Abstract
Background
SPL (SQUAMOSA-promoter binding protein-like) proteins form a large family of plant-specific transcription factors that play essential roles in various aspects of plant growth and development. They are potentially important candidates for genetic improvement of agronomic traits. However, there were limited information about the SPL genes in Jatropha curcas, an important biofuel plant.
Results
In Jatropha, 15 JcSPL genes were identified. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that most of the JcSPLs were closely related to SPLs from woody plant rather than herbaceous plant and distantly related to monocotyledon SPLs. Gene structure, conserved motif and repetitive sequence analysis indicated diverse and specific functions of some JcSPL genes. By combination of target prediction and degradome sequencing analysis, 10 of the 15 JcSPLs were shown to be targets of JcmiR156. Quantitative PCR analysis showed diversified spatial-temporal expression patterns of JcSPLs. It is interesting that the expression levels of JcSPL3 were the highest in all tissues examined in 7- or 10-year-old plants and exhibited increasing trend with plant age, suggesting its important role in the regulation of age development in Jatropha. Overexpression of JcSPL3 in Arabidopsis resulted in earlier flowering time, shorter silique length and reduced biomass of roots.
Conclusions
Through comprehensive and systematic analysis of phylogenetic relationships, conserved motifs, gene structures, chromosomal locations, repetitive sequence and expression patterns, 15 JcSPL genes were identified in Jatropha and characterized in great detail. These results provide deep insight into the evolutionary origin and biological significance of plant SPLs and lay the foundation for further functional characterization of JcSPLs with the purpose of genetic improvement in Jatropha.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
SPL (SQUAMOSA-promoter binding protein-like) proteins form a major family of plant-specific transcription factors that play important roles in plant growth and development. They include a highly conserved 76 amino acid residue SBP (SQUAMOSA-promoter binding protein) domain. This domain contains two zinc-binding sites essential for DNA binding and a bipartite nuclear localization signal (NLS) at the C-terminal [1, 2]. The SPL genes were first identified in Antirrhinum majus for their ability to bind to the floral meristem identity gene SQUAMOSA promoter [3]. Ever since, the orthologous SPL genes have been identified in various plants ranging from the single-cell alage (Chlamydomonas reinhardtii) [4] and moss (Physcomitrella patens) [5], to Arabidopsis thaliana [6], rice (Oryza sativa) [7], and perennial plant silver birth (Betula pendula) [8], apple (Malus domestica) [9] and poplar (Populus trichocarpa) [10]. In these plants, the SPL genes were uncovered to regulate various aspects including flowering time, leaf development, phase transition, plant architecture, organ size, fruit development and stress response.
The SPL genes exist as a large gene family in plants and can be divided into different groups based on cluster analysis [11]. In Arabidopsis, a total of 16 SPL genes were identified and these AtSPLs were classified into eight groups [12]. Ten AtSPLs including AtSPL2–6, AtSPL9–11, AtSPL13 and AtSPL15 were targets of miR156 [13,14,15]. The three small genes AtSPL3, AtSPL4 and AtSPL5 have a target site for miR156 in their 3′-UTR region, and were found to promote vegetative phase change and flowering [16]. The other group AtSPL10, AtSPL11 and AtSPL2 control morphological change in association with shoot maturation in the reproductive phase and the lateral root development [17, 18]. Two paralogous genes AtSPL9 and AtSPL15 act redundantly in controlling the juvenile-to-adult phase transition [12]. In addition, AtSPL9 control trichome distribution, sesquiterpene and anthocyanin biosynthesis [15, 18, 19]. AtSPL13 is essential for the cotyledon-to vegetative-leaf transition [20]. AtSPL6 positively regulates defense genes in innate immunity [21]. Among the six AtSPLs that are not targets of miR156, AtSPL7 is a central regulator for copper homeostasis [22, 23]. AtSPL8 is involved in pollen sac development [24], gibberellin signalling [25] and male fertility [26]. AtSPL14 participates in plant development and sensitivity to fumonisin B1 [27]. The function of three genes AtSPL1, AtSPL12 and AtSPL16 remain unknown and need further investigation.
Furthermore, the SPL genes are potentially important candidates for genetic improvement of agronomic traits. In rice, a point mutation in OsSPL14 could generate an ideal rice plant with a reduced tiller number, increased lodging resistance and enhanced grain yield [28]. Manipulation of BrpSPL9 from Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis optimized the earliness of heading time in Chinese cabbage [29]. Suppression of PvSPL2 from Panicum virgatum increased biomass yield and reduced lignin accumulation and thereby elevated the total amount of solubilized sugars [30]. Overexpression of rSPL10 gene in Pogostemon cablin increased the essential oil content and accelerated plant growth [31].
Jatropha curcas L. is a potential biofuel plant for sustainable environmental development. The seeds contain an average of 34.4% oil that can be processed to produce a high-quality biodiesel fuel [32]. Given that overexpression of specific SPL gene could accelerate leaf initiation rate, increase biomass yield, enhanced salt tolerance and essential oil content, we ask if SPL is involved in the production of oil in J. curcas. There have been several studies regarding the identification of miRNA from J. curcas [33,34,35]. In Jatropha seeds, a total of 24 miR156 family were reported, whereas little information is available about the miR156 target-SPL and the interaction between miR156 and SPL. miR156 has been shown to be the master regulator of vegetative development and stress response by inhibiting the expression of SPL genes [36]. Considering the vital role of miR156/SPL modules in regulation of plant development and growth, we performed a genome-wide investigation of SPL genes in J. curcas. Some of the 15 identified SPL genes were highly conserved based on gene structure, conserved motifs, as well as clustering level. Expression analysis showed that the expression level of JcSPL3 increased with increasing age. These results provide insights into the biological functions of SPL genes in J. curcas.
