Abstract
Background
Mytilidae, also known as marine mussels, are widely distributed in the oceans worldwide. Members of Mytilidae show a tremendous range of ecological adaptions, from the species distributed in freshwater to those that inhabit in deep-sea. Mitochondria play an important role in energy metabolism, which might contribute to the adaptation of Mytilidae to different environments. In addition, some bivalve species are thought to lack the mitochondrial protein-coding gene ATP synthase F0 subunit 8. Increasing studies indicated that the absence of atp8 may be caused by annotation difficulties for atp8 gene is characterized by highly divergent, variable length.
Results
In this study, the complete mitochondrial genomes of three marine mussels (Xenostrobus securis, Bathymodiolus puteoserpentis, Gigantidas vrijenhoeki) were newly assembled, with the lengths of 14,972 bp, 20,482, and 17,786 bp, respectively. We annotated atp8 in the sequences that we assembled and the sequences lacking atp8. The newly annotated atp8 sequences all have one predicted transmembrane domain, a similar hydropathy profile, as well as the C-terminal region with positively charged amino acids. Furthermore, we reconstructed the phylogenetic trees and performed positive selection analysis. The results showed that the deep-sea bathymodiolines experienced more relaxed evolutionary constraints. And signatures of positive selection were detected in nad4 of Limnoperna fortunei, which may contribute to the survival and/or thriving of this species in freshwater.
Conclusions
Our analysis supported that atp8 may not be missing in the Mytilidae. And our results provided evidence that the mitochondrial genes may contribute to the adaptation of Mytilidae to different environments.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Mitochondria are essential eukaryotic organelles, they play important role in ATP (the universal currency of biological energy) production through oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) [1]. The typical mitochondrial genome of animals is a small (16 kb) circular molecule, which includes 13 OXPHOS-related genes, 22 transfer RNA (tRNA) genes and 2 ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes [1, 2], and it usually follows a strictly maternal inheritance. In bivalves, some species of Mytilidae [2, 3], Donacidae [4] and etc. showed a unique Doubly Uniparental Inheritance (DUI) model. In this model, there are two highly divergent male (M-type) and female (F-type) mitochondrial genomes (M-type vs F-type DNA divergence exceeds 20%) [1, 5]. Females with DUI possess only F-type, and males possess two types, but transmit only M-type to their sons. The mitochondrial genomes of bivalve species are also characterized by extraordinary variability in gene arrangement, tRNA gene number, and genome size. And some bivalve species are thought to lack the mitochondrial protein-coding gene ATP synthase F0 subunit 8 (ATP8) [6,7,8]. The presence and absence of atp8 were mainly studied in Mytilidae, and atp8 gene has been identified and proved to be actively transcribed and translated in Mytilus spp. [6, 9, 10]. However, the atp8 gene of Limnoperna fortunei was presumed to be a pseudogene. Whether atp8 gene was actually “missing” in some species has become a concern for researchers [5].
Mytilidae, also known as marine mussels, are widely distributed in the oceans worldwide. Some mussels are important economic species, for instance, Mytilus chilensis, Mytilus. edulis, Mytilus coruscus, Perna viridis [11, 12]. According to the Fishery and Aquaculture Statistics 2018 reported by Food and Agriculture Organization, the total production of M. chilensis (major species) in 2018 was 365,595 tonnes. Members of Mytilidae show a tremendous range of ecological adaptions, from the species distributed in freshwater to those that inhabit in deep-sea. The deep-sea environment is one of the most extreme environments on Earth, with limited food, low oxygen, high hydrostatic pressure, toxic chemicals and extreme temperature [13]. The species of Mytilidae that invaded deep-sea environments are mainly in the subfamily Bathymodiolinae. The evolutionary stepping stone hypothesis believes that the ancestors of Bathymodiolinae progressively adapted to deep-sea environments by exploiting sunken wood and whale carcasses [14]. Bathymodioline species usually have reduced digestive systems [15] and rely instead on endosymbiotic bacteria, transmitted horizontally from the environment to gill tissues, which produce organic carbon with energy from hydrogen sulfide oxidation. [16]. L. fortunei, golden mussel, is a species of Mytilidae with freshwater independent colonization [6, 17]. In freshwater, the low levels of ionic concentration may force organisms to expend more energy regulating osmotic pressure [18]. Given the functional importance of OXPHOS, mutations of the mitochondrial genes can directly affect metabolic performance. Mounting evidence suggests that some non-neutral mutations in mitochondrial genes can contribute to the adaptation of animals to different environments [19,20,21].
Mitochondrial DNA has been one of the most useful tools that are widely used in species identification, phylogenetic studies [22], comparative genomics [23], and management of invasive alien species [24]. Xenostrobus securis, L. fortunei, and Mytilus galloprovincialis and etc., are regarded as notorious invasive species which have caused dramatic and devastating effects on ecosystems [25, 26]. However, the complete mitochondrial genome of X. securis is still unknown. In addition, more mitochondrial genomes may contribute to further understanding the differentiation and evolution of Mytilidae [27, 28]. The emergence of cost-efficient next-generation sequencing allows us to quickly obtain mitochondrial genomes from various data (genomic data, transcriptome data, and metagenomic data) [29, 30]. In the present study, the complete mitochondrial genomes of X. securis, and two deep-sea mussels (Bathymodiolus puteoserpentis, Gigantidas vrijenhoeki) were newly assembled. We re-annotated atp8 gene in Mytilidae, which is aim to answer whether atp8 is not missing in the whole family. Furthermore, we also performed positive selection analysis of 12 protein-coding genes. We aim to provide new insights into the molecular mechanisms of adaptive evolution (to different environments: deep-sea and freshwater) of Mytilidae.
