Abstract
Background
The PIWI/piRNA pathway is a conserved machinery important for germ cell development and fertility. This piRNA-guided molecular machinery is best known for repressing derepressed transposable elements (TE) during epigenomic reprogramming. The extent to which piRNAs are involved in modulating transcripts beyond TEs still need to be clarified, and it may be a stage-dependent event. We chose chicken germline as a study model because of the significantly lower TE complexity in the chicken genome compared to mammalian species.
Results
We generated high-confidence piRNA candidates in various stages across chicken germline development by 3′-end-methylation-enriched small RNA sequencing and in-house bioinformatics analysis. We observed a significant developmental stage-dependent loss of TE association and a shifting of the ping-pong cycle signatures. Moreover, the stage-dependent reciprocal abundance of LINE retrotransposons, CR1-C, and its associated piRNAs implicated the developmental stage-dependent role of piRNA machinery. The stage dependency of piRNA expression and its potential functions can be better addressed by analyzing the piRNA precursors/clusters. Interestingly, the new piRNA clusters identified from embryonic chicken testes revealed evolutionary conservation between chickens and mammals, which was previously thought to not exist.
Conclusions
In this report, we provided an original chicken RNA resource and proposed an analytical methodology that can be used to investigate stage-dependent changes in piRNA compositions and their potential roles in TE regulation and beyond, and also revealed possible conserved functions of piRNAs in developing germ cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Primordial germ cells (PGCs) experience genome-wide epigenetic reprogramming for acquiring germ cell-specific features, such as meiosis, spermatogenesis and oogenesis, and regaining zygotic totipotency upon fertilization [1, 2]. This process is accompanied by burst expression of transposable elements (TEs), primarily autonomous retrotransposons such as long interspersed nuclear elements (LINEs) and long terminal repeats (LTRs) [3, 4]. The activation of transposable elements and their capability of insertion into the host genome through random transposition can lead to epigenomic and genomic instability [5].
The PIWI/piRNA pathway is evolutionarily adapted for effective mitigation of burst TE transcripts from reprogramming and is essential for proper germ cell development and fertility [6,7,8]. PiRNAs, namely, PIWI-interacting RNAs, are germ cell-enriched small RNAs that bind to PIWI protein and form piRNA-induced silencing complexes (piRISCs). Studies in Drosophila showed that the PIWI/piRNA pathway is critical for regulating TE activities in developing germ cells [6, 9]. In mice, defects in the PIWI/piRNA pathway result in aberrant expression of TEs that leads to germ cell depletion and subsequently small testes and infertility [10,11,12,13]. Knockdown of the chicken PIWI proteins, CIWI and CILI, also leads to an upregulation of chicken LINEs – chicken repeat 1 (CR1) elements, and hence supports the conservation of the PIWI/piRNA pathway in TE repression [14, 15].
The molecular mechanisms by which piRNAs modulate TEs are partly implicated through their biogenesis pathway. The primary piRNA precursor transcripts from piRNA clusters are transported to the perinuclear electron-dense region, the so-called nuage structure, for the maturation process [16]. The 5′ end of a piRNA is generated through MITOPLD (in mice)/Zuc (in Drosophila) cleavage and loaded onto the PIWI nucleotide binding pocket in 5′ uracil (1 U) preference fashion [16, 17]. The Drosophila Nibbler, or PARN-family exonucleases in other species, are reported to be involved in trimming the 3′ ends to form 24–32 nt small RNA fragments [18,19,20], which then have their 3′-end modified by 2’-O-methylation via HEN1 and form primary piRNAs [21,22,23]. Mature piRISCs identify transcripts antisense to their piRNA sequences and slice the targeted transcripts by the endonuclease function of PIWI protein at the position corresponding to the 10th nucleotide of piRNA [24, 25]. The cleaved transcript fragments are bounded by other PIWI proteins, such as MIWI, MILI, and MIWI2 in mice, and are then processed into antisense piRNAs, which also form piRISCs capable of slicing other transcripts [26]. This ping-pong cycle machinery of looped sense-antisense targeting, which is mainly processed via MILI in mice, can rapidly amplify secondary piRNAs by consuming TE transcripts [9, 27, 28]. Due to the preferred U for the first nucleotide of primary piRNAs and reverse complementary targeting over the ping-pong cycle, these secondary piRNAs feature the enrichment of adenine at the 10th nucleotide (10A) [27, 29]. Comparatively, Drosophila AGO3 and AUB participate in a ping-pong cycle in which they, respectively, bind with sense and antisense TEs [9, 30, 31]. PiRISCs composed of certain PIWI family members, such as MIWI2 in mice or PIWI in Drosophila, can also transport cytoplasmic piRNAs into the nucleus and mediate epigenetic gene silencing through H3K9 di- or tri-methylation and euchromatic de novo DNA methylation [32,33,34,35,36,37]. Hence, piRNAs may operate via post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS) and transcriptional gene silencing (TGS) to modulate TE expression and possibly beyond.
The emerging evidence implies diverse roles of the PIWI/piRNA pathway along germ cell development in a stage-dependent fashion. For instance, changes in piRISC composition were reported along the different mouse germ cell developmental stages [38]. The conditional inactivation of the Miwi2 gene revealed that MIWI2 is essential for prospermatogonia development in mice [39]. In contrast, MIWI is expressed and involved in ping-pong cycle-independent TE silencing after birth [10, 29]. PiRNA cluster analysis of MILI-interacting piRNAs showed distinct genomic associations, from the pre-pachytene TE-rich piRNA population and pachytene intergenic piRNA population [26]. Moreover, a recent study demonstrated the switching of dominant TE silencing machinery from the PIWI/piRNA pathway in spermatogonia to DNA methylation in meiotic spermatocytes [40], which is a further indication of stage-dependent regulation in the PIWI/piRNA pathway. Here, we extend our investigation to the roles of piRNAs along different germ cell developmental stages.
Since the development of the chicken embryo can be synchronously controlled and the chicken embryo developmental stages are well documented [41,42,43], chicken is a suitable model organism for studying stage-dependent effects of conserved machinery, such as stage-associated piRNA regulation. In addition, TEs constitute less than 10% of the chicken genome, which is significantly lower than TE occupancies in other tetrapod vertebrates, such as 48% in the human genome (hg38) and 41% in the mouse genome (mm10) [44,45,46,47]. Chicken TEs are also less complex than their mammalian counterparts. Moreover, chicken serves as an important evolutionary model for the conservativity of the PIWI/piRNA pathway. Together, these factors make chicken a plausible model for analyzing the roles of piRNAs in and potentially beyond TE modulation throughout different developmental stages. The expression of PIWIL1 in chicken PGCs has been reported [48]. In addition, the presence of piRNAs has been reported in chicken PGCs and adult testes [15, 49, 50]. Nevertheless, the stage-dependent expression and genomic association of chicken piRNAs has yet to be systematically analyzed.
In this study, we performed an in-depth analysis of piRNA clusters based on 3′-end-2’-O methylation-enriched small RNA sequencing on germ cells taken at different developmental stages. Here, we show the stage-dependent transition in piRNA compositions and their roles in TE regulation. Our in-depth investigation of piRNAs before and after spermatogonia formation reveals that piRNA-associated TE regulation may also contribute to gene regulations. In extension, our results display the stage-dependent expression of some genomic loci embedding putative piRNA clusters. We further investigated a functional implication of these stage-dependent clusterable piRNAs and propose a possible role of PIWI/piRNA pathways in germ cell fate decision.
Results
Implementation of a computational workflow for high-confidence piRNA discovery
To identify piRNA candidates among gonadal small RNA pools, we applied sodium periodate oxidation combined with small-RNA high-throughput sequencing (small RNA-seq) and in-house developed computational workflow dedicated to the identification of piRNA candidates (Additional file 1: Figure S1). In vertebrates, only piRNAs but not miRNAs contain a 3′-end 2’-O-methyl modification, which resists oxidation treatment and remains ligatable at the 3′-end for sequencing library construction [51]. This 3′-end 2’-O-methylation signature has been observed in chicken piRNAs [49], thus supporting the applicability of this method in our study. Reads from the oxidized small RNA libraries were then processed through our bioinformatic pipeline. Our implementation of the bioinformatics pipeline aimed to identify potential piRNA reads by eliminating other forms of small RNAs instead of considering only TE-derived reads [52]. Briefly, after genomic mapping, reads that annotated to rRNA, tRNA, and miRNA were removed. To ensure the elimination of false positives, we also eliminated reads that may have originated from predicted microRNA precursors.
Given the expression of chicken PIWI/piRNA pathway-associated genes found in blastoderm [48, 52], cultured PGC [15, 48], and adult testes [49], we validated that these genes are also expressed in enriched embryonic germ cells around spermatogonia formation stages (Additional file 1: Figure S2, S3). Our in-house bioinformatic pipeline was then applied over 3′-end-2’O methylation-enriched small RNA-seq datasets from blastodermal cells (BC), cultured PGCs from E7 gonads (E7PGC), and E11 and E14 embryonic gonads (E11G and E14G, respectively) generated in our lab. PiRNA datasets of adult testes (AT) published by Li et al. [49] were included to evaluate the accuracy of our piRNA candidate analysis pipeline and provide a piRNA dataset of germ cells undergoing meiosis. The small RNA categories and read densities through each step of filtering and final piRNA candidacy are summarized in Additional file 1: Table S1. The high proportion of mapped reads was categorized as piRNA candidates based on our analysis pipeline predictions (Additional file 1: Figure S1C). The reduction of reads mapping to miRNAs in the oxidation-treated libraries compared to the untreated counterparts demonstrated the success of enriching 3’end modified small RNAs.
