Chapter summary
Understanding of how interactions between genes and environment contribute to the development of arthritis is a central issue in understanding the etiology of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), as well as for eventual subsequent efforts to prevent the disease. In this paper, we review current published data on genes and environment in RA as well as in certain induced animal models of disease, mainly those in which adjuvants only or adjuvants plus organ-specific autoantigens are used to induce arthritis. We refer to some new data on environmental and genetic factors of importance for RA generated from a large case–control study in Sweden (1200 patients, 1200 matched controls). We found an increased risk of seropositive but not of seronegative RA in smokers, and there are indications that this effect may be due to a gene–environment interaction involving MHC class II genes. We also found an increased risk of RA in individuals heavily exposed to mineral oils. This was of particular interest because mineral oils are strong inducers of arthritis in certain rodent strains and because polymorphisms in human genetic regions syntenic with genes predisposing for oil-induced arthritis in rats have now been shown to associate with RA in humans. Taken together, our data support the notion that concepts and data on gene-environment interactions in arthritis can now be taken from induced animal models of arthritis to generate new etiological hypotheses for RA.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction and historical background
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a condition that is today defined from a set of rather arbitrarily built criteria; those criteria have been very helpful in identifying an entity for which new therapies can be investigated, and such therapies have lately been amazingly successful [1–4]. Despite the continuing successes in developing therapies, the underlying etiology of the disease, i.e. what eventually triggers it and what genetic context allows it to progress, have remained elusive. Consequently, only vague and often scientifically unproven thoughts have been prevalent in the public as well as in the professional arena when ways of achieving primary or secondary prevention of the disease are being considered.
In parallel, it has often been claimed that the disease is so complicated and multifaceted that it may be an insurmountable task to elucidate the interactions between genes and environment that ultimately determine whether arthritis will occur and persist.
In one way, this situation of rapidly emerging new genetic technologies in genetics but prevalent vague ideas of etiology recalls the situation in the late 1980s, when new knowledge in the field of molecular immunology was paralleled by a rather vague understanding of the molecular pathology of RA. It was frequently claimed then that the situation was far too complicated to permit targeted therapy against single components of the immune system, such as tumor necrosis factor.
Taking the dramatic demonstration in recent years that complicated problems such as finding targeted therapies for RA can indeed be resolved by less complicated solutions than hitherto for unravelling the remaining difficult questions, we have contemplated the issue of gene–environment interactions in RA and subsequent preventive strategies towards the disease as being a reasonable research effort to discuss at the current symposium and in this supplement to Arthritis Research.
What is currently known about genes and environment in the development of RA?
Knowledge about environmental influences on the development of RA are of two kinds. The first – circumstantial – kind of knowledge is derived from twin and kinship studies, which all indicate that the genetic influence is important but probably less influential than environmental effects. Concordance between monozygotic twins with regard to RA has been reported to be between 10% and 15% [5], or even lower [6]. The second – more direct – kind of knowledge derives from case–control or cohort studies on the influence of distinct agents or events on RA, in which exposure to a number of agents have been reported to be associated with RA. Such agents include smoking, which has been shown to be a risk factor in several studies [7, 8], silica [9, 10] and blood transfusion [11]. Taken together, the knowledge of environmental agents predisposing to RA remains rudimentary. Virtually no molecular mechanisms have been proposed for how such agents may work, and no work has been presented to show that agents associated with RA in humans cause arthritis in an animal model of RA.
Although genetic influences on RA have been more extensively studied than environmental effects, current knowledge is nevertheless sketchy, even with regard to the most studied genetic region, the major histocompatibility complex (MHC). Thus, it has been shown that different MHC alleles are associated with RA in different populations [12], and also that the degree of association between a certain allele and RA varies depending on which population of RA patients is selected. That the arthritis denoted RA is associated with certain HLA-DR4 alleles in studies on White populations from the USA or Western Europe but with other alleles in Japanese or Jewish populations [12] clearly indicates that other genes interact with the MHC genes in mediating the susceptibility to arthritis.
