Abstract
Reptiles have achieved highly diverse morphological and physiological traits that allow them to exploit various ecological niches and resources. Morphology of the temporal region of the reptilian skull is highly diverse and historically it has been treated as an important character for classifying reptiles and has helped us understand the ecology and physiology of each species. However, the developmental mechanism that generates diversity of reptilian skull morphology is poorly understood. We reveal a potential developmental basis that generates morphological diversity in the temporal region of the reptilian skull by performing a comparative analysis of gene expression in the embryos of reptile species with different skull morphology. By investigating genes known to regulate early osteoblast development, we find dorsoventrally broadened unique expression of the early osteoblast marker, Runx2, in the temporal region of the head of turtle embryos that do not form temporal fenestrae. We also observe that Msx2 is also uniquely expressed in the mesenchymal cells distributed at the temporal region of the head of turtle embryos. Furthermore, through comparison of gene expression pattern in the embryos of turtle, crocodile, and snake species, we find a possible correlation between the spatial patterns of Runx2 and Msx2 expression in cranial mesenchymal cells and skull morphology of each reptilian lineage. Regulatory modifications of Runx2 and Msx2 expression in osteogenic mesenchymal precursor cells are likely involved in generating morphological diversity in the temporal region of the reptilian skull.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Amniotes (Amniota) consist of two large groups of tetrapod vertebrates, Synapsida and Reptilia, that diverged from one another over 300 million years ago (Ma) (Carroll, 1988;Modesto & Anderson,, Modesto & Anderson, Modesto & Anderson,2004, Benton, 2005). The synapsids are represented today by mammals while reptiles by extant turtles, tuatara, lizards, snakes, crocodiles, birds, and their extinct relatives, including dinosaurs and pterosaurs. Over time, reptiles have evolved highly diverse morphological and physiological traits that allow them to exploit various ecological niches and resources on the land, in water, and in the air.
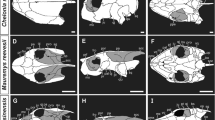
Morphology of the skull of reptiles, especially the temporal region is highly diverse (Figure 1). This morphological diversity observed in the temporal region is broadly categorized into three architectural patterns. The anapsid condition of the skull is observed in basal amniotes such as Scutosaurus and Captorhinus, and in turtles. In these animals, the temporal region of the skull is completely roofed by bones, without temporal openings (fenestrae). The synapsid condition of the skull is recognized in ancestral lineages of extant mammals and is characterized by the presence of a temporal fenestra at lower position of either side of the skull. The diapsid condition of the skull is seen in "non-turtle" extant reptiles and in their extinct relatives. In these animals, two temporal fenestrae exist on either side of the skull. In reptiles with fully diapsid skulls, the upper temporal fenestra is dorsally bordered by the parietal bone, anteriorly by the postorbital bone, and posteriorly by the squamosal bone. The lower temporal fenestra is dorsally surrounded by both the postorbital and squamosal bones, and ventrally by both the jugal and quadratojugal bones. These temporal fenestrae are thought to have evolved to allow space for accommodating the enlarged jaw-closing muscles that enable powerful biting, or to minimize stresses exerted by the contraction of jaw muscles on the skull, or to reduce the weight of the skull itself (Frazzetta, 1968, Carroll, 1982, Rieppel, 1993a, Benton, 2005). During the course of diapsid evolution skull morphology has been rearranged repeatedly, resulting in a variety of modified patterns (Rieppel, 1993a;Rieppel & Gronowski,, Rieppel & Gronowski, Rieppel & Gronowski,1981;Müller,, Müller, Müller,2003, Moazen et al., 2009). Among extant reptiles, fully diapsid skull is only seen in tuatara and crocodiles. Because the lower temporal bar that encloses the lower temporal fenestra ventrally is regarded to be lost once in the common ancestor of lepidosaurs (lizards, snakes, tuatara) and archosaurs (crocodiles and birds) (Rieppel, 1993a;Müller,, Müller, Müller,2003), these reptilian lineages possibly acquired the lower temporal bar secondarily (Müller, 2003, Moazen et al., 2009). Both snakes and birds have lost the upper temporal bar so that their temporal region is free from any bony frames (Pough et al., 2005).
Simplified phylogeny of the Reptilia highlighting diversity of their skull morphology. Paleontological evidence suggests that all reptiles, including extant lizards, snakes, tuatara, crocodiles, birds, and turtles, were derived from ancestor whose temporal region was completely roofed by bone. Earliest diapsid reptiles such as Petrolacosaurus (Araeoscelidia) acquired two temporal openings (fenestrae) on either side of the skull (red vertical bar). Recent molecular phylogenies indicate that turtles (Testudines) were derived from diapsid ancestor, which would require secondary closure of temporal fenestrae (green vertical bar). The bone surrounding anteroventral border of the upper temporal fenestra and anterodorsal border of the lower temporal fenestra in diapsids: the postorbital was colored in pink. The bone surrounding posteroventral border of the upper temporal fenestra and posterodorsal border of the lower temporal fenestra in diapsids: the squamosal was colored in blue. The bone surrounding the anteroventral margin of the lower temporal fenestra in diapsids: the jugal was colored in yellow. Lizards do not have the lower temporal bar. Both upper and lower temporal bars are absent in snakes and birds. Other extinct diapsid lineages such as Ichthyosauria and Sauropterygia were not included in phylogeny for simplicity.
In reptiles, phylogenetic position of turtles is highly controversial. Traditionally, turtles have been regarded as the only surviving clade of stem reptiles based on the pattern of their skull morphology: an anapsid skull whose temporal region is completely roofed with bones (Williston, 1917, Gregory, 1946, Romer, 1968, Gaffney, 1980;Reisz & Laurin,, Reisz & Laurin, Reisz & Laurin,1991, Lee, 1993;Laurin & Reisz,, Laurin & Reisz, Laurin & Reisz,1995, Lee, 1996 1997, Reisz, 1997, Lee, 2001). However, recent comprehensive analysis of morphological traits (Rieppel & deBraga, 1996;deBraga & Rieppel,, deBraga & Rieppel, deBraga & Rieppel,1997, Rieppel, 2000, Hill, 2005, Li et al., 2008, but see Lyson et al., 2010 2013 for opposed conclusion) and molecular phylogenetic studies (Hedges & Poling, 1999;Kumazawa & Nishida,, Kumazawa & Nishida, Kumazawa & Nishida,1999, Iwabe et al., 2005, Hugall et al., 2007, Shedlock et al., 2007, Shen et al., 2011, Tzika et al., 2011, Chiari et al., 2012, Crawford et al., 2012, Fong et al., 2012, Lyson et al., 2012, Wang et al., 2013) suggest that there is a close relationship of turtles to diapsid reptiles, implying that the temporal fenestrae were secondarily closed in turtles. In this study, we employ the hypothesis that turtles are descendent of diapsid reptiles.
Although skull morphology has been regarded as an important character in classification of reptiles and in understanding the ecological and physiological aspects of each reptilian species, the developmental mechanism underlying diversification of reptilian skull morphology is poorly understood (Rieppel, 1993a, Evans, 2008). As a consequence, a general genetic and developmental model of reptile skull diversity does not yet exist. In this paper, we test the hypothesis that changes of skeletal gene expression patterns cause diversification of reptilian skull morphology through comparative analyses of gene expression in the embryos of representative reptilian species and reveal a potential developmental basis underlying reptilian skull evolution. First, we describe the pattern of early phases of cranial morphogenesis in a crocodile species with both upper and lower temporal bars surrounding temporal fenestrae, using molecular markers specific for musculoskeletal tissue precursors. Then, we compare these data with cranial morphogenesis in a turtle species. We found a broader expression of the early osteogenic genes, Runx2 and Msx2 in the mesenchymal cells at the temporal region of turtle embryos, compared to that in crocodile embryos. Finally, to obtain a broader picture of reptilian skull morphogenesis, we examined expression patterns of Runx2 and Msx2 in cranial morphogenesis of a snake species without temporal bars on the skull and compared with the patterns in crocodile and turtle embryos. Our findings suggest that there is a possible correlation between the expression patterns of Runx2 and Msx2 and the architectural pattern seen in the temporal region of the reptilian skull.
Results
In previous studies in which cranial osteogenesis of reptilian embryos was described, whole-mount clearing and staining with Alizarin red was used to detect mineralization of intramembranous bones that comprise the dermatocranium (Kamal et al., 1970;Haluska & Alberch,, Haluska & Alberch, Haluska & Alberch,1983, Rieppel, 1993b, Rieppel, 1993c, Kuratani, 1999;Rieppel & Zaher,, Rieppel & Zaher, Rieppel & Zaher,2001, Sheil, 2003, Sheil, 2005, Boughner et al., 2007;Vickaryous & Hall,, Vickaryous & Hall, Vickaryous & Hall,2008;Sánchez-Villagra et al.,, Sánchez-Villagra et al., Sánchez-Villagra et al.,2009, Werneburg et al., 2009). However, this method is unable to identify the distribution of the precursor cells of bones: osteoblasts, as reported by others (Kerney et al., 2010). To overcome this, we conducted section in situ hybridization analysis, which labels tissues located deep inside of the embryonic body and is effective for detecting tissue-specific domains of expression. We used a probe to Runx2, which is a molecular marker for osteogenic mesenchymal precursor cells (Ducy et al., 1997, Bobola et al., 2003, Abzhanov et al., 2007, Han et al., 2007, Kerney et al., 2010) and described its expression pattern in the temporal region of reptilian embryos where mineralization of bones has not been initiated. Furthermore, to describe distribution pattern of "non-osteoblast" cell lineages relative to that of osteoblasts in the cranial tissue of the embryos, we also examined expression of other tissue-specific markers: MyoD for skeletal muscle precursors (Hacker & Guthrie, 1998, Noden et al., 1999), Sox9 for cartilage precursors (Wright et al., 1995, Bell et al., 1997), Scleraxis (Scx) and Six2 for precursor of connective tissues, including ligaments and tendons (Oliver et al., 1995, Schweitzer, 2001, Dreyer et al., 2004;Edom-Vovard & Duprez,, Edom-Vovard & Duprez, Edom-Vovard & Duprez,2004, Schweitzer et al., 2010).