The characterization analysis results showed that the adult testicular piRNA candidates are shorter in length, mostly ranging from 24 to 27 nt, relative to piRNA candidates from other samples, which range from 26 to 29 nt (Fig. 1a). We further validated the piRNA candidates in each sample with known piRNA characteristics. The resultant piRNA candidates showed strong 5′-end uracil (1 U) enrichment (Fig. 1b), which supported the 1 U-bias of piRNAs due to structural preferences of the nucleotide binding pocket of the PIWI MID domain [53]. In addition, we investigated the ping-pong cycle activities, which are characterized by a frequent mutual overlap of 10 nt at the 5′-end and 1U10A enrichment. We observed frequent 5′-10 nt overlapping (Fig. 1c; Additional file 1: Figure S4) relative to other 5′ overlapping lengths. However, the low sequence overlap rate among embryonic samples implied limited ping-pong cycle activities. The nucleotide enrichment analysis of 5′-10-nt overlapping piRNAs showed a 10A bias in samples other than BC. Interestingly, we observed a gradual loss of 10A feature along germ cell development (Fig. 1d). This observation supported stage-dependent variations in piRNA composition.
PiRNA candidates show distinct piRNA features across different developmental stages. a Length distribution of piRNAs. PiRNA reads per million (piRPM) is calculated for each read length; b Nucleotide enrichment analysis on piRNA candidates in each sequencing sample. c Relative enrichment of pairable piRNAs by the overlapping length. PiRPM is calculated for the number of pairable piRNAs with each overlapping length. d Nucleotide enrichment analysis of piRNA candidates of 10 bp antisense overlapping at the 5′ end in each sequencing sample
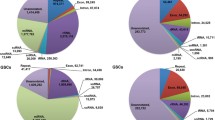
Remarkably, over 90% of the piRNA candidates from BC mapped to TEs, and less than 5% mapped to intergenic regions. In contrast, adult testes showed significantly higher intergenic association over 65% (Fig. 2a). A reduced TE association of piRNA candidates was also observed in cultured E7PGC, E11G and E14G, compared to that from BC. PiRNA candidates from cultured E7PGC had almost 50% of their reads mapped to intergenic regions, but only approximately 35% of the piRNA mapped to TEs. These observations suggested dynamic regulation of genomic associations of piRNAs toward the prevalence of intergenic loci along germ cell development. While the chicken PIWI/piRNA pathway may encompass stage-dependent biosynthesis machineries favoring production of piRNAs in a certain length range [54], we observed no significant correlation between piRNA length distribution and genomic association in a stage-dependent manner (Additional file 1: Figure S5).
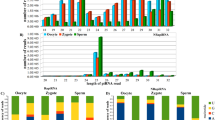
Developmental stage-dependent genomic associations and TE expression modulation of piRNA candidates. a Genomic association varied in stage-dependent fashion. Each feature was calculated in proportion to the respective total piRNA candidates. b PiRNA candidates mapped to TEs. piRPM is calculated for each enlisted category. c The stage-dependent association of piRNAs to subfamilies of LINEs. PiRNA sequences are preferentially mapped antisense to TEs. d Expression of CR1 subfamily members from enriched embryonic germ cells. e Stranded RT-qPCR analysis (N = 3) over CR1-C transcription among cultured E3 circulating PGC (E3PGC), cultured E7 gonadal PGC (E7PGC), and germ cell enriched population, E11Germ and E14Germ, from E11 and E14 Gonads, respectively. ** represents p-value < 0.01
PiRNA candidates demonstrated stage-dependent association to TE subfamilies
Given the involvement of piRNAs in TE regulation [55], their reduced TE association in a stage-dependent manner may be due to TE repression (Fig. 2a, b). This effect may be more prominent for piRNAs assigned to LINEs (Fig. 2c). Expression analysis by RT-qPCR of a purified embryonic chicken germ cell population generally showed a downregulation of LINE components between PGCs and enriched germinal cells at late embryonic stages (Fig. 2d, e). Notably, we observed the dynamic expression of LINEs from the enriched germ cell populations among cultured PGCs from E3 and E7 and freshly isolated germ cells from E11G and E14G. This implies that TE expression may also be regulated in a stage-dependent manner. Indeed, we further observed stage-dependent reciprocal correlations between the expression of LINE members and the abundance of their corresponding piRNAs (Fig. 2c-e). Among the transcriptionally repressed LINE members CR1-C, CR1-F, and CR1-H, there were more LINE associated piRNAs mapped antisense to LINE, than the piRNAs mapped to the sense direction, by 2 to 5 fold. Intriguingly, we observed a high abundance of antisense piRNAs associated with CR1-B, CR1-F, and CR1-G, in accordance with the high repressive strength at BC. In contrast, we observed that the expansion of piRNAs associated with CR1-C occurred later, at E11 (Fig. 2c). Strand-specific RT-qPCR on CR1-C showed a downregulation of both sense and antisense transcripts at E11G and E14G. In addition, both PGCs and gonadal germ cells showed higher levels of antisense transcripts, and this finding supported the positive correlation with the associated antisense piRNAs (Fig. 2d, e). These results indicate that the PIWI/piRNA pathway may have a role in the stage-dependent transient expression of TEs.
Investigating the possibility of piRNA-mediated modulation beyond TEs in chicken embryonic gonads
To evaluate the possible contribution of the developmentally regulated piRNAs in modulating transcriptome beyond TEs, we first tested the hypothesis that differentially expressed piRNAs between E11G and E14G gonads may be involved in modulating spermatogonia formation, which was estimated to occur around E13 [43]. Approximately 20% of piRNA candidates from E11G and E14G were mapped to either the sense or antisense strand of genes/transcripts, in which half of these piRNA-associated transcripts were not TE-associated (Fig. 2a). This finding suggested that piRNAs may have roles beyond but not mutually exclusive with TE regulation.
Among the top 500 piRNA-associated transcripts heavily mapped by piRNAs (with at least 70 piRPM) for E11G and E14G of both Leghorn layer and Cobb500 broiler breeds, we selected the 416 and 414 overlapped genes from the two chicken strains of E11 and E14 testes, respectively. We found 510 transcripts that were potential piRNA associated transcripts of E11G and E14G in union (Fig. 3a), among which 193 transcripts were differentially expressed (fold change > 2) before and after spermatogenesis (E11G vs E14G). Among these candidate transcripts, we identified 58 protein-coding genes, 132 uncharacterized genes from Ensembl, and 3 snoRNAs (Fig. 3b). However, none of the Gene Ontology (GO) terms was significantly enriched with these genes. The differential expressions of 15 of the targets between E11 and E14 germ cells were examined by RT-qPCR (Fig. 3c-f). Three of these genes showed negative correlations between gene expression and the associated piRNAs, which were predominantly mapped on or approximate to TEs within those genes (Fig. 3c, e; Additional file 1: Figure S6). Uniquely mapped piRNAs associated with the 3 candidate genes were highly represented, which indicated that even when considering the repetitive nature of the TE sequences within genes, only a small portion of piRNA reads associated with the aforementioned genes can also be mapped to the identical sequences residing on the other part of the chicken genome. The preferential TE-associated piRNA mappings were also observed in most of the other top piRNA-associated transcripts (Additional file 2: Table S2). However, due to the lack of a strong reciprocal correlation between antisense piRNA mapped reads and the expression of targeted transcripts across different developmental stages, gene silencing based on piRNA-mediated targeting and slicing may not be a common event in embryonic chicken testes. We do not exclude the possibility that some of the piRNA-associated transcripts were regulated by piRNAs via post-transcriptional slicing or piRNA-mediated epigenomic silencing.
