Abstract
Introduction
Mammographic density (MD) is one of the strongest known breast cancer risk factors. Estrogen and progestin therapy (EPT) has been associated with increases in MD. Dense breast tissue is characterized by increased stromal tissue and (to a lesser degree) increased numbers of breast epithelial cells. It is possible that genetic factors modify the association between EPT and MD, and that certain genetic variants are particularly important in determining MD in hormone users. We evaluated the association between MD and 340 tagging single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) from about 30 candidate genes in hormone metabolism/growth factor pathways among women who participated in the Norwegian Breast Cancer Screening Program (NBCSP) in 2004.
Methods
We assessed MD on 2,036 postmenopausal women aged 50 to 69 years using a computer-assisted method (Madena, University of Southern California) in a cross-sectional study. We used linear regression to determine the association between each SNP and MD, adjusting for potential confounders. The postmenopausal women were stratified into HT users (EPT and estrogen-only) and non-users (never HT).
Results
For current EPT users, there was an association between a variant in the prolactin gene (PRL; rs10946545) and MD (dominant model, Bonferroni-adjusted P (Pb) = 0.0144). This association remained statistically significant among current users of norethisterone acetate (NETA)-based EPT, a regimen common in Nordic countries. Among current estrogen-only users (ET), there was an association between rs4670813 in the cytochrome P450 gene (CYP1B1) and MD (dominant model, Pb = 0.0396). In never HT users, rs769177 in the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) gene and rs1968752 in the region of the sulfotransferase gene (SULT1A1/SULT1A2), were significantly associated with MD (Pb = 0.0202; Pb = 0.0349).
Conclusions
We found some evidence that variants in the PRL gene were associated with MD in current EPT and NETA users. In never HT users, variants in the TNF and SULT1A1/SULT1A2 genes were significantly associated with MD. These findings may suggest that several genes in the hormone metabolism and growth factor pathways are implicated in determining MD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Mammographic density (MD) is the radiodense or white area on a mammogram. MD reflects the amount of fibrous stroma and epithelium in the breast [1, 2]. MD has been associated with stromal growth factors [3], as well as the number of epithelial cells, but not with increased epithelial cell proliferation [4].
MD is one of the strongest known breast cancer risk factors [5]. Women with MD of 75% or greater have a risk of breast cancer that is four to five times higher than women of the same age with little or no density (≤ 5%) [6].
Several studies have suggested that MD is at least partially inherited. Studies of twins suggest that genetic factors explain 30 to 60% of the variation in MD [7–9]. A number of studies have assessed the role of genetic variants identified through genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of breast cancer on MD [10, 11], but the results of these studies are inconsistent. A recent meta-analysis of GWAS on MD identified one variant (rs10995190) in the zinc finger protein 365 gene (ZNF365) [12], but this variant only explained about 0.5% of the variance in MD. Thus, a large proportion of the variation is yet to be explained.
MD decreases with older age and menopause [13], and increases in postmenopausal women randomized to hormone treatment [14]. Parity [15] and early age at first full-term pregnancy are both associated with reduced MD [16]. Because of the clear role of hormones on MD, it has been suggested that genes involved in pathways that regulate steroid hormone synthesis and metabolism, hormone receptors, or genes in growth factor pathways may play a role. However, genetic association studies of candidate pathways either involving hormones or growth factors, have been few so far [17, 18]. Many studies have focused on selected variants, and these have not yielded consistent results [19–28]. It seems likely that such variants could determine how women metabolize hormone therapy (HT), or determine the downstream effect of hormones, and therefore some variants would only be important in women taking HT. Few of the studies so far have examined this association according to HT status [18, 21].
Therefore, we decided to investigate which genetic variants were the most important in explaining MD in HT users, and whether the association between genetic variants and MD was modified statistically by HT use. We evaluated the association between MD and 340 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) from about 30 putative genes in hormone metabolism and growth factor pathways.
Materials and methods
Participants
Characteristics of the study participants and details about the study have previously been described [29–31]. Women selected for the study had attended the Norwegian Breast Cancer Screening Program (NBCSP) at least once. This national screening program invites all women aged 50 to 69 years to undergo a mammographic examination every two years. The attendance rate is 76.2% [32].
A questionnaire on various breast cancer risk factors, enclosed within the NBCSP invitation, was sent to a random sample of 17,050 women living in the counties of Oslo, Akershus and Hordaland in 2004. Menstrual and reproductive history, use of oral contraceptive and menopausal hormonal therapy, family history of breast cancer, current weight and height were assessed by the standardized questionnaire. A total of 12,056 (71%) of the invited women attended the screening program and 7,941 (66%) returned a completed questionnaire.
