Abstract
In the past few decades, gout has increased not only in prevalence, but also in clinical complexity, the latter accentuated in part by a dearth of novel advances in treatments for hyperuricemia and gouty arthritis. Fortunately, recent research reviewed here, much of it founded on elegant translational studies of the past decade, highlights how gout can be better managed with cost-effective, well-established therapies. In addition, the advent of both new urate-lowering and anti-inflammatory drugs, also reviewed here, promises for improved management of refractory gout, including in subjects with co-morbidities such as chronic kidney disease. Effectively delivering improved management of hyperuricemia and gout will require a frame shift in practice patterns, including increased recognition of the implications of refractory disease and frequent noncompliance of patients with gout, and understanding the evidence basis for therapeutic targets in serum urate-lowering and gouty inflammation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
In the past few decades in the USA and elsewhere, gout has markedly increased in incidence and prevalence [1–3]. This includes a marked increase in gout in patients over the age of 65, and even more so in patients over 75 years of age, in lockstep with high prevalence of conditions linked with hyperuricemia (chronic kidney disease (CKD), hypertension, metabolic syndrome and diabetes, and congestive heart failure) and rampant use of diuretics and low dose acetylsalicylic acid [1–3]. Gout patients in this day and age are more clinically complex than in past memory, due to various combinations of advanced age, co-morbidities, potential drug-drug interactions, and refractory tophaceous disease [1]. In this light, clinicians are increasingly faced with patients with refractory gout, classic features of which are summarized in Table 1. Until recently, a lack of an innovative pipeline of emerging therapies for hyperuricemia and gouty inflammation has compounded this situation. This review frames what we have recently learned regarding how the current scope of therapeutics for gout and hyperuricemia can be employed more effectively, and in particular for refractory gouty inflammation and hyperuricemia, focusing on new urate-lowering drugs (febuxostat and uricases) and biologic approaches to gouty inflammation via IL-1 inhibition.
Gout therapy: how the current armamentarium is actually employed in the 'real world'
Table 2 summarizes recent assessment of the scope of application of existing therapies for gout in the USA [4], and also highlights that primary care practitioners are, by far, prescribing the most gout therapies. Given that there are currently estimated to be at least approximately 3 million people with active gout, and 3 to 6 million subjects with a history of gout in the USA [5], the numbers summarized in Table 1 suggest that many gout patients receive inadequate therapy. In this context, there appears to be a shortfall in meeting practice guidelines [6, 7] for prescribing of prophylactic colchicine relative to the allopurinol prescription numbers. Overall, the estimated colchicine utilization rate was only 4.6% in office visits for those with gout, versus 8.9% for prednisone and 18% for NSAIDs [4]. As it is elsewhere in the world, allopurinol is the first line choice for serum urate-lowering in the great majority of subjects in the USA. However, there appear to be large differences in prescribing patterns for allopurinol in Caucasians relative to both African-Americans and Asians, suggesting under-treatment of gout in the latter two subgroups.
Advances in treatment of gouty arthritis by better use of the current drug armamentarium
Acute gouty arthritis is mediated by the capacity of monosodium urate crystals to activate multiple pro-inflammatory pathways in the joint, culminating in early activation of resident macrophages, and neutrophil adhesion, migration into the joint, and activation in the synovium and joint space that drive gouty inflammation [8, 9]. Current primary options for anti-inflammatory management of acute gout (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and colchicine) bluntly dampen these inflammatory mechanisms in a cost-effective manner, though are limited by broad drug toxicities, particularly in subjects with significant co-morbidities [8–13]. Moreover, the evidence basis for some of these treatments has been limited by inadequate assessment in randomized, controlled, double-blind clinical trials, an issue due to the intrinsic self-limitation of the acute gout flare.
The recent definition of etoricoxib as an effective COX-2-selective inhibitor in acute gout [14] has opened up a new therapeutic approach, but the cardiovascular safety of COX2 inhibitors remains under review. The establishment, in the past 2 years, of the evidence basis for oral glucocorticosteroid treatment of acute gout is also particularly significant, for example, for subjects with CKD. Specifically, prednisolone 35 mg daily for 5 days and naproxen 500 mg twice daily for 5 days have been demonstrated to be comparable in efficacy and tolerance in a recent trial of acute gout treatment [11]. Prednisolone (6 doses of 30 mg over 5 days) was also comparable in efficacy to indomethacin and better tolerated in an acute gout trial [12].
Dosing guidelines and the evidence basis for colchicine in acute gout treatment have also advanced in the past few years. In older oral colchicine regimens where the drug was given every 1 to 2 hours repeatedly for multiple doses, gastrointestinal toxicity, including severe diarrhea, was limiting, and occurred before a 50% reduction in pain was achieved in most subjects [13]. Intense colchicine regimens have justifiably fallen out of favor. As an example, European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) expert consensus guidelines for oral colchicine in acute gout are for a maximum of three colchicine 0.5 mg tablets per 24 hour period [6]. Furthermore, in a large, randomized, controlled multicenter trial comparing low dose and extended dose colchicine regimens, results strongly supported the lower dose colchicine regimen for acute gout [15]. In this study, within 12 hours of onset of acute gout symptoms patients self-administered 'high dose' colchicine (1.2 mg followed by 0.6 mg every hour for 6 hours (4.8 mg total)) or 'low dose' colchicine (1.2 mg followed by 0.6 mg in 1 hour (1.8 mg total)), or placebo. The 'low dose' colchicine was comparable to 'high dose' colchicine in efficacy, but did not differ from placebo with respect to diarrhea or other gastrointestinal side effects.
Advanced anti-inflammatory therapies for gout
The typical response of acute gout to NSAIDs and COX2 selective inhibition therapy, systemic glucorticosteroids, and colchicine is rapid but incomplete (for example, approximately 50% pain reduction achieved within 2 to 3 days [11, 12, 14, 15]). This has left substantial room for improvement, particularly since a potent alternative, intravenous colchicine, was justifiably withdrawn from active marketing in the USA in 2008 due to serious safety considerations. Among selective targets or strategies for advanced anti-inflammatories for gouty inflammation identified in recent years are the complement C5b-9 membrane attack complex, agonism of phagocyte melanocortin receptor 3 (shown to be a direct peripheral target of adrenocorticotropic hormone), the chemokines CXC1 and CXCL8, tumor necrosis factor-α, and the NLRP3 (NLR family, pyrin domain containing 3) inflammasome (Figure 1), which, via caspase-1 activation, drives IL-1β endoproteolysis and consequent IL-1β maturation and secretion [8, 9].
The NLRP3 inflammasome and IL-1β processing and secretion in crystal-induced inflammation. The figure shows monosodium urate crystal interaction with phagocytes, with crystal recognition at the macrophage surface mediated by innate immune mechanisms, in part employing Toll-like receptor (TLR)2 and TLR4 and associated MyD88 signaling, Fc receptors, and integrins. Crystal uptake with consequent phagolysosome destabilization, and reactive oxygen species generation and lowering of cytosolic K+ all appear to promote activation of the NLRP3 (cryopyrin) inflammasome. Consequent endoproteolytic activation of caspase-1, which drives pro-IL-1β maturation, and consequent secretion of mature IL-1β is a major mechanism stimulating experimental gouty inflammation, and appears to be implicated in human gouty arthritis, as discussed in the text.