Identification of potential piRNA associated genes before (E11G) and after (E14G) spermatogonia formation. a Venn diagram of piRNA-associated target transcripts before and after spermatogonia formation. The top 500 target transcripts were selected from each sample, and the union of reproducible piRNA associated transcripts from E11 and E14 gonads revealed 510 potential piRNA modulated transcripts. b Transcripts with 2-fold difference in normalized piRNA counts are identified, of which 58 are annotated genes. c-d PiRNAs mapped to the sense or antisense of their associated genes. e-f Comparison of relative expression levels of potential piRNA associated genes between enriched germ cells from E11 and E14 gonads (N = 3). *represents p-value < 0.05; **represents p-value < 0.01; ***represents p-value< 0.001. Five genes are reciprocally expressed compared to the amount of associated piRNAs (e), while 12 genes do not have reciprocal relative expression levels to the numbers of piRNAs mapped to them (f)
piRNA cluster analysis identified stage-dependent piRNA expression patterns
To systematically illustrate developmental changes in piRNA compositions, we performed piRNA cluster analysis to identify genomic regions likely transcribing piRNA precursors (Fig. 4a). Our analysis showed that more than 70% of piRNAs can be assigned to potential piRNA clusters, with most being 3–10 kilobases in length and some reaching megabases in length (Additional file 1: Figure S7A). Cross-stage comparison of the genomic loci of piRNA clusters revealed globally similar expression patterns (Fig. 4a). However, some clusters demonstrated significant developmental stage-dependent differential piRNA production (Fig. 4a; Additional file 1: Figure S7B). Moreover, we identified a set of piRNA clusters that exhibited strict stage dependencies. The intersection of joined overlapping piRNA clusters across samples and transcriptome information allowed us to better predict the piRNA cluster boundaries (Additional file 1: Figure S8; see Material and Method). This adjustment granted a slight increase in the number of piRNA candidates that may be assigned to piRNA clusters despite being initially discarded by proTRAC, a software program for piRNA cluster detection (Additional file 1: Table S3). Multidimensional scaling analysis showed a strong association between piRNA cluster expression patterns and developmental stages (Fig. 4b). As demonstrated, the expression profiles of piRNA clusters between E11G and E14G were less distinguishable, suggesting similarities in piRNA modulations before and after spermatogonia formation. Hence, we categorized the expression profiles of piRNA clusters according to the developmental stages, as BC-enriched piRNA clusters (BC-piRC), PGC-enriched piRNA clusters (PGC-piRC), embryonic gonadal-enriched piRNA clusters (EG-piRC), and adult testes-enriched piRNA clusters (AT-piRC). We found that nearly 70% of the 7269 piRNA clusters showed stage dependency, with an expression cutoff of 0.1 piRPKM and 1.5-fold expression enrichment (Fig. 4c). Remarkably, the piRNAs that mapped to these stage-enriched piRNA clusters showed similar genomic association patterns as the mapping results from the piRNA samples: the enriched TE-associated piRNAs in BC-piRCs; the enriched intergenic-associated piRNAs in AT-piRCs; and the “in-between” piRNA pool in PGC-piRCs and EG-piRCs. The developmental stage-specifically upregulated piRNA clusters implied the existence of open genomic regions for piRNA precursor transcription that may play stage-associated regulatory roles.
PiRNA cluster analysis reveals stage-dependent differential expression of piRNA precursors. a PiRNA cluster locus identified in each sample via proTRAC. Each bar represents a cluster at the plus (up) or minus (down) strand. Length and color depth denote the piRNA density in percentile. b Multidimensional scaling reveals the stage-associated piRNA cluster expression profile. Eigenvalues approximate the degree of variation explained by each dimension. c Identification of stage-enriched piRNA clusters (piRCs), each of which has piRPKM 1.5-fold higher than the second-highest stage. Stage-enriched piRNA clusters from blastodermal cells (BC), primordial germ cells (PGC), embryonic gonads from E11 and E14 (EG), and adult testes (AT) are included
Stage-dependent chicken piRNA clusters revealed evolutionary conservation with eutherian piRNA clusters
The conservation of piRNA clusters between avian and eutherian mammals has not been discovered. With the newly identified chicken piRNA clusters from embryonic gonads (Additional file 1: Figure S7), we re-investigated the potential conservation of piRNA clusters with previously reported eutherian-conserved piRNA clusters [56]. We identified several syntenically conserved piRNA clusters between chickens, mice and humans, for example, the intergenic piRNA clusters residing between PRMT8 and TSPAN9, and between GADD45G and DIRAS2 (Fig. 5). Interestingly, the transposable elements from these two conserved clusters are very similar among the three species. Both potentially conserved chicken piRNA clusters are expressed only at E11 and E14 gonads but not in adult testes (Fig. 5). This suggests that the expression of these conserved piRNA clusters is modulated in a developmental stage-dependent manner in chickens.
Potential stage-dependent syntenically conserved piRNA clusters shared between eutherian and chicken. The intergenic chicken piRNA cluster expressions were reported as piRPM at between (a) PRMT8 and TSPAN9; and (b) GADD45G and DIRAS2. These loci were reported syntenically conserved in eutherian by Chirn et al., and are respectively listed at (c) and (d) for comparison. Both human and mouse piRNA clusters are listed. Stage-enriched piRNA clusters from chicken blastodermal cells (BC), primordial germ cells (PGC), embryonic gonads from E11 and E14 (E11G and E14G), and adult testes (AT) are included. The novel syntenically conserved clusters between eutherian and chicken were revealed from our original piRNA datasets from embryonic gonads
piRNAs from E11 and E14 gonad-enriched piRNA clusters preferentially targeting neural lineage-associated genes
The stage-dependent expression of piRNA precursors from each cluster likely contributes to the changes in piRNA composition during germ cell development. We found that stage-enriched piRNA cluster-derived piRNAs targeted similar TEs, which are predominantly CR1 and ERVL elements (Additional file 3: Table S4). On the other hand, these different stage-enriched piRNAs mapped antisense to a large variety of genes (Additional file 1: Figure S9). We then applied GO enrichment analysis via Enrichr [57] using the piRNA-targeted transcripts for potential functional annotations. Surprisingly, the genes targeted by EG-piRC piRNAs were predominantly expressed in the brain, based on the Mouse Gene Atlas category [57], and were primarily associated with synaptic transmission and neural development based on our gene ontology enrichment analysis (Additional file 1: Figure S10, S11; Additional file 3: Table S4). From the gene list associated with GO term: “positive regulation of nervous system development (GO:0051962)”, we randomly selected several EG-piRC piRNA-targeted genes for expression analysis via RT-qPCR on enriched germ cells of different developmental stages. We found that the expression of these genes decreased in germ cell-enriched samples at E14 gonads compared with earlier developmental stages (Additional file 1: Figure S12). Further investigation revealed that piRNAs associated with these genes were predominantly mapped to the TEs embedded within the gene bodies. Since there was a significant representation of uniquely mapped piRNAs to these TE regions, any potential biases resulting from multiple mapping due to identical sequences have been minimized. Nevertheless, whether a specific subset of TE-embedded genes can indeed be modulated by piRNAs and cause significant biological consequences relies on further functional analysis.
Discussion
PIWI/piRNA pathway in chicken and mouse
PIWI family members are known for having stage-specific expression in mouse germline development [10, 33]. Miwi, also known as Piwil1, is expressed from the pachytene stage of meiosis to the haploid round spermatid; Mili, also known as Piwil2, is expressed from PGCs to the round spermatid; and Miwi2, also known as Piwil4, is expressed mainly in quiescent prospermatogonia. However, only the Piwil1 and Piwil2 homologous genes, CIWI and CILI, and not Piwil4 are annotated in the chicken genome [14]. In this study, the RNA transcripts of CIWI and CILI were detected in male embryonic gonads after sex differentiation (E8) to spermatogonial formation (E14). CIWI and CILI transcripts were reported to be detectable in PGCs and adult gonads [14]. These data supported the existence of PIWI/piRNA pathways along chicken germ cell development but also indicated that, unlike in mice, chicken PIWI family genes likely do not exert stage-specific functions.
However, the variations in the length distribution of piRNA candidates, and the gradual loss of the 10A feature conservation in piRNA candidates involved in the ping-pong cycle along germline development, supported the possibility that distinct PIWI/piRNA pathway machineries operate in a stage-dependent manner. Moreover, the dominant expression of CIWI from E8G to E14G further implied roles of CIWI in the chicken PIWI/piRNA pathway (Additional file 1: Figure S3). Whether components within a PIWI complex affect PIWI-piRNA binding and processing machineries remains elusive. Our results showed the upregulation of PIWI/piRNA-associated genes, which may be associated with the stage-dependent co-factor composition within PIWI complexes.
Comparison of the piRNA composition along germ cell developmental timelines between chicken and mouse
Our piRNA-seq analysis revealed changes in piRNA population among BC, cultured E7 PGC, E11 and E14 gonads, and adult testes, which, respectively, correspond to PGC precursors, gonadal PGCs, prospermatogonia, spermatogonia, and mature germ cell population. Since galGal5 chicken genome assembly came from red jungle fowl (origin of domesticated chicken), our “no-mismatch” piRNA candidates analysis pipeline identified piRNA sequences of the wildtype chicken piRNAs prior domestication. We found that the piRNA composition changed from highly TE-associated BC piRNAs to predominantly intergenic region-associated adult testicular piRNAs. Comparatively, emerging studies in mouse germ cell piRNAs have implied a distinctive border for piRNA compositions, which are predominantly TE-associated pre-pachytene piRNAs and predominantly intergenic orientated pachytene piRNAs [13, 58,59,60]. We observed a similar reduction of TE-associated piRNAs from early to late germ cell development between chickens and mice. Since the PIWI/piRNA pathway may contribute to epigenetic silencing via H3K9me3 and DNA methylation onto the piRNA targeted regions [33, 61], piRNAs expressed in primordial germ cells may silence their host transcripts and may thus reduce the transcription activities from the same region in later germ cells. Interestingly, however, piRNAs from cultured E7PGC and gonads from E11 and E14 showed “in-between” genomic associations with similar representation of TEs and non-TE loci. Since chicken male germ cells enter meiosis after sex maturation approximately 10 weeks after hatching [43], the transition of chicken piRNA compositions from TE-targeting piRNAs to intergenic-associated piRNAs in male germ cells might be a progressive event. Moreover, our analysis showed a significant number of intergenic gonadal piRNAs before entering meiosis, suggesting differences in piRNA-associated TGS machineries between chickens and mice.
