Abstract
Cellular signaling by proteases of the blood coagulation cascade through members of the protease-activated receptor (PAR) family can profoundly impact on the inflammatory balance in sepsis. The coagulation initiation reaction on tissue factor expressing cells signals through PAR1 and PAR2, leading to enhanced inflammation. The anticoagulant protein C pathway has potent anti-inflammatory effects, and activated protein C signals through PAR1 upon binding to the endothelial protein C receptor. Activation of the coagulation cascade and the downstream endothelial cell localized anticoagulant pathway thus have opposing effects on systemic inflammation. This dichotomy is of relevance for the interpretation of preclinical and clinical data that document nonuniform responses to anticoagulant strategies in sepsis therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Severe sepsis is an exceedingly common cause of death in medical and surgical intensive care units. The sepsis syndrome involves a complex series of events that are caused by an excessive stimulation of the innate immune system. During the course of this dysregulation, the blood coagulation cascade is triggered, leading to the clinical signs of disseminated intravascular coagulation and microvascular thrombosis. Microvascular thrombosis is controlled by the anticoagulant protein C (PC) pathway, and recombinant human activated protein C (APC) has recently been approved for the treatment of severe sepsis syndrome. There is increasing preclinical and clinical evidence that proteases of the coagulation system affect the inflammatory response, independent of their role in initiating and controlling blood clotting. Here, we review current concepts of the basic mechanism of cell signaling by coagulation complexes. We discuss the role of coagulation complexes in the inflammatory dysregulation that occurs in sepsis and the implications of these findings for anticoagulant therapy in septic patients.
Cell surface multiprotein complexes regulate the blood coagulation cascade
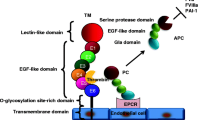
A circulatory system requires mechanisms that prevent blood loss, as well as those that counteract unwanted intravascular obstructions in the form of thrombi. Hemostasis is initiated and propagated through multiprotein complexes assembled on the surface of cells (Fig. 1) [1,2]. Typically, these complexes consist of a cofactor/receptor, an enzyme, and a substrate moiety.
Cell surface coagulation complexes of the procoagulant and anticoagulant pathways. The coagulation pathways are initiated by tissue factor (TF), which serves as the allosteric activator of the enzyme coagulation factor VIIa (VIIa). The TF–VIIa complex binds substrate factor X (X) through multiple contacts at so-called exosites, leading to the formation of a fairly stable TF–VIIa–X complex in which substrate X is converted to product Xa. When Xa is released from this complex, it associates with the cofactor Va to form the Va-Xa (prothrombinase) complex, predominantly on activated platelets that expose procoagulant phospholipid binding sites for Va and Xa. The intrinsic factor VIIIa-IXa complex can generate additional Xa that further amplifies the burst of thrombin generation required for hemostasis. Cell surface receptor mediated events also govern activation of the anticoagulant protein C (PC) pathway, which is localized to endothelial cells. Thrombomodulin (TM) binds thrombin and switches the procoagulant properties of thrombin to anticoagulant functions. Endothelial PC receptor (EPCR) is the receptor for PC and activated protein C (APC), and promotes activation of PC by thrombin–thrombomodulin. When APC is released from EPCR, it can act as a systemic anticoagulant by cleaving cofactors Va and VIIIa on various cell types.
The coagulation cascade is initiated by the cell surface receptor tissue factor (TF), which is expressed constitutively by extravascular cells (pericytes, cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells, keratinocytes) and by vascular monocytes and endothelial cells upon induction by inflammatory cytokines or endotoxin [3]. TF is the high-affinity cellular receptor for coagulation factor VIIa (VIIa). In the absence of TF, VIIa has very low catalytic activity, and binding to TF is necessary to render VIIa functional by an allosteric mechanism [4]. The TF–VIIa complex activates factor X (X) to Xa. Xa in turn is recruited to its cofactor Va into the prothrombinase complex on platelets. Platelets are essential to propagate a burst of thrombin generation that is dependent on procoagulant lipids that are typically exposed on the surface of activated platelets. In a positive feedback loop, thrombin activates the nonenzymatic cofactor VIII to VIIIa, which binds factor IXa to form the intrinsic X activation complex. Additional Xa that is generated by this complex amplifies the production of thrombin, which acts as the central effector protease in hemostasis. Thrombin activates platelets, converts fibrinogen to fibrin, and promotes fibrin cross-linking by activating factor XIII, leading to a stable hemostatic plug at sites of interrupted vascular integrity where TF is exposed on extravascular cells.
