Abstract
Background
Increasing drought induced by global climate changes is altering the structure and function of grassland ecosystems. However, there is a lack of understanding of how drought affects the trade-off of above- and belowground biomass in desert steppe. We conducted a four-year (2015–2018) drought experiment to examine the responses of community above-and belowground biomass (AGB and BGB) to manipulated drought and natural drought in the early period of growing season (from March to June) in a desert steppe. We compared the associations of drought with species diversity (species richness and density), community-weighted means (CWM) of five traits, and soil factors (soil Water, soil carbon content, and soil nitrogen content) for grass communities. Meanwhile, we used the structural equation modeling (SEM) to elucidate whether drought affects AGB and BGB by altering species diversity, functional traits, or soil factors.
Results
We found that manipulated drought affected soil water content, but not on soil carbon and nitrogen content. Experimental drought reduced the species richness, and species modified the CWM of traits to cope with a natural drought of an early time in the growing season. We also found that the experimental and natural drought decreased AGB, while natural drought increased BGB. AGB was positively correlated with species richness, density, CWM of plant height, and soil water. BGB was negatively correlated with CWM of plant height, CWM of leaf dry matter content, and soil nitrogen content, while was positively correlated with CWM of specific leaf area, CWM of leaf nitrogen content, soil water, and soil carbon content. The SEM results indicated that the experimental and natural drought indirectly decreased AGB by reducing species richness and plant height, while natural drought and soil nitrogen content directly affected BGB.
Conclusions
These results suggest that species richness and functional traits can modulate the effects of drought on AGB, however natural drought and soil nitrogen determine BGB. Our findings demonstrate that the long-term observation and experiment are necessary to understand the underlying mechanism of the allocation and trade-off of community above-and belowground biomass.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Grasslands occupy 30% of Earth’s terrestrial area, while also responding sensitively to climate changes [1, 2]. Global climatic changes are expected to increase the risk of extreme drought events [3, 4]. Drought has pervasive impacts on ecosystem structure and function, especially in water-limited grasslands [5, 6]. Several previous studies have observed that the plant community biomass tends to increase, decrease, or remain stable under drought [7,8,9,10]. In addition, drought is one of the main drivers that determine species diversity and leaf morphology [11, 12]. Previous studies have shown that species diversity and functional traits were thought to play a vital role in affecting ecosystem function [13, 14]. These responses of plant to water restriction may relate to the type of drought experienced by an ecosystem [15]. Grasslands are expected to experience a decrease in long-term precipitation, and an increase in the frequency of short-term intense droughts [16, 17]. Meanwhile, some studies have suggested that changes in the timing of drought events can alter plant productivity regardless of precipitation amount [18, 19]. However, we have a very limited understanding of how timing and type of drought affect species diversity, functional traits, and plant biomass and their relationships in desert steppe.
The impact of climate change on biodiversity is greater than any other factor [20]. The control of species diversity including species richness and abundance is received the most focus [20, 21]. The relationship between ecosystem productivity and species diversity has been debated for decades [22]. In general, higher species diversity supports higher plant productivity but remains variation in other geographic regions [20, 23]. Globally, regions with a climate that is either cold or arid support few species than regions where the climates are both warm and wet [11]. Most species diversity-biomass relationship studies have focused on aboveground biomass instead of belowground biomass [13]. In a few studies on the relationship between belowground biomass and species diversity, it was found that there was a positive or uncorrelated relationship between them, due to the selection of diversity indexes and the research sites [24,25,26,27]. Plant biomass is important for ecosystem functions and services [28]. Therefore, examining the drought-induced relationship between biodiversity and biomass can provide support for further understanding of ecosystem management.
Functional traits are measurable characteristics of plants after long-term response and adaptation to the external environment [29, 30]. According to the dominance/mass ratio hypothesis, the functional trait of dominant species can directly affect ecosystem functions [31, 32]. Some traits at a community-level are the predictors of plant community responses to precipitation changes [33, 34]. Shifts in precipitation patterns can lead to changes in traits and species abundance, thereby shaping plant distributions or compositions [12]. The key plant traits, such as plant height, specific leaf area (SLA), leaf dry matter content (LDMC), leaf carbon content (LCC), and leaf nitrogen content (LNC), reflect plant strategies for coping with changing climate conditions [35]. For example, drought or drought in the growing season causes a decrease in plant height and an increase in SLA and LDMC [36]. According to the optimal allocation theory, plants preferentially develop the organs that can obtain the most limited growth resources [37]. Thus, the plant functional traits as potential covariates may lead to the trade-off of biomass under drought [14, 38]. However, the effects of drought-induced changes in plant functional traits on aboveground and belowground biomass remain poorly known [14]. Arid and semi-arid grassland, which is sensitive to precipitation changes, plays an important role in maintaining regional ecosystem function and socioeconomic development [37]. Therefore, understanding the relationship between drought-induced functional traits and biomass is important to understand the consequences of precipitation pattern changes in this region.