Though anecdotal reports have suggested tumor necrosis factor-α antagonism to be beneficial in some cases of refractory human gouty inflammation [16], IL-1β appears to be far more central than tumor necrosis factor-α in experimental urate crystal-induced inflammation in mice [17]. Concordantly, the most investigated biologic drug strategy in humans for gouty inflammation has been neutralization of IL-1, with promising results [9, 17]. A pilot study of ten patients with chronic refractory gouty inflammation given the soluble IL-1 receptor antagonist anakinra (100 mg daily subcutaneously for 3 days) suggested good overall responses [17], though results of larger, randomized, controlled studies of IL-1 inhibition for gouty arthritis are awaited.
Options in the treatment of hyperuricemia: recent establishment of the evidence basis for <6 mg/dL as the serum urate target level in gout
Pharmacologic urate-lowering approaches can employ primary, potent uricosurics (probenecid or benzbromarone), xanthine oxidase inhibitors to inhibit uric acid generation (allopurinol and the recently approved drug febuxostat), or experimental uricase treatment (with Rasburicase™ or pegloticase) to degrade urate [1, 10]. Since the solubility of urate in physiologic solutions is exceeded at approximately 6.7 to 7.0 mg/dL, current guidelines for inhibiting ongoing urate crystal deposition, reduction of total body urate stores, and resolution of macroscopic tophi are for continuing (lifelong) reduction of serum urate concentration to <6 mg/dL (approximately 360 mmol/l), and ideally in the 5 to 6 mg/dL range [18]. As summarized in a detailed, recent review [18], achieving this target level in gout patients ultimately is associated with fewer gout flares, and it also may have direct and indirect beneficial effects on renal function [19, 20]. A more aggressive serum urate-lowering target such as 3 to 5 mg/dL appears appropriate for more rapid tophus de-bulking in those tophaceous gout patients with a body burden of urate assessed to be particularly large [21].
Advances in understanding renal urate handling and uricosuric therapy
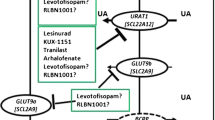
Uricosurics act primarily by inhibiting proximal renal tubule epithelial cell reabsorption of urate anion, thereby enhancing renal uric acid excretion. This remains a compelling approach in some aspects, since reduction of miscible total body urate stores is initiated rapidly, and the velocity of tophus size reduction is comparable to that using allopurinol when similar degrees of serum reduction are achieved [22]. Moreover, uricosurics target the underlying basis for hyperuricemia in the majority of patients. Recent advances in understanding renal disposition of urate include identification of the anion exchanger URAT1 (urate transporter 1; SLC22A12) as a mediator of urate anion reabsorption from the lumen at the apical membrane of the proximal tubule epithelial cell [23], with the electrogenic hexose transporter GLUT9 (glucose transporter 9; SLC2A9) mediating urate anion reabsorption into the peritubular interstitium (and ultimately into the circulation) at the basolateral membrane [24–28]. Probenecid and benzbromarone both inhibit urate anion movement transduced by URAT1 and GLUT9 [24] (Figure 2). The findings related to GLUT9 also raise compelling questions about the relationships between hyperglycemia and increased fructose intake and hyperuricemia [24–29].
Effects of URAT1, GLUT9, and ABCG2 on urate anion disposition by the renal proximal tubule epithelial cell and inhibitory effects of the uricosurics probenecid and benzbromarone on renal urate reabsorption by inhibition of both URAT1 and GLUT9. The schematic summarizes the effects of the uricosurics probenecid and benezbromarone on urate handling in the renal proximal tubule epithelial cell by the URAT1 (SLC22A12) and GLUT9 (SLC2A9) transporters identified as linked with serum urate levels and gout susceptibility in genetic studies, including recent genome-wide association studies. Urate reabsorption at the apical membrane, which interfaces with the tubule lumen, is mediated in large part by the anion exchange function of URAT1. At the basolateral membrane, the hexose transport facilitator GLUT9 electrogenically transports urate anion into the peritubular interstitium, where urate is reabsorbed into the circulation. Recent genome-wide association studies and functional genomics analyses have also uncovered a substantial role for ABCG2 in secretion of urate into the proximal tubule lumen. The depicted model is a simplification, since other molecules that affect urate disposition in the proximal tubule and distally in the nephron are not depicted here, and effects of certain other drugs on renal urate disposition by inhibiting URAT1 or GLUT9 or other transporters are not represented. ABCG, ATP binding cassette sub-family G; GLUT, glucose transporter; URAT1, urate transporter 1.
A major advance that also could point to new and potentially genomics-customized uricosuric strategies is the identification of ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 2 (ABCG2) as one of the functional urate anion secretory transporters at the apical membrane of the renal proximal tubule epithelial cell (Figure 2) [30]. Moreover, genome-wide association studies have linked common URAT1, GLUT9, and now ABCG2 haplotypes or single nucleotide polymorphisms with altered susceptibility to gout [23–28, 30]. For example, the common ABCG2 rs2231142 single nucleotide polymorphism encoding the Q141K mutation in the nucleotide-binding domain of ABCG2 suppresses ABCG2 urate transport rates by approximately 50% in vitro, and in a large, population-based study, rs2231142 was strongly associated with serum urate levels in whites, who have a minor allele frequency of 0.11 [30]. The adjusted odds ratio for gout of 1.68 per risk allele in whites and blacks argues that approximately 10% of all gout cases in whites may be attributable to ABCG2 rs2231142, and the risk allele also is highly prevalent in Asians, who have a higher gout prevalence than whites [30].
Significantly, in current clinical practice, the most available primary uricosuric, probenecid, requires more than once daily dosing and increases the risk of urolithiasis, particularly in acid urine [31]. More selective and potent uricosurics ideally would have a once daily dosing profile and could be designed such that urolithiasis risk is not unduly elevated. All uricosurics also become less effective and ultimately ineffective with progressively lower glomerular filtration rate [10, 31]. This may limit the role of combining uricosurics with xanthine oxidase inhibition in the treatment of refractory hyperuricemia in gout patients since xanthine oxidase inhibition lowers urinary uric acid clearance by excretion. Such a combination approach can normalize serum urate in a substantial fraction of patients on submaximal allopurinol [32]. An approach of this nature, using certain drugs with wider availability than benzbromarone (for example, losartan, and fenofibrate) [33, 34] but with less potent uricosuric action than primary uricosurics such as probenecid, has to date been, at best, only moderately successful, when studied in only small numbers of subjects, as a potential strategy to further lower serum urate where there is suboptimal control with allopurinol. It appears likely that such combination strategies will be particularly constrained in effectiveness in those with stage 3 CKD or worse (creatinine clearance <60 calculated by Cockroft-Gault equation and adjusted for ideal body weight).
