Abstract
Introduction
The clinical significance of elevation of lactate levels within the reference range is not well studied. The objective of this study was to determine the best cutoff threshold for serum lactate within the reference range (0.01 to 2.00 mM) that best discriminated between survivors and nonsurvivors of critical illness and to examine the association between relative hyperlactatemia (lactate above the identified threshold) and mortality.
Methods
This was a retrospective cohort study of adult patients admitted to the medical-surgical intensive care unit (ICU) of a tertiary care academic center. Youden index was calculated to identify the best lactate cutoff threshold that discriminated between survivors and nonsurvivors. Patients with lactate above the identified threshold were defined as having relative hyperlactatemia. Multivariate logistic regression, adjusting for baseline variables, was performed to determine the relationship between the above two ranges of lactate levels and mortality. In addition, a test of interaction was performed to assess the effect of selected subgroups on the association between relative hyperlactatemia and hospital mortality.
Results
During the study period, 2,157 patients were included in the study with mean lactate of 1.3 ± 0.4 mM, age of 55.1 ± 20.3 years, and acute physiology and chronic health evaluation (APACHE) II score of 22.1 ± 8.2. Vasopressors were required in 42.4%. Lactate of 1.35 mM was found to be the best cutoff threshold for the whole cohort. Relative hyperlactatemia was associated with increased hospital mortality (adjusted odds ratio (aOR), 1.60, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.29 to 1.98), and ICU mortality (aOR, 1.66; 95% CI, 1.26 to 2.17) compared with a lactate level of 0.01 to 1.35 mM. This association was consistent among all examined subgroups.
Conclusions
Relative hyperlactatemia (lactate of 1.36 to 2.00 mM) within the first 24 hours of ICU admission is an independent predictor of hospital and ICU mortality in critically ill patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Hyperlactatemia (>2 mM) has been shown to be an independent predictor of mortality in different groups of critically ill patients [1, 2], such as those with sepsis, with or without organ failure [3–11], trauma [12–17], and acute inflammatory response syndrome [7, 18]. It has been also used to guide management of critically ill patients. For example, the Surviving Sepsis Campaign [19] and early goal-directed therapy [20] recommend resuscitation of sepsis patients with lactate >4 mM. In clinical practice, less attention is paid to lactate levels within the reference range (≤2 mM), as their clinical significance is not well understood. Studies have suggested that relative hyperlactatemia in patients with septic shock has been associated with mortality [21–23], indicating that lactate might remain normal before and during resuscitation, thus questioning what is the best cutoff threshold of lactate that should trigger resuscitation. However, data in this area remain limited. Therefore, we sought to determine the best cutoff threshold for serum lactate that is within the reference range (0.01 to 2.00 mM) that best discriminates between survivors and nonsurvivors of critical illness and to examine the association between relative hyperlactatemia (lactate above the identified threshold) and mortality.
Methods
Design and Setting
This was a retrospective cohort study of adult patients admitted to the medical-surgical intensive care unit (ICU) of King Abdulaziz Medical City, a tertiary care academic center in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, from February 2002 until December 2010. The hospital is accredited by the Joint Commission International. The ICU is a 21-bed closed unit with a 24 hours/7 days in-house coverage by board-certified intensivists [24] and admits around 900 patients per year. The ICU has a database for all patients for which data was prospectively collected by a full-time research physician. The study was approved by the institutional review board of the hospital and, because of the nature of the study, consent was waived.
Patients
All patients 18 years of age or older with measured lactate levels were included in this study. We excluded patients with readmission within the same hospitalization and brain death on admission. The following information were noted: age, gender, acute physiology and chronic health evaluation (APACHE) II score [25], admission diagnosis category as defined by the acute physiology and chronic health evaluation (APACHE) II system [25], chronic comorbidities, history of cirrhosis, history of diabetes, Glasgow coma scale (GCS), presence of sepsis on admission, mechanical ventilation requirement in the first 24 hours of admission, the ratio of partial pressure of oxygen to the fraction of inspired oxygen (PaO2/FiO2), requirement for vasopressors (defined as use of any vasopressor infusion except dopamine <5 μg/kg/min), admission bilirubin, creatinine, lactate, and international normalized ratio (INR), ICU and hospital length of stay (LOS), mechanical ventilation duration (MVD), requirement for tracheostomy and renal-replacement therapy (RRT), and ICU and hospital mortality.
Outcomes
Hospital mortality was the primary outcome. ICU mortality, ICU and hospital LOS, MVD and requirement for tracheostomy, and RRT were the secondary outcomes.