Sensitive markers of coagulation factor activation products show that thrombin is generated at low levels within the vasculature under physiologic conditions and at increased rates upon systemic stimulation by inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, which upregulates TF in endothelial cells and monocytes [2]. If the vascular integrity is unperturbed, then low concentrations of intravascular thrombin do not precipitate a thrombotic response. Rather, thrombin activates the essential anticoagulant PC pathway [5], in which APC degrades the cofactors Va and VIIIa on platelets and endothelial cells. APC generation involves two endothelial cell receptors, namely thrombomodulin and endothelial PC receptor (EPCR). Thrombomodulin is a cofactor/receptor for thrombin and changes thrombin's specificity from procoagulant functions to activation of PC [6]. EPCR is an endothelial cell specific receptor for both PC and APC [7]. Recruitment of PC to EPCR enhances the activation of PC by thrombin–thrombomodulin, thus localizing the anticoagulant pathway to the endothelial surface.
The biochemical mechanism of receptor-dependent activation of these enzyme cascades produces unique biologic properties. For example, the initiating events and the downstream hemostatic response may become uncoupled under certain circumstances in vivo. When healthy volunteers are challenged with inflammatory cytokines, measurements of activation peptides derived from X and prothrombin show that increased Xa generation can occur without subsequent thrombin generation [8]. The reason for this seemingly paradoxic finding is the basic mechanism of how X is activated by TF–VIIa. In the TF-initiated coagulation reaction, the TF–VIIa complex binds substrate X and forms a ternary TF–VIIa–X complex (Fig. 1). Only in this complex is the product Xa efficiently generated. Xa has affinity for TF–VIIa and thus does not dissociate immediately, but rather stays with TF in a ternary TF–VIIa–Xa complex. Only upon dissociation from TF–VIIa can Xa bind to Va and thus activate prothrombin. As a consequence, if Xa does not dissociate from TF–VIIa, then no thrombin is generated in vivo. The ternary TF–VIIa–Xa complex is the target for physiologic regulation by TF pathway inhibitor (TFPI), which simultaneously interacts with VIIa and Xa to form a stable quaternary TF–VIIa–Xa–TFPI complex [9]. Inhibition by TFPI provides the physiologic mechanism that effectively counteracts subsequent thrombin generation [10].
The concentration of circulating substrate X is sufficient to saturate TF–VIIa, once the complex is exposed to the blood. In contrast, substrate PC is typically preassembled with the endothelial surface, because it binds efficiently to EPCR under physiologic conditions (Fig. 1). When traces of thrombin are trapped by endothelial cell thrombomodulin, the thrombin–thrombomodulin complex activates PC bound to EPCR. Because APC has similar affinity as PC for EPCR, an early event in the anticoagulant pathway is to generate APC that is associated with the endothelial cell surface. Similar to Xa that is released from TF–VIIa–Xa, APC can subsequently dissociate from EPCR and produce generalized anticoagulant effects by inactivating cofactors Va and VIIIa on other cells. The procoagulant and anticoagulant pathways thus initially generate cell surface associated proteases that may serve functions other than hemostasis or antithrombotic control. Of relevance for sepsis, the proteases generated in the cellular context mediate cell signaling, influencing the inflammatory balance within the vasculature.
Protease-activated receptors mediate cell signaling in vivo
In order to adapt to their extracellular environment, living cells have sensors for extracellular proteolytic activity, namely the protease-activated receptors (PARs) [11,12]. PARs are seven-transmembrane-domain, G-protein-coupled receptors, and the activation mechanism for these receptors was first established for the thrombin receptor PAR1. PARs are activated by cleavage of a specific arginyl peptide bond in the amino-terminal ectodomain, leading to the exposure of a neo-amino terminus that folds back and activates the receptor ('tethered ligand mechanism'). Proteases of the coagulation system are the major activators of PARs, suggesting that PARs have evolved to regulate cellular functions associated with the response to vascular injury.
Of the four known human PARs, PAR1, PAR3, and PAR4 are activated by thrombin. The physiologic importance of thrombin-dependent PAR signaling is clearly demonstrated by the hemostatic defect of mice that lack the platelet expressed, thrombin-sensing PAR4 [13]. PAR1 has been implicated as a proinflammatory receptor in a thrombin-dependent model of crescentic glomerulonephritis [14]. PAR2 is not directly activated by thrombin, but appears to be a less selective sensor for several proteases, including trypsin and mast cell tryptase. PAR2 is involved in leukocyte marginalization and extravasation [15,16] and can support inflammation by a neurogenic mechanism [17], but anti-inflammatory effects were also observed upon PAR2 stimulation [18]. These opposing effects suggest that the specific response to PAR signaling depends on the biologic context and the relevant activating protease in these models of inflammation.
