Abstract
Background
Diabetes mellitus is often associated with microvascular and macrovascular lesions, and hyperglycemia-induced vascular endothelial cell damage is a key factor.
Methods
We investigated long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and mRNAs that are affected by hyperglycemia-induced damage using human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) as a model. HUVECs were cultured under high (25 mmol/L) or normal (5 mmol/L) glucose conditions for 6 d, and then lncRNAs and protein-coding transcripts were profiled by RNA-seq.
Result
Among 40,379 lncRNAs screened, 214 were upregulated (log2 [fold-change] > 1, FDR < 0.05) and 197 were downregulated (log2 [fold-change] < − 1, FDR < 0.05) in response to high-glucose. Furthermore, among 28,431 protein-coding genes screened, 778 were upregulated and 998 were downregulated. A total of 945 lncRNA/mRNA pairs were identified, including 126 differentially expressed lncRNAs predicted to target 201 mRNAs, among which 26 were cis-regulatory interactions. The corresponding lncRNA-mRNA network was composed of 354 lncRNA nodes, 1167 mRNA nodes and 9735 edges. Dozens of lncRNAs with high degree may play important roles in high-glucose-induced HUVEC damage, including ENST00000600527, NONHSAT037576.2, NONHSAT135706.2, ENST00000602127, NONHSAT200243.1, NONHSAT217282.1, NONHSAT176260.1, NONHSAT199075.1, NONHSAT067063.2, NONHSAT058417.2.
Conclusion
These observations may provide novel insights into the regulatory molecules and pathways of hyperglycemia-related endothelial dysfunction in diabetes-associated vascular disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Diabetes-related microvascular and macrovascular complications are directly correlated with the severity and duration of hyperglycemia [1, 2]. Stable and healthy endothelial cells are the basis of normal blood vessels, whereas dysfunction of endothelial cells is a risk indicator of diabetic angiopathy [3, 4]. Protein kinase C, hexosamine pathways, polyol pathways, and advanced glycation end-products are believed to be responsible for dysfunction associated with endothelial cell diabetes mellitus. These factors inhibit the production of nitric oxide by promoting the bioavailability of reactive oxygen species, thus altering the structure and physiology of endothelial cells [4,5,6,7,8]. Hyperglycemia is the main contributor of endothelial dysfunction [9]. Advanced glycation end products of hyperglycemia compromise the bioavailability of nitric oxide, which essentially drives endothelial dysfunction [10]. The effect of advanced glycation end products on monocytes, macrophages and vascular smooth muscle cells enhances the inflammatory response and oxidative stress in the endothelial system [9, 10]. Thus, unlike other cells or tissues, the vascular endothelium is extremely sensitive to blood glucose and is the direct target of hyperglycemia injury [11].
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are non-coding RNA molecules that contain over 200 nucleotides. LncRNAs play important regulatory roles in various diseases, such as cancers [12,13,14,15], atherosclerosis [15], neurodegeneration [11], autoimmune disorders [16,17,18,19,20], and chronic vascular disease [21]. Data from both in vitro hyperglycemia induction and in vivo diabetes mellitus experiments have shown that lncRNA MALAT1 is highly expressed, and that inhibition of its expression can effectively improve endothelial cell inflammation and diabetic retinopathy [22, 23]. Furthermore, high glucose (HG) treatment of vascular endothelial cells is accompanied by increased expression of lncRNA MIAT, and interference with MIAT can promote the proliferation, migration and abnormal angiogenesis of vascular endothelial cells induced by HG [24]. In human endothelial cells, the knockdown of lncRNA AGAP2-AS1 inhibits cell proliferation, tubule formation and acetylated LDL uptake [25]. Additionally, HG or oxidative stress inhibits the expression of lncRNA MEG3 in endothelial cells and diabetic mice. Knockout of lncRNA MEG3 can aggravate retinal vascular dysfunction and increase microvascular leakage and inflammation [26]. These results suggest that lncRNAs may comprise novel therapeutic targets in hyperglycemia-related endothelial dysfunction or diabetes-induced vascular disease. In order to further understand the role of lncRNA in endothelial cell injury in diabetes mellitus, we carried out high throughput sequencing using human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) cultured under normal (CN) or HG conditions.