Materials and methods
Sequences and annotation
The sequencing data were download from NCBI (X. secures SRR7751554, B. puteoserpentis ERR3959529, G. vrijenhoeki SRR10802050) and filtered by Trimmomatic 0.36 [31,32,33]. The mitochondrial genomes of those species were assembled with the NOVOPlasty software [30]. The MITOS web server (http://mitos2.bioinf.uni-leipzig.de/index.py) was used to annotate the mitochondrial genomes [34]. tRNA genes were also predicated by ARWEN v1.2.3 (http://130.235.244.92/ARWEN/) [35]. The AT and GC skews were calculated according to the following formulae: AT-skew = (A − T)/(A + T) and GC-skew = (G − C)/(G + C).
Because of the small size and high variability of atp8, it is difficult for automatic annotation tools [5, 36]. The atp8 sequences were annotated by manually scanning the intergenic regions. ORFfinder (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/orffinder/) was used to find the ORFs. The start codon of atp8 sequences was corrected according to the sequences of related species. TMHMM Server v.2.0 (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/) was used to identify the transmembrane helices of atp8 sequences. The PROTSCALE tool of ExPASy (http://ca.expasy.org/tools/) was applied to calculate the hydrophobicity profiles. In addition, we also annotated the atp8 with HHblits v3.30 [37] referring to a previous study [38]. In brief, A Hidden Markov Model (HMM) was constructed for each ORF using HHblits with PDB70. An HMM for known atp8 genes was constructed with the latest Uniclust30 database. Then, the HMM-HMM alignment was run against ORFs with atp8.
Phylogenetic analyses
In this article, only F-type was included in the analyses. The 12 protein-coding genes of 46 sequences were used to reconstruct the phylogenetic relationships [39]. The Crassostrea gigas (AF177226.1) and Atrina pectinata (KC153059.1) served as outgroups (Table 1). atp8 was excluded in the phylogenetic analysis as atp8 was highly variable in length and amino acid composition. The sequences were aligned with Muscle in MEGA7 [40]. The gap and ambiguously aligned sites were recognized and removed with Gblocks Version 0.91b [41]. ModelTest-NG was used to identify the best-fit models for each gene based on the Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) [42]. Bayesian phylogenetic inference was performed with Mrbayes 3.2.7 [43]. Two independent Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) simulations were carried out with four chains (one cold, three hot) for 1,000,000 generations, sampling every 1000 generations. The initial 25% of sampled trees were discarded as burn-in. Maximum Likelihood (ML) inference was performed using RAxML-NG with 1000 bootstrap replicates [44]. The phylogenetic trees were visualized by Figtree. v1.4.4.
The divergence time was estimated using the program MCMCtree in PAML4.9 [59]. Two nodes were used as calibrations, one of which was from the fossil recode data of Modiolinae (393–408 Mya) and the other was from previous studies [28, 60, 61], the time of divergence between B. themophilus and G. childressi was approximately 21.1–33.0 Mya.
Selection analyses
Comparing the nonsynonymous/synonymous nucleotide substitution ratios (ω = dN/dS) has been widely used to evaluate the adaptive molecular evolution of protein-coding genes. The values of dN/dS mean changes in selective pressure, where the dN/dS < 1, = 1, > 1 correspond to negative purifying selection, neutral evolution and positive selection, respectively. The program CODEML in PAML4.9 was applied to calculate the values of dN/dS [59]. The phylogenetic tree of 12 protein-coding genes inferred with Mrbayes was used for selection analyses. The outgroups were not included in selection analyses. For branch model, One-ratio model (model = 0, NSsites = 0, icode = 4) and Three-ratios model (model = 2, NSsites = 0, icode = 4) were performed. The deep-sea branches (Bathymodiolinae) and freshwater branches (L. fortunei) were used as foreground branches (two foreground branches) and the remaining were used as background branches. In addition, the branch-site model (model = 2, NSsites = 2) was used to determine whether positive selection acted on specific sites on foreground branches. The sites under positive selection were identified with Bayes empirical Bayes posterior probabilities (> 0.95). The likelihood ratio tests were carried out to identify if the alternative model provided a significantly better fit than the null model.
To explore the possible effects of positive selection sites on protein function, the three-dimensional structure of protein was predicted with phyre2 [62]. The protein structure of NuoM in Escherichia coli [63]was used as a template [21, 64]. The positive sites were marked using PyMOL.
Results and discussion
General features
We have successfully obtained the complete mitochondrial genomes of X securis, B. puteoserpentis, and G. vrijenhoeki, with lengths of 14,972 bp, 20,482, and 17,786 bp, respectively. The genomes we assembled showed high similarity with the known sequences of each species (100% for X. securis; 100% for B. puteoserpents; 99.42% for G. vrijenhoeki). It should be pointed that X. secures might be a cryptic species complex, and we cannot rule out the possibility that the mitochondrial genome of X. securis may belong to the M-type [65, 66]. The base composition analysis showed that three assembled genomes were biased toward A and T, with AT content of 59.08% in X securis, 63.55% in B. puteoserpentis, and 66.96% in G. vrijenhoeki. The assembled genomes are all characterized by negative AT skew and positive GC skew (Table 2). The base composition and skewness are consistent with most studies in bivalves [8, 67, 68].