Role of coreceptors in protease-activated receptor signaling by coagulation proteases
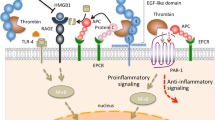
Although originally identified as the prototypical thrombin receptor, PAR1 is recognized increasingly as a target for other proteases. Unlike thrombin, most other proteases depend on cofactors for the efficient cleavage of PAR1 and PAR2 (Fig. 2). In recent studies [19,20,21] we analyzed the specificity of PAR cleavage by coagulation complexes in overexpression systems, as well as in primary endothelial cells. Free Xa inefficiently cleaves PARs [19,22]. However, in the TF-initiated coagulation reaction, Xa transiently bound in the ternary TF–VIIa–Xa complex potently activates PAR1 and PAR2 [20]. Neither Xa generated by the intrinsic activation complex VIIIa-IXa nor Xa bound to Va signal efficiently through PARs [19,20]. TF–VIIa can also activate PAR2 [20,22], but PAR activation by TF–VIIa is much less efficient in comparison with the signaling of the ternary TF–VIIa–Xa complex that is mediated by Xa. Thus, the TF-initiation reaction produces highly efficient and specific signaling through PARs.
Coreceptor-dependent activation of protease-activated receptors (PARs) by coagulation proteases. Relevant signaling complexes are schematically represented and the target PARs are listed. In primary endothelial cells, activated protein C (APC) signaling is mediated through PAR1, whereas tissue factor (TF)-VIIa-Xa can signal when PAR1 is blocked, indicating signaling through PAR2. TF–VIIa inefficiently signals in endothelial cells [20,22].
These experiments lead to the novel concept that protease signaling is mechanistically coupled and is an integrated part of the TF-initiated coagulation pathway. Because downstream coagulation is not triggered unless Xa is released from TF–VIIa, coagulation protease signaling can occur early and separately from massive activation of thrombin generation. More importantly, inhibiting thrombin and blocking the microthrombosis during disseminated intravascular coagulation does not influence directly the early signaling events that are solely dependent on the expression of TF by vascular and extravascular cells.
The concept that cell signaling is coupled to the initiation of a protease cascade may be extended to the anticoagulant pathway (Fig. 2). PC bound to EPCR is activated by thrombin–thrombomodulin, but APC stays associated, at least temporarily, with its endothelial cell receptor EPCR. EPCR serves as an essential coreceptor in the activation of PAR1 and PAR2 by APC in heterologous expression systems [21]. Physiologically relevant primary endothelial cells express both PAR1 and PAR2 but, unlike the finding in heterologous expression systems, APC selectively activates PAR1 in endothelial cells [21]. The activation of the anticoagulant PC pathway on endothelial cells is thus linked to EPCR-dependent PAR1 signaling. Interestingly, EPCR is a major histocompatibility class I-like receptor closely related to CD1d [23], whereas TF is related to interferon receptors [2]. The cellular initiation of the procoagulant and anticoagulant pathways thus appears to have coevolved with the expansion of a more complex immune system in vertebrates. That these receptors orchestrate protease signaling through PARs indicates potential immunomodulatory roles of protease complex signaling.
Preclinical data indicate a separation of thrombotic and inflammatory pathways
Given that the blood coagulation cascade is evolutionarily closely related to enzyme cascades of the innate immune response, it is not surprising that numerous molecular links between coagulation and inflammation have been established in vivo [24]. Inflammatory mediators not only promote coagulation, but also the products of the coagulation system can in turn profoundly affect the inflammatory response. Bacterial septicemia has provided the most convincing example of an association of the TF-initiated coagulation pathway with inflammation in vivo. In a lethal baboon sepsis model, administration of inhibitors of the ternary TF–VIIa–Xa complex (e.g. antibodies to TF, active site blocked VIIa, and TFPI) resulted in marked reductions in mortality, along with therapeutic benefits in reducing the ongoing coagulopathy [25,26,27]. However, lethality was not prevented by complete inhibition of microthrombosis and consumptive coagulopathy with DEGR-Xa, an active site-modified, inactive derivative of Xa that binds to Va, and thus selectively and potently blocks thrombin generation by the prothrombinase complex [28]. Conversely, producing disseminated intravascular coagulation by infusion of purified TF does not recapitulate the proinflammatory effects that result from endotoxin-mediated induction of the endogenous TF-driven coagulation pathways [29]. Taken together, these findings strongly suggest that the initiation phase of the coagulation pathways can sustain an inflammatory lethal response, independent of the downstream effector protease thrombin and coagulation-related effects.
