar plates with and without additional sodium chloride (NaCl, salt) (Supplementary Fig. S1). Shoot weight significantly decreased in plants when 100 mM NaCl was added to the growth medium, while the 200 mM concentration was plant-lethal (Supplementary Fig. S1A). When we assayed for the number of B. japonicum colony forming units (CFU) in liquid culture under salt stress, we observed that addition of NaCl to the liquid culture at a final concentration of 100 mM had no significant effect on the number of CFUs when compared to the rate in commercially available LB (Supplementary Fig. S2A). However, 200 mM and 300 mM significantly impacted bacterial growth. No significant differences in the root colonization of Arabidopsis by B. japonicum were observed between control and plants treated with 100 mM NaCl (Supplementary Fig. S2B). Therefore, 100 mM NaCl was determined to be an appropriate concentration for salt stress treatment in this study.
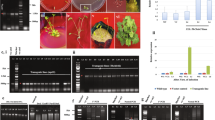
Plant growth and development was reduced by high salinity, but co-cultivation with B. japonicum minimized the effects of salt stress (Fig. 1A, B). B. japonicum mitigation of salt stress effects varied with the growth parameter measured. In B. japonicum-inoculated plants, high salinity significantly reduced shoot weight and root weight but not root length (Fig. 1B-D). The B. japonicum-stimulated increase in shoot weight was observed in non-stressed and salt-stressed plants (Fig. 1B). However, B. japonicum did not increase root weight compared to uninoculated control plants under salt (Fig. 1C). Salt stress played a significant role in contributing to root biomass reduction. Salinity stress also shortened primary root growth by 22% in non-inoculated plants, to lengths matching those of inoculated no-stress plants (Fig. 1D). However, the new root growth in B. japonicum treated roots was not significantly different in non-stressed and salt stressed plants (Fig. 1D). Relative to uninoculated plants, B. japonicum co-cultivation significantly decreased the primary root growth by 37% under non-stress conditions (Fig. 1D).
Effects of B. japonicum on plant growth under salt stress. Arabidopsis developmental phenotypes were analyzed in response to salt stress, in the presence (inoculated) or absence (non-inoculated) of B. japonicum. A Representative images of whole seedlings display root growth differences, while graphs show (B) shoot biomass, (C) root biomass, and (D) new primary root growth comparisons between treatments. Measurements of (E) total chlorophyll and (F) malondialdehyde (MDA) (G) sodium (ppm) content in the shoot tissue of Arabidopsis after fourteen days of co-cultivation with B. japonicum and seven days of salt (100 mM NaCl) stress or control treatment. Data are the mean ± standard error with different letters indicating significant differences. Scale bars indicate 1.3 cm; ANOVA-Tukey, p < 0.05
B. japonicum decreased lipid peroxidation under salinity stress while chlorophyll content remained unaffected.
Surprisingly, inoculating plants with B. japonicum did not alter the chlorophyll content in non-stressed and salt stressed plants. High salinity significantly decreased chlorophyll content in both B. japonicum-inoculated and non-inoculated plants by nearly 30% (Fig. 1E) indicating that chlorophyll production and possibly photosynthesis were negatively impacted by salt stress in both inoculated and non-inoculated plants. MDA is a byproduct of lipid peroxidation and the degree of lipid peroxidation in tissues can be estimated by the amount of MDA present [24]. MDA is the dominant compound measured with the thiobarbituric acid reactive substances test (TBAR), in which the lipid peroxidation products react with thiobarbituric acid (TBA) to yield a pink chromagen called TBARS [25]. In our study, MDA increased by 46.8% under high salinity in non-inoculated plants (Fig. 1F). B. japonicum inoculation significantly lowered the lipid peroxidation indicator under both non-stressed and salt stress conditions relative to uninoculated plants (Fig. 1F), indicating that B. japonicum plays a role in alleviating oxidative stress caused by high salinity.
B. japonicum decreases sodium accumulation in plants.
Measurement of the total sodium content revealed no significant differences between inoculated and uninoculated plants under normal conditions. However, B. japonicum inoculation significantly reduced sodium accumulation under salt stress. In co-inoculated plants grown on 100 mM NaCl for fourteen days, B. japonicum reduced total sodium levels in whole plant tissue by 37.7% relative to the uninoculated salt-stressed plants (Fig. 1G).
B. japonicum influences H2O2 levels and RBOH gene expression in Arabidopsis
B. japonicum-inoculated plants exhibited a 22% increase in H2O2 content in shoot tissue at 0.5 h post inoculation (hpi) compared to non-inoculated plants (Fig. 2A). Levels of H2O2 in B. japonicum- inoculated plants were not significantly different from levels in the control plants between 3–12 hpi. At 3 days post inoculation (dpi) the H2O2 levels in the shoots of B. japonicum-inoculated plants decreased by 27%. In the roots, no significant differences in H2O2 levels were seen between inoculated and non-inoculated plants, except at 3 dpi when the levels were significantly lower in B. japonicum-co-cultivated plants (Fig. 2B). The fluctuations of H2O2 observed in the non-inoculated plants can be attributed to the natural fluctuations patterns that are dependent on an intrinsic circadian rhythm.
Arabidopsis H2O2 levels and RBOH gene expression in response to B. japonicum. H2O2 levels in (A) shoot and (B) root tissues of B. japonicum-inoculated and non-inoculated plants at time points ranging from 0.5 h (hr) to 3 days (d). Data are the mean ± standard error with different letters representing significant differences; ANOVA, Tukey, p < 0.05. Arabidopsis(C) RBOHD, (D) RBOHE and (E) RBOHF gene expression in whole plant tissue at 3, 6 and 9 h post inoculation (hpi) after co-cultivation with B. japonicum. qRT-PCR measurements indicate mean expression levels relative to the IPP2 reference gene ± standard error with asterisks representing significant differences from the corresponding control; Student’s t-Test, p < 0.05
Several studies have shown that early plant responses to PGPR can include Respiratory Burst Oxidase Homolog (RBOH) gene expression that leads to ROS production [26, 27]. RBOHD, RBOHE and RBOHF are known to be expressed in response to biotic and abiotic stress [27, 28]. Gene expression analysis after B. japonicum inoculation revealed significant increases in RBOHE and RBOHF expression at 3, 6 and 9 hpi, and in RBOHD at 6 and 9 hpi, relative to non-inoculated plants (Fig. 2CDE). Elevated RBOH expression indicated that B. japonicum stimulated ROS production in the plants soon after inoculation. Increase in H2O2 production results in priming of plants against biotic and biotic stress [13, 16].
B. japonicum differentially affects ROS scavenging enzymes under salinity stress.
We determined the expression of genes encoding ROS scavenging enzymes six hours after high salinity (100 mM NaCl) treatment, which was preceded by one week of co-cultivation with B. japonicum. The antioxidant enzymes, Manganese Superoxide Dismutase 1 (MSD1, At3g10920), Catalase 3 (CAT3, At1g20620), Ascorbate Peroxidase 1 (APX1, At1g07890), Dehydroascorbate Reductase (DHAR, At1g19570), and Monodehydroascorbate Reductase 2 (MDAR2, At5g03630), are involved in scavenging excess hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in the cell [5, 6, 29]. Salt stress increased H2O2 production in plants (data not shown). In non-inoculated plants, salt stress reduced CAT3 and MDAR2 and increased MSD1 expression in root tissue and DHAR expression in shoot tissue. Salt stress had no effect on CAT3, MDAR2, or MSD1 expression in shoot tissue or on DHAR in root tissue (Fig. 3). These results corroborated the data by Kilian et al. (2007) [30]. Under salt stress, B. japonicum increased the expression of CAT3 in roots and shoots, relative to non-inoculated plants (Fig. 3). B. japonicum co-cultivation also influenced MDAR2 and MSD1 expression in shoots under salt stress, increasing and decreasing each, respectively (Fig. 3). APX1 expression was not significantly altered by salt stress or bacterial co-cultivation (Fig. 3). Antioxidant expression levels were largely similar between all B. japonicum inoculated (non-stressed and salt-stressed) plants, with the exception of CAT3 and MDAR2 in shoots (Fig. 3). Under non-stressed conditions, B. japonicum downregulated the expression of MSD1 in shoot tissue and DHAR in root tissue. Conversely, B. japonicum upregulated MSD1 gene expression in root tissue. These data indicate that ROS regulation in response to salt stress and B. japonicum inoculation is complex. B. japonicum’s influence under non-stressed condtitions varied depending on the gene and plant tissue. Some B. japonicum-driven changes in gene expression were only present under salinity stress as in the case of CAT3, MDAR2, and DHAR in shoot tissue and CAT3 root tissue. Interestingly, the expression of MSD1 and MDAR2 in shoots and roots after B. japonicum treatment followed the same trend as after salt stress.