The demonstration of only a moderate association between HLA-DRB1*0401 in a group of RA patients from a population-based survey [13] but a much higher association in RA populations in hospital settings indicates that HLA-DRB1*0401 may be as much a severity factor as a susceptibility factor. Because the association between MHC class II alleles and RA is the most convincing evidence of a role of HLA-DR restricted T-cell activation in the pathogenesis of RA, these studies also indicate that there is a marked heterogeneity within an RA population as to the role of such T-cell activation, which is smaller in early, mild arthritis.
Other genes contributing to susceptibility to RA have so far been sought mainly in cytokine-associated genes. Several associations have been described between functionally relevant cytokine promotor genes and RA [14–17]. Also, the wide genome scans that have been reported from North America and Europe have suggested that gene regions outside the MHC may be relevant, though the relevant genes within these regions have not yet been identified.
Finally, very few efforts have hitherto been directed towards the investigation of the interactions between genes and environment in the pathogenesis of RA. The rest of this review is concerned with a discussion of how such investigations may be conducted, given the current knowledge of genes and environment and given that leads regarding both potential environmental triggers and genes important for disease may be derived from relevant animal models.
What are relevant animal models for RA, and how can these be used to generate concepts about gene–environment interactions in arthritis?
In the light of the background given above, there are four prerequisites for relevant animal models for RA. First, the disease should be inducible by nonspecific triggers (comparable with cigarette smoking or silica exposure in humans). In addition, the models must be characterized by certain genetic contexts in which MHC class II genes may act as both susceptibility and severity factors. They should also be highly variable in disease course, which should often involve tissue destruction and chronicity. And finally, they should sometimes but not always involve autoimmune reactions towards both cartilage-specific and ubiquitously expressed autoantigens.
Here we restrict ourselves to describing a number of such models in the rat, as that species appears to offer models for several chronic inflammatory diseases that are more similar to the comparable disease in man than is the case in mouse models [18]. Two basic features are critical to the understanding of the arthritis models in the rat. First, triggers can be of several different kinds, including both nonspecific 'nonimmunogenic' substances – such as glucans (from yeast), lipopolysaccharides (from bacteria), squalene (endogenous) or mineral oil (exogenous) [19, 20] – and more specific cartilage-derived antigens such as collagen II or cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) [18, 21] (for an overview, see Table 1). In some strains, exposure to one of the nonspecific stimuli (given intracutaneously or sometimes even percutaneously) may by itself cause arthritis [22–24], whereas in others, stimulation with both nonspecific stimuli and cartilage-derived molecules are prerequisites for the development of arthritis [25]. In some typical situations, the addition of anticarti-lage immunity to the effects of nonspecific stimuli may change the course of the disease from monophasic and nondestructive in character to chronic and destructive.
The second feature of the rat models is the involvement of many polymorphic genes in determining the character of the disease course after a given stimulus. Thus, a non-specific stimulus may produce a monophasic, nondestructive disease in one strain but a chronic, relapsing–remitting, severely destructive disease in another [26]. Interestingly, it has recently been shown that certain sets of genes may be most instrumental in determining the overall susceptibility to disease, while other sets may preferentially determine the chronicity and still others may determine destructiveness. Taken together, these findings show that there is no single disease phenotype associated with one given triggering agent. Rather, both exposure to simple stimulating adjuvants and combinations of adjuvants and autoantigens can give rise to a highly variable disease course, depending on the overall genetic make-up.
In recent years, polymorphic genes determining the phenotype of arthritis in rats have been studied quite intensively and a number of gene regions have been identified that influence susceptibility to arthritis and the destructiveness and severity of the disease. Further production of inbred strains, congenic for small parts of the identified candidate gene regions, have permitted the identification of smaller gene regions that appear to contain the respective susceptibility or severity genes [20]. An interesting aspect of this work is that the same genetic context that predisposes for development of adjuvant arthritis induced by single compounds (oil, pristane, squalene) also predisposes to the development of collagen-induced arthritis, in which the additional presence of certain MHC class II genes is mandatory for the development of disease [20, 26–28].
It thus appears that a certain set of genes may determine the response of the innate immune system to adjuvants, sometimes resulting in arthritis without the addition of further stimuli. The addition of a specific immunity to self-antigens such as collagen will in these cases make the arthritis more severe and destructive. In other genetic contexts, the combination of immunity to self-antigens and a still strong and genetically determined response to adjuvants is necessary to induce disease. Such a multiple-hit mode would explain why similar sets of 'adjuvant-associated' genes influence development of both adjuvant arthritis and collagen-induced arthritis, and how, in addition, mainly MHC-related genes influence the development of collagen-induced arthritis. So far, no single susceptibility gene has been definitely identified using this method, but research in the field is moving so rapidly that this could happen soon.