The PC pathway also has anti-inflammatory effects that are independent of its anticoagulant function. Early studies in dogs demonstrated that infusion of thrombin blocks the lethal inflammatory response to endotoxin [30]. Infusion of thrombin into primates clearly demonstrated that low doses of thrombin act primarily as an anticoagulant by generating APC without activating coagulation or platelets [5]. That thrombin-dependent APC generation mediates protective effects in sepsis models was convincingly shown by direct infusion of APC into baboons challenged with Escherichia coli [31]. APC reduced coagulation abnormalities, organ failure, and lethality. Because DEGR-Xa completely blocked the coagulation abnormalities in the same sepsis model without reversing lethality, the beneficial anti-inflammatory effects of APC must, at least in part, be independent of its anticoagulant role. In other models, APC reduced nitric-oxide-mediated hypotension and cytokine-mediated pulmonary or renal vascular injury [32]. Again, anticoagulation with thrombin inhibition did not exhibit the same beneficial effects, further supporting the notion that anti-inflammatory effects of APC are independent of its anticoagulant action. The preclinical evidence is thus consistent with a physiologically relevant pathway in which thrombin–thrombomodulin dependent APC generation triggers protective anti-inflammatory effects in vivo. The recently demonstrated clinical efficacy of APC in reducing lethality in patients with severe sepsis [33] further emphasizes the importance of the coagulation signaling mediated regulation of inflammatory balance in clinical settings.
Protective effects of the activated protein C-PAR1 signaling pathway
Several in vitro studies indicated that APC has anti-inflammatory effects on monocytes and endothelial cells [34,35,36,37], but the precise mechanism of action of APC remained unclear and several studies had used supraphysiologic concentrations of APC. Large scale expression profiling provided compelling evidence that all gene induction events that follow endothelial cell stimulation with low concentrations of APC are mediated through activation of PAR1 [21]. PAR1-dependent APC signaling induced a number of genes that are known to downregulate proinflammatory signaling pathways (e.g. TNF-α-induced protein A20, tristetraprolin) and that counteract apoptosis (i.e. inhibitor of apoptosis protein 1, Bcl2 homologue A1, GADD45B). Thus, the PC pathway on endothelial cells can be considered an autocrine mechanism that protects the endothelium from damage during ongoing inflammation.
Gene expression profiling also showed that monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1 (also known as chemokine ligand 2) is upregulated by APC-mediated PAR1 signaling, but not by activation of PAR2, providing the first example of a PAR-specific transcriptional response in endothelial cells. The induction of MCP-1 by APC was a puzzling observation, because MCP-1 can have proinflammatory effects by supporting local monocyte recruitment, for example in lesion progression in arteriosclerosis [38,39]. However, in systemic inflammation, such as sepsis, administration of MCP-1 is protective and neutralization of MCP-1 increases lethality in response to endotoxin challenge [40,41]. MCP-1 acts on monocyte/macrophages to suppress proinflammatory interleukin-12 and TNF-α induction. MCP-1 also targets T-cells to induce T-helper-2 polarization and the associated upregulation of anti-inflammatory cytokines interleukin-10 and -13 [38,39]. These cytokines are crucial for control of the systemic inflammation that is responsible for the lethality in sepsis models driven by local inflammation [42]. In contrast to the proinflammatory effects of local upregulation of MCP-1, systemic upregulation of MCP-1 thus predominantly serves to counteract exaggerated, systemic inflammatory responses. The unique property of the APC-PAR1 pathway to induce MCP-1 selectively in endothelial cells throughout the vasculature may accomplish a systemic upregulation of MCP-1 that shifts the balance of the cytokine networks toward anti-inflammatory and protective effects.
Proinflammatory effects of coagulation protease signaling
Upon low-dose endotoxin stimulation monocytes rapidly upregulate TF [43], but TF-directed inhibitors did not influence the cytokine response under these conditions [44]. In contrast, inhibitors of the TF-initiation complex reduce proinflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-6 in lethal sepsis models induced by high-dose endotoxin [26,27], indicating that signaling by coagulation proteases contributes only to exacerbated cytokine production, and not to the initial inflammatory response. In lethal primate models of septicemia, TF is upregulated in endothelial cells of the marginal zone of the spleen, in alveolar lung epithelial cells, splenic macrophages, and renal glomeruli epithelial cells [45]. Multiple intravascular and extravascular cell types can therefore contribute to the TF-driven escalation in the inflammatory response. In the escalation of sepsis, the vascular permeability changes may lead to an increasing contribution of extravascular cells to the proinflammatory effects. The seemingly paradoxic finding that coagulation protease mediated PAR signaling influences both the proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory response may be explained, in part, by the fact that TF-dependent signaling activates multiple cell types, whereas APC signaling is endothelial cell restricted.