A subset (7,174) of the 7,941 women who had completed the health questionnaire was asked to complete a food frequency questionnaire and to provide us with two buccal swabs. Of these, 3,484 women (49%) returned the dietary questionnaire and 3,728 returned buccal swabs. We requested mammograms from the various radiological facilities and we focused the requests on mammograms from women who had completed a food frequency questionnaire and had had a screen film mammography in 2004. About 300 women from Oslo had undergone digital mammography. These women were not included in the current study as assessments from digital images tend to yield somewhat low percent MD compared with digitized screen film mammograms.
We obtained information on HT use and analog screening mammograms from the year 2004 on 2,876 women. Of these, 124 women were excluded for the following reasons; 17 women had had a previous cancer (12 = breast, 5 = ovarian), the breast area could not be determined on mammograms from 3 women, 28 had incomplete data on age, and 73 incomplete data on body mass index (BMI) (height = 46/weight = 67). Three women were excluded because they used progesterone-only HT. After the exclusions, a total of 2,752 women with mammograms and HT data were left for analysis. All the participants signed an informed consent and the study was approved by the Regional Ethics Committee and the Norwegian Data Inspectorate.
Mammographic density analysis
Mammograms (left craniocaudal) were scanned using a high-resolution Kodak Lumisys 85 scanner with automatic feeder (Kodak, Rochester, NY, USA). Computer-assisted readings of absolute areas of dense and non-dense tissues, as well as percent density, were performed using the Madena software [33]. This method provides a continuous measure of density and a separate estimate of the absolute areas of dense and non-dense tissues. Only analog mammograms were included due to concern that the digitally obtained images would not yield comparable density readings. The density assessments were performed by an experienced reader (G.U.), whereas a research assistant trained by G.U. conducted the breast area measurements. Both readers were blinded to all subject characteristics. Percent MD was calculated by dividing the absolute breast density by the total breast area and multiplying it by 100. Some suggest that absolute density is the optimal method [34], but the majority of the studies on MD have used percent density [6], and we therefore limited these results to percent MD.
DNA collection and extraction
Three thousand seven hundred and twenty-eight (3,728) women returned buccal swabs out of which 3,317 were genotyped. Of these, 241 women had to be excluded due to a sample call rate < 80%, yielding 3,076 women. Of these, we had risk factor information and mammograms collected in 2004 on 2,397 women. DNA was extracted from buccal swabs using standard modified protocol for the QIAamp DNA blood kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA).
Selection of SNPs
For AR, COMT, CYP1A1/CYP1A2, CYB1B1, ESR2, HSD17B1, IGFBP1/IGFBP3, IL6, PGR, PPARG, PRL, SULT1A1/SULT1A2, SULT1E1, TGFB1, TNF and VEGF, we selected tag SNPs to capture the genetic variation in each gene. We selected linkage disequilibrium tagging SNPs across each gene, from 20 kb upstream of 5' untranslated region (UTR) to 10 kb downstream of the 3' UTR. Because this study shared an analysis platform with a study of Chinese women, HapMap Caucasians of European descent (CEU) data (release 24) [35] and HapMap Han Chinese in Beijing (CHB) data (release 24), as well as the Snagger [36] or modified Tagger approach were used to capture all common SNPs (minor allele frequency ≥ 5%) in Caucasians or Chinese with minimum pair wise r2 > 0.8. For, ADH1C, AKR1C4, CSHL1, CYP17A1, CYP19A1, ESR1, FGFR2, GHRHR, HCV3289988, HSD3B1/HSD3B2, POU5F1, PRLR, SHBG and SRD5A2, we selected one or a few SNP(s) of interest for each gene (Table 2).
Genotyping of SNPs
Genotyping was done using an Illumina BeadLab System (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) and GoldenGate™ Genotyping technology in the University of Southern California Genomics Center. Samples were run in a 96-well format using Illumina Sentrix Array technology on a BeadArray Reader. BeadStudio Software (version 3.0.9) with Genotyping Module (version 3.0.27) (Illumina) was used for analyzing scanned samples. The SNPs with < 85% call rates were excluded: this resulted in the exclusion of 4% of SNPs. The genotyping concordance rate based on 41 duplicate samples was 84%. Out of 340 SNPs in the hormone metabolism and growth factor pathways, 18 SNPs departed from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) (P < 0.001), leaving 322 SNPs for further analysis. None of these excluded 18 SNPs were associated with MD regardless of the hormone use status (data not shown).
Menopausal status and HT use
The classification of postmenopausal women was limited by our questionnaire where women were asked if they had undergone a) complete cessation of menstruation of at least six months b) previous bilateral oophorectomy c) hysterectomy without bilateral oophorectomy d) used HT before menopause. Out of the 2,397 women, we excluded 342 pre- and perimenopausal women. We also excluded 19 women who had undergone simple hysterectomy without bilateral oophorectomy since these women could not be classified on menopausal status. Our final sample size was 2,036 postmenopausal women. Excluding women with menopause within the past year (N = 177) yielded essentially unchanged results, and did not alter the order of the most important SNPs (results not shown). We therefore present analyses using the six month definition of menopause.
