Abstract
Background
Considering titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) role in plant growth and especially in plant tolerance against abiotic stress, in the present work, TiO2 NPs were green synthesized using an aqueous solution of Aloe vera leaf extract as a capping agent and titanium tetrachloride as a precursor. These green synthesized TiO2 NPs were characterized using different techniques: UV spectrophotometer, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction (XRD). Results revealed that synthesized TiO2 NPs possess a tetragonal morphology with a size ranging from 10 to 25 nm. Additionally, the present work evaluated the effects of three concentrations of TiO2 NPs (0, 30 and 50 ppm) and six NaCl concentrations (0, 25, 50, 100, 150 and 200 mM) and their interactions with respect to germination parameters, vigor indices, oxidative stress and DPPH free radical scavenging of two varieties of soybean (Glycine max L. var. 22 and 35).
Results
Results demonstrated that all germination traits and vigor indices were negatively affected under all salinity levels. Also, the contents of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and malondialdehyde (MDA) were significantly increased by increasing the NaCl concentrations in two soybean varieties. Most interestingly, TiO2 NPs (30 ppm) mediated positive effects on germination parameters, reducing H2O2 and MDA contents by enhancing antioxidant (decreasing IC50) whereas 50 ppm showed an intermediate response under both control and saline soil conditions.
Conclusion
Our findings demonstrate the growth enhancement effects of TiO2 NPs application as well as its ameliorative potential in dealing with salinity.
Highlights
• Pure synthesis of TiO2 NPs using the leaf extract of A. vera as a reducing and stabilizing agent.
• The synthesized TiO2 NPs have a tetragonal shape with a size range from 10 to 25 nm.
• Salinity reduced germination attributes and vigor indices of two soybean varieties.
• H2O2 and MDA contents increased by increasing NaCl concentrations
• TiO2 NPs induced salt tolerance in soybean by enhancing germination traits, DPPH free radical scavenging (Less IC50) and reducing H2O2 and MDA contents
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Salinity, as one of major abiotic stresses, not only restricts plant growth but also retards developmental processes in important crops [1,2,3,4]. Also, salinity obstructs germination by creating a harmful effect on the germination of seeds of many crops by forming an osmotic pressure on the outer side of the seed which inhibits water absorption [5]. At a global level, about 1,125 million hectares of agricultural lands were harshly impacted by salt stress, which resulted in reduced agricultural production and crop yield [6]. Commonly, salinity affects metabolic processes, such as protein synthesis, carbohydrates and lipid metabolism through osmotic and ionic stress [7]. Moreover, inhibition of cellular and membrane dysfunction occurs under salt stress owing to a greater accumulation of sodium ion (Na+) in plant tissues which as well initiates osmotic stress leading to a water deficit in cells and consequently lessens water potential [8].
Nowadays, environmental safety is an emerging global challenge in the twenty-first century for environmental protection and sustainable development. So, an increase in salt tolerance of crops is essential to enhance food production in several regions of the world [3]. In this respect, to mitigate the harmful effects of saline stress, various methods have been adopted to adjust the ion equilibrium and osmotic homeostasis to overcome the impact of salt injury [9]. Among different measures, an efficient and simple approach to recover plant performance under stressful conditions is seed priming with nanoparticles (NPs) [10,11,12]. Seed priming is generally defined as the controlled hydration of the seeds to the level that allows pre-germinative metabolic activity to continue while averting the surfacing of the radicle. NPs are known as stimulating agents for plant growth modulating the physiological, biochemical and physicochemical pathways [13]. One of these, TiO2 is a well-known NP has a wide range of applications in cleaning air products, skincare products, and cosmetics, and for organic matter decomposition in wastewater [14]. Most interestingly that TiO2 NPs have several insightful impacts on the crop features and play a vital role not only in plant growth but also in development due to their chemical stability and non-toxic nature [15]. Mahmoodzadeh et al. [16] reported elevated levels of germination and improved radicle and plumule development in canola seedlings when treated with TiO2 NPs. As well, TiO2 NPs increased growth and production attributes like yield in wheat seedlings thriving under water stress [17]. Wu et al. [18] reported a positive effect of TiO2 NPs on seed germination, when bombarding lettuce seeds via the electrospray technique, even at low pH or using aged seeds.
Likewise, the beneficial impact of TiO2 NPs on seed germination of chickpea (Cicer arietinum) and in fodder crops such as berseem and oat has been reported [19, 20]. By contrast, TiO2 NPs toxicity on plants has been reported as well, with delayed germination [21], this toxicity like various other NPs mainly depends upon their concentration, type, size, and duration of application, assuming that low concentrations are beneficial and high concentrations are toxic. For example, wheat plants subjected to different concentrations of TiO2-NPs indicated that the use of these NPs in a suitable concentration improved germination indices in comparison to control plants, whereas high concentrations had inhibitory effects on wheat germination [22].
Green NP synthesis has emerged as a new trend in nanotechnology development that is both safer and more eco-friendly. Biological agents as sustainable resources like extracts of the plant (flower, leaf, stem, seeds and bark), bacteria, fungi, algae, and actinomycetes are used in the green synthesis process instead of dangerous chemical agents, which might have negative consequences [23, 24]. One of the benefits of green synthesis is its cost-effectiveness, as the approach uses very inexpensive components. Another benefit is the method's simplicity due to the one-step process [25]. Indeed, the use of plant extracts can be more beneficial for NP synthesis than bacterial and chemical methods because of the lack of any threat of bacterial and dangerous chemical contamination with wider implications and easiness. Several plant extracts have been used in previous green synthesis studies due to their ease of production such as Ficus religiosa [26], Citrus limon, C. reticulate, C. sinensis [27], Aloe vera [28, 29] and Moringa oleifera [30, 31].
Soybean (Glycine max L.) is a globally important crop that provides protein and oil for a wide array of products. By weight, soybean seed is made up of roughly 40% protein, 20% oil, 35% carbohydrate and 5% ash [32] and most soybeans are processed for oil and protein meal. Studies of soybean have shown that high salinity may delay or inhibit germination, cause reductions in plant height, leaf size, biomass, number of branches, number of pods and weight of seeds [33, 34]. A major reduction in any one of these categories can severely limit the yield potential of the soybean crop and have catastrophic effects on the farmer’s financial return. Not only does salt stress negatively impact germination and growth of soybean plants, but this abiotic stress can also cause a reduction in the agronomic quality of beans harvested from salt-stressed soybean plants. In the present research, the prime aim is to investigate the effects of soybean seed priming with TiO2 NPs on overall seed development including both seed germination, seedling development and oxidative stress markers under different salt concentrations, then determine the optimized concentration of TiO2 NPs for seed priming.