Implications for the use of anticoagulants in sepsis therapy
The described mechanisms by which the procoagulant and anticoagulant pathways regulate the inflammatory balance in vivo add new aspects of how to approach anticoagulant therapy in septic patients. Inhibitors of the TF-initiation complex are expected to block the proinflammatory signaling of the initiation reaction and thus have anti-inflammatory benefits that are not recapitulated by anticoagulants that target thrombin, a notion that is supported by several preclinical studies [25,26,27,46] (Fig. 3). Antithrombin III (ATIII) can inhibit TF–VIIa, in addition to Xa and thrombin. In the absence of heparin, antithrombin can bind to cell-surface proteoglycans and thereby act as an inhibitor of membrane-associated signaling complexes. Consistent with this notion, recombinant ATIII attenuates the inflammatory response and improves survival similar to other direct TF inhibitors in lethal, preclinical sepsis models [47].
Targets of anticoagulant therapy and their efficacy in providing anti-inflammatory benefit in sepsis. Anticoagulants (shown in red and boxed) showed preclinical efficacy in preventing lethality, whereas anticoagulant mechanisms (shown in blue and circled) failed to protect in sepsis. ATIII, antithrombin III; TF, tissue factor; TFPI, tissue factor pathway inhibitor.
In a large clinical sepsis trial, however, ATIII's benefit in improving 90-day survival was reversed in patients receiving heparin therapy [48]. Heparin displaces ATIII from cell surfaces where coagulation signaling complexes are expressed, and it enhances the inhibitory activity of ATIII toward the fluid-phase protease thrombin. One may expect anti-inflammatory benefits from such enhanced thrombin inhibition through the suppression of fibrin deposition, of leukocyte recruitment to sites of inflammation, and of resulting microcirculatory dysfunction. However, these beneficial effects may be entirely negated by the concomitant reduction in thrombin-dependent APC generation and APC-mediated protective signaling.
There is evidence that the physiologic protective PC pathway is progressively downregulated in sepsis, predominantly through a loss of thrombomodulin and, less pronounced, of EPCR from endothelial cells [49]. APC therapy may rescue the disabled APC pathway in severe sepsis and restore anti-inflammatory APC-PAR1 signaling by utilizing residually expressed EPCR. Notably, blocking EPCR in preclinical sepsis models worsened the inflammation and increased lethality [50]. The clinical observation that only patients with severe sepsis benefited from APC therapy [33] is consistent with the notion that a physiologic protective pathway becomes progressively disabled in the escalation of sepsis syndrome. Anticoagulants that target the TF-pathway directly may provide additional benefit in reducing the inflammatory response. Whether upstream coagulation inhibitors can be clinically applied without disabling the protective PC pathway remains an open question.
The concept is emerging that proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory signaling is separable from the hemostatic response. This concept has implications for potential future improvements in anti-inflammatory therapy targeting the coagulation pathways. For example, APC may be engineered to have reduced activity toward degradation of factors Va and/or VIIIa, or increased affinity for EPCR, resulting in more efficient EPCR-dependent protective signaling in endothelial cells with reduced bleeding complications. Similarly, tailoring inhibitors to specifically reduce signaling by the TF-initiated coagulation complex may yield partial anticoagulants that allow for the release of sufficient quantities of Xa to yield a hemostatic response, while simultaneously controlling the escalation of the inflammatory cytokine response in sepsis.
Conclusion
The recent appreciation of cell signaling as a physiological component of the pro- and anticoagulant pathways has provided a mechanistic understanding for the anti-inflammatory effects of APC in septicemia. Coagulation protease signaling through PARs appears to play an important immuno-modulatory role during systemic inflammation. The elucidation of basic principles of signaling of the pro- and anticoagulant pathways has far reaching implications for strategies in sepsis therapy that target the coagulation system.