It is curious that our piRNA candidate analysis pipeline identified the presence of rRNA and tRNA derived small RNAs at early embryonic stage from the 3′-end modified population after periodate oxidation treatment (Additional file 1, Figure S1). The low number of microRNAs in our 3′-end modification enriched population confirmed the success of oxidation treatment (Additional file 1: Figure S1C, Non-enriched vs. Oxidation Enriched). Our data suggests the presence of rRNAs and tRNAs editing, including methylation. We haven’t been able to obtain direct evidence for 3′-end modification in rRNAs and tRNAs in this study, but 2’-O methylation modifications on rRNA and tRNA have been reported in eukaryotes, including yeast and human. Additionally, other methylation editing may also block the oxidation reaction. The RNA modification information has recently been summarized in RMBase (http://rna.sysu.edu.cn/rmbase/) [62]. Hence, despite RNA modifications in chicken are scarcely studied, the possibility exists that RNA methyltransferase may be highly active in chicken blastodermal cells and leads to 2’-O methylation on rRNA and tRNA, including potentially 3′-end methylation. Alternatively, cleavage of rRNA and tRNA, may also expose 2’-O methylation site at 3′-end, and are therefore included in our 3′-end enriched small RNA population. Further studies may reveal their potential roles in early chicken embryo and germ cell development.
Although our high throughput datasets were generated from multiple chicken breeds, the conclusion of stage-specific piRNA modulation should not be solely attributed to genetic background mediated bias. When taking a full set of piRNA sequencing datasets from blastodermal cells (BC1, BC2), E11 (E11G2) and E14 (E14G2) and adult testes (Adult) sequencing results all from Leghorn breed, we confirmed that all of the stage dependent differences we demonstrated in this paper were also observed within the LH breed (Figs. 1a, c, 2a-c, 4c and Additional file 1: Figure S7B). Studies of genomic occupancy profiling such as ChIP-seq and bisulfite genomic sequencing may further elucidate the links between the PIWI/piRNA pathway and epigenetic regulation along chicken germ cell developmental states. The developmental stage-dependent modulation of TE subfamilies and their importance in establishing or maintaining pluripotency have only recently been appreciated [63,64,65].
Chicken PIWI/piRNA pathway machineries may exhibit multiple regulatory strategies
According to the distribution of piRNA counts within targeted genes, PIWI/piRNA might regulate their expressions through various mechanisms. In mice, PIWI/piRNAs regulate TE expression through the ping-pong cycle, which amplifies the piRNAs that lead to the rapid post-transcriptional degradation of TE transcripts and/or facilitate histone modification and de novo methylation for repressing TE transcriptions [12, 32, 58, 66]. The recently discovered phased primary piRNA processing mechanism, which is triggered by initial piRNA targeting, can generate a series of downstream, non-overlapping primary piRNAs through the PIWI slicer activity and therefore enrich piRNA pools [67, 68]. Mouse PiRNAs were also reported to be involved in silencing of protein-coding genes via transcript deadenylation or direct transcript targeting, endonucleolitic cleavage and degradation [69,70,71,72]. Nevertheless, while piRNAs have a global repressive effect on TEs, piRNA-mediated post-transcriptional regulation may apply to only a small subset of genes [40]. In support of this notion, the moderate expression changes in the piRNA-associated genes, including EDIL3 and PIP5K1B, before and after spermatogonia formation imply minor roles of the PIWI/piRNA pathway in regulating these genes. Interestingly, however, piRNAs mapped to EDIL3 showed strong ping-pong cycle features and were not restricted specifically to the embedded TEs (Fig. 3; Additional file 1: Figure S6). In contrast, PIP5K1B regions produce piRNA candidates mostly from the sense strand centralized around the embedded TEs, whereas few piRNAs mapped to the antisense strand (Additional file 1: Figure S6). This phenomenon resembles the footprint from the piRNA phasing mechanism [73]. Further analysis of the uniquely mapped piRNAs revealed the possibility that a small number of trans-acting antisense piRNAs may trigger the piRNA production from the sense-paired transcript via the phasing mechanism (Additional file 1: Figure S6E-H).
Stage-dependent regulation over piRNA clusters may evolutionarily acquire roles in germ cell development
We observed that more than half of the overall piRNA clusters displayed strong correlations with the germ cell developmental stages. PiRNA profiling analysis in embryonic gonads allowed the discovery of novel conservation of piRNA clusters between chicken and mammalian species. This finding suggests that the earlier conclusion of the lack of conservation of piRNA clusters between eutherian and chicken was mainly due to a lack of information from the prenatal stages [56]. The conservation of piRNA clusters may be stronger than expected, given the stage-dependency features. Apart from the stage-dependent modulation of TE expressions, our data also implied that the piRNAs produced from E11 and E14 gonadal-enriched piRNA clusters may have preferential targeting to genes involved in neural lineage development and functions. The significant drop of expressions of the piRNA-targeted genes in the E14G germ cell-enriched population suggested potential incidence of repressive roles of chicken piRNAs. The delayed response for piRNA targeting and gene suppression may be partially explained by the involvement of piRNA-guided chromatin repression machinery [34, 74].
The potential roles of developmentally enriched piRNA in repressing neural lineage genes may imply a strengthening germ cell fate during a critical period of spermatogonia stem cell formation. When looking closely into the antisense-mapped piRNAs within these genes, we further observed a stronger reciprocal association between the quantity of these piRNAs and the transcripts bearing intragenic TEs of the same direction (Additional file 4: Table S5). It is therefore possible that while piRNAs modulate the intragenic TE components, they also repress the genes bearing identical sequences. This is reminiscent of the recent finding describing suicide shRNAs that repress genes via the off-target mechanism because of sequence similarity [75]. Our ongoing functional analysis would provide further evidence of how selected genes are specifically targeted by stage-dependent piRNAs while the other genes associated with piRNAs may not receive biologically significant repression. Previous researches have reported that spermatogonial stem cells (SSCs) may regain pluripotency in response to inductive culture condition and adapt a different cell fate including neuron-like cells [76,77,78,79,80,81]. This suggests that repression of these genes in SSCs is likely reversible. Nevertheless, whether the PIWI/piRNA pathway activities in chicken gonocytes contribute to the establishment of such reversible epigenetic states remains elusive. This will be worth investigating with respect to piRNA-mediated histone modification (H3K9me3) and DNA methylation profiling.
Conclusions
In this report, we investigated the changes in piRNA compositions in different chicken germ cell developmental stages and explored potential roles of PIWI/piRNA pathways in modulating different stages of germ cell development. We showed a progressive transition of piRNA compositions from TE to intergenic association. Additionally, we showed that piRNAs may be involved in modulating stage-dependent TE expression. Our investigation of the stage-dependent activities of piRNA clusters implied stage-dependent roles in modulating germline development. Unexpectedly, we revealed the potential evolutionary conservation of piRNA clusters between chickens and eutherian mammals.
Methods
Animals and tissue sample collection
The fertilized eggs of Cobb500 broiler (Gallus gallus) and Leghorn chickens were provided by Taiwan Chunky G.P. Farm Co. and Animal Health Research Institute, Council of Agriculture, Executive Yuan, Taiwan, respectively. Fertilized eggs were incubated at 37.5 °C under 50–60% relative humidity. The protocol has been reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at National Taiwan University (NTU-100-EL-55; NTU-101-EL-116). For high-throughput small RNA sequencing, samples E11G1 and E14G1 were collected from eggs of the Cobb500 broiler, samples BC1, BC2, E11G2, and E14G2 were collected from eggs of Leghorn layer. For strand-specific mRNA sequencing and quantitative RT-PCR, samples were collected from eggs of JA57 broiler and Leghorn chicken, respectively. Blastoderms were collected from non-incubated eggs. PGCs were isolated from E3 and E7 embryos of the Arbor Acres broiler (Gallus gallus) purchased from Chu Lin Farm Co., Ltd., Taiwan. Male gonads were dissected from chicken embryos incubated ranging from 8 days (E8, HH34) to 14 days (E14, HH40) for germ cell isolation. Samples were processed for total and small RNA isolation by TRIzol reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and miRNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA), respectively, according to the manufacturers’ instructions. A full set of data solely from Leghorn layer has been extracted from blastodermal cells (BC1, BC2), E11 (E11G2) and E14 (E14G2) and adult testes (Adult) sequencing results to confirm the conclusion.
High-throughput next-generation sequencing of 3′-end-2’O-methylated small RNAs
RNA extracted from 10 to 15 blastodermal embryos, cultured E7 PGC, 8–10 E11 left-side embryonic gonads, and 8–10 E14 left-side embryonic gonads were preceded for small RNA-sequencing and strand-specific total RNA-sequencing (ssRNA-seq). The quality and concentration of RNA samples were determined using Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The RNA integrity numbers (RIN) of all our total RNA samples were between 9.9 and 10.0, which indicates minimized RNA degradation induced complication. Small RNA-seq libraries were constructed using the Illumina TruSeq Small RNA sample preparation kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). For piRNA enrichment, small RNA samples were oxidized by NaIO4 before library construction as described (Additional file 1: Figure S1A) [82]. We used the same oxidation treatment protocol that was applied by Li et al. for the adult testes sample preparation [49]. After adaptor ligation, the small RNA libraries were reverse transcribed, followed by amplification through 15 PCR cycles. Sequencing was performed using either an Illumina MiSeq (for E11G1 and E14G1) or an Illumina Solexa Platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA, for BC1, BC2, E7PGC1, E7PGC2, E11G2, E14G2), with read length setting of 50 bp and 75 bp, respectively. Details for ssRNA-seq analysis are described below.