Advances in understanding allopurinol treatment failure
Given the limitations of uricosuric therapy highlighted above, the first line of pharmacologic therapy to lower serum urate for most gout patients is suppression of xanthine oxidase using allopurinol, which, when effective and well-tolerated, is a cost-effective option [6, 10]. Allopurinol is US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved for doses up to 800 mg daily [35]. Recent expert consensus EULAR guidelines have reinforced FDA dosing guidelines for allopurinol in patients with preserved renal function [6, 35], specifically to initiate allopurinol at 100 mg daily, and then to increase the dose by 100 mg every 1 to 4 weeks until a target serum urate level (<6 mg/dL) is achieved or the maximum appropriate allopurinol dose is reached. FDA dosing guidelines have also advocated 200 to 300 mg allopurinol daily as adequate for most patients with mild gout, and an average dose of 400 to 600 mg allopurinol daily as the expected amount to control hyperuricemia in patients with moderately severe tophaceous gout [35]. In small studies of gout patients, the mean daily dose of allopurinol needed to normalize serum urate was 372 mg [36], and allopurinol dose increases from 300 mg to 600 mg daily markedly increased serum urate-lowering efficiency in patients without stage 3 or worse CKD [37]. Data from recent, large, randomized, controlled clinical trials indicated that allopurinol 300 mg daily lowered serum urate by approximately 33% in a population of gout patients where approximately 25 to 30% had detectable tophi, serum urate was approximately 9.5 to 10 mg/dL, and renal function was largely intact [38, 39].
In clinical practice, noncompliance with allopurinol has recently been elucidated to be a problem in approximately 50% of subjects in the first year of therapy [40]. Moreover, it appears that allopurinol is widely under-dosed overall in clinical practice, since the vast majority of allopurinol prescriptions are for 300 mg daily or less [41]. This circumstance reflects influential maintenance dosing guidelines for allopurinol in CKD dating from the 1980s and calibrated for serum levels (in relationship to estimated glomerular filtration rate) of oxypurinol, which is the major, long-lived active allopurinol metabolite and is primarily excreted by the kidney [35]. The intent of the older guidelines was to lessen the incidence of allopurinol hypersensitivity syndrome, particularly with CKD [35]. These guidelines are now recognized not to be based on evidence, to fail to adequately treat hyperuricemia, and also to fail to prevent allopurinol hypersensitivity syndrome in all patients, including those with CKD [35, 42]. Though HLA-B58 is a newly identified risk factor for severe cutaneous adverse reactions to allopurinol (that is, Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis) [43–45], there remains no reliable way to identify whether an individual patient will develop such toxicity on allopurinol [35, 42].
FDA and more recent EULAR dosing guidelines for allopurinol have suggested the use of reduced doses in renal failure in order to lessen the risk of drug toxicity [6, 35]. For example, the FDA-recommended maximum allopurinol dose is 200 mg daily with a creatinine clearance of 10 to 20 ml/min, and 100 mg daily with a creatinine clearance of <10 ml/min. More recently, dose reduction of allopurinol in moderate CKD was supported via retrospective analysis of renal function-adjusted dosing of allopurinol in relation to drug toxicities [46]. The lack of a definition of safety and tolerability of allopurinol maintenance doses above those previously calibrated for serum oxypurinol levels related to creatinine clearance [46] needs to be considered when weighing the decision to employ more advanced serum urate lowering therapeutic options.
Advanced options for treatment-refractory hyperuricemia in gout: febuxostat
The xanthine oxidase inhibitor febuxostat, now approved in Europe and the USA, is an appropriate choice in circumstances of allopurinol hypersensitivity or intolerance, or failure of allopurinol (at a maximal dose appropriate for the individual patient) to normalize serum urate and, ultimately, improve physical function and quality of life parameters. Febuxostat is a particularly appropriate second line option to allopurinol where uricosuric therapy is contra-indicated, as in stage 3 or worse CKD, and in patients with a history of urolithiasis, an inability to adequately increase hydration, or with identified uric acid overproduction [21].
Febuxostat is a selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase, the drug sitting in the access channel to the molybdenumpterin active site of the enzyme [47]. Febuxostat does not have a purine-like backbone, unlike allopurinol and oxypurinol (Figure 3). Significantly, febuxostat is primarily metabolized by oxidation and glucuronidation in the liver and renal elimination plays a minor role in febuxostat pharmacokinetics, as opposed to allopurinol pharmacology. Febuxostat also does not directly regulate pyrimidine metabolism and it is not reincorporated into nucleotides, in contrast to allopurinol, where such properties have the potential to contribute to certain drug toxicities.
Febuxostat 40 to 120 mg daily (and a safety dose trial of 240 mg daily) has now been analyzed in large, randomized, clinical trials in which tophi were seen in approximately 25 to 30% of subjects, with a maximum dose of 300 mg allopurinol employed in comparison groups [38, 39, 48, 49]. Results of all of these trials unequivocally established the failure of 300 mg allopurinol daily to achieve a serum urate target level of <6 mg/dL in a substantial majority of the patient population studied. In a 52-week trial, febuxostat 80 and 120 mg both achieved the target level of serum urate <6 mg/dL in the majority of subjects, though gout flare rates at 52 weeks were comparable to those in subjects randomized to allopurinol 300 mg daily [38]. In a second, large phase 3 trial, febuxostat 40 mg daily demonstrated serum urate-lowering to target of <6 mg/dL roughly equivalent to allopurinol 300 mg daily in those with intact renal function, and 80 mg febuxostat daily was superior to allopurinol 300 mg or febuxostat 40 mg daily in achieving a serum urate target level of <6 mg/dL, with comparable drug tolerance [48]. In a subset of patients with stage 2 to 3 CKD, febuxostat 40 and 80 mg daily were also superior in achieving the serum urate target level in comparison to renally dose-adjusted allopurinol (200 to 300 mg daily) [48].
Comparison of early gouty arthritis flares, triggered by serum urate-lowering and putative remodeling, was instructive in these studies. The early flares occurred in association with the most intense serum urate-lowering effect in both febuxostat and allopurinol recipients, and early flares were a greater problem when prophylactic colchicine was stopped at 8 weeks as opposed to 6 months into urate-lowering treatment, but gout flares tapered off later in this study [38, 48]. For these reasons, the European Medicines Agency (EMEA) astutely recommended gout flare prophylaxis for a 6 month period when febuxostat is initiated.
Tophus size is reduced by 50 to 80% after 1 year of either febuxostat or allopurinol treatment, with the greatest tophus and gout flare reduction linked to the greatest degree of serum urate-lowering irrespective of drug. A small, open-label extension study in which patients failing initial therapy on allopurinol were switched to febuxostat to achieve serum urate <6 mg/dL suggested that approximately half of febuxostat-treated patients with tophi can achieve elimination of tophi by 2 years, and approximately 70% by 5 years [49]. Quality of life parameters have been favorably impacted by extended febuxostat treatment in uncontrolled studies [49].
