Abstract
Background
In total hip arthroplasty, inadequate femoral component positioning can be associated with instability, impingement and component wear and subsequently with patient dissatisfaction. In this study, we investigated the influence of femoral neck resection height on the final three-dimensional position of a collarless straight tapered stem (Corail®). We asked two questions—(1) is neck resection height correlated with version, tilt, and varus/valgus alignment of the femoral component, and (2) dependent on the resection height of the femoral neck, which area of the stem comes into contact with the femoral cortical bone?
Materials and methods
Three-dimensional computed tomography scans of 40 patients who underwent minimally invasive, cementless total hip arthroplasty were analyzed retrospectively. We analyzed the relationship between femoral neck resection height and three-dimensional alignment of the femoral implant, as well as the contact points of the implant with the femoral cortical bone. This investigation was approved by the local Ethics Commission (No.10-121-0263) and is a secondary analysis of a larger project (DRKS00000739, German Clinical Trials Register May-02-2011).
Results
Mean femoral neck resection height was 10.4 mm (± 4.8) (range 0–20.1 mm). Mean stem version was 8.7° (± 7.4) (range − 2° to 27.9°). Most patients had a varus alignment of the implant. The mean varus/valgus alignment was 1.5° (± 1.8). All 40 patients (100%) had anterior tilt of the implant with a mean tilt of 2.2° (± 1.6). Femoral neck resection height did not correlate with stem version, varus/valgus alignment, or tilt. Independent from femoral neck resection height, in most patients the implant had contact with the ventral and ventromedial cortical bone in the upper third (77.5%) and the middle third (52.5%). In the lower third, the majority of the implants had contact with the lateral and dorsolateral cortical bone (92.5%).
Conclusion
Femoral neck resection height ranging between 0 and 20.1 mm does not correlate with the final position of a collarless straight tapered stem design (Corail®).
Level of evidence
Level 3.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Introduction
Primary total hip arthroplasty (THA) is one of the most common and successful orthopedic operations worldwide [1]. However, malpositioning of the components is associated with an increased risk of complications, such as impingement, dislocation, pelvic osteolysis and wear, and thus early revision [2, 3]. The final position of the cup may be assessed in several ways. To date, most orthopedic surgeons rely on intraoperatively visible or palpable anatomic landmarks and aim at positioning the cup with the naked eye [4] or, alternatively, with intraoperative alignment guides [3] or recently developed computer-assisted methods [5].
According to the concept of combined anteversion, several authors have suggested first preparing the femur (‘femur first’) and then adjusting the position of the cup in accordance with femoral rotation.
The crucial point in cement-free THA seems to be positioning the femoral component. When using a common straight tapered implant, surgeons have little control about its final position. The stem follows the flexion and twist of the proximal femoral channel, ending in the ‘best-fitting’ position [6]. This final position of the stem can be viewed in three different planes. The first plane is stem version. Different studies have reported high variations in postoperative cement-free stem anteversion ranging between − 19° retroversion and up to 52° anteversion [7, 8]. The second aspect is varus/valgus alignment in the coronal plane, and the third aspect is the tilt of the component in the sagittal plane. A recent study showed that there is no correlation between native femoral version and the version of the stem implant after cement-free THA. It also showed that there seems to be no correlation between the resection height of the femoral neck and the final version of the stem implant [9]. Based on these results, we now investigated the influence of the resection height of the femoral neck on the final three-dimensional (3D) position of the femoral component in cement-free THA. To our knowledge, no study has yet analyzed the final 3D position of the femoral component and its association with the resection height of the femoral neck. In the present study, we asked two questions—(1) is neck resection height correlated with version, tilt, and varus/valgus alignment of the femoral component, and (2) dependent on the resection height of the femoral neck, which area of the stem comes into contact with the femoral cortical bone?