Transcriptional levels of the hydrogen peroxide detoxifying enzymes after B. japonicum inoculation and salt treatment. Plants were inoculated with B. japonicum and after 7 days they were treated with 100 mM NaCl for 6 h before sample collection. qRT-PCR analysis of ROS scavenging enzymes from non-inoculated and B. japonicum-inoculated root tissue, with and without 100 mM NaCl treatment in (A) shoot and (B) root tissues. Graphs show expressions of Dehydroascorbate Reductase 1 (DHAR1), Catalase 3 (CAT3), Monodehydroascorbate Reductase 2 (MDAR2), Ascorbate Peroxidase 1 (APX1) and Manganese Superoxide Dismutase (MSD1) relative to the IPP2 reference gene ± standard error, with different letters representing significant differences separately for each gene, ANOVA, Tukey, p < 0.05
B. japonicum induces jasmonate production in Arabidopsis
We measured jasmonate (JA) (Fig. 4) and abscisic acid (ABA) (Supplementary Fig. S3) levels in plants with and without B. japonicum-cocultivation, for up to 6 h, using liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LCMS).
B. japonicum influences jasmonate production in Arabidopsis. Arabidopsis seedlings were treated with B. japonicum (inoculated) or 10 mM MgSO4 (non-inoculated) for up to 6 h. (A) JA 151, (B) JA 133, (C) jasmonoyl-isoleucine (JA-Ile) and (D) JA precursor 12-oxophytodienoic acid (OPDA) levels were measured by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LCMS). Graphs show mean data ± standard error with asterisks representing significant differences from the corresponding non-inoculated control; Student’s t-test, p < 0.05
Treatment with B. japonicum led to increased production of jasmonates: JA-isoleucine (JA-Ile), 12-oxophytodienoic acid (OPDA), and JA 151 and JA 133 (prominent mass spectra peaks that are characteristic of methyl jasmonate in mass spectrometry) [30, 31] in plants at 0.5 and 6 hpi (Fig. 4). B. japonicum induced an increase in JA soon after inoculation and then lowered it to the levels found in uninoculated plants. All jasmonates were significantly higher in B. japonicum-inoculated plants at 6 hpi except for OPDA levels, which dropped to below those in non-inoculated plants after 1 hpi. ABA production was not altered by B. japonicum co-cultivation (Supplementary Fig. S3).
After observing the B. japonicum-induced increase in jasmonate production, we decided to determine the expression of key JA pathway genes, JAR1 and MYC2. JAR1 (At2g46370) encodes a jasmonoyl-isoleucine synthetase that catalyzes the formation of JA-Ile [32] while MYC2 (At1g32640) is a major hub in jasmonate signaling pathways, a regulator of ISR, and a regulator of crosstalk between ABA, JA, salicylic acid, and auxin pathways during plant development [33,34,35]. Although no statistically significant differences were observed in JAR1 and MYC2 expression levels between inoculated and non-inoculated plants at 0.5 hpi, a slight up-regulation of MYC2 was apparent (Fig. 5).
Early JA-related gene expression in response to B. japonicum co-cultivation. Arabidopsis seedlings treated with B. japonicum (inoculated) or 10 mM MgSO4 (non-inoculated) for 0.5 h. Graphs show expression of JAR1 and MYC2 in (A) shoot (JAR1; p = 0.332; MYC2; p = 0.112) and (B) root (JAR1; p = 0.504; MYC2; p = 0.070) tissues. Mean expression relative to the IPP2 reference gene ± standard error. Student's t-Test, p < 0.05
Although inoculation of Col-0 with B. japonicum increased shoot weight under salt and non-salt conditions, inoculation of jar1 mutants with B. japonicum did not lead to significantly increased root or shoot growth under non-stressed conditions or any amelioration under salt stress (Fig. 6A and B). However, salt stress significantly reduced the fresh weight of Col-0 roots compared to those of jar1. This data indicates that JAR1 plays a role in B. japonicum-induced growth under abiotic stress. In the shoots of myc2 mutants, inoculation with B. japonicum resulted in a trend similar to the control in non-stressed conditions. However, under salt stress, there was no significant difference between the inoculated and non-inoculated myc2 mutant plants (Fig. 6C). These data investigated that the PGPR-induced increase in biomass was absent in both jar1 and myc2 plants, indicating that functional MYC2 and JAR1 are needed for B. japonicum to trigger the shoot biomass increase under salt stress.
Shoot and root weight of jar1 and myc2 mutants compared with the Col-0 with and without B. japonicum under salt stress. A Shoot biomass of Col-0 and jar1, B root biomass of Col-0 and jar1, C shoot biomass of Col-0 and myc2, and D root biomass of Col-0 and myc2. Data are the mean ± standard error with different letters indicating significant differences. ANOVA-Tukey, p < 0.05
B. japonicum modulates JA-regulated gene expression during salt stress
Following the early activation of JA production in plants co-cultivated with B. japonicum and the likely consequent B. japonicum-activated priming, we measured expression of JA responsive genes under salt stress 6 h after starting the treatment. Plants were inoculated with the bacterium or control solution for one week prior to salt stress. Multiple JA-regulated genes were down-regulated by the bacterium in response to 100 mM NaCl. Arginine Decarboxylase 2 (ADC2, At4g34710), Dehydroascorbate Reductase (DHAR, At1g19550), Glutathione S-Transferase 1 (GST1, At1g02930), Vegetative Storage Protein 1 (VSP1, At5g24780), Vegetative Storage Protein 2 (VSP2, At5g24770) and an ATAF-like NAC-domain transcription factor (ANAC055, At3g15500) were reduced in root tissue and DHAR was reduced in shoots by B. japonicum relative to non-inoculated plants under salt stress (Fig. 7). Under salt stress, MYC2 expression was reduced in shoot tissue but was not significantly altered in roots by B. japonicum compared to non-inoculated plants (Fig. 7). ADC2, known to be involved in salt tolerance [36], increased in shoots and roots in response to high salinity in non-inoculated plants, but was reduced as part of B. japonicum-influenced salt tolerance. Early Response to Dehydration (ERD1, At5g51070) and Nac Domain Containing Protein 19 (ANAC019, At1g52890) expression levels were not altered by B. japonicum under salt stress (Fig. 7).