Abbreviations
- APC:
-
activated protein C
- ATIII:
-
antithrombin III
- DEGR-Xa :
-
dansyl-Glu-Gly-Arg-chloromethyl ketone modified Xa
- EPCR:
-
endothelial protein C receptor
- MCP:
-
monocyte chemoattractant protein
- PAR:
-
protease-activated receptor
- PC:
-
protein C
- TF:
-
tissue factor
- TFPI:
-
tissue factor pathway inhibitor
- TNF:
-
tumor necrosis factor
- VIIa:
-
coagulation factor VIIa
- X/Xa:
-
coagulation factor X/Xa.
References
Mann KG, Nesheim ME, Church WR, Haley P, Krishnaswamy S: Surface-dependent reactions of the vitamin K-dependent enzyme complexes. Blood 1990, 76: 1-16.
Ruf W, Edgington TS: Structural biology of tissue factor, the initiator of thrombogenesis in vivo. FASEB J 1994, 8: 385-390.
Drake TA, Morrissey JH, Edgington TS: Selective cellular expression of tissue factor in human tissues. Am J Pathol 1989, 134: 1087-1097.
Ruf W, Dickinson CD: Allosteric regulation of the cofactor-dependent serine protease coagulation factor VIIa. Trends Cardiovasc Med 1998, 8: 350-356. 10.1016/S1050-1738(98)00031-0
Hanson SR, Griffin JH, Harker LA, Kelly AB, Esmon CT, Gruber A: Antithrombotic effects of thrombin-induced activation of endogenous protein C in primates. J Clin Invest 1993, 92: 2003-2012.
Esmon CT: Thrombomodulin as a model of molecular mechanisms that modulate protease specificity and function at the vessel surface. FASEB J 1995, 9: 946-955.
Esmon CT, Xu J, Gu JM, Qu D, Laszik Z, Ferrell G, Stearns-Kurosawa DJ, Kurosawa S, Taylor FB Jr, Esmon NL: Endothelial protein C receptor. Thromb Haemost 1999, 82: 251-258.
Van der Poll T, Büller HR, Ten Cate H, Wortel CH, Bauer KA, Van Deventer SJH, Hack CE, Sauerwein HP, Rosenberg RD, Ten Cate JW: Activation of coagulation after administration of tumor necrosis factor to normal subjects. N Engl J Med 1990, 322: 1622-1627.
Baugh RJ, Broze GJ Jr, Krishnaswamy S: Regulation of extrinsic pathway factor Xa formation by tissue factor pathway inhibitor. J Biol Chem 1998, 273: 4378-4386. 10.1074/jbc.273.8.4378
Huang Z-F, Higuchi D, Lasky N, Broze GJ Jr: Tissue factor pathway inhibitor gene disruption produces intrauterine lethality in mice. Blood 1997, 90: 944-951.
Coughlin SR: Thrombin signalling and protease-activated receptors. Nature 2000, 407: 258-264. 10.1038/35025229
O'Brien PJ, Molino M, Kahn M, Brass LF: Protease activated receptors: theme and variations. Oncogene 2001, 20: 1570-1581. 10.1038/sj.onc.1204194
Sambrano GR, Weiss EJ, Zheng Y-W, Coughlin SR: Role of thrombin signalling in platelets in haemostasis and thrombosis. Nature 2001, 413: 26-27. 10.1038/35092573
Cunningham MA, Rondeau E, Chen X, Coughlin SR, Holdsworth SR, Tipping PG: Protease-activated receptor 1 mediates thrombin-dependent, cell-mediated renal inflammation in crescentic glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med 2000, 191: 455-462. 10.1084/jem.191.3.455
Lindner JR, Kahn ML, Coughlin SR, Sambrano GR, Schauble E, Bernstein D, Foy D, Hafezi-Moghadam A, Ley K: Delayed onset of inflammation in protease-activated receptor-2-deficient mice. J Immunol 2000, 165: 6504-6510.
Vergnolle N: Proteinase-activated receptor-2-activating peptides induce leukocyte rolling, adhesion, and extravasation in vivo. J Immunol 1999, 163: 5064-5069.