Materials and methods
This study is a retrospective analysis of data obtained in a registered, prospective controlled trial (DRKS00000739, German Clinical Trials Register). The primary outcome of this larger study was to assess whether the range of motion of the prosthetic joint could be improved by computer-assisted functional optimization of position and containment of the acetabular component. The inclusion criteria were age between 50 and 75 years, an American Society of Anaesthesiologists (ASA) score ≤ 3, unilateral osteoarthritis of the hip (up to Kellgren 2 of the contralateral side), no prior hip surgery, and no hip dysplasia or trauma. Postoperative 3D computer tomography (CD) scans including the femoral condyles as well as pelvic radiographs were available for the study group.
All operations were carried out in the lateral decubitus position using the minimally invasive modified Smith-Petersen approach [10]. Press-fit cups (Pinnacle; DePuy, Warsaw, IN, USA) and cement-free hydroxyapatite-coated stems (Corail®; DePuy) were used. Preoperative planning was performed by using a common planning program for endoprosthesis (mediCAD; Hectec GmbH, Altdorf, Germany). Stem size was confirmed by intra- and postoperative X-rays. No obvious undersizing was detected. The Corail® stem is a straight tapered cement-free stem filling the metaphysis and proximal diaphysis in the mediolateral plane. Although the position of the femoral component is dictated in part by the native femoral neck anteversion, the final position of the ‘best-fit’ stem is a compromise of fitting the straight stem down the canal of the femur and addressing the flexion and twist of the proximal femur. The extent to which anteversion of the final implant may be influenced by the surgeon [6, 7] is yet unclear. Tribological pairing consisted of polyethylene liners and metal heads with a diameter of 32 mm. Six weeks after surgery, a CT scan was obtained from the pelvis down to the femoral condyles (Somatom Sensation 16; Siemens, Erlangen, Germany). This investigation was approved by the local Ethics Committee (No. 10-121-0263). All procedures were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2000.
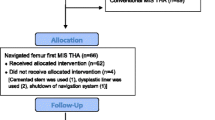
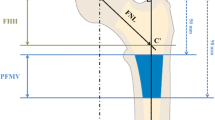
For the current study, due to the complex measurement protocol, 3D CT scans of 40 patients (19 women, 21 men) were chosen randomly from the anonymized whole study collective by an independent observer, analyzed and finally deanonymized (Fig. 1). Characteristics of the study group are shown in Table 1. Femoral neck resection height was defined as the distance between the deepest point of the resection line and the proximal basis of the lesser trochanter (Fig. 2). Resection height and the angle of the femoral component relating to the femoral axis in the sagittal and the coronal plane were measured with the ‘semi-automatical’ function of a newly developed digital planning software for CT scans (Modicas, Erlangen, Germany) (Figs. 3, 4). This software offers the possibility to assess hips in three dimensions, to exactly determine the axes, and to automatically calculate angles. The alignment of the implant in relation to the femoral shaft axis in the coronal plane was defined as varus/valgus deviation (Fig. 3).
The alignment of the implant in relation to the femoral shaft axis in the sagital plane was defined as tilt (Fig. 4).
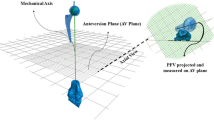
In addition, 3D CT assessment of the prosthetic stem version was obtained by an independent, blinded external institute (MeVis Medical Solutions, Bremen, Germany) as described by Sendtner et al. [7]. For assessing the contact points between implant and femoral cortical bone, the stem was virtually subdivided into three parts—the proximal, middle, and distal third. In the axial, coronal, and sagittal plane, we analyzed which third of the stem came into contact with the anterior, posterior, medial, or lateral part of the femoral cortical bone (Fig. 5).
The screenshot of the used software shows the contact points of the implant with the femoral cortical bone. In this example, the implant has contact with the ventral cortical bone in the upper and middle third and with the dorsolateral cortical bone in the lower third. 1 = ventral, 2 = lateral, 3 = dorsal, 4 = medial
All radiological measurements were carried out by one of the authors (MW) who was familiar with the software.