Differential expression of early osteoblast marker, Runx2, in the head of crocodile and turtle embryos
Osteogenic mesenchymal precursor cells that express Runx2 are first detected in the temporal region of crocodile embryos at stage 14 (Additional file 1) and an almost identical pattern of Runx2 expression was observed in a subsequent embryonic stage (stage 15; Figure 2A). These Runx2-positive cells were localized at the domain dorsal to the oral cavity where the ventral part of the braincase and future palatine and pterygoid bones develop, as well as in a limited domain dorsolateral to the orbit where the future dorsal projection of the postorbital bone forms (Figure 2B). We also detected a population of Runx2-positive cells at the domain ventrolateral to the orbit where future jugal bone and ventral projection of postorbital bone are formed. At this stage, the precursor of the jugal and ventral projection of the postorbital were dorsoventrally continued as a layer of cells but it was thin mediolaterally, especially at the middle part. In the posterior part of the head, we observe a population of Runx2-positive mesenchymal cells that later differentiate into the main body of the postorbital bone (Figures 2E and 2H). In these stages of crocodile embryogenesis, jaw muscle precursors that were derived from cranial mesoderm migrated to the first pharyngeal arch and expressed MyoD was clearly detected at the central domain of the jaw primordia (Figures 2C and 2F; Additional file 1). Expression of Sox9 was detected at cartilage precursors that later differentiate into quadrate and Meckel's cartilages at the domain ventral to jaw muscle precursor, as well as in chondrocytes that form the future braincase (Figures 2D and 2G). Expression of Scx was detected in tendon precursor cells that are distributed within the primordia of the jaw muscles and in the connective tissue within the eye muscles (Additional file 1). Expression of Six2 was somewhat broader than that of other markers, expressed in mesenchymal cells surrounding the eyes, cartilaginous precursors of the braincase, quadrate, and Meckel's, as well as in the mesenchyme at the interface between muscle precursors and the skeletal tissues to which the muscles attach and in a population of the mesenchyme that dorsally surrounds the brain (Additional file 1).
Expression of musculoskeletal tissue marker genes in the head of crocodile embryos at stage 15. (A) Lateral view of the head of a crocodile embryo at stage 15. (B-D) Frontal sections prepared around the plane indicated by the red line in (A). (E-G) Frontal sections prepared around the plane indicated by the blue line in (A). (H) Frontal sections prepared around the plane indicated by the green line in (A). (B, E, and H) Runx2-positive mesenchymal cells are observed at the location where future dermatocranial elements are developed. (C and F) Expression of MyoD is detected at the cranial muscular tissues. (D and G) Cartilaginous tissues, including the braincase, quadrate, and Meckel's, are clearly labeled by Sox9 probe. The red outlined domains in (B, D, E, and G) indicate the location of the pseudotemporal muscle (ptm) deduced from adjacent sections where muscular tissues are labeled by MyoD probe. Scale bar in (A) is 1 mm. Scale bars in (B-H) are 0.5 mm.
In crocodile embryos at stage 17 where none of the dermatocranial elements were positive for Alizarin red in previous studies (Rieppel, 1993b;Vickaryous & Hall,, Vickaryous & Hall, Vickaryous & Hall,2008) (Figure 3A), we could detect Runx2 expression in the cell populations that were localized to the area where the future dermatocranium differentiates (Figure 3B). Although the domain where Runx2-positive cells were populated was almost identical to that in previous stages, the boundary of each precursor of the dermatocranial elements became clearer. Although differentiation of the parietal bone is delayed compared to other dermatocranial elements as described previously (Rieppel 1993b;Vickaryous & Hall,, Vickaryous & Hall, Vickaryous & Hall,2008), a pair of precursors of the parietal were recognized as Runx2-positive cell aggregation at the domain dorsolateral to the cartilaginous braincase (Figures 3B and 3E). We could detect Runx2-negative cell populations between the nascent parietal precursor and the morphologically more developed postorbital precursor and also between precursors of the postorbital and quadratojugal located lateral to Sox9-positive quadrate cartilage (Figure 3E). In this stage, MyoD was expressed in differentiated jaw and eye muscles (Figures 3C and 3F) and Sox9 was expressed in differentiated chondrocranium and splanchnocranium components, including the braincase, quadrate, and Meckel's (Figures 3D and 3G). Expression of Scx was detected in tendinous tissues accompanying MyoD-positive muscles as in previous stages (Figure 3H). Expression of Six2 was detected in the mesenchyme localized around the jaw articulation between quadrate and Meckel's, as well as in adjacent mesenchyme of the braincase, postorbital bone, and jaw muscles (Figure 3I).
Expression of musculoskeletal tissue marker genes in the head of crocodile embryos at stage 17. (A) Lateral view of the head of a crocodile embryo at stage 17. (B-D) Frontal sections prepared around the plane indicated by the red line in (A). (E-I) Frontal sections prepared around the plane indicated by the blue line in (A). (B and E) Expression of Runx2 is more concentrated to the precursors of dermatocranial elements, compared to the previous stages. (C, D, F, and G) Cranial muscular and cartilaginous tissues are clearly labeled by MyoD and Sox9 probes, respectively. (H and I) Expression domains of Scx and Six2 are indicated by arrowheads. The former is expressed in tendinous tissues accompanying cranial muscles and the latter is expressed mainly in connective tissue cells associated with cartilages of the jaw and the braincase. The red outlined domains in (B, D, E, G, H, and I) indicate the location of the pseudotemporal muscle deduced from adjacent sections where muscular tissues are labeled by MyoD probe. Green line in (A) indicates the plane where sections given in Figure 7D, E and F were prepared. Scale bar in (A) is 1 mm. Scale bars in (B-I) are 0.5 mm.
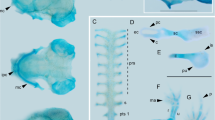
Next, we examined cranial morphogenesis of turtles that have an anapsid skull, using the same method to identify the distribution pattern of precursors of each tissue that constitutes the cranial musculoskeletal system. In turtle embryos at stage 14 (Additional file 2) that correspond to crocodile embryos at stage 14 in external morphology, and in turtle embryos at stage 15 (Figure 4A) that are comparable to crocodile embryos at stage 15, we observed almost identical patterns of expression for each gene. We detected MyoD expression specifically in the primordia of jaw adductor and eye muscles (Figures 4C and 4H; Additional file 2) and Sox9 expression in precursor cells of the braincase, quadrate, and Meckel's cartilages (Figures 4D and 4I; Additional file 2) as in stage-matched crocodile embryos. Expression of Scx was first detected in a layer of mesenchymal cells that was located at the periphery of the jaw adductor and eye muscle precursors in stage 15 turtle embryos (Figure 4E). Expression of Six2 was observed in the mesenchyme surrounding the eye and adjacent mesenchyme of the braincase and jaw cartilages, as well as in some mesenchymal cells within jaw muscle precursors (Figure 4F; see Additional file 2), as in stage-matched crocodile embryos. Interestingly, we observed expression of the early osteoblast marker, Runx2, in a broader domain at the temporal region of the head of turtle embryos, compared to that in stage-matched crocodile embryos. In stage14 turtle embryos, Runx2 expression was detected in a population of cells medial to the precursor of the jaw adductor muscles and the mesenchyme localized at the domain dorsolateral and ventrolateral to the orbit (Additional file 2). The domain of Runx2 expression became further expanded in the head of turtle embryos at stage 15. A thick layer of the mesenchymal cells that express Runx2 completely covered the brain and the precursor of jaw adductor muscle laterally (Figures 4B and 4G).
Expression of musculoskeletal tissue marker genes in the head of turtle embryos at stage 15. (A) Lateral view of the head of a turtle embryo at stage 15. (B-F) Frontal sections prepared around the plane indicated by the red line in (A). (G-I) Frontal sections prepared around the plane indicated by the blue line in (A). (B, G) Runx2-positive mesenchymal cells (arrows) are broadly distributed at lateral portion of the head, from the top of the head to the ventral margin of the first pharyngeal arch. (C and H) Cranial muscular tissues are clearly labeled by MyoD probe. (D and I) Cartilaginous tissues, including the braincase and quadrate, are clearly labeled by Sox9 probe. (E) Scx is expressed in tendon primordia accompanying cranial muscles (arrowheads). (F) Six2 is expressed mainly in connective tissue cells associated with the braincase cartilage and jaw adductor muscle (arrowheads). Note that the anlage of jaw adductor muscle (red outlined domain) is covered by a thick layer of Runx2-positive mesenchyme laterally. Scale bar in (A) is 1 mm. Scale bars in (B-I) are 0.5 mm.
In turtle embryos at stage 17 (Figure 5A) that correspond to crocodile embryos at stage 17 in overall morphology, we observed MyoD expression in differentiating cranial muscles, including external adductor muscles (Figure 5C) and Sox9 expression in the cartilaginous tissues that constitute the braincase, quadrate, and Meckel's (Figure 5D). Scx was specifically expressed in tendinous tissues at the periphery of jaw adductor muscles, as well as in the precursor of the bodenaponeurosis (central tendon of external adductor) just appeared within the jaw adductor muscular tissue (Figure 5E). The expression domain of Six2 was broader in the temporal region of the head compared to that of Scx, diffusively expressed in the mesenchymal cells surrounding jaw adductor muscles, braincase, and jaw cartilages (Figure 5F). A thick layer of Runx2-positive mesenchymal cells that surrounds the braincase and jaw adductor muscle laterally was observed (Figure 5B). Runx2-expressing mesenchyme was also distributed around the quadrate cartilage and the ventral part of the braincase.
Expression of musculoskeletal tissue marker genes in the head of turtle embryos at stage 17. (A) Lateral view of the head of a turtle embryo at stage 17. (B-F) Frontal sections prepared around the plane indicated by the blue line in (A). (B) Runx2-positive mesenchymal cells (arrows) are broadly distributed at the lateral portion of the head, from the top of the head to the ventral margin of the first pharyngeal arch derivative. (C) Cranial muscular tissues are clearly labeled by MyoD probe. (D) Cartilaginous tissues, including the braincase and quadrate, are clearly labeled by Sox9 probe. (E) Scx is expressed in tendinous tissues at the periphery of external adductor muscle (ame) (arrowheads) and in the bodenaponeurosis (boap. central tendon of jaw adductor muscle). (F) Six2 is expressed mainly in connective tissue cells associated with cartilages of the braincase and quadrate, as well as in connective tissue cells within jaw muscles (arrowheads). Note that the external adductor muscle (red outlined domain) is covered by a thick layer of Runx2-positive mesenchyme laterally. Scale bar in (A) is 1 mm. Scale bars in (B-F) are 0.5 mm.