Results and discussion
Phytochemical study and HPLC analysis
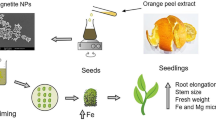
A schematic procedure for the preparation of A. vera aqueous leaf extract is presented in Fig. 1. As the biomaterials and phytochemicals included in the plant extract are completely necessary for the green creation of NPs to avoid the usage of chemical stabilizers, the phytochemical analysis of this extract was carried out, and the results are showed in Table 1. The A. vera aqueous leaf extract was shown to be an excellent source of secondary metabolites from the phytochemical screening, where phenolics, flavonoids, proteins, alkaloids, saponins, and tannins were detected. It was noticed that the aqueous extract of A. vera contained high polyphenols, which may be the cause of the observed biological activity in NPs synthesis. These phytoconstituents are involved as bioreductants and stabilizers during the process of green synthesis, as previously mentioned by Selim et al. [35]. Moreover, Ahmad et al. [36] showed that the terpenoids, flavones, ketones, aldehydes and amides, commonly found in the bioactive chemicals of plant extracts, are added as reducing and stabilizing agents during the NPs synthesis.
HPLC analysis detected the presence of polyphenolics such as chlorogenic acid, rutin, p-coumaric acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, vanillic acid, ferulic acid, coffeic acid, syringic acid and cinnamic acid (Fig. 2 and Table 2). Owing to their functional (hydroxyl) groups, these polyphenolic compounds are known to be efficient hydrogen donors which explains a variety of biological functions [35]. In addition, Sunny et al. [37] verified that these functional groups found in phytoconstituents like phenolics and flavonoids is responsible for the reduction of titanium ions to TiO2 NPs.
Characterization of TiO2 NPs
Morphological characterization of green synthesized TiO2 NPs
TiO2 NPs were prepared through an environmentally friendly technique (Fig. 1) by using A. vera leaves’ liquid extract, which is proved as an efficient extract for the reduction of titanium salt (TiCl4) to NPs [29]. The liquid extract of A. vera leaves was added gradually to the titanium salt solution with stirring, which results in a pinkish brown color from milky off-white after 4 h of stirring. Visual observation of color change was considered as an initial sign of synthesis, and this was in-lined with the results presented by Satti et al. [38].
Spectrophotometric analysis of green synthesized TiO2 NPs
The observed change in color of titanium solution was contemplated as an affirmation of the reduction of TiCl4 salt into TiO2 NPs. The spectral analysis of the change in this color was done between the range of 200—600 nm of light wavelength. The particular peak was obtained between 200 and 300 nm (Fig. 3) which showed the formation of TiO2 NPs. Our results are in-lined with results of Dobrucka [39] and Satti et al. [40] who showed maximum absorption of TiO2 NPs at this range using Echinacea purpurea and Moringa oleifera leaf extract respectively. While those synthesized by Vijayalakshmi and Rajendran [41] and Mustafa et al. [42] revealed maximum absorption peak between 300 and 400 nm. These differences may be attributed to the sensitivity of the UV spectrum to many factors such as shape, size, and agglomeration of the particles as recently confirmed [29].
SEM and TEM analysis of green synthesized TiO2 NPs
Surface, size and the particle morphology of TiO2 NPs were imaged by SEM and TEM (Fig. 4 a, b). Based on the SEM and TEM analysis, TiO2 NPs showed that they are tetragonal in shape and most of the nano-forms are found in the size ranging from 10 to 25 nm (Fig. 4b). Moreover, some of the TiO2 NPs are fused and form tiny aggregations. Our findings are in accordance with those of Mustafa et al. [42] and Rajakumar et al. [43].
FTIR analysis of green synthesized TiO2 NPs
The FTIR was performed to find out the existence of prospective phytochemical groups that were accountable for the preparation and constancy of TiO2 NPs. The infrared spectrum of the TiO2 NPs (Fig. 5a) showed a peak at 3410.49 cm−1 which corresponded to stretching vibrations of the hydroxyl group (-OH). The peak at 2921.63 cm−1 is related to C-H stretch of alkanes. The peak at 1628.59 cm−1 is related to -OH bending of the surface adsorbed water. The peak at 1455.03 cm−1 indicated the C–C stretch and C-H group. While the peak at 614.217 cm−1 is characteristic of Ti–O stretching and Ti–O-Ti bridging stretching modes according to Chahardoli et al. [44, 45]. These functional groups are involved in the reduction of TiCl4 salt into TiO2 NPs [40].
XRD analysis of green synthesized TiO2 NPs
X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of TiO2 NPs was investigated to study the structure and phase formation of the sample. According to Fig. 5b, a well-crystallized anatase profile was observed for TiO2 NPs and the result showed that the structure was in tetragonal structure which is in a good conformity with SEM and TEM analysis. Peaks were absorbed at 25°, 38°, 48°, 53°, 62° and 75° along with miller indices values (1 0 1), (1 1 2), (2 0 0), (1 0 5), (2 0 4) and (2 1 5) respectively. The average crystallite size was measured by Debye Scherrer’s equation according to Oskam et al. [46] as 23 nm. Our results were in line with Hanafy et al. [29] at pH 9 (alkaline conditions) where basic TiO2 NPs exhibited the smallest size and composed of only one crystalline phase (anatase phase).
Effect of TiO2 NPs on morphology and germination attributes of selected soybean varieties
Critical stages for the assembly and establishment of crop plants are seed germination and early seedling growth. In the present study, different concentrations of green synthesized TiO2 NPs were applied to two soybean varieties (G. max L. var; 22 and 35) under salinity and control conditions. The effect of TiO2 NPs on the germination attributes of soybean varieties has been evaluated (Fig. 6a, b) and characterized as length of shoot and radicle, seedling height, radicle and shoot fwt of seedlings (Tables 3 and 4). Two-way ANOVA analysis (Table 5) revealed a significant effect of salt or TiO2 NPs alone or in combination (salt*TiO2 NPs) on all germination parameters. In both soybean varieties, seed germination and growth of seedlings were adversely affected by salinity stress, showing the lowest values at the highest NaCl concentration (200 mM). Similarly, Zafar et al. [5] confirmed that Spinach germination and development was critically reduced by salinity by reducing fresh and dry weights. The decrease in germination and growth under salt stress is due to osmotic and ion toxicity. Moreover, the uptake of nutrients and water is greatly affected under saline stress due to the reduced metabolic activity of seedlings [2, 4, 47].
As a crucial predictor of quick germination and seedling establishment is the seed vigor index, the present study clearly showed that seedling length vigor index (SLVI), shoot length stress index (SLSI) and root length stress index (RLSI) were significantly and dramatically reduced by saline stress at p > 0.05 (Fig. 7 a-f). These results showed agreement with those of Abbasi et al. [48] and Liu et al. [49], who described that salinity stress resulted in reduced plant vigor which could be because of the decrease in osmotic potential or ion toxicity [50].