Statistical methods
The influence of height and alignment of the implant on femoral neck resection was analyzed using simple linear regression models. Differences in neck resection height regarding the position of the implant in relation to the femoral cortical bone were analyzed with analyses of variance (ANOVA). A p value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All analyses were carried out with R 3.3.1 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria).
Results
Femoral neck resection height and alignment of the implant
Mean neck resection height was 10.4 mm (± 4.8), ranging from 0 to 20.1 mm. Mean stem version was 8.7° (± 7.4), ranging from − 2° to 27.9° (Fig. 6).
Thirty-seven patients (92.5%) had varus alignment of the implant, while only three patients (7.5%) had valgus alignment. The mean varus/valgus alignment was 1.5° (± 1.8); positive values represented varus alignment, negative values valgus alignment (Fig. 7). All 40 patients (100%) showed anterior tilt of the implant with a mean tilt of 2.2° (± 1.6) (Fig. 8).
Femoral neck resection height was not correlated with stem version, varus/valgus alignment, or tilt. Slope (95% coefficient interval; CI), coefficient of determination, and p values of the linear regression models are shown in Table 2.
Femoral neck resection height and position of the implant in relation to the femoral cortical bone
Upper third of the implant
In 20 patients (50%), the implant came into contact with the ventral cortical bone, in 11 patients (27.5%) with the ventromedial cortical bone, in four patients (10%) with the medial cortical bone, and in one patient (2.5%) with the dorsal, ventrolateral, or dorsomedial cortical bone. Two patients did not show any contact with the upper third of the implant. No significant differences (ANOVA, p = 0.179) were found when comparing the resection height of patients with contact with the ventral cortical bone (11.4 ± 4.8) to that of patients with contact to the ventromedial cortical bone (7.9 ± 5.0) and medial cortical bone (10.0 ± 5.0).
Middle third of the implant
In 16 patients (40%), the implant came into contact with the ventral cortical bone, in five patients (12.5%) with the ventromedial cortical bone, in four patients (10%) with the ventrolateral cortical bone, in three patients (7.5%) with the medial cortical bone, in six patients (15%) with the lateral cortical bone, and in one patient (2.5%) with the medial and lateral cortical bone. Five patients did not show any contact with the middle third of the implant. No significant difference in resection height was found between the contact areas (ANOVA, p = 0.449).
Lower third of the implant
In 28 patients (70%), the implant came into contact with the dorsolateral cortical bone, in nine patients (22.5%) with the lateral cortical bone, in two patients (5%) with the ventral cortical bone, and in one patient (2.5%) with the dorsal, lateral, and medial cortical bone. No difference in resection height was found between the contact areas in the lower third of the implant (ANOVA, p = 0.862).
Discussion
In answer to the first question posed by this study, we showed that the final position of the stem we used in this clinical trial is not related with the resection height of the femoral neck. We did not find any clinically relevant correlation between neck resection height and version, tilt, or varus/valgus alignment of this commonly used cement-free, hydroxyapatite-coated, straight tapered femoral stem. We therefore concluded that orthopedic surgeons have only little control about the final position of the stem when using this special straight tapered implant in THA. Subsequently, intraoperative measurement of the femoral stem version is crucial for surgeons aiming for optimized combined anteversion of the cup and stem.
This fact leads directly to our second question. We did not find any correlation between femoral neck resection height and the area of the stem we used in our study coming into contact with the femoral cortical bone. Independent of neck resection height, the majority of implants come into contact with the metaphyseal area (upper third) of the ventral and/or medial cortical bone. Furthermore, most implants come into contact with the middle and distal third of the dorsolateral or only the lateral cortical bone.
