Abstract
Background
In soybean, some circadian clock genes have been identified as loci for maturity traits. However, the effects of these genes on soybean circadian rhythmicity and their impacts on maturity are unclear.
Results
We used two geographically, phenotypically and genetically distinct cultivars, conventional juvenile Zhonghuang 24 (with functional J/GmELF3a, a homolog of the circadian clock indispensable component EARLY FLOWERING 3) and long juvenile Huaxia 3 (with dysfunctional j/Gmelf3a) to dissect the soybean circadian clock with time-series transcriptomal RNA-Seq analysis of unifoliate leaves on a day scale. The results showed that several known circadian clock components, including RVE1, GI, LUX and TOC1, phase differently in soybean than in Arabidopsis, demonstrating that the soybean circadian clock is obviously different from the canonical model in Arabidopsis. In contrast to the observation that ELF3 dysfunction results in clock arrhythmia in Arabidopsis, the circadian clock is conserved in soybean regardless of the functional status of J/GmELF3a. Soybean exhibits a circadian rhythmicity in both gene expression and alternative splicing. Genes can be grouped into six clusters, C1-C6, with different expression profiles. Many more genes are grouped into the night clusters (C4-C6) than in the day cluster (C2), showing that night is essential for gene expression and regulation. Moreover, soybean chromosomes are activated with a circadian rhythmicity, indicating that high-order chromosome structure might impact circadian rhythmicity. Interestingly, night time points were clustered in one group, while day time points were separated into two groups, morning and afternoon, demonstrating that morning and afternoon are representative of different environments for soybean growth and development. However, no genes were consistently differentially expressed over different time-points, indicating that it is necessary to perform a circadian rhythmicity analysis to more thoroughly dissect the function of a gene. Moreover, the analysis of the circadian rhythmicity of the GmFT family showed that GmELF3a might phase- and amplitude-modulate the GmFT family to regulate the juvenility and maturity traits of soybean.
Conclusions
These results and the resultant RNA-seq data should be helpful in understanding the soybean circadian clock and elucidating the connection between the circadian clock and soybean maturity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The external environment changes with the day and night cycle. To adapt to such regular alterations, organisms including Bacteria, Archaea and Eukaryotes have developed various, elaborate inner time-keeping mechanisms, known as circadian clocks [1]. Circadian clocks perceive environmental time cues, with light being the most dominant one, and generate a 24-h diurnal rhythmicity by central oscillators to synchronize biological processes with daily changes [2,3,4,5].
In the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana, more than 20 clock related components have been identified, such as CIRCADIAN CLOCK ASSOCIATED 1 (CCA1), LATE ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL (LHY), PSEUDO RESPONSE REGULATOR 5 (PRR5), PRR7, PRR9, GIGANTEA (GI), TIMING OF CAB EXPRESSION 1 (TOC1/PRR1), LUX ARRHYTHMO (LUX), EARLY FLOWERING 3 (ELF3) and ELF4 [6, 7]. These components modulate each other at different time points to form morning-, afternoon-, and evening-phased interlocking transcriptional-translational feedback loops to make up a complex circadian clock network [6]. Moreover, ELF4, ELF3, and LUX can form a tripartite complex, the evening complex (EC), which features expression levels that peak at dusk. Significantly, the EC is essential in maintaining regular circadian rhythms, and its dysfunction results in clock arrhythmia [8,9,10,11].
ELF3, a highly conserved plant-specific nuclear protein, is an indispensable component of the circadian clock. First, it works as a scaffold to directly bind ELF4 and LUX to form the EC [12, 13]. ELF3 can regulate the components of the circadian clock directly or indirectly, however it is regulated by negative feedback. Moreover, ELF3 can interact with various proteins that have distinct roles, including all types of phytochromes (PHYA-PHYE), E3 ubiquitin ligase CONSTITUTIVELY PHOTOMORPHOGENIC 1 (COP1), b-box transcription factor BBX19, bHLH transcription factor PIF4, MADS-box transcription factor SHORT VEGETATIVE PERIOD (SVP), LUX homologous protein NOX, MUT9-like nuclear kinases MLK1-4, circadian clock morning protein TOC1 and photoperiod pathway key protein GI [6]. Thus, ELF3 functions as a key hub, linking circadian clocks with other biological processes to orchestrate growth and development with the external environment.
ELF3 has essential functions in crops. Its monocot homologs BdELF3 and SvELF3 can functionally complement loss of ELF3 in the dicot Arabidopsis [14]. Both Earliness per se-D1 (Eps-D1) in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum) and Eps-Am1 in T. monococcum [15] were proposed to be ELF3 genes. OsELF3.1 promotes flowering through inhibiting the phytochrome signaling pathway [16, 17] and leaf senescence in rice but delays leaf senescence in Arabidopsis [19].
Soybean is a short-day photoperiod-sensitive crop. Maturity is the most important trait in soybean breeding and production. Twelve maturity loci – E1-E11 and J – have been proposed, and some have been identified [20]. Recently, Fu et al. [21] proposed some yet-unmapped maturity QTLs related to the south-to-north extension of Northeast China soybean. Notably, most known maturity loci are homologs of circadian clock genes. E3 [22] and E4 [23] encode phytochrome PHYA, which is involved in the input pathway of the circadian clock. E2 [24] and J [25, 26] are respectively homologous to the afternoon-phased oscillator GI and evening-phased ELF3. A PRR family member GmPRR37/GmPRR3b was also recently identified as related to photoperiodic flowering and regional adaptation [27,28,29]. Wang et al. found that loss-of-function of clock gene GmLCL homologs leads to a late-flowering phenotype [4]. Therefore, the circadian clock should be involved in the regulation of maturity. However, the nature of the circadian clock in soybean is still unclear.