Expression of potential upstream osteogenic regulatory genes in the head of crocodile and turtle embryos
Through comparative analysis of expression patterns of tissue-specific marker genes, we noticed a difference in the spatial pattern of expression of the early osteoblast marker, Runx2 in the head of crocodile and turtle embryos. To reveal potential mechanisms that account for such differential distribution of osteogenic mesenchymal precursor cells between two reptilian lineages with or without temporal fenestrae, we next examined expression patterns of some candidate genes that are known to regulate cranial osteogenesis. In the present study, we focused on Bmp4, Msx1, and Msx2. Bmp4 is a signaling molecule and plays a key role in the Bmp signaling pathway. Because exogenous Bmp4 increases tissue volume in calvarial bone tissue culture, this protein is considered to be involved in calvarial bone growth (Kim et al., 1998, Rice et al., 2003). Both Msx1 and Msx2 are members of the muscle segment homeobox (msh) gene family of transcription factors and both loss-of- and gain-of-function analyses of these genes suggest their essential roles in vertebrate cranial osteogenesis (Satokata & Maas, 1994, Satokata et al., 2000).
In the present analysis, we found that Bmp4 and Msx1 showed almost identical expression patterns through cranial osteogenesis in crocodile and turtle embryos. In crocodile embryos we examined (through stage 14 to stage 17), Bmp4 was strongly expressed in the epithelium of cochlear canal, the mesenchyme surrounding the eye, the mesenchyme distributed in the medial part of jaw primordia, the precursors of the palatine bones, and a population of mesenchymal cells that covered the brain dorsally (Figure 6A; Figures 7A and 7D). In turtle embryos we examined (through stage 14 to stage 17), Bmp4 was expressed in a spatially limited domain: the epitthelium of cochlear canal, the mesenchyme dorsolateral and ventrolateral to the eye and a limited population of the mesenchyme in close proximity of the jaw articulation (Figure 6G; Figure 7G). We observed Msx1 expression in the epithelium of the cochlear canal, the mesenchyme that occupies the domain close to the jaw articulation and lateral to the quadrate and Meckel's cartilages, and a thin layer of mesenchymal cells that covers the brain dorsally in crocodile embryos examined (Figure 6B; Figures 7B and 7E). In turtle embryos, Msx1 was expressed in the epithelium of the cochlear canal, the mesenchyme distributed around the jaw articulation and lateral to quadrate and Meckel's cartilages, as well as in the mesenchyme that populates the domain dorsal to the eye (Figure 6H; Figure 7H).
Expression of Bmp4 , Msx1 , and Msx2 in crocodile and turtle embryos at stage 15. (A-D) Frontal sections prepared around the plane indicated by the red line in Figure 2A. (E, F) Frontal sections prepared around the plane indicated by the blue line in Figure 2A. (G-J) Frontal sections prepared around the plane indicated by the red line in Figure 4A. (K, L) Frontal sections prepared around the plane indicated by the blue line in Figure 4A. (A and G) In both crocodile and turtle embryos, expression of Bmp4 is detected at the mesenchyme distributed in medial part of the jaw primordia (arrows). (B and H) Expression of Msx1 is detected at the mesenchyme that occupies the domain close to jaw articulation and lateral to quadrate and Meckel's cartilages (arrows). (C and E) In crocodile embryos, Msx2 is expressed in a thin layer of mesenchymal cells surrounding dorsal aspect of the brain and in a population of the mesenchyme that occupies the domain between ventrolateral part of quadrate cartilage and surface epidermis (arrows). (I and K) In turtle embryos, Msx2 is expressed in mesenchymal cells that populate lateral aspect of the head (arrows). In contrast to the condition in crocodile embryos, the ventral edge of Msx2-expressing mesenchymal layer is terminated ventral to the eye in turtle embryos and these cells cover MyoD-expressing jaw adductor muscle precursor (J and L) laterally. The red outlined domains in (A-C, and E) indicate the location of the anlagen of the pseudotemporal muscle deduced from adjacent sections where muscular tissues are labeled by MyoD probe. The red outlined domains in (G-I, and K) indicate the location of the anlagen of jaw adductor muscle. Scale bars are 0.5 mm.
Expression of Bmp4 , Msx1 , and Msx2 in crocodile and turtle embryos at stage 17. (A-C) Frontal sections prepared around the plane indicated by the blue line in Figure 3A. (D-F) Sections prepared around the plane indicated as the green line in Figure 3A. (G-I) Sections prepared around the plane indicated as the red line in Figure 5A. (J) Section prepared around the plane indicated as the blue line in Figure 5A. (A, D, and G) In both crocodile and turtle embryos, expression of Bmp4 is detected in the epithelium of the cochlear canal, the mesenchyme surrounding the eye, and the mesenchyme distributed in medial part of the jaw (arrows). (B, E, and H) Expression of Msx1 is detected at the mesenchymal cells that later differentiates into quadratojugal bone (qj) and in a thin layer of mesenchymal cells that covers brain dorsally (arrows at the top of E and H), as well as in the epithelium of the cochlear canal. (C and F) In crocodile embryos, expression of Msx2 is detected at a population of mesenchymal cells in close proximity of postorbital and quadratojugal bones, as well as in a layer of the mesenchyme surrounding the brain dorsally where future a pair of parietal bones are developed. (I and J) In turtle embryos, Msx2 was expressed in a thick layer of mesenchymal cells that populate lateral aspect of the head (arrows). The Msx2-positive mesenchymal cells cover the external adductor muscle precursors (red outlined domains in G- J) laterally. The red outlined domains in (A-F) indicate the location of the pseudotemporal muscle deduced from adjacent sections where muscular tissues are labeled by MyoD probe. The blue outlined domains in (A-J) indicate the location of quadrate cartilage deduced from adjacent sections where cartilaginous tissues are labeled by Sox9 probe. Scale bars are 0.5 mm.
In contrast to Bmp4 and Msx1, we detected differential expression patterns of Msx2 in the head of crocodile and turtle embryos. In crocodile embryos at stage 14 and 15, Msx2 was expressed in a thin layer of mesenchymal cells surrounding the dorsal aspect of the brain (Figures 6C and 6E). In the posterior part of the head, the ventral edge of this Msx2-expressing cell population is located dorsal to the eye. In these crocodilian embryos, Msx2 expression was also observed in a population of the mesenchyme that occupied the domain between the ventrolateral part of quadrate cartilage and surface epidermis (Figures 6C and 6E). These mesenchymal cells expressed Msx1 as well (Figure 6B) and appeared to differentiate into the quadratojugal bone later. In crocodile embryos at stage 17, specific expression of Msx2 was detected at a population of mesenchymal cells in close proximity of Runx2-expressing precursors of postorbital and quadratojugal bones, as well as in a thin layer of the mesenchyme surrounding the brain dorsally where future parietal bones were developed (Figures 7C and 7F). We observed that the space adjacent to Msx2-positive precursors of these dermatocranial elements was filled with Msx2-negative mesenchymal cells. Interestingly, we observed broader expression of Msx2 in turtle embryos, compared to that in stage-matched crocodile embryos. In turtle embryos examined, Msx2 was expressed in mesenchymal cells that populate lateral aspect of the head of embryos (Figures 6I and 6K; Figures 7I and 7J). The ventral edge of the Msx2-expressing mesenchymal layer was terminated ventral to the eye and these cells covered MyoD-expressing external adductor muscle laterally. Showing its dorsoventrally broadened expression pattern, the domain of Msx2 expression largely overlapped with that of Runx2 in turtle embryos (Figures 4B and 4G; Figure 5B).
Expression of Runx2 and Msx2 in the head of snake embryos
To verify a correlation between the expression patterns of Runx2 and Msx2 and reptilian skull morphology, we finally examined expression patterns of these genes, as well as of marker genes for muscular and cartilaginous tissues, in cranial morphogenesis of a snake species where their temporal fenestrae are not encircled by the temporal bars. In snake embryos at stage 26 (Figure 8A) that morphologically correspond to crocodile and turtle embryos at stage 14 or 15, MyoD was expressed in the primordia of the first arch muscles (Figures 8C and 8G). Sox9 was strongly expressed in the precursors of quadrate and Meckel's cartilages and the base of the braincase, as well as in a layer of mesenchyme surrounding the brain laterally (Figures 8D and 8H). In these snake embryos, early osteoblast marker, Runx2 was expressed in the mesenchyme that occupied the space medial to the Sox9-positive quadrate precursor and in a limited population of mesenchymal cells ventral to the orbit (Figure 8B). We also detected Runx2 expression in a layer of mesenchymal cells that surround the brain laterally. In the posterior temporal region, Runx2 was only faintly expressed in the adjacent mesenchyme of the Sox9-positive quadrate precursor (Figure 8F). Expression of Msx2 was detected in the mesenchyme medial to the precursor of the quadrate (Figure 8E). Its expression domain was spatially overlapped with the domain where Runx2-positive cells were distributed, but the former was narrower. We also detected Msx2 expression in a mesenchymal layer that surrounded the brain dorsally (Figures 8E and 8I). In snake embryos at stage 29 (Figure 8J), which morphologically correspond to crocodile and turtle embryos at stage 17, well-differentiated cranial muscular and cartilaginous tissues were specifically labeled by expression of MyoD (Figures 8L and 8P) and Sox9 (Figures 8M and 8Q), respectively. We observed spatially overlapped expression of Runx2 and Msx2 in these embryos: both genes were expressed in the precursors of palatine and pterygoid bones medial to Sox9-positive jaw cartilages and in mesenchymal cells accompanying jaw cartilages, as well as in a layer of loose mesenchyme that later forms a precursor of parietal bones that cover the dorsal part of the brain (Figures 8K, 8N, 8O, and 8R). However, only Runx2 was expressed in the mesenchyme that populated the domain ventral to the orbit, which possibly corresponds to precursors of the maxilla bones of the upper jaw. No Runx2 and/or Msx2 expressing osteogenic mesenchymal precursor cells populated the domain lateral to jaw adductor muscles. In more developed snake embryos (at stage 31; Figure 8S), both Runx2 and Msx2 were specifically expressed in the precursors of the dermatocranial elements, including the parietal that encases the brain dorsally (Figures 8T and 8W). As in previous stages, expression of the former was more expanded. The lateral aspect of the external adductor muscles was never covered by the skeletal tissues that express Runx2 and/or Msx2. The results on expression domains of each gene analyzed in crocodile, turtle, and snake embryos are summarized in Table 1.