Febuxostat is approved for use in European countries at 80 and 120 mg daily. The FDA approved febuxostat for use in the USA in February, 2009. The USA label is for a dose of 40 mg daily, followed by dose increase to 80 mg daily if serum urate is not normalized after at least 2 weeks. Side effects of febuxostat include rash in <2% of subjects, and elevation of hepatic enzymes, diarrhea, and arthralgia may also occur. As is the case for allopurinol, xanthine oxidase inhibition by febuxostat carries the potential for major drug interactions with azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine and theophylline [50].
Uricase therapy: an experimental 'biologic' option for serum urate lowering
Uricases oxidatively degrade uric acid, thereby catalyzing conversion to soluble allantoin, which is much more soluble than uric acid [51]. Uricases also generate 1 mole of the oxidant hydrogen peroxide for each mole of uric acid degraded (Figure 4). Uricase expression was lost in humans and higher primates during the course of evolution [1]. Illustrating the huge role uricase plays in uric acid homeostasis in mammals, normal serum urate in rodents is approximately 1 mg/dL, whereas it is approximately 10 mg/dL in uricase knockout mice. Moreover, untreated hyperuricemia in uricase knockout mice leads to death by renal failure due to severe uric acid urolithiasis.
Enzymatic activity of uricase (uric acid oxidase). Uricase oxidizes uric acid, which is sparingly soluble, to the highly soluble end product allantoin, which is readily excreted in the urine. In doing so, uricase generates not only intermediate forms of uric acid that are subject to further metabolism (including 5-hydroxyisourate), but also the oxidant hydrogen peroxide as a byproduct of the enzymatic reaction. During evolution, humans and higher primates lost expression of not only uricase, but also enzymes that rapidly degrade intermediate forms of uric acid generated by uric acid oxidation.
Various uricase therapies for hyperuricemia have been attempted experimentally for several decades [52]. For example, recent, limited reports or pilot studies have evaluated the off-label use in severe, chronic gout of the non-PEGylated recombinant fungal enzyme rasburicase [52, 53], which is FDA-approved for single course therapy in pediatric tumor lysis syndrome. Unfortunately, rasburicase is both highly antigenic and has a plasma half-life of 18 to 24 hours [52]. Efficacy, tolerability, and sustainability of rasburicase treatment beyond 6 to 12 months appear to be poor for treatment of refractory hyperuricemia in gout [52, 53].
A recent advance has been seen in clinical trials of recombinant porcine-baboon uricase (pegloticase); these trials have evaluated the potential advantages for sustained management of refractory hyperuricemia in gout of PEGylation of this enzyme (Figure 5) to reduce immunogenicity as well as increase circulating half-life [51, 54, 55]. For refractory tophaceous disease, results to date indicate that intravenous PEGylated uricase treatment has the potential to rapidly decrease the pool size of miscible urate, and also to de-bulk tophi in weeks to months [56] rather than the months to years seen to date with therapy with xanthine oxidase inhibitors at conventional doses. Specifically, in a phase 2 and a pivotal placebo-controlled, randomized, 6-month phase 3 trial with open-label extension (approximately 40 and 200 patients, respectively), intravenous administration of pegloticase (up to 8 mg every 2 weeks) induced profound initial reductions of serum urate [55, 57]. In the pivotal phase 3 trial of pegloticase, which assessed a patient population with severe gout overall (and approximately 70% with visible tophi) [57], pre-infusion of fexofenadine, acetaminophen, and hydrocortisone (200 mg) were employed in an attempt to limit infusion reactions [57]. The frequency of responders – subjects who reached a target serum urate level of <6 mg/dL at 6 months – was approximately 42% on 8 mg pegloticase every 2 weeks in the intent to treat analysis [57]. Moreover, de-bulking of tophi in this study was notably rapid in the subset of patients on pegloticase 8 mg every 2 weeks, with complete resolution of tophi in 20% by 13 weeks and approximately 40% by 25 weeks [56].
Molecular models of the uricase tetramer and of the PEGylated uricase pegloticase containing strands of 10 kDa polyethylene glycol (PEG) linked to each uricase tetramer. (a) Schematic model of the uricase tetramer, based on the crystal structure of Aspergillus flavus uricase. Each subunit is shown in a different color (red, blue, green, or yellow). (b) Space-filling model of the A. flavus uricase tetramer, showing the characteristic tunnel (or barrel) structure of the native enzyme tetramer. (c) Space-filling model of A. flavus uricase tetramer, rotated around the vertical axis so that the tunnel is not visible. (d) Space-filling model of the uricase tetramer in the same orientation as in (b) but to which nine strands of 10 kDa PEG per uricase subunit are attached. The structures of the PEG strands (shown in various shades of gray) were generated as described in [54]. The scale of (d) is about half that of (a-c). Figure 5 and the legend are reprinted with permission from [54].
Frequent early acute gout flares (up to approximately 80%) in the first few months of pegloticase therapy [55] tapered off with more prolonged therapy in responders. Infusion reactions were moderate to severe in approximately 8 to 11% of subjects, and included flushing, urticaria, and hypotension, and, by undefined mechanisms, noncardiac chest pain or muscle cramping [55, 57]. Anaphylaxis was uncommon (approximately 2%) in the phase 3 pegloticase study [57]. However, high titer antibodies to pegloticase emerged in many patients as treatment evolved over a few months, including IgM and IgG antibodies that did not directly neutralize the enzyme but appeared to adversely alter both its pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics [58]. High titer anti-pegloticase antibodies were also strongly linked with infusion reactions and were rare in serum urate responders (as assessed at the 6-month time-point) [58]. Hence, the dense polyethylene glycol (PEG) multimers linked to pegloticase [54] (Figure 5) do not prevent antigenicity, and also have been suggested to independently modulate the immune response to pegloticase in some subjects [58].
All uricase therapies have the potential to induce oxidative stress, since degradation of the high micromolar plasma concentrations of urate in gout patients by uricases has the capacity to generate substantial amounts of hydrogen peroxide [1, 59, 60]. Whether increased nitric oxide bioavailability [61, 62] and the profound, rapid decrement in the serum antioxidant activity normally exerted by serum urate [1] contribute to oxidative challenge by uricase therapy is not yet clear. Circulating oxidative stress triggered by hydrogen peroxide generation alone is subject to marked dampening by the normal abundance of catalase on erythrocytes [51, 59, 60] and potentially by other plasma antioxidant defenses. Yet methemoglobinemia and/or hemolysis have been unequivocal indicators of uricase-induced oxidative stress [1, 59, 60]. Importantly, with Rasburicase™ therapy, methemoglobinemia and hemolysis (fortunately <1% in incidence) were linked to glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency in some but not all affected subjects [59, 60]; subsequently, this deficiency has become an exclusion criterion for any uricase therapy. It has been suggested that assessment for erythrocyte catalase activity should be done prior to uricase therapy [59, 60]. In my opinion, monitoring for treatment-induced subclinical methemoglobinemia also could ultimately be informative.
Uricases, by oxidizing urate (Figure 4), generate the intermediate form 5-hydroxyisourate, and subsequent hydrolysis of this produces 2-oxo-4-hydroxy-4-carboxy-5-ureidoimidazoline, which is decarboxylated to S-(+)-allantoin [63]. The enzymes carrying out rapid degradation of these urate oxidation intermediates were lost in human evolution along with uricase [63]. It has been suggested that addition of these enzymes to uricase therapy would be useful if the aforementioned uric acid oxidation intermediates are found to have noxious biologic properties [63].
