Abstract
Introduction
Pre-clinical data suggest p53-dependent anthracycline-induced apoptosis and p53-independent taxane activity. However, dedicated clinical research has not defined a predictive role for TP53 gene mutations. The aim of the current study was to retrospectively explore the prognosis and predictive values of TP53 somatic mutations in the BIG 02-98 randomized phase III trial in which women with node-positive breast cancer were treated with adjuvant doxorubicin-based chemotherapy with or without docetaxel.
Methods
The prognostic and predictive values of TP53 were analyzed in tumor samples by gene sequencing within exons 5 to 8. Patients were classified according to p53 protein status predicted from TP53 gene sequence, as wild-type (no TP53 variation or TP53 variations which are predicted not to modify p53 protein sequence) or mutant (p53 nonsynonymous mutations). Mutations were subcategorized according to missense or truncating mutations. Survival analyses were performed using the Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test. Cox-regression analysis was used to identify independent predictors of outcome.
Results
TP53 gene status was determined for 18% (520 of 2887) of the women enrolled in BIG 02-98. TP53 gene variations were found in 17% (90 of 520). Nonsynonymous p53 mutations, found in 16.3% (85 of 520), were associated with older age, ductal morphology, higher grade and hormone-receptor negativity. Of the nonsynonymous mutations, 12.3% (64 of 520) were missense and 3.6% were truncating (19 of 520). Only truncating mutations showed significant independent prognostic value, with an increased recurrence risk compared to patients with non-modified p53 protein (hazard ratio = 3.21, 95% confidence interval = 1.740 to 5.935, P = 0.0002). p53 status had no significant predictive value for response to docetaxel.
Conclusions
p53 truncating mutations were uncommon but associated with poor prognosis. No significant predictive role for p53 status was detected.
Trial registration
ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00174655
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
One of the commonest genetic lesions in breast cancer is mutation of the tumor suppressor gene TP53, encoding the p53 protein. p53 is a transcription factor that mediates antiproliferative mechanisms in response to various forms of cellular stresses, in particular DNA damage [1]. Different types of DNA damage activate p53 through different pathways, resulting in different responses including senescence, cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis [2].
Experimental models of breast cancer also show that mutation of p53 may confer an aggressive tumor behavior that is not seen in p53-null models [3]. Most mutant p53 proteins lose their ability to bind wild-type p53 responsive elements and to regulate the expression of p53 transcriptional targets, thus losing tumor suppressor activity. However, cellular preservation of mutated p53 may confer malignant potential such as the capacity to metastasize, through gains of function activities (reviewed in [4] Oren and Rotter, 2010).
TP53 mutation is generally associated with a poor prognosis, predicting poor disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) in breast cancer patients [5, 6]. As a predictive biomarker for treatment response, the role of p53 remains a matter of debate. More than a decade ago, p53 emerged as an important factor in the activity of DNA-damaging chemotherapies [7]. Indeed, preclinical studies suggested p53-dependent anthracycline-induced apoptosis and p53-independent taxane activity [7, 8]. Many clinical studies undertaken in the last decade have sought to validate these results. Most studies have retrospectively assessed p53 in subgroups from biologically unselected breast cancer trials [9–13]. Clinical data remains conflicting and inconclusive, and no robust predictive correlation has surfaced. An important recent study is the neoadjuvant phase III EORTC 10994/BIG 00-01 trial, which is the only study to be prospectively powered to assess the predictive role of p53 [14]. p53 status was assessed using an RNA-based technique, which detects functionally important p53 mutations using a yeast-based assay [15]. The prognostic role of p53 was confirmed, but p53 was not predictive of response or resistance to docetaxel.
The methods used to evaluate TP53 status and the diversity of observed mutations constitute sources of heterogeneity when analyzing the clinical impact of mutations. More than 75% of TP53 mutations are missense mutations that produce mutant proteins, and up to 25% of mutations are small insertions or deletions that produce truncated proteins. Determination of p53 status by immunohistochemistry (IHC) is plagued by high false-positive rates (overexpression of p53 wild-type protein), high false-negative rates (truncating mutations that stain negative), and a poor level of correlation with TP53 gene mutations [9]. IHC has been surpassed by direct DNA sequencing, functional assays in yeast and p53 genetic signatures. Studies that have used gene resequencing to assess TP53 status have produced more consistent results for the prognostic value of mutations [5, 16]. However, results of gene resequencing should be interpreted in terms of downstream p53 protein functions as TP53 gene mutations impact differently on protein functions, as evidenced in functional assays in yeast or human cells [17, 18]. Indeed, assessment of the transactivation capacity of p53 mutant proteins on different p53 target sequences has shown great variability of activities between mutant proteins and target sequences. Whereas hotspot missense mutations in the DNA-binding domain lead to a general loss of specific transactivation capacity on all target sequences, missense mutations outside the DNA-binding domain more often retain transcriptional activity on some promoters. Moreover, some mutant proteins may have dominant-negative effects on wild-type p53 or exert pro-oncogenic effects independently of wild-type p53 [19]. The TP53 Function Database created at the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), Lyon, France, allows the classification of TP53 mutations according to their predicted impact on p53 protein activities [19].
In the late 1990s, the Breast International Group (BIG) 02-98 phase III randomized trial was one of many clinical trials launched to explore the role of adjuvant taxanes in early breast cancer (http://ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00174655) [20]. Improved outcomes from the addition of taxanes to anthracycline-based therapy have been reported in many [20–25] but not all trials [26–28]. A recent meta-analysis reported superior outcomes from the addition of a taxane to anthracycline-based regimens in high-risk disease [29]. The absolute benefit deriving from the addition of taxanes is modest, less than 10% absolute improvement in DFS. A key issue for clinical practice is that despite taxane benefit for clinical trial cohorts, there is no predictive marker for the identification of individuals that are most likely to benefit from taxane.
With this background of inconsistent data for clinical utility of p53 status and absence of predictive markers for taxane use, we undertook a retrospective, exploratory analysis in BIG 02-98 to investigate the prevalence, and prognostic and predictive value of different types of TP53 mutations. Mutation classifications based on the IARC TP53 Function Database were used to estimate the functional impact of TP53 gene variations, rather than their presence per se.