Precipitation manipulation experiment is a direct way to study shifts in community compositions and ecosystem functions following short-term precipitation change [39, 40]. Over the two decades, the studies on experimentally reducing precipitation have greatly increased to investigate how increased aridity might influence the ecosystems [41, 42]. However, community responses to extreme drought vary geographically [43, 44]. The semiarid grassland region of northern China is desirable for investigating the effects of extreme drought on the structure and function of grassland ecosystems, and the predicted effects can guide semiarid grassland to cope with future climate change. Here, we conducted a four-year experiment that imposed extreme drought, including two types: (1) a 66% reduction of rainfall from May to August (-66%) and (2) a 100% reduction of rainfall from June to July (-60 Days). This allowed us to examine the changes in the desert steppe under a manipulative drought experiment. We asked the following questions: (1) Whether the responses of species diversity, community-level trait, and soil property respond to the two types of experimental drought in desert steppe are different? (2) How do changes the above- and belowground biomass in the four consecutive years under different treatments? (3) How does extreme drought modulate the relationships between species diversity, community-level traits, and above- and belowground biomass?
Results
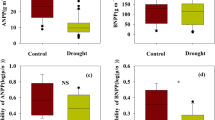
The annual precipitation gradually decreased from 2015 to 2017 and increased in 2018 due to increased precipitation in July and August (Additional file 1: Figure S1). Interestingly, only the precipitation in the early growing season (March to June) was correlated with the above- and belowground biomass (Additional file 1: Table S1). The precipitation of early time in the growing season (March to June) from 2015 to 2018 was 56.2 mm, 77.9 mm, 28.8 mm, and 21.4 mm, respectively (Additional file 1: Figure S1), which described as a natural interannual drought phenomenon. As a result, the strong correlation showed that drought of early time in growing season played an important role for the plant biomass.
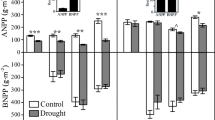
There were no differences in above- and belowground biomass, species diversity, CWM of traits and soil carbon and nitrogen content between -66% and -60 Days (Additional file 1: Table S2), so we combined the two treatments to represent experimental drought in the description below. The species richness and AGB were significantly affected by drought, year and their interaction (p < 0.05, Additional file 1: Table S3, Fig. 1a, c). Specifically, manipulated drought (-66% and -60 Days) significantly reduced AGB and species richness excluded species richness in 2015(Additional file 1: Table S2, Fig. 1a, c). The density was positively corrected with drought and year, and the BGB was significantly affected by year and the interaction of drought and year (p < 0.05, Additional file 1: Table S3, Fig. 1b, d). Surprisedly, BGB was increased with years, regardless of manipulated drought (Additional file 1: Table S2, Fig. 1d).
Effects of extreme drought (CONT, control; − 66%, reduce 66% in rainfall from May to August; − 60 Days, reduce 100% in rainfall from June to July) on plant community characteristics of desert steppe during the treatment years (2015–2018). AGB aboveground plant biomass, BGB belowground root biomass. Variables are shown as mean ± SE (n = 6). Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between years for the same treatments in p < 0.05. Statistical significance of drought effect in each year is depicted as **p < 0.0 1 and *p < 0.05
The CWM of height in desert steppe was significantly affected by drought, year and their interaction (Additional file 1: Table S3, Fig. 2a). The CWM of height in 2018 was significantly lower than that in 2015–2016 under manipulated drought (− 66% and − 60 Days) (p < 0.05; Fig. 2a). However, CWM of SLA, LDMC, and LNC were largely varied across years (Additional file 1: Table S3, Fig. 2b, c, e). CWM of SLA, and LNC increased following the year and reached their maximum in 2018 (Fig. 2b, e). In contrast, CWM of LDMC was decreased following the year and reached their minimum in 2018 (Fig. 2c). CWM of LCC had significant differences only under the manipulated drought of 60 days in 2015–2016 (Fig. 2d).
Effects of extreme drought (CONT, control; − 66%, reduce 66% in rainfall from May to August; − 60 Days, reduce 100% in rainfall from June to July) on plant community trait during the treatment years (2015–2018). SLA specific leaf area, LDMC leaf dry matter content, LCC leaf carbon content, LNC leaf nitrogen content. Variables are shown as mean ± SE (n = 6). Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between years for the same treatments in p < 0.05. Statistical significance of drought effect in each year is depicted as **p < 0.0 1 and *p < 0.05
Drought, year and their interaction had a significant influence on soil water content (p < 0.05, Additional file 1: Table S3, Fig. 3c). There were significant differences in soil water content between 2015 and 2016 and 2018 under different drought treatments (p < 0.05; Fig. 3c). The soil water content in 2015 and 2017 was significantly lower than that in 2016 and 2018 under CONT, while significantly higher in 2018 than that in 2015 under -66% and -60 Days drought treatment (p < 0.05; Fig. 3c). The soil carbon content and soil nitrogen content are only affected by years (p < 0.01, Additional file 1: Table S3, Fig. 3a, b). Under − 66% treatment, the soil carbon content in 2017 was significantly higher than that in 2015–2016 and 2018, and soil nitrogen content in 2015 was significantly higher than that in 2016–2018 (p < 0.05; Fig. 3a, b).
Effects of extreme drought (CONT, control; − 66%, reduce 66% in rainfall from May to August; − 60 Days, reduce 100% in rainfall from June to July) on soil characteristics during the treatment years (2015–2018). Soil Carbon, 0–20 cm soil carbon content; Soil Nitrogen, 0–20 cm soil nitrogen content; Soil Water, 0–20 cm soil water content. Variables are shown as mean ± SE (n = 6). Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between years for the same treatments in p < 0.05. Statistical significance of drought effect in each year is depicted as ** p < 0.0 1 and * p < 0.05
Across the four years, AGB was positive correlated with species diversity (species richness and density) (p < 0.001; Fig. 4a, b), CWM of plant height (p < 0.001; Fig. 4c) and soil water (p < 0.01; Fig. 5a). BGB was positive correlated with CWM of SLA (p < 0.001; Fig. 4d), LNC (p < 0.001; Fig. 4f), soil water (p < 0.01; Fig. 5b) and soil carbon (p < 0.01; Fig. 5c). However, we found significant negative relationships between BGB and CWM of LDMC (p < 0.001; Fig. 4e), plant height (p < 0.05; Fig. 4g) and soil nitrogen (p < 0.05; Fig. 5d).