HT use was assessed by asking two questions about 1) ever use of HT with a proposed list of HT preparations and 2) current use of HT. If a woman had used the specified HT for more than three months at the time of completing the questionnaire, she was considered a current user. A woman could have used both estrogen-only (ET) and combined estrogen and progestin therapies (EPT) in her lifetime, but only one of these currently. Current EPT users were subdivided further into norethisterone acetate (NETA) regimen users or non-NETA users.
Statistical analyses
We used multivariate linear regression to examine the relation between percentage MD and SNPs. The MD variable was treated in a continuous manner, without any transformations, as the model's residuals satisfied the normality and homoscedasticity assumptions. We adjusted all analyses for age at screening (continuous) and BMI (kg/m2, continuous).
We ran these analyses on both additive and dominant models. However, because the results were largely similar between the two genetic models, and few women were homozygote for the variants of many SNPs, we only present the dominant model (results available upon request). We conducted analyses, with and without Bonferroni adjustments for multiple comparisons (the number of SNPs per gene) within each stratum defined by hormone use. We also ran a test for heterogeneity between HT users and non-users and present the P values for this interaction (Pint). In the results section, we specifically comment on results where the stratum-specific two-sided P values are less than 0.01 and the Bonferroni-adjusted P values (Pb) are less than 0.05.
We estimated least squares means (marginal means) on MD and all our explanatory variables among never, current and past EPT users. Least squares means are the group mean after having controlled for a covariate (age and BMI). We subdivided HT users into ET or EPT. EPT users were further subdivided into NETA users or non-users.
Results
Characteristics of the study population by strata of EPT use (no, past and current) are shown in Table 1. As previously described, MD was higher in current EPT users than in past or never users [31]. There were statistically significant differences in percent density, BMI and in age at screening between never, past and current EPT users. Table 2 shows the number of SNPs successfully genotyped for each gene we investigated.
Among all postmenopausal women, there was no association between SNPs and MD after Bonferroni adjustments (Table S1 in Additional file 1). Among postmenopausal never HT users, there was an association between MD and a variant in the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) gene (rs769177; Pb = 0.020), and with a variant in the sulfotransferase (SULT1A1/SULT1A2) gene (rs1968752; Pb = 0.035) (Table S2 in Additional file 2).
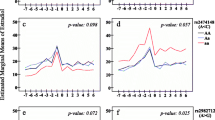
For postmenopausal current ET users (Table 3) there was an association between a variant in the cytochrome P450 (CYP1B1) gene (rs4670813, Pb = 0.0396) and MD. In current EPT users (Table 4) a variant in the prolactin (PRL) gene (rs10946545, Pb = 0.0144) was significantly associated with MD. The results from the analysis of all SNPs in all women combined, and in ET users and EPT users separately, as well as the interaction tests are shown in Table S3 in Additional file 3. Mean percent mammographic density was highest in homozygous wild-type carriers of PRL rs10946545 who currently used EPT (Figure 1).
Mean percent mammographic density by prolactin ( PRL ) rs10946545 genotype and hormone therapy use. A figure that presents mean percent mammographic density by the PRL gene (rs10946545) in women with two wild-type alleles and with one or two variant (minor) alleles in never hormone therapy (HT) users and in current estrogen and progestin therapy (EPT) users.
NETA is an EPT-based regimen common in Nordic countries. The results remained statistically significant when analyses were restricted to NETA users (results not shown).
When we adjusted for parity (parous/nulliparous), the three PRL SNPs that were significant in the EPT users remained statistically significant before Bonferroni correction (rs10946545 P = 0.0028/rs2744117 P = 0.0218/rs1156546 P = 0.0345). None of these were statistically significant after Bonferroni adjustment. In the interaction test between these three SNPs and EPT, two of the three SNPs remained statistically significant (rs10946545 Pint = 0.0051/rs1156446 Pint = 0.0317) after adjustment for parity.
Discussion
In this study of postmenopausal Norwegian women, we found that MD was associated with several variants in growth factor and hormone metabolism genes (PRL, CYP1B1, SULT1A1/SULT1A2 and TNF). However, different variants appeared to be important depending on the women's HT use.
There have been a number of studies of genetic variations and MD [18–28]. However, few studies have examined this association by HT use or tested the interaction with hormone use. Below, we discuss our results by subgroup of HT use.
Among postmenopausal never HT users (N = 1,008), we found associations between MD and variants in the TNF and the SULT1A1/SULT1A2 genes. TNF refers to a group of cytokines that are important in inflammation, as well as in growth, differentiation and cell death. TNF has been implicated in tumor regression [37, 38], and there is some evidence that TNF genetic variants are associated with breast cancer risk [39]. Our findings are consistent with this. As far as we know, no other study has examined the association between TNF variants and MD. One cross-sectional study on postmenopausal American women found no statistically significant associations between circulating TNF levels and MD after adjustment for BMI [40]. However, the study did not take HT use into account. In our study, one TNF variant was important in never users and in all women, the latter association possibly because more than half of the women were never users. However, this variant was not important in EPT users, nor was the interaction between never users and EPT users statistically significant. Two other TNF variants showed statistical significance in the interaction between never users and EPT users, but not after Bonferroni adjustments. The exact role of TNF genetic variation on mammographic density is thus unclear, however, if inflammation is an important aspect of breast cancer development, then it seems reasonable that TNF variants may play a role.