Materials and methods
Study population
The current study is a retrospective study on primary tumor samples from a larger population of patients participating in the clinical trial BIG 02-98. Details of patients and methods in this trial have been described previously by Francis et al. [20]. Briefly, BIG 02-98 was a multicenter, randomized phase III adjuvant trial of 2887 women aged 18 to 70 years with operable, clinical stage T1 to T3 invasive breast adenocarcinoma, with at least one positive axillary lymph node. Between 1998 and 2001, patients were randomly assigned at a ratio of 1:1:2:2 to one of the following four adjuvant chemotherapy regimen arms: Arm A: sequential control = four cycles of doxorubicin (A) 75 mg/m2, followed by three cycles of classical cyclophosphamide, methotrexate and 5-fluorouracil (CMF); Arm AC: concurrent control = four cycles of AC 60/600 mg/m2, followed by three cycles of CMF; Arm A-T: sequential docetaxel = three cycles of A 75 mg/m2 followed by three cycles of docetaxel (T) 100 mg/m2 followed by three cycles of CMF; Arm AT: concurrent docetaxel = four cycles of AT 50/75 mg/m2 followed by three cycles of CMF. The planned cumulative doxorubicin dose was higher in the control arms (A: 300 mg/m2; AC: 240 mg/m2) than in the docetaxel arms (A-T: 225 mg/m2; AT: 200 mg/m2). A-T and AT had different docetaxel dose intensity but the same cumulative dose (300 mg/m2). Endocrine therapy and radiotherapy were administered according to local guidelines. Adjuvant trastuzumab was not available. Institutional Ethics Committees approved the protocol at all participating sites and patients provided written informed consent.
p53 substudy cohort
From BIG 02-98, patients who had formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) primary tissue submitted centrally and for which there was sufficient remaining tumor tissue for TP53 gene analysis were selected for the p53 biomarker study. A total of 666 cases were selected, of whom 520 were successfully analyzed for exons 5 to 8. The substudy population was representative of the entire BIG-02-98 population for all baseline patient and tumor characteristics. [See Additional file 1.] The translational study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Jules Bordet Institute (IJB) in Brussels, Belgium, which served as the coordinating center for this retrospective study.
Tumor material and immunohistochemistry
The study protocol requested central collection of one FFPE tumor sample for each patient. Slides were prepared by the Pathology Department at IJB and sent to the European Institute of Oncology (EIO), Milan, Italy for central pathology analyses and genomic DNA extraction. Slide review, IHC and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) were performed on whole tissue sections from FFPE samples. Tumor grade was centrally reviewed. Unstained tumor specimens were stained for estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PgR), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) and Ki-67 (all specific monoclonal or polyclonal (for HER2) antibodies were purchased from Dako, Glostrup, Denmark). IHC results were reported as the percentage of invasive tumor cells showing definite immunoreactivity. FISH was performed for HER2 according to the manufacturer's instructions (Abbott-Vysis Inc., Downers Grove, IL, USA). Thresholds for positivity were defined as: ER: ≥ 1%; PgR: ≥ 1%, HER2: IHC 3+ (more than 10% invasive tumor cells with intense and circumferential membrane staining) or 2+ and FISH positive (HER2:CEP17 ratio > 2). The Ki-67 threshold used in the distinction of luminal A and luminal B subtypes was defined as ≥ 14%, based on published work by Cheang et al. [30].
Four breast cancer subtypes were defined using central laboratory defined parameters, as follows: (1) highly endocrine responsive (luminal A): ER-positive, PgR-positive, HER2-negative and Ki-67 low; (2) incompletely endocrine responsive (luminal B): ER-positive and PgR-negative, independent of other parameters, or ER-positive, PgR-positive and at least one of grade 3, HER2-positive and/or Ki-67 high; (3) HER2-positive: ER-negative, PgR-negative and HER2-positive; and (4) triple-negative: ER-negative, PgR-negative and HER2-negative. [See Additional file 2.]
DNA extraction
Genomic DNA was extracted from two to three serial sections of FFPE-archived specimens (10 μm thick). Dewaxing was obtained by xylene and ethanol with alternating vortexing and centrifuging. DNA was then extracted with a commercially available kit (DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit, Qiagen N.V., Venlo, The Netherlands). Tissue was lysed overnight with proteinase K digestion in denaturing condition and DNA bound to spin column silica membrane. The contaminants were washed away and DNA was eluted with 100 μL of sterile distilled water. The final DNA concentration was evaluated by OD260 (GeneQuant II, Pharmacia Biotech, Uppsala, Sweden).
TP53mutation screening and sample classifications
Genomic DNA was screened for TP53 mutations at IARC. Exons 5 to 8 of TP53 were analyzed in all available samples by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Exon 4 was analyzed in a subset of samples with sufficient available tumor material. Direct sequencing of genomic DNA has been described in the IARC protocol [31]. Mutations were screened on both DNA strands and were confirmed in an independent PCR product.
TP53 gene sequencing reported all variations. These variations were used to classify samples according to p53 protein status, which take into account the predicted impact of genetic variations on p53 proteins. Thus, a variation is considered a mutation when it is predicted to modify p53 protein sequence. Tumors were classified as wild-type p53 or mutated p53. (See Table 1.)
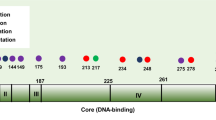
Mutated p53 protein status was further subcategorized as missense or truncating. (See Table 1.) Missense mutations produce proteins that are changed by one amino acid. Truncating mutations include nonsense, frameshift insertions and deletions, and variations in consensus splice sites. Annotations from the IARC TP53 Database [19] were used to also stratify missense mutations according to their transactivation activities in yeast functional assays, or to their position inside or outside DNA-binding motifs (L1/L2/L3 loops) [17, 32]. Sample subclassification was done when sequencing result was obtained for all exons 5 to 8. Two samples were not subclassified because the sequencing result was missing for one exon.
Statistical analyses
The study was based on the hypotheses that p53 mutated tumors would have the worst clinical outcome and the largest benefit from the addition of docetaxel. Statistics were performed using SAS version 9.1. (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) and Minitab version 13 software (Minitab Inc., State College, PA, USA). The chi-square test was used to compare the distributions of clinicopathological parameters by randomized treatment arm (anthracycline control arms, A and AC, versus taxane arms, A-T and AT), and by p53 status (wild-type p53 versus p53 mutated). Fisher's exact test was used to compare the distributions of clinicopathological parameters by p53 mutation subcategorization (wild-type p53 versus missense mutation; wild-type p53 versus truncating mutation).