Methods
Cell culture
HUVECs were purchased from the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC, Wuhan, China), and were maintained in Modified Eagle’s Medium (MEM; Hyclone/Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Gibco, Gaithersburg, MD USA), penicillin (100 U/mL; Gibco), and streptomycin (100 μg/mL; Gibco) at 37 °C in a humidified 5% CO2 chamber. Confluent HUVECs were starved overnight before exposure to media with normal or HG. HUVECs assigned to the Control (CN) group were maintained for 6 d in 5 mmol/L glucose and 20 mmol/L mannitol to account for changes that may be triggered by osmolarity differences. The remaining HUVECs of the HG group were maintained for the same duration in glucose-enriched (final glucose concentration 25 mmol/L) media. There were three biological duplicates in each group of HUVECs.
RNA preparation and RNA-seq
TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) was used to isolate and purify total RNA according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The quantity and quality of the RNA were determined using a NanoDrop 2000 instrument (Thermo, Fisher Scientific). The RNA integrity was assessed by electrophoresis with denaturing agarose gels. Libraries were constructed according to the standard TruSeq protocol. Sequencing was performed on the Illumina HiSeq 2500 according to the manufacturer’s protocol at Ao-Ji Biotech (Shanghai, China).
Identification of lncRNAs by using a computational approach
Quality control of the RNA-Seq reads was conducted using FastQC (v0.11.3). Reads were trimmed using the software SEQTK for known Illumina TruSeq adapter sequences, poor reads and ribosome RNA reads. Trimmed reads were aligned to homo sapiens genome (hg38) using Hisat2 (version: 2.0.4) [27]. Transcripts were assembled using Stringtie (v1.3.0) and then were compiled together by gffcompare (v0.9.8) [28, 29], Transcripts with class codes “i,” “u,” and “x,” were considered to be potential novel long transcripts. Pfam [30], CPC [31] and CNCI [32] were used to compute the coding potential of each novel transcript. Transcripts with a Pfam score < 0, CNCI < 0 and CPC non-significant were considered to lack coding potential. Transcripts were matched with annotation databases, including NONCODE (v5) (http://www.noncode.org) [33] and Ensembl [34] The matched transcripts were considered to be known lncRNAs, and others were considered to be novel lncRNAs. All lncRNAs were quantified using Stringtie. According to the positional association between lncRNA and mRNA in the genome, lncRNA was classified into six types: Bidirectional, exonic_antisense, exonic_sense, intergenic, intronic_antisense and intronic_sense [35].
Prediction and functional analysis of target genes of differentially expressed lncRNAs
Chromosome localizations, sequence complementarity and correlation coefficients between lncRNA and mRNA pairs were analyzed in order to identify the lncRNAs’ cis- and trans-target genes. In brief, a distinction was made according to chromosome location: if lncRNAs were located in the range of 10 KB upstream and 20 KB downstream of the coding gene, they were considered likely to be cis-regulatory [26, 27]. The trans-regulatory interaction potential between lncRNAs and mRNAs was analyzed by RNAplex software [28], with binding energy of <− 30 as the threshold. Furthermore, the Pearson correlation coefficients (PCCs) between lncRNAs and mRNAs were calculated, with a cutoff of PCC ≥ 0.6. The functions of these candidate coding genes were assessed using gene ontology (GO) function and pathway analysis using ClusterProfiler.
The lncRNA-mRNA-coexpression network
The lncRNA and mRNA co-expression network was constructed according to the normalized fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads of the unit genes. We calculated the PCC between differentially expressed lncRNAs and differentially expressed mRNAs. LncRNA-mRNA pairs with significant correlations (PCC > 0.99 and p < 0.01) were chosen to build the co-expression network and visualized by Cytoscape. The number of directly linked neighbors for each node was calculated and was defined as the nodes degree.
RT-PCR validation
Seven lncRNAs were randomly selected for verification of the RNA-Seq results by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR), which was performed on a Roche LightCycler 480 machine (Roche Applied Science, Germany) with the SYBR green assay (TaKaRa, Japan). The qRT-PCR amplification reactions were carried out via the following program: 95 °C for 10 min, 40 cycles with 95 °C for 15 s and 60 °C for 20 s. The primer sequences for qRT-PCR are provided in Table 1. With GAPDH as an internal control, the relative expression was computed according to the 2−ΔΔCt method.