Our study has several limitations. First, we used the single cement-free stem from only one manufacturer. The Corail® stem is a clinically successful implant made of forged titanium alloy (TiAl6V4) [11, 12]. The implant is straight with a quadrangular cross-section. The proximal part is flared in the sagittal and coronal plane to provide 3D stabilization in the metaphyseal area. Therefore, our findings may not be transferable to other stem designs, such as wedge-hip-stems that provide stabilization in the diaphyseal area. Second, we used a minimally invasive anterolateral approach with the patient in the lateral decubitus position. Theoretically, the surgical approach (anterior, antero-lateral, lateral, or dorsal) may have an impact on final stem anteversion, as shown by Bernasek et al. who found a higher prevalence of varus stem outlier in a minimally invasive modified Watson-Jones approach compared to a lateral approach [13].
Third, the mean resection height in our study collective was 10.4 mm (± 4.8), which was the goal of our surgical team. Higher or deeper osteotomy may cause deviations in femoral component rotation and should be considered in subsequent studies. Fourth, the individual anatomy of the femoral neck, shaft and medullary canal can vary, so femoral neck resection height sometimes needs to be adapted.
A wide range of stem versions for cement-free THA have been described in the literature. Sendtner et al. found cement-free stems ranging between − 19° retroversion and up to 33° anteversion. These findings were in accordance with the results of Wines et al. and Bargar et al. who described a postoperative range of cement-free stem versions from − 15° up to 52° and 1° up to 39°, respectively [7, 8]. These ranges are mainly caused by the natural anteroposterior and mediolateral bow of the femoral canal, the thickness of the posterior cortex, and the width of the medullary canal [14,15,16]. Our study confirmed this wide range of rotation in cement-free stems ranging from − 2.0° retroversion to 27.9° anteversion. Our results are in contrast to the findings of Dimitrou et al. who showed a correlation between the osteotomy angle and femoral version and between the level of the osteotomy and the frontal plane of the stem, respectively. They also used a non-anatomical straight tapered stem, but a posterolateral approach. Therefore, this approach might have influenced their results, as mentioned before.
To our knowledge, no study has so far considered the influence of femoral neck resection height on the final position and alignment of a straight tapered cement-free implant. We therefore believe that our trial contributes to the understanding of the concept of cement-free THA for this stem design.
In conclusion, we showed that femoral neck resection height ranging between 0 and 20.1 mm does not correlate with the final position of a straight tapered cement-free implant. Thus, surgeons cannot control the final position of this specific implant by adapting femoral neck resection height. For exact modulation between cup and stem we recommend the concept of combined anteversion/‘femur first’ and the use of an image-free navigation system.
References
Learmonth ID, Young C, Rorabeck C (2007) The operation of the century: total hip replacement. Lancet 370:1508–1519. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60457-7
Kennedy JG, Rogers WB, Soffe KE, Sullivan RJ, Griffen DG, Sheehan LJ (1998) Effect of acetabular component orientation on recurrent dislocation, pelvic osteolysis, polyethylene wear, and component migration. J Arthroplasty 13:530–534
Lewinnek GE, Lewis JL, Tarr R, Compere CL, Zimmerman JR (1978) Dislocations after total hip-replacement arthroplasties. J Bone Joint Surg Am 60:217–220
Saxler G, Marx A, Vandevelde D, Langlotz U, Tannast M, Wiese M, Michaelis U, Kemper G, Grutzner PA, Steffen R, von Knoch M, Holland-Letz T, Bernsmann K (2004) The accuracy of free-hand cup positioning–a CT based measurement of cup placement in 105 total hip arthroplasties. Int Orthop 28:198–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-004-0542-5
Dorr LD, Malik A, Wan Z, Long WT, Harris M (2007) Precision and bias of imageless computer navigation and surgeon estimates for acetabular component position. Clin Orthop Relat Res 465:92–99. https://doi.org/10.1097/BLO.0b013e3181560c51
Bargar WL, Jamali AA, Nejad AH (2010) Femoral anteversion in THA and its lack of correlation with native acetabular anteversion. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468:527–532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-009-1040-2
Sendtner E, Tibor S, Winkler R, Worner M, Grifka J, Renkawitz T (2010) Stem torsion in total hip replacement. Acta Orthop 81:579–582. https://doi.org/10.3109/17453674.2010.524596