DFS was calculated from the date of randomization to the date of disease recurrence, second primary cancer or death from any cause. OS was calculated from the date of randomization to the date of last follow-up or death from any cause. Survival curves were estimated using the method of Kaplan-Meier and curves for different classifications were compared using the log-rank test. Multivariate Cox regression models, with backward selection, were used to test the prognostic effect of p53 status after adjusting for other important prognostic variables. Multivariate DFS analysis included patient characteristics (age, menopausal status, body mass index (BMI)), tumor characteristics (tumor size, number of positive lymph nodes, histopathological type, histological grade, IHC defined subtypes, p53 mutation status) and treatment characteristics (mastectomy, radiotherapy, use of tamoxifen, chemotherapy arm (A+AC versus A-T+AT arms), chemotherapy schedule (sequential or concurrent)).
Results
Results of BIG 02-98
After an 8-year median follow-up, the second efficacy results of BIG 02-98 did not show significant improvement in DFS from the incorporation of docetaxel compared with the doxorubicin-based control (hazard ratio (HR) = 0.91, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 0.80 to 1.05, P = 0.187). However, sequential A-T significantly improved DFS compared with the sequential control arm A (HR = 0.81, 95% CI = 0.67 to 0.99, P = 0.036), and significantly improved both DFS (HR = 0.84, 95% CI = 0.72 to 0.99, P = 0.035) and OS (HR = 0.79, 95% CI = 0.65 to 0.98, P = 0.028) compared with concurrent AT [33].
p53 substudy cohort
From BIG 02-98, 2172 of 2887 (75%) patients had FFPE primary tissue submitted centrally. Of these 2172 patients, 666 patients had sufficient remaining tumor tissue for TP53 gene analysis, of whom 520 (18% of the original trial population) were successfully analyzed for exons 5 to 8. Of the 520 tumors, 116 were also analyzed for exon 4. The remaining 142 samples could not be analyzed due to poor DNA quality.
The substudy population was representative of entire BIG-02-98 population for all baseline patient and tumor characteristics. [See Additional file 1.] DFS was similar for patients included and not included in this substudy. [See Additional file 3.]
The majority of patients in this p53 substudy were less than 50 years old, premenopausal and nonobese. (See Table 2.) Most tumors were infiltrating ductal carcinoma, ≤ 20 mm, grade 2 or 3, ER-positive and HER2-negative. Regarding the IHC-defined breast cancer subtypes, most tumors were classified as luminal B, of which, 59 were positive for HER2 (19%, not shown). Between the control (A + AC) and docetaxel (A-T + AT) arms, characteristics differed for ER/PgR status and IHC-defined subtypes: a significantly higher proportion of ER- and PgR-negative tumors were present in the control arms (P = 0.046). In keeping with this, there was a trend for a higher proportion of the HER2 subtype and triple-negative subtype in the control arms (P = 0.052).
p53 mutations and sample characteristics
A total of 96 variations within exon 5 to 8 were found in 90 samples (90 of 520, 17%). [See Additional file 4 for full data.] In the 90 patients with a TP53 gene variation, 85 patients had only one variation, four patients had two variations, and one patient had three variations. Most variations were missense and were located at classical hotspot codons, except for one specific mutation at codon 259 (p.D259N) that was found in six samples. It is of note that no in-frame deletions or insertions were found in these series. In the patient with three gene variations, each of the three variations was located in introns and was predicted to not affect protein sequence (not shown).
TP53 gene status was used to predict p53 protein status and classify patients as wild-type or mutated. Nonsynonymous mutations were further distinguished as missense or truncating. (See Table 1.)
The presence of a mutated p53 protein was associated with older age, postmenopausal status, ductal morphology, higher tumor grades and ER/PgR negativity. (See Table 3.) A strong correlation between IHC-defined subtypes and p53 status was found: the proportion of p53 mutated samples in each IHC subtype showed that the HER2 and triple-negative subtypes had the highest rates of p53 mutations, with 22% (7 of 32) and 36% (24 of 66) of mutated samples respectively, compared to 10% (8 of 84) in the luminal A subtype and 13% (45 of 315) in the luminal B subtype.
Prognostic value of p53 mutations
At an 8-year median follow-up, the number of DFS events in the entire BIG 02-98 population was 916 of 2887 patients (32%). In this p53 substudy cohort, the number of DFS events was 164 of 520 patients (32%). Survival curves (DFS and OS) for patients included in this p53 substudy are shown in Figure 1. There was no statistically significant difference in DFS or OS based on p53 mutated status. However, when subclassifying mutations, truncating mutations but not missense mutations were found to be associated with a significant reduction in DFS and OS (P < 0.001). Further stratification of missense mutations, based on their transactivation capacities or location in the 3D structure of p53 protein, did not reveal classes of mutations with different prognostic value (data not shown). Thus, in univariate analysis only p53 truncating mutations were associated with poor survival.
Multivariate DFS analysis was performed including patient characteristics (age, menopausal status, BMI), tumor characteristics (tumor size, number of positive lymph nodes, histopathological type, histological grade, IHC-defined subtypes, p53 mutation status) and treatment characteristics (mastectomy, radiotherapy, use of tamoxifen, chemotherapy arm (A+AC versus A-T+AT arms), chemotherapy schedule (sequential or concurrent)). The presence of p53 truncating mutations was associated with an increased risk of recurrence (HR = 3.21, 95% CI 1.74 to 5.94, P = 0.0002) compared to the absence of mutation within exons 5 to 8. In this multivariate model, only p53 truncating mutations, number of positive lymph nodes (≥ 4 nodes: HR = 1.99, 95% CI: 1.44 to 2.76, P < 0.0001) and the HER2 subtype (HR = 2.36, 95% CI 1.21 to 4.60, P = 0.0122) had independent prognostic value. (See Table 4.)
Similar results were obtained for OS. In a multivariate OS analysis, p53 truncating mutations were associated with poor OS compared to the absence of mutation within exons 5 to 8 (HR = 2.75, 95% CI: 1.50 to 5.04, P = 0.0011).
Predictive value of p53 status
In keeping with efficacy results in the entire BIG 02-98 population, this substudy population showed a favorable trend but not a significant benefit in DFS from the addition of docetaxel (HR = 0.77, 95% CI: 0.56 to 1.06). Analyses of the predictive value of p53 status for prediction of improvement in DFS from addition of docetaxel are shown in Figure 2a (p53 wild-type and mutant) and Figure 2b (p53 wild-type, missense and truncating mutations). None of these predictive analyses were statistically significant.