Effect of TiO2 NPs and different NaCl concentrations on seedling length vigor index (SLVI, a and b), shoot length stress index (SLSI, c and d) and root length stress index (RLSI, e and f) of two soybean varieties (35 and 22) respectively. Data represent means ± standard errors (error bars) of three biological replicates. Different letters indicate significant difference (p < 0·05), according to a Duncan multiple range test
Conversely, the priming of seeds with TiO2 NPs clearly enhanced the germination attributes of two soybean varieties under control and salt stressed conditions. Under control conditions, 30 ppm TiO2 NPs increased seedling height and total fwt by 8.3 and 19.5 percent in var 35 (Table 3), and 23.7 and 20.6 percent in var 22 (Table 4). As well, priming with TiO2 NPs significantly boosted the SLVI in both soybean varieties (Fig. 7a and b) which was in line with Sunny et al. [37]. In accordance with our results, several studies showed that seeds treated with TiO2 NPs suspensions exhibited increased germination rates, enhanced root lengths and improved seedling growth of oilseed rape [16], G. max [51], Arabidopsis thaliana [52] and cabbage [53]. Similarly, as early as 2013, a study by Raskar and Laware [54] showed that TiO2 NPs at concentrations ranging from 10 to 40 ppm enhanced seed germination, promptness index, and seedling growth of onions, which indicated that lower concentrations were not harmful to seed germination and early seedling growth. However, concentrations that are higher than 50 ppm could inhibit seed germination and seedling growth in onions. Most recently, Sunny et al. [37] observed that the root, shoot lengths and seedling growth of Vigna radiate exposed to TiO2 NPs exhibited a good increase compared to control. It is worth mentioning that NPs increased the seed germination and seedling growth by their ability to penetrate the seed coat, resulting in increasing water/nutrient absorption and activating the embryo [55,56,57]. Most specifically, Sunny et al. [37] revealed that the TiO2 NPs can produce more new holes during seed penetration, which are useful in transferring more nutrients efficiently, resulting in a faster germination and development rate.
Likewise, the performance was best when TiO2 NPs were used at 30 ppm, and a significant difference between nano-priming and salinity stress was observed as shown in Fig. 7 for SLVI, SLSI and RLSI. For instance, at 50 mM NaCl, nano-priming with 30 ppm caused a considerable increase in SLSI and RLSI (88.89 and 97.06) for soybean var 22 as compared to unprimed one (62.50 and 85.63). In accordance with our results, Shah et al. [58] showed that priming with TiO2 NPs has a constructive impact on the growth of maize seedlings under salinity stress conditions. This might be due to the quick completion of metabolic activities at the pre-germination stage during the priming process [59, 60], this preeminence of seed subjected to priming led to augmented seed germination levels and higher growth levels of the seedlings. According to Mahmoodzadeh et al. [16], TiO2 NPs improved seed germination and facilitated radicle and plumule growth in seedlings of canola crops. Jaberzadeh et al. [17] described that TiO2 NPs improved wheat plant development and yield-related traits under drought stress. Higher root and shoot lengths coupled with increased seedling fresh and dry weights are the attributes of early and rapid germination, resulting in higher seedling vigor.
Oxidative damage, Reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation and DPPH free radical scavenging under different treatments of salinity and TiO2 NPs
Salinity affects plants by imposing various complications such as ion toxicity, osmotic stress, nutritional deficiency, and genotoxicity, resulting in ROS overproduction and oxidative stress [61]. The effect of salt stress on oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation was assessed in terms of H2O2 and MDA contents, which can be used as an indication to evaluate the tolerance of plants to oxidative stress as well as the sensitivity of plants to salt stress [62]. Our results showed that lipid peroxidation was influenced by salinity stress in both varieties of soybean, as confirmed by the changes in MDA content under control and treated plants as shown in Fig. 8 (b and d). In control, unprimed seedlings, an increase of 63.3 and 129.5% in MDA concentration was observed in soybean var 35 at 100 and 200 mM NaCl, respectively. The increase in MDA content under salt stress was also found in cowpea [3], fenugreek plants [4] and alfalfa [63]. In accordance with our results, data from Jbir-Koubaa et al. [64] suggested that salinity stress might cause a shock and photo-oxidative stress, which would cause MDA accumulation in leaves.
Effect of TiO2 NPs and different NaCl concentrations on hydrogen peroxide (H2O2, mg/g fwt) and malondialdehyde (MDA, nmol/g fwt) content of soybean var 35 (a and b) and soybean var 22 (c and d), respectively. Data represent means ± standard errors (error bars) of three biological replicates. Different letters indicate significant difference (p < 0·05), according to a Duncan multiple range test. fwt: fresh weight; MDA: malondialdehyde
Moreover, our results (Fig. 8 a and c) showed a significant and gradual increase in H2O2 content by increasing NaCl concentrations. Similarly, Rehman et al. [65] discovered a 2- and threefold increase in MDA content, as well as a 2.5- and threefold increase in H2O2 production when exposed to 100 and 200 mM NaCl, respectively, illustrating salt-induced oxidative stress. Salt-stressed plants accumulate higher Na+ ions which cause a reduction in the water status of leaves; it may be responsible for the higher levels of H2O2 and MDA as previously mentioned by Khan [66]. H2O2 is a weak oxidizing agent and can inactivate a few enzymes directly, usually by oxidation of essential thiol (-SH) groups. Once inside the cell, H2O2 can probably react with Fe2+ and possibly Cu2+ ions to form hydroxyl radicals and this may be the origin of many of its toxic effects. It is therefore biologically advantageous for cells to control the amount of H2O2 that is allowed to accumulate [67]. Besides, Kong et al. [68] stated that MDA was an important resistant physiological index of a plant under stress.
In this respect, priming with TiO2 NPs reduced the level of oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation in salt-stressed plants, which was witnessed by a decrease in H2O2 content and MDA in both varieties. At the rate of 30 ppm, TiO2 NPs proved best and reduced H2O2 content and MDA by 11.9 and 9.6%; respectively at 25 mM NaCl stressed soybean (var 35) (Fig. 8 a and b). Most intriguingly, the beneficial effects of TiO2 NPs on soybean plants against salinity-induced oxidative damage may be associated with improved activity of enzymatic antioxidants, as previously reported by Abdel Latef et al. [69] on broad bean plants under salt stress and at lower TiO2 NP concentrations (0.01%). Moreover, Mohammadi et al. [70] and Laware and Raskar [71] showed that in plants treated with TiO2 NPs, a decrease in H2O2 level coupled with a decrease in MDA may possibly be due to the increased level of superoxide dismutase and peroxidase.