Bioinformatic filtering for piRNA candidates
Periodate oxidation-treated small RNA-seq datasets for blastodermal cells, E7 PGCs, E11 and E14 gonads were generated in our laboratory. We also obtained the oxidized small RNA sequencing for adult testes (GSM1096613) from Li et al. [49]. For all in-house generated small RNA-seq, we applied adaptor trimming via cutadapt [83] with a 3′ adaptor sequence “TGGAATTCTCGGGTGCCAAGGAACTCCAGTCAC” and parameters -m 15 -M 45 to restrict a small RNA size for the follow-up analysis. We applied FastQC [84] to identify adaptor sequences to be trimmed by cutadapt for adult testes small RNA-seq. Adaptor-trimmed small RNA reads were mapped to the galGal5 genome via Tophat2 (v2.0.12) [85], with parameters -g 1 -N 0 --read-gap-length 0 --read-edit-dist 0 --read-realign-edit-dist 0 --max-insertion-length 0 --max-deletion-length 0, to filter out non-chicken reads and reads containing indels or mismatches (Additional file 1: Table S1). We used chicken galGal5 Refseq transcriptome obtained from UCSC genome browser [86, 87] as the splice junction database to identify reads spanning splice junctions. For stringent piRNA candidate selection, we removed reads mapping to galGal5 rRNA and tRNA sequences from Rfam [88] and Ensembl database (release 87) [89], then to chicken miRNA precursors from miRBase (release 19) [90] and predicted novel miRNA precursors identified via miRDeep (v2.0.0.7; default parameter setting), with parameters -n -c -j -l 18 -m -p [91]. We applied Bowtie (v 1.1.1) [92] with parameters allowing no mismatches for identifying miRNAs with complete sequence match. Finally, we reckoned sequencing reads with 24–34 nt as piRNA candidates (Additional file 1: Figure S1B).
Strand-specific RNA-seq analysis
We constructed strand-specific paired-end mRNA sequencing for blastodermal cells and E11 and E14 gonads following Illumina TruSeq stranded total RNA sample preparation with 12 PCR-cycle amplification, and then sequenced via Illumina HiSeq sequencing system, with read length setting to 100 bp. The raw RNA-seq reads were curated by trimming adaptors and low score reads, followed by genomic mapping using Tophat2 (v2.0.12) [85] with standard settings for paired-end sequencing. We applied reference guided sequence assembly using Cufflinks (v2.2.1) [93, 94] with default parameters, followed by merging transcriptome assemblies and filtering out potential isoforms. We then annotated the merged contigs based on galGal5 Refseq and Ensembl databases (release 90). Gene expression quantification for each dataset was calculated based on the merged transcriptome annotations, including novel transcripts.
piRNA cluster analysis
We adapted proTRAC (v2.0.5) and reconfigured it to allow the discovery of dual-stranded piRNA clusters, in addition to single- and bi-directional piRNA clusters [95]. For cross-stage comparison, we merged the piRNA clusters in each profile based on their genomic position. Considering that the transcriptional activities between an expressing piRNA precursor and its sense-overlapping expressing mRNA precursor may not be distinguishable by sequencing information, because both precursors are transcribed via RNA Pol II [96], we extended a candidate piRNA cluster to cover its overlapping transcripts with FPKM > = 1 in at least one in-house RNA-seq dataset (Additional file 1: Figure S8). The expressions of piRNA clusters were measured as the number of piRNA reads per kilobase per million reads (piRPKM) for cross-sample comparison. Data analyses including multidimensional scaling, Heatmap [97], and violin plots [98] were conducted via R [99].
PGC isolation and in vitro culture
Circulating PGCs (cPGCs) were derived from embryonic blood of E3 embryo (HH15–16), initiated by seeding approximately 2 μL of blood in 48-well plates with 300 μL of FAcs medium [100]. Gonadal PGCs (gPGCs) were derived from E7 embryonic gonads (HH28–30), initiated by seeding homogenized embryonic gonads in 500 μL of FAcs medium in 24-well plates as described [100]. Every 2 days, one-third of the total medium was changed with fresh medium until reaching > 70% confluence. Suspending cells were collected and subcultured in larger wells. One million cells were obtained by in vitro PGC cultures for approximately 1 month for both cPGCs and gPGCs, which were subjected to further RNA isolation processing. PGC cultures were maintained at 37.5 °C incubator with 5% CO2 supply.
Germ cell purification from E11 and E14 embryonic gonads
We harvested male gonads from E11 and E14 embryos. For one batch of purification of the same stage, we pooled approximately 40 E11 embryonic male gonads or approximately 30 E14 embryonic male gonads. The pooled gonads of the same stage were homogenized by Gibco™ 0.25% trypsin-EDTA (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) treatment at 37 °C for 6 min. The homogenized cells were filtered through 70 μm Falcon™ Cell Strainers (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA); resuspended in DMEM with 1% FBS and 1 mM EDTA supplement at approximately 6 × 106 cells per 150 mm tissue culture treated dish; and then placed in an incubator (37.5 °C, 5% CO2) for 4 h. Germ cell-enriched populations (suspension) and germ-depleted populations (adherent) were collected separately and dissolved in TRIzol reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) for RNA extraction. We kept a small portion of the sample to check for germ cell enrichment efficiency via immunofluorescent staining.
Immunocytochemistry
We applied immunofluorescent staining to evaluate the germ cell enrichment efficiency. Cells were loaded onto slides, fixed (4% PFA in PBS) for 20 min at room temperature, quenched (10 mM Tris pH 7.5, 50 mM KCl, 20 mM EDTA) for 5 min, permeabilized (0.1% Saponin in PBS) for 5 min, with PBS wash in each step. Samples were blocked (1% BSA in PBS) overnight at 4 °C. The cells were incubated at room temperature with primary anti-CVH antibody (#9C4-2E4; Biotem, Apprieu, France) at 1:1000 dilution in 1% BSA for 1 h, washed several times with PBS, and then incubated with secondary goat anti-mouse DyLight® 594 antibody (#ab96873; Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA) at 1:10000 dilution in 1% BSA for 1 h. We then applied Hoechst 33,342 nucleic acid staining (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) at 1:10000 dilution in 1% BSA for 5 min. After several washes, samples were mounted and stored at − 20 °C. Fluorescent images were observed under a fluorescence microscope. Germ cell-enriched populations with isolation efficiency above 80% were used for the subsequent expression analysis via RT-qPCR.
RT-qPCR primer design
All in-house developed primers were designed via Primer3 [101, 102] against gene or transcript sequences obtained from UCSC genome browser [86, 87]. For the design of primers against chicken LINE sequences, we obtained 10 longest sequences for each of CR1-B to CR1-H from the galGal5 genome sequence, and then identified consensus sequences via R-packages [99] for Multiple Sequence Alignment (msa) [103] and Biological Sequences Retrieval and Analysis (seqinr) [104]. Primer target specificity was validated via in-silico PCR in UCSC genome browser [87].
Total RNA isolation from enriched germ cells and reverse transcription real-time PCR (RT-qPCR)
For total RNA extraction, equal volume of ethanol was added to a sample in TRIzol, and then loaded onto a filter column provided by the miRNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA). The RNA extraction protocol was then performed according to the manufacturers’ instruction, with the exception of two-time DNase treatments (once on-column, and once prior to cDNA synthesis) to ensure minimal DNA contamination. One microgram (1 μg) of extracted RNAs was reverse transcribed according to instructions provided by the Invitrogen™ SuperScript® III First-Strand Synthesis System (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The temperature settings for reverse transcription were 5 min at 25 °C, 60 min at 50 °C, and 15 min at 70 °C, and the samples were then chilled on ice. For qPCR, KAPA SYBR® FAST qPCR Master Mix (Kapa Biosystems, Wilmington, MA, USA) was used, followed by real-time PCR in Roche Light Cycler® 480II for 10 min 95 °C preheat, then 40 PCR cycles of 10 s at 95 °C, 10 s at 50 °C, and 10 s at 70 °C. The primers used for qPCR are listed in Additional file 1: Table S6.
Change history
19 June 2018
Following publication of the original article [1], the authors reported that one of the authors’ names is spelled incorrectly.
Abbreviations
- 1U:
-
Enriched uracil at the 1st nucleotide
- 10A:
-
Enriched adenine at the 10th nucleotide
- AT:
-
Adult testes
- AT-piRISC:
-
Adult testes-enriched piRNA cluster
- BC:
-
Blastodermal cell
- BC-piRC:
-
BC-enriched piRNA cluster
- CR1:
-
Chicken repeat 1 element
- E11G:
-
Embryonic day 11 gonads
- E14G:
-
Embryonic day 14 gonads
- E7PGC:
-
Cultured PGCs from E7 gonads
- EG-piRC:
-
E11 and E14 gonadal-enriched piRNA cluster
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- H3K9me3:
-
Tri-methylation on histone H3 lysine 9
- HH:
-
Hamburger–hamilton stages
- LINE:
-
Long interspersed nuclear element
- LTR:
-
Long terminal repeats
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- PGC:
-
Primordial germ cell
- PGC-piRC:
-
PGC-enriched piRNA cluster
- piRISC:
-
piRNA induced silencing complex
- PTGS:
-
Post-transcriptional gene silencing
- SSC:
-
Spermatogonial stem cell
- TE:
-
Transposable element
- TGS:
-
Transcriptional gene silencing
References
Hajkova P. Epigenetic reprogramming in the germline: towards the ground state of the epigenome. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci. 2011;366(1575):2266–73.