Overall, it is not yet known if there is significant subclinical oxidative stress at the tissue level, rather than simply at the erythrocyte level [59, 60], with uricase treatment in gout patients. Because of this issue, close monitoring of uricase-treated gout patients appears in order. Whether potential concomitant oxidative stress due to selected co-medications, congestive heart failure, anemia, hyperlipidemia, and CKD influences uricase safety remains to be defined.
At the time of writing this review, uricase therapy for tophaceous gout for which treatment has failed remains an unapproved, experimental approach that will be substantially more expensive than oral therapies, and consensus, evidence-based therapeutic guidelines are needed, whereas only draft guidelines have been proposed for uricase [52]. Tophus debulking is impressively rapid (months) in responders, but uricase therapies tested to date have all been substantially limited by drug immunogenicity. The safety of this particular 'biologic' approach, especially beyond a term of 6 to 12 months, will require further investigation.
In my opinion, any form of uricase therapy (over a finite term) is appropriate only for carefully selected patients that would benefit from accelerated, tophus de-bulking to address incapacitating tophi linked with active synovitis, and where other serum urate lowering therapies have failed or cannot achieve this objective [52]. As an 'induction therapy', uricase could ultimately be replaced by less intensive maintenance oral urate-lowering therapy with other agents, once evidence of normalization of body urate stores, including resolution of clinically detectable tophi and gross synovitis, is achieved.
Do cardiovascular safety signals in urate-lowering trials in gout reflect the influence of inflammation?
There have been death signals in both congestive heart failure patients on experimental oxypurinol therapy [64] and febuxostat-treated gout patients [48]. Moreover, there is higher cardiovascular mortality in hyperuricemia gout patients, related in part to co-morbidities in gout, and also possibly to independent effects of hyperuricemia on the vasculature [65, 66].
Clinical trials to date in which death signals have arisen with serum urate-lowering strategies all have limitations in interpretability due to small numbers of events and subjects and relatively short durations of treatment. Hence, statistical significance may not be in lockstep with clinical and biological significance in such studies to this point. One constant associated with the more intense serum urate lowering achievable in recent trials of emerging antihyperuricemics is increased risk for acute gout flares in the first few months of therapy [38, 55]. In my opinion, the known association of atrial and ventricular arrythmias and quantifiable altered heart rate variability with systemic inflammation (putatively mediated by specific cytokines markedly up-regulated in acute gouty inflammation, such as IL-6 and CXCL8) [67–69] deserves direct investigation as a potential factor in cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in gout patients undergoing serum-urate lowering therapy.
Challenges in translating novel gout and hyperuricemia therapies to better clinical practice
Compliance of gout patients with therapy appears lower than that for therapy of a variety of other common medical conditions, including hypertension, diabetes, osteoporosis, and hyperlipidemia [70]. Younger gout patients with fewer co-morbidities and fewer office visits are the least compliant gout patients, and we need to address systematic failures in both physician and patient education in gout treatment. Physicians appear to underestimate the impact of gout on quality of life and physical function [71–74]. Gout patients have more co-morbidities, poorer quality of life and physical function, increased health care costs, and increased adverse cardiovascular outcomes than controls [65, 71–75].
Not only patient education, but also quality of care in gout treatment have significant room for improvement [76–78]. The identification of certain improved outcomes with sustained serum urate lowering below 6 mg/dL has ushered in a new era of gout therapy, where practitioners 'treat to target' in lowering serum urate [18]. Now the true definition of 'treatment-refractory' gout and gout-specific quality of life and disability will need careful assessment and direct attention in clinical practice. Such efforts would be timely, since 'treatment-refractory' gout, associated with an overall decrease in quality of life [79], has been proposed as a specific indication for aggressive urate-lowering strategies and possibly for initially lower serum urate targets than the widely used metric of <6 mg/dL [21].
The future of gout treatment is intriguing. For example, promising genomics and imaging technologies have the potential to improve prevention, diagnosis, and therapy by identifying disease earlier and tailoring treatment strategies. Examples include single nucleotide polymorphism and haplotype identification for renal urate transporters in patients with hyperuricemia [80]. Dual energy computed tomography, which is highly sensitive and specific in visualizing tissue stores of monosodium urate crystals as well as renal uric acid urolithiasis [81, 82], has the potential, for example, to assist in diagnosis of gout in patients with hyperuricemia or joint pain, and to better quantify tophus dissolution in therapy.
Whether using well-established or newer and emerging approaches and agents for gout and hyperuricemia management, the bottom line will remain that gout and hyperuricemia treatments need to be better translated into a collective of favorable outcomes for both control of gouty inflammation and management of hyperuricemia, as well as improved outcomes of gout-related quality of life and co-morbidities. This will require careful attention to both drug safety and cost-effectiveness of established versus emerging therapies, relative to quantifiable patient-centered outcomes, in a financially challenging era.
Note
This review is part of a series on Gout edited by Alex So.
Other articles in this series can be found at http://arthritis-research.com/series/gout
Abbreviations
- ABCG2:
-
ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 2
- CKD:
-
chronic kidney disease
- EULAR:
-
European League Against Rheumatism
- FDA:
-
Food and Drug Administration
- GLUT:
-
glucose transporter
- IL:
-
interleukin
- NSAID:
-
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
- PEG:
-
polyethylene glycol
- URAT:
-
urate transporter.
References
Bieber JD, Terkeltaub RA: Gout: on the brink of novel therapeutic options for an ancient disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50: 2400-2414. 10.1002/art.20438.
Saag KG, Choi H: Epidemiology, risk factors, and lifestyle modifications for gout. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006, 8 (Suppl 1): S2-10.1186/ar1907.
Wallace KL, Riedel AA, Joseph-Ridge N, Wortmann R: Increasing prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia over 10 years among older adults in a managed care population. J Rheumatol. 2004, 31: 1582-1587.
Krishnan E, Lienesch D, Kwoh CK: Gout in ambulatory care settings in the United States. J Rheumatol. 2008, 35: 498-501.
Lawrence RC, Felson DT, Helmick CG, Arnold LM, Choi H, Deyo RA, Gabriel S, Hirsch R, Hochberg MC, Hunder GG, Jordan JM, Katz JN, Kremers HM, Wolfe F: National Arthritis Data Work-group. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the United States. Part II. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58: 26-35. 10.1002/art.23176.
Zhang W, Doherty M, Bardin T, Pascual E, Barskova V, Conaghan P, Gerster J, Jacobs J, Leeb B, Lioté F, McCarthy G, Netter P, Nuki G, Perez-Ruiz F, Pignone A, Pimentao J, Punzi L, Roddy E, Uhlig T, Zimmermann-Gorska I: EULAR evidence based recommendations for gout. Part II: Management. Report of a task force of the EULAR Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics (ESCISIT). Ann Rheum Dis. 2006, 65: 1312-1324. 10.1136/ard.2006.055269.