Sulfotransferase 1A1 and 1A2 are enzymes that are encoded by the SULT1A1 and SULT1A2 genes. Sulfotransferase enzymes catalyze hormones, drugs and xenobiotic compounds [41]. In a review of 18 studies of SNPs located in genes of the estrogen pathway, SULT1A1/SULT1A2 did not show any association with MD on the overall study population [42]. In a study on American premenopausal women, it was concluded that SNPs in SULT1A1 locus may influence percent density [43]. In our study, SULT1A1/SULT1A2 was important in never users, but not in HT users. A possible explanation could be that the SULT variants interact with exposures important for MD in women not using hormones, although it may also be a chance finding.
There were few current ET users in our study (N = 78), but among them we observed a negative association between MD and rs4670813 (CYP1B1). CYP1B1 belongs to the cytochrome P450 super family of enzymes and is important in the metabolism of estrogen that may affect breast cancer risk. CYP1B1 catalyzes formation of potentially carcinogenic catechol estrogens and forms 4-hydroxylation of estrone [44]. CYP1B1 expression levels have also been reported to be lower in tumors than in adjacent benign tissue [45], suggesting that a key factor in breast carcinogenesis is not increased 4-hydroxylation but reduced estradiol metabolism. Thus, both increased and reduced CYP1B1 activity has been hypothesized to be associated with breast cell proliferation. In the SWAN study, CYP1B1; rs162555 was associated with a higher MD in pre- and early perimenopausal women [27]. In a cross-sectional study on postmenopausal women who participated in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies, there was no evidence of an association between MD and genotypes in women randomized to ET [21]. In a case-control study of American postmenopausal women (PACE), the authors found an association between CYP1B1; rs1056827 and breast cancer risk in ever EPT users [46]. As long as the functional role of rs4670813 is unknown, the mechanism behind our observed negative association between MD and rs4670813 remains elusive.
The most significant findings in our study were the association between a variant in PRL gene (rs10946545) and MD in current EPT users (N = 248) and in users of NETA-based EPT. Prolactin, also known as luteotropic hormone, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRL gene [47]. It is produced by the pituitary gland and in lesser amounts by several other tissues, including breast tissue. Prolactin plays an important role in breast development, differentiation and lactation [48], but may also have procarcinogenic effects [49, 50]. There are prolactin receptors in both normal breast tissue and in breast tumor tissue [51–53]. Our findings are consistent with the results in a case-control study on Polish women. In that study, two SNPs (rs7718468 and rs13436213) in the prolactin receptor (PRLR) gene were associated with breast cancer risk in postmenopausal women [54]. In our study, we found this association in current EPT users. Adjustments for parity did not obliterate the association, and the association was observed in strata of both parous and nulliparous women (results not shown). How parity and prolactin interact with hormones important for breast epithelial proliferation is not yet clear, but may be important in breast cancer development. Parity has previously been found to primarily reduce risk of estrogen receptor and progestin receptor positive (ER+PR+) cancer, while breastfeeding reduces risk of both ER+ PR+ and ER-PR- cancer [55]. Whether PRL plays a role in this interaction is unknown. When we adjusted for parity, the SNPs in the PRL gene remained statistically significant, suggesting that the number of children does not attenuate the association between variants in PRL and MD.
In a case-control study within the prospective Nurses' Health Study, plasma level of prolactin was positively associated with the risk of breast cancer [56]. Data from a randomized, placebo-controlled study suggested that EPT use in postmenopausal women increased the PRL concentration [57]. However, that study did not examine the role of genetic variations. In the first family linkage study on MD, a locus on chromosome 5p was associated with MD, and the PRLR is at a region surrounding this locus [28]. Taken together, current data suggest that both PRL and PRLR may be important for MD.
Summing up, our results indicate that a number of genetic variants that determine how women metabolize HT, or how HT exerts its effect on the breast, might be associated with MD in HT users.
Strengths and weaknesses
There are several strengths of this study. First, our study investigated the association between genetic variations in the hormone metabolism and growth factor pathways and MD in HT users and non-users, and in ET and EPT users. Not many other studies have investigated these relations. Another strength of this study is the sample size (N = 2,036), and that it is population based. A third strength is that we had risk factor information available, although we only used age at screening, height/weight, hormone use and parity in this analysis. A weakness of the study is that we were not able to identify a study with similar types of hormone users, and thus have not been able to replicate our findings in another study. Further validation is therefore important. Another weakness is that we had only information on current height and weight (2004). We obtained the mammograms from three different screening facilities with different equipment and personnel. Even though the mammography procedures are standardized within the NBCSP, there is variation between radiographers on how to position and compress the breasts. Nevertheless, these potential sources of errors are not likely to be associated with genotype and would be expected to give a bias toward the null. We did not perform longitudinal studies, nor studies to establish the functional consequences of the SNPs, thereby restricting the ability to assess causation. To adjust for multiple comparisons we used Bonferroni adjustment. This is rather conservative, and we may thus have failed to identify other stratum-specific estimates that are biologically relevant.