Results
Phylogeny of plant SPL family proteins
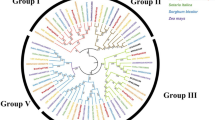
To gain an understanding of the evolutionary status of SPLs from J. curcas in all plants, putative SPL family proteins were originally extracted from the Pfam database by using the conserved SBP domain (PF03110) as query. After filtering redundant and short sequences, 833 SPL proteins were obtained from 60 different species (Additional file 1). The largest number of SPL sequences were found in Musa malaccensis with 53 sequences, and Chlorophyta contained the least number of SPL, with 1 to 4 sequences. The results showed that SPLs existed as a middle-sized gene family in green plants. These plant SPL proteins could be classified into eight clades. Each clade contained at least one AtSPL protein. Clade 1–5 contained previously well reported AtSPL protein families. Among the groups, clade 6 contained the largest number of sequences with 195 SPL proteins, while clade 1 contained the least number with 33 SPL proteins. However, the function of SPLs in clade 6 were mostly unknown. These suggested that the majority of SPL genes are still unexplored and worth of further functional investigation. There were 15 SPL proteins found from the Pfam database in Jatropha species. To reveal the possible roles of JcSPLs, a phylogenetic tree was constructed based on OsSPLs, GmSPLs (Glycine max), AtSPLs and PtSPLs (Fig. 1a). The results showed that they were divided into eight groups and all JcSPLs were grouped together with their orthologous Arabidopsis counterparts except JcSPL16 and JcSPL11. Among them, AtSPL7 and JcSPL7, AtSPL8 and JcSPL8, AtSPL9 and JcSPL9, AtSPL6 and JcSPL6, AtSPL13 and JcSPL13 were likely to be orthologous genes. Three pairs of JcSPLs including JcSPL13/16, JcSPL6/11 and JcSPL1/12 shared high sequence similarity and were presumed to be paralogous genes. Furthermore, most of the JcSPL genes showed a closer relationship with woody plant Glycine and Populus SPL genes rather than herbaceous plant Arabidopsis SPL genes, and JcSPL genes were rather distantly related to the rice SPL genes. These suggested that SPL genes could originate from a common ancestor and had undergone divergent differentiation after the separation of each lineage.
Phylogenetic and structure analysis of plant SPL proteins. a Phylogenetic relationship analysis of whole plant SPL proteins. Phylogenetic tree was constructed from 115 SPL proteins using the Maximum-likehood method in MEGA 7. b Overall structure analysis of plant SPL proteins. The alignment was marked in AliView to show all amino acids (upper) or majority rule consensus residues (lower). The red box represents the SBP domain
Overall structure analysis of all plant SPL proteins revealed that clade 1 were the smallest of the SPL proteins, while clade 6 and clade 7 were the largest (Fig. 1b). Proteins in clade 2–5 and clade 8 had similar protein size. Sequence conservation analysis showed that the SBP domain with approximately 78 amino acid residues were highly conserved across all clades, indicating that they could all bind to the promoters of floral meristem identity gene SQUAMOSA and its orthologous genes. The diversity of SPL clades suggested that they were involved in regulating different aspects of plant growth and development besides flowering control.
Identification of SPL genes in Jatropha
To identify the SPL genes in the Jatropha genome, the SBP domain was used as a query to search against the Jatropha genome. There was a total of 20 full-length SPL genes identified. By combination of both the Pfam database and genome data, the Jatropha proteins were then named based on known Arabidopsis homologues. After removing the splice variants, there were finally 15 loci in Jatropha (Additional file 2). Nevertheless, when we tried to clone one SPL gene (ID: XM_012236245.2) from Jatropha cDNA library, there was a point mutation (A343T) in the coding region which lead to premature termination of protein translation (Additional file 3). Therefore, we kept its splice variant (XM_012236246.2) for further analysis and that was named as JcSPL3. Comparing to the 16 AtSPLs from Arabidopsis [1], no homologue for AtSPL15 was found in Jatropha. Among the 15 JcSPL genes, JcSPL13 was in clade 5, four genes JcSPL1, JcSPL12, JcSPL14 and JcSPL10 were classified in clade 6, and JcSPL7 and JcSPL8 were in clade 7 and clade 8, respectively. The group member in clade 5, 6, 7 and 8 were consistent with those of AtSPLs. The smallest protein was JcSPL3 (142 aa) with a molecular weight (MW) of 16.1 kDa (Additional file 2), while the largest protein was JcSPL14 (1068 aa) with a MW of 118.6 kDa. The theoretical pI of JcSPL proteins ranged from 6.10 (JcSPL7) to 9.44 (JcSPL16). The protein length, MW and pI of JcSPL proteins were similar to PtSPL proteins from Populus [10].
Multiple sequence alignment of all JcSPLs showed the SBP domain were highly conserved at certain positions (Fig. 2a). They contained three conserved domains, including zinc finger 1 (Zn1), zinc finger 2 (Zn2), and bipartite nuclear localization signal (NLS) (Fig. 2b). The Zn1 (Cys3His-type) in JcSPL7 was replaced with Cys4 signature sequence, which type was also found in Arabidopsis and Populus. The Zn2 (Cys2HisCys-type) was the same in all JcSPLs. The NLS was located at the C-terminus of SBP domain with KRRRR signature sequence that partly overlapped with Zn2 structure. The SBP domain organization was highly conserved among moss [1], Arabidopsis and Populus, indicating the SBP domain organization was anciently established in plants.
The 15 JcSPL genes were further mapped onto the 11 linkage groups (LGs) of J. curcas [37]. These JcSPL genes were unevenly distributed across seven LGs (Additional file 4), with four genes on LG8, and three genes on LG1 and LG7. LG5 contained two JcSPL genes, while LG3, LG4 and LG6 only displayed one JcSPL gene, respectively. The majority of JcSPL genes were located on the top and bottom regions on LG1, LG3, LG4, LG6, LG7 and LG8. Two genes JcSPL13 and JcSPL11 were on the middle part of LG5. The synonymous (Ks) and non-synonymous (Ka) substitution rates ratios (Ka/Ks) for six pairs of JcSPLs were less than 1.0, indicating purifying selection (Additional file 5).
Gene structure, motif and sequence analysis of JcSPL genes
To provide further insight into the evolutionary relationships of JcSPL genes, the full-length JcSPL proteins were used to construct a phylogenetic tree. It showed that they were clustered into eight subgroups (Fig. 3a). The gene structure analysis revealed that the conserved SBP domain were interrupted by the first intron in all 13 JcSPLs except JcSPL5 and JcSPL6, in which the SBP domain were interrupted by the second intron. The position of intron in the SBP domain were highly conserved and located in the 47th amino acid, which were also found in Arabidopsis [6] and Populus [10]. However, the intron length varied greatly with the range from 86 bp in JcSPL7 to 3967 bp in JcSPL9. The closely related members within the same group usually shared similar exon/intron structures in terms of length and number. The intron number existing in the 15 JcSPLs ranged from 1 to 10. The JcSPL genes in Group 1 were the smallest and had only one or two introns, while JcSPL genes in Group 7 were the largest and included eight to ten introns. The other JcSPL genes had two or three introns. The intron number of JcSPLs were similar to those of AtSPLs, PtSPLs and CclSBPLs from Citrus Clementina [10, 38], suggesting the conservation of SPL gene structures among plants.