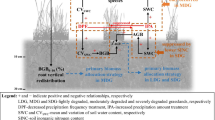
As mentioned above, the precipitation in the early growing season (March to June) and experimental drought combining the two treatments were selected as exogenous variables in the structural equation model (SEM). The SEM was performed to quantify the direct vs indirect effects of how drought, precipitation in the early growing season (March to June), soil factors and CWM of plant traits on AGB or BGB. The model including the drought, precipitation, species richness, plant height and soil N was the best fit (χ2 = 16.936, P = 0.110; RMSEA = 0.087; GFI = 0.943) to explain 60% variance of AGB and 56% variance of BGB (Fig. 6).
Structural equation modeling (SEM) depicting the effect paths of extreme drought treatments, precipitation in the early growing season (March to June), functional trait and soil properties on above- and belowground biomass. Square boxes indicate variables included in the model. Single headed arrows indicate paths. Numbers on path is the standardized regression weights. Total explained variance (R2) of biomass is on the right corner of boxes. Using the *, ** and*** to show the significance along the paths at the level of P < 0.05, P < 0.01and P < 0.001. Results of model fitting: \({\upchi }^{2}\)=16.936, P = 0.110, RMSEA = 0.087, GFI = 0.943
The SEM models showed that increasing precipitation in the early growing season directly increased AGB and indirectly increased AGB through its positive impact on plant height (Table 1). The increasing plant height directly increased AGB and BGB (Table 1). The drought had a negative direct impact on AGB, also, the indirect impact of drought on AGB was through its negative impact on species richness and plant height (Table 1). The increasing species richness directly increased AGB (Table 1). Increasing soil N content and precipitation in the early growing season directly decreased BGB (Table 1).
Discussion
The response of ecosystems to changing precipitation is driven in part by species diversity and plant community functional traits. Thus, elucidating the variation of species diversity and CWM of traits under drought is critically important for improving predictions of ecosystem responses to changing precipitation. In semiarid grasslands of northern China, water is the limiting constraint to ecosystem development [45]. Here, we conducted an extreme drought experiment of four years to determine how desert steppe ecosystem modify plant community in response to the drought.
Our findings demonstrated that the species diversity was sensitive to experimental drought. We found that experimental drought (− 66% and − 60 Days), compared with the control, significantly reduced species richness in 2016–2018 (Fig. 1). Experimental drought (− 66% and − 60 Days) changed biodiversity that can be explained by species turnover/re-ordering caused by the cumulative effect of extreme drought (Additional file 1: Table S4). Experimental drought can modify species either through shifts in genotypic abundance and phenotypic plasticity by acting as an environment filter [46, 47]. On a temporal scale, there was no significant difference in species richness under experimental drought, which is contrary to other findings that suggested that plant species richness is more sensitive to drought in the arid ecosystem [2, 46]. One possible explanation for this difference could be the low soil moisture caused by extreme drought reduced the number of reproductive buds in many species [48, 49].
The relationship between functional traits of plants reflects the adaptation strategies of plants to the environment [46]. Plants usually adopt combinations of functional traits to adapt to changing environments [50]. In this study, we found that CWM of traits had no response to experimental drought but had significant response to natural drought (Fig. 1), which might be attributed to changes in species composition (Additional file 1: Table S4). We observed CWM of SLA and LNC increased, while CWM of plant height and LDMC decreased year by year. Previous studies respectively showed that plant height was significantly positively correlated with LDMC [50, 51], SLA was significantly negatively correlated with LDMC [52, 53], and SLA was significantly positively correlated with LNC [54, 55]. Our results are consistent with previous studies that showed that plants adapted to drought by changing leaf morphology and nutrient distribution [56, 57]. Not surprisingly, drought treatment of − 66% directly decreased soil water content except in 2017 (Fig. 3c, Additional file 1: Table S2). We also found that soil carbon and nitrogen content were not altered by experimental drought (− 66% and − 60 Days) (Fig. 3a, b, Additional file 1: Table S2). This can be explained by that drought can reduce plant nutrient input and increase soil nutrient loss, but also reduce soil nutrient loss by inhibiting soil organic matter decomposition [58, 59]. Plant nutrient contents usually reflect soil nutrient availability [60], however, we do not observe a match between plant nutrient concentrations and soil nutrient supply which also have been reported by other findings [61, 62]. This mismatch may be due to the lower soil moisture content, which results in limited nutrient flow and nutrient uptake by plants [63, 64].
