Abstract
Introduction
Our previous study has reported that, in patients with untreated new-onset lupus (UNOL), there was an abnormal increase in the number of CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells that correlated with disease activity and significantly decreased after treatment. However, little is known about the nature of this cell entity. The aim of this study was to explore the nature of abnormally increased CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells in UNOL patients.
Methods
The expressions of surface (CD4, CD25, CD127, chemokine receptor 4 [CCR4], glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor [GITR], and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 [CTLA-4]) and intracellular (Foxp3) molecules as well as cytokine synthesis of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from 22 UNOL patients were analyzed by flow cytometry. The proliferative and suppressive capacities of different T-cell subgroups from UNOL patients were also assessed.
Results
In UNOL patients, the percentages of CD127low/- in CD25high, CD25low, and CD25- subpopulations of CD4+Foxp3+ T cells were 93.79% ± 3.48%, 93.66% ± 2.31%, and 91.98% ± 2.14%, respectively (P > 0.05), whereas the expressions of Foxp3 showed significant differences in CD25high (91.38% ± 2.57%), CD25low (71.89% ± 3.31%), and CD25- (9.02% ± 2.21%) subpopulations of CD4+CD127low/- T cells (P < 0.01). The expressions of surface CCR4, GITR, and CTLA-4 on CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells were significantly less than CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ T cells (P < 0.05). Moreover, unlike CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ T cells, CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells also synthesized interferon-gamma, interleukin (IL)-4, IL-2, and IL-17 (P < 0.05), though less than CD4+CD25+Foxp3- T cells. The suppressive capacity was most prominent in CD4+CD25highCD127low/-, followed by CD4+CD25lowCD127low/-. CD4+CD25-CD127- T cells showed the least suppressive capacity, which was similar to the effector T cells.
Conclusions
CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells in UNOL patients are different from regulatory T cells, both phenotypically and functionally. CD127 is not an appropriate surface marker for intracellular Foxp3 in CD4+CD25- T cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a systemic autoimmune disease characterized by polyclonal activation of B and T lymphocytes. It remains controversial whether the frequency and function of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) are altered in SLE patients [1]. In our previous study, we found that, in patients with untreated new-onset lupus (UNOL), there was an abnormal increase in the number of CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells (instead of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs) that correlated with disease activity and significantly decreased after glucocorticoid treatment [2]. As Foxp3 is currently thought to be one of the best markers for naturally occurring Tregs (nTregs), it is intriguing to explore the nature of this abnormally increased cell entity in UNOL patients.
To answer this question requires direct functional assay and indirect phenotypic analysis. The crucial step of function assay is to find a proper surface substitute for intracellular Foxp3 in CD4+CD25- T cells. A study has suggested that low expression of CD127 (receptor alpha chain of interleukin-7 [IL-7]) could be used as a surface marker for intracellular Foxp3 in human CD4+CD25+ Tregs [3]. Whether this is still true in CD4+CD25- T cells remains to be defined.
Other cell surface molecules, including glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor (GITR), cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4), and chemokine receptor 4 (CCR4), have been investigated in Tregs. GITR has been found to be increased on CD4+CD25+ Tregs and plays a key role in dominant immunological self-tolerance [4, 5]. CTLA-4 is also predominantly expressed on CD4+CD25+ Tregs from thymus and peripheral blood and participates in the maintenance of immunologic self-tolerance [6]. Another cell surface molecule, CCR4, is selectively expressed on Th2-type cells and Tregs [7–9]. Foxp3-transduced naïve CD4+CD25- T cells have increased expression of CCR4 and obtain suppressive function as CD4+CD25+ Tregs [10].
Following our report, a recent study declared that these CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells functionally resembled conventional Tregs by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) CD4+CD25-CD127- T cells as a substitute for CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells from SLE patients [11]. In our current study, however, by analyzing the correlation of CD127 and Foxp3 on CD4+CD25-, CD4+CD25low, and CD4+CD25high T cells, we found that, unlike in CD4+CD25high T cells, CD127low/- was not a perfect surface marker for intracellular Foxp3 in CD4+CD25- T cells; therefore, CD4+CD25-CD127low/- T cells could not be used as a live substitute for CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells to perform functional assay. We then set out to examine surface expressions of GITR, CTLA-4, and CCR4 and (importantly) cytokine synthesis function of CD4+CD25-Foxp3+, CD4+CD25+Foxp3+, and CD4+CD25+Foxp3- T cells. We found that CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells in UNOL patients are different from Tregs, both phenotypically and functionally.
