Abstract
Background
The common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus) is one of the most studied primate model organisms. However, the marmoset genomes available in the public databases are highly fragmented and filled with sequence gaps, hindering research advances related to marmoset genomics and transcriptomics.
Results
Here we utilize single-molecule, long-read sequence data to improve and update the existing genome assembly and report a near-complete genome of the common marmoset. The assembly is of 2.79 Gb size, with a contig N50 length of 6.37 Mb and a chromosomal scaffold N50 length of 143.91 Mb, representing the most contiguous and high-quality marmoset genome up to date. Approximately 90% of the assembled genome was represented in contigs longer than 1 Mb, with approximately 104-fold improvement in contiguity over the previously published marmoset genome. More than 98% of the gaps from the previously published genomes were filled successfully, which improved the mapping rates of genomic and transcriptomic data on to the assembled genome.
Conclusions
Altogether the updated, high-quality common marmoset genome assembly provide improvements at various levels over the previous versions of the marmoset genome assemblies. This will allow researchers working on primate genomics to apply the genome more efficiently for their genomic and transcriptomic sequence data.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus) is a small, new-world monkey, which can be handled in laboratories with relative ease [1,2,3]. Mouse is a widely used model animal, however the genetic, physiological, and anatomical differences between mice and primates prevent their application for human studies, thus insisting on the necessity of non-human primate (NHP) models [1, 2]. Common marmosets have an effective breeding capacity relatively among primates, and they show some characteristics which are more related to humans than the other NHPs [2]. Common marmosets have been utilized as models for numerous neurological diseases [2], and a multiscale brain atlas project called Brain/MINDS had been initiated with a 10-year roadmap [4]. In addition, marmosets were the first transgenic NHPs to be generated with germline transmission [1], while also their embryonic stem cell lines and induced pluripotent stem cell lines are being widely researched [5, 6]. In light of the increasing importance of marmosets as an alternative NHP model animal for biomedical and neuroscience research, the genome was first sequenced by the marmoset genome sequencing and analysis consortium [7]. The 2.26 Gb assembled genome from a female marmoset, although was sorted out into chromosomes, contained many shorter contigs and also 187,214 gap regions. These hard to assemble gap regions cannot be ignored, as they can lead to false positive results [8], and the gap regions could harbor many functionally relevant genes [9]. Recent studies have uncovered that many genes were wrongly labelled as missing in bird genomes, because of the locality of those genes being GC-rich and hence had posed challenges in identifying them [9]. To improve such poorly assembled regions of the marmoset genome, second-generation sequencing technology (Illumina) based short reads were employed, which helped fill approximately one-third (65,384) of the gap regions [10]. However, the genome still remains largely fragmented (contig N50 = 61 kbp) aside from the numerous undetermined bps. Sequence gaps and fragmented contigs are characteristic features in genome assemblies, however, with the rise of third-generation sequencing technologies such as Pacific Biosciences (PacBio) and Oxford Nanopore sequencing technologies, a large number of genomes are being updated to high contiguity genomes with the help of longer reads [11, 12]. As an example, the genomes of apes assembled using first and second-generation sequencing data were abounded with tens to hundreds of thousands of gaps impacting multi-genome sequence alignments which limited sequence based discoveries [13]. Recently, the ape genomes of Gorilla, Orangutan, and, Chimpanzee, were sequenced and reassembled using PacBio reads resulting in large scale improvements in the respective genomes [13]. Similarly, for the common marmoset, after first- and second-generation sequencing technologies left the genome fragmented with many gaps, we have employed PacBio sequencing, a third-generation, single-molecule sequencing technology, and here, we report the updated version of the common marmoset genome with fewer gaps and high contiguity.