Seisenberger S, Andrews S, Krueger F, Arand J, Walter J, Santos F, Popp C, Thienpont B, Dean W, Reik W. The dynamics of genome-wide DNA methylation reprogramming in mouse primordial germ cells. Mol Cell. 2012;48(6):849–62.
Walsh CP, Chaillet JR, Bestor TH. Transcription of IAP endogenous retroviruses is constrained by cytosine methylation. Nat Genet. 1998;20(2):116–7.
Hajkova P, Erhardt S, Lane N, Haaf T, El-Maarri O, Reik W, Walter J, Surani MA. Epigenetic reprogramming in mouse primordial germ cells. Mech Dev. 2002;117(1–2):15–23.
Kidwell MG, Holyoake AJ. Transposon-induced hotspots for genomic instability. Genome Res. 2001;11(8):1321–2.
Lin H, Spradling AC. A novel group of pumilio mutations affects the asymmetric division of germline stem cells in the Drosophila ovary. Development. 1997;124(12):2463–76.
Cox DN, Chao A, Baker J, Chang L, Qiao D, Lin H. A novel class of evolutionarily conserved genes defined by piwi are essential for stem cell self-renewal. Genes Dev. 1998;12(23):3715–27.
Thomson T, Lin H. The biogenesis and function of PIWI proteins and piRNAs: progress and prospect. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2009;25:355–76.
Brennecke J, Aravin AA, Stark A, Dus M, Kellis M, Sachidanandam R, Hannon GJ. Discrete small RNA-generating loci as master regulators of transposon activity in Drosophila. Cell. 2007;128(6):1089–103.
Deng W, Lin H. Miwi, a murine homolog of piwi, encodes a cytoplasmic protein essential for spermatogenesis. Dev Cell. 2002;2(6):819–30.
Kuramochi-Miyagawa S, Kimura T, Ijiri TW, Isobe T, Asada N, Fujita Y, Ikawa M, Iwai N, Okabe M, Deng W, et al. Mili, a mammalian member of piwi family gene, is essential for spermatogenesis. Development. 2004;131(4):839–49.
Carmell MA, Girard A, van de Kant HJ, Bourc'his D, Bestor TH, de Rooij DG, Hannon GJ. MIWI2 is essential for spermatogenesis and repression of transposons in the mouse male germline. Dev Cell. 2007;12(4):503–14.
Unhavaithaya Y, Hao Y, Beyret E, Yin H, Kuramochi-Miyagawa S, Nakano T, Lin H. MILI, a PIWI-interacting RNA-binding protein, is required for germ line stem cell self-renewal and appears to positively regulate translation. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(10):6507–19.
Kim TH, Yun TW, Rengaraj D, Lee SI, Lim SM, Seo HW, Park TS, Han JY. Conserved functional characteristics of the PIWI family members in chicken germ cell lineage. Theriogenology. 2012;78(9):1948–59.
Rengaraj D, Lee SI, Park TS, Lee HJ, Kim YM, Sohn YA, Jung M, Noh SJ, Jung H, Han JY. Small non-coding RNA profiling and the role of piRNA pathway genes in the protection of chicken primordial germ cells. BMC Genomics. 2014;15:757.
Watanabe T, Chuma S, Yamamoto Y, Kuramochi-Miyagawa S, Totoki Y, Toyoda A, Hoki Y, Fujiyama A, Shibata T, Sado T, et al. MITOPLD is a mitochondrial protein essential for nuage formation and piRNA biogenesis in the mouse germline. Dev Cell. 2011;20(3):364–75.
Parker JS, Roe SM, Barford D. Structural insights into mRNA recognition from a PIWI domain-siRNA guide complex. Nature. 2005;434(7033):663–6.
Feltzin VL, Khaladkar M, Abe M, Parisi M, Hendriks GJ, Kim J, Bonini NM. The exonuclease nibbler regulates age-associated traits and modulates piRNA length in Drosophila. Aging Cell. 2015;14(3):443–52.
Anastasakis D, Skeparnias I, Shaukat AN, Grafanaki K, Kanellou A, Taraviras S, Papachristou DJ, Papakyriakou A, Stathopoulos C. Mammalian PNLDC1 is a novel poly(a) specific exonuclease with discrete expression during early development. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(18):8908–20.
Czech B, Hannon GJ. A happy 3′ ending to the piRNA maturation story. Cell. 2016;164(5):838–40.
Kirino Y, Mourelatos Z. The mouse homolog of HEN1 is a potential methylase for Piwi-interacting RNAs. Rna. 2007;13(9):1397–401.
Kirino Y, Mourelatos Z. Mouse Piwi-interacting RNAs are 2'-O-methylated at their 3′ termini. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007;14(4):347–8.
Saito K, Sakaguchi Y, Suzuki T, Suzuki T, Siomi H, Siomi MC. Pimet, the Drosophila homolog of HEN1, mediates 2'-O-methylation of Piwi- interacting RNAs at their 3′ ends. Genes Dev. 2007;21(13):1603–8.
Khurana JS, Theurkauf W. piRNAs, transposon silencing, and Drosophila germline development. J Cell Biol. 2010;191(5):905–13.
Juliano C, Wang J, Lin H. Uniting germline and stem cells: the function of Piwi proteins and the piRNA pathway in diverse organisms. Annu Rev Genet. 2011;45:447–69.
Aravin AA, Sachidanandam R, Girard A, Fejes-Toth K, Hannon GJ. Developmentally regulated piRNA clusters implicate MILI in transposon control. Science. 2007;316(5825):744–7.
De Fazio S, Bartonicek N, Di Giacomo M, Abreu-Goodger C, Sankar A, Funaya C, Antony C, Moreira PN, Enright AJ, O'Carroll D. The endonuclease activity of Mili fuels piRNA amplification that silences LINE1 elements. Nature. 2011;480(7376):259–63.
Czech B, Hannon GJ. One loop to rule them all: the ping-pong cycle and piRNA-guided silencing. Trends Biochem Sci. 2016;41(4):324–37.
Reuter M, Berninger P, Chuma S, Shah H, Hosokawa M, Funaya C, Antony C, Sachidanandam R, Pillai RS. Miwi catalysis is required for piRNA amplification-independent LINE1 transposon silencing. Nature. 2011;480(7376):264–7.
Gunawardane LS, Saito K, Nishida KM, Miyoshi K, Kawamura Y, Nagami T, Siomi H, Siomi MC. A slicer-mediated mechanism for repeat-associated siRNA 5′ end formation in Drosophila. Science. 2007;315(5818):1587–90.
Wang W, Han BW, Tipping C, Ge DT, Zhang Z, Weng Z, Zamore PD. Slicing and binding by Ago3 or Aub trigger Piwi-bound piRNA production by distinct mechanisms. Mol Cell. 2015;59(5):819–30.
Aravin AA, Bourc'his D. Small RNA guides for de novo DNA methylation in mammalian germ cells. Genes Dev. 2008;22(8):970–5.
Aravin AA, Sachidanandam R, Bourc'his D, Schaefer C, Pezic D, Toth KF, Bestor T, Hannon GJ. A piRNA pathway primed by individual transposons is linked to de novo DNA methylation in mice. Mol Cell. 2008;31(6):785–99.
Pezic D, Manakov SA, Sachidanandam R, Aravin AA. piRNA pathway targets active LINE1 elements to establish the repressive H3K9me3 mark in germ cells. Genes Dev. 2014;28(13):1410–28.
Tseng YT, Liao HF, Yu CY, Mo CF, Lin SP. Epigenetic factors in the regulation of prospermatogonia and spermatogonial stem cells. Reproduction. 2015;150(3):R77–91.
Zamudio N, Barau J, Teissandier A, Walter M, Borsos M, Servant N, Bourc'his D. DNA methylation restrains transposons from adopting a chromatin signature permissive for meiotic recombination. Genes Dev. 2015;29(12):1256–70.
Kojima-Kita K, Kuramochi-Miyagawa S, Nagamori I, Ogonuki N, Ogura A, Hasuwa H, Akazawa T, Inoue N, Nakano T. MIWI2 as an effector of DNA methylation and gene silencing in embryonic male germ cells. Cell Rep. 2016;16(11):2819–28.
Iwasaki YW, Siomi MC, Siomi H. PIWI-interacting RNA: its biogenesis and functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 2015;84:405–33.
Bao J, Zhang Y, Schuster AS, Ortogero N, Nilsson EE, Skinner MK, Yan W. Conditional inactivation of Miwi2 reveals that MIWI2 is only essential for prospermatogonial development in mice. Cell Death Differ. 2014;21(5):783–96.
Inoue K, Ichiyanagi K, Fukuda K, Glinka M, Sasaki H. Switching of dominant retrotransposon silencing strategies from posttranscriptional to transcriptional mechanisms during male germ-cell development in mice. PLoS Genet. 2017;13(7):e1006926.
Fasenko GM. Egg storage and the embryo. Poult Sci. 2007;86(5):1020–4.
Hamburger V, Hamilton HL. A series of normal stages in the development of the chick embryo. 1951. Dev Dyn. 1992;195(4):231–72.
Swift CH. Origin of the sex-cords and definitive spermatogonia in the male chick. Am J Anat. 1916;20(3):375–410.
International Chicken Genome Sequencing C. Sequence and comparative analysis of the chicken genome provide unique perspectives on vertebrate evolution. Nature. 2004;432(7018):695–716.