Materials and methods
Patients and healthy controls
Twenty-two UNOL patients of Chinese ethnicity (19 women and 3 men) were recruited in this study. All patients fulfilled the SLE classification criteria of the American College of Rheumatology. The mean age was 27.8 ± 9.1 years, and disease duration was 42 ± 28 days. Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index (SLEDAI) was 9.3 ± 5.2. Twenty-five gender- and age-matched healthy volunteers were involved as healthy controls. This study was approved by the ethics committee of Peking Union Medical College Hospital, and informed consent was obtained from each patient and healthy volunteer.
Antibodies
Except as otherwise indicated, the monoclonal antibodies and reagents were obtained from eBioscience, Inc. (San Diego, CA, USA): fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated anti-human CD4 (L3T4), PEcy5-conjugated anti-human CD25 (IL-2R), phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated anti-human GITR, PE-conjugated anti-human CTLA-4, allophycocyanin-conjugated anti-human Foxp3, and PE-conjugated anti-human IL-17 and their respective isotype controls. PEcy7-conjugated CCR4, PE-conjugated anti-human interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), PE-conjugated anti-human IL-2, and PE-conjugated anti-human IL-4 and their matched isotype controls were purchased from BD Pharmingen (San Diego, CA, USA).
Preparation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells and cell culture
Peripheral blood was collected, and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were prepared by Ficoll-Hypaque density gradient centrifugation. For intracellular cytokine staining, freshly isolated PBMCs were cultured in complete RPMI 1640 media (Invitrogen Ltd., Paisley, UK) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (HyClone, Logan, UT, USA), 100 U/mL penicillin, and 100 μg/L streptomycin, as well as 20 ng/mL phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and 500 ng/mL ionomycin (Sigma-Aldrich), in the presence of 10 μg/mL Brefeldin A (BD Pharmingen) in a humidified CO2-containing atmosphere at 37°C for 6 hours.
Flow cytometry analysis
PBMCs were washed in phosphate-buffered saline containing 2% fetal calf serum and 0.09% NaN3. Cells (1 × 106) were incubated with FITC-CD4 (20 μL) and PEcy5-CD25 (20 μL) and with PEcy7-CCR4 (5 μL), PE-GITR (20 μL), or PE-CTLA4 (20 μL) at 4°C for 30 minutes. Subsequently, cells were perforated, and intracellular staining for Foxp3 and for PE-anti-IFN-γ (20 μL), PE-anti-IL-4 (20 μL), PE-anti-IL-2 (20 μL), or PE-anti-IL-17 (20 μL) was performed according to the instructions of the manufacturer. Stained cells were then analyzed by a FACScanto (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA).
Functional assays
For the assessment of T-cell proliferation, FACS-sorted CD4+CD25-CD127+, CD4+CD25highCD127low/-, CD4+CD25lowCD127low/-, and CD4+CD25-CD127- from PBMCs of UNOL patients were stimulated by soluble anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody (200 ng/mL) in U-bottom 96-well plates. For the assessment of suppressive function of different T-cell subpopulations, 5 × 104 CD4+CD25highCD127low/-, CD4+CD25lowCD127low/-, or CD4+CD25-CD127- T cells were respectively cultured in the presence of CD4+CD25-CD127+ T cells (cell ratio 1:1) and irradiated PBMCs (1 × 105) in RPMI 1640 plus 10% fetal calf serum at 37°C in a humidified CO2-containing atmosphere for 72 hours. CCK-8 solution was added, and optical density value was measured 4 hours later.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 13.0 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Numbers of CD4+ subpopulations were compared using the Student t test. A P value of less than 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
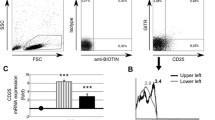
Correlations of CD127 and Foxp3 expressions on CD4+CD25-, CD4+CD25low, and CD4+CD25highT cells from UNOL patients
CD4+ T cells were divided into three subgroups by CD25 expression: CD4+CD25high, CD4+CD25low, and CD4+CD25- T cells. We gated CD127low/- expression on Foxp3+ T cells and backgated Foxp3 expression on CD127low/- T cells, respectively. We found that all CD4+Foxp3+ T cells had a low expression level of CD127, regardless of CD25 expression. Percentages of CD127low/- in CD25high, CD25low, and CD25- subpopulations of CD4+Foxp3+ T cells were 93.79% ± 3.48%, 93.66% ± 2.31%, and 91.98% ± 2.14%, respectively (P > 0.05) (Figure 1). On the other hand, the expressions of Foxp3 on CD4+CD127low/- T cells showed significant differences in CD25high (91.38% ± 2.57%), CD25low (71.89% ± 3.31%), and CD25- (9.02% ± 2.21%) subpopulations (P < 0.01) (Figure 2). Foxp3 expressions in CD4+CD127low/- T cells were high in CD25high but low in CD25- subpopulations. This result suggested that, unlike in CD4+CD25high T cells, CD127low/- was not a perfect candidate surface marker for intracellular Foxp3 in CD4+CD25- T cells and that CD4+CD25-CD127low/- T cells could not be used as a live substitute for CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells to perform functional assay.