Regulation of antioxidant machinery ameliorates the effects of salt stress in plants, as reported in many plant studies, DPPH assays are widely used to measure the antioxidant activity [72]. In this respect, in this study, antioxidant activity was determined by evaluating DPPH free radical scavenging activities and IC50 at all salt treatments. Our results (Fig. 9 a and b) showed that IC50, on basis of ANOVA results, was significantly influenced by different salt concentrations and TiO2 NPs applied. The antioxidant activity (DPPH free radical scavenging) of soybean seedlings increased under salt-stressed conditions. Increased antioxidant was also observed by Taârit et al. [72] in high salinity stressed (75 mM) rosette leaves. Besides, Valifard et al. [73] reported that increased level of antioxidants was found in Salvia mirzayanii leaves as a result of mild salinity stress. In general, plants develop protective mechanisms in response to stress by increasing the levels of antioxidants and enzymatic activities which regulate ROS levels. In this experiment, the increase in antioxidants (as stated by DPPH free radical scavenging and IC50) may be attributed to the stress induced in soybean seedlings in response to NaCl as previously mentioned by Islam et al. [74] on wheat grass. At 100 mM NaCl, leaf extracts displayed the highest DPPH free radical quenching activity (less IC50) as compared to other treatment. The results also showed that high salt-stressed (150 and 200 mM) suppresses the accumulation of antioxidants (Fig. 9). This suppression occurs under high salt-stress because high salt-stress can unbalance cellular ions, and produce active oxygen species, ion toxicity, and osmotic stress as previously mentioned by Cheeseman [75].
Most interestingly, priming with 30 ppm TiO2 NPs caused more enhancement in the antioxidant capacity of soybean by more DPPH free radical scavenging and lessening IC50 (Fig. 9). As a result, TiO2 NPs enhanced the antioxidant defense system to protect the plant against oxidative damage caused by salt stress, thus regulating ROS levels. Plants primed with TiO2 NPs exhibited better performance under saline conditions by increasing DPPH radical scavenging activities (decreasing IC50, Fig. 9), which correlated well with their decreased H2O2 contents and reduced levels of MDA.
Pearson’s correlation analysis
To determine the relationship between the measured germination parameters and oxidative markers under NaCl stress and TiO2 NPs application, a Pearson’s correlation was performed as listed in Tables 6 and 7. There was a positive correlation between any two of germination parameters (radicle length, shoot length, seedling height, radicle fwt, shoot fwt and total fwt) for both soybean varieties. The highest correlation coefficient was that between shoot fwt and total fwt (r = 0.998**, p < 0.01) for soybean var 35 and (r = 0.996**, p < 0.01) for soybean var 22. The findings in our study were consistent with previous studies in rice and common beans [76, 77]. Moreover, these germination parameters exhibited a negative correlation with H2O2 and MDA. In contrast, H2O2 was positively correlated with MDA in soybean var 35 (r = 0.976**, p < 0.01) and soybean var 22 (r = 0.156*, p < 0.05).
Conclusion
Ameliorating salinity tolerance and eradication of detrimental consequences of salinity are major research challenges. In the present study, salinity reduced germination and increased oxidative stress in both varieties of soybean. In this respect, the ongoing study reports the green synthesis of TiO2 NPs by using the reducing and stabilizing potential of A. vera leaf aqueous extract, which helps soybean tolerate salinity. It was discovered that 30 ppm TiO2 NPs is the most effective in improving germination attributes such as shoot, radicle, and whole seedling length, and fwt of shoot and radicle. Also, seed priming with TiO2 NPs reduced the contents of H2O2 and MDA while enhancing the DPPH free radical scavenging activities of two soybean varieties (soybean var. 35 is the most susceptible to salt stress than var. 22). It is assumed that TiO2 NPs have a potential to ameliorate tolerance in soybean plants against salinity. Further studies are needed to show the role of TiO2 NPs applications in ameliorating salinity in soybean plants under field conditions.
Materials and methods
Aloe vera plant collection and preparation of leaves extract
A. vera L. plant was obtained from Horticulture Department, Faculty of Agriculture, Zagazig University, Egypt after permission from Zagazig University and was identified by Dr Samir S. Teleb at the Department of Botany and Microbiology, Faculty of Science, Zagazig University according to Eggli and Newton [78]. Healthy and fresh leaves were collected and washed with tap water followed by distilled water to remove dirt and any contaminants. Following the method of Hanafy et al. [29], 250 g of the leaves were added to 1000 mL distilled water and boiled for 2 h at 90 °C. After cooling, the extract was purified by filtration using Whatman No.1 filter paper. Then the extract was filtered and stored at − 4 °C for further investigations.
Phytochemical screening
Preliminary phytochemical screening of the A. vera extract was carried out to identify the active constituents, using standard methods [79, 80].
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis
HPLC was used to detect, identify and quantify a number of phenolic compounds in the A. vera extract using an Agilent Technologies 1100 series liquid chromatograph equipped with an auto sampler and a diode-array detector following a modifed method by Kim et al. [81]. The analytical column was an Eclipse XDB-C18 (150 X 4.6 µm; 5 µm) with a C18 guard column (Phenomenex, Torrance, CA). The mobile phase consisted of acetonitrile (solvent A) and 2% acetic acid in water (v/v) (solvent B). The flow rate was kept at 0.8 mL/min for a total run time of 70 min and the gradient programme was as follows: 100% B to 85% B in 30 min, 85% B to 50% B in 20 min, 50% B to 0% B in 5 min and 0% B to 100% B in 5 min. The injection volume was 50 µL and peaks were monitored simultaneously at 280. All samples were filtered through a 0.45 µm Acrodisc syringe filter (Gelman Laboratory, MI) before injection. Peaks were identified by congruent retention times and UV spectra and compared with those of the standards.
Green synthesis of TiO2 NPs
The TiO2 NPs were prepared using TiCl4 as a precursor following the method of Hanafy et al. [29]. Briefly, 100 mL of A. vera leaves extract was added dropwise to a 100 mL of 1.0 N TiCl4 solution in deionized water. The mixture was kept under constant stirring for 4 h at room temperature, and the pH value was adjusted to 9 (basic) by adding NH4OH and HCl. The obtained suspension was filtered using Whatman No.1 filter paper to separate the formed NPs which was then washed with double distilled water repeatedly to remove the by-products and finally dried at 100 °C overnight. Further, the attained dry powder was calcined at 400 °C for 4 h to decompose all biomolecules at a high temperature where only the stable metal oxide NPs were kept [82]. Figure 1 shows a flow chart for the synthesis of TiO2 NPs.