B. japonicum alters JA-regulated gene expression during salt stress. QRT-PCR analysis of JA-associated genes from non-inoculated and B. japonicum-inoculated tissue, with and without 100 mM NaCl treatment. Treatments were one week ± B. japonicum and 6 h ± 100 mM NaCl in (A) shoot and (B) root tissues. Mean expression relative to the IPP2 reference gene ± standard error, with different letters representing significant differences separately for each gene, GLIM, Sequential Bonferroni, p < 0.05
B. japonicum differentially influences Response to Desiccation genes under salt stress
Response to Desiccation (RD) genes, RD20 (At2g33380), RD22 (At5g25610), RD26 (At4g27410) and RD29B (At5g52300) have demonstrated responses to drought, salinity, ABA, and jasmonic acid [37,38,39]. In our study, salinity increased all four tested RD genes in roots and all but RD26 in shoots without bacteria present (Fig. 8). B. japonicum differentially modulated salinity-induced RD gene expression, relative to non-inoculated salt-stressed plants. In inoculated salt-stressed plants, expression levels of RD29B and RD20 were significantly reduced while expression of RD22 was increased in the roots (Fig. 8B), and in shoots, B. japonicum enhanced RD20 and decreased RD22 expression (Fig. 8A and B). RD22 expression is associated with drought and salt tolerance [40] and has been shown to be activated through MYC2 [41]. A schematic diagram representing Arabidopsis JA-associated genes analyzed in this work for their potential roles in B. japonicum-stimulated salt tolerance is shown in Supplementary Figure S4.
B. japonicum differentially stimulates Response to Desiccation genes during salt stress. Arabidopsis seedlings were treated with B. japonicum (inoculated) or 10 mM MgSO4 (non-inoculated) for seven days before being transferred to agar plates containing either no additional salt or 100 mM NaCl for six hours. (A, B) Graphs display qRT-PCR expression data relative to the IPP2 reference gene from (A) shoot and (B) root tissues. Mean relative expression ± standard error with different letters representing significant differences, separately for each gene, ANOVA, p < 0.05
Discussion
B. japonicum inhibits sodium accumulation and enhances shoot growth under salt stress in Arabidopsis
In this work, we used the interaction between B. japonicum and Arabidopsis to investigate the beneficial effects of PGPR to plants under salt stress. Previous studies have shown that salt stress reduces shoot and root development. In our study, B. japonicum significantly alleviated salt stress, returning shoot weight and MDA levels to those of the unstressed, uninoculated controls and limiting salt accumulation in the plant. Primary root length was shorter with B. japonicum co-cultivation [23] but no change was evident in the primary root length of B. japonicum inoculated plants with and without salt stress. Although we did not investigate the reason behind shortened primary root in B. japonicum inoculated plants under non-stress conditions in this study, we presume it to be due production of auxin by B. japonicum as discussed in our earlier investigation [23]. B. japonicum produces auxin and alters Arabidopsis root architecture through regulation of auxin efflux transporters PIN2, PIN3, PIN7 and ABCB19 [23]. However, under salt stress production of JA after B. japonicum inoculation may have played a role in the reduction of root weight, because exogenous application of methyl jasmonate (MeJA) under salt stress reduces root length and jar1 mutants have longer roots and higher root fresh weight than mock plants [42]. Our results concur with the data obtained by Song et al. (2021) [42] showing the salt treatment significantly reduced the fresh weight of Col-0 compared to jar1 (Fig. 6). Thus, indicating that JA is a negative regulator of root growth under salt stress. Since phytohormones, including JA and auxin, have been linked to PR length inhibition [23, 42, 43], more investigations are needed to decipher the crosstalk between the B. japonicum induced-auxin and JA under salt stress.
In order to maintain a balanced level of sodium ions, which is necessary for normal cellular functions, plants moderate the uptake and release of these ions in various ways [2]. Excess cytosolic sodium can have toxic effects on plant growth and reproduction [44]. In our data, measurements of sodium in the plants using Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES) revealed that B. japonicum dramatically limited sodium accumulation in Arabidopsis. We hypothesized that the mechanisms used included sodium exclusion, priming or eventual ROS reduction/signaling.
Although JA is increased and is a suspected agent in B. japonicum-activated priming of Arabidopsis, multiple/various pathways were activated in the primed plants in response to salt stress. Using forward genetics, we focused on elucidating the mechanism through which B. japonicum confers salt tolerance to plants. Despite the overwhelming evidence that PGPR improve plant tolerance to abiotic stress, including salinity, the specific genetic mechanisms involved have remained elusive [45]. JA has been associated with salt tolerance in plants [46]. Exogenous jasmonate applications in the forms of seed priming, root drench and foliar spray have also been shown to improve multiple stress tolerance characteristics [47]. However, other studies have contrary results: exogenous application of methyl jasmonate decreased sodium uptake in salt-sensitive rice seedlings compared to salt-tolerant plants [48], and promoted the translocation of sodium ions from root to shoot in maize while concurrently reducing the amount of sodium ions in both roots and shoots [49]. According to Song et al. (2015), exogenous application of JA decreased salt stress tolerance, by enhancing H2O2 accumulation and reducing CAT2 expression, and jar1 mutant had increase salt tolerance [42] Song et al. (2015) showed that JA acts through a MYC-mediated repression of CAT2 expression. In rice, a JA mutant with lower JA accumulation than the wildtype, had higher salt tolerance (53). These contrasting conclusions about the role of JA show that researchers still have a long way to go in order to decipher complex interconnections involved in plant response to abiotic stress. Using PGPR adds another layer of complexity because they produce a myriad of metabolites and interact with multiple plant pathways. Although our study is not an exhaustive investigation of the mechanisms involved in the B. japonicum-Arabidopsis interaction under salt stress, it contributes to a better understanding of the role of PGPR in plant response to salinity.
B. japonicum modulates jasmonate and hydrogen peroxide content toward priming in plants
B. japonicum activated jasmonate production in Arabidopsis as early as 0.5 hpi. The jasmonate group is composed of jasmonic acid (JA), its precursors, and its derivatives. JA-Ile is the biologically active form of JA that interacts with JAZ and COI1 proteins to result in activation of MYC transcription factors, including MYC2 [34, 50, 51]. JA 151, represents both endogenous and synthesized JA and JA 133 is specific to endogenous plant JA [52]. OPDA is necessary for the biosynthesis of biologically active JA-Ile, and it has also been shown to be critical to plant defense functions [53, 54]. In spite of the enhanced production of jasmonates in our study, no changes were observed in JAR1 transcript levels and MYC2 expression was not significantly up-regulated at 0.5 hpi. This is not surprising because in several PGPR-induced biological processes (e.g. ISR) that are regulated through JA, their inductions are not accompanied by increased JA production in the plants [21].
Studies have reported that co-cultivation with PGPR increases H2O2 content in the plants, which is a sign of the oxidative burst response and an aspect of PGPR priming [6, 10]. B. japonicum inoculation induced a transient increase in H2O2 within the first 0.5 h of co-cultivation and RBOH genes (responsible for ROS production) were upregulated at all measured time points (3—9 hpi). This early and temporal induction of ROS in biotic interactions, called oxidative burst, has been associated with biotic and abiotic stress tolerance in plants [51]. Both the increase in jasmonate production and the oxidative burst followed by a lowered basal H2O2 content are evidence of plant priming by B. japonicum [21, 55]. Primed plants demonstrate enhanced resistance to abiotic stress [16].
B. japonicum differentially enhances oxidative stress responses in plants under high salinity
B. japonicum modulation of H2O2 upon inoculation led us to investigate B. japonicum-induced ROS production mediation of the plant response to salt stress. ROS production has been implicated in plant responses to pathogens, wounding, ABA, ozone, and heavy metals [56, 57]. Plant exposure to high salinity increases ROS levels [6, 9, 58]. Excessive cellular ROS causes oxidative stress, which, in turn, leads to lipid peroxidation, the oxidation of fatty acids by ROS. Malondialdehyde (MDA) is a byproduct of lipid peroxidation that serves as an indicator of membrane lipid damage caused by oxidative stress [59]. High concentrations of NaCl disrupt cellular functions and structures [45] through lipid peroxidation. In our study there was an increase in lipid peroxidation in plants subjected to salt stress, but pretreating the plants with B. japonicum lowered MDA levels under both the control and high salinity conditions.