Conclusions
We found some evidence that variants in the PRL gene were associated with MD in current EPT and NETA users. Variants in TNF and SULT1A1/SULT1A2 were associated with MD in never HT users. These findings may suggest that several genes in the hormone metabolism/growth factor pathways are implicated in determining MD. Some genetic variants in combination with specific HT may increase MD in susceptible women. Exploring the functional role of the SNPs associated with MD will further clarify the biological mechanisms involved.
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
body mass index
- CYP1B1:
-
cytochrome P450 gene
- EPT:
-
estrogen and progestin therapy
- ET:
-
current estrogen-only users
- GWAS:
-
genome-wide association studies
- HWE:
-
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
- HT:
-
hormone therapy
- MD:
-
mammographic density
- NBCSP:
-
the Norwegian Breast Cancer Screening Program
- NETA:
-
norethisterone acetate
- Pb:
-
Bonferroni-adjusted P
- PRL:
-
prolactin gene
- PRLR:
-
prolactin receptor
- SNP:
-
single nucleotide polymorphism
- SULT1A1/SULT1A2:
-
sulfotransferase gene
- TNF:
-
tumor necrosis factor gene
- UTR:
-
untranslated region
- ZNF365 gene:
-
zinc finger protein 365.
References
Boyd NF, Martin LJ, Bronskill M, Yaffe MJ, Duric N, Minkin S: Breast tissue composition and susceptibility to breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010, 102: 1224-1237. 10.1093/jnci/djq239.
Byng JW, Yaffe MJ, Jong RA, Shumak RS, Lockwood GA, Tritchler DL, Boyd NF: Analysis of mammographic density and breast cancer risk from digitized mammograms. Radiographics : a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. 1998, 18: 1587-1598.
Guo YP, Martin LJ, Hanna W, Banerjee D, Miller N, Fishell E, Khokha R, Boyd NF: Growth factors and stromal matrix proteins associated with mammographic densities. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2001, 10: 243-248.
Hawes D, Downey S, Pearce CL, Bartow S, Wan P, Pike MC, Wu AH: Dense breast stromal tissue shows greatly increased concentration of breast epithelium but no increase in its proliferative activity. Breast Cancer Res. 2006, 8: R24-10.1186/bcr1408.
Vachon CM, van Gils CH, Sellers TA, Ghosh K, Pruthi S, Brandt KR, Pankratz VS: Mammographic density, breast cancer risk and risk prediction. Breast Cancer Res. 2007, 9: 217-10.1186/bcr1829.
McCormack VA, dos Santos Silva I: Breast density and parenchymal patterns as markers of breast cancer risk: a meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2006, 15: 1159-1169. 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-06-0034.
Boyd NF, Dite GS, Stone J, Gunasekara A, English DR, McCredie MR, Giles GG, Tritchler D, Chiarelli A, Yaffe MJ, Hopper JL: Heritability of mammographic density, a risk factor for breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002, 347: 886-894. 10.1056/NEJMoa013390.
Pankow JS, Vachon CM, Kuni CC, King RA, Arnett DK, Grabrick DM, Rich SS, Anderson VE, Sellers TA: Genetic analysis of mammographic breast density in adult women: evidence of a gene effect. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1997, 89: 549-556. 10.1093/jnci/89.8.549.
Ursin G, Lillie EO, Lee E, Cockburn M, Schork NJ, Cozen W, Parisky YR, Hamilton AS, Astrahan MA, Mack T: The relative importance of genetics and environment on mammographic density. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2009, 18: 102-112. 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-07-2857.
Lee E, Haiman CA, Ma H, Van Den Berg D, Bernstein L, Ursin G: The role of established breast cancer susceptibility loci in mammographic density in young women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2008, 171: 258-260.
Tamimi RM, Cox D, Kraft P, Colditz GA, Hankinson SE, Hunter DJ: Breast cancer susceptibility loci and mammographic density. Breast Cancer Res. 2008, 10: R66-10.1186/bcr2127.
Lindstrom S, Vachon CM, Li J, Varghese J, Thompson D, Warren R, Brown J, Leyland J, Audley T, Wareham NJ, Loos RJ, Paterson AD, Rommens J, Waggott D, Martin LJ, Scott CG, Pankratz VS, Hankinson SE, Hazra A, Hunter DJ, Hopper JL, Southey MC, Chanock SJ, Silva IdS, Liu J, Eriksson L, Couch FJ, Stone J, Apicella C, Czene K, et al: Common variants in ZNF365 are associated with both mammographic density and breast cancer risk. Nat Genet. 2011, 43: 185-187. 10.1038/ng.760.