Nanoparticles characterization
The characterization of TiO2 NPs was done through different characterization techniques, i.e., ultraviolet (UV) visible spectrophotometer, scanning electron microscope (SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) and X-ray diffraction (XRD).
-
The UV visible spectrophotometry was done by using a UV–visible spectrophotometer, RIGOL (Model Ultra-3660) to verify the preparation of TiO2 NPs by analyzing the wavelength of the TiO2 NPs solution, keeping the range between 200 and 600 nm of the light wavelength.
-
The morphology of the prepared particles was examined by SEM (JEOL JSM 6510 lv) and TEM (JEOL JEM-2100) at the Electron Microscope Unit (Faculty of Agriculture, Mansoura University).
-
FTIR spectra were carried out in the wave number range of 4000 to 400 cm−1 using an IR spectrometer [JASCO model (FT/IR–460 Plus)] to record chemical bonds and the functional groups of the synthesized NPs.
-
XRD was examined at room temperature on an X-ray diffractometer, using a CuKα radiation (Bruker D8 ADVANCE) in order to identify the crystal phase and to estimate the average particle size as well. It was done using a CuKα-radiation (λ = 0.154 nm). Both FTIR and XRD were carried out at the MICROANALYTICAL CENTER (Faculty of Science, Cairo University).
Preparation of TiO2 NPs suspension
The suspension of TiO2 NPs was prepared at different concentrations of 0, 30 and 50 ppm in distilled, deionized water. The suspensions were sonicated for 4 h in a bath sonicator (Branson’s Model B200 ultrasonic) to ensure distribution of the NPs and to avoid aggregation and agglomeration.
Seed materials, seed priming, stress treatments, and growth conditions
Different varieties of soybean were purchased after permission from Food and Legumes Research Department, Field Crops Research Institute, Agricultural Research Center, Giza, Egypt (March, 2022). Seeds of two varieties of soybean (G. max L. var. 22 and 35) were used in this experiment. Surface sterilization of seeds was carried out with 0.5% sodium hypochlorite for 10 min. Sterilized seeds were subjected to nanopriming of TiO2 NPs solution at 0 (T1), 30 (T2) and 50 (T3) ppm for 24 h at 27 °C. Following this, seeds were transferred to germination box containing sterilized sawdust, after one week of seedling emergence, NaCl with different concentrations (0 (control), 25, 50, 100, 150, 200 mM) were applied. Each treatment was replicated 3 times, for each soybean variety, a total of 54 germination boxes (18*3) were used, each containing 5 seeds. Further, all germination boxes were placed in the incubator at 98% relative humidity and 25–28 °C with dark and light photoperiod.
Sampling
After three weeks from NaCl application, the seedlings in the germination box were washed with distilled H2O to remove the NaCl solution adhered to the seedlings. Then, seedlings were blotted with tissue paper to remove the water and were collected from each treatment for measuring germination parameters and the rest of the seedlings were stored for further biochemical analysis.
Measurement techniques
Determination of seed germination and seedling vigor indices
During the experiment, seed germination was observed, and the seed was considered as germinated after radical emergence of 5 mm. Three weeks after NaCl application, seedlings were collected for measurement of radicle and shoot length (cm) and seedling fresh weight (fwt, g). For each replication, three seedlings were randomly selected, and sample data was selected from their average values. Also, the vigor index and seedling growth stress indices [83] were calculated using the following equations:
Quantification of ROS levels (H2O2 and MDA)
The hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) content of the seedlings was measured according to Alexievia et al. [84]. Briefly, known seedling fresh weights were homogenized with 5 mL of trichloroacetic acid (0.1% w/v) in an ice bath and then centrifuged (8000 rpm, 15 min). At that time, 0.5 mL of the supernatant was added to 0.5 mL of potassium phosphate buffer (pH 6.8, 10 mM) and 1 mL of potassium iodide (1 M). Finally, the absorbance of the mixture was recorded at 390 nm. H2O2 (mg g−1 fwt) content was estimated by a standard calibration curve previously made for various H2O2 concentrations.
The malondialdehyde (MDA) content was determined by homogenizing a known fresh weight of seedlings with 5 mL of 5% (w/v) trichloroacetic acid and centrifuging at 8000 rpm for 10 min [85]. Subsequently, 0.4 mL of 5% trichloroacetic acid containing 0.67% (w/v) thiobarbituric acid was added to 0.4 mL of the supernatant. The absorbance was recorded via a spectrophotometer at 532 nm and 600 nm. MDA was quantified by an extinction coefficient (155 mM−1 cm−1) and expressed as nmol g−1 fwt following the formula:
where ɛ is the specific extinction coefficient (= 155 mM cm−1), V is the volume of the extract, wt is the weight of the leaf, A is the absorbance.
DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) radical scavenging assay
In accordance with the method of Blois [86] and Desmarchelier et al. [87], the free radical scavenging ability of the extracts was tested by the DPPH radical scavenging assay. This assay depends on the donating ability of hydrogen atoms of the sample extract which was determined by the decolorization of methanol solution of DPPH where DPPH produces a violet/ purple color in methanol solution and fades to shades of yellow color in the presence of antioxidants. A solution of 0.1 mM DPPH in methanol was prepared, and 2.4 mL of this solution was blended with 1.6 mL of extract in methanol at different concentrations. Control was prepared as above but without the sample extracts and methanol was used for the baseline correction. The reaction mixture was vortexed thoroughly and left in the dark for 30 min. Then, by using a UV spectrophotometer, the absorbance of the mixture was measured at 517 nm. Utilizing the following equation, the percentage of DPPH radical scavenging activity was computed [88]:
where, A0 is the absorbance of the control, and A1 is the absorbance of the sample extracts. % of inhibition was designed against concentration, and from the graph, IC50 (the microgram of extract to scavenge 50% of the radicals) was calculated. Lesser IC50 value shows superior antioxidant activity.
Statistical and comparative analyses
Analysis of variance (one and two-way) was used for measuring the difference between treatments and varieties via software statistical package for the social sciences (SPSS). Significant differences in resulting data were recognized at p < 0.05 level by using Duncan multiple range test (95% level of probability). Analysis was carried out in triplicate and mean ± SE (standard error) of three parallel measurements. Pearson's correlation coefficients (r) were carried out to understand the relationship between germination traits and oxidative stress using SPSS. Figures were assembled using OriginPro 8.5 for data analysis and graphing software.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- DPPH:
-
2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl
- FTIR:
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- fwt:
-
Fresh weight
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- POX:
-
Peroxidase
- r :
-
Pearson's correlation coefficients
- RLSI:
-
Root length stress tolerance index
- SE:
-
Standard error
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- SLSI:
-
Shoot length stress tolerance index
- SLVI:
-
Seedling length vigor index
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- TiCl4 :
-
Titanium tetrachloride
- TiO2 NPs:
-
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
References
Rameeh V. Ions uptake, yield and yield attributes of rapeseed exposed to salinity stress. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr. 2012;12:851–61. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162012005000037.