Value of p53 mutations in predicting DFS benefit from adding docetaxel to control anthracycline-based therapy. (a) Wild-type p53 versus mutant p53 protein. (b) p53 wild-type versus missense mutant versus truncated mutant. Treatment comparisons were made between (i) anthracycline control arms (A+AC) and sequential docetaxel (A-T); (ii) anthracycline control arms (A+AC) and concurrent docetaxel (AT); and (iii) anthracycline control arms (A+AC) and combined docetaxel arms (A-T+AT). A, doxorubicin; C, cyclophosphamide; DFS, disease-free survival; T, docetaxel.
Discussion
In this retrospective exploratory study performed on samples collected in the context of the prospective BIG 02-98 randomized phase III clinical trial, we show that p53 truncating mutations have a significant independent prognostic value in node-positive breast cancer patients treated with adjuvant chemotherapy. However, no significant value for p53 status in predicting response to docetaxel therapy was found in this cohort.
TP53 mutations were detected in a minority of patients (16.3%). Most mutations (75%) were missense, while the remaining (22%) were truncating. The prevalence and type of TP53 mutations found are similar with previous studies that have restricted their analysis to exons 5 to 8 and used DNA as starting material (73% of missense mutation in IARC TP53 Database, R15). The presence of mutated p53 was associated with patient characteristics of increased age and postmenopausal status, and tumor characteristics of ductal morphology, higher grades and ER/PR negativity, in agreement with previous studies [5, 34, 35]. The highest rates of mutations were seen in the HER2 and triple-negative subtypes, as reported in other studies [12, 36, 37].
Most mutations were found at classical hotspot codons and were loss of function mutations as assessed in yeast functional assays [17]. The only exception was a specific hotspot at codon 259, which was found in six samples. The resulting mutation, p.D259N, has been infrequently reported in human cancers (only 14 occurrences in the IARC TP53 Database, none in breast cancers [19]) and retains partial activity in yeast functional assays [17]. We ruled out PCR contamination and technical causation. The origin of this mutation remains to be determined.
Truncating mutations had an independent prognostic value against a large range of clinical and molecular variables. These results confirm and extend those obtained in previous studies, including our own performed on a large consecutive series of breast cancers [5]. Interestingly, missense mutations were not associated with poor survival in the current study. Discrimination between missense mutations according to location inside or outside DNA-binding motifs, mutations that retain or do not retain transactivation activities, or have dominant-negative effects did not differentiate missense mutations with poorer survival (data not shown). This is in contrast with our previous study, which showed that missense mutations within DNA-binding motifs (but not those outside these motifs) and non-missense mutations were associated with poor prognosis [5]. There was no obvious difference between the type of missense mutation found in this series and earlier studies to explain these discrepant results. Inconsistency of results regarding the prognostic value of missense mutations across studies may be due to the fact that missense mutations may retain some activity, beyond the specific activity detectable in a particular study. This is in contrast to more consistent results for truncating mutations, which are true loss of function mutations.
The multivariate model for the prognostic value of p53 included many variables, notably it included BMI- and IHC-defined molecular subtypes. BMI was included as obesity was found to have an independent poor prognostic value in this trial as well as in other studies [38, 39]. In this substudy however, BMI had no independent prognostic value. The independent predictors of poor DFS and OS were p53 truncating mutations, high number of positive lymph nodes and the HER2 subtype. It is of note that BIG 02-98 was conducted prior to the use of adjuvant HER2-targeted therapies. The prognostic value of HER2 subtype is thus independent of HER2-targeted treatment in these patients. Interestingly, the triple-negative subtype did not have prognostic value in the univariate analysis and had no independent prognostic value. Many studies in early breast cancer have reported that the triple-negative subtype is particularly aggressive and associated with a high rate of recurrence and early death. A possible explanation for the lack of adverse outcomes in the triple-negative subtype in the current study may be the limited sample size.
In this study, p53 mutations had no significant predictive value. This study adds to the conflicting body of clinical evidence regarding the potential clinical role of p53 as a single biomarker for prediction of chemotherapy response. Other studies assessing TP53 gene sequence have presented data in support of reduced anthracycline activity in TP53 mutated tumors [9–11]. However, the predictive correlations were not robust enough for TP53 gene status, as a single biomarker, to be considered a clinical tool to guide treatment decisions. Three recent neoadjuvant studies in early breast cancer have reported a predictive role for TP53 mutations. In a phase II Xeloda in Neoadjuvant (XeNa) trial assessing capecitabine and docetaxel, with trastuzumab if HER2-positive, a secondary study endpoint was evaluation of TP53 status and response to chemotherapy [12]. TP53 mutations, detected by AmpliChip p53 (Roche Diagnostics, Pleasanton, CA, USA), correlated significantly with improved pathological complete response rate compared with TP53 wild-type (30% versus 10%, respectively, P = 0.0032). In a study using dose-dense epirubicin-cyclophosphamide, TP53 mutations were detected using a yeast functional assay. Pathological complete responses, which occurred in 19% (15 of 80 patients), were restricted to tumors with a TP53 mutation (28 of 80 patients) [40]. In another small study that included only triple-negative breast cancers patients treated with neoadjuvant cisplatin, nonsense and frameshift TP53 mutations were associated with good response to treatment [41]. The lack of a control arm in these three studies limits interpretation of prognosis versus prediction, and of general versus specific agent chemosensitivity.
An important recent study is the neoadjuvant phase III EORTC 10994/BIG 00-01 trial which is the only study to be prospectively powered to assess the value of p53 status for prediction of docetaxel benefit [14]. Using an RNA-based technique that detects functionally important p53 mutations, the prognostic role of p53 was confirmed, but p53 was not predictive of response or resistance to docetaxel.
The negative results from the prospective EORTC study and our BIG 02-98 substudy, with a background of inconsistent results, suggest that p53 status as an isolated marker may be inadequate to predict treatment response to docetaxel. p53 is not a drug target, but rather a surrogate measure for cellular capacity for apoptosis, and cell proliferation control. The complexity of p53 function, post-transcriptional effects and up- and down-stream signaling pathway cross-talks may limit the power of p53 status as a sole biomarker, in particular for treatments that combine drugs that have different mode of action towards p53.
A strength of the current study is the biological distinction of nonsynonymous mutations as missense (in and out of DNA-binding motifs) and truncating. Grouping all mutations together for assessment of outcomes assumes homogeneity in the impact of different mutations. Use of a dichotomous classification did not identify a prognostic or predictive correlation, whereas the more specific classification system revealed the independent prognostic significance value of the truncating mutations. A limitation of this approach however, is that such a cohort contain few patients, limiting to some degree the confidence with which conclusions may be drawn for the subsets.