The detailed length of exon and intron were further analyzed (Additional file 6). It was found that the exon length of JcSPLs ranged from 77 to 850 bp with an average of 290 bp, which were similar to those of AtSPLs with an average of 297 bp. The intron length of JcSPLs ranged from 55 to 3966 bp with an average of 482 bp, while the largest intron length in AtSPLs was only 648 bp and the average was 124 bp. It could be concluded that, the exon size distribution of JcSPLs were similar to those of PtSPLs and AtSPLs, while the intron size distribution differed greatly among three of them [10]. These indicated the important role of intron in plant evolution.
Further analysis of conserved motifs of JcSPL family were performed. There was a total of 20 motifs identified for the 15 JcSPL proteins (Fig. 3b, Additional file 7). The number of motifs in each JcSPL varied from 2 to 15. Motif 1 and motif 2 (SBP domain) were found in all JcSPLs. Most closely related members contained similar motif types and number. Moreover, Motif 12 was only found in JcSPLs from Group 4, and motif 14 and motif 16 was unique in JcSPL13 and JcSPL7, respectively. In addition to the conserved SBP domain, other conserved motifs including motif 13 and motif 18 which correspond to the ANK domain were found in Jatropha, Salvia and Arabidopsis SPLs [39]. The diversity and specificity of motifs among these JcSPLs indicated the diverse and specific functions of JcSPLs.
The 2.0 kb sequence upstream of each JcSPL gene were then retrieved as promoter for repetitive element and cis-element analysis. It was found that all JcSPLs showed repetitive sequence features including either simple sequence repeat (SSR) or tandem repeat (TR) in the promoter and gene regions (Fig. 4a). The SSR markers occurred more frequently than TR, which were similar to CclSBPLs [38]. The SSR were found in all JcSPLs except JcSPL4 and JcSPL7, while TR were found in 11 JcSPLs, among which JcSPL5 had six TR sequences.
SPL genes belong to transcription factors and they were also tightly regulated at the transcriptional level [13]. The cis-acting elements in the promoter regions of all JcSPLs were investigated (Fig. 4b). The CAAT-box and TATA-box that were core promoter element were found in all JcSPL genes (Additional file 8). The cis-acting elements involved in the light response were the most abundant, followed by hormone response including abscisic acid, methyl jasmonate, salicylic acid, gibberellin and auxin responsiveness, and then stress response [40]. The putative elements involved in growth and development and stress response were absent in the promoter regions of JcSPL4 and JcSPL6. There were seven and four JcSPL genes containing the CAT-box and GCN4 motif, which were functional in the meristem and endosperm expression, respectively. Besides, the promoter of JcSPL16 showed elements involved in flavonoid biosynthesis and cell cycle regulation, while JcSPL2 had elements involved in circadian control. These suggested that JcSPLs could participate in various physiological and developmental regulation.
Posttranscriptional regulation of JcSPLs
Several members of SPL family were reported to be post-transcriptionally regulated by miR156 in different plants [13, 28]. In order to get deep understanding of the functional roles of JcSPL genes in Jatropha, we evaluated the potential regulation of JcSPLs by miRNA through both psRNATarget prediction and degradome sequencing. The mature miR156 was found to be present in Jatropha seeds by small RNA sequencing reported earlier [34]. Six miR156 genes (JcmiR156a-f) that exhibited obvious expression levels were identified and were used for further analysis. The MFold-predicted secondary structure of the miR156 precussor sequence showed a hairpin loop with mature miR156 in its stem region, a characteristics of miRNA precussor (Additional file 9). Then we used the six miR156 sequences and psRNATarget to predict the potential targets in all 15 JcSPLs. The results showed that 10 JcSPLs were identified as targets of JcmiR156 (Fig. 5a). Most miR156-targeted JcSPL genes were clustered into Group 1–4 (Fig. 3a). The JcmiR156 target sites for three JcSPLs in Group 1 were located in the 3′ UTRs, while the target sites for all the other JcSPLs were in their last exons.
Target sequences prediction and RLM 5′-RACE validation of JcSPLs cleaved by the miR156 and expression of miR156. a Target sequences of 10 JcSPLs through psRNATarget prediction. Left are the multiple alignment of miR156 complementary sequences with their targets. Right are the gene structure of corresponding JcSPLs. Blue box indicates SBP site. Purple box indicates the miR156 target site. b RLM-5′-RACE validation of JcSPL9 cleavage sites by JcmiR156a. The red box indicates PCR products for RLM 5′-RACE. The arrow indicates cleavage sites verified by RLM 5′-RACE with the sequencing frequency (sequencing reads/total sequenced clones) of cloned PCR products. c Relative expression of miR156a and JcSPL3. The expression levels at 1-month-old plants were set as 1.0. The value was shown as the mean ± the standard deviation (n = 3)
Furthermore, degradome sequencing approach were applied to validate the miR156-mediated regulation of JcSPLs. A mixture of nine samples including leaf, stem and root tissues from 1-month-, 7-year- and 10-year-old plants, respectively, were used for library construction. The acquired sequences were matched to Jatropha genome assembly JatCur_1.0 [36]. After analysis, a total of 9 JcSPL transcripts were identified to be cleaved by miR156 and miR157 family genes (Additional file 10). These JcSPL genes were consistent with psRNATarget prediction, except that JcSPL4 was not found, which may be due to the relatively low expression levels of this gene (Additional file 11). Among the 9 JcSPL targets, 8 JcSPLs were identified to be cleaved by 19 miR156 family genes and 3 miR157 family genes, while JcSPL5 were targets of 14 miR156 family genes and one miR157 gene. Considering that miR157 shares 14 nt to 16 nt sequence similarity with miR156 and there was no previous report about miR157-mediated cleavage of SPL, we concluded here that the identified 9 JcSPLs were predominantly regulated by miR156. The cleavage sites in the JcSPL gene sequences were clearly shown in T-plots and were confirmed to be exactly the same as predicted sites (Additional file 12). The target member distribution in clades and cleavage site distribution in targets were similar to those of PtSPLs and AtSPLs, suggesting miR156-mediated regulation of SPLs were highly conserved across plants.