Abdelhameed RE, Metwally RA. Mitigation of salt stress by dual application of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and salicylic acid. Agrochimica. 2018;62:353–66.
Metwally RA, Abdelhameed RE. Synergistic effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in growth and physiology of salt-stressed Trigonella foenum-graecum plants. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. 2018;16:538–44.
Abdelhameed RE, Abdel Latef AAH, Shehata RS. Physiological Responses of Salinized Fenugreek Plants to Foliar Application of Salicylic Acid. Plants. 2021;10:657. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10040657.
Zafar S, Perveen S, Kamran Khan M, Shaheen MR, Hussain R, Sarwar N, et al. Effect of zinc nanoparticles seed priming and foliar application on the growth and physio-biochemical indices of spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) under salt stress. PLoS ONE. 2022;17(2):e0263194. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0263194.
Kumar S, Li G, Yang J, Huang X, Ji Q, Liu Z, Ke W, Hou H. Effect of Salt Stress on Growth, Physiological Parameters, and Ionic Concentration of Water Dropwort (Oenanthe javanica) Cultivars. Front Plant Sci. 2021;12:660409. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.660409.
Parida AK, Das AB. Salt tolerance and salinity effects on plants: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2005;60:324–49.
Munns R, Tester M. Mechanisms of Salinity Tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2008;59:651–81.
Ibrahim E. Seed priming to alleviate salinity stress in germinating seeds. J Plant Physiol. 2016;192C:38–46.
Iqbal M, Ashraf M. Seed treatment with auxins modulates growth and ion partitioning in salt-stressed wheat Plants. J Integr Plant Biol. 2007;49:1003–15.
Shah T, Latif S, Saeed F, Ali I, Ullah S, Abdullah Alsahli A, Ahmad P. Seed priming with titanium dioxide nanoparticles enhances seed vigor, leaf water status, and antioxidant enzyme activities in maize (Zea mays L.) under salinity stress. J King Saud University-Sci. 2021;10:004.
Al-Salama Y. Effect of seed priming with ZnO nanoparticles and saline irrigation water in yield and nutrients uptake by wheat plants. Environ Sci Proc. 2022;16:37.
Abdelhameed RE, Abu-Elsaad NI, Abdel Latef AAH, Metwally RA. Tracking of Zinc Ferrite Nanoparticle Effects on Pea (Pisum sativum L.) Plant Growth, Pigments, Mineral Content and Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Colonization. Plants (Basel). 2021;10(3):583.
Castiglione MR, Giorgetti L, Geri C, Cremonini R. The effects of nano-TiO2 on seed germination, development and mitosis of root tip cells of (Vicia narbonensis L.) and ( Zea mays L.). Nanoparicle Res. 2011;13:2443–9.
Mishra V, Mishra RK, Dikshit A, Pandey AC. Interactions of nanoparticles with plants: An Emerging Prospective in the Agriculture Industry, Editor(s): Ahmad P, Rasool S, In: Emerging Technologies and Management of Crop Stress Tolerance. Academic Press, Elsevier; 2014. p. 159–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-800876-8.00008-4.
Mahmoodzadeh H, Nabavi M, Kashefi H. Effect of nanoscale titanium dioxide particles on the germination and growth of canola (Brassica napus). J Ornamental Hort Plants. 2013;3:25–32.
Jaberzadeh A, Moaveni P, Moghadam HRT, Zahedi H. Influence of bulk and nanoparticles titanium foliar application on some agronomic traits, seed gluten and starch contents of wheat subjected to water deficit stress. Notulae Botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj-Napoca. 2013;41:201–7.
Wu S, Huang L, Head, J, Ball, M, Tang, Y, Chen, D. Electrospray facilitates the germination of plant seeds. Aerosol and Air Quality Research. 2014; 14. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2014.06.0212.
Hajra A, Mondal N. Effects of ZnO and TiO2 nanoparticles on germination, biochemical and morphoanatomical attributes of (Cicer arietinum L). Energy Ecol Environ. 2017;2: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40974-017-0059-6.
Maity A, Natarajan N, Pastor M, Vijay D, Gupta CK, Wasnik VK. Nanoparticles influence seed germination traits and seed pathogen infection rate in forage sorghum (Sorghum bicolour) and cowpea (Vigna unguiculata). Indian J Exp Biol. 2018;56(6):363–72.
Castiglione MR, Giorgetti L, Geri C, Cremonini R. The effects of nano-TiO2 on seed germination, development and mitosis of root tip cells of Vicia narbonensis L. and Zea mays L. J Nanopart Res. 2011;13:2443–9.
Mahmoodzadeh H, Aghili R. Effect on germination and early growth characteristics in wheat plants (Triticum aestivum L.) seeds exposed to TiO2 nanoparticles. J Chem Health Risks. 2014;4:467–72.
Parashar UK, Saxena PS, Srivastava A. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Dig J Nanomater Biostruc. 2009;4:159–66.
Ahmed S, Ahmad M, Swami BL, Ikram S. A review on plant extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: A green expertise. Adv Res. 2016;7:17–28.
Vadlapudi V. Green synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles. Middle-East J Sci Res. 2014;19:834–42.
Kirtee W, Choudhari A, Chikate R, Kaul-Ghanekar R. Synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles using Ficus religiosa extract. Carbon Sci Techn. 2013;5:203–10.
Sujitha MV, Kannan S. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Citrus fruits aqueous extract and its characterization. Spectrochim Acta Part A: Molec Biomolec Spectrosc. 2013;102:15–23.
Supriya G, Kumari S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using (Aloe vera) extract and assessing their antimicrobial activity against skin infections. 2019;60–65. https://doi.org/10.26438/ijsrbs/v6si1.6065.
Hanafy MS, Abdel Fadeel DA, Elywa MA, Kelany NA. Green synthesis and characterization of TiO2 nanoparticles Using (Aloe vera) Extract at Different pH Value. Sci J King Faisal Univ/Basic Appl Sci. 2020;21(1):103–10.
Swetha TV, Rajeshkumar S, Lakshmi T, Roy A. Zinc oxide nanoparticles green synthesis using (Moringa oleifera) and tulasia formulation and its anti-inflammatory activity. Drug Invent Today. 2019;11(10):2366–9.