Greendale GA, Reboussin BA, Slone S, Wasilauskas C, Pike MC, Ursin G: Postmenopausal hormone therapy and change in mammographic density. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003, 95: 30-37. 10.1093/jnci/95.1.30.
McTiernan A, Martin CF, Peck JD, Aragaki AK, Chlebowski RT, Pisano ED, Wang CY, Brunner RL, Johnson KC, Manson JE, Lewis CE, Kotchen JM, Hulka BS, Women's Health Initiative Mammogram Density Study Investigators: Estrogen-plus-progestin use and mammographic density in postmenopausal women: Women's Health Initiative randomized trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005, 97: 1366-1376. 10.1093/jnci/dji279.
Dite GS, Gurrin LC, Byrnes GB, Stone J, Gunasekara A, McCredie MR, English DR, Giles GG, Cawson J, Hegele RA, Chiarelli AM, Yaffe MJ, Boyd NF, Hopper JL: Predictors of mammographic density: insights gained from a novel regression analysis of a twin study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2008, 17: 3474-3481. 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-07-2636.
Butler LM, Gold EB, Greendale GA, Crandall CJ, Modugno F, Oestreicher N, Quesenberry CP, Habel LA: Menstrual and reproductive factors in relation to mammographic density: the Study of Women's Health Across the Nation (SWAN). Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008, 112: 165-174. 10.1007/s10549-007-9840-0.
Kelemen LE, Sellers TA, Vachon CM: Can genes for mammographic density inform cancer aetiology?. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008, 8: 812-823. 10.1038/nrc2466.
Lee E, Ingles SA, Van Den Berg D, Wang W, Lavallee C, Huang MH, Crandall CJ, Stanczyk FZ, Greendale GA, Ursin G: Progestogen levels, progesterone receptor gene polymorphisms, and mammographic density changes: results from the Postmenopausal Estrogen/Progestin Interventions Mammographic Density Study. Menopause. 2012, 19: 302-310. 10.1097/gme.0b013e3182310f9f.
Haiman CA, Bernstein L, Berg D, Ingles SA, Salane M, Ursin G: Genetic determinants of mammographic density. Breast Cancer Res. 2002, 4: R5-10.1186/bcr434.
Haiman CA, Hankinson SE, De Vivo I, Guillemette C, Ishibe N, Hunter DJ, Byrne C: Polymorphisms in steroid hormone pathway genes and mammographic density. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2003, 77: 27-36. 10.1023/A:1021112121782.
Lord SJ, Mack WJ, Van Den Berg D, Pike MC, Ingles SA, Haiman CA, Wang W, Parisky YR, Hodis HN, Ursin G: Polymorphisms in genes involved in estrogen and progesterone metabolism and mammographic density changes in women randomized to postmenopausal hormone therapy: results from a pilot study. Breast Cancer Res. 2005, 7: R336-344.
Maskarinec G, Lurie G, Williams AE, Le Marchand L: An investigation of mammographic density and gene variants in healthy women. Int J Cancer. 2004, 112: 683-688. 10.1002/ijc.20448.
van Duijnhoven FJ, Bezemer ID, Peeters PH, Roest M, Uitterlinden AG, Grobbee DE, van Gils CH: Polymorphisms in the estrogen receptor alpha gene and mammographic density. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2005, 14: 2655-2660. 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-05-0398.
Warren R, Skinner J, Sala E, Denton E, Dowsett M, Folkerd E, Healey CS, Dunning A, Doody D, Ponder B, Luben RN, Day NE, Easton D: Associations among mammographic density, circulating sex hormones, and polymorphisms in sex hormone metabolism genes in postmenopausal women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2006, 15: 1502-1508. 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-05-0828.
Lillie EO, Bernstein L, Ingles SA, Gauderman WJ, Rivas GE, Gagalang V, Krontiris T, Ursin G: Polymorphism in the androgen receptor and mammographic density in women taking and not taking estrogen and progestin therapy. Cancer Res. 2004, 64: 1237-1241. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-2887.
Chambo D, Kemp C, Costa AM, Souza NC, Guerreiro da Silva ID: Polymorphism in CYP17, GSTM1 and the progesterone receptor genes and its relationship with mammographic density. Brazilian journal of medical and biological research = Revista brasileira de pesquisas medicas e biologicas/Sociedade Brasileira de Biofisica [et al]. 2009, 42: 323-329.
Crandall CJ, Sehl ME, Crawford SL, Gold EB, Habel LA, Butler LM, Sowers MR, Greendale GA, Sinsheimer JS: Sex steroid metabolism polymorphisms and mammographic density in pre- and early perimenopausal women. Breast Cancer Res. 2009, 11: R51-10.1186/bcr2340.