The GmFT (FLOWERING LOCUS T) family has essential functions in flowering and maturity. It has at least ten members in the soybean genome due to three whole-genome duplications proposed to occur over evolutionary history [30, 31]. Some members such as GmFT2a, GmFT2b and GmFT5a exert a conserved role as with FT in Arabidopsis and Hd3a in rice to promote flowering [30, 32,33,34]. Other members such as GmFT1a and GmFT4 are neofunctionalized to inhibit flowering [35, 36]. Consistently, genetic analysis showed that GmFT2a and GmFT4 are the maturity alleles E9 and E10, respectively [37, 38]. CRISPR/Cas9 studies further provided knockout evidence to demonstrate the essential role of the GmFT family in flowering and maturity [39,40,41]. A seesaw model was proposed, where flowering promoter members GmFT2a/GmFT5a and flowering inhibitor members GmFT1a/GmFT4 function antagonistically to determine the direction of soybean development [36]. However, although these genes are regulated by different photoperiod conditions, how the circadian clock regulates GmFT family is yet unclear.
In this study, we used RNA-Seq time-series transcriptomal data to analyze the circadian clock of soybean. Moreover, to better avoid potential bias resulting from a specific genetic background, we used two geographically and phenotypically distinct soybean cultivars, the conventional-juvenile cultivar ‘Zhonghuang 24’ (ZH24) from North China and the long-juvenile cultivar ‘Huaxia 3’ (HX3) from South China. Most importantly, these cultivars are genetically distinct because they differ by > 1.6 million genetic variations at the whole genome level [26]. Of these, one single-nucleotide deletion causes a loss-of-function mutation in J/GmELF3a and confers long juvenility to HX3. First, the soybean circadian clock was dissected at the transcriptomal level using RNA-Seq analysis then verified at the level of several individual circadian clock-related genes by qPCR analysis. Second, the oscillation rhythmicity was explored at the levels of gene expression, alternative splicing and chromosome activation. Third, differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were screened at different time points. Finally, the rhythmicity of the GmFT family was further analyzed and one model of GmELF3a regulating the GmFT family was proposed. This time-series transcriptome analysis provides a new perspective for the study of plant circadian rhythms, and suggests that rhythmicity is widespread at different levels. The findings are valuable for exploring the gene expression rhythmicity of soybean.
Results
Soybean exhibits a different circadian clock from the known canonical Arabidopsis model
Transcriptomes of the unifoliate leaves sampled on the third continuous light day after entraining seedlings of both cultivars for seven short days (12 h light and 12 h night) (Fig. 1 A), were sequenced from a minimum of 53,600,114 reads to a maximum of 95,131,850, with an average of 72,751,819 reads (Table S1). These reads were mapped to the genome with more than 94.6 % reads mapped to the reference genome, more than 92.1 % reads properly paired and mapped, and more than 91.3 % mapped uniquely (Table S1). In all, the mapped reads were distributed along with the gene density (Fig. S1). Thus, transcriptome sequencing was high-quality.
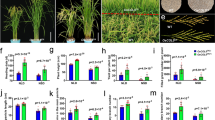
The soybean circadian clock is stable regardless of GmELF3a functionality. (A) Schematic illustration for the experimental design to entrain soybean seedlings for 7 days, followed by 24 h light exposure for 5 days to examine the rhythmicity of expression for selected circadian clock-related genes. (B) The circadian clock was dissected with time-series transcriptomes by detecting the expression rhythmicity of the soybean homologs of circadian clock-related genes: CCA1, ELF3, ELF3L, ELF4, GI, LHY, LUX, PRR3, PRR5, PRR7, RVE1, RVE7 and TOC1. CCA1 indicates GmCCA1 family, ELF3 indicates GmELF3 family, etc. The expression levels were normalized to show the circadian rhythmicity. (C) Quantitative PCR verification of gene expression rhythmicity of soybean homologs of the known evening-phased evening complex components ELF3 and ELF4. (D) Quantitative PCR verification of gene expression rhythmicity of soybean homologs of the known afternoon-phased circadian clock component GIGANTEA and clock-related light signaling gene Phytochrome A. GmActin was used as the reference gene for expression normalization. HPE, hour post entrainment. Although this experiment exposed plants to light constantly, the grey bars indicate the 12-hour periods that would represent nighttime in a 12 h day:12 h night photoperiod
With these transcriptomal data, the soybean circadian clock was analyzed in detail based on the homologs of known circadian clock components. On the whole, these components had sequential expression peaks in a 24-hour rhythmicity (Fig. 1B). GmCCA1s (indicating GmCCA1 family genes), GmLHYs and GmRVE7s (REVEILLE 7) were morning-phased, peaking at dawn then decreasing until early night. GmPRR3s, GmPRR5s and GmPRR7s were afternoon-phased with the highest expression in the afternoon. GmELF4s and GmELF3s were evening-phased, peaking at dusk and in the evening, respectively. The aforementioned genes exhibited a consistent expression profile with their counterparts in Arabidopsis [12].
However, we found that some circadian clock genes featured different expression profiles from their counterparts in Arabidopsis. For example, GmRVE1s was evening-phased while Arabidopsis RVE1 (REVEILLE 1) is morning-phased [42]. GmGIs peaked around dusk while its Arabidopsis counterpart peaked in the afternoon. GmLUXs and GmTOC1s peaked in the early night while their Arabidopsis counterparts peaked around dusk [6]. Noticeably, ELF3 homologs were divided into two clades. One clade of GmELF3s (including GmELF3a, GmELF3b, and GmELF3c) was evening-phased as predicted, while the other clade of GmELF3Ls was morning-phased (including GmELF3Ld and GmELF3Le). These results support that the soybean circadian clock diverges from the known Arabidopsis canonical model [6].
To further evaluate the transcriptome data and the soybean circadian clock model, we performed a quantitative PCR experiment with three biological replicates to assess the expression of the homologs of the known evening-phased clock components ELF3 and ELF4, and the homologs of the known afternoon-phased clock component GIGANTEA, as well as the two genes encoding phytochrome A, which is involved in light signaling of the circadian clock. We found that the ELF3 homologs J/GmELF3a, GmELF3b, GmELF3c and GmELF4a all showed a robust and very similar circadian clock rhythmicity in both cultivars with a peak in the evening and a trough at dawn, although the functional J/GmELF3a was expressed at a higher level in ZH24 than was the nonfunctional j/Gmelf3a in HX3 (Fig. 1 C). GmGIa (also referred as E2) and GmGIb were evening-phased in both cultivars, similar to the expression pattern of GmELF4a (Fig. 1D). These results are consistent with the transcriptome data and show that our transcriptome data are reliable.