In addition, the cleavage site of JcSPL9 was validated by 5′ rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) experiments (Fig. 5b). The expression of miR156 was investigated by stem-loop PCR. The results showed that the expression level of miR156 decreased significantly with plant age (Fig. 5c), while JcSPL3 exhibited an opposite trend of expression.
Expression patterns of JcSPL genes
In Jatropha, there were dramatic variability in the leaf morphology from different ages of plants (Additional file 13). The 1-month-old plants produced small and deltoid leaves, while the leaves of 1-year-old trees were five-lobed in shape. The expression patterns of genes could indicate their biological functions. To determine the spatial-temporal expression patterns of JcSPL genes, qRT-PCR experiments were performed in various tissues including leaf, stem and root from 1-month-, 1-year-, 7-year- and 10-year-old trees. In general, all JcSPL genes exhibited tissue-specific and age-specific expression patterns (Fig. 6). In particular, JcSPL5 and JcSPL8 showed much higher expression levels than all other JcSPL genes in both leaf and stem tissues from 1-month- or 1-year-old plants, whereas JcSPL3 showed the highest transcript abundance than all other JcSPL genes in leaf, stem and root tissues from 7-year- or 10-year-old plants. Furthermore, JcSPL10 exhibited lower expression levels than other JcSPL genes in all tissues from 1-month- or 1-year-old trees, whereas eight JcSPL genes (JcSPL2/9/10/11/12/13/14/16) were expressed at lower levels than other JcSPL genes in all tissues from 7-year- or 10-year-old trees.
Expression patterns of the JcSPLs in different tissues. The expression levels of JcSPLs were normalized to the levels of JcSPL1 in each tissue. The JcUBQ gene was used as an internal control. The value was shown as mean value from three biological replicates. Error bars represent the standard deviation
The expression patterns of some genes exhibited significant trends during different developmental stages in certain tissues (Fig. 7). Generally, the expression patterns of JcSPLs can be divided into three categories. The first and second categories included genes whose expression peaked in 1-year-old and 7-year-old tissues, respectively, while the third category contained genes whose expression in tissues increased as the plants age. In particular, all JcSPL genes except JcSPL3 exhibited higher expression levels in 1-year-old leaf tissue than those from leaf at other stages. It was worth noting that, the expression levels of JcSPL3 were consistently increased along with the plant age development in leaf tissue, suggesting its role in regulation of age development. Ten JcSPL genes (JcSPL1/4/7/8/10/11/12/13/14/16) showed higher expression in 1-year-old stem tissue compared to stem from other stages, while other four JcSPL genes (JcSPL2/3/5/6) showed preferential expression in 7-year-old stem tissue compared to stem from other stages. There were eight JcSPL genes (JcSPL4/5/6/8/9/10/11/16) that showed higher expression in 7-year-old root tissue compared to root from other stages, while four JcSPL genes (JcSPL1/7/12/14) showed higher expression in 1-year-old root tissue compared to root from other stages. The other three genes JcSPL2, JcSPL3 and JcSPL13 showed consistent increasing trend with the plant age development in root tissue, suggesting their specific role in plant root development. In particular, three genes JcSPL1, JcSP12 and JcSPL14 belonging to the same subgroup showed similar expression patterns in all samples examined, implying their functional redundancy. However, other JcSPL genes even in the same subgroup exhibited diversified expression patterns, indicating that they could play specific roles in various tissues under different developmental stages.
Expression patterns of the JcSPLs in different developmental stages. The expression levels of JcSPLs in each stage were normalized to the levels in 1-month-old leaf tissue. The JcUBQ gene was used as an internal control. The value was shown as mean value from three biological replicates. Error bars represent the standard deviation
With regard to the interesting expression patterns of JcSPL3, the subcellular localization of JcSPL3 protein was further examined. Confocal microscopy observation of the JcSPL3-GFP florescence signals showed that JcSPL3 were mainly distributed in the nucleus (Additional file 14), indicating its potential binding ability in vivo.
Functional analysis of JcSPL3
JcSPL3 exhibited an obvious increasing trend with plant age development and we speculated that this gene may be important for the growth and development of Jatropha. Therefore, the function of JcSPL3 was investigated by overexpression in Arabidopsis (Fig. 8). Three independent transgenic lines were selected for phenotypic observation. The plants overexpressing JcSPL3 flowered significantly earlier than the wild-type plants in terms of both flowering time and the number of rosette leaves to flowering (Fig. 8a), and produced fewer lateral roots than wild-type (Fig. 8b). The expression level of JcSPL3 in the overexpressed lines was about 50 times more than the wild-type (Fig. 8c). The average time to flowering of the transgenic plants ranged from 23.5 to 24.3 days, while that of the wild-type plants was 28.3 days (Fig. 8d). The average number of rosette leaves at flowering ranged from 4 to 6 in the transgenic plants, and was 12.5 in the wild-type plants (Fig. 8e). In addition, the siliques of transgenic plants were approximately 50% as long as those of the control plants (Fig. 8f). These data indicated that JcSPL3 may act as a floral activator and might be involved in the Jatropha flowering process.
Discussion
SPLs are plant-specific transcription factors that play significant regulatory roles in plant growth and development. Since its discovery in A. majus, the orthologous SPL genes have been identified in algae, moss, Arabidopsis and crops. However, less study is reported from perennial woody plants [8, 10]. In this study, the evolutionary status of Jatropha SPL genes was initially investigated. After filtering the short and partial sequences in the Pfam database, a total of 833 full-length SPL genes were found from 60 species which represent plant lineages of green algae, moss, lycopodiophyta and angiosperm. However, no SPL genes were discovered in the Pfam database from gymnosperms. To our knowledge, there were limited papers reporting about the identification and functional analysis of SPL genes from gymnosperm [5, 38]. More information about SPLs from gymnosperm would further help clarify the evolutionary process of plant SPLs.
Phylogenetic analysis of plant SPLs divided them into eight groups (Fig. 1). Among these groups the relatively small SPL genes were clustered in clade 1, whereas the relatively large SPL genes were distributed in clade 6. Moreover, the miR156-targeted SPL genes, based on the information from Arabidopsis and Jatropha, were distributed into clade 1–5. In addition, the orthologous genes from different species were more closely related than their members in other groups from the same species. These all indicated that the SPL genes may originate from a common ancestor of green plants.