Results and discussions
De novo assembly and pseudo-chromosome construction
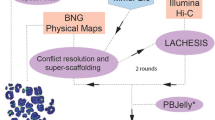
The long-read sequence data obtained from the PacBio RSII sequencer amounted to 114.80 Gb, covering approximately 43 × of the genome (Fig. S1). In the context of the size of the genome, the lengths of the PacBio reads (N50: 16.41 kbp; average sequence length: 11 kbp) were only slightly shorter than the contiguous gap-free regions from the previous marmoset genome assembly (N50: 61 kbp; average sequence length: 24 kbp). After assembling the sequence data with several assembly tools as part of the assembly workflow (Fig. 1), SMARTdenovo and wtdbg assemblies produced better results compared to the other assemblers in terms of contiguity, with N50 values reaching more than 6 Mb (Table S1). SMARTdenovo produced a slightly shorter N50 in comparison to wtdbg, but was chosen as the final assembly considering that SMARTdenovo had relatively longer average contig lengths and the least number of contigs. After constructing pseudo-chromosomes for all the assemblies (Table S2), the alternate assemblies were used to fill the gaps in the SMARTdenovo pseudo-chromosomes, resulting in 1771 sequence gaps. The final assembly size was 2.79 Gb, with a scaffold N50 value of 143.89 Mb corresponding to the chromosome lengths, and a contig N50 value of 6.38 Mb (Table 1). The obtained contig N50 value compared favorably against the recently updated genome assemblies using PacBio reads, whose average contig N50 was 6.34 Mb (Table 2). The N50 values were better for the other genome assemblies, only when multiple additional technologies such as Hi-C, CHICAGO, and BioNano optical maps were employed. When considering assemblies which used only third-generation sequence data for updating the genome, the marmoset genome assembly’s contig N50 ranked the best among them, in spite of the relatively longer genome size (Table 2). The assembly was estimated to comprise 39.37% repeat content. As expected in the primate genomes, the LINE1 elements contributed to most (21.44%) of the repeats. SINES (9.18%) and LTR elements (5.24%) were also distributed throughout the genome (Table S3). Only a very small percentage (0.07%) of the repeats was left unclassified. A total of 18,385 gene models, along with 78,992 alternatively spliced transcripts, were obtained using the combined approach.
Evaluation of the assembly
As of March 31, 2019, the NCBI database for assembly of the common marmoset genome contained four assemblies: i) the first genome submitted at 2010 [7], ii) the improved genome using Illumina submitted at 2015 [10], iii) an Ion-torrent based genome submitted at 2015, and iv) an Illumina based genome anchored by Hi-C and CHICAGO libraries submitted at 2017 (Table S4). The ion-torrent based assembly contained more than one Gb of the genome missing and hence was ignored for the evaluation purpose, while the rest of the assemblies were designated names in this manuscript, according to their submission years as CJ2010, CJ2015, and CJ2017, respectively. The genome assembly presented in this study was designated as CJ2019. When BUSCO [27] was executed for the assemblies, the BUSCO scores yielded 92.9% completeness for both CJ2017 and CJ2019 assemblies, and 92.1 and 91.9% completeness for CJ2010 and CJ2015 assemblies respectively. This indicated that all the assemblies had high level of completeness at the level of conserved genes. The major differences between the current assembly and the previous assemblies were observed in contiguity, number of sequence gaps, and mapping rates of sequence data.
Improved contiguity
Using the contig N50 value as a metric, CJ2019 produced 217.76, 104.42, and 41.06 fold contiguity improvements over CJ2010, CJ2015, and CJ2017 assemblies, respectively (Fig. S2). The CJ2019 assembly also showed a range of 36.88 to 177.22 fold improvements in contig N75 values over the previous marmoset assemblies (Fig. S2). To further insist on the quality of the CJ2019 assembly at the contiguity level, 2.50 Gb of the 2.79 Gb genome was represented in contigs which were longer than 1 Mb. Also, 54 contigs were of length more than 10 Mb, while it should be noted that there was not even a single contig which managed to reach a length of 1 Mb in any of the previous marmoset assemblies. When the N(x) values are plotted, although the scaffold N(x) values were similar across the assemblies (Fig. 2a), the other assemblies fell below in comparison to the CJ2019 contig graph (Fig. 2b). All the assemblies produced scaffolds in the range of chromosomal lengths, with the N50 values reaching 132.17 Mb, 140.45 Mb, 129.2 Mb, and 143.89 Mb for CJ2010, CJ2015, CJ2017, and CJ2019 assemblies respectively.
Reduced sequence gaps
The other major improvement in the CJ2019 assembly is a significant reduction in the number of sequence gaps (Table 3). While the CJ2015 genome closed approximately 41% of the gaps in the CJ2010 genome, the current CJ2019 genome resulted in 1771 gaps, closing more than 98% of the sequence gaps from the previous versions of the marmoset genome. This resulted in more than 99% of the genome being sequenced, leaving only complex regions such as centromeric repeats, and large segmental duplications to be filled. The closing of the gaps greatly facilitated the mapping of all kinds of data onto the CJ2019 assembly, increasing the space for repeat and gene identifications.