Wicker T, Robertson JS, Schulze SR, Feltus FA, Magrini V, Morrison JA, Mardis ER, Wilson RK, Peterson DG, Paterson AH, et al. The repetitive landscape of the chicken genome. Genome Res. 2005;15(1):126–36.
Zhang G, Li C, Li Q, Li B, Larkin DM, Lee C, Storz JF, Antunes A, Greenwold MJ, Meredith RW, et al. Comparative genomics reveals insights into avian genome evolution and adaptation. Science. 2014;346(6215):1311–20.
Smit AF. Interspersed repeats and other mementos of transposable elements in mammalian genomes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1999;9(6):657–63.
Jean C, Oliveira NM, Intarapat S, Fuet A, Mazoyer C, De Almeida I, Trevers K, Boast S, Aubel P, Bertocchini F, et al. Transcriptome analysis of chicken ES, blastodermal and germ cells reveals that chick ES cells are equivalent to mouse ES cells rather than EpiSC. Stem Cell Res. 2015;14(1):54–67.
Li XZ, Roy CK, Dong X, Bolcun-Filas E, Wang J, Han BW, Xu J, Moore MJ, Schimenti JC, Weng Z, et al. An ancient transcription factor initiates the burst of piRNA production during early meiosis in mouse testes. Mol Cell. 2013;50(1):67–81.
Xu L, Qiu L, Chang G, Guo Q, Liu X, Bi Y, Zhang Y, Wang H, Li Z, Guo X, et al. Discovery of piRNAs pathway associated with early-stage spermatogenesis in chicken. PLoS One. 2016;11(4):e0151780.
Zhuang F, Fuchs RT, Robb GB. Small RNA expression profiling by high-throughput sequencing: implications of enzymatic manipulation. J Nucleic Acids. 2012;2012:360358.
Shao P, Liao JY, Guan DG, Yang JH, Zheng LL, Jing Q, Zhou H, Qu LH. Drastic expression change of transposon-derived piRNA-like RNAs and microRNAs in early stages of chicken embryos implies a role in gastrulation. RNA Biol. 2012;9(2):212–27.
Cora E, Pandey RR, Xiol J, Taylor J, Sachidanandam R, McCarthy AA, Pillai RS. The MID-PIWI module of Piwi proteins specifies nucleotide- and strand-biases of piRNAs. Rna. 2014;20(6):773–81.
Hayashi R, Schnabl J, Handler D, Mohn F, Ameres SL, Brennecke J. Genetic and mechanistic diversity of piRNA 3′-end formation. Nature. 2016;539(7630):588–92.
Toth KF, Pezic D, Stuwe E, Webster A. The piRNA pathway guards the germline genome against transposable elements. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;886:51–77.
Chirn GW, Rahman R, Sytnikova YA, Matts JA, Zeng M, Gerlach D, Yu M, Berger B, Naramura M, Kile BT, et al. Conserved piRNA expression from a distinct set of piRNA cluster loci in eutherian mammals. PLoS Genet. 2015;11(11):e1005652.
Kuleshov MV, Jones MR, Rouillard AD, Fernandez NF, Duan Q, Wang Z, Koplev S, Jenkins SL, Jagodnik KM, Lachmann A, et al. Enrichr: a comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(W1):W90–7.
Kuramochi-Miyagawa S, Watanabe T, Gotoh K, Totoki Y, Toyoda A, Ikawa M, Asada N, Kojima K, Yamaguchi Y, Ijiri TW, et al. DNA methylation of retrotransposon genes is regulated by Piwi family members MILI and MIWI2 in murine fetal testes. Genes Dev. 2008;22(7):908–17.
Weick EM, Miska EA. piRNAs: from biogenesis to function. Development. 2014;141(18):3458–71.
Manakov SA, Pezic D, Marinov GK, Pastor WA, Sachidanandam R, Aravin AA. MIWI2 and MILI have differential effects on piRNA biogenesis and DNA methylation. Cell Rep. 2015;12(8):1234–43.
Lee YC. The role of piRNA-mediated epigenetic silencing in the population dynamics of transposable elements in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS Genet. 2015;11(6):e1005269.
Xuan JJ, Sun WJ, Lin PH, Zhou KR, Liu S, Zheng LL, Qu LH, Yang JH. RMBase v2.0: deciphering the map of RNA modifications from epitranscriptome sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(D1):D327–34.
Gerdes P, Richardson SR, Mager DL, Faulkner GJ. Transposable elements in the mammalian embryo: pioneers surviving through stealth and service. Genome Biol. 2016;17:100.
Chuong EB, Elde NC, Feschotte C. Regulatory activities of transposable elements: from conflicts to benefits. Nat Rev Genet. 2017;18(2):71–86.
Hackett JA, Kobayashi T, Dietmann S, Surani MA. Activation of lineage regulators and transposable elements across a pluripotent Spectrum. Stem Cell Rep. 2017;8(6):1645–58.
Aravin A, Gaidatzis D, Pfeffer S, Lagos-Quintana M, Landgraf P, Iovino N, Morris P, Brownstein MJ, Kuramochi-Miyagawa S, Nakano T, et al. A novel class of small RNAs bind to MILI protein in mouse testes. Nature. 2006;442(7099):203–7.
Homolka D, Pandey RR, Goriaux C, Brasset E, Vaury C, Sachidanandam R, Fauvarque MO, Pillai RS. PIWI slicing and RNA elements in precursors instruct directional primary piRNA biogenesis. Cell Rep. 2015;12(3):418–28.
Yang Z, Chen KM, Pandey RR, Homolka D, Reuter M, Janeiro BK, Sachidanandam R, Fauvarque MO, McCarthy AA, Pillai RS. PIWI slicing and EXD1 drive biogenesis of nuclear piRNAs from cytosolic targets of the mouse piRNA pathway. Mol Cell. 2016;61(1):138–52.
Goh WS, Falciatori I, Tam OH, Burgess R, Meikar O, Kotaja N, Hammell M, Hannon GJ. piRNA-directed cleavage of meiotic transcripts regulates spermatogenesis. Genes Dev. 2015;29(10):1032–44.
Gou LT, Dai P, Yang JH, Xue Y, Hu YP, Zhou Y, Kang JY, Wang X, Li H, Hua MM, et al. Pachytene piRNAs instruct massive mRNA elimination during late spermiogenesis. Cell Res. 2015;25(2):266.
Watanabe T, Cheng EC, Zhong M, Lin H. Retrotransposons and pseudogenes regulate mRNAs and lncRNAs via the piRNA pathway in the germline. Genome Res. 2015;25(3):368–80.
Zhang P, Kang JY, Gou LT, Wang J, Xue Y, Skogerboe G, Dai P, Huang DW, Chen R, Fu XD, et al. MIWI and piRNA-mediated cleavage of messenger RNAs in mouse testes. Cell Res. 2015;25(2):193–207.
Han BW, Wang W, Li C, Weng Z, Zamore PD, Noncoding RNA. piRNA-guided transposon cleavage initiates zucchini-dependent, phased piRNA production. Science. 2015;348(6236):817–21.
Kress C, Montillet G, Jean C, Fuet A, Pain B. Chicken embryonic stem cells and primordial germ cells display different heterochromatic histone marks than their mammalian counterparts. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2016;9:5.
Putzbach W, Gao QQ, Patel M, van Dongen S, Haluck-Kangas A, Sarshad AA, Bartom ET, Kim KA, Scholtens DM, Hafner M, et al. Many si/shRNAs can kill cancer cells by targeting multiple survival genes through an off-target mechanism. Elife. 2017;6:e29702.
Kanatsu-Shinohara M, Inoue K, Lee J, Yoshimoto M, Ogonuki N, Miki H, Baba S, Kato T, Kazuki Y, Toyokuni S, et al. Generation of pluripotent stem cells from neonatal mouse testis. Cell. 2004;119(7):1001–12.
Guan K, Nayernia K, Maier LS, Wagner S, Dressel R, Lee JH, Nolte J, Wolf F, Li M, Engel W, et al. Pluripotency of spermatogonial stem cells from adult mouse testis. Nature. 2006;440(7088):1199–203.
Huang YH, Chin CC, Ho HN, Chou CK, Shen CN, Kuo HC, Wu TJ, Wu YC, Hung YC, Chang CC, et al. Pluripotency of mouse spermatogonial stem cells maintained by IGF-1- dependent pathway. FASEB J. 2009;23(7):2076–87.
Li B, Wang XY, Tian Z, Xiao XJ, Xu Q, Wei CX, Y F, Sun HC, Chen GH. Directional differentiation of chicken spermatogonial stem cells in vitro. Cytotherapy. 2010;12(3):326–31.
Wang X, Chen T, Zhang Y, Li B, Xu Q, Song C. Isolation and culture of pig Spermatogonial stem cells and their in vitro differentiation into neuron-like cells and adipocytes. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(11):26333–46.
Azizi H, Conrad S, Hinz U, Asgari B, Nanus D, Peterziel H, Hajizadeh Moghaddam A, Baharvand H, Skutella T. Derivation of pluripotent cells from mouse SSCs seems to be age dependent. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:8216312.
Seitz H, Ghildiyal M, Zamore PD. Argonaute loading improves the 5′ precision of both MicroRNAs and their miRNA* strands in flies. Curr Biol. 2008;18(2):147–51.
Martin M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. 2011;17(1):10-12.
FastQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc. Accessed July 2014.
Kim D, Pertea G, Trapnell C, Pimentel H, Kelley R, Salzberg SL. TopHat2: accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome Biol. 2013;14(4):R36.