Combined with the observation that the light signaling genes GmPhyA3 (E3) and GmPhyA2 (E4) both exhibited similarly robust rhythmicity in the two cultivars (Fig. 1D), all of the assayed genes displayed a comparable oscillation amplitude in ZH24 and HX3, except for the slight differences in J/GmELF3a and GmGIa (E2), indicating that the expression of all genes showed a similarly robust rhythmicity with consistent phasing in the two cultivars (Fig. 1 C and 1D). These results showed that 7 day entrainment of soybean seedlings generates a self-sustained circadian rhythmicity, and the circadian clock is conserved in two geographically, phenotypically and genetically distinct soybean cultivars, even in the genetic background with the j/Gmelf3a dysfunctional allele.
Soybean genes oscillate in a differentially-phased rhythmicity
Because soybean has a different circadian clock from Arabidopsis, it is necessary to explore the expression patterns of all soybean genes, which is a valuable reference for future studies on gene function in soybean. We performed a clustering analysis to obtain an overview of the rhythmicity of all genes in both cultivars. Soybean genes were grouped into six clusters (C1-C6) with different expression profiles (Fig. 2 A and 2B and Table S2), and the clusters had different numbers of genes from each of the two cultivars. Clusters C1-C6 had 5,582, 4,829, 12,194, 6,266, 9,832 and 7,485 genes, respectively, in HX3, and 6,355, 5,033, 5,677, 5,029, 10,330 and 13,764 genes, respectively, in ZH24; the top two clusters were C3 and C5 in HX3, and C6 and C5 in ZH24 (Fig. 2 C).
Gene clustering of Huaxia 3 and Zhonghuang 24. (A and B) Genes are clustered based on scaled expression in Huaxia 3 and Zhonghuang 24. Expression, scaled gene expression. Mean, mean of gene expression (log values); DN, day and night. The black part of the bar indicates the supposed night in continuous light condition. (C) Intersection of gene clusters between Huaxia 3 and Zhonghuang 24. Width is scaled to cluster size of Zhonghuang 24. (D) Polymorphism count ratio of gene body and its flanking regions. Red shows genes that clustered consistently in Huaxia 3 and Zhonghuang 24. Green shows genes that clustered differently in Huaxia 3 and Zhonghuang 24. The polymorphism count of the genes with the same clustering groups were used as the control. U10K, U5K, U2K, and U1K are the upstream regions of 10, 5, 2 and 1 kilobases, respectively. D1K, D2K, D5K and D10K are the downstream regions of 1, 2, 5, and 10 kilobases, respectively. BODY, gene body
The clusters had different expression patterns. Cluster C1 was highly expressed at dawn (H48) and C3 around dusk, and were considered day-night transit clusters (Fig. 2 A and 2B). C2 peaked in the day (H51, H54, and H57) and was a day cluster (Fig. 2 A and 2B). Genes in C5, C6, and C4 were highly expressed in the early (H63), middle (H66) and late night (H69) respectively, and were considered night clusters (Fig. 2 A and 2B). In both cultivars, there were many more genes in the night clusters than in the day clusters, indicating that gene expression is preferentially activated at night. This is consistent with the growth of plants in darkness.
GO (gene ontology) enrichment analysis showed that day-night transit clusters C1 and C3 respectively enriched lipid and carbohydrate metabolism related GO terms, and ribosome biogenesis related GO terms. Day cluster C2 had enriched chloroplast and photosynthesis related GO terms. Night clusters C5, C6 and C4 had enriched protein biosynthesis and metabolism related GO terms, protein phosphorylation related GO terms, and transcription regulation related GO terms, respectively (Table S3). These GO results were consistent with the properties of different clusters. Such results provided a reasonable explanation of catabolism peaking at night and anabolism occurring during the day.
Each cluster had different member genes in the two cultivars. Out of the total of 46,188 detected genes, less than half (19,017, 41.2 %) had the same clustering in the two cultivars (Fig. 2 C). To further elucidate possible reasons for the clustering difference, the distribution of polymorphisms was analyzed. Comparing the genes with the same clustering in the two cultivars, the genes with different clustering exhibited higher polymorphism levels in the upstream 5 K (kilobase) region, the gene body and the downstream regions, but not in the upstream 2 to 1 K regions (Fig. 2D). Thus, clustering differences in the two cultivars may be attributed to genomic variations.
Soybean has a circadian rhythmicity of alternative splicing
As shown before, gene expression exhibited a circadian rhythmicity in soybean, so we wanted to determine whether alternative splicing exhibits some rhythmicity as well. In our time-series RNA-Seq analysis, 56,800 genes were assembled. A total of 34,458 (60.7 %) genes including 32,537 (57.3 %) known genes and 1,921 (3.4 %) new genes were not found to be alternatively spliced. A total of 22,342 (39.3 %) genes had alternative splicing transcripts. Of these, 10,163 (17.9 %) known alternatively spliced genes had no new alternatively spliced transcripts, while 11,724 (20.6 %) known alternatively spliced genes and 455 (0.8 %) new genes had new alternatively spliced transcripts (Fig. 3A). There were 25,274 new alternative splicing transcripts, which accounted for 21.8 % of 115,838 assembled transcripts (Fig. 3B). In all alternative splicing transcripts, there were 23,796 intron retention (IR, 37.7 %), 18,785 alternative 3’ acceptor site (AA, 29.7 %), 11,447 alternative 5’ donor site (AD, 18.1 %), 9,123 exon skipping (ES, 14.4 %) and 43 mutual exon (ME, 0.1 %) events (Fig. 3 C). Taking into account the occurrence of alternative splicing events on an alternative splicing transcript, these five events were grouped into three clades, one included AA and AD, one included ES and IR, and one included ME (Fig. 3D). Moreover, when measured by the total expression of alternative splicing events on alternative splicing transcripts, these events showed a circadian rhythmicity to some extent (Fig. 3E). They appeared to have low expression during the day and high expression at night (Fig. 3E). Around dusk or dawn, the alternative splicing ratio experienced a sharp drop (Fig. 3 F). Moreover, the alternative splicing ratios at night were higher than during the day (Fig. 3 F). This indicated that night is the main time for regulation of gene expression level in soybean.