Measurement of lactate
Lactate was measured on admission to ICU by sending venous or arterial blood to the hospital central laboratory and was measured via Abbott Laboratories, Abbott Park, IL 60064, USA, with a limit of detection of 0.006 mM. All patients who had at least one measurement of lactate within 24 hours of admission to ICU were included in the analysis. For patients with multiple lactate measurements, the highest value of lactate level within the first 24 hours of ICU admission was recorded and entered into the database, and this value was used for analysis.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis software (SAS, version 9.0; SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA) was used to analyze the data. Continuous data are presented as means with standard deviations, and categoric data, as frequencies and percentages. The χ2 or Student t test was used to test significant differences between study groups, as appropriate. Youden index was calculated to identify the best cutoff threshold of lactate that discriminates between survivors and nonsurvivors [26]. Patients having serum lactate above the identified cutoff threshold were defined as having relative hyperlactatemia and were compared with the control group of patients with lactate below that cutoff threshold. We also calculated the Youden index among patients with sepsis and patients in shock (defined as requiring vasopressors) to determine the best cutoff in these specific groups.
To determine the association between relative hyperlactatemia and hospital mortality, bivariate and then multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed. The variables entered in the model included age, gender, APACHE II score, admission diagnosis category, history of cirrhosis, presence of sepsis on admission, mechanical ventilation, vasopressor use, INR, and RRT. The variables were selected based on statistical as well as on clinical rationales. We tested for interaction to determine the effect modification of selected subgroups on the association between relative hyperlactatemia and hospital mortality. These subgroups included the following: male versus female patients; age older than 50 years versus age younger than 50 years; sepsis versus no sepsis; diabetes versus no diabetes; different admission diagnosis categories; cirrhosis versus no cirrhosis; mechanically ventilated versus not mechanically ventilated; required vasopressors versus no vasopressors; PaFiO2 ratio >200 versus PaFiO2 ratio <200. Results were reported as adjusted odds ratio (aOR) and 95% confidence interval (CI). A two-sided P value <0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
Results
Baseline characteristics of patients with lactate within reference range
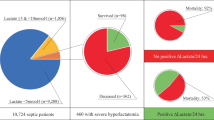
Of 10,791 patients admitted to the ICU during the study period, 4,538 (42.1%) had lactate levels measured within 24 hours of admission to ICU. Of those with measured lactate, 2,157 (47.5%) patients had lactate levels within the reference range (0.01-2.00 mM). Table 1 describes the baseline characteristics of these patients. The mean age was 55.1 ± 20.3 years: 37.6% of them were female patients; APACHE II score was 22.1 ± 8.2; 22.5% had sepsis diagnosis on admission; 75% were mechanically ventilated; and 42.4% were receiving vasopressors. The mean lactate was 1.3 ± 0.4 mM. The overall ICU and hospital mortality were 14.1% and 30.0%, respectively.
Youden index
Table 2 summarizes the sensitivities and specificities, along with the 95% CI, for different lactate cutoff points among patients with lactate within the reference range. Moreover, Youden index for each of these cutoff points is presented. The best cutoff threshold that was found to discriminate between survivors and nonsurvivors was 1.35 mM, as it corresponded to the highest Youden index.
Baseline characteristics of patients with relative hyperlactatemia
Compared with control group, patients with relative hyperlactatemia were older, had higher APACHE II scores, were more likely to have chronic liver disease and sepsis on admission, were more likely to be mechanically ventilated and to be receiving vasopressors, and had higher INRs (Table 3).
Outcomes of patients with relative hyperlactatemia
Hospital mortality was higher in patients with relative hyperlactatemia compared with the control group (36.7% versus 25.3%; P < 0.0001). Similarly, ICU mortality was higher (18.4% versus 11.0%; P = 0.0003) (Table 4). On multivariate logistic regression analysis, relative hyperlactatemia was an independent predictor of hospital mortality (aOR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.29 to 1.98), and ICU mortality (aOR, 1.66; 95% CI, 1.26 to 2.17) (Table 4).
Subgroup analysis
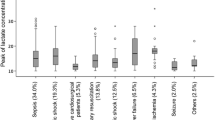
The association between relative hyperlactatemia on hospital mortality in different subgroups is shown in Figure 1. Relative hyperlactatemia was associated with increased hospital mortality, which was consistent among all subgroups, as indicated by the test of interaction. Youden index calculations showed that the cutoff threshold among patients with sepsis and those who were in shock was not different from that of the whole population.