Results
LncRNA-sequencing data analysis
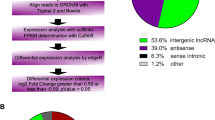
We characterized the lncRNA landscape of expression by performing deep RNA-seq experiments on three CN and three HG-induced HUVECs samples. After SEQTK quality assessment, more than 33 million total original reads for each sample were obtained, and the proportion of bases with quality values greater than 20 (Q20) was > 94%. These results indicate that the quality of the sequencing results was acceptable (Table 2). After filtering out the adaptor sequence and low quality reads, the percentage of clean reads within the raw reads accounted for 94% of the total sequences in the two groups. Hisat2 software was used to map the clean reads to homo sapiens reference genome. As shown in Table 2, approximately 97% of the trimmed reads were mapped onto the reference genome. In total, we screened 40,380 lncRNAs from the six samples, including 387 novel and 39,993 known lncRNAs, of which 36,550 were shared lncRNAs detected in both the HG and CN HUVEC groups (Fig. 1a, Supplemental Table S1). Most of the identified lncRNAs were transcribed from protein-coding exons (sense and antisense); others were from introns and intergenic regions (Fig. 1b). Furthermore, 24,304 lncRNA transcripts could be found in all chromosomes, with the majority located on chromosome 1 (Fig. 1c).
Identification of differentially expressed lncRNAs
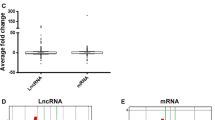
EdgeR was used to filter differentially expressed lncRNAs (DELs) between the HG-induced and CN HUVEC groups. Among the lncRNAs, 214 were significantly upregulated (log2 (fold-change) > 1, FDR < 0.05) and 197 were significantly downregulated (log2 (fold-change) < − 1, FDR < 0.05) in response to HG exposure (Fig. 2). Additionally, several of the DELs had a fold change value equal to positive infinity and negative infinity, meaning that these lncRNAs were completely switched-on or off with HG induction. The top five upregulated DELs were NONHSAT180405.1, MSTRG.31780.5, NONHSAT086922.2, NONHSAT022138.2, NONHSAT094345.2 and the top five downregulated DELs were NONHSAT056661.2, NONHSAT204850.1, NONHSAT217441.1, MSTRG.9798.2, NONHSAT152502.1 (Supplemental Table S2).
Characterization of differentially expressed lncRNAs in High Glucose (HG) versus Control Normal (CN) cells. a Correlation plots, b volcano plots, and c heatmap of differentially expressed lncRNAs. For panels a and b, blue indicates > 2 fold decreased expression and red indicates > 2 fold increased expression of the dysregulated lncRNAs in HG-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) (p < 0.05). The gray indicates no significant change. For panel C, red indicates high expression and green indicates low expression of genes with > 2 fold dysregulation for each of the 6 samples
qRT-PCR verification of DELs
To verify our findings, the expression profiles of six differentially expressed lncRNAs were randomly selected for qRT-PCR analysis. There were three repeats per group and five repeats per sample in the qPCR. The results show that the expression of the lncRNAs had similar trends as with the sequencing results, indicating that our sequencing results were reliable (Fig. 3).
Regulatory analysis of DELs and DEGs
lncRNAs act via cis- and trans-regulation of target genes for biological function. To evaluate the regulatory pathways associated with the lncRNAs, we assessed the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the same HUVEC samples. Of 28,431 protein-coding genes that were screened, 778 were upregulated and 998 downregulated by HG treatment. By comparing the DELs and the DEGs, a total of 945 matched lncRNA-mRNAs pairs for 126 DELs and 201 DEGs were predicted, of which 26 lncRNA/mRNA interactions were cis-regulatory, with either positive or negative correlations of the lncRNAs with their predicted target genes. An additional 715 interactions were trans-regulatory, including 2 that were both cis- and trans-regulatory (Supplemental Table S3).