For ROS to serve as a signaling molecule, its levels have to be tightly regulated, and ROS neutralization is a component of stress tolerance [4, 60]. Plants use a wide range of scavenging systems to maintain ROS homeostasis, including scavenging enzymes APX, SOD and CAT [6]. Among the early steps to regulate elevated ROS levels is the conjugation of superoxide (O2−) to H2O2 by superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity [6]. In wheat, jasmonates have been shown to increase SOD, CAT and APX in response to salt-induced oxidative stress, whereas salt treatment alone decreased them [61]. Endogenous JA in tomato activated ROS antioxidants in response to high salt [62]. A possible mechanism by which B. japonicum moderates the effects of stress, such as increased lipid peroxidation, may be by enhancing the antioxidant defense system. The B. japonicum-mediated basal H2O2 reduction at 3 dpi in Arabidopsis may involve ROS scavenging pathways. Few significant changes were present under non-salinity conditions between the inoculated and non-inoculated treatment. This may be because the gene expression analysis for genes encoding ROS scavenging enzymes was done six days after B. japonicum inoculation. However, our data clearly show a B. japonicum-induced modulation of H2O2 levels 0.5 hpi to 3 dpi.
Plant stress-responsive genes, downstream of MYC2, are modulated by B. japonicum under salinity stress
JA has been shown to positively regulate salinity tolerance in plants [32, 43, 63]. Transgenic wheat and Arabidopsis plants constitutively expressing a JA synthesis gene displayed increased salt tolerance requiring functional MYC2, but not ABA synthesis [43]. Pseudomonas putida MTCC5279 ameliorated drought stress in chickpea plants by differentially modulating stress-responsive genes at different stages of drought stress, including slight down-regulation of MYC2 [64]. MYC2 regulates crosstalk between JA signaling and several phytohormones (ABA, IAA, SA and GA); participates in JA-regulated plant development; and is required for PGPR activated ISR [33]. Pseudomonas PS01 increased salt tolerance while up-regulating LOX2 (a JA biosynthesis gene) and down-regulating APX2 and GLY17 in Arabidopsis under high salt conditions [32]. In our data, MYC2 expression was elevated in B. japonicum inoculated plants at 0.5 hpi, although this was not statistically significant. However, in loss-of-function mutants jar1 and myc2, inoculation with B. japonicum did not lead to the typical PGPR-induced increase in biomass both under salt stress and non-stress conditions indicating that MYC2 and JAR1 are essential for B. japonicum to promote growth and confer salt tolerance.
Treatment with B. japonicum did not increase ABA levels in the plants, yet it altered expression of several ABA-responsive genes such as RD22, RD20, RD26, RD29B, and EDR1. The effects on the ABA-responsive genes were more apparent after salt stress and we suspect that JA influenced the B. japonicum-induced regulation of these genes. Although ABA regulates the drought-induced expression of MYC2 and RD22, ABA does not mediate RD22 seed-specific activity [65], suggesting that other factors can also stimulate RD22 expression [66]. RD20, a calcium binding protein, is induced by ABA and has roles in oxylipin metabolism during abiotic stress [67]. RD26 overexpression plants highly express RD20 [39] and RD26 targets RD20 [68]. Although RD26 has been primarily linked to an ABA dependent pathway, in ABA-deficient mutants (aba2) under salt stress, RD26 was highly induced, suggesting its involvement in a separate pathway during salt stress [39]. RD26 has also been shown to bind and activate the ERD1 promoter, a jasmonic acid induced stress gene [38, 69]. Jasmonic acid has been shown to influence RD29B through priming [70] and under abiotic stress through the CBF/DREB1 transcription factor [71]. In abiotic stress conditions, MYC2 contributes to the activation of RD29B [70], although whether this MYC2-induced transcription is due to an ABA-dependent pathway or stress-related JA pathways is still unclear. The association of RD20, RD22, RD26, and RD29B with the JA pathway under abiotic stress [37, 38, 70] suggests that B. japonicum most likely induces plant salt tolerance through the JA pathway.
Soil microbes are known to trigger and manipulate plant mechanisms, including hormone signaling, to enhance salt stress tolerance in plants [72]. Although increases in ABA are often seen in plants under salt stress, not all PGPR promote plant ABA production. Under high salinity, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SQR9 was found to reduce maize ABA content to the no-stress level [73]. B. amyloliquefaciens FZB42 induced salt tolerance in Arabidopsis likely by activating plant ET/JA signaling but not ABA-dependent pathways [63]. MYC2 acts as an activator or as a repressor to regulate JA responses [74].
Different PGPR use unique stress resistance strategies. Pinedo and coworkers found that Burkholderia phytofirmans PsJN differentially induced transcriptomic changes in Arabidopsis RD29A, RD29B, APX2, GLY17, PDF1.2 and LOX2 over time, especially in roots, under salt stress [10]. Hormonal crosstalk between multiple phytohormone signaling pathways likely produced the complex response levels and timing required to enhance salt tolerance [10]. Abiotic stress such as salinity and drought increase ethylene levels in plants through induction of a key enzyme, 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase (ACC synthase), in ethylene biosynthesis. High levels of ethylene result in plant damage, limit nutrient uptake and inhibit root growth [75]. PGPR produced ACC-deaminase can hydrolyze ACC to ammonia and a-ketobutyrate, thereby reducing the concentration of ethylene in the plants and alleviating ethylene-induced stress [75] For example, the PGPR Enterobacter sp. UPMR18 was found to improve salinity tolerance in okra, with the help of the bacterium’s ACC deaminase capability as well as by influencing increased ROS scavenging activity in plants [76].
PGPR have been shown to increase [77] and decrease [32] ROS scavenging activity in plants toward enhanced salt tolerance [9]. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 volatile compounds promoted salt tolerance through up-regulation of POD, CAT, SOD and JA synthesis in Arabidopsis [78].
Conclusion
Our results suggest that B. japonicum confers salt tolerance through a JA-regulated pathway under abiotic stress. Our results contribute to understanding how soil microbes improve plant tolerance to salt stress and open doors to the possibilities of managing salinity stress using soil microbiota.
Methods
Plant material and growth conditions
All plants used in this study were in the Arabidopsis thaliana, Columbia (Col-0) background. Col-0 seeds were obtained from the Arabidopsis Biological Resource Center (ABRC), while myc2 (aka jin1) (ABRC stock number CS13115) and jar1(ABRC stock number CS8072) seeds were kindly provided by Thomas Eulgem [79]. Plants were grown vertically, with a twelve/twelve hour (h) day/night cycle, under 120–150 μmol m−2 s−1 light, at 22 °C. Seeds were surface sterilized (three minutes [min] in 10% [v/v] NaClO and 0.05% Tween 80 solution, one min in 70% EtOH, four sterile water rinses) and cold treated at 4 °C for two days before being sown onto a germination medium (1% [w/v] agar [Fisher Scientific], half-strength Murashige and Skoog [½ MS] supplemented with 0.5% sucrose, 0.01% myo-inositol and 0.05% MES, pH 5.7). After four days, uniform seedlings were transferred to a treatment medium (1% agar, ½ MS, pH 5.7), eight to ten seedlings per square Petri dish, for each treatment period. Shoots and roots were weighed after seven days of salt stress treatment.
Bradyrhizobium japonicum IRAT FA3 cultivation and plant inoculation
B. japonicum IRAT FA3 was cultured in half strength Luria–Bertani (LB) liquid medium at 28 °C on a shaker at 100 rpm. Bacterial inoculum was prepared after 24 h of growth by centrifugation of bacterial cell culture for ten min at 1,500 rpm followed by resuspension of bacterial cells in sterile 10 mM MgSO4. The bacterial titer was adjusted to 1.0 optical density at 600 nm (1.8 × 109 colony-forming units mL−1). To treat plants with the bacteria, ten microliters of inoculum were applied onto the roots of vertically grown four-day-old seedlings on agar.
Primary root growth assay
Seedlings, at four days old, were treated with or without PGPR and placed on half-strength Murashige and Skoog media with or without 100 mM NaCl. Initial primary root measurements were taken, the total primary root lengths of plants were measured ten days after inoculation, and new growth after inoculation and salt stress was calculated. Plants were photographed ten days after inoculation. All experiments were repeated at least three times. Each treatment contained six replicates with eight-ten plants per replicate.