In Jatropha genome, there were 15 JcSPL genes identified, among which five JcSPLs contained splice variants (Additional file 2). To verify the sequences of JcSPL genes retrieved from the J. curcas genome database [36], we cloned and sequenced these JcSPLs. The cDNA amplification results showed that there was a point mutation in the gene XM_012236245.2 (Additional file 3). To exclude the possibility of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) site in this gene among different individuals, we randomly chose five plants and extracted their DNA for amplification. The PCR sequencing results showed that the gene sequences were consistent with those obtained from cDNA library. Therefore, we speculate that this nucleotide error was caused by whole genome sequencing. In our study, the other splice variant JcSPL3 was chosen for further analysis. The number of JcSPL genes identified in Jatropha was similar to that in Arabidopsis, but was significantly less than that in Populus, apple and maize [7, 9, 10]. In those plants the SPLs have undergone gene duplications. This relatively small number of gene family was also reported for other transcription factor families in the Jatropha genome, such as the WRKY gene family, which have not undergone any recent gene duplication [36]. In Arabidopsis, four pairs of 16 AtSPLs (AtSPL10/11, AtSPL9/15, AtSPL1/12 and AtSPL14/16) were likely to be paralogous genes. The number of homologous JcSPL gene pairs was similar to that in Arabidopsis and C. clementina, indicating that SPL genes were conserved throughout plant genome.
Based on the phylogenetic relationship, the 15 JcSPLs were classified into eight groups (Fig. 3), which was similar to the phylogenetic tree of AtSPLs [12], but inconsistent to the classification of PtSPLs [10] and CclSPLs [38]. This inconsistency may be due to different method of phylogenetic construction. According to the phylogenetic tree, three pairs of JcSPL genes were presumed to be segment duplicated genes. It also revealed that JcSPLs were more closely clustered with Populus SPLs rather than AtSPLs (Fig. 1) and most JcSPLs were closely grouped together with their orthologous Arabidopsis counterparts. For example, JcSPL3/4/5 were clustered together with AtSPL3/4/5 in one group. Moreover, JcSPL3/4/5 were relatively small and had a miR156 target site in the 3′ UTR, which were also similar to AtSPL3/4/5, suggesting that JcSPL3/4/5 may have similar function in regulating flowering time and phase transition in Jatropha.
Gene structure and conserved motifs analysis revealed that members in the same group always showed similar structure and motifs (Fig. 4), suggesting possible redundant function of these JcSPLs, such as JcSPL3/4/5 and JcSPL1/12. The number of conserved motifs in JcSPLs was more than those in AtSPLs, indicating that some JcSPLs may have species-specific role. Moreover, there were about two-thirds of the JcSPLs contained the miR156 target sites and nine JcSPLs were confirmed by degradome sequencing to be cleaved by miR156 (Additional file 12). The complementary site to miR156 in the three small JcSPLs in Group 1 located in the 3′-UTR region, whereas in other seven JcSPLs it located in the last exon. This is also found in SPL genes of other plants including Arabidopsis and Populus, indicating the conservation of miR156-mediated regulation of SPLs in plant kingdom.
Expression pattern analysis revealed that most JcSPLs exhibited differential expression in various tissues and developmental stages (Figs. 6 and 7), indicating diverse function of JcSPLs in Jatropha growth and development. Previous reports have shown that most of paralogous SPL genes in the same group exhibited similar expression patterns [10, 38]. In Jatropha, three genes JcSPL1, JcSPL12 and JcSPL14 belonging to Group 7 showed similar expression patterns, whereas other genes even in the same group showed distinct expression, suggesting specific functions of these genes. Interestingly, the expression levels of JcSPL3 increased significantly with the age of the plant in both leaf and root tissues (Fig. 7). Studies have shown that AtSPL3 is responsible for plant phase transition and this transition is conserved in both annual herbaceous plants and perennial plants [2, 41, 42]. In Jatropha, there was a significant variability in the morphology of the leaves from 1-month- and 1-year-old shoots of plants. In our study, the expression of JcSPL3 increased significantly in leaf from 1-year-old plants compared to that from 1-month-old plants. These together strongly suggest that JcSPL3 may be responsible for the vegetative phase transition in Jatropha. This was confirmed by overexpression of Jatropha SPL3 into Arabidopsis, which revealed earlier flowering phenotype. In addition, the levels of JcSPL3 also showed increasing trend in roots with increasing age. The roles of SPLs in control of lateral root development were previously characterized [18, 43]. These suggest that JcSPL3 could also play a role in the root development (Fig. 8b). Together, these results in our study uncover the functional roles of Jatropha SPL genes and provide important candidates for further functional characterization with the aim of genetic improvement of growth and development traits.
Conclusions
The phylogeny of plant SPL proteins from the PFAM database were performed. Through comprehensive and systematic analysis of phylogenetic relationships, conserved motifs, gene structures, chromosomal locations, repetitive sequence, posttranscriptional regulation, expression patterns and subcellular localization, 15 JcSPL genes were identified in Jatropha and characterized in great detail. Interestingly, the expression patterns of JcSPL3 indicate its important role in the regulation of age development in Jatropha. These results provide deep insight into the evolutionary origin and biological significance of plant SPLs. Moreover, our study provides potential candidates for further functional characterization of JcSPLs with an aim of genetic improvement in Jatropha.
Methods
Analysis of plant SPL family
All SBP domain (PF03110) containing proteins were identified using the PFAM database (http://pfam.xfam.org/family/SBP#tabview=tab1). The full-length protein sequences were extracted using the uniprot IDs from uniprot database (http://www.uniprot.org/). After removing redundant and short sequences, a total of 833 sequences were obtained. For phylogenetic analysis, a bootstrapped neighbour joining tree was constructed using the MEGA 7. Overall structure analysis was performed in AliView. Sequence conservation logos were generated using the WebLogo platform (http://weblogo.berkeley.edu/logo.cgi).