Steinhoff M, Vergnolle N, Young SH, Tognetto M, Amadesi S, Ennes HS, Trevisani M, Hollenberg MD, Wallace JL, Caughey GH, Mitchell SE, Williams LM, Geppetti P, Mayer EA, Bunnett NW: Agonists of proteinase-activated receptor 2 induce inflammation by a neurogenic mechanism. Nature Med 2000, 6: 151-158. 10.1038/72247
Cocks TM, Fong B, Chow JM, Anderson GP, Frauman AG, Goldie RG, Henry PJ, Carr MJ, Hamilton JR, Moffatt JD: A protective role for protease-activated receptors in the airways. Nature 1999, 398: 156-160. 10.1038/18223
Riewald M, Kravchenko VV, Petrovan RJ, O'Brien PJ, Brass LF, Ulevitch RJ, Ruf W: Gene induction by coagulation factor Xa is mediated by activation of PAR-1. Blood 2001, 97: 3109-3116. 10.1182/blood.V97.10.3109
Riewald M, Ruf W: Mechanistic coupling of protease signaling and initiation of coagulation by tissue factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001, 98: 7742-7747. 10.1073/pnas.141126698
Riewald M, Petrovan RJ, Donner A, Mueller BM, Ruf W: Activation of endothelial cell protease activated receptor 1 by the protein C pathway. Science 2002, 296: 1880-1882. 10.1126/science.1071699
Camerer E, Huang W, Coughlin SR: Tissue factor- and factor X-dependent activation of protease-activated receptor 2 by factor VIIa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000, 97: 5255-5260. 10.1073/pnas.97.10.5255
Oganesyan V, Oganesyan N, Terzyan S, Qu D, Dauter Z, Esmon NL, Esmon CT: The crystal structure of the endothelial protein C receptor and a bound phospholipid. J Biol Chem 2002, 277: 24851-24854. 10.1074/jbc.C200163200
Opal SM: Phylogenetic and functional relationships between coagulation and the innate immune response. Crit Care Med 2000,28(suppl):S77-S80.
Taylor FB Jr, Chang A, Ruf W, Morrissey JH, Hinshaw L, Catlett R, Blick K, Edgington TS: Lethal E. coli septic shock is prevented by blocking tissue factor with monoclonal antibody. Circ Shock 1991, 33: 127-134.
Creasey AA, Chang ACK, Feigen L, Wun T-C, Taylor FB Jr, Hinshaw LB: Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) reduces mortality from E. coli septic shock. J Clin Invest 1993, 91: 2850-2860.
Taylor FB Jr, Chang ACK, Peer G, Li A, Ezban M, Hedner U: Active site inhibited factor VIIa (DEGR VIIa) attenuates the coagulant and interleukin-6 and -8, but not tumor necrosis factor, responses of the baboon to LD 100 Escherichia coli . Blood 1998, 91: 1609-1615.
Taylor FB Jr, Chang ACK, Peer GT, Mather T, Blick K, Catlett R, Lockhart MS, Esmon CT: DEGR-factor Xa blocks disseminated intravascular coagulation initiated by Escherichia coli without preventing shock or organ damage. Blood 1991, 78: 364-368.
Asakura H, Suga Y, Aoshima K, Ontachi Y, Mizutani T, Kato M, Saito M, Morishita E, Yamazaki M, Takami A, Miyamoto K-I, Nakao S: Marked difference in pathophysiology between tissue factor- and lipopolysaccharide-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation models in rats. Crit Care Med 2002, 30: 161-164.
Taylor FB Jr, Chang A, Hinshaw LB, Esmon CT, Archer LT, Beller BK: A model for thrombin protection against endotoxin. Thromb Res 1984, 36: 177-185.
Taylor FB, Chang A, Esmon CT, D'Angelo A, Vigano-D'Angelo S, Blick KE: Protein C prevents the coagulopathic and lethal effects of Escherichia coli infusion in the baboon. J Clin Invest 1987, 79: 918-925.
Isobe H, Okajima K, Uchiba M, Mizutani A, Harada N, Nagasaki A, Okabe K: Activated protein C prevents endotoxin-induced hypotension in rats by inhibiting excessive production of nitric oxide. Circulation 2001, 104: 1171-1175.
Bernard GR, Vincent JL, Laterre PF, LaRosa SP, Dhainaut JF, Lopez-Rodriguez A, Steingrub JS, Garber GE, Helterbrand JD, Ely EW, Fisher CJ Jr: Efficacy and safety of recombinant human activated protein C for severe sepsis. N Engl J Med 2001, 344: 759-762. 10.1056/NEJM200103083441001
Shu F, Kobayashi H, Fukudome K, Tsuneyoshi N, Kimoto M, Terao T: Activated protein C suppresses tissue factor expression on U937 cells in the endothelial protein C receptor-dependent manner. FEBS Lett 2000, 477: 208-212. 10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01740-3
Grey ST, Tsuchida A, Hau H, Orthner CL, Salem HH, Hancock WW: Selective inhibitory effects of the anticoagulant activated protein C on the responses of human mononuclear phagocytes to LPS, IFN-γ, or phorbol ester. J Immunol 1994, 153: 3664-3672.