To further understand the regulatory functions of the differentially expressed lncRNAs, all predicted target genes were annotated according to GO and pathway function entries using ClusterProfiler. Among the GO Enrichment terms (Fig. 4a) the most abundant in the biological process categories were Mitotic cell cycle, Cell cycle, Cell division, Microtubule cytoskeleton organization, DNA replication, Chromosome segregation, Spindle organization, Cytoskeleton organization, Cholesterol biosynthetic process, and Centromere complex assembly. The most abundant GO terms in the cellular component categories were, Molecular function Centromeric region, Chromosome, spindle, Chromosome, Replication fork, Nuclear chromosome, Condensed nuclear chromosome, Microtubule, Microtubule cytoskeleton, Cytoskeleton, and Nucleoplasm. Among the Pathway Enrichment terms (Fig. 4b), the most abundant were beta-Alanine metabolism, Primary immunodeficiency, Carbohydrate digestion and absorption, Arginine and proline metabolism, Histidine metabolism, Fatty acid elongation, Homologous recombination, Colorectal cancer, Mucin type O-Glycan biosynthesis, Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC), Aldosterone-regulated sodium reabsorption, Cardiac muscle contraction, Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), Endocrine and other factor-regulated calcium reabsorption, Dilated cardiomyopathy, Valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation, Fatty acid metabolism, Apoptosis, NF-kappa B signaling pathway, Endometrial cancer, Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes, and Hippo signaling pathway.
lncRNA-mRNA co-expression network
To visualize the co-expression network, pairs of lncRNAs and mRNAs that had PCC > 0.99 and p < 0.01 were assessed using Cytoscape software. As shown in Fig. 5, the lncRNA–mRNA network was composed of 354 lncRNA nodes, 1167 mRNA nodes and 9735 edges. According to the nodes and connections, the top 10 LncRNAs that could connect with highest protein coding genes were ENST00000600527 (degree = 241), NONHSAT037576.2 (degree = 234), NONHSAT135706.2 (degree = 233), ENST00000602127 (degree = 226), NONHSAT200243.1 (degree = 221), NONHSAT217282.1 (degree = 219), NONHSAT176260.1 (degree = 216), NONHSAT199075.1 (degree = 204), NONHSAT067063.2 (degree = 197), and NONHSAT058417.2 (degree = 192) (Fig. 5). In our analysis, we found some famous lncRNAs, which could connect with more than 100 protein coding genes, such as: MUC20-OT1 (ENST00000600527 and ENST00000602127), TIMM23B-AGAP6 (ENST00000444438), DAPK1-IT1 (ENST00000431813), and ZNF528-AS1 (ENST00000594119). Taking ENST00000431813 (DAPK1-IT1) as an example, we constructed a network diagram of its interaction with mRNA (Fig. 6).
A lncRNA-gene-network based on Pearson’s correlation coefficient analysis of differentially expressed lncRNAs (DELs) from High Glucose (HG) versus Control Normal (CN) human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Pink nodes indicate upregulated mRNAs or lncRNAs, and green nodes indicate downregulated mRNAs or lncRNAs
Discussion
Using microarray analysis, a variety of lncRNAs have been determined to be dysregulated in HG-induced HUVECs [36]. In addition, mechanistic studies indicate a role for specific lncRNAs in endothelial cell dysfunction induced by diabetes or HG [22,23,24,25,26]. Both clinical and experimental studies indicate that impairment of vascular smooth muscle cells by diabetes and HG contribute to the increased incidence of diabetic cardiomyopathy [37]. Furthermore, a large number of studies have shown that lncRNAs are involved in the injury of vascular smooth muscle induced by diabetes mellitus. For example, lncRNA-ES3 can regulate calcification/senescence of vascular smooth muscle cells through an miR-34c-5p/BMF axis that is activated upon HG induction [38]. The lncRNA SENCR shows high abundance of expression in vascular cells [37, 39, 40], and can regulate fork-head box protein O1 and transient receptor potential cation channel 6, thereby promoting the proliferation and migration of smooth muscle cells. HG exposure of T2DM db/db mice can inhibit the expression and function in smooth muscle cells, and overexpression of SENCR reverses the inhibitory effect of HG on vascular smooth muscle cells [40]. Given the important role of these lncRNAs, we rationalized that it is likely that other uncharacterized lncRNAs participate in the processes of endothelial cell pathogenesis caused by diabetes. Further, RNA-seq—as a highly sensitive approach towards identifying differentially expressed RNAs—could be used for the purpose of identifying the roles of these yet uncharacterized lncRNAs.