Improved mapping rates
When marmoset RNAseq reads from 12 different brain tissues were aligned against the assemblies, the average mapping rate was below 80% for all the previous assemblies. In contrast, the CJ2019 genome assembly displayed more than 80% alignment in all but one of the samples (Fig. 3a). On average, the mapping rates were 8.26, 9.93, and 5.13% higher than the CJ2010, CJ2015, and CJ2017 assemblies respectively. Also, Human Gencode (Release 29) transcripts, mapped more to the CJ2019 genome than the previous versions. When BAC-end data were mapped, against the current chromosomal genomes (CJ2010 and CJ2015) at NCBI, the difference in mapping rates was more than 12% (Fig. 3b). Compared to the CJ2017 assembly, the concordant mapping rate of BAC-end data was increased by 6.30%. The increase in mapping rates is further proof that the genome has been improved significantly.
Possible structural errors
CJ2017 and CJ2019 genome assemblies were aligned against each other with minimap2 [28] and visualized using dot plots generated by d-genies [29]. Numerous small and large inversions were observed between the two assemblies. Hi-C scaffolding can erroneously introduce inversions in short contigs [30], and this can be attributed to the small inversions observed in the dot plots (Fig. 4a). However, larger inversions, such as that observed in chromosome 16 (Fig. 4b), could be actual misassembled structural errors. The mapping of long-range paired BAC-end reads did not support the chromosome 16 inversion of CJ2019 genome, indirectly hinting that the make-up at this particular location is more accurate in CJ2017 genome. It has to be noted that the original marmoset genome assembly was constructed with human genome as a guiding factor, and hence some parts are effectively humanized and could be actually structural errors. A new common marmoset genome, as a part of the Vertebrate Genome Project, is under development, which includes 55.69 x coverage of 10x genomics data, 105.81 x coverage of Arima Hi-C data, 154.52 x coverage of BioNano optical map data, along with PacBio and Illumina sequence reads [31]. Although vast improvements in terms of contiguity, sequence gaps, and mapping rates of various genomic elements could be observed in the CJ2019 assembly, structural errors could potentially remain which would need the combination of the above data to effectively resolve them.
Conclusions
The high-quality genome constructed as part of this manuscript has shown vast improvements in terms of contiguity, gaps, genomic features, and mapping rates of sequence data and will be widely useful for researchers involved in the field of primate genomics.
Methods
Sample preparation and sequencing
The liver sample (Animal I2075) from the Central Institute for Experimental Animals (CIEA), Japan, was originally used to improve the Marmoset genome using Illumina [10], with ample part of the animal’s samples retained for future use. Briefly, an 8-year, 4-month-old male marmoset liver was used for DNA extraction using the phenol-chloroform-isoamyl alcohol extraction method. The genomic DNA for long-read sequencing in this study was extracted from the kidney of the same animal described above. The genomic DNA was extracted using QIAGEN Genomic-tip 500/G (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instruction. To avoid blood contamination, bloodletting was performed completely at the dissection. The genomic sample was sequenced using PacBio RSII sequencer on 93 SMRT cells. In addition, RNA sequencing was also employed to improve the prediction of gene models. Two male marmosets (Animals: I5998 and I6289) that were 2 years old and obtained from CLEA Japan Inc. were deeply anaesthetized with isoflurane and euthanized by exsanguination from the femoral artery. Twelve tissue samples from the brain (Table S5) were collected and immediately frozen using liquid nitrogen and were rapidly broken down in solution D using a polytron homogenizer, before extracting the total RNA by the acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform method. The quality and the concentration of the sample were measured using the 2100 Bioanalyzer instrument with the Agilent RNA 6000 Nano kit. The cDNA sequencing libraries were constructed with 1000 nanograms of total RNA using the TruSeq RNA Sample Prep Kit (Illumina), following the instructions in the TruSeq RNA Sample Preparation V2 Guide (Illumina). MiSeq Reagent Kit v3 (600-cycles) was used for sequencing the RNA samples (2 * 150 bp PE reads) with the MiSeq sequencer.