Borstad GC, Bryant LR, Abel MP, Scroggie DA, Harris MD, Alloway JA: Colchicine for prophylaxis of acute flares when initiating allopurinol for chronic gouty arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2004, 31: 2429-2432.
Cronstein BN, Terkeltaub R: The inflammatory process of gout and its treatment. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006, 8 (Suppl 1): S3-10.1186/ar1908.
Martinon F, Pétrilli V, Mayor A, Tardivel A, Tschopp J: Gout-associated uric acid crystals activate the NLRP3 inflammasome. Nature. 2006, 440: 237-241. 10.1038/nature04516.
Terkeltaub RA: Clinical practice. Gout. N Engl J Med. 2003, 349: 1647-1655. 10.1056/NEJMcp030733.
Janssens HJ, Janssen M, Lisdonk van de EH, van Riel PL, van Weel C: Use of oral prednisolone or naproxen for the treatment of gout arthritis: a double-blind, randomised equivalence trial. Lancet. 2008, 371: 1854-1860. 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60799-0.
Man CY, Cheung IT, Cameron PA, Rainer TH: Comparison of oral prednisolone/paracetamol and oral indomethacin/paracetamol combination therapy in the treatment of acute goutlike arthritis: a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial. Ann Emerg Med. 2007, 49: 670-677. 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2006.11.014.
Terkeltaub RA: Colchicine Update: 2008. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 38: 411-419. 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2008.08.006.
Rubin BR, Burton R, Navarra S, Antigua J, Londoño J, Pryhuber KG, Lund M, Chen E, Najarian DK, Petruschke RA, Ozturk ZE, Geba GP: Efficacy and safety profile of treatment with etoricoxib 120 mg once daily compared with indomethacin 50 mg three times daily in acute gout: a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50: 598-606. 10.1002/art.20007.
Terkeltaub R, Furst D, Bennett K, Kook K, Davis M: Low dose (1.8 mg) vs high dose (4.8 mg) oral colchicine regimens in patients with acute gout flare in a large, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58 (Suppl 9): 1944-
Tausche AK, Richter K, Grässler A, Hänsel S, Roch B, Schröder HE: Severe gouty arthritis refractory to anti-inflammatory drugs: treatment with anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha as a new therapeutic option. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004, 63: 1351-1352. 10.1136/ard.2003.015743.
So A, De Smedt T, Revaz S, Tschopp J: A pilot study of IL-1 inhibition by anakinra in acute gout. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007, 9: R28-10.1186/ar2143.
Perez-Ruiz F, Lioté F: Lowering serum uric acid levels: what is the optimal target for improving clinical outcomes in gout?. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 57: 1324-1328. 10.1002/art.23007.
Perez-Ruiz F, Calabozo M, Herrero-Beites AM, García-Erauskin G, Pijoan JI: Improvement of renal function in patients with chronic gout after proper control of hyperuricemia and gouty bouts. Nephron. 2000, 86: 287-291. 10.1159/000045783.
Siu YP, Leung KT, Tong MK, Kwan TH: Use of allopurinol in slowing the progression of renal disease through its ability to lower serum uric acid level. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006, 47: 51-59. 10.1053/j.ajkd.2005.10.006.
Edwards NL: Treatment-failure gout: a moving target. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58: 2587-2590. 10.1002/art.23803.
Perez-Ruiz F, Calabozo M, Pijoan JI, Herrero-Beites AM, Ruibal A: Effect of urate-lowering therapy on the velocity of size reduction of tophi in chronic gout. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 47: 356-60. 10.1002/art.10511.
Endou H, Anzai N: Urate transport across the apical membrane of renal proximal tubules. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2008, 27: 578-584. 10.1080/15257770802136024.
Anzai N, Ichida K, Jutabha P, Kimura T, Babu E, Jin CJ, Srivastava S, Kitamura K, Hisatome I, Endou H, Sakurai H: Plasma urate level is directly regulated by a voltage-driven urate efflux transporter URATv1 (SLC2A9) in humans. J Biol Chem. 2008, 283: 26834-26838. 10.1074/jbc.C800156200.
Bannasch D, Safra N, Young A, Karmi N, Schaible RS, Ling GV: Mutations in the SLC2A9 gene cause hyperuricosuria and hyperuricemia in the dog. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4: e1000246-10.1371/journal.pgen.1000246.
Caulfield MJ, Munroe PB, O'Neill D, Witkowska K, Charchar FJ, Doblado M, Evans S, Eyheramendy S, Onipinla A, Howard P, Shaw-Hawkins S, Dobson RJ, Wallace C, Newhouse SJ, Brown M, Connell JM, Dominiczak A, Farrall M, Lathrop GM, Samani NJ, Kumari M, Marmot M, Brunner E, Chambers J, Elliott P, Kooner J, Laan M, Org E, Veldre G, Viigimaa M, et al: SLC2A9 is a high-capacity urate transporter in humans. PLoS Med. 2008, 5: e197-10.1371/journal.pmed.0050197.
Brandstätter A, Kiechl S, Kollerits B, Hunt SC, Heid IM, Coassin S, Willeit J, Adams TD, Illig T, Hopkins PN, Kronenberg F: Sex-specific association of the putative fructose transporter SLC2A9 variants with uric acid levels is modified by BMI. Diabetes Care. 2008, 31: 1662-1667. 10.2337/dc08-0349.
Vitart V, Rudan I, Hayward C, Gray NK, Floyd J, Palmer CN, Knott SA, Kolcic I, Polasek O, Graessler J, Wilson JF, Marinaki A, Riches PL, Shu X, Janicijevic B, Smolej-Narancic N, Gorgoni B, Morgan J, Campbell S, Biloglav Z, Barac-Lauc L, Pericic M, Klaric IM, Zgaga L, Skaric-Juric T, Wild SH, Richardson WA, Hohenstein P, Kimber CH, Tenesa A, et al: SLC2A9 is a newly identified urate transporter influencing serum urate concentration, urate excretion and gout. Nat Genet. 2008, 40: 437-442. 10.1038/ng.106.
Choi HK, Curhan G: Soft drinks, fructose consumption, and the risk of gout in men: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2008, 336: 309-312. 10.1136/bmj.39449.819271.BE.
Woodward OM, Köttgen A, Coresh J, Boerwinkle E, Guggino WB, Köttgen M: Identification of a urate transporter, ABCG2, with a common functional polymorphism causing gout. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009, 106: 10338-10342. 10.1073/pnas.0901249106.
Terkeltaub R, Bushinsky DA, Becker MA: Recent developments in our understanding of the renal basis of hyperuricemia and the development of novel antihyperuricemic therapeutics. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006, 8 (Suppl 1): S4-10.1186/ar1909.
Reinders MK, van Roon EN, Houtman PM, Brouwers JR, Jansen TL: Biochemical effectiveness of allopurinol and allopurinol-probenecid in previously benzbromarone-treated gout patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2007, 26: 1459-1465. 10.1007/s10067-006-0528-3.