In the present study, a total of 214 upregulated and 197 downregulated lncRNAs (|FC| > 2, FDR < 0.05) were identified through RNA-seq using an HG-induced HUVEC model. Quality control assays were performed to ensure the reliability of the experiments, and several lncRNAs were validated using RT-qPCR. Furthermore, DEGs in the same cells were identified, and the lncRNA and mRNA expression profiles were compared. Using a variety of bioinformatics approaches, we revealed pathways and processes associated with dysregulation of lncRNA expression. It is well known that the AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications plays an important role in endothelial cell injury induced by diabetes mellitus. In Enrichment Analysis based on lncRNA-mRNA co-expression networks, up to 45 lncRNAs were found to be associated with this pathway, especially ENST00000600527, NONHSAT217282.1, NONHSAT067063.2, NONHSAT093248.2, NONHSAT118785.2, ENST00000444438, NONHSAT200447.1, NONHSAT108582.2, ENST00000508000, ENST00000594119, NONHSAT186088.1. Therefore, our findings are consistent with current understanding of processes by which diabetes promotes endothelial cell injury. On the basis of our findings, the information obtained in this study should be useful for identifying additional pathways and processes that contribute to the pathogenesis of diabetes.
Moreover, we identified some known lncRNAs may participate in high-glucose treated HUVEC. DAPK1-IT1, DAPK1 intronic transcript 1, has proved involved in cancer progression [41, 42], chemotherapy insensitivity [43], Atherogenesis [44, 45], etc. In our study, we constructed the coexpression subnet of DAPK1-IT1 and function was analyzed with KEGG pathway (Fig. 6), found may function with Terpenoid backbone biosynthesis, Steroid biosynthesis, Vitamin digestion and absorption, Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum, Phagosome, and some of these pathways have been proved to be involved in the occurrence and development of diabetes. LINC00969 was identified as a competitive endogenous RNA (CERNA) of miR-335-3p in vitro, which positively regulates the expression of Thioredoxin interacting protein (TXNIP) [46]. We will conduct further clinical studies on other lincRNAs in the future.
Conclusion
The potential roles of lncRNAs in diabetic complications were investigated by bioinformatics analysis. These findings may help us to understand the possible molecular mechanism of HG-induced HUVECs and may provide a more comprehensive understanding of the lncRNA expression profile that is dysregulated during diabetes.
Availability of data and materials
The sequences can be accessed after (1 May 2021) at (https://dataview.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/object/PRJNA534362?reviewer=kbilbcamsojq6imld1g394slf2) with (PRJNA534362). Until then, the sequences are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- lncRNAs:
-
Long non-coding RNAs
- HUVECs:
-
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- HG:
-
High glucose
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- ARVC:
-
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy
References
Hayward RA, Reaven PD, Emanuele NV, Investigators V. Follow-up of glycemic control and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(10):978.
Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HA. 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(15):1577–89.
Kapral MK, Fung K, Tu JV, Booth GL. Relation between age and cardiovascular disease in men and women with diabetes compared with non-diabetic people:a population-based retrospective cohort study. Digest World Core Med J. 2006;368(9529):29–36.
Giacco F, Brownlee M. Oxidative stress and diabetic complications. Circ Res. 2010;107(9):1058–70.
Matough FA, Budin SB, Hamid ZA, Alwahaibi N, Mohamed J. The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in diabetic complications. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2012;12(1):5–18.
Sasaki S, Inoguchi T. The role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of diabetic vascular complications. Diabetes Metab J. 2012;36(4):255–61.
Vikram A, Tripathi DN, Kumar A, Singh S. Oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetic complications. Int J Endocrinol. 2014;2014:679754.
Wu H, Cai L, de Haan JB, Giacconi R. Targeting oxidative stress in diabetic complications: new insights. J Diabetes Res. 2018;2018:1909675.
Avogaro A, de Kreutzenberg SV, Fadini G. Endothelial dysfunction: causes and consequences in patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2008;82(Suppl 2):S94–S101.
Soldatos G, Cooper ME, Jandeleit-Dahm KA. Advanced-glycation end products in insulin-resistant states. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2005;7(2):96–102.
Kaiser N, Sasson S, Feener EP, Boukobza-Vardi N, Higashi S, Moller DE, Davidheiser S, Przybylski RJ, King GL. Differential regulation of glucose transport and transporters by glucose in vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Diabetes. 1993;42(1):80–9.