Alternative splicing shows the circadian rhythmicity. (A) Statistics of alternative splicing (AS) events in assembled genes. (B) Statistics of alternative splicing (AS) events in assembled transcripts. (C) Alternative splicing events are counted based on the transcript with the highest expression for each gene. (D) Correlations of alternative splicing events. (E) Total expression levels of alternative splicing events. (F) Ratio of the total expression between alternative splicing transcripts and all transcripts. AA, alternative 3’ acceptor site; AD, alternative 5’ donor site; ES, exon skipping; ME, mutual exon and IR, intron retention. HX3, Huaxia 3. ZH24, Zhonghuang 24. Grey bar, the supposed night in continuous light conditions
Soybean chromosomes are activated in a circadian rhythmicity
Thousands of genes are organized in each chromosome. It is thus interesting to elucidate whether a chromosome is activated in circadian rhythmicity. The activation level of a chromosome can be measured as the number of reads mapped on the chromosome. We found that chromosomes exhibited a diurnal rhythmicity (Fig. 4 A). Consistent with the transcriptome sequencing being well replicated, the rhythmicity was robustly similar among replicates. Although the two cultivars are genetically distinct, the rhythmicity of all chromosomes was similar and mostly conserved in the two cultivars. However, three chromosomes – Chr01, Chr03, and Chr07 – differed in the activation level but had similar rhythmicity; Chr06 differed in oscillation phase and amplitude (Fig. 4 A). Moreover, the chromosomes were clustered into six groups (chromosome group, CG) with different expression profiles. CG1 was morning-phased (including Chr11, Chr18 and Chr19); CG2 was dawn-phased (including Chr13 and Chr15); CG3 was evening-phased (including Chr01, Chr07, Chr08 and Chr10); CG4 was night-phased (including Chr06, Chr09, Chr12, Chr17 and Chr20); CG5 was noon-phased (including Chr02, Chr03 and Chr14); and CG6 was afternoon-phased (including Chr04, Chr05, and Chr16) (Fig. 4B). Time points were also clustered into three groups (time-point group, TG). TG1, which included 48 and 51 HPE, is in the morning. TG2, including 63, 66 and 69 HPE, is in the night. TG3, which included 54, 57 and 60 HPE, is in the afternoon (Fig. 4B).
No genes were consistently differentially expressed over different timepoints
Because genes exhibited a circadian rhythmicity in the two cultivars, we wanted to figure out the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) potentially responsible for the phenotypic juvenility difference. However, although there were hundreds of DEGs at different time-points, few DEGs overlapped at more than two time-points (Fig. 5 A and 5B). Considering that a multiple-timepoint sampling strategy may be adopted to reduce the fluctuation of peaks and troughs, we simulated a 12-hour spaced sampling strategy and combined two 12-hour spaced samples (for example, 48 and 60 HPE samples) into one merged sample (48/60 HPE sample). We also found that DEGs of merged samples hardly overlapped (Fig. 5 C). These results indicated that DEGs are highly impacted by sampling timing and no conventional DEGs can be reliably claimed to be genes resulting from the phenotypic differences. Therefore, to more thoroughly dissect one gene or one treatment, it is necessary to perform a circadian rhythmicity analysis.
Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between Huaxia 3 and Zhonghuang 24 change significantly over time points. (A) The intersection of DEGs at different time points. The area of an ellipse indicates the number of DEGs that overlapped in two related time points. (B) The Venn diagram of DEGs at four time-points, 48, 51, 54 and 57. (C) The Venn diagram of DEGs at four time-point combinations, 48/60, 51/63, 54/66 and 57/69. 48/60 means the supposed mixed samples sampled at 48 and 60 h after continuous light treatment. 51/63, 54/66 and 57/69 are similar to 48/60
GmELF3a phase- and amplitude-modulates the expression of GmFT family genes
Oscillations have a phase and an amplitude. We further analyzed the oscillation of the flowering-related GmFT family, which is homologous to florigen-encoding gene FLOWERING LOCUS T. In soybean, the GmFT family has essential but divergent functions in flowering regulation, with some members (GmFT1a/4) inhibiting flowering and some members (GmFT2a/5a) promoting flowering. We found that these two types of GmFTs responded differently in the two cultivars (Fig. 6 A). Both types exhibited obviously different amplitudes of expression vibration in the two cultivars (Fig. 6 A). Flowering inhibitors GmFT1a/4 phased differently in the two cultivars: they phased in the evening in HX3 but in the afternoon in ZH24, while flowering promoter GmFT5a phased similarly in the two cultivars (Fig. 6 A). These results indicated that GmELF3 might phase-modulate the flowering-inhibiting members of the GmFT family and amplitude-modulate the flowering-promoting members to regulate the juvenility and maturity traits of soybean (Fig. 6B).
J/GmELF3a regulates juvenility and maturity through phase/amplitude modulating of GmFT family genes. (A) The expression rhythmicity of the GmFT family in two cultivars Huaxia 3 and Zhonghuang 24. The inset shows the rhythmicity phasing of GmFT4 and GmFT5a with the expression levels normalized. (B) A model of J/GmELF3a regulating juvenility and maturity. The dashed line indicates the unchanged rhythmicity of GmELF3 homologs in a loss-of-function GmELF3a mutant. PM, phase modulation; AM, amplitude modulation
Discussion
The circadian clock in soybean is different from that in Arabidopsis. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis showed consistent results in ELF3, ELF4 and GI. One member of PRR3/PRR7, GmPRR37/GmPRR3b, also exhibited day-phased expression with a peak in the afternoon, which is consistent with our results [29]. qPCR results and RNA-Seq analysis showed that the expression phases of several circadian clock components in soybean were significantly different from the expression phases of their counterparts in Arabidopsis. The results confirmed that the soybean circadian clock is different from the known canonical model proposed in Arabidopsis [6]. Moreover, Song et al. [43] suggested it is necessary to fill the gap between laboratory and natural conditions in terms of the circadian clock in soybean. The circadian clock needs to be further explored under natural conditions to help understand its relationship to the maturity trait.