Expressions of GITR, CTLA-4, CCR4 and effector T cell-related cytokines on CD4 + subpopulations from UNOL patients
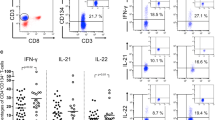
Expressions of GITR, CTLA-4, CCR4, and effector T cell-related cytokines (IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-2, and IL-17) on CD4+CD25-Foxp3+, CD4+CD25+Foxp3-, CD4+CD25+Foxp3+, and CD4+CD25-Foxp3-T cells from UNOL patients and healthy controls
As shown in Table 1 and Figure 3, in UNOL patients, there was no significant difference between CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ and CD4+CD25+Foxp3- T cells in the expressions of GITR, CTLA-4, and CCR4 (P > 0.05), whereas they were both less than CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ T cells (P < 0.01). Moreover, the expressions of effector T cell (Teff)-related cytokines, including IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-2, and IL-17, were analyzed to examine cytokine synthesis capacity of CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells. As shown in Table 2 and Figure 4, in UNOL patients, unlike Tregs (CD4+CD25+Foxp3+), CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells also synthesized IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-2, and IL-17 (P < 0.05), though less than Teffs (CD4+CD25+Foxp3-).
Expressions of glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor (GITR), cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4), and chemokine receptor 4 (CCR4) on CD4+ subpopulations from patients with untreated new-onset lupus (UNOL). (A) CD4+ CD25- Foxp3+. (B) CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+. (C) CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3-. (D) CD4+ CD25- Foxp3-.
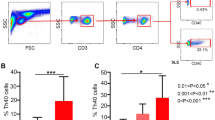
Functional assays of T-cell subgroups from UNOL patients
CD4+CD25-CD127+ (Teffs), CD4+CD25highCD127low/- (Tregs), CD4+CD25lowCD127low/-, and CD4+CD25-CD127- T cells from UNOL patients were sorted respectively. First, all four subgroups were stimulated with anti-CD3 and assessed for their proliferative ability. CD4+CD25highCD127low/- Tregs (0.205 ± 0.043) were found to be anergic compared with CD4+CD25-CD127+ Teffs (0.421 ± 0.102). Similarly, CD4+CD25lowCD127low/- (0.210 ± 0.062) and CD4+CD25-CD127- (0.272 ± 0.081) T cells showed a reduced proliferative response (Figure 5).
Then, CD4+CD25highCD127low/-, CD4+CD25lowCD127low/-, and CD4+CD25-CD127- T cells were respectively cocultured with CD4+CD25-CD127+ Teffs. The suppressive capacity as shown by optical density was most prominent in CD4+CD25highCD127low/- (0.213 ± 0.032), followed by CD4+CD25lowCD127low/- (0.281 ± 0.061) and CD4+CD25-CD127- (0.387 ± 0.087). CD4+CD25-CD127- T cells showed the least suppressive capacity, which was similar to the Teffs, in line with its lesser expression of Foxp3 (9.02% ± 2.21%) (Figure 5).
Discussion
Foxp3 is currently thought to be one of the best markers for nTregs. It plays a pivotal role in the development and maturation of Tregs. Foxp3-deficient mice develop systemic autoimmune disease, and evidence from adoptive transfer experiments suggests that this is the direct result of nTreg defect. Moreover, overexpression of Foxp3 in murine CD4+ T cells is sufficient to generate Tregs in vitro. In humans, Foxp3 deficiency also leads to a systemic autoimmune disease known as IPEX (immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy X-linked syndrome). It has been shown, however, that the expression of Foxp3 is necessary, but not sufficient, to confer regulatory function of Tregs. Foxp3 is also expressed on some activated CD4+ T cells [12]. Bonelli and colleagues [13] reported that Foxp3 expression on CD4+ T cells significantly correlated with CD69 expression and that Foxp3 might be associated with T-cell activation.