Lee YH, Lee CH, Lee J: Effect of fenofibrate in combination with urate lowering agents in patients with gout. Korean J Intern Med. 2006, 21: 89-93.
Takahashi S, Moriwaki Y, Yamamoto T, Tsutsumi Z, Ka T, Fukuchi M: Effects of combination treatment using anti-hyperuricaemic agents with fenofibrate and/or losartan on uric acid metabolism. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003, 62: 572-575. 10.1136/ard.62.6.572.
Chao J, Terkeltaub R: A critical reappraisal of allopurinol dosing, safety, and efficacy for hyperuricemia in gout. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2009, 11: 135-140. 10.1007/s11926-009-0019-z.
Perez-Ruiz F, Alonso-Ruiz A, Calabozo M, Herrero-Beites A, García-Erauskin G, Ruiz-Lucea E: Efficacy of allopurinol and benzbromarone for the control of hyperuricaemia. A pathogenic approach to the treatment of primary chronic gout. Ann Rheum Dis. 1998, 57: 545-549. 10.1136/ard.57.9.545.
Reinders MK, Haagsma C, Jansen TL, van Roon EN, Delsing J, Laar van de MA, Brouwers JR: A randomised controlled trial on the efficacy and tolerability with dose-escalation of allopurinol 300–600 mg/day versus benzbromarone 100–200 mg/day in patients with gout. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008, 68: 892-897. 10.1136/ard.2008.091462.
Becker MA, Schumacher HR, Wortmann RL, MacDonald PA, Eustace D, Palo WA, Streit J, Joseph-Ridge N: Febuxostat compared with allopurinol in patients with hyperuricemia and gout. N Engl J Med. 2005, 353: 2450-2461. 10.1056/NEJMoa050373.
Schumacher HR, Becker MA, Wortmann RL, Macdonald PA, Hunt B, Streit J, Lademacher C, Joseph-Ridge N: Effects of febuxostat versus allopurinol and placebo in reducing serum urate in subjects with hyperuricemia and gout: a 28-week, phase III, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 59: 1540-1548. 10.1002/art.24209.
Riedel AA, Nelson M, Joseph-Ridge N, Wallace K, MacDonald P, Becker M: Compliance with allopurinol therapy among managed care enrollees with gout: a retrospective analysis of administrative claims. J Rheumatol. 2004, 31: 1575-1581.
Sarawate CA, Brewer KK, Yang W, Patel PA, Schumacher HR, Saag KG, Bakst AW: Gout medication treatment patterns and adherence to standards of care from a managed care perspective. Mayo Clin Proc. 2006, 81: 925-934. 10.4065/81.7.925.
Dalbeth N, Stamp L: Allopurinol dosing in renal impairment: walking the tightrope between adequate urate lowering and adverse events. Semin Dial. 2007, 20: 391-395. 10.1111/j.1525-139X.2007.00270.x.
Hung SI, Chung WH, Liou LB, Chu CC, Lin M, Huang HP, Lin YL, Lan JL, Yang LC, Hong HS, Chen MJ, Lai PC, Wu MS, Chu Cy, Wang KH, Chen CH, Fann CS, Wu JY, Chen YT: HLA-B*5801 allele as a genetic marker for severe cutaneous adverse reactions caused by allopurinol. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005, 102: 4134-4139. 10.1073/pnas.0409500102.
Lonjou C, Borot N, Sekula P, Ledger N, Thomas L, Halevy S, Naldi L, Bouwes-Bavinck JN, Sidoroff A, de Toma C, Schumacher M, Roujeau JC, Hovnanian A, Mockenhaupt M, RegiSCAR Study Group: A European study of HLA-B in Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis related to five high-risk drugs. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2008, 18: 99-107. 10.1097/FPC.0b013e3282f3ef9c.
Dainichi T, Uchi H, Moroi Y, Furue M: Stevens-Johnson syndrome, drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis caused by allopurinol in patients with a common HLA allele: what causes the diversity?. Dermatology. 2007, 215: 86-88. 10.1159/000102045.
Perez-Ruiz F, Hernando I, Villar I, Nolla JM: Correction of allopurinol dosing should be based on clearance of creatinine, but not plasma creatinine levels: another insight to allopurinol-related toxicity. J Clin Rheumatol. 2005, 11: 129-133. 10.1097/01.rhu.0000164822.98163.22.
Okamoto K, Eger BT, Nishino T, Kondo S, Pai EF, Nishino T: An extremely potent inhibitor of xanthine oxidoreductase. Crystal structure of the enzyme-inhibitor complex and mechanism of inhibition. J Biol Chem. 2003, 278: 1848-1855. 10.1074/jbc.M208307200.
Becker M, Schumacher HR, Espinoza L, Wells A, MacDonald P, Lloyd E, Lademacher C: A phase 3 randomized, controlled, multicenter, double-blind trial (RCT) comparing efficacy and safety of daily febuxostat (FEB) and allopurinol (ALLO) in subjects with gout [abstract]. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58 (Suppl 9): L11-
Schumacher HR, Becker MA, Lloyd E, MacDonald PA, Lademacher C: Febuxostat in the treatment of gout: 5-yr findings of the FOCUS efficacy and safety study. Rheumatology. 2009, 48: 188-194. 10.1093/rheumatology/ken457.
Hu M, Tomlinson B: Febuxostat in the management of hyperuricemia and chronic gout: a review. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2008, 4: 1209-1220.
Sundy JS, Hershfield MS: Uricase and other novel agents for the management of patients with treatment-failure gout. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2007, 9: 258-264. 10.1007/s11926-007-0041-y.
Terkeltaub R: Learning how and when to employ uricase as bridge therapy in refractory gout. J Rheumatol. 2007, 34: 1955-1958.
Richette P, Brière C, Hoenen-Clavert V, Loeuille D, Bardin T: Ras-buricase for tophaceous gout not treatable with allopurinol: an exploratory study. J Rheumatol. 2007, 34: 2093-2098.
Sherman MR, Saifer MG, Perez-Ruiz F: PEG-uricase in the management of treatment-resistant gout and hyperuricemia. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008, 60: 59-68. 10.1016/j.addr.2007.06.011.
Sundy JS, Becker MA, Baraf HS, Barkhuizen A, Moreland LW, Huang W, Waltrip RW, Maroli AN, Horowitz Z: Reduction of plasma urate levels following treatment with multiple doses of pegloticase (polyethylene glycol-conjugated uricase) in patients with treatment-failure gout: Results of a phase II randomized study. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58: 2882-2891. 10.1002/art.23810.
Baraf HS, Becker MA, Edwards NL, Gutierrez-Urenz SR, Sundy JS, Treadwell EL: Tophus response to pegloticase (PGL) therapy: Pooled results from GOUT1 and GOUT2, PGL phase 3 randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58 (Suppl 9): S176-
Sundy JS, Baraf HS, Becker MA, Edwards NL, Gutierrez-Urena SR, Treadwell EL, Horowitz Z: Efficacy and safety of intravenous (IV) pegloticase (PGL) in subjects with treatment failure gout (TFG): Phase 3 results from GOUT1 and GOUT2 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58 (Suppl 9): S400-
Becker MA, Treadwell EL, Baraf HS, Edwards NL, Gutierrez-Urena SR, Sundy JS, Horowitz Z: Immunoreactivity and clinical response to pegloticase (PGL): Pooled data from GOUT1 and GOUT2 PGL phase 3 randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58 (Suppl 9): 1945-
Góth L: Rasburicase therapy may cause hydrogen peroxide shock. Orv Hetil. 2008, 149: 1587-1590. 10.1556/OH.2008.28422.