Expression of the genes that regulate the development of cranial musculoskeletal tissues in snake embryos. (A) Lateral view of the head of a snake embryo at stage 26. (B-E) Frontal sections prepared around the plane indicated by the red line in (A). (F-I) Frontal sections around the blue line in (A). (J) The head of a snake embryo at stage 29. (K-N) Frontal sections around the red line in (J). (O-R) Frontal sections around the blue line in (J). (S) The head of a snake embryo at stage 31. (T-W) Frontal sections around the red line in (S). (B, F, K, O, and T) Expression of Runx2. (C, G, L, P, and U) Expression of MyoD. (D, H, M, Q, and V) Expression of Sox9. (E, I, N, R, and W) Expression of Msx2. In snake embryos, expression of Runx2 and Msx2 are detected in the precursor cells of dermatocranial elements (arrows), as in crocodile and turtle embryos. However, these mesenchymal cells are not seen in the temporal region lateral to the jaw adductor muscles. Instead, these cells are distributed in the vicinity of the brain, laterally covering it, and differentiate into the parietal bone in older embryos. Open arrowheads in (F, K, N, O, R, T, and W) indicate the mesenchyme around Sox9-positive jaw cartilages, where the expression of Runx2 and Msx2 is detected. The red outlined domains in (O, Q, R, T, V, and W) indicate the location of the external adductor muscle deduced from adjacent sections where muscular tissues are labeled by MyoD probe. Scale bars in (A), (J), and (S) are 1 mm. Scale bars in other pictures are 0.5 mm.
Discussion
Potential developmental basis of anapsid skull in turtles
Skull morphology, especially the osteological configuration of the temporal region, has historically been treated as the most important character in the classification of major lineages of reptiles. Based on their anapsid skull, turtles have been regarded as a sole descendent of stem reptiles (Williston, 1917, Gregory, 1946, Romer, 1968, Gaffney, 1980;Reisz & Laurin,, Reisz & Laurin, Reisz & Laurin,1991, Lee, 1993;Laurin & Reisz, 1995, Lee, 1996 1997, Reisz, 1997, Lee, 2001) despite the contrary argument that turtles were derived from an ancestor with a diapsid skull (Lakjer, 1926, Goodrich, 1930). Recent phylogenetic studies where the interrelationships of both extant and extinct reptiles were surveyed through comprehensive analysis of multiple osteological traits concluded that turtles were closely related to lepidosaurian diapsids (Rieppel & deBraga, 1996;deBraga & Rieppel , deBraga & Rieppel deBraga & Rieppel 1997Rieppel 2000, Hill, 2005, Li et al., 2008). Furthermore, results of molecular phylogenetic studies have strongly suggested diapsid affinity of turtles (Hedges & Poling, 1999;Kumazawa & Nishida,, Kumazawa & Nishida, Kumazawa & Nishida,1999, Iwabe et al., 2005, Hugall et al., 2007, Shedlock et al., 2007Shen et al. 2011, Tzika et al., 2011, Chiari et al., 2012, Crawford et al., 2012, Fong et al., 2012, Lyson et al., 2012, Wang et al., 2013). If turtles were derived from a diapsid ancestor, then the anapsid skull of turtles evolved independently from that of ancestral lineages of reptiles by secondary closure of the temporal fenestrae. However, although the phylogenetic position of turtles within amniotes still remains inconclusive (Lyson et al., 2010 2013, Kuratani et al., 2011), there has been no study in which the process of development of their anapsid skull is described with molecular markers for labeling precursor cells of the dermatocranium. In the present study, we examined early cranial morphogenesis of representative reptilian species through comparative analysis of gene expression patterns and found unique expression patterns of Runx2 and Msx2 in turtle embryos that are not observed in crocodile and snake embryos.
Runx2 is widely known as a transcription factor that plays a fundamental role in osteoblast differentiation in vertebrate embryos (Ducy et al., 1997, Komori et al., 1997, Mundlos et al., 1997, Nakashima et al., 2002, Ishii et al., 2003, Dobreva et al., 2006, Kerney et al., 2010) and its transcript has been used as a molecular marker for preosteoblasts or osteoblast progenitors (Ducy et al., 1997, Karsenty, 2001, Bobola et al., 2003, Ishii et al., 2003, Abzhanov et al., 2007, Han et al., 2007;Tokita & Schneider , Tokita & Schneider Tokita & Schneider 2009). In turtle embryos where mineralization of dermal bones of the skull has not yet occurred, mesenchymal cells that express Runx2 were broadly distributed in the lateral domain of the head, from the top of the head to the ventral margin of the jaw (Figure 9). This means that turtle embryos have wider distribution of the cells that have a potential to differentiate into bones in the temporal region of the head, compared to other lineages of reptiles. The reduction of the amount of Runx2 mRNA causes developmental defects in calvarial bones, called cleidocranial dysplasia, in mouse embryos (Lou et al., 2009). In contrast, early onset of Runx2 expression that eventually results in an increase of the amount of its mRNA in the cranial mesenchyme accelerates the timing of mineralization of cranial dermal bones in mouse embryos and brings about craniosynostosis characterized by overgrowth of bones (Maeno et al., 2011). Similar result has been obtained from experiments using avian embryos (Merrill et al., 2008). We speculate that heterotopy in the preosteoblast distribution observed in early stage turtle embryos may lead to the increase of the amount of Runx2 expression that results in the increase of the level of ossification in the temporal region of their skull and this would be a primary factor to build the anapsid skull where the temporal region is completely covered with bone.
Potential developmental basis that generates morphological diversity in the temporal region of the reptilian skull. All extant reptilian lineages are considered to be derived from ancestor with diapsid skull. In crocodiles that have both upper and lower temporal bars like the stem Diapsida (e.g., Petrolacosaurus), osteogenic mesenchymal precursor cells which express Runx2 and/or Msx2 are distributed at the domain where future temporal bars are formed in the head of early stage embryo (top of the middle column). Through ontogeny (black arrow), these osteoblast precursors may differentiate into the dermatocranial elements including upper and lower temporal bars (bottom of the middle column). Between these bony bars, both upper and lower temporal fenestrae are clearly recognized. In turtles (left white arrow), distribution of osteogenic mesenchymal precursor cells is broadened in a dorsal-ventral direction, filling the whole lateral portion of the head of early embryos (top of the left column). Through ontogeny, these osteoblast precursors may differentiate into the dermatocranial elements roofing the temporal region of the head (bottom of the left column). In snakes that have modified diapsid skull where temporal bars are absent, osteogenic mesenchymal precursor cells do not fill lateral domain of the head of embryo. Rather, these cells are mainly distributed in the vicinity of the brain (top of the right column). Through ontogeny, these osteoblast precursors may differentiate into the dermatocranial elements accompanying the braincase, without forming bony temporal bars (bottom of the right column). A condensed mesenchymal layer that differentiates into the braincase in later stages is highlighted by dotted line in the head of embryos.
In this study, we focused on several candidate molecules that potentially regulate Runx2 expression and examined their expression patterns in reptilian embryos. Bmp4 is known to be involved in osteogenesis of vertebrates where it regulates expression of other osteogenic regulatory genes, including Msx1, Msx2, and Runx2 (Marazzi et al., 1997, Kim et al., 1998, Hollnagel et al., 1999, Tribulo et al., 2003, Zhang et al., 2003, Brugger et al., 2004). Msx1 is a transcription factor known to regulate growth and patterning of calvarial bones in mouse embryos (Satokata & Maas, 1994, Han et al., 2007, Roybal et al., 2010). Although, as previously reported in mouse embryos (Rice et al., 2003, Han et al., 2007), both Bmp4 and Msx1 are expressed in limited populations of cranial mesenchyme in embryos of crocodiles and turtles, we could not detect any substantial differences in their expression domains between the two species. On the other hand, we observed spatially different expression patterns of Msx2 in the head of embryos of all reptilian species we examined. Expression of Msx2 was detected in cranial mesenchyme and dermal bone precursors as reported in mouse embryos (Jabs et al., 1993, Ishii et al., 2003, Rice et al., 2003, Han et al., 2007, Roybal et al., 2010). Furthermore, its expression spatially overlapped with that of Runx2 in reptilian embryos, as in mouse embryos (Ishii et al., 2003, Rice et al., 2003, Han et al., 2007). In turtle embryos, expression domain of Msx2 in the mesenchyme distributed in the temporal region of the head was broad in a dorsal-ventral direction, showing similar pattern with Runx2 in the mesenchyme. A mutation in the homeobox of Msx2 gene causes craniosynostosis in human and mouse (Jabs et al., 1993, Liu et al., 1999). Similarly, overexpression of Msx2 promotes osteogenesis (Cheng et al., 2003, Ichida et al., 2004) and causes overgrowth of dermal bones of the skull by increasing the number of proliferative osteoblasts (Dodig et al., 1999, Liu et al., 1999). In contrast, loss-of-function of Msx2 results in defects of skull ossification in mammals (Satokata et al., 2000, Wilkie et al., 2000, Ishii et al., 2003, Antonopoulou et al., 2004, Han et al., 2007). Furthermore, Msx2 is known to positively regulate downstream Runx2 expression (Ishii et al., 2003, Han et al., 2007, Watanabe et al., 2008). Considering the evidence provided by previous studies, regulatory changes in Msx2 expression in turtle embryos may influence expression patterns of downstream Runx2, which regulate osteoblast differentiation. Dorsoventrally broadened distribution of osteogenic mesenchymal precursor cells in the temporal region of the head owing to the regulatory alteration of these osteogenic genes may allow this reptilian lineage to reacquire the anapsid skull. Although the precise mechanism underlying regulatory change of Msx2 expression in the head of turtle embryos has not been identified, recent findings that early stage arrest of Msx2 expression in neural crest-derived odontoblasts may account for the absence of teeth in turtles (Tokita et al., 2012) supports the hypothesis that this transcription factor may play a pivotal role in the development of their unique cranial morphology.
The development of the dermatocranium occurs in multiple steps (Ishii et al., 2003). The first phase includes the genesis, migration, and initial specification of osteogenic mesenchymal precursor cells. The second phase consists of the differentiation of the mesenchyme into osteoblasts. And the last phase includes deposition of osteogenic extracellular matrix around the osteoblasts and mineralization of the matrix. The dermatocranium of vertebrates is formed from cranial mesenchyme derived from two distinct embryonic sources: neural crest and mesoderm (Jiang et al., 2002;Gross & Hanken , Gross & Hanken Gross & Hanken 2005;Noden & Trainor,, Noden & Trainor, Noden & Trainor,2005). Unfortunately, fate mapping studies of each dermatocranial element as performed in avian and mammalian embryos (Le Lièvre, 1978, Noden, 1978 1983, Couly et al., 1993;Köntges & Lumsden,, Köntges & Lumsden, Köntges & Lumsden,1996, Jiang et al., 2002) have not been done in non-avian reptiles. Interestingly, the pattern of migration and distribution of cranial neural crest cells from which some cranial dermal bones should form is almost identical in early stage embryos of crocodiles and turtles (Meier & Packard, 1984;Hou & Takeuchi,, Hou & Takeuchi, Hou & Takeuchi,1994;Kundrát,, Kundrát, Kundrát,2008). Such data may support that differentiation or maturation processes of osteogenic mesenchyme are more responsible for producing diversity of reptilian skull morphology. We speculate that the developmental program, which determines cranial mesenchymal populations where early-phase osteogenic transcription factors Msx2 and Runx2 are activated, may be important in the patterning of reptilian skull morphology.