Vachon CM, Sellers TA, Carlson EE, Cunningham JM, Hilker CA, Smalley RL, Schaid DJ, Kelemen LE, Couch FJ, Pankratz VS: Strong evidence of a genetic determinant for mammographic density, a major risk factor for breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2007, 67: 8412-8418. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1076.
Qureshi SA, Couto E, Hilsen M, Hofvind S, Wu AH, Ursin G: Mammographic density and intake of selected nutrients and vitamins in Norwegian women. Nutr Cancer. 2011, 63: 1011-1020. 10.1080/01635581.2011.605983.
Qureshi SA, Couto E, Hofvind S, Wu AH, Ursin G: Alcohol intake and mammographic density in postmenopausal Norwegian women. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012, 131: 993-1002. 10.1007/s10549-011-1812-8.
Couto E, Qureshi SA, Hofvind S, Hilsen M, Aase H, Skaane P, Vatten L, Ursin G: Hormone therapy use and mammographic density in postmenopausal Norwegian women. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012, 132: 297-305. 10.1007/s10549-011-1810-x.
Hofvind S, Geller B, Vacek PM, Thoresen S, Skaane P: Using the European guidelines to evaluate the Norwegian Breast Cancer Screening Program. Eur J Epidemiol. 2007, 22: 447-455. 10.1007/s10654-007-9137-y.
Ursin G, Ma H, Wu AH, Bernstein L, Salane M, Parisky YR, Astrahan M, Siozon CC, Pike MC: Mammographic density and breast cancer in three ethnic groups. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2003, 12: 332-338.
Stone J, Ding J, Warren RM, Duffy SW, Hopper JL: Using mammographic density to predict breast cancer risk: dense area or percentage dense area. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12: R97-10.1186/bcr2778.
IHMP. [http://www.hapmap.org]
Edlund CK, Lee WH, Li D, Van Den Berg DJ, Conti DV: Snagger: a user-friendly program for incorporating additional information for tagSNP selection. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008, 9: 174-10.1186/1471-2105-9-174.
Fransen L, Muller R, Marmenout A, Tavernier J, Van der Heyden J, Kawashima E, Chollet A, Tizard R, Van Heuverswyn H, Van Vliet A: Molecular cloning of mouse tumour necrosis factor cDNA and its eukaryotic expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985, 13: 4417-4429. 10.1093/nar/13.12.4417.
Kriegler M, Perez C, DeFay K, Albert I, Lu SD: A novel form of TNF/cachectin is a cell surface cytotoxic transmembrane protein: ramifications for the complex physiology of TNF. Cell. 1988, 53: 45-53. 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90486-2.
Yang Y, Feng R, Bi S, Xu Y: TNF-alpha polymorphisms and breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011, 129: 513-519. 10.1007/s10549-011-1494-2.
Reeves KW, Weissfeld JL, Modugno F, Diergaarde B: Circulating levels of inflammatory markers and mammographic density among postmenopausal women. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011, 127: 555-563. 10.1007/s10549-010-1249-5.
Dooley TP, Mitchison HM, Munroe PB, Probst P, Neal M, Siciliano MJ, Deng Z, Doggett NA, Callen DF, Gardiner RM: Mapping of two phenol sulphotransferase genes, STP and STM, to 16p: candidate genes for Batten disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994, 205: 482-489. 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2691.
Dumas I, Diorio C: Estrogen pathway polymorphisms and mammographic density. Anticancer research. 2011, 31: 4369-4386.
Yong M, Schwartz SM, Atkinson C, Makar KW, Thomas SS, Stanczyk FZ, Westerlind KC, Newton KM, Holt VL, Leisenring WM, Lampe JW: Associations between polymorphisms in glucuronidation and sulfation enzymes and sex steroid concentrations in premenopausal women in the United States. The J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2011, 124: 10-18. 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2010.12.014.
Mitrunen K, Hirvonen A: Molecular epidemiology of sporadic breast cancer. The role of polymorphic genes involved in oestrogen biosynthesis and metabolism. Mutat Res. 2003, 544: 9-41. 10.1016/S1383-5742(03)00016-4.
Zhao YN, Zhang W, Chen YC, Fang F, Liu XQ: Relative imbalances in the expression of catechol-O-methyltransferase and cytochrome P450 in breast cancer tissue and their association with breast carcinoma. Maturitas. 2012, 72: 139-145. 10.1016/j.maturitas.2012.03.003.
Reding KW, Weiss NS, Chen C, Li CI, Carlson CS, Wilkerson HW, Farin FM, Thummel KE, Daling JR, Malone KE: Genetic polymorphisms in the catechol estrogen metabolism pathway and breast cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2009, 18: 1461-1467. 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-08-0917.
Evans AM, Petersen JW, Sekhon GS, DeMars R: Mapping of prolactin and tumor necrosis factor-beta genes on human chromosome 6p using lymphoblastoid cell deletion mutants. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1989, 15: 203-213. 10.1007/BF01534871.