Analysis of JcSPL genes
Sequences of 16 AtSPLs genes were retrieved from the Arabidopsis TAIR database (http://www.arabidopsis.org/). To identify the JcSPL genes, BLAST search against J. curcas genome assembly JatCur_1.0 were carried out using AtSPLs as queries (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/?term=Jatropha). All putative proteins were further confirmed to contain SBP domain in the PFAM database. Originally 21 JcSPL genes were retrieved. After filtering the splice variants and keeping one representative transcript, 15 JcSPL genes were obtained. Molecular weight (Mw) and theoretical isoelectric point (pI) parameters were predicted using the ExPASy program (http://web.expasy.org/protparam/).
Chromosome locations of all JcSPL genes were generated using MapChart 2.1 based on the Jatropha linkage map [35]. The ratio between nonsynonymous and synonymous nucleotide substitutions (Ka/Ks) was calculated using KaKs_Calculator 2.0 for selected pairs of homologous genes [44].
The exon/intron structure analysis of JcSPL genes were performed with the Gene Structure Display Server (http://gsds.cbi.pku.edu.cn/). Protein conserved motifs were predicted using the MEME program (http://meme-suite.org/tools/meme). An E-value cut off of Ie− 10 was used.
The repetitive sequence analysis in the promoter (2.0 kb upstream of the coding sequence) and coding sequence of JcSPLs were determined by SSRIT database (http://archive.gramene.org/db/markers/ssrtool) and Tandem Repeat Finder database (https://tandem.bu.edu/trf/trf.html). The cis-acting elements analysis in the promoter region of all JcSPLs genes were performed by using the PlantCARE database (http://www.dna.affrc.go.jp/PLACE/signalscan. html) [40].
Prediction of JcSPLs targeted by miR156
The sequence of JcmiR156a-f was obtained from the data in the paper by Galli et al. [34]. The identified pre-miRNA secondary structure was predicted using the mfold Web Server (http://unafold.rna.albany.edu/?q=mfold/RNA-Folding-Form). psRNATarget (http://plantgrn.noble.org/psRNATarget/) was used to predict the targets of JcmiR156 by searching the coding regions and 3′-UTRs of all JcSPLs for complementary sequences of JcmiR156a-f using default parameters.
Degradome sequencing
Fully expanded leaves, stem and root were harvested from 1-month-old plants grown in the greenhouse. The fourth leaves from lateral branches, stem with 5 cm length and lateral roots were harvested from 1-year-, 7-year- and 10-year-old plants growing outdoors. Total RNA of nine tissues including leaf, stem and root from 1-month-old, 1-year-, 7-year- and 10-year-old plants were extracted using the Plant Qiagen RNeasy Kit (Qiagen China, Shanghai) following the manufacturer’s instructions. The on-column DNase digestion were used for DNA removal and the RNA integrity was checked on an agarose gel. All RNA samples from nine tissues were pooled together in equal amounts and used for library constructions as described previously with minor modifications [45]. In brief, poly(A)-enriched RNA was ligated to RNA adaptor and the ligated products were used to generate first-strand cDNA by reverse transcription. The cDNA was then amplified for 6 cycles (94 °C for 30 s, 60 °C for 20 s, and 72 °C for 3 min) and ligated to double adaptor. The final cDNA library was purified and used for sequencing with the Illumina HiSeq2000 following the manufacturer’s instruction. After adaptor sequences and low-quality reads were removed, CleaveLand 3.0 pipeline was used to detect potentially cleaved targets, with Jatropha miRNA and mRNA sequences as references. T-plots were generated according to the abundance of the resulting mRNA tags relative to the overall profile of degradome reads that matched the target. All targets were classified into five categories. In category 0, the most abundant tag was the only one degradome tag detected, and it was located at the expected cleavage site. In category 1, there were more maximum positions. In category 2, the abundance of cleavage tags fell between the maximum and median values. In category 3, the abundance of cleavage tags was below the median value. In category 4, only one raw read was matched at the cleavage position of the transcript.
5′-race
The RNA Ligase-Mediated (RLM) 5′-RACE experiment was performed following the instructions of the RACE kit FirstChoice™ RLM-RACE Kit (Invitrogen). Gene-specific primers (Additional file 15) were designed to conduct nested PCRs, and PCR products were gel purified, cloned and sequenced.
Stem-loop reverse transcription (RT) PCR
The relative expression level of miR156 were examined by stem-loop PCR [46]. Briefly, total RNA was extracted and reverse transcription was performed using specific stem-loop RT primers for miRNA (Additional file 15). The Jatropha UBQ gene was used as the internal control.
Quantitative RT PCR (qRT-PCR)
Total RNA was extracted by using the Qiagen plant RNA extraction kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Qiagen, Germany). qRT-PCR was performed in triplicates using the SYBR Premix Ex Taq™ II Kit (TaKaRa, Dalian, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Three biological replicates were performed. The Jatropha UBQ gene was used as the internal control. The primers were listed in Additional file 15.
Subcellular localization
The coding sequence of JcSPL3 was cloned from the leaf cDNA library and fused to C-terminal Green florescence protein (GFP) tag (JcSPL3-GFP) in the expression vector pCambia1301-GFP. The construct was transiently expressed in tobacco leaf epidermal cells according to the protocol described by Wydro et al. [47]. Infiltrated leaves were mounted on slides and imaged using a confocal laser-scanning microscope (Nikon C2-ER) with a standard filter set. The empty GFP vector was used as control.
Arabidopsis transformation
The full-length CDS sequence of JcSPL3 was cloned into binary expression vector pCambia2301 and transferred into the Agrobacterium strain GV3101. Arabidopsis thaliana (Col) was transformed using the floral dip method [48]. T1 seeds were harvested and selected on MS medium with kanamycin 50 μg/ml. Plants were grown in growth chamber under long-day conditions.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available in the manuscript and its additional files.
Abbreviations
- NLS:
-
Nuclear localization signal
- LG:
-
Linkage groups
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeat
- TR:
-
Tandem repeat
- SBP:
-
SQUAMOSA-promoter binding protein
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR
- GFP:
-
Green florescence protein
References
Birkenbihl RP, Jach G, Saedler H, Huijser P. Functional dissection of the plant-specific SBP-domain: overlap of the DNA-binding and nuclear localization domains. J Mol Biol. 2005;352(3):585–96.
Yamasaki K, Kigawa T, Inoue M, Tateno M, Yamasaki T, Yabuki T, et al. A novel zinc-binding motif revealed by solution structures of DNA-binding domains of Arabidopsis SBP-family transcription factors. J Mol Biol. 2004;337(1):49–63.