Taken together, these animal data indicate that exposure to nonspecific triggers affecting mainly the innate immune system may in certain genetic contexts suffice to induce arthritis, whereas in other genetic contexts participation of the adaptive immune system is mandatory. In addition, it is reasonable to believe that different combinations of these mechanisms may be important in different phases of arthritis development.
Can concepts of mechanisms, potential triggers and potential candidate genes generated in experimental rodent models be meaningfully transferred and tested in humans?
A classic question in research on all inflammatory humans diseases is whether experience from animal models is at all relevant and valuable for the human diseases, in particular when defined triggers are used in animals, and where almost nothing is known about whether there are triggers in humans, and if there are, what they might be. The alternative in human disease, however, would be to be restricted to whole-genome scans in the search for relevant disease genes, and to a very unfocused investigation of environmental factors in the search for potential triggers of disease. In the face of this choice, we have set out to study both candidate genes and environmental factors, taking our lead from the animal experience discussed in the previous section.
Thus, a case–control study has been initiated in Sweden, using an ongoing population-based, multicenter surveillance program for early incident cases of RA as the basis for identification of cases, and a well-established system for identification of controls matched for age, sex and area of residence (P Stolt et al., manuscript submitted for publication). For these individuals, both cases and controls, extensive information has been accumulated about environmental exposure preceding the onset of arthritis for cases and during a comparable period for controls. Also, blood samples for genotyping, serology and other laboratory investigations have been accumulated from cases as well as controls at the time of onset for cases (and the same time for controls). The future strategy is obviously to test potential effects of environmental agents in a conventional case–control setting and simultaneously to try to use information about synteny between rodent (here rat) genes and human genes to identify relevant candidate genes or candidate gene regions for RA. Polymorphisms within these candidate regions should be investigated as to their influence both on susceptibility to RA and on the course of the disease. So far, the research team has accumulated 1200 cases and 1200 controls and has started to test the viability of the approach.
The first environmental exposure we set out to investigate was smoking, which has previously been shown to be a risk factor for RA, although quantification of the risk has been somewhat ambiguous and we do not know whether the risk is in any way confined to individuals with a certain genetic make-up. The first investigation (P Stolt et al., manuscript submitted for publication) thus showed a significantly increased relative risk of RA in ever-smokers compared with never-smokers (RR = 1.5), that this risk was confined to individuals who smoked for a long time, and that smoking was a risk factor only for rheumatoid-factor (RF)-positive RA, but not for RF-negative RA. The latter observations suggested that there might be a sequence of events whereby smoking induces production of RF, which in turn contributes to the development of RA. The other – and not exclusive – possibility would be that RF positivity is merely a marker for a certain genotype, and that mainly individuals with this genotype would have an increased risk of RA after smoking. As RF-positive RA has in several studies been linked to presence of certain HLA-DR allotypes, mainly the 'shared epitope', we thus also stratified our patients according to whether they were shared epitope (SE)-positive. The increased relative risk of developing RA in smokers was restricted to the group of individuals who carried the SE genes (L Padyukov et al., manuscript in preparation). Although still confined to results from a subanalysis of the first 500 patients investigated in our RA cohort, this preliminary finding may be the first documentation of a gene–environment interaction in development of RA, and thereby it may also be of value in supporting the general scope of our research approach.
A second striking finding in our analysis of odds ratios for the development of RA after various environmental exposures relates to mineral oils. An odds ratio of 1.9 was found for individuals exposed to hydraulic oils (almost all men). Because exposure to mineral oil by subcutaneous injection or the percutaneous route was previously shown to induce arthritis in certain rodent strains (see above), this observation in RA suggests that disease mechanisms similar to those in rodents may be involved in some cases of RA. We have not yet been able to investigate to what extent the risk associated with this exposure to oil is restricted to individuals with a certain genetic constitution. However, a recent family study in the UK showed an increased risk of RA in individuals carrying a certain allelic form of a gene region on human chromosome 17, defined by means of synteny with a genetic region that determines susceptibility to oil-induced arthritis in rats [29, 30]. This observation is, as far as we know, the first to identify a gene region of importance for the development of RA following leads from animal studies on non-MHC arthritis susceptibility gene regions.