Our results indicated that the aboveground biomass was significantly reduced by experimental drought treatment every year, which has been shown in several studies [65, 66]. However, the significant increase in belowground biomass due to experimental drought (-66% and -60 Days) occurred only in 2017. This difference from the optimal distribution theory may be due to the extreme drought alters in root distribution rather than the total amount of root biomass [67, 68]. Meanwhile, our findings demonstrated that AGB tended to decrease year by year and belowground biomass to increase, which in agreement with previous findings that have shown consecutive precipitation treatments can cause cumulative influence on ecosystem productivity [68, 69]. The positive relationships between species diversity and AGB are consistent with the results of the positive linear relationship common in species diversity—biomass relationship models [70, 71]. Our results showed that AGB was positively correlated with plant height, while BGB was negatively correlated with LDMC and plant height and positively correlated with SLA and LNC. These results support the other findings that some traits are good predictors of ecosystem function [72, 73]. The SEM results showed that CWM of plant height controlled by experimental drought and precipitation in the early growing season (March to June) exerted a direct effect on AGB. This is consistent with the CWM of traits determine the ecosystem function, which supports the mass ratio hypothesis [74, 75]. And it also proves that plant height is an important and comprehensive trait to reflect the ability of plants to adapt to changes in the environment [76]. Not surprisingly, drought and rainfall in March-June had direct impacts on AGB, confirming that in the previous findings [77, 78]. Our findings were consistent with others that precipitation and soil N had direct effects on belowground biomass [79]. These results suggest that precipitation in the early growing season has an important effect on plant biomass.
Conclusion
This study showed that natural drought of early time in growing season can reduce the aboveground biomass and increased the belowground biomass, suggesting that the rainfall of early time in growing season plays an important role in maintaining ecosystem structure and function in desert steppe. Community-level plant height is an important predictor for AGB in desert steppe. Plant investment in the root system is a strategy for plants to adapt to soil nutrient reduction and drought of the early time in growing season, which provides deep insight into the mechanism of the above- and belowground biomass allocation of plants.
Methods
Experimental site
This study was conducted in the Urat Desert‐grassland Ecosystem Research Station (106° 58′ E, 41° 25′ N, 1,650 m above sea level) located in western Inner Mongolia, China. The region has a temperate continental monsoon climate, and the mean annual precipitation is 139.5 mm, about 70% occurring during the growing season [80]. The main soil type in the study area is brown calcium, and the dominant species in the desert steppe are Stipa glareosa, Peganum harmala, and Allium polyrhizum (Additional file 1: Table S4).
Experimental treatments
The extreme drought experiment was established in 2014 and was conducted from 2015 to 2018. This experiment involved three treatments: (1) a control (ambient precipitation, without shelters), (2) a − 66% drought treatment (66% reduction from May 1 to August 31, with shelters), (3) and a − 60 Days drought treatment (100% reduction from June 1 to July 31, with shelters). There are eighteen 6 × 6 m plots in total, which are randomly distributed in location and organized into six blocks. Each plot was located at least 2 m from the nearest neighboring plot and established a 1-m external buffer to minimize the edge effects. To prevent hydrological exchange with the surrounding soil, a 1 m deep sheet of plastic flashing was established in each plot. The roofs consisted of strips of clear polycarbonate plastic was situated 2 m above the ground at the highest point, which allowed for the circulation of air and avoided microclimatic changes. Polycarbonate plastic has been confirmed to have minimal influence on photosynthetically active radiation [81].
Sampling and analysis
During the peak of each growing season from 2015 to 2018, a quadrat (1 × 1 m) was set up in each experimental plot for vegetation investigation and sampling. Quadrat was marked to prevent subsequent resampling in the next year. We measured the maximum height of each species and recorded species richness (the number of plant species) in each quadrat. The density was defined as the number of plants per square meter. Besides, we harvested all aboveground biomass (AGB) by species in each quadrat. Finally, we estimated belowground biomass (BGB) using a root auger (8 cm diameter) to measure root mass at a depth of 0–20 cm. The roots samples were taken back to the laboratory and then were washed free of soil over a mesh sieve (mesh size of 0.25 mm). All above- and belowground biomasses were dried at 65 °C in an oven for 48 h and weighed in the lab.
We determined five key functional traits to reflect the plant morphology and growth investment [82, 83]: plant height, specific leaf area (SLA), leaf dry matter content (LDMC), leaf carbon content (LCC), and leaf nitrogen content (LNC). These traits were measured for the dominant species making up 90% of the total plant cover in each plot. The five traits on 10 individuals per species in each plot were obtained by using the standard methodologies [84]. We calculated community-weighted means (CWM) of single-trait by multiplying the trait value of each species by its relative biomass in the community [85]. CWM can reflect the characteristics of community functional traits [86]. In each plot, three soil samples (0–10 cm depth) were collected to determine soil water, and one mixed soil sample from three random replicates was collected to measure soil organic carbon and total nitrogen content. Leaf carbon and nitrogen content (%), as well as soil organic carbon and total nitrogen content (g Kg−1), were measured by using an Elemental Analyzer [36] (Costech ECS 4010, Italy) with a reduction temperature of 650 °C and a combustion temperature of 980 °C.
Data analysis
We analyzed the response of each variable to extreme drought using separate repeated measures mixed model ANOVAs with year, treatment, and their interaction as fixed factor and block as a random factor (Additional file 1: Table S3). One-way ANOVA was conducted to assess the significant differences of species richness, Density, AGB, BGB, CWM of Height, CWM of SLA, CWM of LDMC, CWM of LCC, CWM of LNC, Soil Carbon, Soil Nitrogen, and Soil Water over to extreme drought among years. A level of P < 0.05 was considered significant. Data are presented as mean ± standard error throughout.