The presumption of a homogeneous role of p53 across diverse biological subgroups may also account for inconsistent findings. In distinct breast cancer subgroups, p53 mutations may have variable prevalence, and impact differently on prognosis and treatment sensitivity. As part of the I-SPY neoadjuvant initiative (CALGB 150007), a recent study reported TP53 status determined by gene chip technology and sequencing in women treated with anthracycline- then taxane-based therapy [42]. In the luminal A subtype, 14 of 48 patients has a TP53 mutation, and there was no differential efficacy of either treatment based on TP53 status. In contrast, TP53 mutations had a much higher prevalence in the luminal B, basal-like and HER2 subgroups, in whom, anthracycline efficacy was independent of TP53 status and taxane efficacy was greater in the presence of wild-type TP53. In the current study, mutated p53 was indeed more prevalent in HER2 and triple-negative subtypes. However, small numbers precluded analyses by subgroups.
A critical issue in the clinical translation of p53 is the impact of gene variations on p53 protein function. Herein the classification of p53 mutations was based on estimated downstream impact on protein sequence. A reported alternative for identification of 'functional' loss of wild-type p53 is a p53 transcriptional fingerprint. Several gene expression signatures have been reported that distinguish between wild-type and mutant p53 [36, 43, 44]. Interestingly some TP53 wild-type tumors expressing the mutation-associated 32-gene signature behaved aggressively, while some TP53 mutant tumors lacking the signature had favorable outcome [43]. In another recent report, a 39-gene and a 30-gene p53 signature were developed in ER-positive and -negative breast cancer, respectively [45]. It is of note that there was no overlap in genes across the two signatures. The ER-positive p53 signature in ER-positive disease was predictive of poor prognosis and increased chemosensitivity. The ER-negative p53 signature in ER-negative disease was associated with improved prognosis, but had no prediction of treatment response. Downstream functional assessment of p53 status may also capture the impact of other p53 variables that may influence tumor outcome and treatment sensitivity, such as p53 codon polymorphisms [46] and p53 protein isoforms [47]. Further studies using downstream functional assessment of p53 status are thus needed to better understand the impact of p53 mutations on tumor phenotype.
The current study has limitations. This is a retrospective exploratory analysis, which was not considered in the initial statistical trial design or trial sample size determination. In the trial, all patients received polychemotherapy so it is impossible to determine interactions between single-agent activity and p53 status. Only exons 5 to 8 of TP53 gene were screened for mutation due to the limited amount of DNA available. According to previous studies, up to 20% of mutations may fall outside these exons (IARC TP53 Database, R15). To evaluate the number of misclassified samples due to this partial sequencing, 84 samples were successfully sequenced for exon 4, the next most mutated exon in breast cancers (IARC TP53 Database, R15). One truncating and 13 missense mutations were found. Since all missense mutations retained transactivation activity, only 1 of 84 (1.2%) was considered a true deleterious mutation. As mutations in other exons are expected to be rare (less than 1% of mutations reported in breast cancers fall outside exons 4 to 8), we estimate that less than 2% of samples may have been misclassified as wild-type in our series.
Conclusions
Despite an abundant literature on the prognostic and predictive value of p53 status in breast cancer, a limited number of studies have used gene sequencing to assess p53 status and even fewer studies have been performed in the context of controlled clinical trials. The results confirm that loss of wild-type p53 through protein truncating mutations is associated with poor prognosis. Our results point to differences in the prognostic value of different types of mutations and to the difficulty of assessing the predictive value of a molecular marker in treatment regimens that combine drugs with different modes of action regarding this marker.
Abbreviations
- A:
-
doxorubicin
- BIG:
-
Breast International Group
- BMI:
-
body mass index
- C:
-
cyclophosphamide
- CI:
-
confidence interval
- DFS:
-
disease-free survival
- EIO:
-
European Institute of Oncology
- ER:
-
estrogen receptor
- F:
-
5-fluorouracil
- FFPE:
-
formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded
- FISH:
-
fluorescence in situ hybridization
- HER2:
-
human epidermal growth factor receptor 2
- HR:
-
hazard ratio
- IARC:
-
International Agency for Research on Cancer
- IHC:
-
immunohistochemistry
- IJB:
-
Institut Jules Bordet
- M:
-
methotrexate
- OS:
-
overall survival
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- PgR:
-
progesterone receptor
- T:
-
docetaxel.
References
Levine AJ: p53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell. 1997, 88: 323-331. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81871-1.
Vousden KH, Prives C: Blinded by the light: the growing complexity of p53. Cell. 2009, 137: 413-431. 10.1016/j.cell.2009.04.037.
Lang GA, Iwakuma T, Suh YA, Liu G, Rao VA, Parant JM, Valentin-Vega YA, Terzian T, Caldwell LC, Strong LC, El-Naggar AK, Lozano G: Gain of function of a p53 hot spot mutation in a mouse model of Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Cell. 2004, 119: 861-872. 10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.006.
Oren M, Rotter V: Mutant p53 gain-of-function in cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010, 2: a001107-10.1101/cshperspect.a001107.
Olivier M, Langerød A, Carrieri P, Bergh J, Klaar S, Eyfjord J, Theillet C, Rodriguez C, Lidereau R, Bièche I, Varley J, Bignon Y, Uhrhammer N, Winqvist R, Jukkola-Vuorinen A, Niederacher D, Kato S, Ishioka C, Hainaut P, Børresen-Dale AL: The clinical value of somatic TP53 gene mutations in 1,794 patients with breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2006, 12: 1157-1167. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1029.
Pharoah PD, Day NE, Caldas C: Somatic mutations in the p53 gene and prognosis in breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Br J Cancer. 1999, 80: 1968-1973. 10.1038/sj.bjc.6690628.
O'Connor PM, Jackman J, Bae I, Myers TG, Fan S, Mutoh M, Scudiero DA, Monks A, Sausville EA, Weinstein JN, Friend S, Fornace AJ, Kohn KW: Characterization of the p53 tumor suppressor pathway in cell lines of the National Cancer Institute anticancer drug screen and correlations with the growth-inhibitory potency of 123 anticancer agents. Cancer Res. 1997, 57: 4285-4300.
Wahl A, Donaldson K, Fairchild C, Lee FY, Foster SA, Demers GW, Galloway DA: Loss of normal p53 function confers sensitization to Taxol by increasing G2/M arrest and apoptosis. Nat Med. 1996, 2: 72-79. 10.1038/nm0196-72.