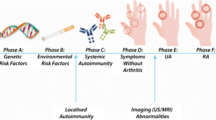
Hopefully, these two observations may pave the way for a future investigation of whether exposure to oil confers an even higher risk of RA in individuals carrying certain alleles of this 17q region, but, more importantly, may also make possible functional studies of how a particular potential trigger of arthritis influences the immune system in individuals carrying a certain set of susceptibility genes (see summary picture of strategy in Fig. 1).
When and in which patients is there a role for organ-specific autoimmunity?
The animal model studies indicate that specific autoimmune reactions to organ-specific antigen, such as collagen II, may contribute to both the onset and the severity of arthritis, but that this phenomenon is restricted to individuals carrying specific MHC class II alleles. Transferred to the human situation, such findings indicate that specific immunity to organ-specific antigens should be performed in the context of genetic characterization of subgroups of patients. So far, this has been done to some extent for collagen II and on a very small scale for other organ-restricted antigens.
However, an immune response to collagen II in both T and B cells has been reported in individuals carrying the SE genes, albeit at a rather low frequency [31–33]. Furthermore, HLA-DRB1*0401 transgenic mice have been shown to be susceptible to collagen-induced arthritis and to mount a strong immune response to collagen II [34]. Taken together, these data thus indicate that collagen autoimmunity may after all contribute to arthritis in a genetically defined subset of RA patients. The identification of this subset by genetic and other means may permit us to investigate further which environmental and genetic factors favor the onset of a collagen immunity, and also to investigate how collagen immunity may add to the effects of other agents, for example adjuvants, in making RA more severe (Fig. 2 presents a hypothetical model of this situation).
Concluding remarks
We provide arguments for, but not really against, the use of data and ideas generated in induced animal models to generate viable research strategies to study gene–environment interaction of importance for human arthritis. Privileged by the opportunity to contribute to a volume on arthritis research in connotation with one of the most importance breakthroughs in therapy of RA, we have felt it possible to present this unbalanced but hopefully productive view on how to attack still underlying fundamental problems in rheumatology. We believe that the encouragement given to rheumatology from the progress in therapeutics will greatly help us in solving also these further questions about origin and potential future prevention of the disease.
Glossary of terms
RF = rheumatoid factor; SE = shared epitope.
References
Elliott MJ, Maini RN, Feldmann M, Kalden JR, Antoni C, Smolen JS, Leeb B, Breedveld FC, Macfarlane JD, Bijl H, et al: Ran-domised double-blind comparison of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor alpha (cA2) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1994, 344: 1105-1110. 10.1016/S0140-6736(94)90628-9.
Maini RN, Breedveld FC, Kalden JR, Smolen JS, Davis D, Macfarlane JD, Antoni C, Leeb B, Elliott MJ, Woody JN, Schaible TF, Feldmann M: Therapeutic efficacy of multiple intravenous infusions of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody combined with low-dose weekly methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998, 41: 1552-1563. 10.1002/1529-0131(199803)41:3<565::AID-ART28>3.3.CO;2-#.
Lipsky PE, van der Heijde DM, St Clair EW, Furst DE, Breedveld FC, Kalden JR, Smolen JS, Weisman M, Emery P, Feldmann M, Harriman GR, Maini RN: Infliximab and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Trial in Rheumatoid Arthritis with Concomitant Therapy Study Group. N Engl J Med. 2000, 343: 1594-1602. 10.1056/NEJM200011303432202.
Bathon JM, Martin RW, Fleischmann RM, Tesser JR, Schiff MH, Keystone EC, Genovese MC, Wasko MC, Moreland LW, Weaver AL, Markenson J, Finck BK: A comparison of etanercept and methotrexate in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2000, 343: 1586-1593. 10.1056/NEJM200011303432201.
MacGregor AJ, Snieder H, Rigby AS, Koskenvuo M, Kaprio J, Aho K, Silman AJ: Characterizing the quantitative genetic contribution to rheumatoid arthritis using data from twins. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43: 30-37. 10.1002/1529-0131(200001)43:1<30::AID-ANR5>3.0.CO;2-B.