Then, the simple regression models with a standard 95% confidence range were used to assess whether CWM of traits and soil factors could explain AGB and BGB. We constructed a priori model (Additional file 1: Figure S2) based on the simple regression and the correlation coefficients of each variable (Additional file 1: Table S5). Drought treatment and the precipitation in the early time were treated as exogenous variables; species diversity, CWM of trait, and soil factors were considered as endogenous variables; AGB and BGB were regarded as the response variable. We assessed the best fitting model using a Chi-square test, root mean square error of approximation, and goodness-of-fit index [32], which was performed by AMOS 20.0 (Amos Development, Spring House, PA, USA). We eliminated the non-significant state variables and pathways by estimating regression weight estimates to simplify the initial model and finally obtained the final model containing the pathways that we failed to reject.
Data analysis and plotting were run with the SPSS16.0 and SigmaPlot12.0 for Windows statistics program, respectively. The simple regression models were performed using the trendline function in the basic Trendline package of R software (v4.0.0, R Core Team, 2020).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AGB:
-
Aboveground biomass
- BGB:
-
Belowground biomass
- CWM:
-
Community-weighted means
- SLA:
-
Specific leaf area
- LDMC:
-
Leaf dry matter content
- LCC:
-
Leaf carbon content
- LNC:
-
Leaf nitrogen content
- Soil N:
-
Soil nitrogen content
References
Churkina G, Running SW. Contrasting climatic controls on the estimated productivity of global terrestrial biomes. Ecosystems. 1998;1(2):206–15.
Cleland EE, Collins SL, Dickson TL, Farrer EC, Gross KL, Gherardi LA, Hallett LM, Hobbs RJ, Hsu JS, Turnbull L, et al. Sensitivity of grassland plant community composition to spatial vs. temporal variation in precipitation. Ecology. 2013;94(8):1687–96.
Easterling DR, Meehl GA, Parmesan C, Changnon SA, Karl TR, Mearns LO. Climate extremes: observations, modeling, and impacts. Science. 2000;289(5487):2068–74.
Smith MD. An ecological perspective on extreme climatic events: a synthetic definition and framework to guide future research. J Ecol. 2011;99(3):656–63.
Knapp AK, Hoover DL, Wilcox KR, Avolio ML, Koerner SE, La Pierre KJ, Loik ME, Luo YQ, Sala OE, Smith MD. Characterizing differences in precipitation regimes of extreme wet and dry years: implications for climate change experiments. Global Change Biol. 2015;21(7):2624–33.
Copeland SM, On SPH, Latimer AM, Damschen EI, Eskelinen AM, Fernandez-Going B, Spasojevic MJ, Anacker BL, Thorne JH. Ecological effects of extreme drought on Californian herbaceous plant communities. Ecol Monogr. 2016;86(3):295–311.
Huxman TE, Smith MD, Fay PA, Knapp AK, Shaw MR, Loik ME, Smith SD, Tissue DT, Zak JC, Weltzin JF, et al. Convergence across biomes to a common rain-use efficiency. Nature. 2004;429(6992):651–4.
McConnaughay KDM, Coleman JS. Biomass allocation in plants: Ontogeny or optimality? A test along three resource gradients. Ecology. 1999;80(8):2581–93.
Frank DA. Drought effects on above- and belowground production of a grazed temperate grassland ecosystem. Oecologia. 2007;152(1):131–9.
Kreyling J, Beierkuhnlein C, Elmer M, Pritsch K, Radovski M, Schloter M, Wollecke J, Jentsch A. Soil biotic processes remain remarkably stable after 100-year extreme weather events in experimental grassland and heath. Plant Soil. 2008;308(1–2):175–88.
Harrison S, Spasojevic MJ, Li D. Climate and plant community diversity in space and time. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(9):4464–70.
Griffin-Nolan RJ, Bushey JA, Carroll CJW, Challis A, Chieppa J, Garbowski M, Hoffman AM, Post AK, Slette IJ, Spitzer D, et al. Trait selection and community weighting are key to understanding ecosystem responses to changing precipitation regimes. Funct Ecol. 2018;32(7):1746–56.
Wu GL, Zhang ZN, Wang D, Shi ZH, Zhu YJ. Interactions of soil water content heterogeneity and species diversity patterns in semi-arid steppes on the Loess Plateau of China. J Hydrol. 2014;519:1362–7.
Yin QL, Tian TT, Han XH, Xu JS, Chai YF, Mo J, Lei ML, Wang L, Yue M. The relationships between biomass allocation and plant functional trait. Ecol Indic. 2019;102:302–8.
Schaeffer SM, Homyak PM, Boot CM, Roux-Michollet D, Schimel JP. Soil carbon and nitrogen dynamics throughout the summer drought in a California annual grassland. Soil Biol Biochem. 2017;115:54–62.
Knapp AK, Smith MD. Variation among biomes in temporal dynamics of aboveground primary production. Science. 2001;291(5503):481–4.
Bradford JB, Schlaepfer DR, Lauenroth WK, Palmquist KA. Robust ecological drought projections for drylands in the 21st century. Global Change Biol. 2020;26(7):3906–19.
Knapp AK, Fay PA, Blair JM, Collins SL, Smith MD, Carlisle JD, Harper CW, Danner BT, Lett MS, McCarron JK. Rainfall variability, carbon cycling, and plant species diversity in a mesic grassland. Science. 2002;298(5601):2202–5.