The present study demonstrated that the circadian clock in soybean is conserved even in two geographically, phenotypically and genetically distinct cultivars, indicating that the time-keeping mechanism is inherently required to be stable to properly synchronize biological processes with daily changes. ELF3, a highly conserved plant-specific nuclear protein, is an indispensable component of the circadian clock. ELF3 functions as a scaffold to directly bind ELF4 and LUX to form the EC [12, 13]. ELF3 has essential functions in crops [14,15,16,17,18,19]. Loss-of-function of elf3 results in arrhythmic circadian output in Arabidopsis and barley [8, 44, 45]. However, in soybean, regardless of the functional status of the J/GmELF3a gene, the circadian rhythmicity was regular and similar in two distinct cultivars (Fig. 1), suggesting that the circadian clock was self-sustained in the loss-of-function mutant of J/GmELF3a. Similarly, in chickpea (Cicer arietinum), another Fabaceae species, the ELF3 premature mutant did not disturb the circadian clock [46]. Possibly due to evolutionary whole-genome duplication events, J/GmELFa have four homologs in the soybean genome, GmELF3b, GmELF3c, GmELF3Ld and GmELF3Le (Fig. S2). Phylogenetic analysis showed that two paralogs GmELF3b and GmELF3c were clustered with J into one clade. qPCR and transcriptomal data showed that they exhibited a similar circadian rhythmicity in two cultivars, indicating that the two homologs can function redundantly with J to compensate the loss-of-function of j in HX3 [25, 26]. Moreover, the two homologs in the other clade exhibited a totally different expression profile. This suggests that GmELF3Ld and GmELF3Le might have evolved new functional diversity in addition to sustaining the circadian clock.
All detectable genes oscillated with differentially-phased rhythmicity, meaning that no genes were constantly expressed. All genes reached peaks of expression at different time points, and were clustered into six groups, C1-C6. The enrichment of chloroplast and photosynthesis related GO terms in day cluster C2 is consistent with the biochemical and physiological requirements of plants. The protein biosynthesis and transcription regulation related GO enrichment in night clusters indicates that transcription is highly activated to turn over the proteins during the night. Consistently, the majority of genes were included in night clusters, indicating that genes are more active at night and transcription is more likely to take place at night. This makes sense evolutionarily because plants should have enough resources during the day to use light energy for photosynthesis, while at night, plants can make use of material and energy accumulated during the day for transcription and translation.
Alternative splicing events exhibited a circadian rhythmicity as with genes or transcripts, indicating that the circadian clock is involved in post-transcriptional regulation of a gene, which is consistent with Yang et al. [47]. In Medicago truncatula, the circadian clock component MtJMJC5 underwent cold-dependent alternative splicing [48]. Possibly consistent with the high activation level of transcription, the alternative splicing ratios reached a peak in the night. Similar to Yang et al. [47], the most dominant alternative splicing event was IR while the second was AA.
Soybean chromosomes are like genes in that they are expressed with a circadian rhythmicity. Chromosome remodeling might be involved in circadian oscillations, as indicated by work in mammals [49,50,51,52,53]. In mouse liver, Xu et al. [52] found that the chromatin structure protein cohesin regulates circadian gene expression through long-range chromosome interactions, indicating that high-order chromosome structure will impact circadian rhythmicity. For time points, three groups were identified in the present study, TG1, TG2, and TG3. Night time points were in one group (TG2), while day time points were separated into two groups, morning and afternoon. These results indicated that morning and afternoon are representative of different environments to a large extent for soybean growth and development. Interestingly, the key components of the circadian clock were grouped into morning-, day-, and evening-phased. This finding is likely related to the light-quality difference in the morning and in the afternoon.
Due to the oscillation of gene expression, we did not find any consistent DEGs at different time-points. Therefore, we cannot identify which genes are affected by the functional status of J/GmELF3a. However, when we investigated the circadian rhythmicity of the GmFT family in the two cultivars, we found that flowering-promoting members and flowering-inhibiting members responded differentially to the function of J. Based on our results, we proposed a model where GmFLF3a phase-modulated the flowering-inhibiting members of the GmFT family and amplitude-modulated the flowering-promoting members to regulate the juvenility and maturity traits of soybean. However, more research is required to further elucidate the details.
Considering that nucleotide sequence determines gene expression, the patterning based on dynamic expression data can mimic the evolution based on protein/nucleotide data for homologs of a gene. GmELF3Ls exhibited a different expression profile from GmELF3s, indicating that GmELF3Ls should have divergent functions from GmELF3. There is a similar case in pea (Pisum sativum) where two EARLY FLOWERING3 (ELF3) homologs PHOTOPERIOD (PPD) and HIGH RESPONSE (HR) have divergent functions [54]. Thus, our RNA-seq data is a valuable resource to evaluate the functional divergence between homologs.
Conclusions
The soybean circadian clock is significantly different from the canonical model in Arabidopsis, and is conserved regardless of the functional status of J/GmELF3a. Circadian rhythmicity is exhibited not only at an individual gene level but also at a chromosome level. GmFLF3a might phase-modulate and amplitude-modulate the GmFT family to regulate the juvenility and maturity traits of soybean. These results and the resultant RNA-seq data should be helpful to understand the soybean circadian clock and elucidate the connection between the circadian clock and soybean maturity.