Stress treatments
To determine an appropriate salt concentration, four-day-old seedlings were placed on half strength MS plates amended with a concentration of 0, 50, 100, or 200 mM NaCl. Shoot and root weights were measured fourteen days after stress application. One of the salt concentrations (100 mM) was chosen for stress experiments based on shoot weight results. Each treatment contained six replicates with eight-ten plants per replicate. Salt stress was applied seven days after inoculation with B. japonicum, except in the case of primary root growth experiments.
Sodium, carbon, and nitrogen content determination
Plants were collected after seven days of salt stress application and fourteen total days of B. japonicum treatment, briefly rinsed, blotted dry, placed in 50 mL Falcon tubes, and placed in a drying oven at 104°F for four days. Samples were transferred to two milliliter round bottom tubes, ground with beads, and analyzed by the Environmental Sciences Research Laboratory (ESRL) at the University of California, Riverside. For sodium content, samples were digested using an Anton-Paar microwave assisted digestion process. Digestion was done using a one:three ratio of nitric and hydrochloric acid. Measurements were done using an Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES) system.
Root colonization assay under stress
Arabidopsis plants were grown on MS-agar plates and subjected to stress as described above. After 10 days of co-cultivation, one cm root pieces were cut from the root using a sterile razor blade. Roots from ten plants were combined into one replicate. Roots were washed in sterile dH2O twice and then placed in 100 µl of phosphate buffered saline (137 mM NaCl, 10 mM Na2HPO4, 2.7 mM KCl, 2 mM KH2PO4) as performed by Allard-Massicote et al., (2016) [80]. The roots in PBS were sonicated for a total of ten—thirty second pulses on a low setting in an ultrasonic bath (CPX3800, Fisherbrand). Ten microliters of a 10–3 dilution of each sonicated solution were plated on half strength LB agar plates. Colonies were counted after two to three days of incubation at 28℃. This was replicated six times with three technical replicates per biological replicate. The averages of the technical replicates were used for statistical analysis.
B. japonicum growth under stress
B. japonicum was grown in liquid culture composed of tryptone 10 g/L, yeast extract 5 g/L, and a final sodium chloride concentration of 0 mM, 50 mM 100 mM, 200 mM or 300 mM and incubated at 28 °C at 100 rpm. The optical density at 600 nm was measured after 24 h.
RNA isolation and reverse transcription–qRT-PCR
Arabidopsis shoot and root tissues (30–50 mg) were separated and collected from plants for RNA extraction six hours after salt stress application. Total RNA extraction was performed using GeneJet plant RNA purification kit (ThermoScientific, K082) according to the manufacturer's instructions. First-strand cDNA was synthesized from two μg of total RNA by using the Revert Aid™ H Minus First Strand cDNA synthesis kit (ThermoScientific, K1622) according to the instructions of the manufacturer and treated with DNase I (ThermoScientific, EN0521). Gene-specific primers used in the qRT-PCR reaction to determine gene expression are listed in Table 1. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis was performed using Maxima SYBR Green qPCR MasterMix (2x) (ThermoScientific, K0252) on a Biorad Connect CFX system. Expression of all genes was normalized relative to the IPP2 reference gene. All experiments were done in triplicate and repeated three times.
Lipid peroxidation assay
Approximately thirty mg of shoot tissue was collected after seven days of salt stress, ground in liquid nitrogen, and used for quantification. Lipid peroxidation was determined using the thiobarbituric acid (TBA) test as described by Hodges et al. (1999) and Zhao et al. (2017) [25, 90]. Absorbances were read with a spectrophotometer at 440, 532, and 600 nm. The MDA contents were calculated using the formula below:
MDA equivalents (nmol mL−1) = 1 [(A-B))/157 000] × 10 6 where A = [(Abs 532RSII–Abs 600RSII)] and B = [(Abs 440RSII–Abs600RSII) × 0.0571], with Abs as absorbance using reagent solution II (RSII). MDA equivalents (nmol g−1 FW) = MDA equivalents (nmol mL−1) x total volume of the extracts (mL) / g FW or number of seedlings. Reagent solution I (RSI) is 20% (w/v) TCA and 0.01% butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), and reagent solution II (RSII) is RSI and 0.65% (w/v) 2-thiobarbituric acid (TBA). TCA was used as the reference solution.
Determination of chlorophyll content
Chlorophyll content was determined according to Zhao et al. (2017) [80]. Approximately 30 mg of shoot tissue were collected after seven days of salt stress, ground in liquid nitrogen, and used for quantification. The tissue was homogenized in two mL 80% (v/v) aqueous acetone and incubated under shaking conditions at room temperature for thirty min in the dark. Absorbance of the supernatant obtained after centrifugation at 12,000 g for five min at room temperature was determined at 663 and 645 nm. Chlorophyll content was determined using the formula below:
where C represents the total chlorophyll (a + b) content.
Hydrogen peroxide measurement
At fourteen days-old, plants were inoculated and harvested at 0.5 h, 3 h, 6 h, and 12 h and three days post inoculation. Shoot and root tissues were separated at collection. Samples were frozen, weighed, and kept on dry ice in the dark until the hydrogen peroxide assay was performed. Once all samples were collected, the tissue was ground and the appropriate amount of ice cold 20 mM K2HPO4 buffer was added to each sample according to Le et al. (2016) [91]. Hydrogen peroxide quantification was performed using the Amplex Red Hydrogen Peroxide/Peroxidase Assay Kit (Invitrogen A22188) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The assay was performed using three biological replicates and three technical replicates. Fluorescence was measured at 525 nm using a Promega Glomax MultiDetection System with a Green Optical Kit.
Quantification of jasmonic acid and abscisic acid
Arabidopsis plants were inoculated with B. japonicum and harvested at 0, 0.5, 1, 3, and 6 h after inoculation. Whole plants were frozen in liquid nitrogen, then freeze-dried, and fifty mg of tissue were homogenized; ten mg of which were used for each sample. Ten replicates, each consisting of approximately ten to twelve plates, were used in statistical analyses. Jasmonic acid and abscisic acid were extracted and quantified using ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry by the Metabolomics Core Facility at the University of California, Riverside according to Sheflin et al. (2019) [92].
Statistical analysis
All experiments consisted of at least three biological replicates with the mean and standard error shown in figures. SPSS Statistics v. 26 (IBM) was used to make all figures and conduct all statistical analyses. Data that fit ANOVA assumptions were analyzed using an ANOVA and Tukey’s Honest Significant Difference post-hoc test. Data that did not fit these assumptions were analyzed using the normal Generalized Linear Model with the identity link function and Sequential Bonferroni correction.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated and/or analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. No sequencing, genomic, or phylogenetic data were generated during this study.
References
He M, He C-Q, Ding N-Z. Abiotic Stresses: General Defenses of Land Plants and Chances for Engineering Multistress Tolerance. Front Plant Sci. 2018;9:1771.
Ji H, Pardo JM, Batelli G, Van Oosten MJ, Bressan RA, Li X. The Salt Overly Sensitive (SOS) pathway: established and emerging roles. Mol Plant. 2013;6:275–86.
Mustafa G, Akhtar MS. Crops and Methods to Control Soil Salinity. In M. S. Akhtar (ed.), Salt Stress, Microbes, and Plant Interactions: Mechanisms and Molecular Approaches. Singapore: Springer; 2019. p. 237–51. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8805-7_11.
Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Gollery M, Van Breusegem F. Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2004;9(10):490–8.
Brotman Y, Landau U, Cuadros-Inostroza Á, Takayuki T, Fernie AR, Chet I, et al. Trichoderma-Plant Root Colonization: Escaping Early Plant Defense Responses and Activation of the Antioxidant Machinery for Saline Stress Tolerance. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(3):e1003221.