Kandioler-Eckersberger D, Ludwig C, Rudas M, Kappel S, Janschek E, Wenzel C, Schlagbauer-Wadl H, Mittlböck M, Gnant M, Steger G, Jakesz R: TP53 mutation and p53 overexpression for prediction of response to neoadjuvant treatment in breast cancer patients. Clin.Cancer Res. 2000, 6: 50-56.
Geisler S, Lonning PE, Aas T, Johnsen H, Fluge O, Haugen DF, Lillehaug JR, Akslen LA, Børresen-Dale AL: Influence of TP53 gene alterations and c-erbB-2 expression on the response to treatment with doxorubicin in locally advanced breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2001, 61: 2505-2512.
Di Leo A, Tanner M, Desmedt C, Paesmans M, Cardoso F, Durbecq V, Chan S, Perren T, Aapro M, Sotiriou C, Piccart MJ, Larsimont D, Isola J, TAX 303 translational study team: p-53 gene mutations as a predictive marker in a population of advanced breast cancer patients randomly treated with doxorubicin or docetaxel in the context of a phase III clinical trial. Ann Oncol. 2007, 18: 997-1003. 10.1093/annonc/mdm075.
Glück S, Ross JS, Royce M, McKenna EF, Perou CM, Avisar E, Wu L: TP53 genomics predict higher clinical and pathologic tumor response in operable early-stage breast cancer treated with docetaxel-capecitabine ± trastuzumab. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012, 132: 781-911. 10.1007/s10549-011-1412-7.
Lara JF, Thor AD, Dressler LG, Broadwater G, Bleiweiss IJ, Edgerton S, Cowan D, Goldstein LJ, Martino S, Ingle JN, Henderson IC, Norton L, Winer EP, Hudis CA, Ellis MJ, Berry DA, Hayes DF, Cancer and Leukemia Group B: p53 Expression in node-positive breast cancer patients: results from the cancer and leukemia group B 9344 trial (159905). Clin Cancer Res. 2011, 17: 5170-5178. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0484.
Bonnefoi H, Piccart M, Bogaerts J, Mauriac L, Fumoleau P, Brain E, Petit T, Rouanet P, Jassem J, Blot E, Zaman K, Cufer T, Lortholary A, Lidbrink E, André S, Litière S, Lago LD, Becette V, Cameron DA, Bergh J, Iggo R, EORTC 10994/BIG 1-00 Study Investigators: TP53 status for prediction of sensitivity to taxane versus non-taxane neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer (EORTC 10994/BIG 1-00): a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12: 527-539. 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70094-8.
Bonnefoi H, Ducraux A, Movarekhi S, Pelte MF, Bongard S, Lurati E, Iggo R: p53 as a potential predictive factor of response to chemotherapy: feasibility of p53 assessment using a functional test in yeast from trucut biopsies in breast cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 2002, 86: 750-755. 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600105.
Olivier M, Hainaut P, Borresen-Dale A: Prognostic and predictive value of TP53 mutations in human cancer. 25 years of p53 research. Edited by: Hainaut P, Wiman K. 2005, The Netherlands: Springer, 321-338.
Kato S, Han SY, Liu W, Otsuka K, Shibata H, Kanamaru R, Ishioka C: Understanding the function-structure and function-mutation relationships of p53 tumor suppressor protein by high-resolution missense mutation analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003, 100: 8424-8429. 10.1073/pnas.1431692100.
Resnick MA, Inga A: Functional mutants of the sequence-specific transcription factor p53 and implications for master genes of diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003, 100: 9934-9939. 10.1073/pnas.1633803100.
IARC TP53 Database. [http://www-p53.iarc.fr/]
Francis P, Crown J, Di Leo A, Buyse M, Balil A, Andersson M, Nordenskjöld B, Lang I, Jakesz R, Vorobiof D, Gutiérrez J, van Hazel G, Dolci S, Jamin S, Bendahmane B, Gelber RD, Goldhirsch A, Castiglione-Gertsch M, Piccart-Gebhart M, BIG 02-98 Collaborative Group: Adjuvant chemotherapy with sequential or concurrent anthracycline and docetaxel: Breast International Group 02-98 randomized trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008, 100: 121-133. 10.1093/jnci/djm287.
Henderson IC, Berry DA, Demetri GD, Cirrincione CT, Goldstein LJ, Martino S, Ingle JN, Cooper MR, Hayes DF, Tkaczuk KH, Fleming G, Holland JF, Duggan DB, Carpenter JT, Frei E, Schilsky RL, Wood WC, Muss HB, Norton L: Improved outcomes from adding sequential paclitaxel but not from escalating doxorubicin dose in an adjuvant chemotherapy regimen for patients with node-positive primary breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2003, 21: 976-983. 10.1200/JCO.2003.02.063.
Mamounas EP, Bryant J, Lembersky B, Fehrenbacher L, Sedlacek SM, Fisher B, Wickerham DL, Yothers G, Soran A, Wolmark N: Paclitaxel after doxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide as adjuvant chemotherapy for node-positive breast cancer: results from NSABP B-28. J Clin Oncol. 2005, 23: 3686-3696. 10.1200/JCO.2005.10.517.
Roché H, Fumoleau P, Spielmann M, Canon JL, Delozier T, Serin D, Symann M, Kerbrat P, Soulié P, Eichler F, Viens P, Monnier A, Vindevoghel A, Campone M, Goudier MJ, Bonneterre J, Ferrero JM, Martin AL, Genève J, Asselain B: Sequential adjuvant epirubicin-based and docetaxel chemotherapy for node-positive breast cancer patients: the FNCLCC PACS 01 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2006, 24: 5664-5671. 10.1200/JCO.2006.07.3916.
Martin M, Pienkowski T, Mackey J, Pawlicki M, Guastalla JP, Weaver C, Tomiak E, Al-Tweigeri T, Chap L, Juhos E, Guevin R, Howell A, Fornander T, Hainsworth J, Coleman R, Vinholes J, Modiano M, Pinter T, Tang SC, Colwell B, Prady C, Provencher L, Walde D, Rodriguez-Lescure A, Hugh J, Loret C, Rupin M, Blitz S, Jacobs P, Murawsky M, Riva A, Vogel C, Breast Cancer International Research Group 001 Investigators: Adjuvant docetaxel for node-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005, 352: 2302-2313. 10.1056/NEJMoa043681.