Abraham JM, Meltzer SJ. Long noncoding RNAs in the pathogenesis of Barrett's esophagus and esophageal carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2017;153(1):27–34.
Prensner JR, Chinnaiyan AM. The emergence of lncRNAs in cancer biology. Cancer Discov. 2011;1(5):391–407.
Yang X, Xie X, Xiao YF, Xie R, Hu CJ, Tang B, Li BS, Yang SM. The emergence of long non-coding RNAs in the tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2015;360(2):119–24.
Zhang Z, Salisbury D, Sallam T. Long noncoding RNAs in atherosclerosis: JACC review topic of the week. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;72(19):2380–90.
Xu F, Jin L, Jin Y, Nie Z, Zheng H. Long noncoding RNAs in autoimmune diseases. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019;107(2):468–75.
Zhao CN, Mao YM, Liu LN, Li XM, Wang DG, Pan HF. Emerging role of lncRNAs in systemic lupus erythematosus. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;106:584–92.
Chen YG, Satpathy AT, Chang HY. Gene regulation in the immune system by long noncoding RNAs. Nat Immunol. 2017;18(9):962–72.
Tang Y, Zhou T, Yu X, Xue Z, Shen N. The role of long non-coding RNAs in rheumatic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017;13(11):657–69.
Wu GC, Pan HF, Leng RX, Wang DG, Li XP, Li XM, Ye DQ. Emerging role of long noncoding RNAs in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 2015;14(9):798–805.
Gangwar RS, Rajagopalan S, Natarajan R, Deiuliis JA. Noncoding RNAs in cardiovascular disease: pathological relevance and emerging role as biomarkers and therapeutics. Am J Hypertens. 2018;31(2):150–65.
Liu JY, Yao J, Li XM, Song YC, Wang XQ, Li YJ, Yan B, Jiang Q. Pathogenic role of lncRNA-MALAT1 in endothelial cell dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5:e1506.
Puthanveetil P, Chen S, Feng B, Gautam A, Chakrabarti S. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 regulates hyperglycaemia induced inflammatory process in the endothelial cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2015;19(6):1418–25.
Yan B, Yao J, Liu JY, Li XM, Wang XQ, Li YJ, Tao ZF, Song YC, Chen Q, Jiang Q. lncRNA-MIAT regulates microvascular dysfunction by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Circ Res. 2015;116(7):1143–56.
Kurian L, Aguirre A, Sancho-Martinez I, Benner C, Hishida T, Nguyen TB, Reddy P, Nivet E, Krause MN, Nelles DA, et al. Identification of novel long noncoding RNAs underlying vertebrate cardiovascular development. Circulation. 2015;131(14):1278–90.
Qiu GZ, Tian W, Fu HT, Li CP, Liu B. Long noncoding RNA-MEG3 is involved in diabetes mellitus-related microvascular dysfunction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;471(1):135–41.
Kim D, Langmead B, Salzberg SL. HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods. 2015;12(4):357–60.
Pertea M, Kim D, Pertea GM, Leek JT, Salzberg SL. Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat Protoc. 2016;11(9):1650–67.
Pertea M, Pertea GM, Antonescu CM, Chang TC, Mendell JT, Salzberg SL. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat Biotechnol. 2015;33(3):290–5.
Sun L, Zhang Z, Bailey TL, Perkins AC, Tallack MR, Xu Z, Liu H. Prediction of novel long non-coding RNAs based on RNA-Seq data of mouse Klf1 knockout study. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012;13:331.
Kong L, Zhang Y, Ye ZQ, Liu XQ, Zhao SQ, Wei L, Gao G. CPC: assess the protein-coding potential of transcripts using sequence features and support vector machine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(Web Server issue):W345–9.
Sun L, Luo H, Bu D, Zhao G, Yu K, Zhang C, Liu Y, Chen R, Zhao Y. Utilizing sequence intrinsic composition to classify protein-coding and long non-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41(17):e166.
Fang S, Zhang L, Guo J, Niu Y, Wu Y, Li H, Zhao L, Li X, Teng X, Sun X, et al. NONCODEV5: a comprehensive annotation database for long non-coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(D1):D308–14.