Miller G, Suzuki N, Ciftci-Yilmaz S, Mittler R. Reactive oxygen species homeostasis and signalling during drought and salinity stresses. Plant, Cell Environ. 2010;33(4):453–67.
Yang Q, Chen Z-Z, Zhou X-F, Yin H-B, Li X, Xin X-F, et al. Overexpression of SOS (Salt Overly Sensitive) genes increases salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Mol Plant. 2009;2(1):22–31 Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19529826.
Gachomo E, Kefela I, Houngnandan P, Baba-Moussa L, Kotchoni S. BRADYRHIZOBIUM JAPONICUM IRAT FA3 INCREASES BIOMASS, YIELD AND DROUGHT TOLERANCE IN PLANTS. J Biol Nat. 2014;6(1):12–23.
Bharti N, Pandey SS, Barnawal D, Patel VK, Kalra A. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria Dietzia natronolimnaea modulates the expression of stress responsive genes providing protection of wheat from salinity stress. Sci Rep. 2016;6:34768 Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27708387.
Pinedo I, Ledger T, Greve M, Poupin MJ. Burkholderia phytofirmans PsJN induces long-term metabolic and transcriptional changes involved in Arabidopsis thaliana salt tolerance. Front Plant Sci. 2015;6:466 Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26157451.
Boiero L, Perrig D, Masciarelli O, Penna C, Cassán F, Luna V. Phytohormone production by three strains of Bradyrhizobium japonicum and possible physiological and technological implications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007;74(4):874–80. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0731-9.
Chabot R, Antoun H, Cescas MP. Growth promotion of maize and lettuce by phosphate-solubilizing Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar. phaseoli. Plant Soil. 1996;184(2):311–21. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010460.
Trdá L, Fernandez O, Boutrot F, Héloir M-C, Kelloniemi J, Daire X, et al. The grapevine flagellin receptor VvFLS2 differentially recognizes flagellin-derived epitopes from the endophytic growth-promoting bacterium Burkholderia phytofirmans and plant pathogenic bacteria. New Phytol. 2014;201(4):1371–84. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12592.
Bordiec S, Paquis S, Lacroix H, Dhondt S, Ait Barka E, Kauffmann S, et al. Comparative analysis of defence responses induced by the endophytic plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium Burkholderia phytofirmans strain PsJN and the non-host bacterium Pseudomonas syringae pv. pisi in grapevine cell suspensions. J Exp Bot. 2011;62(2):595–603. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq291.
Lamb C, Dixon RA. THE OXIDATIVE BURST IN PLANT DISEASE RESISTANCE. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 1997;48(1):251–75. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.48.1.251.
Conrath U, Beckers GJM, Langenbach CJG, Jaskiewicz MR. Priming for Enhanced Defense. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2015;53(June):97–119.
Zhang H, Kim M-S, Sun Y, Dowd SE, Shi H, Paré PW. Soil Bacteria Confer Plant Salt Tolerance by Tissue-Specific Regulation of the Sodium Transporter HKT1. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 2008;21(6):737–44. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-21-6-0737.
Katz V, Fuchs A, Conrath U. Pretreatment with salicylic acid primes parsley cells for enhanced ion transport following elicitation. FEBS Lett. 2002;520(1–3):53–7. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(02)02759-X.
Shoresh M, Yedidia I, Chet I. nvolvement of Jasmonic Acid/Ethylene Signaling Pathway in the Systemic Resistance Induced in Cucumber by Trichoderma asperellum T203. Phytopathology®. 2005;95(1):76–84. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-95-0076.
Pieterse CMJ, van Wees SCM, van Pelt JA, Knoester M, Laan R, Gerrits H, et al. A Novel Signaling Pathway Controlling Induced Systemic Resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 1998;10(9):1571–80. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.10.9.1571.
Pieterse CMJ, Van Pelt JA, Ton J, Parchmann S, Mueller MJ, Buchala AJ, et al. Rhizobacteria-mediated induced systemic resistance (ISR) in Arabidopsis requires sensitivity to jasmonate and ethylene but is not accompanied by an increase in their production. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol. 2000;57(3):123–34 Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0885576500902911.
Ryu C-M, Farag MA, Hu C-H, Reddy MS, Kloepper JW, Paré PW. Bacterial Volatiles Induce Systemic Resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2004;134(3):1017–26. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.026583.
Schroeder MM, Gomez MY, McLain NK, Gachomo EW. Bradyrhizobium japonicum IRAT FA3 alters Arabidopsis thaliana root architecture via regulation of auxin efflux transporters PIN2, PIN3, PIN7 and ABCB19. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-05-21-0118-R.
Davey MW, Stals E, Panis B, Keulemans J, Swennen RL. High-throughput determination of malondialdehyde in plant tissues. Anal Biochem. 2005;347(2):201–7 Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0003269705007165.
Hodges DM, DeLong JM, Forney CF, Prange RK. Improving the thiobarbituric acid-reactive-substances assay for estimating lipid peroxidation in plant tissues containing anthocyanin and other interfering compounds. Planta. 1999;207(4):604–11. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004250050524.
Arthikala MK, Montiel J, Sánchez-López R, Nava N, Cárdenas L, Quinto C. Respiratory burst oxidase homolog gene a is crucial for rhizobium infection and nodule maturation and function in common bean. Front Plant Sci. 2017;8(November):1–15.
Marino D, Andrio E, Danchin EGJ, Oger E, Gucciardo S, Lambert A, et al. A Medicago truncatula NADPH oxidase is involved in symbiotic nodule functioning. New Phytol. 2011;189(2):580–92.
Ma L, Zhang H, Sun L, Jiao Y, Zhang G, Miao C, et al. NADPH oxidase AtrbohD and AtrbohF function in ROS-dependent regulation of Na +/K + homeostasis in Arabidopsis under salt stress. J Exp Bot. 2012;63(1):305–17.
Suzuki N, Mittler R. Reactive oxygen species and temperature stresses: A delicate balance between signaling and destruction. Physiol Plant. 2006;126(1):45–51.
Kilian J, Whitehead D, Horak J, Wanke D, Weinl S, Batistic O, et al. The AtGenExpress global stress expression data set: Protocols, evaluation and model data analysis of UV-B light, drought and cold stress responses. Plant J. 2007;50(2):347–63.
Skrzypek E, Miyamoto K, Saniewski M, Ueda J. Identification of jasmonic acid and its methyl ester as gum-inducing factors in tulips. J Plant Res. 2005;118(1):27–30. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-004-0190-2.
Chu TN, Tran BTH, Van Bui L, Hoang MTT. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium Pseudomonas PS01 induces salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Res Notes. 2019;12(1):1–7. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-019-4046-1.
Kazan K. Auxin and the integration of environmental signals into plant root development. Ann Bot. 2013;112(9):1655–65 Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24136877.
Dombrecht B, Gang PX, Sprague SJ, Kirkegaard JA, Ross JJ, Reid JB, et al. MYC2 differentially modulates diverse jasmonate-dependent functions in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2007;19(7):2225–45.
Liu Y, Du M, Deng L, Shen J, Fang M, Chen Q, et al. Myc2 regulates the termination of jasmonate signaling via an autoregulatory negative feedback loop[open]. Plant Cell. 2019;31(1):106–27.
Fu Y, Guo C, Wu H, Chen C. Arginine decarboxylase ADC2 enhances salt tolerance through increasing ROS scavenging enzyme activity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Growth Regul. 2017;83(2):253–63. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-017-0293-0.
Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. Gene networks involved in drought stress response and tolerance. J Exp Bot. 2007;58(2):221–7.
Nakashima K, Takasaki H, Mizoi J, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. NAC transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochim Biophys Acta - Gene Regul Mech. 2012;1819(2):97–103 Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1874939911001817).