De novo assembly and pseudo-chromosome construction
The sequenced reads were input to several assembly tools as recommended in the benchmark article [32], including Canu [33], SMARTdenovo [34], wtdbg [35], miniasm [36], Flye [37], Falcon [38], and MECAT [39], as part of the assembly workflow (Fig. 1). MECAT aborted with a segmentation fault, while Falcon produced relatively shorter contigs, and both were subsequently left out from the further analysis. Quiver [40] was executed in two iterative rounds to polish all the assemblies. In the case of wtdbg and miniasm assemblies, an additional round of quiver was performed owing to their relatively high error rates in the consensus sequences. RaGOO [41] was used to construct pseudo-chromosomes from the assembled contigs by using the previous marmoset genome [10], as a reference. To fill the gaps, a hybrid assembly was constructed by mapping, using minimap2, the flanking regions of sequence gaps in the SMARTdenovo assembly against the contiguous regions of the other assemblies, and replacing the gaps with nucleotide bps. Two rounds of consensus polishing by Pilon [42], using Illumina data from the same sample [10], was also executed to polish the assemblies further.
Genome annotation
Repeat content was assessed using RepeatModeler and RepeatMasker [43]. The repeats, in the contiguous sequences of the assembly, were first identified by RepeatModeler to construct repeat family libraries, which were in turn used by RepeatMasker to annotate and mask the repetitive regions of the assembled pseudo-chromosomes. For gene annotation, a random set of 1000 multi-exon genes were obtained from Ensembl (Release version 95) database’s common marmoset gene annotation to train gene models using Augustus [44]. In addition, a combination of ab-initio based, homology based, and transcriptome-based strategies were applied to predict and update the predicted genes. In the homology based approach, protein sequences were collected from a) the recently assembled Chimpanzee and Orangutan genomes [13], from NCBI, b) NCBI’s NR protein database for the Gorilla genome, and c) the Gencode (Release 29) database for the Human genome, and were aligned against the assembled genome using funannotate [45], which in-turn uses diamond [46], and exonerate [47]. Parallelly, Marmoset ESTs downloaded from NCBI were input to PASA [48], to model gene structures from the EST alignments. These EST and protein alignments were provided as hints for the Augustus ab-initio gene prediction program with the trained gene model as the species parameter on the assembled genome, which was earlier soft-masked for repeats using RepeatMasker. Later, RNAseq reads from the 12 different brain tissues (Table S5), as well as marmoset samples from the study, SRP051959 [49], were de novo assembled into transcripts using Trinity [50]. PASA was used once again, in conjunction with the Trinity transcripts, to update the UTR and alternate splicing information of the predicted genes.
Evaluation of the assembly
BUSCO was used to evaluate the completeness of the evolutionarily conserved genes in the assemblies. To further evaluate the quality of the de novo assembly, different sets of DNA and RNA data were aligned against the assembled genomes. RNAseq reads, Human Gencode transcripts, and BAC-end data, were aligned against the genome assemblies using STAR [51], GMAP [52], and bowtie2 [53] aligners respectively. Minimap2 [28] was used to align the whole genome assemblies against each other, and d-geneis [29] was used to obtain and visualize dot plots from the alignments.
Availability of data and materials
All data has been submitted to the DNA DataBank of Japan (DDBJ). The Bioproject, the Biosample, and the DDBJ read archive accession numbers for the genome data are PRJDB8242, SAMD00169834, and DRA008324 respectively. The genome assembly has the accession numbers: BJKT01000001–BJKT01000065. The RNAseq data has accession numbers: DRA008173, DRA006301, and DRA008220.
Abbreviations
- SMRT:
-
Single Molecule Real Time
- RNA:
-
RiboNucleic Acid
- LINE:
-
Long Interspersed Nuclear Elements
- SINE:
-
Short Interspersed Nuclear Elements
- LTR:
-
Long Terminal Repeats
- NCBI:
-
National Center for Biotechnology Information
- NR:
-
Non Redundant database
- CDS:
-
Coding sequence
- EST:
-
Expressed Sequence Tags
- bp:
-
basepair
- kbp:
-
kilo basepair
- Mb:
-
mega basepair
- Gb:
-
Giga basepair
- BAC-end:
-
Bacterial Artificial Clone end
References
Sasaki E, Suemizu H, Shimada A, Hanazawa K, Oiwa R, Kamioka M, et al. Generation of transgenic non-human primates with germline transmission. Nature. 2009;459:523–7.