Kinsella RJ, Kahari A, Haider S, Zamora J, Proctor G, Spudich G, Almeida-King J, Staines D, Derwent P, Kerhornou A, et al. Ensembl BioMarts: a hub for data retrieval across taxonomic space. Database. 2011;2011:bar030.
Knauss JL, Sun T. Regulatory mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs in vertebrate central nervous system development and function. Neuroscience. 2013;235:200–14.
Singh KK, Mantella LE, Pan Y, Quan A, Sabongui S, Sandhu P, Teoh H, Al-Omran M, Verma S. A global profile of glucose-sensitive endothelial-expressed long non-coding RNAs. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016;94(9):1007–14.
Riches K, Angelini TG, Mudhar GS, Kaye J, Clark E, Bailey MA, Sohrabi S, Korossis S, Walker PG, Scott DJ, et al. Exploring smooth muscle phenotype and function in a bioreactor model of abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Transl Med. 2013;11:208.
Lin X, Zhan JK, Zhong JY, Wang YJ, Wang Y, Li S, He JY, Tan P, Chen YY. Liu XB et al: lncRNA-ES3/miR-34c-5p/BMF axis is involved in regulating high-glucose-induced calcification/senescence of VSMCs. Aging. 2019;11(2):523–35.
Bell RD, Long X, Lin M, Bergmann JH, Nanda V, Cowan SL, Zhou Q, Han Y, Spector DL, Zheng D, et al. Identification and initial functional characterization of a human vascular cell-enriched long noncoding RNA. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014;34(6):1249–59.
Zou ZQ, Xu J, Li L, Han YS. Down-regulation of SENCR promotes smooth muscle cells proliferation and migration in db/db mice through up-regulation of FoxO1 and TRPC6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2015;74:35–41.
Lou W, Ding B, Zhong G, Du C, Fan W, Fu P. Dysregulation of pseudogene/lncRNA-hsa-miR-363-3p-SPOCK2 pathway fuels stage progression of ovarian cancer. Aging. 2019;11(23):11416–39.
Elaine Hardman W, Primerano DA, Legenza MT, Morgan J, Fan J, Denvir J. mRNA expression data in breast cancers before and after consumption of walnut by women. Data Brief. 2019;25:104050.
Kuang P, Chen P, Wang L, Li W, Chen B, Liu Y, Xu Y, Wang H, Zhao S, Ye L, et al. RNA sequencing analysis of small cell lung cancer reveals candidate chemotherapy insensitivity long noncoding RNAs and microRNAs. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(4):121.
Yan Y, Song D, Wu J, Wang J. Long non-coding RNAs link oxidized low-density lipoprotein with the inflammatory response of macrophages in Atherogenesis. Front Immunol. 2020;11:24.
Wang CH, Shi HH, Chen LH, Li XL, Cao GL, Hu XF. Identification of key lncRNAs associated with atherosclerosis progression based on public datasets. Front Genet. 2019;10:123.
Yu L, Hao Y, Xu C, Zhu G, Cai Y. LINC00969 promotes the degeneration of intervertebral disk by sponging miR-335-3p and regulating NLRP3 inflammasome activation. IUBMB Life. 2019;71(5):611–8.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge Mr. Qiang Fan (Ao-Ji Bio-tech Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) for technical assistance in RNA-seq. We thank LetPub (www.letpub.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Funding
This present research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81770803), key Program of Nature Science Foundation of Anhui Education Committee (grant no. KJ2019A0353), Science and Technology Development Fund of the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College (grant no. BYYFYKJ201716), and Key Project of Natural Science Foundation of Bengbu Medical College (grant no. BYKY1736ZD). The funding body played no role in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XYP and GXJ designed the study; XLH and XLL performed the experiments; EQX and QW carried out the data analysis; EQX and LGZ wrote the manuscript; All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The Authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1: Table S1
. List of 40,380 lncRNAs screened from HG and CN HUVEC groups.
Additional file 2: Table S2
. The top upregulated and downregulated DELs.
Additional file 3: Table S3
. Expression correlations of 715 lncRNA-mRNAs trans-regulatory pairs.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, E., Hu, X., Li, X. et al. Analysis of long non-coding RNA expression profiles in high-glucose treated vascular endothelial cells. BMC Endocr Disord 20, 107 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12902-020-00593-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12902-020-00593-6