Karolchik D, Hinrichs AS, Furey TS, Roskin KM, Sugnet CW, Haussler D, Kent WJ. The UCSC table browser data retrieval tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32(Database issue):D493–6.
Tyner C, Barber GP, Casper J, Clawson H, Diekhans M, Eisenhart C, Fischer CM, Gibson D, Gonzalez JN, Guruvadoo L, et al. The UCSC genome browser database: 2017 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(D1):D626–34.
Nawrocki EP, Burge SW, Bateman A, Daub J, Eberhardt RY, Eddy SR, Floden EW, Gardner PP, Jones TA, Tate J, et al. Rfam 12.0: updates to the RNA families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(Database issue):D130–7.
Aken BL, Ayling S, Barrell D, Clarke L, Curwen V, Fairley S, Fernandez Banet J, Billis K, Garcia Giron C, Hourlier T, et al. The Ensembl gene annotation system. Database (Oxford). 2016;2016
Kozomara A, Griffiths-Jones S. miRBase: annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(Database issue):D68–73.
Friedlander MR, Chen W, Adamidi C, Maaskola J, Einspanier R, Knespel S, Rajewsky N. Discovering microRNAs from deep sequencing data using miRDeep. Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26(4):407–15.
Langmead B, Salzberg SL. Fast gapped-read alignment with bowtie 2. Nat Methods. 2012;9(4):357–9.
Trapnell C, Williams BA, Pertea G, Mortazavi A, Kwan G, van Baren MJ, Salzberg SL, Wold BJ, Pachter L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28(5):511–5.
Roberts A, Pimentel H, Trapnell C, Pachter L. Identification of novel transcripts in annotated genomes using RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics. 2011;27(17):2325–9.
Rosenkranz D, Zischler H. proTRAC--a software for probabilistic piRNA cluster detection, visualization and analysis. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012;13:5.
Zhang Z, Wang J, Schultz N, Zhang F, Parhad SS, Tu S, Vreven T, Zamore PD, Weng Z, Theurkauf WE. The HP1 homolog rhino anchors a nuclear complex that suppresses piRNA precursor splicing. Cell. 2014;157(6):1353–63.
Kolde R. Pheatmap: pretty Heatmaps. In: R package version 1.0.8; 2015.
Adler D. Vioplot: violin plot. In: R package version 0.2; 2005.
R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. In: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2016.
Whyte J, Glover JD, Woodcock M, Brzeszczynska J, Taylor L, Sherman A, Kaiser P, McGrew MJ. FGF, insulin, and SMAD signaling cooperate for avian primordial germ cell self-renewal. Stem Cell Reports. 2015;5(6):1171–82.
Koressaar T, Remm M. Enhancements and modifications of primer design program Primer3. Bioinformatics. 2007;23(10):1289–91.
Untergasser A, Cutcutache I, Koressaar T, Ye J, Faircloth BC, Remm M, Rozen SG. Primer3--new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(15):e115.
Bodenhofer U, Bonatesta E, Horejs-Kainrath C, Hochreiter S. Msa: an R package for multiple sequence alignment. Bioinformatics. 2015;31(24):3997–9.
Gouy M, Milleret F, Mugnier C, Jacobzone M, Gautier C. ACNUC: a nucleic acid sequence data base and analysis system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984;12(1 Pt 1):121–7.
Acknowledgements
This article is dedicated to the memory of Prof. Hsei-Wei Wang (1969~ 2015), National Yan-Ming University, Taiwan. We would like to express our sincere gratitude to Prof. Wang’s comments and support for this project. We thank National Taiwan University – The Core Technological Platform and Services of the Center for System Biology for assisting in developing the piRNA identification platform. Special thanks to Dr. Hervé Seitz from Laboratoire de Biologie Moléculaire Eucaryote (LBME), Université de Toulouse, France, for providing critical intellectual input and extensive discussion, and the 3’-end-2’O-methylated small RNA enrichment protocol. We thank Chun-Yi Hsiao, Yu-Yun Kao, Yih-Shien Chiang, Yih-Shien Chiang, and Jui-Hua Riva Chu (Technology Commons, College of Life Science, NTU) for support with experimental settings for oxidation-enriched small RNA-seq library preparation and the MiSeq platform analysis. We thank Dr. Chu-Fan Mo, Prof. Shih-Shun Lin, Dr. Chia-Wei Lu, Hung-Chun Tang, and Hsin-Ting Hsieh for helpful discussion and technical support. We are grateful for Taiwan Chunky G.P. Farm Co., Ltd. for supplying fertilized eggs to initiate this study. We thank T. Rio Frio, S. Baulande and P. Legoix-Né (ICgex platform, Institut Curie), A. Lermine (bioinformatics platform, Institut Curie) for support. We thank Julien Jarroux from Morillon’s lab for advice on the RNA-seq library preparation.
Funding
This study is supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan (102–2314-B-002-070-MY3, this Grant associated with the MOST Ta-You Wu memorial award; 106–2311-B-002-009-); National Taiwan University – Cutting-Edge Steering Research Project (101R7602D3; 102R7602D3; 103R7602D3). This work has benefited from the facilities and expertise of the NGS platform of Institut Curie (supported by the Agence Nationale de la Recherche and the Canceropôle Ile-de-France). Morillon’s lab is supported by the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (REGULncRNA, DNA-Life; ANR-10-EQPX-03; ANR10-INBS-09-08) and the European Research Council (ERC DARK, Consolidator Grant (CoG), LS2, ERC-2013-CoG). Pain’s lab is supported by the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (CRB-ANIM-ANR-11-INBS-0003).
Availability of data and materials
All sequencing data were submitted to Gene Expression Omnibus at accession number GSE98005 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=gse98005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KWC, YTT, and SPL conceived the study. YTT and KWC developed the methodology and piRNA identification pipeline, incubated embryonic eggs, extracted gonadal RNAs, performed RT-qPCR experiments and data collection. YCC (Yi-Chen), SCW, and BP established E3 and E7 PGC cultures and extracted RNAs. YTT and KWC performed piRNA sequencing. YTT, CYY, MP, and AM performed transcriptome sequencing and data collection; KWC compiled piRNA cluster analysis with the transcriptome datasets and performed bioinformatic and statistical analysis. HFL, YCC (Yi-Chun), YFET, and IHL assisted in the data analysis. SPL led the periodic discussion sessions for interpretation of raw data, while all authors provided intellectual input to the developed story. KWC, YTT, and SPL wrote the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript critically and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The protocols for all animal related experiments have been reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at National Taiwan University (NTU-100-EL-55; NTU-101-EL-116).
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Additional information
The original version of this article was revised: the name of one of the authors had been spelled incorrectly. It should be Antonin Morillon, not Antonin Morillion.
Additional files
Additional file 1:
Figure S1. High-confidence piRNA candidate identification pipeline. Figure S2. Examination of germ cell isolation efficiency using immunocytochemistry. Figure S3. Expression of potential spermatogonial stem cell (SSC) markers and genes encoding PIWI/piRNA pathway components in embryonic germ cells. Figure S4. Scheme for assessing ping-pong cycle piRNAs. Figure S5. Genomic association for piRNA candidates at each stage at a specific piRNA length. Figure S6. PiRNA distribution at the associated transcripts that reciprocally expressed compare to the quantity of mapped piRNAs (EDIL3, ANGPTL2, and PIP5K1B). Figure S7. PiRNA cluster analysis results. Figure S8. Schematic presentation of merging piRNAs from multiple stages. Figure S9. Venn diagram of number of transposable elements (TEs) and genes targeted by piRNAs from stage-enriched piRNA clusters. Figure S10. Stage-enriched piRNA clusters may contribute to stage-dependent regulatory roles. Figure S11. Ontology analysis of gene sets targeted by piRNAs from stage-enriched piRNA clusters under Enrichr: GO Biological Process 2015 category. Figure S12. Expression analysis via RT-qPCR on piRNA targeted genes associated with neural development. Table S1. Bioinformatic filtering results from high-confidence piRNA identification pipeline. Table S2. Number of piRNAs (in piRPM) mapped to TEs embedded in the transcripts that are differentially associated between E11G and E14G piRNAs. Table S3. Number of clusterable piRNAs before and piRNA cluster boundaries after adjustment. Table S4. Genes and TEs targeted by stage-enriched piRNA cluster-derived piRNAs. Table S5. Number of piRNAs (in piRPM) mapped to TEs embedded in the transcripts that are highly associated with piRNAs enriched in embryonic (E11 and E14) gonadal piRNA clusters (EG-piRC). Table S6. RT-qPCR primer sets. (DOCX 3433 kb)
Additional file 2:
Table S2. Number of piRNAs (in piRPM) mapped to TEs embedded in the transcripts that are differentially associated between E11G and E14G piRNAs. (XLS 109 kb)
Additional file 3:
Table S4. Genes and TEs targeted by stage-enriched piRNA cluster-derived piRNAs. (XLS 69 kb)
Additional file 4:
Table S5. Number of piRNAs (in piRPM) mapped to TEs embedded in the transcripts that are highly associated with piRNAs enriched in embryonic (E11 and E14) gonadal piRNA clusters (EG-piRC). (XLS 74 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, KW., Tseng, YT., Chen, YC. et al. Stage-dependent piRNAs in chicken implicated roles in modulating male germ cell development. BMC Genomics 19, 425 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-4820-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-4820-9