Bachelot A, Binart N: Reproductive role of prolactin. Reproduction. 2007, 133: 361-369. 10.1530/REP-06-0299.
Clevenger CV, Furth PA, Hankinson SE, Schuler LA: The role of prolactin in mammary carcinoma. Endocr Rev. 2003, 24: 1-27. 10.1210/er.2001-0036.
Touraine P, Martini JF, Zafrani B, Durand JC, Labaille F, Malet C, Nicolas A, Trivin C, Postel-Vinay MC, Kuttenn F, Kelly PA: Increased expression of prolactin receptor gene assessed by quantitative polymerase chain reaction in human breast tumors versus normal breast tissues. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998, 83: 667-674. 10.1210/jc.83.2.667.
Ginsburg E, Vonderhaar BK: Prolactin synthesis and secretion by human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1995, 55: 2591-2595.
Gill S, Peston D, Vonderhaar BK, Shousha S: Expression of prolactin receptors in normal, benign, and malignant breast tissue: an immunohistological study. J Clin Pathol. 2001, 54: 956-960. 10.1136/jcp.54.12.956.
Perks CM, Keith AJ, Goodhew KL, Savage PB, Winters ZE, Holly JM: Prolactin acts as a potent survival factor for human breast cancer cell lines. Br J Cancer. 2004, 91: 305-311.
Nyante SJ, Faupel-Badger JM, Sherman ME, Pfeiffer RM, Gaudet MM, Falk RT, Andaya AA, Lissowska J, Brinton LA, Peplonska B, Vonderhaar BK, Chanock S, Garcia-Closas M, Figueroa JD: Genetic variation in PRL and PRLR, and relationships with serum prolactin levels and breast cancer risk: results from a population-based case-control study in Poland. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13: R42-10.1186/bcr2864.
Ma H, Henderson KD, Sullivan-Halley J, Duan L, Marshall SF, Ursin G, Horn-Ross PL, Largent J, Deapen DM, Lacey JV, Bernstein L: Pregnancy-related factors and the risk of breast carcinoma in situ and invasive breast cancer among postmenopausal women in the California Teachers Study cohort. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12: R35-10.1186/bcr2589.
Hankinson SE, Willett WC, Michaud DS, Manson JE, Colditz GA, Longcope C, Rosner B, Speizer FE: Plasma prolactin levels and subsequent risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999, 91: 629-634. 10.1093/jnci/91.7.629.
Kalleinen N, Polo-Kantola P, Irjala K, Porkka-Heiskanen T, Vahlberg T, Virkki A, Polo O: 24-hour serum levels of growth hormone, prolactin, and cortisol in pre- and postmenopausal women: the effect of combined estrogen and progestin treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008, 93: 1655-1661. 10.1210/jc.2007-2677.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Norwegian Cancer Society (171743 - PR-2009-0210).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
ME carried out the statistical analyses and drafted the manuscript. EL participated in the genetic data cleaning, analysis and interpretation of data and manuscript revision. EC provided expertise in the statistical program (SAS) and cleaned all the hormone therapy variables. AO took part in the genetic statistical analyses in SAS. DVDB coordinated tagging SNP selection and performed the genotyping. SQ participated in data cleaning and acquisition of data. LA, SH and TG contributed to the analysis and interpretation of data. GU participated in the design of the study and in SNP selection, and supervised the analysis and manuscript preparation. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript and revised it critically for important intellectual content.
Electronic supplementary material
13058_2012_3142_MOESM1_ESM.XLS
Additional file 1: Table S1. Table S1 in Additional file 1. The frequency and the minor allele frequency (MAF) of the single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) evaluated and association with percent mammographic density (Beta, se, P) for all postmenopausal women (N= 2,036). This is a list of all the SNPs and the frequency and minor allele frequency in the population for all postmenopausal women. (XLS 82 KB)
13058_2012_3142_MOESM2_ESM.XLS
Additional file 2: Table S2. Table S2 in Additional file 2. Top twenty single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with percent mammographic density in postmenopausal never hormone therapy users ( N = 1,008). This is a table of the top SNPs associated with MD in never HT users, sorted by P values. (XLS 27 KB)
13058_2012_3142_MOESM3_ESM.DOC
Additional file 3: Table S3. Table S3 in Additional file 3. P values from analysis of all single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in all postmenopausal women combined, among estrogen therapy (ET) users only, and among combined estrogen and progestin therapy (EPT) users only, as well as results from interaction tests of ET users and EPT users versus never hormone therapy (HT) users. A table that presents the P values for all women and the different strata in addition to P for interaction values between HT users and non-users. (DOC 438 KB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Ellingjord-Dale, M., Lee, E., Couto, E. et al. Polymorphisms in hormone metabolism and growth factor genes and mammographic density in Norwegian postmenopausal hormone therapy users and non-users. Breast Cancer Res 14, R135 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr3337
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr3337