Okano H, Hikishima K, Iriki A, Sasaki E. The common marmoset as a novel animal model system for biomedical and neuroscience research applications. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012;17:336–40.
Kishi N, Sato K, Sasaki E, Okano H. Common marmoset as a new model animal for neuroscience research and genome editing technology. Dev Growth Differ. 2014;56:53–62.
Okano H, Sasaki E, Yamamori T, Iriki A, Shimogori T, Yamaguchi Y, et al. Brain/MINDS: a Japanese national brain project for marmoset neuroscience. Neuron. 2016;92:582–90.
Sasaki E, Hanazawa K, Kurita R, Akatsuka A, Yoshizaki T, Ishii H, et al. Establishment of novel embryonic stem cell lines derived from the common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus). Stem Cells. 2005;23:1304–13.
Tomioka I, Maeda T, Shimada H, Kawai K, Okada Y, Igarashi H, et al. Generating induced pluripotent stem cells from common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus) fetal liver cells using defined factors, including Lin28. Genes Cells. 2010;15:959–69.
Worley KC, Warren WC, Rogers J, Locke D, Muzny DM, Mardis ER, et al. The common marmoset genome provides insight into primate biology and evolution. Nat Genet. 2014;46:850–7.
Domanska D, Kanduri C, Simovski B, Sandve GK. Mind the gaps: overlooking inaccessible regions confounds statistical testing in genome analysis. BMC Bioinformatics. 2018;19(481).
Peona V, Weissensteiner MH, Suh A. How complete are “complete” genome assemblies?-an avian perspective. Mol Ecol Resour. 2018;18:1188–95.
Sato K, Kuroki Y, Kumita W, Fujiyama A, Toyoda A, Kawai J, et al. Resequencing of the common marmoset genome improves genome assemblies and gene-coding sequence analysis. Sci Rep. 2015;16894.
Matthews BJ, Dudchenko O, Kingan SB, Koren S, Antoshechkin I, Crawford JE, et al. Improved reference genome of Aedes aegypti informs arbovirus vector control. Nature. 2018;563(7732):501–7.
Jiao Y, Peluso P, Shi J, Liang T, Stitzer MC, Wang B, et al. Improved maize reference genome with single-molecule technologies. Nature. 2017;546(7659):524–7.
Kronenberg ZN, Fiddes IT, Gordon D, Murali S, Cantsilieris S, Meyerson OS, et al. High-resolution comparative analysis of great ape genomes. Science. 2018;360:eaar6343.
Zhang L, Cai X, Wu J, Liu M, Grob S, Cheng F, et al. Improved Brassica rapa reference genome by single-molecule sequencing and chromosome conformation capture technologies. Hortic Res. 2018;5(1):50.
Low WY, Tearle R, Bickhart DM, Rosen BD, Kingan SB, Swale T, et al. Chromosome-level assembly of the water buffalo genome surpasses human and goat genomes in sequence contiguity. Nat Commun. 2019;10(260).
Korlach J, Gedman G, Kingan SB, Chin CS, Howard JT, Audet JN, et al. De novo PacBio long-read and phased avian genome assemblies correct and add to reference genes generated with intermediate and short reads. Gigascience. 2017;6:1–16.
Shields EJ, Sheng L, Weiner AK, Garcia BA, Bonasio R. High-quality genome assemblies reveal long non-coding RNAs expressed in ant brains. Cell Rep. 2018;23:3078–90.
Bickhart DM, Rosen BD, Koren S, Sayre BL, Hastie AR, Chan S, et al. Single-molecule sequencing and chromatin conformation capture enable de novo reference assembly of the domestic goat genome. Nat Genet. 2017;49:643–50.
Holt C, Campbell M, Keays DA, Edelman N, Kapusta A, Maclary E, et al. Improved genome assembly and annotation for the rock pigeon (Columba livia). G3:Genes|Genomes|Genetics. 2018;8:1391–8.
Edger PP, VanBuren R, Colle M, Poorten TJ, Wai CM, Niederhuth CE, et al. Single-molecule sequencing and optical mapping yields an improved genome of woodland strawberry (Fragaria vesca) with chromosome-scale contiguity. GigaScience. 2018;7:1–7.