Fujita M, Fujita Y, Maruyama K, Seki M, Hiratsu K, Ohme-Takagi M, et al. A dehydration-induced NAC protein, RD26, is involved in a novel ABA-dependent stress-signaling pathway. Plant J. 2004;39(6):863–76.
Kim K, Jang Y-J, Lee S-M, Oh B-T, Chae J-C, Lee K-J. Alleviation of salt stress by enterobacter sp. EJ01 in tomato and Arabidopsis is accompanied by up-regulation of conserved salinity responsive factors in plants. Mol Cells. 2014;37(2):109–17 Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24598995.
Abe H, Urao T, Ito T, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. Arabidopsis AtMYC2 (bHLH) and AtMYB2 (MYB) function as transcriptional activators in abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell. 2003;15(1):63–78.
Song R-F, Li T-T, Liu W-C. Jasmonic Acid Impairs Arabidopsis Seedling Salt Stress Tolerance Through MYC2-Mediated Repression of CAT2 Expression. Front Plant Sci. 2021;12:730228. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.730228.
Blumwald E, Aharon GS, Apse MP. Sodium transport in plant cells. Biochim Biophys Acta - Biomembr. 2000;1465(1–2):140–51.
Zhao Y, Dong W, Zhang N, Ai X, Wang M, Huang Z, et al. A wheat allene oxide cyclase gene enhances salinity tolerance via jasmonate signaling. Plant Physiol. 2014;164(2):1068–76.
Meng N, Yu BJ, Guo JS. Ameliorative effects of inoculation with Bradyrhizobium japonicum on Glycine max and Glycine soja seedlings under salt stress. Plant Growth Regul. 2016;80(2):137–47.
Kang DJ, Seo YJ, Lee JD, Ishii R, Kim KU, Shin DH, et al. Jasmonic acid differentially affects growth, ion uptake and abscisic acid concentration in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive rice cultivars. J Agron Crop Sci. 2005;191(4):273–82.
Ali Q, Shahid S, Nazar N, Hussain AI, Ali S, Chatha SAS, et al. Use of phytohormones in conferring tolerance to environmental stress. In: Plant Ecophysiology and Adaptation under Climate Change: Mechanisms and Perspectives II. Singapore: Springer; 2020. p. 245–355.
Kang DJ, Seo YJ, Lee JD, Ishii R, Kim KU, Shin DH, Park SK, Jang SW, Lee IJ. Jasmonic acid differentially affect growth, ion uptake and abscisic acid concentration in salt-tolerant and salt sensitive rice culture. J Agron Crop Sci. 2005;191:273–82.
Shahzad AN 2011. The role of Jasmonic Acid (JA) and Abscisic Acid (ABA) in salt resistance of maize (Zea mays L.). Available from: GEB - The role of Jasmonic Acid (JA) and Abscisic Acid (ABA) in salt resistance of maize (Zea mays L.) - Shahzad, Ahmad Naeem (uni-giessen.de).
Hazman M, Hause B, Eiche E, Nick P, Riemann M. 2015 Increased tolerance to salt stress in OPDA-deficient rice ALLENE OXIDE CYCLASE mutants is linked to an increased ROS-scavenging activity. J Exp Bot. 2015;66(11):3339–52. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv142.
Ruan J, Zhou Y, Zhou M, Yan J, Khurshid M, Weng W, et al. Jasmonic acid signaling pathway in plants. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(10):2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102479.
Creelman RA, Mullet JE. Jasmonic acid distribution and action in plants: regulation during development and response to biotic and abiotic stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1995;92(10):4114 LP – 4119 Available from: http://www.pnas.org/content/92/10/4114.abstract.
Stintzi A, Weber H, Reymond P, Browse J, Farmer EE. Plant defense in the absence of jasmonic acid: The role of cyclopentenones. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2001;98(22):12837 LP – 12842 Available from: http://www.pnas.org/content/98/22/12837.abstract.
Gleason C, Leelarasamee N, Meldau D, Feussne I. OPDA Has Key Role in Regulating Plant Susceptibility to the Root-Knot Nematode Meloidogyne hapla in Arabidopsis. Frontiers in Plant Science. 2016;7:1565 Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fpls.2016.01565.
Pieterse CMJ, Zamioudis C, Berendsen RL, Weller DM, Van Wees SCM, Bakker PAHM. Induced systemic resistance by beneficial microbes. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2014;52:347–75.
Yoshioka H, Sugie K, Park H-J, Maeda H, Tsuda N, Kawakita K, et al. Induction of Plant gp91 phox Homolog by Fungal Cell Wall, Arachidonic Acid, and Salicylic Acid in Potato. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 2001;14(6):725–36. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI.2001.14.6.725.
Orozco-Cárdenas ML, Narváez-Vásquez J, Ryan CA. Hydrogen peroxide acts as a second messenger for the induction of defense genes in tomato plants in response to wounding, systemin, and methyl jasmonate. Plant Cell. 2001;13(1):179–91 Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11158538.
Pieterse CMJ, Van Wees SCM, Ton J, Van Pelt JA, Van Loon LC. Signalling in rhizobacteria-induced systemic resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Biol. 2002;4(5):535–44.
Awasthi JP, Saha B, Chowardhara B, Devi SS, Borgohain P, Panda SK. Qualitative Analysis of Lipid Peroxidation in Plants under Multiple Stress Through Schiff’s Reagent: A Histochemical Approach. Bio-protocol. 2018;8(8):e2807–e2807 Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34286024.
Nadarajah KK. Ros homeostasis in abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(15):1–29.
Qiu ZB, Guo JL, Zhu AJ, Zhang L, Zhang MM. Exogenous jasmonic acid can enhance tolerance of wheat seedlings to salt stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf [Internet]. 2014;104(1):202–8. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.03.014.
Abouelsaad I, Renault S. Enhanced oxidative stress in the jasmonic acid-deficient tomato mutant def-1 exposed to NaCl stress. J Plant Physiol. 2018;226:136–44.
Liu J, Moore S, Chen C, Lindsey K. Crosstalk Complexities between Auxin, Cytokinin, and Ethylene in Arabidopsis Root Development: From Experiments to Systems Modeling, and Back Again. Mol Plant. 2017;10(12):1480–96 Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29162416. Cited 2020 Apr 15.
Tiwari S, Lata C, Chauhan PS, Nautiyal CS. Pseudomonas putida attunes morphophysiological, biochemical and molecular responses in Cicer arietinum L. during drought stress and recovery. Plant Physiol Biochem PPB. 2016;99:108–17.
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K. The plant hormone abscisic acid mediates the drought-induced expression but not the seed-specific expression of rd22, a gene responsive to dehydration stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Gen Genet. 1993;238(1–2):17–25.
Shi H, Ye T, Yang F, Chan Z. Arabidopsis PED2 positively modulates plant drought stress resistance. J Integr Plant Biol. 2015;57(9):796–806.
Partridge M, Murphy DJ. Roles of a membrane-bound caleosin and putative peroxygenase in biotic and abiotic stress responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem [Internet]. 2009;47(9):796–806. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2009.04.005.
Puranik S, Sahu PP, Srivastava PS, Prasad M. NAC proteins: Regulation and role in stress tolerance. Trends in Plant Science. 2012;17:369–81.
Tran L-SP, Nakashima K, Sakuma Y, Simpson SD, Fujita Y, Maruyama K, et al. Isolation and Functional Analysis of Arabidopsis Stress-Inducible NAC Transcription Factors That Bind to a Drought-Responsive cis-Element in the early responsive to dehydration stress 1 Promoter[W]. Plant Cell. 2004;16(9):2481–98. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.104.022699.
Liu N, Avramova Z. Molecular mechanism of the priming by jasmonic acid of specific dehydration stress response genes in Arabidopsis. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2016;9(1):1–23.
Hu Y, Jiang L, Wang F, Yu D. Jasmonate regulates the INDUCER OF CBF expression-C-repeat binding factor/dre binding factor1 Cascade and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2013;25(8):2907–24.