Svendsen AJ, Holm NV, Kyvik K, Petersen PH, Junker P: Relative importance of genetic effects in rheumatoid arthritis: historical cohort study of Danish nationwide twin population. BMJ. 2002, 324: 264-10.1136/bmj.324.7332.264.
Uhlig T, Hagen KB, Kvien TK: Current tobacco smoking, formal education, and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1999, 26: 47-54.
Reckner Olsson A, Skogh T, Wingren G: Comorbidity and lifestyle, reproductive factors, and environmental exposures associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001, 60: 934-939. 10.1136/ard.60.10.934.
Klockars M, Koskela RS, Jarvinen E, Kolari PJ, Rossi A: Silica exposure and rheumatoid arthritis: a follow up study of granite workers 1940–81. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1987, 294: 997-1000.
Turner S, Cherry N: Rheumatoid arthritis in workers exposed to silica in the pottery industry. Occup Environ Med. 2000, 57: 443-447. 10.1136/oem.57.7.443.
Symmons DP, Bankhead CR, Harrison BJ, Brennan P, Barrett EM, Scott DG, Silman AJ: Blood transfusion, smoking, and obesity as risk factors for the development of rheumatoid arthritis: results from a primary care-based incident case-control study in Norfolk, England. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40: 1955-1961.
Nepom GT: Major histocompatibility complex-directed susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Adv Immunol. 1998, 68: 315-332.
Silman AJ, Hennessy E, Ollier B: Incidence of rheumatoid arthritis in a genetically predisposed population. Br J Rheumatol. 1992, 31: 365-368.
Cantagrel A, Navaux F, Loubet-Lescoulie P, Nourhashemi F, Enault G, Abbal M, Constantin A, Laroche M, Mazieres B: Interleukin-1beta, interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, interleukin-4, and interleukin-10 gene polymorphisms: relationship to occurrence and severity of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1999, 42: 1093-1100. 10.1002/1529-0131(199906)42:6<1093::AID-ANR5>3.0.CO;2-P.
van Krugten MV, Huizinga TW, Kaijzel EL, Zanelli E, Drossaers-Bakker KW, van de Linde P, Hazes JM, Zwinderman AH, Breedveld FC, Verweij CL: Association of the TNF +489 polymorphism with susceptibility and radiographic damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Genes Immun. 1999, 1: 91-96. 10.1038/sj.gene.6363632.
Waldron-Lynch F, Adams C, Amos C, Zhu DK, McDermott MF, Shanahan F, Molloy MG, O'Gara F: Tumour necrosis factor 5' promoter single nucleotide polymorphisms influence susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in immunogenetically defined multiplex RA families. Genes Immun. 2001, 2: 82-87. 10.1038/sj/gene/6363738.
Yamada R, Tanaka T, Unoki M, Nagai T, Sawada T, Ohnishi Y, Tsunoda T, Yukioka M, Maeda A, Suzuki K, Tateishi H, Ochi T, Nakamura Y, Yamamoto K: Association between a single-nucleotide polymorphism in the promoter of the human interleukin-3 gene and rheumatoid arthritis in Japanese patients, and maximum-likelihood estimation of combinatorial effect that two genetic loci have on susceptibility to the disease. Am J Hum Genet. 2001, 68: 674-685. 10.1086/318789.
Larsson P, Kleinau S, Holmdahl R, Klareskog L: Homologous type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Characterization of the disease and demonstration of clinically distinct forms of arthritis in two strains of rats after immunization with the same collagen preparation. Arthritis Rheum. 1990, 33: 693-701.
Lorentzen JC, Erlandsson H, Mussener A, Mattsson L, Kleinau S, Nyman U, Klareskog L: Specific and long-lasting protection from collagen-induced arthritis and oil-induced arthritis in DA rats by administration of immunogens. Scand J Immunol. 1995, 42: 82-89.
Holm BC, Xu HW, Jacobsson L, Larsson A, Luthman H, Lorentzen JC: Rats made congenic for Oia3 on chromosome 10 become susceptible to squalene-induced arthritis. Hum Mol Genet. 2001, 10: 565-572. 10.1093/hmg/10.6.565.