There exists substantial diversity in the skull morphology within turtles and most living turtle species do not have fully anapsid skulls and instead possess varying degrees of dorsal and/or ventral emargination on their skull (Jones et al., 2012, Werneburg, 2012a). In the present study, we could not sample and analyze the embryos of turtle species with fully anapsid skull, such as marine turtles (Kuratani, 1999, Jones et al., 2012), alligator snapping turtle () (Sheil, Macrochelys temminckii 2005), and big-headed turtle (Platysternon megacephalum), owing to difficulty in the access to the materials. Instead, we analyzed the embryos of a soft-shelled turtle species with highly emarginated skull. In fact, soft-shelled turtles have only a narrow bar of bone across the temporal region lateral to the external adductor muscles due to large scale emargination from the dorsal and ventral margins of the cheek (Ogushi, 1911, Sheil, 2003). In normal development of soft-shelled turtles, the postorbital bone does not grow in a posterior direction significantly, keeping its relatively small size within the dermatocranium (Sheil, 2003;Sánchez-Villagra et al.,, Sánchez-Villagra et al., Sánchez-Villagra et al.,2009). Therefore, the small postorbital bone of soft-shelled turtles does not largely contribute to the formation of a bony roof at the temporal region of the skull.
It is interesting that we observed dorsoventrally broadened distribution of the mesenchymal cells that express Runx2 at the temporal region of the embryos of a soft-shelled turtle species with highly emarginated skull. Dermal bone development occurs through a multi-step molecular pathway regulated by different transcription factors (Zhang, 2010). As an initial step, Runx2 is required for the differentiation of mesenchymal cells into preosteoblasts. In subsequent stage where these preosteoblasts differentiate into mature osteoblasts, Osx, a downstream gene of Runx2, is necessary (Nakashima et al., 2002, Nishio et al., 2006). Furthermore, in the later stages where the osteoblasts produce osteogenic extracellular matrix and the mineralization of these extracellular matrix is occurred, many additional molecules such as bone sialoprotein, osteopontin, and osteocalcin are involved (Zhang, 2010). We speculate that in soft-shelled turtles only a limited population of cells within Runx2-positive preosteoblasts distributed in the temporal region of the head is allowed to differentiate into mature osteoblasts and eventually osteocytes through regulation of expression of down stream genes (e.g. Osx), to form a pair of relatively small postorbital bones. Although the regulatory mechanism of Osx expression in osteogenic mesenchyme is not fully understood, both Runx2-dependent and -independent pathways have been suggested (Lee et al., 2003;Celil & Campbell,, Celil & Campbell, Celil & Campbell,2005, Maehata et al., 2006, Xing et al., 2007, Zhang, 2010). Histological analysis reveals that late stage soft-shelled turtle embryos have a layer of (non-muscular) fibrous connective tissue lateral to the external adductor muscles (Additional file 3). Judging from its position, the connective tissue layer appears to be derived from Runx2-positive preosteoblasts and have a potential to ossify themselves as other connective tissues represented by tendons and ligaments (Okawa et al., 1998;Tokita et al., 2007). Interestingly, similar type of connective tissue layer is absent in the temporal region of crocodile and snake embryos (Additional file 3). Those histological observations support the above hypothesis that later processes of cranial osteogenesis may largely contribute to the construction of the main body of each dermatocranial element from the osteogenic mesenchymal progenitor pool.
The dorsoventrally broadened distribution of preosteoblasts observed in turtle embryos might be a developmental synapomorphy re-acquired by the common ancestor of turtles. In the course of chelonian evolution, each chelonian lineage may develop the temporal dermal bones (e.g. postorbital, parietal, jugal) with various sizes and shapes, through regulatory changes of the osteogenic down stream molecules. Future studies should investigate expression pattern of Runx2 and Msx2 in the head of embryos of turtle species with fully anapsid skull, as well as expression pattern of downstream genes that regulate differentiation of mature osteoblasts and osteocytes in turtle embryos, to verify a correlation between the gene expression pattern and their skull morphology.
Heterotopy in distribution of osteogenic mesenchymal precursor cells and diversification of reptilian skull morphology
The frame-like skulls possessed by diapsid reptiles evolved in response to functional forces (Rieppel, 1993a, Moazen et al., 2009, Herrel et al., 2007, Curtis et al., 2011) and several studies have suggested heterochrony as a driving force for producing this morphological diversity (Rieppel, 1993a, Whiteside, 1986, Irish, 1989). The ancestral lineage of diapsid reptiles possessed upper and lower temporal bars that encircle temporal fenestrae (Müller, 2003, Moazen et al., 2009). The lower temporal bar that encloses lower temporal fenestra ventrally was probably lost once in the common ancestor of lepidosaurs and archosaurs, possibly as the outcome of paedomorphosis: incomplete ossification of a quadrato-maxillary ligament between jugal and quadratojugal bones (Rieppel, 1993a;Müller,, Müller, Müller,2003). If this is true, the lower temporal bar that possibly results from peramorphosis (hypermorphosis): complete ossification of a quadrato-maxillary ligament was independently re-acquired in the lineages of tuatara and crocodiles, as well as in several extinct reptilian lineages (Rieppel, 1993a;Müller,, Müller, Müller,2003). Furthermore, disappearance of upper temporal bar, which is regarded as an extreme condition of reduction of the dermatocranium in reptiles, may have independently evolved in the skull of geckos (Gekkonidae), miniaturized fossorial lizards (e.g., Typhlosaurus, Dibamus), amphisbaenian, and snakes, as the outcome of paedomorphosis represented by the retardation of ossification (Rieppel, 1993a, Irish, 1989;Cundall & Irish,, Cundall & Irish, Cundall & Irish,2008). In the present study, we revealed a possible correlation between distribution pattern of Runx2 and/or Msx2-expressing osteogenic mesenchymal precursor cells and the skull morphology of each reptilian lineage (Figure 9). In early stage crocodile embryos, we observed focal distribution of osteogenic mesenchyme around the domain where future temporal bars are formed. In early stage snake embryos, osteogenic mesenchymal cells were primarily found adjacent to the primordium of the braincase and the spatial pattern presaged the absence of bony temporal bars in the temporal region of adult animal.
Conclusions
Regulatory modifications of Runx2 and Msx2 expression in osteogenic mesenchymal precursor cells are likely involved in generating morphological diversity in the temporal region of the reptilian skull, including secondary closure of the temporal fenestrae in turtles. Our findings demonstrate that not only heterochrony in ossification of the dermatocranium that has been traditionally regarded as the major factor producing diversity of reptilian cranial morphology but also heterotopy in distribution of the osteogenic precursor cells may play a fundamental role in this process and it should be further investigated in future studies of reptilian cranial development and evolution.
Materials and methods
Sample collection and staging of embryos
Fertilized eggs of Chinese soft-shelled turtle, Pelodiscus sinensis, were purchased commercially from a local breeder in Japan. Fertilized eggs of Siamese crocodile, Crocodylus siamensis, were provided by a local breeder in Thailand. Fertilized eggs of corn snake, Pantherophis guttatus, were obtained by the first author after mating several pairs of the reproductively mature adults in the laboratory. Staging of P. sinensis embryos was performed after Tokita and Kuratani (2001). Because there is no embryonic staging system for C. siamensis at present, we used the system for Alligator mississippiensis embryos (Ferguson, 1985) where each stage was determined based on external morphology of the embryos, for staging of this species. Staging of P. guttatus (Zehr, embryos was performed on the basis of staging table of Thamnophis sirtalis 1962). Interspecific comparisons of gene expression pattern were performed in the embryos that are comparable to each other in terms of overall external morphology. Because snake embryos are limbless, we mainly employed external features of the head of the embryos as primary criteria for determining the stages for comparison. All animal experiments were approved by the University of Tsukuba Committee for Animal Care (No.10-034).
Molecular cloning
Total RNA was extracted from embryos using ISOGEN reagent (NIPPON GENE CO., LTD).
RT–PCR was performed to amplify fragments of P. sinensis Runx2, Six2 and C. siamensis Bmp4, Msx2, MyoD, Runx2, Scleraxis (Scx), Six2, Sox9 and P. guttatus Msx2, Runx2, Sox9 messenger RNA. Primer sequences used for isolation of the fragments of these genes are available upon request. Because Bmp4, Msx1, Msx2, MyoD, Scx, Sox9 of Pelodiscus and MyoD of Pantherophis were already sequenced and sequence data were deposited in the database by other researchers, we isolated the orthologous fragments by RT–PCR with primers constructed by referring to the reported sequence data. The fragments were isolated using the pGEM T-easy vector systems (Promega) or TOPO® TA cloning kit (Invitrogen) and sequenced using an ABI 3130 sequencer (Applied Biosystems). To identify the orthologous genes of the isolated fragments, comparable sequence data were surveyed using a BLAST search, and phylogenetic trees with neighbor joining method were constructed after sequence alignment using the CLUSTALX software. All new DNA sequence data were deposited in the DDBJ database (AB811933-AB811944).
Gene expression analysis
Embryos were fixed in 4% PFA, dehydrated using an methanol series, placed in xylene, embedded in paraffin, and sliced with a microtome. Serial sections were hybridized with digoxigenin-labeled RNA riboprobes as described in Neubüser et al. (1995) with slight modifications. To identify the expression domain of Msx1 in crocodile tissues, chicken Msx1 antisense riboprobe was hybridized. Generally, hetero-specific RNA probes easily hybridize among reptilian lineages (Harris et al., 2006, Tokita et al., 2012). In this study, we only analyzed reptilian embryos at the ontogenetic stages where early cranial osteogenesis occurs. To confirm the expression pattern of each gene in the cranial tissues, two to five individuals representing each embryonic stage were sampled for analysis. The consistency of the gene expression patterns among all individual embryos at the same stage was confirmed. Multiple sections representing several longitudinal (anterior-posterior) planes prepared from the same individual were hybridized with the probes and the sections prepared at corresponding longitudinal planes were compared between different individuals. Corresponding longitudinal planes between different reptilian species were determined based on overall histological configuration of the head of the embryos. For visualization of each cranial tissue and interspecific comparison of general histology of the head, Miligan's Trichrome staining was performed following standard protocols. To identify each anatomical structure in cranial musculoskeletal tissues of the embryos, we took the results of other's researches into account: (Schumacher, 1973, Rieppel, 1993b;Vickaryous & Hall,, Vickaryous & Hall, Vickaryous & Hall,2008;Bona & Desojo,, Bona & Desojo, Bona & Desojo,2011) for crocodile, (Schumacher, 1973, Rieppel, 1990, Rieppel, 1993c;Sánchez-Villagra et al.,, Sánchez-Villagra et al., Sánchez-Villagra et al.,2009, Werneburg, 2012a 2012b) for turtle, and (Kamal et al., 1970, Haas, 1973, Zaher, 1994;Buchtová et al.,, Buchtová et al., Buchtová et al.,2007) for snake.