Góth L, Bigler NW: Catalase deficiency may complicate urate oxidase (rasburicase) therapy. Free Radic Res. 2007, 41: 953-955. 10.1080/10715760701482451.
Zharikov S, Krotova K, Hu H, Baylis C, Johnson RJ, Block ER, Patel J: Uric acid decreases NO production and increases arginase activity in cultured pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008, 295: C1183-1190. 10.1152/ajpcell.00075.2008.
Gersch C, Palii SP, Kim KM, Angerhofer A, Johnson RJ, Henderson GN: Inactivation of nitric oxide by uric acid. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2008, 27: 967-978. 10.1080/15257770802257952.
Ramazzina I, Folli C, Secchi A, Berni R, Percudani R: Completing the uric acid degradation pathway through phylogenetic comparison of whole genomes. Nat Chem Biol. 2006, 2: 144-148. 10.1038/nchembio768.
Hare JM, Mangal B, Brown J, Fisher C, Freudenberger R, Colucci WS, Mann DL, Liu P, Givertz MM, Schwarz RP, OPT-CHF Investigators: Impact of oxypurinol in patients with symptomatic heart failure. Results of the OPT-CHF study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008, 51: 2301-2309. 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.01.068.
Feig DI, Kang DH, Johnson RJ: Uric acid and cardiovascular risk. N Engl J Med. 2008, 359: 1811-1821. 10.1056/NEJMra0800885.
Krishnan E, Svendsen K, Neaton JD, Grandits G, Kuller LH, MRFIT Research Group: Long-term cardiovascular mortality among middle-aged men with gout. Arch Intern Med. 2008, 168: 1104-1110. 10.1001/archinte.168.10.1104.
Issac TT, Dokainish H, Lakkis NM: Role of inflammation in initiation and perpetuation of atrial fibrillation: a systematic review of the published data. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007, 50: 2021-2028. 10.1016/j.jacc.2007.06.054.
Streitner F, Kuschyk J, Veltmann C, Brueckmann M, Streitner I, Brade J, Neumaier M, Bertsch T, Schumacher B, Borggrefe M, Wolpert C: Prospective study of interleukin-6 and the risk of malignant ventricular tachyarrhythmia in ICD-recipients – a pilot study. Cytokine. 2007, 40: 30-34. 10.1016/j.cyto.2007.07.187.
Ucar HI, Tok M, Atalar E, Dogan OF, Oc M, Farsak B, Guvener M, Yilmaz M, Dogan R, Demircin M, Pasaoglu I: Predictive significance of plasma levels of interleukin-6 and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery. Heart Surg Forum. 2007, 10: E131-135. 10.1532/HSF98.20061175.
Briesacher BA, Andrade SE, Fouayzi H, Chan KA: Comparison of drug adherence rates among patients with seven different medical conditions. Pharmacotherapy. 2008, 28: 437-443. 10.1592/phco.28.4.437.
Becker MA, MacDonald PA, Hunt BJ, Lademacher C, Joseph-Ridge N: Determinants of the clinical outcomes of gout during the first year of urate-lowering therapy. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2008, 27: 585-591. 10.1080/15257770802136032.
Schumacher HR, Taylor W, Joseph-Ridge N, Perez-Ruiz F, Chen LX, Schlesinger N, Khanna D, Furst DE, Becker MA, Dalbeth N, Edwards NL: Outcome evaluations in gout. J Rheumatol. 2007, 34: 1381-1385.
Taylor WJ, Schumacher HR, Baraf HS, Chapman P, Stamp L, Doherty M, McQueen F, Dalbeth N, Schlesinger N, Furst DE, Vazquez-Mellado J, Becker MA, Kavanaugh A, Louthrenoo W, Bardin T, Khanna D, Simon LS, Yamanaka H, Choi HK, Zeng X, Strand V, Grainger R, Clegg D, Singh JA, Diaz-Torne C, Boers M, Gow P, Barskova VG: A modified Delphi exercise to determine the extent of consensus with OMERACT outcome domains for studies of acute and chronic gout. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008, 67: 888-891. 10.1136/ard.2007.079970.
Singh JA, Strand V: Gout is associated with more comorbidities, poorer health-related quality of life and higher healthcare utilisation in US veterans. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008, 67: 1310-1316. 10.1136/ard.2007.081604.
Wu EQ, Patel PA, Yu AP, Mody RR, Cahill KE, Tang J, Krishnan E: Disease-related and all-cause health care costs of elderly patients with gout. J Manag Care Pharm. 2008, 14: 164-175.
Neogi T, Hunter DJ, Chaisson CE, Allensworth-Davies D, Zhang Y: Frequency and predictors of inappropriate management of recurrent gout attacks in a longitudinal study. J Rheumatol. 2006, 33: 104-109.
Singh JA: Quality of life and quality of care for patients with gout. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2009, 11: 154-160. 10.1007/s11926-009-0022-4.
Mikuls TR: Quality of care in gout: from measurement to improvement. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2007, 25 (6 Suppl 47): 114-119.
Kim SY, Choi HK: Gout and quality of life. J Rheumatol. 2009, 36: 865-868. 10.3899/jrheum.090034.
Dehghan A, Köttgen A, Yang Q, Hwang SJ, Kao WL, Rivadeneira F, Boerwinkle E, Levy D, Hofman A, Astor BC, Benjamin EJ, van Duijn CM, Witteman JC, Coresh J, Fox CS: Association of three genetic loci with uric acid concentration and risk of gout: a genome-wide association study. Lancet. 2008, 372: 1953-1961. 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61343-4.
Graser A, Johnson TR, Bader M, Staehler M, Haseke N, Nikolaou K, Reiser MF, Stief CG, Becker CR: Dual energy CT characterization of urinary calculi: initial in vitro and clinical experience. Invest Radiol. 2008, 43: 112-119. 10.1097/RLI.0b013e318157a144.
Choi HK, Al-Arfaj A, Eftekhari A, Munk PL, Shojania K, Reid G, Nicolaou S: Dual energy computed tomography in tophaceous gout. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008,
Acknowledgements
Dr John Scavulli (Kaiser Permanente, San Diego, CA, USA) provided the author with a helpful review of gout care in the USA. Supported by the Research Service of the Department of Veterans Affairs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
RT serves as consultant for Takeda, Savient, BioCryst, ARDEA, Altus, Novartis, Regeneron, Pfizer, URL Pharma, and UCB, and is also is the past recipient of research grant support from Takeda.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terkeltaub, R. Gout. Novel therapies for treatment of gout and hyperuricemia. Arthritis Res Ther 11, 236 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1186/ar2738
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/ar2738