El-Sayed A, Amr A, Kamel O, El-Saidi M, Abdelhamid A. Eco-friendly fabric modification based on AgNPs Moringa for mosquito repellent applications. Cellulose. 2020; 27: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03355-8.
Soares TCB, Good-God PIV, Miranda FD, Soares YJB, Schuster I, Piovesan ND, Barros EG, Moreira MA. QTL mapping for oil content in soybean cultivated in two tropical environments. Pesq Agrop Brasileira. 2008;43(11):1533–41.
Chang RZ, Chen YW, Shao GH, Wan CW. Effect of salt stress on agronomic characters and chemical quality of seeds in soybean. Soybean Science. 1994;13:101–5.
Phang T-H, Guihua S, Hon-Ming L. Salt Tolerance in Soybean. J Integr Plant Biol. 2008;50:10. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7909.2008.00760.x.
Selim YA, Azb MA, Ragab I, Abd El-Azim MHM. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Extract of Deverra tortuosa and their Cytotoxic Activities. Sci Rep. 2020;10:3445.
Ahmad A, Hashmi SS, Palma JM, Corpas FJ. Influence of metallic, metallic oxide, and organic nanoparticles on plant physiology. Chemosphere. 2022;290:133329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133329.
Sunny NE, Mathew SS, Venkat Kumar S, Saravanan P, Rajeshkannan R, Rajasimman M, Vasseghian Y. Effect of green synthesized nano-titanium synthesized from Trachyspermum ammi extract on seed germination of Vigna radiate. Chemosphere. 2022;300:134600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134600.
Satti SH, Raja NI, Javed B, Akram A, Mashwani Z-u-R, Ahmad MS. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles elicited agromorphological and physicochemical modifications in wheat plants to control (Bipolaris sorokiniana.). PLoS ONE. 2021;16(2):e0246880.
Dobrucka R. Synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Echinacea purpurea herba. Iran J Pharm Res. 2017;16(2):756–62.
Satti SH, Raja NI, Ikram M, Oraby HF, Mashwani Z-U-R, Mohamed AH, Singh A. Omar AA Plant-Based Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Trigger Biochemical and Proteome Modifications in Triticum aestivum L. under Biotic Stress of Puccinia striiformis. Molecules. 2022;27:4274. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27134274.
Vijayalakshmi R, Rajendran V. Synthesis and characterization of nano-TiO2 via different methods. Arch Appl Sci Res. 2012;4(2):1183–90.
Mustafa N, Raja N, Ilyas N, Ikram M, Mashwani Z, Ehsan M. Foliar applications of plant-based titanium dioxide nanoparticles to improve agronomic and physiological attributes of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) plants under salinity stress. Green Process Synth. 2021;10(1):246–57. https://doi.org/10.1515/gps-2021-0025.
Rajakumar G, Rahuman AA, Roopan SM, Chung IM, Anbarasan K, Karthikeyan V. Efficacy of larvicidal activity of green synthesized titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Mangifera indica extract against blood-feeding parasites. Parasitol Res. 2015;114(2):571–81.
Chahardoli A, Qalekhani F, Shokoohinia Y, Fattahi A. Luteolin mediated synthesis of rod-shaped rutile titanium dioxide nanoparticles: Assay of their biocompatibility. J Ind Eng Chem. 2022;111:211–8.
Chahardoli A, Hosseinzadeh L, Shokoohinia Y, Fattahi A. Production of rutile titanium dioxide nanoparticles by trans-ferulic acid and their biomedical applications. Mater Today Commun. 2022;33:104305.
Oskam G, Nellore A, Lee Penn R, Searson PC. The growth kinetics of Tio2 nanoparticles from titanium (IV) alkoxide at high water/titanium ratio. J Phys Chem B. 2003;107(8):1734–8.
Parida AK, Das AB. Salt tolerance and salinity effects on plants: A review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2005;60(3):324–49.
Abbasi GH, Akhtar J, Haq MA, Ali S, Chen ZH, Malik W. Exogenous potassium differentially mitigates salt stress in tolerant and sensitive maize hybrids. Pak J Bot. 2014;46:135–46.
Liu S, Guo X, Feng G, Maimaitiaili B, Fan J, He X. Indigenous arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi can alleviate salt stress and promote growth of cotton and /Maize in saline fields. Plant Soil. 2015;398:195–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2656-5.
Farooq M, Hussain M, Wakeel A, Siddique KHM. Salt stress in maize: effects, resistance mechanisms, and management. A Rev Agron Sustain Dev. 2015;35:461–81.
Rezaei F, Moaveni P, Mozafari H. Effect of different concentrations and time of nano TiO2 spraying on quantitative and qualitative yield of soybean (Glycine max L.) at Shahr-e-Qods, Iran". Biol Forum. 2015;7:957–64.
Szymanska R, Kolodziej K, Slesak I, Zimak-Piekarczyk P, Orzechowska A, Gabruk M. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles (100–1000 mg/l) can affect vitamin E response in (Arabidopsis thaliana). Environ Pollut. 2016;213:957–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.03.026.
Andersen CP, King G, Plocher M, Storm M, Pokhrel LR, Johnson MG. Germination and early plant development of ten plant species exposed to titanium dioxide and cerium oxide nanoparticles. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2016;35:2223–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.3374.
Raskar S, Laware SL. Effect of titanium dioxide nano particles on seed germination and germination indices in onion. Plant Sci Feed. 2013;3(9):103–7.
Hatami M, Ghorbanpour M, Salehiarjom H. Nano-anatase TiO2 modulates the germination behavior and seedling vigority of some commercially important medicinal and aromatic plants. J Biol Environ Sci. 2014;8:53–9.
Zhang M, Gao B, Chen J, Li Y. Effects of graphene on seed germination and seedling growth. J Nanopart Res. 2015;17:78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-2885-9.
Cox A, Venkatachalam P, Sahi S, Sharm N. Silver and titanium nanoparticle toxicity in plants: a review of current research. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2016;107:147–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.05.022.
Shah T, Munsif F, D’amato R, Nie L. Lead toxicity induced phytotoxic impacts on rapeseed and clover can be lowered by biofilm forming lead tolerant bacteria. Chemosphere. 2020;246:125766.
Farooq M, Irfan M, Aziz T, Ahmad I, Cheema SA. Seed Priming with ascorbic acid improves drought resistance of Wheat. J Agron Crop Sci. 2013;199:12–22.
Shah T, Latif S, Khan H, Munsif F, Nie L. Ascorbic Acid Priming Enhances Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Winter Wheat under Low Temperature Due to Late Sowing in Pakistan. Agronomy. 2019;9:757. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9110757.
Lin CC, Kao CH. Effect of NaCl stress on H2O2 metabolism in rice leaves. Plant Growth Regul. 2000;30:151–5.