Warren WC, Hillier LW, Tomlinson C, Minx P, Kremitzki M, Graves T, et al. A new chicken genome assembly provides insight into avian genome structure. G3: Genes|Genomes|Genetics. 2017;7:109–17.
Gordon D, Huddleston J, Chaisson MJP, Hill CM, Kronenberg ZN, Munson KM, et al. Long-read sequence assembly of the gorilla genome. Science. 2016;352(6281).
Nyima T, Zeng X, Li X, Bai L, Wang Y, Xu T, et al. Improved high-quality genome assembly and annotation of Tibetan hulless barley. bioRxiv. 2018;409136.
VanBuren R, Wai CM, Colle M, Wang J, Sullivan S, Bushakra JM, et al. A near complete, chromosome-scale assembly of the black raspberry (Rubus occidentalis) genome. Gigascience. 2018;7(8).
Xia M, Han X, He H, Yu R, Zhen G, Jia X, et al. Improved de novo genome assembly and analysis of the Chinese cucurbit Siraitia grosvenorii, also known as monk fruit or luo-han-guo. Gigascience. 2018;7(6).
Mattingsdal M, Jentoft S, Tørresen OK, Knutsen H, Hansen MM, Robalo JI, et al. A continuous genome assembly of the corkwing wrasse (Symphodus melops). Genomics. 2018;110(6):399–403.
Simão FA, Waterhouse RM, Ioannidis P, Kriventseva EV, Zdobnov EM. BUSCO: assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics. 2015;31(19):3210–2.
Li H. Minimap2: pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics. 2018;34(18):3094–100.
Cabanettes F, Klopp C. D-GENIES: dot plot large genomes in an interactive, efficient and simple way. PeerJ. 2018;6:e4958.
Ghurye J, Rhie A, Walenz BP, Schmitt A, Selvaraj S, Pop M, et al. Integrating hi-C links with assembly graphs for chromosome-scale assembly. PLoS Comput Biol. 2019;15(8):e1007273.
Marmoset genome data at Vertebrate Genome Project. Available at: https://vgp.github.io/genomeark/Callithrix_jacchus. Accessed on Oct 28, 2019.
Jayakumar V, Sakakibara Y. Comprehensive evaluation of non-hybrid genome assembly tools for third-generation PacBio long-read sequence data. Brief Bioinform. 2017;20(3):866–76.
Koren S, Walenz BP, Berlin K, Miller JR, Bergman NH, Phillippy AM. Canu: scalable and accurate long-read assembly via adaptive κ-mer weighting and repeat separation. Genome Res. 2017;27:722–36.
SMARTdenovo. Available at: https://github.com/ruanjue/smartdenovo. Accessed on Oct 1, 2019.
Ruan J, Li H. Fast and accurate long-read assembly with wtdbg2. bioRxiv. 2019;530972.
Li H. Minimap and miniasm: fast mapping and de novo assembly for noisy long sequences. Bioinformatics. 2016;32:2103–10.
Kolmogorov M, Yuan J, Lin Y, Pevzner PA. Assembly of long, error-prone reads using repeat graphs. Nat Biotechnol. 2019;37:540–6.
Chin CS, Peluso P, Sedlazeck FJ, Nattestad M, Concepcion GT, Clum A, et al. Phased diploid genome assembly with single-molecule real-time sequencing. Nat Methods. 2016;13:1050–4.
Le Xiao C, Chen Y, Xie SQ, Chen KN, Wang Y, Han Y, et al. MECAT: fast mapping, error correction, and de novo assembly for single-molecule sequencing reads. Nat Methods. 2017;14:1072–4.
Chin C-S, Alexander DH, Marks P, Klammer AA, Drake J, Heiner C, et al. nonhybrid, finished microbial genome assemblies from long-read SMRT sequencing data. Nat Methods. 2013;10(6):563–9.
Alonge M, Soyk S, Ramakrishnan S, Wang X, Goodwin S, Sedlazeck FJ, et al. RaGOO: fast and accurate reference-guided scaffolding of draft genomes. Genome Biol. 2019;20(1):224.
Walker BJ, Abeel T, Shea T, Priest M, Abouelliel A. Pilon: an integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement. PLoS One. 2014;9:e112963.