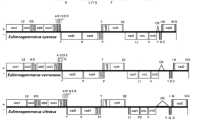
For these three species, all genes encoded on the heavy strand (H-strand) except tRNA Gly in Light (L-strand). Each genome has 13 protein-coding genes and 2 ribosomal RNA genes (Fig. 1). However, the number of tRNAs is varied. Twenty-two typical tRNAs were identified in X securis. 27 tRNAs (four more tRNAHis and one more tRNALeu) and 23 tRNAs (one more tRNALeu) were identified in B. puteoserpentis and G. vrijenhoeki, respectively. The lengths of intergenic region between tRNAHis were 470 bp, 441 bp, 455 bp and 468 bp, respectively, which leads B. puteoserpentis to have the largest mitochondrial genome among Bathymodiolinae. In the assembled genomes of X securis, B. puteoserpentis, and G. vrijenhoeki, the total lengths of protein-coding genes were 11,060, 10,947, and 10,993, accounting for 73.87%, 53.45%, 61.81% of the whole genome, respectively. The protein-coding genes of X securis started with ATG and ATA, while both of B. puteoserpentis and G. vrijenhoeki started with ATG, ATA, ATT, and GTG. For these three species, the protein-coding genes mainly started with codon ATG. The stop codons of all species were either TAA or TAG except nad1 and cox3 of X. securis which had an incomplete stop codon of T. The presence of incomplete stop codons is a common feature of the mitochondrial genes among animals [5, 69, 70]. The incomplete stop codon is thought to be completed by polyadenylation of the transcript.
ATP8 annotation
Some species are thought to lack atp8 gene that encodes a subunit of mitochondrial ATP synthase [6, 7]. Increasing studies indicated that the absence of atp8 may be caused by annotation difficulties for atp8 gene is characterized by highly divergent, variable length. Sometimes, atp8 gene could not be detected by automatic annotation software, the annotation of atp8 gene usually requires manual inspection and comparison to atp8 sequences from other species. In this study, we manually annotated atp8 in the sequences that we assembled and the sequences lacking atp8. Twelve atp8 sequences were manually annotated in the intergenic region (Table 3). The results of manual annotation were highly consistent with the results of HMM. However, HMM method was unable to detect atp8 in some species (e.g. L. fortunei, X. secures and Modiolinae,), probably due to the lack of atp8 sequences from related species and the low sequence similarity with known atp8 genes. For newly annotated atp8, start codons were ATG or GTG or ATC, and stop codons were either TAG or TAA. ATP8 usually has higher conservation of the secondary structure compared to the primary sequence [71]. The newly annotated atp8 sequences all have one predicted transmembrane domain, a similar hydropathy profile, as well as the C-terminal region with positively charged amino acids (R, H, and K). (Table 3, Figs. 2 and 3) [72].
In this study, all species of Mytilidae possessed an annotated atp8 gene, which allows us to further understand the features of atp8 gene in a family. The lengths of atp8 in Mytilidae were short and variable, ranging from 37 – 139 aa (Table 3 and Fig. 3). The longest atp8 was from Mytilaster solisianus (KM655841.1), and the shortest atp8 was from P. canaliculus. It should be noted that the annotation of the start codons and stop codons might be inaccurate in some species due to the lack of additional data. The atp8 sequence of M. solisianus was much longer than that of related species. We are not sure whether this sequence used an incomplete stop codon (TA or T), which caused the fact that the real length was shorter than the current length. The alignment of atp8 gene indicated that atp8 sequences were highly divergent that they showed similarity only in related species. The conserved ‘MPQL’ amino acid signature at the N-terminus, the typical characteristic for metazoan ATP8 proteins [71], was only found in L. fortunei (VPQL) (Fig. 3). However, the conserved ‘PQ’ amino acid signature was found in many species, for instance, Bathymodiolinae, Limnoperninae, Lithophaginae, P. viridis, P. canaliculus, Arcuatula senhousia and some species of Modiolinae [72]. Although not all species of Mytilidae have this feature, it still can contribute to identifying atp8 gene from ORFs in some species of Mytilidae.
Given the characteristics of atp8 gene, it is not surprising that atp8 gene was once presumed to have lost in many species. Although atp8 gene of L. fortunei has the ‘MPQL’ amino acid signature at the N-terminus, it was still annotated as a pseudogene in an incorrect position [6]. In almost all lineages of animals, there has been strong selection to maintain a minimal set of 37 genes [5]. Researchers need to be cautious of assertions that a mitochondrial gene is missing [73]. Our results supported that atp8 gene may not be missing in the Mytilidae. Although we have no right to claim that whole Bivalvia class possesses an atp8 gene, we provided further evidence that a family possesses the atp8 gene. In the future, studies of transcriptional activity and function of these atp8 genes may be necessary. Moreover, we strongly encourage researchers to identify whether atp8 gene was not missing in other families.
Phylogenetic relationship within Mytilidae
To further examine the relationship among the Mytilidae species, the phylogenetic trees were reconstructed using Maximum Likelihood and Bayesian inference methods with a concatenated alignment. The tree topologies resulting from these two methods were consistent. The results supported that the Mytilidae is subdivided into two major clades [22]. The clade 1 contained the subfamilies Bathymodiolinae, Modiolinae, Limnoperninae, and Lithophaginae and the genus Xenostrobus (Arcuatulinae), and clade 2 included subfamilies Brachidontinae, Mytilinae, Crenellinae, Septiferinae, and genus Arcuatula (Arcuatulinae) (Fig. 4). The estimated divergence time between the two clades was around 399.37 Mya (95% HPD interval 392.74- 407.65 Mya), which is close to the estimated time in other analyses (Fig. 5) [22, 74].