Discussion
Among critically ill patients with lactate levels within the reference range (0.01 to 2.00 mM), we found lactate of 1.35 mM to be the best cutoff threshold that discriminated between survivors and nonsurvivors. Relative hyperlactatemia was an independent predictor of hospital and ICU mortality.
The first demonstration of lactate in human blood was in shock patients, by Johann Joseph Scherer in 1843 [27]. Subsequent work led to the demonstration that tissue hypoxia was associated with increased lactate level [27]. Elevated lactate is frequently seen in critically ill patients and is primarily a consequence of inadequate oxygen delivery, usually associated with significant cardiopulmonary compromise, as seen in cardiogenic, hypovolemic, and septic shock [28].
In an unstressed individual, the basal lactate concentration is 1.0 ± 0.5 mM. In critically ill patients, a lactate level of ≤2 mM is considered to be within the reference range [29], and therefore, hyperlactatemia is defined as lactate of >2 mM. A wealth of literature exists on hyperlactatemia (>2 mM) [2, 4, 6, 10] but not on lactate within the reference range.
We found that a significant percentage (47.5%) of critically ill patients who had lactate measured within 24 hours of ICU admission had an admitting lactate level of ≤2 mM, with overall hospital mortality of 30%. It has been reported that 24% to 34% of patients with severe sepsis and septic shock have lactate levels within the reference range [10, 22]. Trzeciak et al. [30] evaluated 1,177 patients with primary or secondary diagnosis of infection and had serum lactate measured and found that most (70.3%) patients had lactate of 0.0 to 2.0 mM [30].
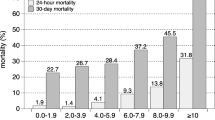
The evidence linking lactate within the reference range (0.01 to 2.0 mM) to mortality is also limited. We found that relative hyperlactatemia was an independent predictor of both hospital and ICU mortality. Nichol et al. [31], in their prospective observational study of 7,155 consecutive critically ill patients, found that increased admission lactate within the reference range was independently associated with increased hospital mortality in general critically ill patients. Trzeciak et al. [30] found that patients with infections and lactate <2 mM had a mortality of 15% compared with 25% for patients with lactate 2.1 to 3.9 mM and 38% for those with lactate ≥4 mM (P < 0.001). In our study, we found that a lactate of 1.35 mM was the best cutoff threshold to discriminate between survivors and nonsurvivors among critically ill patients who had lactate within the reference range. Interestingly, this cutoff threshold was similar in patients with sepsis and also in patients with shock. This may be of significant importance in identifying severe sepsis early, which is one of the main targets of sepsis-management quality-improvement initiatives.
Whether patients with relative hyperlactatemia should be treated differently is unknown. Rivers et al. [20], in the early goal-directed therapy study for severe sepsis or septic shock, excluded patients with MAP >65 mm Hg and lactate <4 mM from early intervention. The Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guidelines also recommended lactate of >4 mM (even in the absence of hypotension) as one of the criteria for initiating early-goal-directed therapy [19]. Whether early intervention in patients with relative hyperlactatemia will improve outcomes is a question that may be intuitive but requires further study.
Our study should be viewed in terms of its strengths and limitations. Strengths include the analysis of prospectively collected data by a full-time research physician, large sample size, 24/7 coverage of the unit by board-certified intensivists [24] rendering uniform care to all patients. The lactate was measured in the central laboratory, thus minimizing possible false readings of various point-of-care devices because of different methods of measurements used in many ICUs [32]. As for limitations, the study is single centered, lactate levels were not measured in all patients, and the analysis was performed by using a single, not serial values. Finally, we do not have data about the interventions and medications that can affect the lactate level.
Conclusions
Relative hyperlactatemia (lactate of 1.36 to 2.00 mM) within the first 24 hours of ICU admission is an independent predictor of hospital and ICU mortality in critically ill patients. Further studies are required to examine the most appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic approach to patients with relative hyperlactatemia.
Key messages
-
Among critically ill patients with lactate within the reference range, lactate of 1.35 mM was found to be the best cutoff threshold that discriminated between survivors and nonsurvivors.
-
Relative hyperlactatemia within the first 24 hours of ICU admission is an independent predictor of hospital and ICU mortality in critically ill patients.
-
Association between hospital mortality and relative hyperlactatemia was consistent among all subgroups, including patients with sepsis and those with shock.
Abbreviations
- aOR:
-
adjusted odds ratio
- APACHE:
-
acute physiology and chronic health evaluation
- CI:
-
confidence interval
- GCS:
-
Glasgow Coma Score
- ICU:
-
intensive care unit
- INR:
-
International normalized ratio
- LOS:
-
length of stay
- MVD:
-
mechanical ventilation duration
- PaO2/FiO2:
-
ratio of partial pressure of oxygen to the fraction of inspired oxygen
- RRT:
-
renal replacement therapy
- SAS:
-
statistical analysis software.