Methods
Plant materials
Two geographically, phenotypically and genetically distinct soybean cultivars, conventional juvenile Zhonghuang 24 (ZH24) and long juvenile Huaxia 3 (HX3) were used. ZH24 is a conventional juvenile soybean cultivar from North China, and HX3 is a long juvenile cultivar from South China. In HX3, a frame-shift mutation of J (GmELF3) confers the long juvenility trait [26]. These cultivars can be publicly acquired from Chinese Crop Germplasm Resources Information System, Institute of Crop Sciences, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. Seeds were germinated in soil and seedlings were grown in a growth chamber at 25℃ and a daytime period of 12 h. The light intensity was set as 20,000-lux and the relative humidity was set as 50 %. Seven days after emergence, plants had unifoliate leaves fully expanded and were further treated in continuous light (24 h light/day). Unifoliate leaves (the first true leaves) were sampled and pooled as a biological replicate from three plants every 3 h for 5 consecutive days, and three biological replicates were used at each timepoint. The samples were frozen quickly in liquid nitrogen then stored at -80℃ .
RNA extraction, cDNA synthesis and real-time quantitative PCR analysis
Total RNA was extracted from the pooled sample leaves following the manual of the TRNzol Universal RNA Extraction Kit (Tiangen, China). cDNA was synthesized with TransScript® One-Step gDNA Removal and cDNA Synthesis SuperMix (Transgen, China). Using the primers listed in Table S4, gene expression was evaluated with real-time quantitative PCR in the Applied Biosystems® QuantStudio™ 7 Flex Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, USA).
RNA sequencing, read alignment and expression evaluation
The leaf samples in the third consecutive day were put on dry ice and delivered to Annoroad Gene Technology (Beijing, China). RNA-Seq library preparation and sequencing were performed using the Illumina Hiseq X Ten sequencing platform. The RNA-seq data were deposited into the NCBI SRA database under accession number PRJNA635449. The Williams 82 reference genome and Phytozome annotations (http://www.phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/) were used as the reference for bioinformatics analysis. Clean reads were aligned to the reference genome by HiSat2 with default parameters [55], the transcripts were assembled, and the expression levels were evaluated by Stringtie [55]. The transcriptome related information was extracted and visualized by Ballgown [55]. Alignment statistics were analyzed with SAMtools [56]. Saturation analysis was performed using an in-house script.
Alternative splicing
After merging all transcript isoforms into one composite gene model, alternative splicing sites were analyzed and counted. The alternative splicing events that occurred at the beginning or end of transcript isoforms were omitted. Consecutive events of exon skipping and mutual exon were counted as one event. Five types of alternative splicing were taken into account, that is, alternative 3’ acceptor site (AA), alternative 5’ donor site (AD), exon skipping (ES), mutual exon (ME) and intron retention (IR). Event expression was measured by the expression level multiplied by the event count of one alternative isoform. The alternative splicing ratio was defined as the ratio between total event expression and total gene expression.
GO enrichment analysis, KEGG pathway analysis and clustering analysis
Using GO term annotation in AgriGO (http://systemsbiology.cau.edu.cn/agriGOv2/) [57], GO enrichment analysis was performed with the R package TopGO [58]. KEGG pathway analysis was performed with the R package clusterProfiler [59]. Clustering analysis was mainly performed with the R package ComplexHeatmap [60].
Availability of data and materials
The RNA-seq data is available in the NCBI SRA database under accession number PRJNA635449.
Abbreviations
- AA:
-
Alternative 3’ acceptor site
- AD:
-
Alternative 5’ donor site
- CCA1:
-
CIRCADIAN CLOCK ASSOCIATED 1
- DEG:
-
Differentially expressed gene
- ELF3:
-
EARLY FLOWERING 3
- ELF4:
-
EARLY FLOWERING 4
- ES:
-
Exon skipping
- GI:
-
GIGANTEA
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- HX3:
-
Huaxia 3 (long juvenility)
- IR:
-
Intron retention
- LHY:
-
LATE ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL
- LUX:
-
LUX ARRHYTHMO
- ME:
-
Mutual exon
- PHYA:
-
PHYTOCHROME A
- PRR5:
-
PSEUDO RESPONSE REGULATOR 5
- PRR7:
-
PSEUDO RESPONSE REGULATOR 7
- PRR9:
-
PSEUDO RESPONSE REGULATOR 9
- RVE1:
-
REVEILLE 1
- RVE7:
-
REVEILLE 7
- TOC1/PRR1:
-
TIMING OF CAB EXPRESSION 1
- ZH24:
-
Zhonghuang 24 (conventional juvenility)
References
Edgar RS, Green EW, Zhao Y, van Ooijen G, Olmedo M, Qin X, et al. Peroxiredoxins are conserved markers of circadian rhythms. Nature. 2012;485:459–64.
Oztas O, Selby CP, Sancar A, Adebali O. Genome-wide excision repair in Arabidopsis is coupled to transcription and reflects circadian gene expression patterns. Nat Commun. 2018;9:1503.
Liu Y, Ma M, Li G, Yuan L, Xie Y, Wei H, et al. Transcription factors FHY3 and FAR1 regulate light-induced CIRCADIAN CLOCK ASSOCIATED1 gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2020;32:1464–78.
Wang Y, Yuan L, Su T, Wang Q, Gao Y, Zhang S, et al. Light- and temperature-entrainable circadian clock in soybean development. Plant Cell Environ. 2020;43:637–48.
Simon NML, Graham CA, Comben NE, Hetherington AM, Dodd AN. The circadian clock influences the long-term water use efficiency of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2020;183:317–30.
Huang H, Nusinow DA. Into the evening: complex interactions in the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Trends Genet. 2016;32:674–86.
Panter PE, Muranaka T, Cuitun-Coronado D, Graham CA, Yochikawa A, Kudoh H, et al. Circadian regulation of the plant transcriptome under natural conditions. Front Genet. 2019;10:1239.
Hicks KA, Millar AJ, Carre IA, Somers DE, Straume M, Meeks-Wagner DR, et al. Conditional circadian dysfunction of the Arabidopsis early-flowering 3 mutant. Science. 1996;274:790–2.
Doyle MR, Davis SJ, Bastow RM, McWatters HG, Kozma-Bognar L, Nagy F, et al. The ELF4 gene controls circadian rhythms and flowering time in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature. 2002;419:74–7.
Hazen SP, Schultz TF, Pruneda-Paz JL, Borevitz JO, Ecker JR, Kay SA. LUX ARRHYTHMO encodes a Myb domain protein essential for circadian rhythms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:10387–92.