The subfamily Bathymodiolinae was monophyletic, which is the same with previous studies [28, 60]. In this study, the Bathymodiolinae were divided into three separate clades, corresponding to the Gigantidas, Bathymodiolus, and “Bathymodiolus”. The Gigantidas was clustered with “Bathymodiolus” and then sister to Bathymodiolus, which is consistent with previous analysis [60], but different from zhang’s study [28]. It should be noted that although the Gigantidas clustered with “Bathymodiolus”, the node was not supported enough according to bootstrap value and posterior probability. Our results indicated that the subfamily Arcuatulinae was polyphyletic as genera Xenostrobus and Arcuatula were divided into the clade1 and clade2, respectively. In clade1, the genus Xenostrobus and (Modiolinae + Bathymodiolinae) were grouped in a subclade with high supporting values (100% BP and 1.00 BPP). The placement of Genus Xenostrobus was different between our results and a previous study based on 5 genes [74]. The tree of the previous study showed that Xenostrobus was clustered with Bathymodiolinae and then sister to Modiolinae. However, the gene order of 13 protein-coding genes and 2 rRNA (excepting tRNA) between Modiolinae and Bathymodiolinae was consistent, which supported our result (Fig. 1). Further increasing the sequences of Xenostrobus may contribute to resolving the phylogenetic relationship among Genus Xenostrobus, Modiolinae, and Bathymodiolinae.
In clade 2, Brachidontinae were divided into three well-supported clades: [1] Geukensia [2] Brachidontes [3] Mytilisepta + Perumytilus + Semimytilus, which was similar to the results of nuclear genes18S and 28S [75]. However, the placement of Geukensia was inconsistent. Moreover, a previous study [22] and our result indicated that Perna perna (KM655841.1) had an unusual phylogenetic status, which showed high similarity with two Brachiodontes species rather than P. viridis and Perna canaliculus according to gene order and phylogenetic trees (Figs. 1 and 4) [22]. The sequence of P. perna (KM655841.1) showed 99.83% sequence identity with cox1 sequences of M. solisianus, which suggested that the sequence may belong to M. solisianus rather than P. perna.
Positive selection analyses
Purifying selection has been widely recognized as the predominant force acting on the molecular evolution of mitochondrial genomes. However, some studies have demonstrated that relaxation of purifying selection or episodic positive selection on mitochondrial genomes may occur in species that have different types of locomotion [76] or species living in extreme environments [77,78,79]. The One-ratio model analysis the ω values of these 12 genes ranged from 0.0024 to 0.0435, where cox1-3 have lower ω values than other genes (Table 4). All the ω values were less than 1, indicating that the 12 genes of Mytilidae experienced constrained selection pressure to maintain their function. Members of Mytilidae show a tremendous range of ecological adaptions. To examine whether heterogeneous selective pressures act on the branches living in different environments (freshwater, deep-sea, and shallow sea), the Three-ratios model analysis was implemented. The likelihood ratio tests showed that the Three-ratios models have significantly better fit than the null models at cox1, atp6, cob, nad2, and nad5 (Table 4), suggesting divergence in selective pressure among the branches. In deep-sea branches, the ω values of those genes excepting cox1 are higher than those of other branches, suggesting those genes experienced relaxation of purifying selection. Relaxation of purifying selection in deep-sea branches has been found in many studies including deep-sea sea cucumbers and Boudemos sp. (Calamyzinae) [77, 80]. The relaxed purifying selection may be beneficial for deep-sea species to adapt to the reduction of oxygen levels and metabolic rates in extreme environments. In freshwater branches, only the ω value of atp6 was higher than that of shallow-sea branches, but still lower than the ω value of deep-sea branches.
To identify whether positive selection acts on a few sites in freshwater branches or deep-sea branches, the branch-site model analysis was carried out. In deep-sea branches, although several sites of the genes (atp6, cob, nad2, nad4, nad5, and nad6) were recognized as positive sites according to BEB analysis (> 95%), the p-values of likelihood ratio tests were > 0.05 (Table S1). In freshwater branches, sites of nad2, nad4, and nad5 were identified as positive sites with BEB analysis (> 95%), however, only the p-value of nad4 was significant, which means nad4 may contribute to the adaptation of L. fortunei in freshwater (Table 5). Successful adaption to the freshwater environment may have required increased demand for energy involved in processes such as the osmotic balance [21]. NADH dehydrogenase, the largest and the most complicated enzyme of the respiratory chain, receives electrons from the oxidation of NADH and provides electrons for reduction of quinone to quinol [81]. nad4 together with nad2 and nad5 were considered to be the actual proton pumping devices as they showed homology with a class of Na + / H + antiporters [82]. Mutation in the members of NADH dehydrogenase would change the metabolic capacity which may further affect the fitness of an organism. To explore the possible effects of positive selection sites on nad4, the protein model was generated using the E. coli structure as a template. Most of the positive sites were directly located in the TMα7a which plays the most important role in the transportation of hydrogen ion (Fig. 6a). A positive site was found near the end of TMα9, which is adjacent to a positive site located in TMα7a. Intriguingly, both positive sites are polar amino acids, and these substitutions could change the environment between TMα7a and TMα9 (Fig. 6b) [21, 83]. This possible interaction was similar to a previous study of nad2 in freshwater dolphins [21]. We speculated that the mutations in NADH dehydrogenase may contribute to the survival and/or thriving of these species in freshwater.