Martín M, Seguí MA, Antón A, Ruiz A, Ramos M, Adrover E, Aranda I, Rodríguez-Lescure A, Grosse R, Calvo L, Barnadas A, Isla D, Martinez del Prado P, Ruiz Borrego M, Zaluski J, Arcusa A, Muñoz M, López Vega JM, Mel JR, Munarriz B, Llorca C, Jara C, Alba E, Florián J, Li J, López García-Asenjo JA, Sáez A, Rios MJ, Almenar S, Peiró G, Lluch A, GEICAM 9805 Investigators: Adjuvant docetaxel for high-risk, node-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010, 363: 2200-2210. 10.1056/NEJMoa0910320.
Fountzilas G, Skarlos D, Dafni U, Gogas H, Briasoulis E, Pectasides D, Papadimitriou C, Markopoulos C, Polychronis A, Kalofonos HP, Siafaka V, Kosmidis P, Timotheadou E, Tsavdaridis D, Bafaloukos D, Papakostas P, Razis E, Makrantonakis P, Aravantinos G, Christodoulou C, Dimopoulos AM: Postoperative dose-dense sequential chemotherapy with epirubicin, followed by CMF with or without paclitaxel, in patients with high-risk operable breast cancer: a randomized phase III study conducted by the Hellenic Cooperative Oncology Group. Ann Oncol. 2005, 16: 1762-1771. 10.1093/annonc/mdi366.
Goldstein LJ, O'Neill A, Sparano JA, Perez EA, Shulman LN, Martino S, Davidson NE: Concurrent doxorubicin plus docetaxel is not more effective than concurrent doxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide in operable breast cancer with 0 to 3 positive axillary nodes: North American Breast Cancer Intergroup Trial E 2197. J Clin Oncol. 2008, 26: 4092-4099. 10.1200/JCO.2008.16.7841.
Ellis P, Barrett-Lee P, Johnson L, Cameron D, Wardley A, O'Reilly S, Verrill M, Smith I, Yarnold J, Coleman R, Earl H, Canney P, Twelves C, Poole C, Bloomfield D, Hopwood P, Johnston S, Dowsett M, Bartlett JM, Ellis I, Peckitt C, Hall E, Bliss JM, TACT Trial Management Group; TACT Trialists: Sequential docetaxel as adjuvant chemotherapy for early breast cancer (TACT): an open-label, phase III, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2009, 373: 1681-1692. 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60740-6.
De Laurentiis M, Cancello G, D'Agostino D, Giuliano M, Giordano A, Montagna E, Lauria R, Forestieri V, Esposito A, Silvestro L, Pennacchio R, Criscitiello C, Montanino A, Limite G, Bianco AR, De Placido S: Taxane-based combinations as adjuvant chemotherapy of early breast cancer: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. J Clin Oncol. 2008, 26: 44-53. 10.1200/JCO.2007.11.3787.
Cheang MC, Chia SK, Voduc D, Gao D, Leung S, Snider J, Watson M, Davies S, Bernard PS, Parker JS, Perou CM, Ellis MJ, Nielsen TO: Ki67 index, HER2 status, and prognosis of patients with luminal B breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009, 101: 736-750. 10.1093/jnci/djp082.
IARC TP53 Database - Detection of TP53 mutations by direct sequencing.
Petitjean A, Mathe E, Kato S, Ishioka C, Tavtigian SV, Hainaut P, Olivier M: Impact of mutant p53 functional properties on TP53 mutation patterns and tumor phenotype: lessons from recent developments in the IARC TP53 database. Hum Mutat. 2007, 28: 622-629. 10.1002/humu.20495.
Di Leo A, Francis P, Crown JP, de Azambuja E, Quinaux E, Gutierrez J, Nordenskjold B, Andersson M, Margeli Vila M, Piccart-Gebhart M, Jakesz R, Viale G, Olsen S: Overall survival benefit for sequential doxorubicin-docetaxel compared to concomitant doxorubicin and docetaxel in node-positive breast cancer. 8-yr. results of the Breast International Group (BIG) 2-98 phase III adjuvant trial [abstract]. Cancer Res. 2009, 69: s601-
Bull SB, Ozcelik H, Pinnaduwage D, Blackstein ME, Sutherland DA, Pritchard KI, Tzontcheva AT, Sidlofsky S, Hanna WM, Qizilbash AH, Tweeddale ME, Fine S, McCready DR, Andrulis IL: The combination of p53 mutation and neu/erbB-2 amplification is associated with poor survival in node-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004, 22: 86-96.
Powell B, Soong R, Iacopetta B, Seshadri R, Smith DR: Prognostic significance of mutations to different structural and functional regions of the p53 gene in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2000, 6: 443-451.
Langerød A, Zhao H, Borgan Ø, Nesland JM, Bukholm IR, Ikdahl T, Kåresen R, Børresen-Dale AL, Jeffrey SS: TP53 mutation status and gene expression profiles are powerful prognostic markers of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2007, 9: R30-10.1186/bcr1675.
Turpin E, Bièche I, Bertheau P, Plassa LF, Lerebours F, de Roquancourt A, Olivi M, Espié M, Marty M, Lidereau R, Vidaud M, de Thé H: Increased incidence of ERBB2 overexpression and TP53 mutation in inflammatory breast cancer. Oncogene. 2002, 21: 7593-7597. 10.1038/sj.onc.1205932.
de Azambuja E, McCaskill-Stevens W, Francis P, Quinaux E, Crown JP, Vicente M, Giuliani R, Nordenskjöld B, Gutiérez J, Andersson M, Vila MM, Jakesz R, Demol J, Dewar J, Santoro A, Lluch A, Olsen S, Gelber RD, Di Leo A, Piccart-Gebhart M: The effect of body mass index on overall and disease-free survival in node-positive breast cancer patients treated with docetaxel and doxorubicin-containing adjuvant chemotherapy: the experience of the BIG 02-98 trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010, 119: 145-153. 10.1007/s10549-009-0512-0.
Ryu SY, Kim CB, Nam CM, Park JK, Kim KS, Park J, Yoo SY, Cho KS: Is body mass index the prognostic factor in breast cancer?: a meta-analysis. J Korean Med Sci. 2001, 16: 610-614.
Bertheau P, Turpin E, Rickman DS, Espié M, de Reyniès A, Feugeas JP, Plassa LF, Soliman H, Varna M, de Roquancourt A, Lehmann-Che J, Beuzard Y, Marty M, Misset JL, Janin A, de Thé H: Exquisite sensitivity of TP53 mutant and basal breast cancers to a dose-dense epirubicin-cyclophosphamide regimen. PLoS Med. 2007, 4: e90-10.1371/journal.pmed.0040090.