Jain M, Mathur G, Kou S, Sarin NB. Ameliorative effects of proline on salt stress induced lipid peroxidation in cell lines of groundnut (Arachis hypogea L.). Plant Cell Rep. 2001;20:463–8.
Wang X, Han J. Changes of proline content, activity, and active isoforms of antioxidative enzymes in two Alfalfa cultivars under salt stress. Agric Sci China. 2009;8:431–40.
Jbir-Koubaa RS, Charfeddine S, Ellouz W. Investigation of the response to salinity and to oxidative stress of interspecific potato somatic hybrids grown in a greenhouse. Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Cult. 2015;120:933–47.
Rehman S, Abbas G, Shahid M, Saqib M, Farooq ABU, Hussain M, Murtaza B, Amjad M, Naeem MA, Farooq A. Effect of salinity on cadmium tolerance, ionic homeostasis and oxidative stress responses in conocarpus exposed to cadmium stress: Implications for phytoremediation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019;171:146–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.12.077.
Khan M. Nano-titanium dioxide (Nano-TiO2) mitigates NaCl stress by enhancing antioxidative enzymes and accumulation of compatible solutes in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.). J Plant Sci. 2016;11:1–11.
Wang KJ, Zhang YJ, Yang CR. Antioxidant phenolic compounds from rhizomes of (Polygonum paleaceum). J Ethnopharmacol. 2005;96:483–7.
Kong W, et al. Non-destructive determination of Malondialdehyde (MDA) distribution in oilseed rape leaves by laboratory scale NIR hyperspectral imaging. Sci. 2016;6:35393. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep35393.
Abdel Latef AAH, Srivastava AK, El-sadek MSA, Kordrostami M, Tran LSP. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles improve growth and enhance tolerance of broad bean plants under saline soil conditions. Land Degrad Develop. 2018;29:1065–73. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2780.
Mohammadi R, Reza M, Alireza A. Effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on Chickpea response to cold stress. Biological trace element research. 2013;152: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-013-9631-x.
Laware SL, Raskar S. Effect of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on hydrolytic and antioxidant enzymes during seed germination in onion. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci. 2014;3:749–60.
Taârit MB, Msaada K, Hosni K, Marzouk B. Fatty acids, phenolic changes and antioxidant activity of clary sage (Salvia sclarea L.) rosette leaves grown under saline conditions, Ind. Ind Crop Prod. 2012;38:58–63.
Valifard MS, Mohsenzadeh B, Kholdebarin V, Rowshan. Effects of salt stress on volatile compounds, total phenolic content and antioxidant activities of (Salvia mirzayanii), S. Afr J Bot. 2014;93:92–7.
Islam MZ, Park BJ, Lee YT. Bioactive phytochemicals and antioxidant capacity of wheat grass treated with salicylic acid under organic soil cultivation Chem. Biodiversity. 2021;18:e2000861.
Cheeseman JM. Mechanism of salinity tolerance in plants. Plant Physiol. 1988;87:547–50. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/701596.
Chunthaburee S, Dongsansuk A, Sanitchon J, Pattanagul W , Theerakulpisut P, Physiological and biochemical parameters for evaluation and clustering of rice cultivars differing in salt tolerance at seedling stage. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2015;05:013.
Kouam EB, Ndo SM, Mandou MS, Chotangui AH, Tankou CM. Genotypic variation in tolerance to salinity of common beans cultivated in Western Cameroon as assessed at germination and during early seedling growth. Open Agric. 2017;2:600–10.
Eggli L, Newton E. Etymological Dictionary of Succulent Plant Names. Berlin Heidelberg New York in: Springer-Verlag; 2004.
Senguttuvan J, Paulsamy S, Karthika K. Phytochemical analysis and evaluation of leaf and root parts of the medicinal herb, Hypochaeris radicata L. for in vitro antioxidant activities. Asian Pac. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2014;4(Suppl 1):S359–67.
Iqbal E, Abu Salim K, Lim LBL. Phytochemical screening, total phenolics and antioxidant activities of bark and leaf extracts of Goniothalamus from Brunei Darussalam. J King Saud Univ–Sci. 2015;27(3):224–32.
Kim KH, Tsao R, Yang R, Cui SW. Phenolic acid profiles and antioxidant activities of wheat bran extracts and the effect of hydrolysis conditions. Food Chem. 2006;95:466–73.
Sundrarajan M, Krishnan B, Bhavani M, Sonamuthu J, Ambika S, Arumugam S, Nithya P, Sumath R. Obtaining titanium dioxide nanoparticles with spherical shape and antimicrobial properties using M. citrifolia leaves extract by hydrothermal method. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2017;171:117–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.05.003.
Wu H, Guo J, Wang C, Li K, Zhang X, Yang Z, M Li,Wang B .An effective screening method and a reliable screening trait for salt tolerance of (Brassica napus) at the germination stage. Front Plant Sci. 2019; 10:530. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00530.
Alexievia V, Sergiev I, Mapelli S, Karanov E. The effect of drought and ultraviolet radiation on growth and stress markers in pea and wheat. Plant Cell Environ. 2001;24:1337–44.
Heath R, Packer L. Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts of fatty acid peroxidation chlorophyll. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968;126:189–98.
Blois MS. Antioxidant determinations by the use of a stable free radical. Nature. 1958;181:1199–200.
Desmarchelier C, Bermudez MJN, Coussio J, Ciccia G, Boveris A. Antioxidant and prooxidant activities in aqueous extract of Argentine plants. Int J Pharmacogn. 1997;35:116–20.
Rahman MM, Islam MB, Biswas M. In vitro antioxidant and free radical scavenging activity of different parts of Tabebuia pallida growing in Bangladesh. BMC Res Notes. 2015;8:621. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-015-1618-6.
Acknowledgements
We greatly appreciate the financial support from the Academy of Scientific Research and Technology, Egypt.
Experimental research and field studies on plants
"All relevant institutional, national and international guidelines and legislation were compiled or adhered to in the production of this study".
Funding
Open access funding provided by The Science, Technology & Innovation Funding Authority (STDF) in cooperation with The Egyptian Knowledge Bank (EKB). The work has been partially funded from the Egyptian Academy of Scientific Research and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: HA, REA and HSH; Methodology: REA, HA and MHA; Formal analysis and investigation: REA, HA and MHA; Writing: REA; Review and editing: REA, HA, HSH and MHA. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Abdalla, H., Adarosy, M.H., Hegazy, H.S. et al. Potential of green synthesized titanium dioxide nanoparticles for enhancing seedling emergence, vigor and tolerance indices and DPPH free radical scavenging in two varieties of soybean under salinity stress. BMC Plant Biol 22, 560 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-022-03945-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-022-03945-7