Carlsen S, Hansson AS, Olsson H, Heinegard D, Holmdahl R: Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP)-induced arthritis in rats. Clin Exp Immunol. 1998, 114: 477-484. 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00739.x.
Kleinau S, Erlandsson H, Holmdahl R, Klareskog L: Adjuvant oils induce arthritis in the DA rat. I. Characterization of the disease and evidence for an immunological involvement. J Autoimmun. 1991, 4: 871-880.
Sverdrup B, Klareskog L, Kleinau S: Common commercial cosmetic products induce arthritis in the DA rat. Environ Health Perspect. 1998, 106: 27-32.
Griffiths MM, Cannon GW, Leonard PA, Reese VR: Induction of autoimmune arthritis in rats by immunization with homologous rat type II collagen is restricted to the RT1av1 haplotype. Arthritis Rheum. 1993, 36: 254-258.
Lorentzen JC, Olsson T, Klareskog L: Susceptibility to oil-induced arthritis in the DA rat is determined by MHC and non-MHC genes. Transplant Proc. 1995, 27: 1532-1534.
Griffiths DJ: Rheumatoid arthritis: a viral aetiology?. Hosp Med. 2000, 61: 378-379.
Joe B, Remmers EF, Dobbins DE, Salstrom JL, Furuya T, Dracheva S, Gulko PS, Cannon GW, Griffiths MM, Wilder RL: Genetic dissection of collagen-induced arthritis in Chromosome 10 quantitative trait locus speed congenic rats: evidence for more than one regulatory locus and sex influences. Immuno-genetics. 2000, 51: 930-944. 10.1007/s002510000231.
Dahlman I, Lorentzen JC, de Graaf KL, Stefferl A, Linington C, Luthman H, Olsson T: Quantitative trait loci disposing for both experimental arthritis and encephalomyelitis in the DA rat; impact on severity of myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and antibody isotype pattern. Eur J Immunol. 1998, 28: 2188-2196. 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199807)28:07<2188::AID-IMMU2188>3.3.CO;2-2.
Barton A, Eyre S, Myerscough A, Brintnell B, Ward D, Ollier WE, Lorentzen JC, Klareskog L, Silman A, John S, Worthington J: High resolution linkage and association mapping identifies a novel rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility locus homologous to one linked to two rat models of inflammatory arthritis. Hum Mol Genet. 2001, 10: 1901-1906. 10.1093/hmg/10.18.1901.
Lorentzen JC, Glaser A, Jacobsson L, Galli J, Fakhrai-rad H, Klareskog L, Luthman H: Identification of rat susceptibility loci for adjuvant-oil-induced arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998, 95: 6383-6387. 10.1073/pnas.95.11.6383.
Ronnelid J, Lysholm J, Engstrom-Laurent A, Klareskog L, Heyman B: Local anti-type II collagen antibody production in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid. Evidence for an HLA-DR4-restricted IgG response. Arthritis Rheum. 1994, 37: 1023-1029.
Berg L, Ronnelid J, Sanjeevi CB, Lampa J, Klareskog L: Interferon-gamma production in response to in vitro stimulation with collagen type II in rheumatoid arthritis is associated with HLA-DRB1(*)0401 and HLA-DQ8. Arthritis Res. 2000, 2: 75-84. 10.1186/ar71.
Tarkowski A, Klareskog L, Carlsten H, Herberts P, Koopman WJ: Secretion of antibodies to types I and II collagen by synovial tissue cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1989, 32: 1087-1092.
Sønderstrup G, Cope AP, Patel S, Congia M, Hain N, Hall FC, Parry SL, Fugger LH, Michie S, McDevitt HO: HLA class II trans-genic mice: models of the human CD4+ T-cell immune response. Immunol Rev. 1999, 172: 335-343.
Acknowledgements
Our studies referred to here were financially supported by the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Rheumatism Association, King Gustaf V:s 80 years Foundation, the insurance company AFA and the Karolinska Institutet. The participants in the EIRA study group, in particular Dr Patrik Stolt, are gratefully acknowledged for generously sharing their data with us.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klareskog, L., Lorentzen, J., Padyukov, L. et al. Genes and environment in arthritis: can RA be prevented?. Arthritis Res Ther 4 (Suppl 3), S31 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1186/ar566
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/ar566