Ilangumaran G, Smith DL. Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria in Amelioration of Salinity Stress: A Systems Biology Perspective. Front Plant Sci. 2017;8:1768 Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29109733.
Chen L, Liu Y, Wu G, Veronican Njeri K, Shen Q, Zhang N, et al. Induced maize salt tolerance by rhizosphere inoculation of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SQR9. Physiol Plant. 2016;158(1):34–44.
Wasternack C, Song S. Jasmonates: Biosynthesis, metabolism, and signaling by proteins activating and repressing transcription. J Exp Bot. 2017;68:1303–21 Oxford University Press.
Glick BR. Bacteria with ACC deaminase can promote plant growth and help to feed the world. Microbiol Res. 2014;169:30–9.
Habib SH, Kausar H, Saud HM. Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria Enhance Salinity Stress Tolerance in Okra through ROS-Scavenging Enzymes. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:6284547. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6284547.
Chatterjee P, Samaddar S, Anandham R, Kang Y, Kim K, Selvakumar G, et al. Beneficial Soil Bacterium Pseudomonas frederiksbergensis OS261 Augments Salt Tolerance and Promotes Red Pepper Plant Growth [Internet]. Front Plant Sci. 2017;8(705) Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fpls.2017.00705.
Liu S, Tian Y, Jia M, Lu X, Yue L, Zhao X, et al. Induction of Salt Tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana by Volatiles From Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 via the Jasmonic Acid Signaling Pathway. Front Microbiol. 2020;11(November):1–15.
Schroeder MM, Lai Y, Shirai M, Alsalek N, Tsuchiya T, Roberts P, et al. A novel Arabidopsis pathosystem reveals cooperation of multiple hormonal response-pathways in host resistance against the global crop destroyer Macrophomina phaseolina. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):20083. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-56401-2.
Allard-Massicotte R, Tessier L, Lécuyer F, Lakshmanan V, Lucier JF, Garneau D, et al. Bacillus subtilis early colonization of Arabidopsis thaliana roots involves multiple chemotaxis receptors. MBio. 2016;7(6):e01664-16.
Surgun-acar Y, Zemheri-navruz F. 24-Epibrassinolide promotes arsenic tolerance 728 in Arabidopsis thaliana L . by altering stress responses at biochemical and 729 molecular level. J Plant Physiol [Internet]. 2019;238(February):12–9. Available 730 from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2019.05.002
Orman-Ligeza B, Parizot B, de Rycke R, Fernandez A, Himschoot E, van Breusegem F, et al. RBOH-mediated ROS production facilitates lateral root emergence in Arabidopsis. Dev. 2016;143(18):3328–39.
Bian C, Duan Y, Wang J, Xiu Q, Wang J, Hou Y, et al. Validamycin A induces broad-spectrum resistance involving salicylic acid and jasmonic acid/ethylene signaling pathways. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 2020;33(12):1424–37.
Noshi M, Yamada H, Hatanaka R, Tanabe N, Tamoi M, Shigeoka S. Arabidopsis 723 dehydroascorbate reductase 1 and 2 modulate redox states of ascorbate724 glutathione cycle in the cytosol in response to photooxidative stress. Biosci 725 Biotechnol Biochem [Internet]. 2017;81(3):523–33. Available from: 726 https://doi.org/10.1080/09168451.2016.1256759
Liu X, Hong L, Li X-Y, Yao Y, Hu B, Li L. Improved Drought and Salt Tolerance in Transgenic Arabidopsis Overexpressing a NAC Transcriptional Factor from Arachis hypogaea. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2011;75(3):443–50. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.100614.
Kuo HY, Kang FC, Wang YY. Glucosinolate Transporter1 involves in salt-induced jasmonate signaling and alleviates the repression of lateral root growth by salt in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci. 2020;297:110487 (December 2019).
Leng L, Liang Q, Jiang J, Zhang C, Hao Y, Wang X, et al. A subclass of HSP70s regulate development and abiotic stress responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Plant Res. 2017;130(2):349–63.
Lim CW, Lee SC. Functional roles of the pepper MLO protein gene, CaMLO2, in abscisic acid signaling and drought sensitivity. Plant Mol Biol. 2014;85(1–2):1–10.
Blair EJ, Bonnot T, Hummel M, Hay E, Marzolino JM, Quijada IA, et al. Contribution of time of day and the circadian clock to the heat stress responsive transcriptome in Arabidopsis. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):4814.
Zhao J, Missihoun TD, Bartels D. The role of Arabidopsis aldehyde dehydrogenase genes in response to high temperature and stress combinations. J Exp Bot [Internet]. 2017;68(15):4295–308 Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28922758.
Le CT, Brumbarova T, Ivanov R, Stoof C, Weber E, Mohrbacher J, Fink-Straube C, Bauer P. Zinc finger of arabidopsis thaliana12 (ZAT12) Interacts with Fer-Like iron deficiency-induced transcription factor (FIT) Linking Iron Deficiency and Oxidative Stress Responses. Plant Physiol. 2016;170(1):540–57. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.01589.
Sheflin AM, Kirkwood JS, Wolfe LM, Jahn CE, Broeckling CD, Schachtman DP, et al. High-throughput quantitative analysis of phytohormones in sorghum leaf and root tissue by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019;411(19):4839–48.
Acknowledgements
We thank Chengliang Sun for assistance with the determination of salt stress parameters, Erika Hay for assistance with RBOH gene expression measurements, and Caovinh Le, Nguyen C. Tran for assistance in data collection.
Funding
This work was supported by startup funds awarded to E.W.G. from the University of California, Riverside.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
E.W.G. conceived the project, E.W.G., M.Y.G. and N.K.M. contributed to research design and data analyses. M.Y.G., and M.C. performed experiments. E.W.G., M.Y.G., M.M.S. and M.H. contributed to the preparation of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experiments on plants were performed according to the University of California, national, and international guidelines and legislation.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1:
Supplementary Fig. S1. Determination of salt stress experimentalparameters by measuring effects on Arabidopsis shoot and root weight. (A) Shoot and (B) root fresh weights were measured 14 days after the addition of 0mM (control), 50 mM, 100 mM or 200 mM NaCl stress treatment. Data are the means ± standard error with different lettersindicating significant differences. ANOVA; Tukey, p < 0.05. Null seedlings did not survive treatment. Supplemental Fig. S2. Growth of B. japonicum under salt treatment. (A)Growth of B. japonicum in halfstrength Luria Broth without NaCl and supplementation with increasingNaCl concentrations compared to the commercially manufactured rate (½ LB) was determined after 24 hours. (B) Quantificationof root colonization by B. japonicumunder 100 mM salinity stress after 10 days of inoculation and stress treatment.(A, B) Data are mean colony forming units (CFU) ± standard error for 6experimental replicates. Letters indicate significant differences. (A) ANOVA; Tukey, p < 0.05. (B) Student’s t-test; p < 0.05 No significant differenceswere found. Supplementary Fig. S3. Abscisic acid (ABA) production in A. thaliana under B.japonicum inoculation.A. thaliana seedlingswere treated with B. japonicum(inoculated)or 10 mM MgSO4(non-inoculated) for up to 6 hours. ABA levels were measured by liquidchromatography mass-spectrometry (LCMS). Graphs show the means ± standarderror. No significant differences were seen between inoculated andnon-inoculated treatments at each timepoint. Student’s t-test, p < 0.05. Supplemental Fig. S4. Schematic diagramrepresenting A. thalianaJA-associated genes analyzed in B.japonicuminoculated salt treated plants.Lines indicate known signaling pathways under abiotic stress. Dashedlinesdenote putative induction by B. japonicum.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Gomez, M.Y., Schroeder, M.M., Chieb, M. et al. Bradyrhizobium japonicum IRAT FA3 promotes salt tolerance through jasmonic acid priming in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol 23, 60 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-022-03977-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-022-03977-z