Tarailo-Graovac M, Chen N. Using RepeatMasker to identify repetitive elements in genomic sequences. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2009;25:4.10.1–4.10.14.
Stanke M, Waack S. Gene prediction with a hidden Markov model and a new intron submodel. Bioinformatics. 2003;19(Suppl 2):ii215–25.
Funannotate. Available at: https://github.com/nextgenusfs/funannotate. Accessed on Oct 1, 2019.
Buchfink B, Xie C, Huson DH. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat Methods. 2015;12(1):59–60.
Slater G, Birney E. Automated generation of heuristics for biological sequence comparison. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005;6(1):31.
Haas BJ, Delcher AL, Mount SM, Wortman JR, Smith RK, Hannick LI, et al. Improving the Arabidopsis genome annotation using maximal transcript alignment assemblies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31(19):5654–66.
Peng X, Thierry-Mieg J, Thierry-Mieg D, Nishida A, Pipes L, Bozinoski M, et al. Tissue-specific transcriptome sequencing analysis expands the non-human primate reference transcriptome resource (NHPRTR). Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(D1):D737–42.
Grabherr MG, Haas BJ, Yassour M, Levin JZ, Thompson DA, Amit I, et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29(7):644–52.
Dobin A, Davis CA, Schlesinger F, Drenkow J, Zaleski C, Jha S, et al. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics. 2013;29(1):15–21.
Wu TD, Watanabe CK. GMAP: a genomic mapping and alignment program for mRNA and EST sequences. Bioinformatics. 2005;21(9):1859–75.
Langmead B, Salzberg SL. Fast gapped-read alignment with bowtie 2. Nat Methods. 2012;9(4):357–9.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
About this supplement
This article has been published as part of BMC Genomics, Volume 21 Supplement 3, 2020: 18th International Conference on Bioinformatics. The full contents of the supplement are available at https://bmcgenomics.biomedcentral.com/articles/supplements/volume-21-supplement-3.
Funding
Publication of this supplement is funded by grants from the Strategic Research Program for Brain Sciences; and by grants from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT) of Japan to E.S., H.O., and Y.S.; Y.S. was also supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers 16H06279 and 18H04127 of Japan. V.J. and Y.S. were also supported by Innovative Areas [no. 221S0002] from MEXT, Japan, and Program for Promoting Platform of Genomics based Drug Discovery from the Japan Agency AMED under Grant Number JP19kk0305008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.S. and H.O. designed the resequencing project; V.J. executed genome assembly, annotation and comparative analysis; H. I, M.S. and S.H. performed RNA extraction and sequencing; W.K. performed DNA extraction; K.S. performed quality and adapter trimming of Illumina sequence data; E.S. and T.I. provided samples for genomic sequencing; Y.S. coordinated manuscript writing and high-throughput sequencing. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The animal experiment protocol was approved by the CIEA Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (approval nos. 16041 and 17031). Also, all the animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (approval nos. 12025 and 13071). The study was conducted in accordance with the guidelines of CIEA that comply with the Guidelines for Proper Conduct of Animal Experiments published by the Science Council of Japan. Animal care was conducted in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (Institute for Laboratory Animal Resources, 2011).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
H.O is a paid Scientific Advisory Board of SanBio Co. Ltd. And K Pharma Inc. The other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1.
Parameters used for the tools.
Additional file 2: Figure S1.
Histogram of the sequenced read lengths.
Additional file 3: Figure S2.
Comparison of the N50 and N75 values across all the assembled genomes.
Additional file 4: Table S1.
Assembly statistics of the marmoset genome from different assemblers.
Additional file 5: Table S2.
Pseudo-chromosome statistics of the marmoset genome assemblies from different assemblers.
Additional file 6: Table S3.
Repeat statistics of the final marmoset genome assembly.
Additional file 7: Table S4.
Summary of the marmoset genome assemblies in the NCBI Assembly database.
Additional file 8: Table S5.
RNAseq of brain tissue samples.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Jayakumar, V., Ishii, H., Seki, M. et al. An improved de novo genome assembly of the common marmoset genome yields improved contiguity and increased mapping rates of sequence data. BMC Genomics 21 (Suppl 3), 243 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-020-6657-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-020-6657-2