Silver DP, Richardson AL, Eklund AC, Wang ZC, Szallasi Z, Li Q, Juul N, Leong CO, Calogrias D, Buraimoh A, Fatima A, Gelman RS, Ryan PD, Tung NM, De Nicolo A, Ganesan S, Miron A, Colin C, Sgroi DC, Ellisen LW, Winer EP, Garber JE: Efficacy of neoadjuvant Cisplatin in triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010, 28: 1145-1153. 10.1200/JCO.2009.22.4725.
Pradhan SM, Carey L, Edmiston S, Hylton N, Parrish E, Moore D, Conway K, I-SPY Clinical Investigators: P53 mutation and differential response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in women with locally advanced breast cancer: results from the I-SPY trial (CALGB 150007/1500012 and ACRIN 6657) [abstract]. J Clin Oncol. 2009, 27: s11099-
Miller LD, Smeds J, George J, Vega VB, Vergara L, Ploner A, Pawitan Y, Hall P, Klaar S, Liu ET, Bergh J: An expression signature for p53 status in human breast cancer predicts mutation status, transcriptional effects, and patient survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005, 102: 13550-13555. 10.1073/pnas.0506230102.
Troester MA, Herschkowitz JI, Oh DS, He X, Hoadley KA, Barbier CS, Perou CM: Gene expression patterns associated with p53 status in breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2006, 6: 276-10.1186/1471-2407-6-276.
Coutant C, Rouzier R, Qi Y, Lehmann-Che J, Bianchini G, Iwamoto T, Hortobagyi GN, Symmans WF, Uzan S, Andre F, de Thé H, Pusztai L: Distinct p53 gene signatures are needed to predict prognosis and response to chemotherapy in ER-positive and ER-negative breast cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2011, 17: 2591-2601. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1045.
He XF, Su J, Zhang Y, Huang X, Liu Y, Ding DP, Wang W, Arparkorn K: Association between the p53 polymorphisms and breast cancer risk: meta-analysis based on case-control study. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011, 130: 517-529. 10.1007/s10549-011-1583-2.
Bourdon JC, Khoury MP, Diot A, Baker L, Fernandes K, Aoubala M, Quinlan P, Purdie CA, Jordan LB, Prats AC, Lane DP, Thompson AM: p53 mutant breast cancer patients expressing p53γ have as good a prognosis as wild-type p53 breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13: R7-10.1186/bcr2811.
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by a grant from the Association for International Cancer Research (AICR, UK), and the Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC, Milan, Italy).
The authors would like to thank all the investigators and staff at the participating institutions, team members in the BrEAST Data Centre and BIG Headquarters and, above all, the patients, without whom the BIG 02-98 study would not have been possible.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
Prudence A. Francis: conference travel support from Sanofi-Aventis. Martine Piccart-Gebhart: Institut Jules Bordet has numerous contracts in which Dr. Piccart-Gebhart is an investigator (Sanofi-Aventis, Amgen, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roche, Glaxo SK, Boehringer, PharmaMar). All other authors declare they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
LF-C participated in the study design; undertook TP53 gene mutation screening; and participated in the drafting of the manuscript. CO participated in the study design; performed data analysis; and drafted the manuscript. PF-L participated in TP53 gene mutation screening. KS participated in TP53 gene mutation screening. EQ participated in the study design; performed the statistical analysis; and drafted the manuscript. MB participated in the design of the study and performed the statistical analysis. MSD participated in the study design and coordination; performed data analysis; participated in the statistical analysis; and drafted the manuscript. EDA participated in the study design and coordination; performed data analysis; and drafted the manuscript. PH has given final approval of the version to be published. PD performed the central pathology analyses, DNA extraction, slide review, IHC and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). DL supervised the central laboratory; and tissue and slide preparation. PAF conceived of the original trial design and co-ordination; performed data analysis; and drafted the manuscript. JC conceived of the original trial design and co-ordination; performed data analysis; and drafted the manuscript. MP-G conceived of the original trial design and co-ordination; performed data analysis; and drafted the manuscript. GV participated in the study design and coordination; undertook central pathology analyses, slide review, IHC and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH); performed DNA extraction, performed data analysis; and drafted the manuscript. ADL conceived the original trial design and co-ordination; performed data analysis; and drafted the manuscript. MO designed and coordinated the p53 sub-study, supervised TP53 sequencing, performed analysis and interpretation of data; and drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Lynnette Fernández-Cuesta, Catherine Oakman contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
13058_2011_2977_MOESM1_ESM.PDF
Additional file 1: Table S1, Characteristics of patients analyzed for TP53 mutations compared with the entire BIG-02-98 cohort. From BIG 02-98, 666 patients with centrally submitted FFPE primary tissue and sufficient remaining tumor tissue for TP53 gene analysis were selected for the p53 biomarker study. Of these, 520 tumors were successfully analyzed for exons 5-8. This table contains baseline patient and tumor characteristics, showing that the substudy population was representative of the entire BIG-02-98 population. (PDF 61 KB)
13058_2011_2977_MOESM2_ESM.PDF
Additional file 2: Table S2, Immunohistochemistry (IHC) subtypes as defined in this study. Four breast cancer subtypes (luminal A, luminal B, HER2-positive and triple-negative) were defined using central laboratory defined parameters (ER, PgR, HER2, grade and Ki-67). (PDF 52 KB)
13058_2011_2977_MOESM3_ESM.PDF
Additional file 3: Figure S1, Representativeness of the p53 cohort: disease-free survival for patients included in the p53 substudy and patients not included in the p53 substudy from the BIG 02-98 trial. Kaplan-Meier curve confirming similar disease-free survival for BIG 02-98 patients included and not included in this substudy. (PDF 24 KB)
13058_2011_2977_MOESM4_ESM.PDF
Additional file 4: Table S3, TP53 gene variations found in the p53 substudy. From 520 analyzed tumors, 96 variations within exon 5 to 8 were found in 90 samples (90 of 520, 17%). This table lists TP53 gene variation data for the 90 samples. Eighty-five patients had only one variation, four patients (ID: 10120, 10202, 42618, 62514) had two variations, and one patient had three variations (ID: 22205). (PDF 104 KB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Fernández-Cuesta, L., Oakman, C., Falagan-Lotsch, P. et al. Prognostic and predictive value of TP53mutations in node-positive breast cancer patients treated with anthracycline- or anthracycline/taxane-based adjuvant therapy: results from the BIG 02-98 phase III trial. Breast Cancer Res 14, R70 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr3179
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr3179