Wines AP, McNicol D (2006) Computed tomography measurement of the accuracy of component version in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 21:696–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2005.11.008
Worlicek M, Weber M, Craiovan B, Worner M, Vollner F, Springorum HR, Grifka J, Renkawitz T (2016) Native femoral anteversion should not be used as reference in cementless total hip arthroplasty with a straight, tapered stem: a retrospective clinical study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 17:399. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-016-1255-9
Michel MC, Witschger P (2007) MicroHip: a minimally invasive procedure for total hip replacement surgery using a modified Smith-Peterson approach. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil 9:46–51
Hallan G, Lie SA, Furnes O, Engesaeter LB, Vollset SE, Havelin LI (2007) Medium- and long-term performance of 11,516 uncemented primary femoral stems from the Norwegian arthroplasty register. J Bone Joint Surg Br 89:1574–1580. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.89B12.18969
Soballe K, Hansen ES, B.‐Rasmussen H, Jorgensen PH, Bunger C (1992) Tissue ingrowth into titanium and hydroxyapatite-coated implants during stable and unstable mechanical conditions. J Orthop Res 10:285–299. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.1100100216
Bernasek TL, Lee WS, Lee HJ, Lee JS, Kim KH, Yang JJ (2010) Minimally invasive primary THA: anterolateral intermuscular approach versus lateral transmuscular approach. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 130:1349–1354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-009-1035-1
Widmer KH, Zurfluh B (2004) Compliant positioning of total hip components for optimal range of motion. J Orthop Res 22:815–821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orthres.2003.11.001
Yoshimine F (2005) The influence of the oscillation angle and the neck anteversion of the prosthesis on the cup safe-zone that fulfills the criteria for range of motion in total hip replacements. The required oscillation angle for an acceptable cup safe-zone. J Biomech 38:125–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2004.03.012
Yoshimine F, Ginbayashi K (2002) A mathematical formula to calculate the theoretical range of motion for total hip replacement. J Biomech 35:989–993
Authors’ contributions
MW developed the design of the study, was responsible for its coordination, drafted the manuscript and evaluated data. MaW evaluated the data and helped to draft the manuscript. TS participated in the coordination of the study and evaluated data. MWö was one of the performing surgeons and helped with data collection and interpretation of data for the work. FZ participated in data interpretation for the study and performed the statistical analysis. PG was one of the performing surgeons and helped with data collection/interpretation. TR was one of the performing surgeons, conceived the study, developed its design and was responsible for coordination and data collection. BC was one of the performing surgeons and was responsible for coordination, data collection/interpretation and proofreading of the final manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
Funding for this clinical trial was provided by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF; grant number 01EZ0915) and ‘Deutsche Arthrose Hilfe e. V.’, (Frankfurt, Germany).
The help of Ms. S. Gneiting, Ms. C. Jendrewski, Ms. M. Riedl, Mr. M. Schubert, Mr. A. Hapfelmeier, Mr. B. Messmer, Mr. L. Dohmen and Dr. M. Haimerl in this project is appreciated. We also want to thank Mrs. Monika Schoell for proofreading the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Availability of data and materials
All data supporting the findings of the current study are contained within the manuscript.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This investigation was approved by the local Ethics Commission (No.10-121-0263). All procedures were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2000. All patients provided informed consent to participate in this study.
Funding
Funding for this clinical trial was provided by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF; Grant Number 01EZ0915) and ‘Deutsche Arthrose Hilfe e. V.’, (Frankfurt, Germany).
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Worlicek, M., Weber, M., Wörner, M. et al. The final implant position of a commonly used collarless straight tapered stem design (Corail®) does not correlate with femoral neck resection height in cement-free total hip arthroplasty: a retrospective computed tomography analysis. J Orthop Traumatol 19, 20 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s10195-018-0513-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s10195-018-0513-z