Felton AJ, Slette IJ, Smith MD, Knapp AK. Precipitation amount and event size interact to reduce ecosystem functioning during dry years in a mesic grassland. Global Change Biol. 2020;26(2):658–68.
Harrison S, Spasojevic MJ, Li DJ. Climate and plant community diversity in space and time. P Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020;117(9):4464–70.
Chen YX, Huang YY, Niklaus PA, Castro-Izaguirre N, Clark AT, Bruelheide H, Ma KP, Schmid B. Directed species loss reduces community productivity in a subtropical forest biodiversity experiment. Nat Ecol Evol. 2020;4(4):660–660.
Grace JB, Anderson TM, Seabloom EW, Borer ET, Adler PB, Harpole WS, Hautier Y, Hillebrand H, Lind EM, Partel M, et al. Integrative modelling reveals mechanisms linking productivity and plant species richness. Nature. 2016;529(7586):390.
Rabosky DL, Hurlbert AH. Species richness at continental scales is dominated by ecological limits. Am Nat. 2015;185(5):572–83.
Li Y, Dong S, Liu S, Su X, Wang X, Zhang Y, Zhao Z, Gao X, Li S, Tang L. Relationships between plant diversity and biomass production of alpine grasslands are dependent on the spatial scale and the dimension of biodiversity. Ecol Eng. 2019;127:375–82.
Gastine A, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Leadley PW. No consistent effects of plant diversity on root biomass, soil biota and soil abiotic conditions in temperate grassland communities. Appl Soil Ecol. 2003;24(1):101–11.
Tilman D, Reich PB, Knops J, Wedin D, Mielke T, Lehman C. Diversity and productivity in a long-term grassland experiment. Science. 2001;294(5543):843–5.
Craine JM, Reich PB, Tilman GD, Ellsworth D, Fargione J, Knops J, Naeem S. The role of plant species in biomass production and response to elevated CO2 and N. Ecol Lett. 2003;6(7):623–30.
Wu GL, Liu Y, Tian FP, Shi ZH. Legumes functional group promotes soil organic carbon and nitrogen storage by increasing plant diversity. Land Degrad Dev. 2017;28(4):1336–44.
Kimball S, Funk JL, Spasojevic MJ, Suding KN, Parker S, Goulden ML. Can functional traits predict plant community response to global change? Ecosphere. 2016;7:12.
Costa DS, Gerschlauer F, Pabst H, Kuhnel A, Huwe B, Kiese R, Kuzyakov Y, Kleyer M. Community-weighted means and functional dispersion of plant functional traits along environmental gradients on Mount Kilimanjaro. J Veg Sci. 2017;28(4):684–95.
Bruelheide H, Dengler J, Purschke O, Lenoir J, Jimenez-Alfaro B, Hennekens SM, Botta-Dukat Z, Chytry M, Field R, Jansen F, et al. Global trait-environment relationships of plant communities. Nat Ecol Evol. 2018;2(12):1906–17.
Zuo XA, Zhang J, Lv P, Zhou X, Li YL, Luo YY, Luo YQ, Lian J, Yue XY. Plant functional diversity mediates the effects of vegetation and soil properties on community-level plant nitrogen use in the restoration of semiarid sandy grassland. Ecol Indic. 2016;64:272–80.
Sandel B, Goldstein LJ, Kraft NJ, Okie JG, Shuldman MI, Ackerly DD, Cleland EE, Suding KN. Contrasting trait responses in plant communities to experimental and geographic variation in precipitation. New Phytol. 2010;188(2):565–75.
Le Bagousse-Pinguet Y, Gross N, Maestre FT, Maire V, de Bello F, Fonseca CR, Kattge J, Valencia E, Leps J, Liancourt P. Testing the environmental filtering concept in global drylands. J Ecol. 2017;105(4):1058–69.
Forrestel EJ, Donoghue MJ, Edwards EJ, Jetz W, du Toit JCO, Smith MD. Different clades and traits yield similar grassland functional responses. P Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017;114(4):705–10.
Yue XY, Zuo XA, Yu Q, Xu C, Lv P, Zhang J, Knapp AK, Smith MD. Response of plant functional traits of Leymus chinensis to extreme drought in Inner Mongolia grasslands. Plant Ecol. 2019;220(2):141–9.
Kobe RK, Iyer M, Walters MB. Optimal partitioning theory revisited: nonstructural carbohydrates dominate root mass responses to nitrogen. Ecology. 2010;91(1):166–79.
van Wijk MT. Understanding plant rooting patterns in semi-arid systems: an integrated model analysis of climate, soil type and plant biomass. Global Ecol Biogeogr. 2011;20(2):331–42.
Beier C, Beierkuhnlein C, Wohlgemuth T, Penuelas J, Emmett B, Korner C, de Boeck HJ, Christensen JH, Leuzinger S, Janssens IA, et al. Precipitation manipulation experiments—challenges and recommendations for the future. Ecol Lett. 2012;15(8):899–911.
Sardans J, Penuelas J. Potassium: a neglected nutrient in global change. Global Ecol Biogeogr. 2015;24(3):261–75.
He MZ, Dijkstra FA. Drought effect on plant nitrogen and phosphorus: a metaanalysis. New Phytol. 2014;204(4):924–31.
Gessler A, Schaub M, McDowell NG. The role of nutrients in drought-induced tree mortality and recovery. New Phytol. 2017;214(2):513–20.