The structure analysis of nad4 (a) The topology diagram of nad4 of Limnoperna fortunei. In transparent blue, representation of N-terminal part not similar with Escherichia Coli. The positions of positive sites were indicated in red. b The structure analysis of positive sites. Upper-right side: L. fortunei model; Lower-right side: Mytilus edulis model. The positions of positive sites were indicated in red, and the amino acid in close proximity was indicated in yellow
Conclusions
Here, the mitochondrial genomes of three marine mussels (Xenostrobus securis, Bathymodiolus puteoserpentis, and Gigantidas vrijenhoeki) were assembled using the sequences deposited in NCBI. We annotated atp8 in the sequences that we assembled and the sequences lacking atp8. The newly annotated atp8 sequences all have one predicted transmembrane domain, a similar hydropathy profile, as well as the C-terminal region with positively charged amino acids. Our results supported that atp8 may not be missing in the Mytilidae. Furthermore, we reconstructed the phylogenetic trees of Mytilidae and carried out positive selection analysis. The results showed that the deep-sea bathymodiolines experienced more relaxed evolutionary constraints. And signatures of positive selection were detected in nad4 of Limnoperna fortunei, which may contribute to the survival and/or thriving of this species in freshwater.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are available in the Genbank repository, accessions number: ON128252–ON128254.
References
Breton S, Milani L, Ghiselli F, Guerra D, Stewart DT, Passamonti M. A resourceful genome: updating the functional repertoire and evolutionary role of animal mitochondrial DNAs. Trends Genet. 2014;30(12):555–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2014.09.002.
Passamonti M, Ricci A, Milani L, Ghiselli F: Mitochondrial genomes and Doubly Uniparental Inheritance: new insights from Musculista senhousia sex-linked mitochondrial DNAs (Bivalvia Mytilidae). BMC Genomics. 2011;12(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-442.
Śmietanka B, Lubośny M, Przyłucka A, Gérard K, Burzyński A: Mitogenomics of Perumytilus purpuratus (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) and its implications for doubly uniparental inheritance of mitochondria. PeerJ. 2018;6. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.5593.
Theologidis I, Fodelianakis S, Gaspar MB, Zouros E. Doubly uniparental inheritance (DUI) of mitochondrial DNA in Donax trunculus (Bivalvia: Donacidae) and the problem of its sporadic detection in Bivalvia. Evolution. 2008;62(4):959–70. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.2008.00329.x.
Ghiselli F, Gomes-Dos-Santos A, Adema CM, Lopes-Lima M, Sharbrough J, Boore JL. Molluscan mitochondrial genomes break the rules. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2021;376(1825):20200159. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2020.0159.
Uliano-Silva M, Americo JA, Costa I, Schomaker-Bastos A, de Freitas RM, Prosdocimi F. The complete mitochondrial genome of the golden mussel Limnoperna fortunei and comparative mitogenomics of Mytilidae. Gene. 2016;577(2):202–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2015.11.043.
Liao D, Zhou Y, Tong J, Cao S, Yu X, Fu B, Yang D. Characterization and phylogenetic analysis of the complete mitochondrial genome from Rock Scallop (Crassadoma gigantea) using next-generation sequencing. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2018;3(2):827–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/23802359.2018.1483752.
Xu K, Kanno M, Yu H, Li Q, Kijima A. Complete mitochondrial DNA sequence and phylogenetic analysis of Zhikong scallop Chlamys farreri (Bivalvia: Pectinidae). Mol Biol Rep. 2011;38(5):3067–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-9974-8.
Breton S, Stewart DT, Hoeh WR. Characterization of a mitochondrial ORF from the gender-associated mtDNAs of Mytilus spp. (Bivalvia: Mytilidae): identification of the “missing” ATPase 8 gene. Mar Genomics. 2010;3(1):11–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margen.2010.01.001.
Lubośny M, Przyłucka A, Śmietanka B, Breton S, Burzyński A: Actively transcribed and expressed atp8 gene in Mytilus edulis mussels. PeerJ. 2018;6. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.4897.
Zeng Q, Zhao B, Wang H, Wang M, Teng M, Hu J, Bao Z, Wang Y. Aquaculture Molecular Breeding Platform (AMBP): a comprehensive web server for genotype imputation and genetic analysis in aquaculture. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac424.
Rajagopal S, Venugopalan VP, van der Velde G, Jenner HA. Greening of the coasts: a review of the Perna viridis success story. Aquat Ecol. 2006;40(3):273–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-006-9032-8.
McMullin ER, Bergquist DC, Fisher CR. Metazoans in extreme environments: adaptations of hydrothermal vent and hydrocarbon seep fauna. Gravit Space Biol Bull. 2000;13(2):13–23.
Distel DL, Baco AR, Chuang E, Morrill W, Cavanaugh C, Smith CR. Do mussels take wooden steps to deep-sea vents? Nature. 2000;403(6771):725–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/35001667.
Barry JP, Buck KR, Kochevar RK, Nelson DC, Fujiwara Y, Goffredi SK, Hashimoto J. Methane-based symbiosis in a mussel, Bathymodiolus platifrons, from cold seeps in Sagami Bay. Japan Invertebrate Biology. 2002;121(1):47–54. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7410.2002.tb00128.x.
Wentrup C, Wendeberg A, Schimak M, Borowski C, Dubilier N. Forever competent: deep-sea bivalves are colonized by their chemosynthetic symbionts throughout their lifetime. Environ Microbiol. 2014;16(12):3699–713. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.12597.
Calcino AD, de Oliveira AL, Simakov O, Schwaha T, Zieger E, Wollesen T, Wanninger A. The quagga mussel genome and the evolution of freshwater tolerance. DNA Res. 2019;26(5):411–22. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dsz019.
Tseng YC, Hwang PP. Some insights into energy metabolism for osmoregulation in fish. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2008;148(4):419–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2008.04.009.