White B, Schmidt M, Murphy C, Livingstone W, O'Toole D, Lawler M, O'Neill L, Kelleher D, Schwarz HP, Smith OP: Activated protein C inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced nuclear translocation of nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) and tumour necrosis factor α (TNF-α) production in the THP-1 monocytic cell line. Br J Haematol 2000, 110: 130-134. 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2000.02128.x
Joyce DE, Gelbert L, Ciaccia A, DeHoff B, Grinnell BW: Gene expression profile of antithrombotic protein C defines new mechanisms modulating inflammation and apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2001, 276: 11199-11203. 10.1074/jbc.C100017200
Luther SA, Cyster JG: Chemokines as regulators of T cell differentiation. Nature Immunology 2001, 2: 102-107. 10.1038/84205
Gerard C, Rollins B: Chemokines and disease. Nat Immunol 2001, 2: 108-115. 10.1038/84209
Zisman DA, Kunkel SL, Tsai WC, Bucknell K, Wilkowski J, Standiford TJ: MCP-1 protects mice in lethal endotoxemia. J Clin Invest 1997, 99: 2832-2836.
Bone-Larson CL, Hogaboam CM, Steinhauser ML, Oliveira SH, Lukacs NW, Strieter RM, Kunkel SL: Novel protective effects of stem cell factor in a murine model of acute septic peritonitis. Dependence on MCP-1. Am J Pathol 2000, 157: 1177-1186.
Walley KR, Lukacs NW, Standiford TJ, Strieter RM, Kunkel SL: Balance of inflammatory cytokines related to severity and mortality of murine sepsis. Infect Immun 1996, 64: 4733-4738.
Franco RF, De Jonge E, Dekkers PEP, Timmerman JJ, Spek CA, Van Deventer SJH, Van Deursen P, Van Kerkhoff L, Van Gemen B, Ten Cate H, Van der Poll T, Reitsma PH: The in vivo kinetics of tissue factor messenger RNA expression during human endo-toxemia: relationship with activation of coagulation. Blood 2000, 96: 554-559.
De Jonge E, Dekkers PEP, Creasey AA, Hack CE, Paulson SK, Karim A, Kesecioglu J, Levi M, Van Deventer SJH, Van der Poll T: Tissue factor pathway inhibitor dose-dependently inhibits coagulation activation without influencing the fibrinolytic and cytokine response during human endotoxemia. Blood 2000, 95: 1124-1129.
Drake TA, Cheng J, Chang A, Taylor FB Jr: Expression of tissue factor, thrombomodulin, and E-selectin in baboons with lethal E. coli sepsis. Am J Pathol 1993, 142: 1458-1470.
Miller DL, Welty-Wolf K, Carraway MS, Ezban M, Ghio A, Suliman H, Piantadosi CA: Extrinsic coagulation blockade attenuates lung injury and proinflammatory cytokine release after intratracheal lipopolysaccharide. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2002, 26: 650-658.
Minnema MC, Chang ACK, Jansen PM, Lubbers YTP, Pratt BM, Whittaker BG, Taylor FB, Hack CE, Friedman B: Recombinant human antithrombin III improves survival and attenuates inflammatory responses in baboons lethally challenged with Escherichia coli . Blood 2000, 95: 1117-1123.
Warren BL, Eid A, Singer P, Pillay SS, Carl P, Novak I, Chalupa P, Atherstone A, Penzes I, Kubler A, Knaub S, Keinecke HO, Heinrichs H, Schindel F, Juers M, Bone RC, Opal SM: Caring for the critically ill patient. High-dose antithrombin III in severe sepsis: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2001, 286: 1869-1878. 10.1001/jama.286.15.1869
Faust SN, Levin M, Harrison OB, Goldin RD, Lockhart MS, Kondaveeti S, Laszik Z, Esmon CT, Heyderman RS: Dysfunction of endothelial protein C activation in severe meningococcal sepsis. N Engl J Med 2001, 345: 408-416. 10.1056/NEJM200108093450603
Taylor FB Jr, Stearns-Kurosawa DJ, Kurosawa S, Ferrell G, Chang ACK, Laszik Z, Kosanke S, Peer G, Esmon CT: The endothelial cell protein C receptor aids in host defense against Escherichia coli sepsis. Blood 2000, 95: 1680-1686.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
None declared.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riewald, M., Ruf, W. Science review: Role of coagulation protease cascades in sepsis. Crit Care 7, 123 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1186/cc1825
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/cc1825