Griffin-Nolan RJ, Carroll CJW, Denton EM, Johnston MK, Collins SL, Smith MD, Knapp AK. Legacy effects of a regional drought on aboveground net primary production in six central US grasslands. Plant Ecol. 2018;219(5):505–15.
Grime JP, Brown VK, Thompson K, Masters GJ, Hillier SH, Clarke IP, Askew AP, Corker D, Kielty JP. The response of two contrasting limestone grasslands to simulated climate change. Science. 2000;289(5480):762–5.
Bai YF, Wu JG, Xing Q, Pan QM, Huang JH, Yang DL, Han XG. Primary production and rain use efficiency across a precipitation gradient on the Mongolia plateau. Ecology. 2008;89(8):2140–53.
Luo WT, Zuo XA, Griffin-Nolan RJ, Xu C, Ma W, Song L, Helsen K, Lin YC, Cai JP, Yu Q, et al. Long term experimental drought alters community plant trait variation, not trait means, across three semiarid grasslands. Plant Soil. 2019;442(1–2):343–53.
Cornwell WK, Ackerly DD. Community assembly and shifts in plant trait distributions across an environmental gradient in coastal California. Ecol Monogr. 2009;79(1):109–26.
Stampfli A, Zeiter M. Mechanisms of structural change derived from patterns of seedling emergence and mortality in a semi-natural meadow. J Veg Sci. 2008;19(4):563-U516.
Zeiter M, Scharrer S, Zweifel R, Newbery DM, Stampfli A. Timing of extreme drought modifies reproductive output in semi-natural grassland. J Veg Sci. 2016;27(2):238–48.
Muscarella R, Uriarte M. Do community-weighted mean functional traits reflect optimal strategies? Proc Biol Sci. 1827;2016(283):20152434.
Mudrak O, de Bello F, Dolezal J, Leps J. Changes in the functional trait composition and diversity of meadow communities induced by Rhinanthus minor L. Folia Geobot. 2016;51(1):1–11.
Al Haj Khaled R, Duru M, Theau JP, Plantureux S, Cruz P. Variation in leaf traits through seasons and N-availability levels and its consequences for ranking grassland species. J Veg Sci. 2005;16(4):391–8.
Li YL, Johnson DA, Su YZ, Cui JY, Zhang TH. Specific leaf area and leaf dry matter content of plants growing in sand dunes. Bot Bull Acad Sinica. 2005;46(2):127–34.
He JS, Wang ZH, Wang XP, Schmid B, Zuo WY, Zhou M, Zheng CY, Wang MF, Fang JY. A test of the generality of leaf trait relationships on the Tibetan Plateau. New Phytol. 2006;170(4):835–48.
Wright IJ, Reich PB, Westoby M. Strategy shifts in leaf physiology, structure and nutrient content between species of high- and low-rainfall and high- and low-nutrient habitats. Funct Ecol. 2001;15(4):423–34.
Deleglise C, Meisser M, Mosimann E, Spiegelberger T, Signarbieux C, Jeangros B, Buttler A. Drought-induced shifts in plants traits, yields and nutritive value under realistic grazing and mowing managements in a mountain grassland. Agr Ecosyst Environ. 2015;213:94–104.
Jung V, Albert CH, Violle C, Kunstler G, Loucougaray G, Spiegelberger T. Intraspecific trait variability mediates the response of subalpine grassland communities to extreme drought events. J Ecol. 2014;102(1):45–53.
Ren CJ, Zhao FZ, Shi Z, Chen J, Han XH, Yang GH, Feng YZ, Ren GX. Differential responses of soil microbial biomass and carbon-degrading enzyme activities to altered precipitation. Soil Biol Biochem. 2017;115:1–10.
Deng L, Peng CH, Kim DG, Li JW, Liu YL, Hai XY, Liu QY, Huang CB, Shangguan ZP, Kuzyakov Y. Drought effects on soil carbon and nitrogen dynamics in global natural ecosystems. Earth-Sci Rev. 2021;214:25.
Reich PB, Oleksyn J. Global patterns of plant leaf N and P in relation to temperature and latitude. P Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101(30):11001–6.
Luo W, Elser JJ, Lü XT, Wang Z, Bai E, Yan C, Wang C, Li MH, Zimmermann NE, Han X, et al. Plant nutrients do not covary with soil nutrients under changing climatic conditions. Global Biogeochem Cycles. 2015;29(8):1298–308.
de la Riva EG, Perez-Ramos IM, Tosto A, Navarro-Fernandez CM, Olmo M, Maranon T, Villar R. Disentangling the relative importance of species occurrence, abundance and intraspecific variability in community assembly: a trait-based approach at the whole-plant level in Mediterranean forests. Oikos. 2016;125(3):354–63.
Luo W, Zuo X, Ma W, Xu C, Li A, Yu Q, Knapp AK, Tognetti R, Dijkstra FA, Li MH, et al. Differential responses of canopy nutrients to experimental drought along a natural aridity gradient. Ecology. 2018;99(10):2230–9.
He M, Dijkstra FA. Drought effect on plant nitrogen and phosphorus: a meta-analysis. New Phytol. 2014;204(4):924–31.
Zhang BW, Cadotte MW, Chen SP, Tan XR, You CH, Ren TT, Chen ML, Wang SS, Li WJ, Chu CJ, et al. Plants alter their vertical root distribution rather than biomass allocation in response to changing precipitation. Ecology. 2019;100:11.
Bai YF, Han XG, Wu JG, Chen ZZ, Li LH. Ecosystem stability and compensatory effects in the Inner Mongolia grassland. Nature. 2004;431(7005):181–4.