Greenway R, Barts N, Henpita C, Brown AP, Arias Rodriguez L, Rodriguez Pena CM, Arndt S, Lau GY, Murphy MP, Wu L, et al. Convergent evolution of conserved mitochondrial pathways underlies repeated adaptation to extreme environments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(28):16424–30. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2004223117.
Shen X, Pu Z, Chen X, Murphy RW, Shen Y. Convergent evolution of mitochondrial genes in deep-sea fishes. Front Genet. 2019;10:925. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00925.
Caballero S, Duchene S, Garavito MF, Slikas B, Baker CS. Initial evidence for adaptive selection on the NADH subunit two of freshwater dolphins by analyses of mitochondrial genomes. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(5): e0123543. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0123543.
Lee Y, Kwak H, Shin J, Kim S-C, Kim T, Park J-K: A mitochondrial genome phylogeny of Mytilidae (Bivalvia: Mytilida). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 2019;139 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2019.106533.
Wang X, Shang Y, Wu X, Wei Q, Zhou S, Sun G, Mei X, Dong Y, Sha W, Zhang H. Divergent evolution of mitogenomics in Cetartiodactyla niche adaptation. Org Divers Evol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13127-022-00574-8.
van de Crommenacker J, Bourgeois YXC, Warren BH, Jackson H, Fleischer-Dogley F, Groombridge J, Bunbury N, Austin J. Using molecular tools to guide management of invasive alien species: assessing the genetic impact of a recently introduced island bird population. Divers Distrib. 2015;21(12):1414–27. https://doi.org/10.1111/ddi.12364.
de Paula RS. Reis MdP, de Oliveira Júnior RB, Andrade GR, de Carvalho MD, Cardoso AV, Jorge EC: Genetic and functional repertoires of Limnoperna fortunei (Dunker, 1857) (Mollusca, Mytilidae): a review on the use of molecular techniques for the detection and control of the golden mussel. Hydrobiologia. 2020;847(10):2193–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-020-04196-z.
Pascual S, Villalba A, Abollo E, Garci M, González AF, Nombela M, Posada D, Guerra A. The mussel Xenostrobus securis: a well-established alien invader in the Ria de Vigo (Spain, NE Atlantic). Biol Invasions. 2009;12(7):2091–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-009-9611-4.
Kyuno A, Shintaku M, Fujita Y, Matsumoto H, Utsumi M, Watanabe H, Fujiwara Y, Miyazaki J-I. Dispersal and Differentiation of Deep-Sea Mussels of the GenusBathymodiolus(Mytilidae, Bathymodiolinae). Journal of Marine Biology. 2009;2009:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/625672.
Zhang K, Sun J, Xu T, Qiu JW, Qian PY: Phylogenetic Relationships and Adaptation in Deep-Sea Mussels: Insights from Mitochondrial Genomes. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041900.
Nachtigall PG, Grazziotin FG, Junqueira-de-Azevedo ILM. MITGARD: an automated pipeline for mitochondrial genome assembly in eukaryotic species using RNA-seq data. Brief Bioinform. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbaa429.
Dierckxsens N, Mardulyn P, Smits G. NOVOPlasty: de novo assembly of organelle genomes from whole genome data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(4): e18. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw955.
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B. Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics. 2014;30(15):2114–20. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170.
Ryu T, Kim JG, Lee J, Yu OH, Yum S, Kim D, Woo S. First transcriptome assembly of a newly discovered vent mussel, Gigantidas vrijenhoeki, at Onnuri Vent Field on the northern Central Indian Ridge. Mar Genomics. 2021;57: 100819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margen.2020.100819.
Ucker M, Ansorge R, Sato Y, Sayavedra L, Breusing C, Dubilier N. Deep-sea mussels from a hybrid zone on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge host genetically indistinguishable symbionts. ISME J. 2021;15(10):3076–83. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-021-00927-9.
Bernt M, Donath A, Juhling F, Externbrink F, Florentz C, Fritzsch G, Putz J, Middendorf M, Stadler PF. MITOS: improved de novo metazoan mitochondrial genome annotation. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2013;69(2):313–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2012.08.023.
Laslett D, Canback B. ARWEN: a program to detect tRNA genes in metazoan mitochondrial nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics. 2008;24(2):172–5. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm573.
Monnens M, Thijs S, Briscoe AG, Clark M, Frost EJ, Littlewood DTJ, Sewell M, Smeets K, Artois T, Vanhove MPM. The first mitochondrial genomes of endosymbiotic rhabdocoels illustrate evolutionary relaxation of atp8 and genome plasticity in flatworms. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;162:454–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.025.
Steinegger M, Meier M, Mirdita M, Vohringer H, Haunsberger SJ, Soding J. HH-suite3 for fast remote homology detection and deep protein annotation. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019;20(1):473. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-019-3019-7.
Plazzi F, Puccio G, Passamonti M. Comparative large-scale mitogenomics evidences clade-specific evolutionary trends in mitochondrial DNAs of Bivalvia. Genome Biol Evol. 2016;8(8):2544–64. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evw187.
Liu F, Li Y, Yu H, Zhang L, Hu J, Bao Z, Wang S. MolluscDB: an integrated functional and evolutionary genomics database for the hyper-diverse animal phylum Mollusca. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49(D1):D988–97. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa918.
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol Biol Evol. 2016;33(7):1870–4. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054.
Castresana J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol. 2000;17(4):540–52. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026334.
Darriba D, Posada D, Kozlov AM, Stamatakis A, Morel B, Flouri T. ModelTest-NG: a new and scalable tool for the selection of DNA and protein evolutionary models. Mol Biol Evol. 2020;37(1):291–4. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msz189.