Onai K, Ishiura M. PHYTOCLOCK 1 encoding a novel GARP protein essential for the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Genes Cells. 2005;10:963–72.
Nusinow DA, Helfer A, Hamilton EE, King JJ, Imaizumi T, Schultz TF, et al. The ELF4-ELF3-LUX complex links the circadian clock to diurnal control of hypocotyl growth. Nature. 2011;475:398–402.
Herrero E, Kolmos E, Bujdoso N, Yuan Y, Wang M, Berns MC, et al. EARLY FLOWERING4 recruitment of EARLY FLOWERING3 in the nucleus sustains the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Plant Cell. 2012;24:428–43.
Huang H, Gehan MA, Huss SE, Alvarez S, Lizarraga C, Gruebbling EL, et al. Cross-species complementation reveals conserved functions for EARLY FLOWERING 3 between monocots and dicots. Plant Direct. 2017;1:e00018.
Alvarez MA, Tranquilli G, Lewis S, Kippes N, Dubcovsky J. Genetic and physical mapping of the earliness per se locus Eps-A (m) 1 in Triticum monococcum identifies EARLY FLOWERING 3 (ELF3) as a candidate gene. Funct Integr Genomics 2016;16:365 – 82.
Zhao J, Huang X, Ouyang X, Chen W, Du A, Zhu L, et al. OsELF3-1, an ortholog of Arabidopsis EARLY FLOWERING 3, regulates rice circadian rhythm and photoperiodic flowering. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e43705.
Yang Y, Peng Q, Chen G-X, Li X-H, Wu C-Y. OsELF3 is involved in circadian clock regulation for promoting flowering under long-day conditions in rice. Mol Plant. 2013;6:202–15.
Itoh H, Tanaka Y, Izawa T. Genetic relationship between phytochromes and OsELF3-1 reveals the mode of regulation for the suppression of phytochrome signaling in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019;60:549–61.
Sakuraba Y, Han S-H, Yang H-J, Piao W, Paek N-C. Mutation of Rice EARLY FLOWERING3.1 (OsELF3.1) delays leaf senescence in rice. Plant Mol Biol. 2016;92:223–34.
Xia Z, Zhai H, Liu B, Kong F, Yuan X, Wu H, et al. Molecular identification of genes controlling flowering time, maturity, and photoperiod response in soybean. Entwicklungsgeschichte und Systematik der Pflanzen|Plant. Syst Evol. 2012;298(7):1217–27.
Fu M, Wang Y, Ren H, Du W, Wang D, Bao R, et al. Genetic dynamics of earlier maturity group emergence in south-to-north extension of Northeast China soybeans. Theor Appl Genet. 2020;133:1839–57.
Watanabe S, Hideshima R, Xia Z, Tsubokura Y, Sato S, Nakamoto Y, et al. Map-based cloning of the gene associated with the soybean maturity locus E3. Genetics. 2009;182:1251–62.
Liu B, Kanazawa A, Matsumura H, Takahashi R, Harada K, Abe J. Genetic redundancy in soybean photoresponses associated with duplication of the phytochrome A gene. Genetics. 2008;180:995–1007.
Watanabe S, Xia Z, Hideshima R, Tsubokura Y, Sato S, Yamanaka N, et al. A map-based cloning strategy employing a residual heterozygous line reveals that the GIGANTEA gene is involved in soybean maturity and flowering. Genetics. 2011;188:395–407.
Lu S, Zhao X, Hu Y, Liu S, Nan H, Li X, et al. Natural variation at the soybean J locus improves adaptation to the tropics and enhances yield. Nat Genet. 2017;49:773–9.
Yue Y, Liu N, Jiang B, Li M, Wang H, Jiang Z, Pan H, Xia Q, Ma Q, Han T, Nian H. A single nucleotide deletion in J encoding GmELF3 confers long juvenility and is associated with adaption of tropic soybean. Mol Plant. 2017;10:656–8.
Li C, Li Y-H, Li Y, Lu H, Hong H, Tian Y, et al. A domestication-associated gene GmPRR3b regulates the circadian clock and flowering time in soybean. Mol Plant. 2020;13:745–9.
Lu S, Dong L, Fang C, Liu S, Kong L, Cheng Q, et al. Stepwise selection on homeologous PRR genes controlling flowering and maturity during soybean domestication. Nat Genet. 2020;52:428–36.
Wang L, Sun S, Wu T, Liu L, Sun X, Cai Y, et al. Natural variation and CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutation in GmPRR37 affect photoperiodic flowering and contribute to regional adaptation of soybean. Plant Biotechnol J. 2020;18:1869–81.
Sun H, Jia Z, Cao D, Jiang B, Wu C, Hou W, et al. GmFT2a, a soybean homolog of FLOWERING LOCUS T, is involved in flowering transition and maintenance. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e29238.
Wu F, Sedivy EJ, Price WB, Haider W, Hanzawa Y. Evolutionary trajectories of duplicated FT homologues and their roles in soybean domestication. Plant J. 2017;90:941–53.
Kong F, Liu B, Xia Z, Sato S, Kim BM, Watanabe S, et al. Two coordinately regulated homologs of FLOWERING LOCUS T are involved in the control of photoperiodic flowering in soybean. Plant Physiol. 2010;154:1220–31.
Nan H, Cao D, Zhang D, Li Y, Lu S, Tang L, et al. GmFT2a and GmFT5a redundantly and differentially regulate flowering through interaction with and upregulation of the bZIP transcription factor GmFDL19 in soybean. PLoS ONE 2014;9:e97669.
Chen L, Cai Y, Qu M, Wang L, Sun H, Jiang B, et al. Soybean adaption to high-latitude regions is associated with natural variations of GmFT2b, an ortholog of FLOWERING LOCUS T. Plant Cell Environ. 2020;43:934–44.
Zhai H, Lü S, Liang S, Wu H, Zhang X, Liu B, et al. GmFT4, a homolog of FLOWERING LOCUS T, is positively regulated by E1 and functions as a flowering repressor in soybean. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e89030.