Abbreviations
- Am:
-
Jaw adductor muscle or the anlage of jaw adductor muscle
- Ame:
-
External adductor muscle
- Bc:
-
Braincase
- Bp:
-
Basicranial plate cartilage
- Br:
-
Brain
- C:
-
precursor of jaw cartilages (quadrate and Meckel's)
- Co:
-
Cochlear canal
- E:
-
Eye
- Em:
-
Eye muscles or the anlagen of eye muscles
- Itm:
-
Intramandibular muscle
- J:
-
Jugal bone
- Jm:
-
Anlage of jaw muscle complex
- Mc:
-
Meckel's cartilage
- Mx:
-
Primordium of maxilla bone
- Oc:
-
Oral cavity
- P:
-
Parietal bone or precursor of parietal bone
- Pc:
-
Parachordal cartilage
- Pg:
-
Primordium of pterygoid bone
- Pgm:
-
Pterygoid muscle
- Pl:
-
Primordium of palatine bone
- Po:
-
Postorbital bone or primordium of postorbital bone
- Ptm:
-
Pseudotemporal muscle
- Q:
-
Quadrate cartilage or precursor of quadrate cartilage
- Qj:
-
Quadratojugal bone or primordium of quadratojugal bone
- T:
-
Trabecular cartilage
- Tr:
-
Ganglion of trigeminal nerve
- 1a:
-
First pharyngeal arch
- 2a:
-
Second pharyngeal arch
References
Abzhanov A, Rodda SJ, McMahon AP, Tabin CJ: Regulation of skeletogenic differentiation in cranial dermal bone. Development 2007, 134: 3133-3144. 10.1242/dev.002709
Antonopoulou I, Mavrogiannis LA, Wilkie AOM, Morriss-Kay GM: Alx4 and Msx2 play phenotypically similar and additive roles in skull vault differentiation. J Anat 2004, 204: 487-499. 10.1111/j.0021-8782.2004.00304.x
Bell DM, Leung KKH, Wheatley SC, Ng LJ, Zhou S, Ling KW, Sham MH, Koopman P, Tam PPL, Cheah KSE: Sox9 directly regulates the type-II collagen gene. Nat Genet 1997, 16: 174-178. 10.1038/ng0697-174
Benton MJ: Vertebrate palaeontology 3rd edition. Malden: Blackwell Publishing; 2005.
Bobola N, Carapuco M, Ohnemus S, Kanzler B, Leibbrandt A, Neubuser A, Drouin J, Mallo M: Mesenchymal patterning by Hoxa2 requires blocking Fgf-dependent activation of Ptx1. Development 2003, 130: 3403-3414. 10.1242/dev.00554
Bona P, Desojo JB: Osteology and cranial musculature of Caiman latirostris (Crocodylia: Alligatoridae). J Morphol 2011, 272: 780-795. 10.1002/jmor.10894
Boughner JC, Buchtová M, Fu K, Diewert V, Hallgrímsson B, Richman JM: Embryonic development of Python sebae - I: Staging criteria and macroscopic skeletal morphogenesis of the head and limbs. Zoology 2007, 110: 212-230. 10.1016/j.zool.2007.01.005
Brugger SM, Merrill AE, Torres-Vazquez J, Wu N, Ting M-C, Cho JY-M, Dobias SL, et al.: A phylogenetically conserved cis-regulatory module in the Msx2 promoter is sufficient for BMP-dependent transcription in murine and Drosophila embryos. Development 2004, 131: 5153-5165. 10.1242/dev.01390
Buchtová M, Boughner JC, Fu K, Diewert VM, Richman JM: Embryonic development of Python sebae - II: Craniofacial microscopic anatomy, cell proliferation and apoptosis. Zoology 2007, 110: 231-251. 10.1016/j.zool.2007.01.006
Carroll RL: Early evolution of reptiles. Annu Rev Ecol Systemat 1982, 13: 87-109. 10.1146/annurev.es.13.110182.000511
Carroll RL: Vertebrate palaeontology and evolution. San Francisco: WH Freeman; 1988.
Celil AB, Campbell PG: BMP-2 and insulin-like growth factor-I mediate Osterix (Osx) expression in human mesenchymal stem cells via the MAPK and protein kinase D signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 2005, 280: 31353-31359. 10.1074/jbc.M503845200
Cheng S-L, Shao J-S, Charlton-Kachigian N, Loewy AP, Towler DA: MSX2 promotes osteogenesis and suppresses adipogenic differentiation of multipotent mesenchymal progenitors. J Biol Chem 2003, 278: 45969-45977. 10.1074/jbc.M306972200
Chiari Y, Cahais V, Galtier N, Delsuc F: Phylogenomic analyses support the position of turtles as the sister group of birds and crocodiles (Archosauria). BMC Biology 2012, 10: 65. 10.1186/1741-7007-10-65
Couly GF, Coltey PM, Le Douarin NM: The triple origin of skull in higher vertebrates: a study in quail-chick chimeras. Development 1993, 117: 409-429.
Crawford NG, Faircloth BC, McCormack JE, Brumfield RT, Winker K, Glenn TC: More than 1000 ultraconserved elements provide evidence that turtles are the sister group of archosaurs. Biol Lett 2012, 8: 783-786. 10.1098/rsbl.2012.0331
Cundall D, Irish F: The snake skull. In Biology of the Reptilia Volume 20. Edited by: Gans C, Gaunt AS, Adler K. Ithaca: Society for the study of Amphibians and Reptiles; 2008:349-692.
Curtis N, Jones MEH, Shi J, O’Higgins P, Evans SE, Fagan MJ: Functional relationship between skull form and feeding mechanics in Sphenodon , and implications for diapsid skull development. PLoS ONE 2011, 6: e29804. 10.1371/journal.pone.0029804
deBraga M, Rieppel O: Reptile phylogeny and the interrelationships of turtles. Zool J Linn Soc 1997, 120: 281-354. 10.1111/j.1096-3642.1997.tb01280.x
Dobreva G, Chahrour M, Dautzenberg M, Chirivella L, Kanzler B, Fariñas I, Karsenty G, Grosschedl R: SATB2 is a multifunctional determinant of craniofacial patterning and osteoblast differentiation. Cell 2006, 125: 971-986. 10.1016/j.cell.2006.05.012
Dodig M, Tadic T, Kronenberg MS, Dacic S, Liu YH, Maxson R, Rowe DW, Lichtler AC: Ectopic Msx2 overexpression inhibits and Msx2 antisense stimulates calvarial osteoblast differentiation. Dev Biol 1999, 209: 298-307. 10.1006/dbio.1999.9258
Dreyer SD, Naruse T, Morello R, Zabel B, Winterpacht A, Johnson RL, Lee B, Oberg KC: Lmx1b expression during joint and tendon formation: localization and evaluation of potential downstream targets. Gene Expression Patterns 2004, 4: 397-405. 10.1016/j.modgep.2004.01.006
Ducy P, Zhang R, Geoffroy V, Ridall AL, Karsenty G: Osf2/Cbfa1: a transcriptional activator of osteoblast differentiation. Cell 1997, 89: 747-754. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80257-3
Edom-Vovard F, Duprez D: Signals regulating tendon formation during chick embryonic development. Dev Dyn 2004, 229: 449-457. 10.1002/dvdy.10481
Evans SE: The skull of lizards and tuatara. In Biology of the Reptilia Volume 20. Edited by: Gans C, Gaunt AS, Adler K. Ithaca: Society for the study of Amphibians and Reptiles; 2008:1-347.
Ferguson MWJ: Reproductive biology and embryology of the crocodilians. In Biology of the Reptilia Volume 14. Edited by: Maderson PFA, Gans C, Billett F. New York: Academic Press; 1985:329-491.
Fong JJ, Brown JM, Fujita MK, Boussau B: A phylogenomic approach to vertebrate phylogeny supports a turtle-archosaur affinity and a possible paraphyletic lissamphibia. PLoS ONE 2012, 7: e48990. 10.1371/journal.pone.0048990
Frazzetta TH: Adaptive problems and possibilities in the temporal fenestration of tetrapod skulls. J Morphol 1968, 125: 145-157. 10.1002/jmor.1051250203
Gaffney ES: Phylogenetic relationships of the major groups of amniotes. In The terrestrial environment and the origin of land vertebrates. Edited by: Panchen AL. London: Academic Press; 1980:593-610.
Goodrich ES: Studies on the structure and development of vertebrates. New York: Dover Editions; 1930.
Gregory WK: Pareiasaurs versus placodonts as near ancestors to the turtles. Bull Am Mus Nat Hist 1946, 86: 275-326.
Gross JB, Hanken J: Cranial neural crest contributes to the bony skull vault in adult Xenopus laevis : insights from cell labeling studies. J Exp Zool B. Mol Dev Evol 2005, 304: 169-176.
Haas G: Muscles of the jaws and associated structures in the Rhynchocephalia and Squamata. In Biology of the Reptilia Volume 4. Edited by: Gans C. New York: Academic Press; 1973:285-490.
Hacker A, Guthrie S: A distinct developmental programme for the cranial paraxial mesoderm in the chick embryo. Development 1998, 125: 3461-3472.
Haluska F, Alberch P: The cranial development of Elaphe obsoleta (Ophidia, Colubridae). J Morphol 1983, 178: 37-55. 10.1002/jmor.1051780104
Han J, Ishii M, Bringas P, Maas RL, Maxson R, Chai Y: Concerted action of Msx1 and Msx2 in regulating cranial neural crest cell differentiation during frontal bone development. Mech Dev 2007, 124: 729-745. 10.1016/j.mod.2007.06.006
Harris MP, Hasso SM, Ferguson MWJ, Fallon JF: The development of archosaurian first-generation teeth in a chicken mutant. Curr Biol 2006, 16: 371-377. 10.1016/j.cub.2005.12.047
Hedges SB, Poling LL: A molecular phylogeny of reptiles. Science 1999, 283: 998-1001. 10.1126/science.283.5404.998
Herrel A, Schaerlaeken V, Meyers JJ, Metzger KA, Ross CF: The evolution of cranial design and performance in squamates: consequences of skull-bone reduction on feeding behavior. Integr Comp Biol 2007, 47: 107-117. 10.1093/icb/icm014
Hill RV: Integration of morphological data sets for phylogenetic analysis of Amniota: the importance of integumentary characters and increased taxonomic sampling. Syst Biol 2005, 54: 530-547. 10.1080/10635150590950326
Hollnagel A, Oehlmann V, Heymer J, Rüther U, Nordheim A: Id genes are direct targets of bone morphogenetic protein induction in embryonic stem cells. J Biol Chem 1999, 274: 19838-19845. 10.1074/jbc.274.28.19838
Hou L, Takeuchi T: Neural crest development in reptilian embryos studied with monoclonal antibody, HNK-1. Zool Sci 1994, 11: 423-431.