Ronquist F, Teslenko M, van der Mark P, Ayres DL, Darling A, Hohna S, Larget B, Liu L, Suchard MA, Huelsenbeck JP. MrBayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst Biol. 2012;61(3):539–42. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys029.
Kozlov AM, Darriba D, Flouri T, Morel B, Stamatakis A. RAxML-NG: a fast, scalable and user-friendly tool for maximum likelihood phylogenetic inference. Bioinformatics. 2019;35(21):4453–5. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz305.
Ozawa G, Shimamura S, Takaki Y, Yokobori SI, Ohara Y, Takishita K, Maruyama T, Fujikura K, Yoshida T. Updated mitochondrial phylogeny of Pteriomorph and Heterodont Bivalvia, including deep-sea chemosymbiotic Bathymodiolus mussels, vesicomyid clams and the thyasirid clam Conchocele cf. bisecta. Marine Genomics. 2017;31:43–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margen.2016.09.003.
Robicheau BM, Breton S, Stewart DT. Sequence motifs associated with paternal transmission of mitochondrial DNA in the horse mussel, Modiolus modiolus (Bivalvia: Mytilidae). Gene. 2017;605:32–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2016.12.025.
Zhang Z, Ma P, Hu L, Liu Y, Wang H. The complete mitochondrial genome of a marine mussel, Modiolus comptus (Mollusca: Mytilidae), and its phylogenetic implication. Mitochondrial DNA Part B. 2019;4(2):4057–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/23802359.2019.1688728.
Li X, Wu X, Yu Z. Complete mitochondrial genome of the Asian green mussel Perna viridis (Bivalvia, Mytilidae). Mitochondrial DNA. 2012;23(5):358–60. https://doi.org/10.3109/19401736.2012.690756.
Ranjard L, Wong TKF, Külheim C, Rodrigo AG, Ragg NLC, Patel S, Dunphy BJ. Complete mitochondrial genome of the green-lipped mussel, Perna canaliculus (Mollusca: Mytiloidea), from long nanopore sequencing reads. Mitochondrial DNA Part B. 2018;3(1):175–6. https://doi.org/10.1080/23802359.2018.1437810.
Gaitán-Espitia JD, Quintero-Galvis JF, Mesas A, D’Elía G: Mitogenomics of southern hemisphere blue mussels (Bivalvia: Pteriomorphia): Insights into the evolutionary characteristics of the Mytilus edulis complex. Scientific Reports. 2016;6(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep26853.
Burzynski A, Smietanka B. Is interlineage recombination responsible for low divergence of mitochondrial nad3 Genes in Mytilus galloprovincialis? Mol Biol Evol. 2009;26(7):1441–5. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msp085.
Śmietanka B, Burzyński A, Wenne R. Comparative Genomics of Marine Mussels (Mytilus spp.) Gender Associated mtDNA: Rapidly Evolving atp8. J Mol Evol. 2010;71(5–6):385–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-010-9393-4.
Ort BS, Pogson GH. Molecular population genetics of the male and female mitochondrial DNA Molecules of the California sea mussel. Mytilus californianus Genetics. 2007;177(2):1087–99. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.107.072934.
Lee Y-C, Lee Y-H. The F type mitochondrial genome of hard-shelled mussel: Mytilus coruscus(Mytiloida, Mytilidae). Mitochondrial DNA. 2014;27(1):624–5. https://doi.org/10.3109/19401736.2014.908375.
Lubośny M, Śmietanka B, Przyłucka A, Burzyński A. Highly divergent mitogenomes of Geukensia demissa (Bivalvia, Mytilidae) with extreme AT content. J Zool Syst Evol Res. 2020;58(2):571–80. https://doi.org/10.1111/jzs.12354.
Uliano-Silva M, Americo J, Bastos AS, Furtado C, Rebelo MDF, Prosdocimi F. Complete mitochondrial genome of the brown mussel Perna perna (Bivalve, Mytilidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A. 2015;27(6):3955–6. https://doi.org/10.3109/19401736.2014.989502.
Bennett KF, Bailey AW, Brambert DJ, Ferhati EW, Karson CA, Nafasat U, Wadleigh JK, Wright AH. The F type mitochondrial genome of the scorched mussel: Brachidontes exustus, (Mytiloida, Mytilidae). Mitochondrial DNA. 2014;27(2):1501–2. https://doi.org/10.3109/19401736.2014.953111.
Lubosny M, Przylucka A, Smietanka B, Burzynski A: Semimytilus algosus: first known hermaphroditic mussel with doubly uniparental inheritance of mitochondrial DNA. Scientific Reports. 2020;10(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-67976-6.
Yang Z. PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol Biol Evol. 2007;24(8):1586–91. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msm088.
Lorion J, Kiel S, Faure B, Kawato M, Ho SY, Marshall B, Tsuchida S, Miyazaki J, Fujiwara Y. Adaptive radiation of chemosymbiotic deep-sea mussels. Proc Biol Sci. 2013;280(1770):20131243. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2013.1243.
Miyazaki J, de Oliveira ML, Fujita Y, Matsumoto H, Fujiwara Y. Evolutionary process of deep-sea bathymodiolus mussels. PLoS ONE. 2010;5(4): e10363. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0010363.
Kelley LA, Mezulis S, Yates CM, Wass MN, Sternberg MJ. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat Protoc. 2015;10(6):845–58. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2015.053.
Efremov RG, Sazanov LA. Structure of the membrane domain of respiratory complex I. Nature. 2011;476(7361):414–20. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10330.
Hirst J. Mitochondrial complex I. Annu Rev Biochem. 2013;82:551–75. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-070511-103700.