References
Jansen TC, van Bommel J, Schoonderbeek FJ, Sleeswijk Visser SJ, van der Klooster JM, Lima AP, Willemsen SP, Bakker J: Early lactate-guided therapy in intensive care unit patients: a multicenter, open-label, randomized controlled trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2010, 182: 752-761. 10.1164/rccm.200912-1918OC
Khosravani H, Shahpori R, Stelfox HT, Kirkpatrick AW, Laupland KB: Occurrence and adverse effect on outcome of hyperlactatemia in the critically ill. Crit Care 2009, 13: R90. 10.1186/cc7918
Nguyen HB, Loomba M, Yang JJ, Jacobsen G, Shah K, Otero RM, Suarez A, Parekh H, Jaehne A, Rivers EP: Early lactate clearance is associated with biomarkers of inflammation, coagulation, apoptosis, organ dysfunction and mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock. J Inflamm (Lond) 2010, 6.
Shapiro NI, Howell MD, Talmor D, Nathanson LA, Lisbon A, Wolfe RE, Weiss JW: Serum lactate as a predictor of mortality in emergency department patients with infection. Ann Emerg Med 2005, 45: 524-528. 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2004.12.006
Vorwerk C, Loryman B, Coats TJ, Stephenson JA, Gray LD, Reddy G, Florence L, Butler N: Prediction of mortality in adult emergency department patients with sepsis. Emerg Med J 2009, 26: 254-258. 10.1136/emj.2007.053298
Jansen TC, van Bommel J, Woodward R, Mulder PG, Bakker J: Association between blood lactate levels, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment subscores, and 28-day mortality during early and late intensive care unit stay: a retrospective observational study. Crit Care Med 2009, 37: 2369-2374. 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181a0f919
Cicarelli DD, Vieira JE, Bensenor FE: [Lactate as a predictor of mortality and multiple organ failure in patients with the systemic inflammatory response syndrome.]. Rev Bras Anestesiol 2007, 57: 630-638.
Bakker J, Gris P, Coffernils M, Kahn RJ, Vincent JL: Serial blood lactate levels can predict the development of multiple organ failure following septic shock. Am J Surg 1996, 171: 221-226. 10.1016/S0002-9610(97)89552-9
van Beest P, Kuiper M, Spronk PE: Lactate: an unusually sensitive parameter of ensuing organ failure? Crit Care Med 2010, 38: 337. author reply 337-338
Mikkelsen ME, Miltiades AN, Gaieski DF, Goyal M, Fuchs BD, Shah CV, Bellamy SL, Christie JD: Serum lactate is associated with mortality in severe sepsis independent of organ failure and shock. Crit Care Med 2009, 37: 1670-1677. 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31819fcf68
del Portal DA, Shofer F, Mikkelsen ME, Dorsey PJ Jr, Gaieski DF, Goyal M, Synnestvedt M, Weiner MG, Pines JM: Emergency department lactate is associated with mortality in older adults admitted with and without infections. Acad Emerg Med 2010, 17: 260-268. 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2010.00681.x
Manikis P, Jankowski S, Zhang H, Kahn RJ, Vincent JL: Correlation of serial blood lactate levels to organ failure and mortality after trauma. Am J Emerg Med 1995, 13: 619-622. 10.1016/0735-6757(95)90043-8
Blow O, Magliore L, Claridge JA, Butler K, Young JS: The golden hour and the silver day: detection and correction of occult hypoperfusion within 24 hours improves outcome from major trauma. J Trauma 1999, 47: 964-969. 10.1097/00005373-199911000-00028
Hung KK: Best Evidence Topic report: BET 2: Serum lactate as a marker for mortality in patients presenting to the emergency department with trauma. Emerg Med J 2009, 26: 118-119.