Ansley RJ, Boutton TW, Jacoby PW. Root biomass and distribution patterns in a semi-arid mesquite savanna: responses to long-term rainfall manipulation. Rangeland Ecol Manag. 2014;67(2):206–18.
Zhang B, Cadotte MW, Chen S, Tan X, You C, Ren T, Chen M, Wang S, Li W, Chu C, et al. Plants alter their vertical root distribution rather than biomass allocation in response to changing precipitation. Ecology. 2019;100(11):e02828.
Sala OE, Gherardi LA, Reichmann L, Jobbagy E, Peters D. Legacies of precipitation fluctuations on primary production: theory and data synthesis. Philos T R Soc B. 2012;367(1606):3135–44.
Bai Y, Wu J, Pan Q, Huang J, Wang Q, Li F, Buyantuyev A, Han X. Positive linear relationship between productivity and diversity: evidence from the Eurasian Steppe. J Appl Ecol. 2007;44(5):1023–34.
Bhandari J, Zhang Y. Effect of altitude and soil properties on biomass and plant richness in the grasslands of Tibet, China, and Manang District. Nepal Ecosphere. 2019;10:788.
Schumacher J, Roscher C. Differential effects of functional traits on aboveground biomass in semi-natural grasslands. Oikos. 2009;118(11):1659–68.
Zuo XA, Zhang J, Lv P, Wang SK, Yang Y, Yue XY, Zhou X, Li YL, Chen M, Lian J, et al. Effects of plant functional diversity induced by grazing and soil properties on above- and belowground biomass in a semiarid grassland. Ecol Indic. 2018;93:555–61.
Lavorel S. Plant functional effects on ecosystem services. J Ecol. 2013;101(1):4–8.
Zhang Q, Buyantuev A, Li FY, Jiang L, Niu JM, Ding Y, Kang S, Ma WJ. Functional dominance rather than taxonomic diversity and functional diversity mainly affects community aboveground biomass in the Inner Mongolia grassland. Ecol Evol. 2017;7(5):1605–15.
Shi Y, Su C, Wang M, Liu X, Liang C, Zhao L, Zhang X, Minggagud H, Feng G, Ma W. Modern climate and soil properties explain functional structure better than phylogenetic structure of plant communities in Northern China. Front Ecol Evol. 2020;8:24.
Shi Z, Thomey ML, Mowll W, Litvak M, Brunsell NA, Collins SL, Pockman WT, Smith MD, Knapp AK, Luo Y. Differential effects of extreme drought on production and respiration: synthesis and modeling analysis. Biogeosciences. 2014;11(3):621–33.
Denton EM, Dietrich JD, Smith MD, Knapp AK. Drought timing differentially affects above- and belowground productivity in a mesic grassland. Plant Ecol. 2017;218(3):317–28.
Zheng SX, Ren HY, Lan ZC, Li WH, Wang KB, Bai YF. Effects of grazing on leaf traits and ecosystem functioning in Inner Mongolia grasslands: scaling from species to community. Biogeosciences. 2010;7(3):1117–32.
Liu LX, Zhao XY, Chang XL, Lian J. Impact of Precipitation Fluctuation on Desert-Grassland ANPP. Sust Basel. 2016;8:12.
Yahdjian L, Sala OE. A rainout shelter design for intercepting different amounts of rainfall. Oecologia. 2002;133(2):95–101.
Valencia E, Maestre FT, Le Bagousse-Pinguet Y, Quero JL, Tamme R, Borger L, Garcia-Gomez M, Gross N. Functional diversity enhances the resistance of ecosystem multifunctionality to aridity in Mediterranean drylands. New Phytol. 2015;206(2):660–71.
Guittar J, Goldberg D, Klanderud K, Telford RJ, Vandvik V. Can trait patterns along gradients predict plant community responses to climate change? Ecology. 2016;97(10):2791–801.
Cornelissen JHC, Lavorel S, Garnier E, Diaz S, Buchmann N, Gurvich DE, Reich PB, ter Steege H, Morgan HD, van der Heijden MGA, et al. A handbook of protocols for standardised and easy measurement of plant functional traits worldwide. Aust J Bot. 2003;51(4):335–80.
Kichenin E, Wardle DA, Peltzer DA, Morse CW, Freschet GT. Contrasting effects of plant inter- and intraspecific variation on community-level trait measures along an environmental gradient. Funct Ecol. 2013;27(5):1254–61.
Debouk H, de Bello F, Sebastia MT. Functional trait changes, productivity shifts and vegetation stability in mountain grasslands during a short-term warming. Plos One. 2015;10:10.
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to Dr. Julio Di Rienzo for the support of FDiversity software.
Funding
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (42071140 and 41622103), the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research program (2019QZKK0305) and Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (1100000036). Aside from providing funds, funders played no role in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XZ and QY designed this experiment; PY, YH, XG, AG, and CX contributed significantly to analysis and manuscript preparation; XL performed the data analyses and wrote the manuscript; XZ, PY, and XZ helped perform the analysis with constructive discussions. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The research was performed in accordance with Chinese Law and international guidelines.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1.
Additional figures and tables.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Zuo, X., Yue, P. et al. Drought of early time in growing season decreases community aboveground biomass, but increases belowground biomass in a desert steppe. BMC Ecol Evo 21, 106 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-021-01842-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-021-01842-5