Colgan DJ, da Costa P. Invasive and non-invasive lineages in Xenostrobus (Bivalvia: Mytilidae). Molluscan Research. 2013;33(4):272–80. https://doi.org/10.1080/13235818.2013.826574.
Colgan DJ. Fine-scale spatial partitioning of genetic variation and evolutionary contestability in the invasive estuarine mussel Xenostrobus securis. Mar Biol Res. 2017;13(10):1059–72. https://doi.org/10.1080/17451000.2017.1331361.
Yang M, Gong L, Sui J, Li X. The complete mitochondrial genome of Calyptogena marissinica (Heterodonta: Veneroida: Vesicomyidae): Insight into the deep-sea adaptive evolution of vesicomyids. PLoS ONE. 2019;14(9): e0217952. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0217952.
Liu J, Zeng Q, Wang H, Teng M, Guo X, Bao Z, Wang S. The complete mitochondrial genome and phylogenetic analysis of the dwarf surf clam Mulinia lateralis. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2019;5(1):140–1. https://doi.org/10.1080/23802359.2019.1698352.
Chen L, Wahlberg N, Liao CQ, Wang CB, Ma FZ, Huang GH. Fourteen complete mitochondrial genomes of butterflies from the genus Lethe (Lepidoptera, Nymphalidae, Satyrinae) with mitogenome-based phylogenetic analysis. Genomics. 2020;112(6):4435–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.07.042.
Xu W, Ding J, Lin S, Xu R, Liu H. Comparative mitogenomes of three species in Moenkhausia: Rare irregular gene rearrangement within Characidae. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;183:1079–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.05.049.
Gissi C, Iannelli F, Pesole G. Evolution of the mitochondrial genome of Metazoa as exemplified by comparison of congeneric species. Heredity (Edinb). 2008;101(4):301–20. https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.2008.62.
Gissi C, Iannelli F, Pesole G. Complete mtDNA of Ciona intestinalis reveals extensive gene rearrangement and the presence of an atp8 and an extra trnM gene in ascidians. J Mol Evol. 2004;58(4):376–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-003-2559-6.
Gan HM, Grandjean F, Jenkins TL, Austin CM. Absence of evidence is not evidence of absence: Nanopore sequencing and complete assembly of the European lobster (Homarus gammarus) mitogenome uncovers the missing nad2 and a new major gene cluster duplication. BMC Genomics. 2019;20(1):335. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-5704-3.
Audino JA, Serb JM, Marian JEAR. Phylogeny and anatomy of marine mussels (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) reveal convergent evolution of siphon traits. Zool J Linn Soc-Lond. 2020;190(2):592–612. https://doi.org/10.1093/zoolinnean/zlaa011.
Trovant B, Orensanz JM, Ruzzante DE, Stotz W, Basso NG. Scorched mussels (BIVALVIA: MYTILIDAE: BRACHIDONTINAE) from the temperate coasts of South America: phylogenetic relationships, trans-Pacific connections and the footprints of Quaternary glaciations. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2015;82 Pt A:60–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2014.10.002.
Shen YY, Shi P, Sun YB, Zhang YP. Relaxation of selective constraints on avian mitochondrial DNA following the degeneration of flight ability. Genome Res. 2009;19(10):1760–5. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.093138.109.
Sun S, Sha Z, Xiao N. The first two complete mitogenomes of the order Apodida from deep-sea chemoautotrophic environments: New insights into the gene rearrangement, origin and evolution of the deep-sea sea cucumbers. Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics. 2021;39: 100839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbd.2021.100839.
Yang M, Dong D, Li X. The complete mitogenome of Phymorhynchus sp. (Neogastropoda, Conoidea, Raphitomidae) provides insights into the deep-sea adaptive evolution of Conoidea. Ecol Evol. 2021;11(12):7518–31. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.7582.
Wang X, Zhou S, Wu X, Wei Q, Shang Y, Sun G, Mei X, Dong Y, Sha W, Zhang H. High-altitude adaptation in vertebrates as revealed by mitochondrial genome analyses. Ecol Evol. 2021;11(21):15077–84. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.8189.
Cejp B, Ravara A, Aguado MT. First mitochondrial genomes of Chrysopetalidae (Annelida) from shallow-water and deep-sea chemosynthetic environments. Gene. 2022;815: 146159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2021.146159.
Cermakova P, Madarova A, Barath P, Bellova J, Yurchenko V, Horvath A. Differences in mitochondrial NADH dehydrogenase activities in trypanosomatids. Parasitology. 2021;148(10):1161–70. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182020002425.
da Fonseca RR, Johnson WE, O’Brien SJ, Ramos MJ, Antunes A. The adaptive evolution of the mammalian mitochondrial genome. BMC Genomics. 2008;9:119. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-9-119.
Yang S, Lu X, Wang Y, Xu L, Chen X, Yang F, Lai R. A paradigm of thermal adaptation in penguins and elephants by tuning cold activation in TRPM8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(15):8633–8. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1922714117.
Funding
We acknowledge the grant support from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFD1200805), the Project of Sanya Yazhouwan Science and Technology City Management Foundation (SKJC-KJ-2019KY01), and the Key R&D Project of Shandong Province (2021ZLGX03). We thank the Reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BZ and JL designed the experiments. BZ, SG, MZ, HL, JS, HW and QZ performed the experiments. BZ, SG, QZ, JL wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1:
TableS1. Branch-site model analyses in deep sea branches
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, B., Gao, S., Zhao, M. et al. Mitochondrial genomic analyses provide new insights into the “missing” atp8 and adaptive evolution of Mytilidae. BMC Genomics 23, 738 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-022-08940-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-022-08940-8