Klein J, Saedler H, Huijser P. A new family of DNA binding proteins includes putative transcriptional regulators of the Antirrhinum majus floral meristem identity gene SQUAMOSA. Mol Gen Genet 1996;250(1):7–16. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02191820.
Kropat J, Tottey S, Birkenbihl RP, Depège N, Huijser P, Merchant S. A regulator of nutritional copper signaling in Chlamydomonas is an SBP domain protein that recognizes the GTAC core of copper response element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(51):18730–5.
Riese M, Höhmann S, Saedler H, Münster T, Huijser P. Comparative analysis of the SBP-box gene families in P. patens and seed plants. Gene. 2007;401(1–2):28–37.
Cardon G, Höhmann S, Klein J, Nettesheim K, Saedler H, Huijser P. Molecular characterisation of the Arabidopsis SBP-box genes. Gene. 1999;237(1):91–104.
Xie K, Wu C, Xiong L. Genomic organization, differential expression, and interaction of SQUAMOSA promoter-binding-like transcription factors and microRNA156 in rice. Plant Physiol. 2006;142(1):280–93.
Lännenpää M, Jänönen I, Hölttä-Vuori M, Gardemeister M, Porali I, Sopanen T. A new SBP-box gene BpSPL1 in silver birch (Betula pendula). Physiol Plant. 2004;120(3):491–500.
Li J, Hou H, Li X, Xiang J, Yin X, Gao H, et al. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the SBP-box family genes in apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.). Plant Physiol Biochem. 2013;70:100–14.
Li C, Lu S. Molecular characterization of the SPL gene family in Populus trichocarpa. BMC Plant Biol. 2014;14:131.
Preston JC, Hileman LC. Functional evolution in the plant SQUAMOSA-PROMOTER BINDING PROTEIN-LIKE (SPL) gene family. Front Plant Sci. 2013;4:80.
Schwarz S, Grande AV, Bujdoso N, Saedler H, Huijser P. The microRNA regulated SBP-box genes SPL9 and SPL15 control shoot maturation in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol. 2008;67(1–2):183–95.
Wu G, Poethig RS. Temporal regulation of shoot development in Arabidopsis thaliana by miR156 and its target SPL3. Development. 2006;133(18):3539–47.
Wang JW, Czech B, Weigel D. miR156-regulated SPL transcription factors define an endogenous flowering pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell. 2009;138(4):738–49.
Yu N, Cai WJ, Wang S, Shan CM, Wang LJ, Chen XY. Temporal control of trichome distribution by microRNA156-targeted SPL genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell. 2010;22(7):2322–35.
Yamaguchi A, Wu MF, Yang L, Wu G, Poethig RS, Wagner D. The microRNA-regulated SBP-box transcription factor SPL3 is a direct upstream activator of LEAFY, FRUITFULL, and APETALA1. Dev Cell. 2009;17(2):268–78.
Shikata M, Koyama T, Mitsuda N, Ohme-Takagi M. Arabidopsis SBP-box genes SPL10, SPL11 and SPL2 control morphological change in association with shoot maturation in the reproductive phase. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009;50(12):2133–45.
Yu N, Niu QW, Ng KH, Chua NH. The role of miR156/SPLs modules in Arabidopsis lateral root development. Plant J. 2015;83(4):673–85.
Gou JY, Felippes FF, Liu CJ, Weigel D, Wang JW. Negative regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis by a miR156-targeted SPL transcription factor. Plant Cell. 2011;23(4):1512–22.
Martin RC, Asahina M, Liu PP, Kristof JR, Coppersmith JL, Pluskota WE, et al. The regulation of post-germinative transition from the cotyledonto vegetative-leaf stages by microRNA-targeted SQUAMOSA PROMOTER-BINDING PROTEIN LIKE13 in Arabidopsis. Seed Sci Res. 2010;20:89–96.
Padmanabhan MS, Ma S, Burch-Smith TM, Czymmek K, Huijser P, Dinesh-Kumar SP. Novel positive regulatory role for the SPL6 transcription factor in the N TIR-NB-LRR receptor-mediated plant innate immunity. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(3):e1003235.
Yamasaki H, Hayashi M, Fukazawa M, Kobayashi Y, Shikanai T. SQUAMOSA promoter binding protein-Like7 is a central regulator for copper homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2009;21(1):347–61.
Araki R, Mermod M, Yamasaki H, Kamiya T, Fujiwara T, Shikanai T. SPL7 locally regulates copper-homeostasis-related genes in Arabidopsis. J Plant Physiol. 2018;224–225:137–43.
Unte US, Sorensen AM, Pesaresi P, Gandikota M, Leister D, Saedler H, Huijser P. SPL8, an SBP-box gene that affects pollen sac development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2003;15(4):1009–19.
Zhang Y, Schwarz S, Saedler H, Huijser P. SPL8, a local regulator in a subset of gibberellin-mediated developmental processes in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol. 2007;63(3):429–39.
Xing S, Salinas M, Höhmann S, Berndtgen R, Huijser P. miR156-targeted and nontargeted SBP-box transcription factors act in concert to secure male fertility in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2010;22(12):3935–50.
Stone JM, Liang X, Nekl ER, Stiers JJ. Arabidopsis AtSPL14, a plant-specific SBP-domain transcription factor, participates in plant development and sensitivity to fumonisin B1. Plant J. 2005;41(5):744–54.
Jiao Y, Wang Y, Xue D, Wang J, Yan M, Liu G, et al. Regulation of OsSPL14 by OsmiR156 defines ideal plant architecture in rice. Nat Genet. 2010;42(6):541–4.
Wang Y, Wu F, Bai J, He Y. BrpSPL9 (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis SPL9) controls the earliness of heading time in Chinese cabbage. Plant Biotechnol J. 2014;12(3):312–21.
Wu Z, Cao Y, Yang R, Qi T, Hang Y, Lin H, et al. Switchgrass SBP-box transcription factors PvSPL1 and 2 function redundantly to initiate side tillers and affect biomass yield of energy crop. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2016;9:101.
Yu ZX, Wang LJ, Zhao B, Shan CM, Zhang YH, Chen DF, et al. Progressive regulation of sesquiterpene biosynthesis in Arabidopsis and patchouli (Pogostemon cablin) by the miR156-targeted SPL transcription factors. Mol Plant. 2015;8(1):98–110.