Sammour T, Kahokehr A, Caldwell S, Hill AG: Venous glucose and arterial lactate as biochemical predictors of mortality in clinically severely injured trauma patients: a comparison with ISS and TRISS. Injury 2009, 40: 104-108. 10.1016/j.injury.2008.07.032
Cerovic O, Golubovic V, Spec-Marn A, Kremzar B, Vidmar G: Relationship between injury severity and lactate levels in severely injured patients. Intensive Care Med 2003, 29: 1300-1305. 10.1007/s00134-003-1753-8
Roumen RM, Redl H, Schlag G, Sandtner W, Koller W, Goris RJ: Scoring systems and blood lactate concentrations in relation to the development of adult respiratory distress syndrome and multiple organ failure in severely traumatized patients. J Trauma 1993, 35: 349-355. 10.1097/00005373-199309000-00004
Kasirajan K, Mascha EJ, Heffernan D, Sifuentes J III: Determinants of in-hospital mortality and length of stay for acute intestinal gangrene. Am J Surg 2004, 187: 482-485. 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2003.12.049
Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Carlet JM, Bion J, Parker MM, Jaeschke R, Reinhart K, Angus DC, Brun-Buisson C, Beale R, et al.: Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2008. Crit Care Med 2008, 36: 296-327. 10.1097/01.CCM.0000298158.12101.41
Rivers E, Nguyen B, Havstad S, Ressler J, Muzzin A, Knoblich B, Peterson E, Tomlanovich M: Early goal-directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med 2001, 345: 1368-1377. 10.1056/NEJMoa010307
Levraut J, Ichai C, Petit I, Ciebiera JP, Perus O, Grimaud D: Low exogenous lactate clearance as an early predictor of mortality in normolactatemic critically ill septic patients. Crit Care Med 2003, 31: 705-710. 10.1097/01.CCM.0000045561.85810.45
Hernandez G, Castro R, Romero C, de la Hoz C, Angulo D, Aranguiz I, Larrondo J, Bujes A, Bruhn A: Persistent sepsis-induced hypotension without hyperlactatemia: is it really septic shock? J Crit Care 2011, 26: 435. e439-414
Cannon CM: Multicenter Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock Collaborative Group: The GENESIS Project (GENeralization of Early Sepsis InterventionS): a multicenter quality improvement collaborative. Acad Emerg Med 2010, 17: 1258.
Arabi Y: Pro/Con debate: should 24/7 in-house intensivist coverage be implemented? Crit Care 2008, 12: 216. 10.1186/cc6905
Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP, Zimmerman JE: APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med 1985, 13: 818-829. 10.1097/00003246-198510000-00009
Bewick V, Cheek L, Ball J: Statistics review 13: receiver operating characteristic curves. Crit Care 2004, 8: 508-512. 10.1186/cc3000
Kompanje EJ, Jansen TC, van der Hoven B, Bakker J: The first demonstration of lactic acid in human blood in shock by Johann Joseph Scherer (1814-1869) in January 1843. Intensive Care Med 2007, 33: 1967-1971. 10.1007/s00134-007-0788-7
Cohen R: Disorders of lactic acid metabolism. Clin Endocrinol Metab 1976, 613-625.
Mizock BA: Lactic acidosis. Dis Mon 1989, 35: 233-300.
Trzeciak S, Dellinger RP, Chansky ME, Arnold RC, Schorr C, Milcarek B, Hollenberg SM, Parrillo JE: Serum lactate as a predictor of mortality in patients with infection. Intensive Care Med 2007, 33: 970-977. 10.1007/s00134-007-0563-9
Nichol AD, Egi M, Pettila V, Bellomo R, French C, Hart G, Davies A, Stachowski E, Reade MC, Bailey M, et al.: Relative hyperlactatemia and hospital mortality in critically ill patients: a retrospective multi-centre study. Crit Care 2010, 14: R25. 10.1186/cc8888
Karon BS, Scott R, Burritt MF, Santrach PJ: Comparison of lactate values between point-of-care and central laboratory analyzers. Am J Clin Pathol 2007, 128: 168-171. 10.1309/HBQEFDPH34MKK5GP
Acknowledgements
Financial support: None
Data access and responsibility: Dr. Asgar Rishu (PI) had full access to all of the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
AHR participated in conception and design, participated in analysis and interpretation of data, drafted the manuscript, critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content, and approved the final version to be published. RK participated in analysis and interpretation of data, helped to draft the manuscript, critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content, and approved the final version to be published. HMA participated in analysis and interpretation of data, critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content, and approved the final version to be published. HMT helped in statistical analysis and interpretation of data, critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content, and approved the final version to be published. SAQ participated in conception and design, helped in drafting the manuscript, critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content, and approved the final version to be published. GAG participated in conception and design, critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content, and approved the final version to be published. YMA participated in conception and design, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data, critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content, and approved the final version to be published.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Rishu, A.H., Khan, R., Al-Dorzi, H.M. et al. Even Mild Hyperlactatemia Is Associated with Increased Mortality in Critically Ill Patients. Crit Care 17, R197 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/cc12891
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/cc12891