In our previous study, we found that a significant increase of CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells in UNOL patients correlated with disease activity and that the cell number significantly decreased after glucocorticoid treatment [2]. Whether these cells are Tregs or activated Teffs remains to be determined. Functional assay would be a direct way to identify the nature of CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells if only we could find a proper surface substitute for intracellular Foxp3 in CD4+CD25- T cells. A study showed that low expression of CD127 could be used as a surface marker for intracellular Foxp3 in human CD4+CD25+ Tregs [3]. CD127 is expressed not only on lymphocytes, but also on monocytes and dendritic cells. Its ligand, IL-7, is a pivotal cytokine involved in the development and survival of T and B lymphocytes [14]. In addition, thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) signals through CD127 in a heterodimeric complex with TSLP receptor [15]. TSLP-activated dendritic cells might participate in the homeostatic maintenance of CD4+ and development of Tregs in thymus [16].
In this study, we gated and backgated expressions of CD127 and Foxp3 in CD4+CD25- T cells. We confirmed that CD4+CD25highCD127low/- could be used as a substitute for isolating CD4+CD25highFoxp3+ Tregs, whereas the expression of Foxp3 on CD4+CD127low/- T cells showed significant differences in CD25high (91.38% ± 2.57%), CD25low (71.89% ± 3.31%), and CD25- (9.02% ± 2.21%) subpopulations. Foxp3 expression on CD4+CD127low/- T cells was high in both CD25high and CD25low subpopulations but low in CD25- subpopulations. This result suggested that, unlike in CD4+CD25high T cells, CD127 was not a perfect surface marker for intracellular Foxp3 in CD4+CD25- T cells. It is also important to note that, although the CD25low population lies adjacent to CD25- on a FACS plot (as shown in Figure 2), they belong to two different cell entities as their Foxp3 expressions as well as their suppressive capacity and response to in vitro stimulation were different. If the sorted CD25- subgroup was 'contaminated' with CD25low, it would bias function analysis of CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells from Teffs to Tregs [11].
Another possible explanation of the differences between the study of Bonelli and colleagues [13] and ours is that there may be a difference between untreated, newly diagnosed patients and those more chronically ill who were drawn from an outpatient population. It is possible that, as a consequence of illness, true CD25+ Tregs have become CD25-, whereas this has not occurred yet in patients with new-onset disease.
In our study, we found that the expressions of GITA, CTLA-4, and CCR4 on CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells resembled CD4+CD25+Foxp3- Teffs and were significantly less than CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs. Moreover, unlike CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs, CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells also synthesized IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-2, and IL-17, though less than CD4+CD25+Foxp3-Teffs, suggesting that the abnormally increased CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells in UNOL patients were not simple and pure Tregs.
Conclusions
CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells in UNOL patients are different from Tregs, both phenotypically and functionally. CD127 is not an appropriate surface marker for intracellular Foxp3 in CD4+CD25- T cells.
Abbreviations
- CCR4:
-
chemokine receptor 4
- CTLA-4:
-
cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4
- FACS:
-
fluorescence-activated cell sorting
- FITC:
-
fluorescein isothiocyanate
- GITR:
-
glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor
- IFN-γ:
-
interferon-gamma
- IL:
-
interleukin
- nTreg:
-
naturally occurring regulatory T cell
- PBMC:
-
peripheral blood mononuclear cell
- PE:
-
phycoerythrin
- SLE:
-
systemic lupus erythematosus
- Teff:
-
effector T cell
- Treg:
-
regulatory T cell
- TSLP:
-
thymic stromal lymphopoietin
- UNOL:
-
untreated new-onset lupus.
References
Horwitz DA: Regulatory T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus: past, present and future. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008, 10: 227-10.1186/ar2511.
Zhang B, Zhang X, Tang FL, Zhu LP, Liu Y, Lipsky PE: Clinical significance of increased CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells in patients with new-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008, 67: 1037-1040. 10.1136/ard.2007.083543.
Kramer S, Schimpl A, Hunig T: Immunopathology of interleukin (IL) 2-deficient mice: thymus dependence and suppression by thymus-dependent cells with an intact IL-2 gene. J Exp Med. 1995, 182: 1769-1776. 10.1084/jem.182.6.1769.
Shimizu J, Yamazaki S, Takahashi T, Ishida Y, Sakaguchi S: Stimulation of CD25(+)CD4(+) regulatory T cells through GITR breaks immunological self-tolerance. Nat Immunol. 2002, 3: 135-142. 10.1038/ni759.