Liu W, Jiang B, Ma L, Zhang S, Zhai H, Xu X, et al. Functional diversification of FLOWERING LOCUS T homologs in soybean: GmFT1a and GmFT2a/5a have opposite roles in controlling flowering and maturation. New Phytol. 2018;217:1335–45.
Zhao C, Takeshima R, Zhu J, Xu M, Sato M, Watanabe S, et al. A recessive allele for delayed flowering at the soybean maturity locus E9 is a leaky allele of FT2a, a FLOWERING LOCUS T ortholog. BMC Plant Biol. 2016;16:20.
Samanfar B, Molnar SJ, Charette M, Schoenrock A, Dehne F, Golshani A, et al. Mapping and identification of a potential candidate gene for a novel maturity locus, E10, in soybean. Theor Appl Genet. 2017;130:377–90.
Cai Y, Chen L, Sun S, Wu C, Yao W, Jiang B, et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated deletion of large genomic fragments in soybean. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19:3835.
Cai Y, Chen L, Liu X, Guo C, Sun S, Wu C, et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeted mutagenesis of GmFT2a delays flowering time in soya bean. Plant Biotechnol J. 2018;16:176–85.
Cai Y, Wang L, Chen L, Wu T, Liu L, Sun S, et al. Mutagenesis of GmFT2a and GmFT5a mediated by CRISPR/Cas9 contributes for expanding the regional adaptability of soybean. Plant Biotechnol J 2020;18:298–309.
Rawat R, Schwartz J, Jones MA, Sairanen I, Cheng Y, Andersson CR, et al. REVEILLE1, a Myb-like transcription factor, integrates the circadian clock and auxin pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:16883–8.
Song YH, Kubota A, Kwon MS, Covington MF, Lee N, Taagen ER, et al. Molecular basis of flowering under natural long-day conditions in Arabidopsis. Nat Plants. 2018;4:824–35.
Reed JW, Nagpal P, Bastow RM, Solomon KS, Dowson-Day MJ, Elumalai RP, et al. Independent action of ELF3 and phyB to control hypocotyl elongation and flowering time. Plant Physiol. 2000;122:1149–60.
Müller LM, Mombaerts L, Pankin A, Davis SJ, Webb AAR, Goncalves J, et al. Differential effects of day/night cues and the circadian clock on the barley transcriptome Plant Physiol 183(2):765–779.
Ridge S, Deokar A, Lee R, Daba K, Macknight RC, Weller JL, et al. The chickpea EARLY FLOWERING 1 (Efl1) locus is an ortholog of Arabidopsis ELF3. Plant Physiol. 2017;175:802–15.
Yang Y, Li Y, Sancar A, Oztas O. The circadian clock shapes the Arabidopsis transcriptome by regulating alternative splicing and alternative polyadenylation. J Biol Chem. 2020;295(22):7608–19.
Shen Y, Wu X, Liu D, Song S, Liu D, Wang H. Cold-dependent alternative splicing of a Jumonji C domain-containing gene MtJMJC5 in Medicago truncatula. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;474:271–6.
Aguilar-Arnal L, Hakim O, Patel VR, Baldi P, Hager GL, Sassone-Corsi P. Cycles in spatial and temporal chromosomal organization driven by the circadian clock. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013;20:1206–13.
Chen H, Chen J, Muir LA, Ronquist S, Meixner W, Ljungman M, et al. Functional organization of the human 4D nucleome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112:8002–7.
Zhao H, Sifakis EG, Sumida N, Millan-Arino L, Scholz BA, Svensson JP, et al. PARP1- and CTCF-mediated interactions between active and repressed chromatin at the lamina promote oscillating transcription. Mol Cell. 2015;59:984–97.
Xu Y, Guo W, Li P, Zhang Y, Zhao M, Fan Z, et al. Long-range chromosome interactions mediated by cohesin shape circadian gene expression. PLoS Genet. 2016;12:e1005992.
Mermet J, Yeung J, Hurni C, Mauvoisin D, Gustafson K, Jouffe C, et al. Clock-dependent chromatin topology modulates circadian transcription and behavior. Genes Dev. 2018;32:347–58.
Rubenach AJS, Hecht V, Vander Schoor JK, Liew LC, Aubert G, Burstin J, et al. EARLY FLOWERING3 redundancy fine-tunes photoperiod sensitivity. Plant Physiol. 2017;173:2253–64.
Pertea M, Kim D, Pertea GM, Leek JT, Salzberg SL. Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat Protoc. 2016;11:1650–67.
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, et al. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:2078–9.
Tian T, Liu Y, Yan H, You Q, Yi X, Du Z, et al. agriGO v2.0: a GO analysis toolkit for the agricultural community, 2017 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45:W122–9.
Alexa A, Rahnenfuhrer J, Lengauer T. Improved scoring of functional groups from gene expression data by decorrelating GO graph structure. Bioinformatics. 2006;22:1600–7.
Yu G, Wang L-G, Han Y, He Q-Y. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS. 2012;16:284–7.
Gu Z, Eils R, Schlesner M. Complex heatmaps reveal patterns and correlations in multidimensional genomic data. Bioinformatics. 2016;32(18):2847–9.
Acknowledgements
We thank the staff at the MARA Key Lab of Soybean Biology (Beijing), Institute of Crop Sciences, The Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences for their contributions.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Key Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province (2020B020220008), the Key R & D and Promotion projects in Henan (192102110019), the National Key R & D Program of China (2017YFD0101400) and the China Agriculture Research System (CARS-04). The funding bodies played no role in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.Y., B.J., H.N., T.L. and S.S. conceived and designed the project. Y.Y. and B.J. performed the data analysis. Z.J. and M.C. performed the experimental treatment and sampling. Y.Y., B.J., T.H., E.S., T.W. and S.S. wrote and revised the paper. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, Y., Jiang, Z., Sapey, E. et al. Transcriptomal dissection of soybean circadian rhythmicity in two geographically, phenotypically and genetically distinct cultivars. BMC Genomics 22, 529 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-021-07869-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-021-07869-8