Hugall AF, Foster R, Lee MSY: Calibration choice, rate smoothing, and the pattern of tetrapod diversification according to the long nuclear gene RAG-1. Syst Biol 2007, 56: 543-563. 10.1080/10635150701477825
Ichida F, Nishimura R, Hata K, Matsubara T, Ikeda F, Hisada K, Yatani H, et al.: Reciprocal roles of MSX2 in regulation of osteoblast and adipocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem 2004, 279: 34015-34022. 10.1074/jbc.M403621200
Irish FJ: The role of heterochrony in the origin of a novel bauplan: evolution of the ophidian skull. Geobios Memoire special 1989, 12: 227-233.
Ishii M, Merrill AE, Chan Y-S, Gitelman I, Rice DPC, Sucov HM, Maxson RE: Msx2 and Twist cooperatively control the development of the neural crest-derived skeletogenic mesenchyme of the murine skull vault. Development 2003, 130: 6131-6142. 10.1242/dev.00793
Iwabe N, Hara Y, Kumazawa Y, Shibamoto K, Saito Y, Miyata T, Katoh K: Sister group relationship of turtles to the bird-crocodilian clade revealed by nuclear DNA-coded proteins. Mol Biol Evol 2005, 22: 810-813. 10.1093/molbev/msi075
Jabs EW, Müller U, Li X, Ma L, Luo W, Haworth IS, Klisak I, Sparkes R, Warman ML, Mulliken JB: A mutation in the homeodomain of the human MSX2 gene in a family affected with autosomal dominant craniosynostosis. Cell 1993, 75: 443-450. 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90379-5
Jiang X, Iseki S, Maxson RE, Sucov HM, Morriss-Kay GM: Tissue origins and interactions in the mammalian skull vault. Dev Biol 2002, 241: 106-116. 10.1006/dbio.2001.0487
Jones MEH, Werneburg I, Curtis N, Penrose R, O'Higgins P, Fagan MJ, Evans SE: The head and neck anatomy of sea turtles (Cryptodira: Chelonioidea) and skull shape in testudines. PLoS ONE 2012, 7: e47852. 10.1371/journal.pone.0047852
Kamal AM, Hammonda HG, Mokhtar FM: The development of the osteocranium of the Egyptian cobra: I. the embryonic osteocranium. Acta Zool 1970, 51: 1-17. 10.1111/j.1463-6395.1970.tb00414.x
Karsenty G: Minireview : transcriptional control of osteoblast. Endocrinology 2001, 142: 2731-2733. 10.1210/en.142.7.2731
Kerney R, Gross JB, Hanken J: Early cranial patterning in the direct-developing frog Eleutherodactylus coqui revealed through gene expression. Evol Dev 2010, 12: 373-382. 10.1111/j.1525-142X.2010.00424.x
Kim HJ, Rice DP, Kettunen PJ, Thesleff I: FGF-, BMP- and Shh-mediated signalling pathways in the regulation of cranial suture morphogenesis and calvarial bone development. Development 1998, 125: 1241-1251.
Komori T, Yagi H, Nomura S, Yamaguchi A, Sasaki K, Deguchi K, Shimizu Y, Bronson RT, Gao Y-H, Inada M, Sato M, Okamoto R, Kitamura Y, Yoshiki S, Kishimoto T: Targeted disruption of Cbfa1 results in a complete lack of bone formation owing to maturational arrest of osteoblasts. Cell 1997, 89: 755-764. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80258-5
Köntges G, Lumsden A: Rhombencephalic neural crest segmentation is preserved throughout craniofacial ontogeny. Development 1996, 122: 3229-3242.
Kumazawa Y, Nishida M: Complete mitochondrial DNA sequences of the green turtle and blue-tailed mole skink: statistical evidence for archosaurian affinity of turtles. Mol Biol Evol 1999, 16: 784-792. 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026163
Kundrát M: HNK-1 immunoreactivity during early morphogenesis of the head region in a nonmodel vertebrate, crocodile embryo. Naturwissenschaften 2008, 95: 1063-1072. 10.1007/s00114-008-0426-4
Kuratani S: Development of the chondrocranium of the loggerhead turtle, Caretta caretta . Zool Sci 1999, 16: 803-818. 10.2108/zsj.16.803
Kuratani S, Kuraku S, Nagashima H: Evolutionary developmental perspective for the origin of turtles: the folding theory for the shell based on the developmental nature of the carapacial ridge. Evol Dev 2011, 13: 1-14. 10.1111/j.1525-142X.2010.00451.x
Lakjer T: Studien über die Trigeminus-versorgte Kaumuskulatur der Sauropsiden. Copenhagen: C.A. Reitzel; 1926.
Laurin MR, Reisz R: A reevaluation of early amniote phylogeny. Zool J Linn Soc 1995, 113: 165-223. 10.1111/j.1096-3642.1995.tb00932.x
Lee MH, Kwon TG, Park HS, Wozney JM, Ryoo HM: BMP-2-induced Osterix expression is mediated by Dlx5 but is independent of Runx2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003, 309: 689-694. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.08.058
Lee MSY: The origin of the turtle body plan: bridging a famous morphological gap. Science 1993, 261: 1716-1720. 10.1126/science.261.5129.1716
Lee MSY: Correlated progression and the origin of turtles. Nature 1996, 379: 812-815. 10.1038/379812a0
Lee MSY: Pareiasaur phylogeny and the origin of turtles. Zool J Linn Soc 1997, 120: 197-280. 10.1111/j.1096-3642.1997.tb01279.x
Lee MSY: Molecules, morphology, and the monophyly of diapsid reptiles. Contrib Zool 2001, 70: 1-22.
Le Lièvre CS: Participation of neural crest-derived cells in the genesis of the skull in birds. J Embryol Exp Morphol 1978, 47: 17-37.
Li C, Wu X-C, Rieppel O, Wang L-T, Zhao L-J: An ancestral turtle from the late triassic of southwestern China. Nature 2008, 456: 497-501. 10.1038/nature07533
Liu YH, Tang Z, Kundu RK, Wu L, Luo W, Zhu D, Sangiorgi F, Snead ML, Maxson RE: Msx2 gene dosage influences the number of proliferative osteogenic cells in growth centers of the developing murine skull: a possible mechanism for MSX2-mediated craniosynostosis in humans. Dev Biol 1999, 205: 260-274. 10.1006/dbio.1998.9114
Lou Y, Javed A, Hussain S, Colby J, Frederick D, Pratap J, Xie R, et al.: A Runx2 threshold for the cleidocranial dysplasia phenotype. Hum Mol Genet 2009, 18: 556-568.
Lyson TR, Bever GS, Bhullar B-AS, Joyce WG, Gauthier JA: Transitional fossils and the origin of turtles. Biol Lett 2010, 6: 830-833. 10.1098/rsbl.2010.0371
Lyson TR, Sperling EA, Heimberg AM, Gauthier JA, King BL, Peterson KJ: MicroRNAs support a turtle + lizard clade. Biol Lett 2012, 8: 104-107. 10.1098/rsbl.2011.0477
Lyson TR, Bever GS, Scheyer TM, Hsiang AY, Gauthier JA: Evolutionary origin of the turtle shell. Curr Biol 2013, 23: 1113-1119. 10.1016/j.cub.2013.05.003
Maehata Y, Takamizawa S, Ozawa S, Kato Y, Sato S, Kubota E, Hata R: Both direct and collagen-mediated signals are required for active vitamin D3-elicited differentiation of human osteoblastic cells: roles of osterix, an osteoblast-related transcription factor. Matrix Biol 2006, 25: 47-58. 10.1016/j.matbio.2005.09.001
Maeno T, Moriishi T, Yoshida CA, Komori H, Kanatani N, Izumi S-I, Takaoka K, Komori T: Early onset of Runx2 expression caused craniosynostosis, ectopic bone formation, and limb defects. Bone 2011, 49: 673-682. 10.1016/j.bone.2011.07.023
Marazzi G, Wang Y, Sassoon D: Msx2 is a transcriptional regulator in the BMP4-mediated programmed cell death pathway. Dev Biol 1997, 186: 127-138. 10.1006/dbio.1997.8576
Meier S, Packard DS: Morphogenesis of the cranial segments and distribution of neural crest in the embryos of the snapping turtle, Chelydra serpentina . Dev Biol 1984, 102: 309-323. 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90196-9
Merrill AE, Eames BF, Weston SJ, Heath T, Schneider RA: Mesenchyme-dependent BMP signaling directs the timing of mandibular osteogenesis. Development 2008, 135: 1223-1234. 10.1242/dev.015933
Moazen M, Curtis N, O’Higgins P, Evans SE, Fagan MJ: Biomechanical assessment of evolutionary changes in the lepidosaurian skull. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009, 106: 8273-8277. 10.1073/pnas.0813156106
Modesto SP, Anderson JS: The phylogenetic definition of reptilia. Syst Biol 2004, 53: 815-821. 10.1080/10635150490503026
Müller J: Early loss and multiple return of the lower temporal arcade in diapsid reptiles. Naturwissenschaften 2003, 90: 473-476. 10.1007/s00114-003-0461-0
Mundlos S, Otto F, Mundlos C, Mulliken JB, Aylsworth AS, Albright S, Lindhout D, Cole WG, Henn W, Knoll JHM, Owen MJ, Mertelsmann R, Zabel BU, Olsen BR: Mutations involving the transcription factor CBFA1 cause cleidocranial dysplasia. Cell 1997, 89: 773-779. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80260-3
Nakashima K, Zhou X, Kunkel G, Zhang Z, Deng JM, Behringer RR, de Crombrugghe B: The novel zinc finger-containing transcription factor osterix is required for osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Cell 2002, 108: 17-29. 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00622-5
Neubüser A, Koseki H, Balling R: Characterization and developmental expression of Pax9 , a paired-box-containing gene related to Pax1 . Dev Biol 1995, 170: 701-716. 10.1006/dbio.1995.1248
Nishio Y, Dong Y, Paris M, O'Keefe RJ, Schwarz EM, Drissi H: Runx2-mediated regulation of the zinc finger Osterix/Sp7 gene. Gene 2006, 372: 62-70.