McHugh RS, Whitters MJ, Piccirillo CA, Young DA, Shevach EM, Collins M, Byrne MC: CD4(+)CD25(+) immunoregulatory T cells: gene expression analysis reveals a functional role for the glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor. Immunity. 2002, 16: 311-323. 10.1016/S1074-7613(02)00280-7.
Takahashi T, Tagami T, Yamazaki S, Uede T, Shimizu J, Sakaguchi N, Mak TW, Sakaguchi S: Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by CD25(+)CD4(+) regulatory T cells constitutively expressing cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4. J Exp Med. 2000, 192: 303-310. 10.1084/jem.192.2.303.
Curiel TJ, Coukos G, Zou L, Alvarez X, Cheng P, Mottram P, Evdemon-Hogan M, Conejo-Garcia JR, Zhang L, Burow M, Zhu Y, Wei S, Kryczek I, Daniel B, Gordon A, Myers L, Lackner A, Disis ML, Knutson KL, Chen L, Zou W: Specific recruitment of regulatory T cells in ovarian carcinoma fosters immune privilege and predicts reduced survival. Nat Med. 2004, 10: 942-949. 10.1038/nm1093.
Iellem A, Mariani M, Lang R, Recalde H, Panina-Bordignon P, Sinigaglia F, D'Ambrosio D: Unique chemotactic response profile and specific expression of chemokine receptors CCR4 and CCR8 by CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells. J Exp Med. 2001, 194: 847-853. 10.1084/jem.194.6.847.
Imai T, Nagira M, Takagi S, Kakizaki M, Nishimura M, Wang J, Gray PW, Matsushima K, Yoshie O: Selective recruitment of CCR4-bearing Th2 cells toward antigen-presenting cells by the CC chemokines thymus and activation-regulated chemokine and macrophage-derived chemokine. Int Immunol. 1999, 11: 81-88. 10.1093/intimm/11.1.81.
Yagi H, Nomura T, Nakamura K, Yamazaki S, Kitawaki T, Hori S, Maeda M, Onodera M, Uchiyama T, Fujii S, Sakaguchi S: Crucial role of FOXP3 in the development and function of human CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells. Int Immunol. 2004, 16: 1643-1656. 10.1093/intimm/dxh165.
Bonelli M, Savitskaya A, Steiner CW, Rath E, Smolen JS, Scheinecker C: Phenotypic and functional analysis of CD4+ CD25- Foxp3+ T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 2009, 182: 1689-1695.
Allan SE, Crome SQ, Crellin NK, Passerini L, Steiner TS, Bacchetta R, Roncarolo MG, Levings MK: Activation-induced FOXP3 in human T effector cells does not suppress proliferation or cytokine production. Int Immunol. 2007, 19: 345-354. 10.1093/intimm/dxm014.
Bonelli M, von Dalwigk K, Savitskaya A, Smolen JS, Scheinecker C: Foxp3 expression in CD4+ T cells of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a comparative phenotypic analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008, 67: 664-671. 10.1136/ard.2007.074690.
Kang J, Der SD: Cytokine functions in the formative stages of a lymphocyte's life. Curr Opin Immunol. 2004, 16: 180-190. 10.1016/j.coi.2004.02.002.
Palmer MJ, Mahajan VS, Trajman LC, Irvine DJ, Lauffenburger DA, Chen J: Interleukin-7 receptor signaling network: an integrated systems perspective. Cell Mol Immunol. 2008, 5: 79-89. 10.1038/cmi.2008.10.
Willerford DM, Chen J, Ferry JA, Davidson L, Ma A, Alt FW: Interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain regulates the size and content of the peripheral lymphoid compartment. Immunity. 1995, 3: 521-530. 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90180-9.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by New Century Excellent Talents, Ministry of Education of China (NCET-04-0191), National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (30972731), Natural Sciences Foundation of Beijing (7052052), and the National Program for Key Basic Research Project (2007CB512405 for Immunology), Ministry of Science and Technology, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
HY and WZ developed the study, analyzed the data, and drafted the manuscript. LZ and YL participated in the data collection, performed the data analysis, and helped in the drafting of the manuscript. XZ and FZ participated in the development of the study, data analysis, and the drafting of the manuscript. FT and WH conceived the study and drafted the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Hua-xia Yang, Wen Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Hx., Zhang, W., Zhao, Ld. et al. Are CD4+CD25-Foxp3+cells in untreated new-onset lupus patients regulatory T cells?. Arthritis Res Ther 11, R153 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1186/ar2829
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/ar2829