Kavitha KR, Beemkumar N, Rajasekar R. Experimental investigation of diesel engine performance fuelled with the blends of Jatropha curcas, ethanol, and diesel. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019;26:8633–9.
Wang CM, Liu P, Sun F, Li L, Liu P, Ye J, Yue GH. Isolation and identification of miRNAs in Jatropha curcas. Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8(3):418–29.
Vishwakarma NP, Jadeja VJ. Identification of miRNA encoded by Jatropha curcas from EST and GSS. Plant Signal Behav. 2013;8(2):e23152.
Galli V, Guzman F, de Oliveira LF, Loss-Morais G, Körbes AP, Silva SD, et al. Identifying microRNAs and transcript targets in Jatropha seeds. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e83727.
Zhang L, Ding H, Jiang H, Wang H, Chen K, Duan J, et al. Regulation of cadmium tolerance and accumulation by miR156 in Arabidopsis. Chemosphere. 2019;242:125168.
Wu P, Zhou C, Cheng S, Wu Z, Lu W, Han J, et al. Integrated genome sequence and linkage map of physic nut (Jatropha curcas L.), a biodiesel plant. Plant J. 2015;81(5):810–21.
Zeng RF, Zhou JJ, Liu SR, Gan ZM, Zhang JZ, Hu CG. Genome-wide identification and characterization of SQUAMOSA-promoter-binding protein (SBP) genes involved in the flowering development of Citrus Clementina. Biomolecules. 2019;14:9.
Zhang L, Wu B, Zhao D, Li C, Shao F, Lu S. Genome-wide analysis and molecular dissection of the SPL gene family in Salvia miltiorrhiza. J Integr Plant Biol. 2014;56(1):38–50.
Lescot M, Déhais P, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, Van de Peer Y, et al. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30:325–7.
Wan LC, Wang F, Guo X, Lu S, Qiu Z, Zhao Y, et al. Identification and characterization of small non-coding RNAs from Chinese fir by high throughput sequencing. BMC Plant Biol. 2012;12:146.
Wang JW, Park MY, Wang LJ, Koo Y, Chen XY, Weigel D, Poethig RS. miRNA control of vegetative phase change in trees. PLoS Genet. 2011;7(2):e1002012.
Gao R, Wang Y, Gruber MY, Hannoufa A. miR156/SPL10 modulates lateral root development, branching and leaf morphology in Arabidopsis by silencing AGAMOUS-LIKE 79. Front. Plant Sci. 2018;8:2226.
Wang D, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Zhu J, Yu J. KaKs_Calculator 2.0: a toolkit incorporating gamma-series methods and sliding window strategies. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2010;8(1):77–80.
Ma Z, Coruh C, Axtell MJ. Arabidopsis lyrata small RNAs: transient MIRNA and small interfering RNA loci within the Arabidopsis genus. Plant Cell. 2010;22(4):1090–103.
Varkonyi-Gasic E, Wu R, Wood M, Walton EF, Hellens RP. Protocol: a highly sensitive RT-PCR method for detection and quantification of microRNAs. Plant Methods 2007;3. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-4811-3-12.
Wydro M, Kozubek E, Lehmann P. Optimization of transient agrobacterium-mediated gene expression system in leaves of Nicotiana benthamiana. Acta Biochim Pol. 2006;53:289–98.
Zhang X, Henriques R, Lin SS, Niu QW, Chua NH. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana using the floral dip method. Nat Protoc. 2006;1(2):641–6.
Acknowledgements
We express our greatest gratitude to Prof. Guojiang Wu from South China Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Science for providing the Jatropha Plants.
Funding
This study was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant Number 31600538) and Fundamental Research Funds of Chinese Academy of Forestry (grant Number CAFYBB2018QB003 and CAFYBB2017SY023). The funding body initially approved the project and played no role in the design of the study or collection, analysis and interpretation of data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NY designed, analyzed and wrote the manuscript. JCY and GTY participated in the sequence analysis and data interpretation; RSL and WTZ performed the qRT-PCR and subcellular localization experiments. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1.
Detailed information of the plant SPL proteins used for phylogenetic analysis.
Additional file 2.
Sequence information of identified JcSPL genes.
Additional file 3.
The predicted gene structure and sequence alignment of JcSPL3. a Schematic representation of the alternative processing of predicted JcSPL3 genes. b Sequence alignment of predicted JcSPL3 and cloned genes (Upper), and chromatogram information.
Additional file 4.
Chromosomal localization of the JcSPLs. Chromosomal localization of the JcSPLs based on the linkage map. The scale is in centimorgan.
Additional file 5.
The Ka/Ks ratios of the JcSPLs family.
Additional file 6.
Size distribution of exons and introns in JcSPLs and AtSPLs. a Size distribution of exons in JcSPLs and AtSPLs. b Detailed size distribution of small exons in JcSPLs and AtSPLs. c Size distribution of introns in JcSPLs and AtSPLs. d Detailed size distribution of small introns in JcSPLs and AtSPLs.
Additional file 7.
E-value and consensus sequence of twenty motifs identified in the JcSPLs.
Additional file 8.
Detailed information of the cis-acting elements in the promoters of JcSPLs.
Additional file 9.
Secondary structure of the JcMIR156 family.
Additional file 10.
The miR156-mediated cleavage site in 10 JcSPLs confirmed by degradome sequencing.
Additional file 11.
Detailed information of miR156-targeted cleavage of JcSPLs by degradome sequencing.
Additional file 12.
Target plots of the targets cleaved by the miR156 family through degradome sequencing. The T-plots show the distribution of the degradome tags along the full-length of the target mRNA sequence (bottom). The red line represents the sliced target trancripts and is marked with arrow.
Additional file 13.
Leaf morphology in different ages of plants. Scale bars represents 1 cm.
Additional file 14.
Subcellular localization of JcSPL3 protein. Confocal laser scanning microscopy of JcSPL3 using GFP-fusion proteins in Nitotiana benthamiana. Merged indicates combined GFP fluorescene and chlorophyll autofluorescene. Scale bars = 20 μm.
Additional file 15.
Primers used in this study.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, N., Yang, JC., Yin, GT. et al. Genome-wide characterization of the SPL gene family involved in the age development of Jatropha curcas. BMC Genomics 21, 368 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-020-06776-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-020-06776-8