Noden DM: The control of avian cephalic neural crest cytodifferentiation. I. Skeletal and connective tissues. Dev Biol 1978, 67: 296-312. 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90201-4
Noden DM: The role of the neural crest in patterning of avian cranial skeletal, connective, and muscle tissues. Dev Biol 1983, 96: 144-165. 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90318-4
Noden DM, Trainor PA: Relations and interactions between cranial mesoderm and neural crest populations. J Anat 2005, 207: 575-601. 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2005.00473.x
Noden DM, Marcucio R, Borycki AG, Emerson CP: Differentiation of avian craniofacial muscles: I. Patterns of early regulatory gene expression and myosin heavy chain synthesis. Dev Dyn 1999, 216: 96-112. 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0177(199910)216:2<96::AID-DVDY2>3.0.CO;2-6
Ogushi K: Anatomische Studien an der japanischen dreikralligen Lippenschidkröte ( Trionyx japonicus ). Morphologisches Jahrbuch 1911, 43: 1-106.
Okawa A, Nakamura I, Goto S, Moriya H, Nakamura Y, Ikegawa S: Mutation in Npps in a mouse model of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine. Nat Genet 1998, 19: 271-273. 10.1038/956
Oliver G, Wehr R, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Cheyette BN, Hartenstein V, Zipursky SL, Gruss P: Homeobox genes and connective tissue patterning. Development 1995, 121: 693-705.
Pough FH, Janis CM, Heiser JB: Vertebrate life 7th edition. Upper Saddle River: Pearson Prentice Hall; 2005.
Reisz RR: The origin and early evolutionary history of amniotes. Trends Ecol Evol 1997, 12: 218-222. 10.1016/S0169-5347(97)01060-4
Reisz RR, Laurin M: Owenetta and the origin of turtles. Nature 1991, 349: 324-326. 10.1038/349324a0
Rice R, Rice DP, Olsen BR, Thesleff I: Progression of calvarial bone development requires Foxc1 regulation of Msx2 and Alx4. Dev Biol 2003, 262: 75-87. 10.1016/S0012-1606(03)00355-5
Rieppel O: The structure and development of the jaw adductor musculature in the turtle Chelydra serpentina . Zool J Linn Soc 1990, 98: 27-62. 10.1111/j.1096-3642.1990.tb01218.x
Rieppel O: Patterns of diversity in the reptilian skull. In The Skull. Volume 2. Edited by: Hanken J, Hall BK. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 1993:344-390.
Rieppel O: Studies on skeleton formation in reptiles. v. Patterns of ossification in the skeleton of Alligator mississippiensis DAUDIN (Reptilia, Crocodylia). Zool J Linn Soc 1993, 109: 301-325. 10.1111/j.1096-3642.1993.tb02537.x
Rieppel O: Studies on skeleton formation in reptiles: patterns of ossification in the skeleton of Chelydra serpentina (Reptilia, Testudines). J Zool 1993, 231: 487-509. 10.1111/j.1469-7998.1993.tb01933.x
Rieppel O: Turtles as diapsid reptiles. Zool Scrip 2000, 29: 199-212. 10.1046/j.1463-6409.2000.00039.x
Rieppel O, Gronowski RW: The loss of the lower temporal arcade in diapsid reptiles. Zool J Linn Soc 1981, 72: 203-217. 10.1111/j.1096-3642.1981.tb01570.x
Rieppel O, deBraga M: Turtles as diapsid reptiles. Nature 1996, 384: 453-455. 10.1038/384453a0
Rieppel O, Zaher H: The development of the skull in Acrochordus granulatus (Schneider) (Reptilia: Serpentes), with special consideration of the otico-occipital complex. J Morphol 2001, 249: 252-266. 10.1002/jmor.1053
Romer AS: Notes and comments on vertebrate paleontology. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 1968.
Roybal PG, Wu NL, Sun J, Ting M-C, Schafer CA, Maxson RE: Inactivation of Msx1 and Msx2 in neural crest reveals an unexpected role in suppressing heterotopic bone formation in the head. Dev Biol 2010, 343: 28-39. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.04.007
Sánchez-Villagra MR, Müller H, Sheil CA, Scheyer TM, Nagashima H, Kuratani S: Skeletal development in the Chinese soft-shelled turtle Pelodiscus sinensis (Testudines: Trionychidae). J Morphol 2009, 270: 1381-1399. 10.1002/jmor.10766
Satokata I, Maas R: Msx1 deficient mice exhibit cleft palate and abnormalities of craniofacial and tooth development. Nat Genet 1994, 6: 348-356. 10.1038/ng0494-348
Satokata I, Ma L, Ohshima H, Bei M, Woo I, Nishizawa K, Maeda T, Takano Y, Uchiyama M, Heaney S, Peters H, Tang Z, Maxson R, Maas R: Msx2 deficiency in mice causes pleiotropic defects in bone growth and ectodermal organ formation. Nat Genet 2000, 24: 391-395. 10.1038/74231
Schumacher G-H: The head muscles and hyolaryngeal skeleton of turtles and crocodilians. In Biology of the Reptilia Volume 4. Edited by: Gans C. New York: Academic Press; 1973:101-199.
Schweitzer R, Chyung JH, Murtaugh LC, Brent AE, Rosen V, Olson EN, Lassar A, Tabin CJ: Analysis of the tendon cell fate using Scleraxis, a specific marker for tendons and ligaments. Development 2001, 128: 3855-3866.
Schweitzer R, Zelzer E, Volk T: Connecting muscles to tendons: tendons and musculoskeletal development in flies and vertebrates. Development 2010, 137: 2807-2817. 10.1242/dev.047498
Shedlock AM, Botka CW, Zhao S, Shetty J, Zhang T, Liu JS, Deschavanne PJ, Edwards SV: Phylogenomics of nonavian reptiles and the structure of the ancestral amniote genome. Proc. Natl Acad Sci USA 2007, 104: 2767-2772. 10.1073/pnas.0606204104
Sheil CA: Osteology and skeletal development of Apalone spinifera (Reptilia: Testudines: Trionychidae). J Morphol 2003, 256: 42-78. 10.1002/jmor.10074
Sheil CA: Skeletal development of Macrochelys temminckii (Reptilia: Testudines: Chelydridae). J Morphol 2005, 263: 71-106. 10.1002/jmor.10290
Shen XX, Liang D, Wen JZ, Zhang P: Multiple genome alignments facilitate development of NPCL markers: a case study of tetrapod phylogeny focusing on the position of turtles. Mol Biol Evol 2011, 28: 3237-3252. 10.1093/molbev/msr148
Tokita M, Kuratani S: Normal embryonic stages of the Chinese softshelled turtle Pelodiscus sinensis (Trionychidae). Zool Sci 2001, 18: 705-715. 10.2108/zsj.18.705
Tokita M, Kiyoshi T, Armstrong KN: Evolution of craniofacial novelty in parrots through developmental modularity and heterochrony. Evol Dev 2007, 9: 590-601. 10.1111/j.1525-142X.2007.00199.x
Tokita M, Schneider RA: Developmental origins of species-specific muscle pattern. Dev Biol 2009, 331: 311-325. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.05.548
Tokita M, Chaeychomsri W, Siruntawineti J: Developmental basis of toothlessness in turtles: insight into convergent evolution of vertebrate morphology. Evolution 2012, 67: 260-273.
Tribulo C, Aybar MJ, Nguyen VH, Mullins MC, Mayor R: Regulation of Msx genes by a Bmp gradient is essential for neural crest specification. Development 2003, 130: 6441-6452. 10.1242/dev.00878
Tzika AC, Helaers R, Schramm G, Milinkovitch MC: Reptilian-transcriptome v1.0, a glimpse in the brain transcriptome of five divergent Sauropsida lineages and the phylogenetic position of turtles. EvoDevo 2011, 2: 19. 10.1186/2041-9139-2-19
Vickaryous MK, Hall BK: Development of the dermal skeleton in Alligator mississippiensis (Archosauria, Crocodylia) with comments on the homology of osteoderms. J Morphol 2008, 269: 398-422. 10.1002/jmor.10575
Wang Z, Pascual-Anaya J, Zadissa A, Li W, Niimura Y, Huang Z, et al.: The draft genomes of soft-shell turtle and green sea turtle yield insights into the development and evolution of the turtle-specific body plan. Nat Genet 2013, 45: 701-706. 10.1038/ng.2615
Watanabe T, Nakano K, Muraoka R, Shimizu T, Okafuji N, Kurihara S, Yamada K, Kawakami T: Role of Msx2 as a promoting factor for Runx2 at the periodontal tension sides elicited by mechanical stress. Eur J Med Res 2008, 13: 425-431.
Werneburg I: Temporal bone arrangements in turtles: an overview. J Exp Zool B. Mol Dev Evol 2012, 318: 235-249. 10.1002/jez.b.22450
Werneburg I: Jaw musculature during the dawn of turtle evolution. Organ Divers Evol 2012, 13: 225-254.
Werneburg I, Hugi J, Müller J, Sánchez-Villagra MR: Embryogenesis and ossification of Emydura subglobosa (Testudines, Pleurodira, Chelidae) and patterns of turtle development. Dev Dyn 2009, 238: 2770-2786. 10.1002/dvdy.22104
Whiteside DI: The head skeleton of the Rhaetian sphenodontid Diphydontosaurus avonensis gen. et sp. nov., and the modernizing of a living fossil. Phil Trans Biol Sci 1986, 312: 379-430. 10.1098/rstb.1986.0014
Wilkie AO, Tang Z, Elanko N, Walsh S, Twigg SRF, Hurst JA, Wall SA, Chrzanowska KH, Maxson RE: Functional haploinsufficiency of the human homeobox gene MSX2 causes defects in skull ossification. Nat Genet 2000, 24: 387-390. 10.1038/74224
Williston SW: The phylogeny and classification of reptiles. J Geol 1917, 25: 411-421. 10.1086/622507
Wright E, Hargrave MR, Christiansen J, Cooper L, Kun J, Evans T, Gangadharan U, Greenfield A, Koopman P: The Sry -related gene Sox9 is expressed during chondrogenesis in mouse embryos. Nat Genet 1995, 9: 15-20. 10.1038/ng0195-15
Xing W, Singgih A, Kapoor A, Alarcon CM, Baylink DJ, Mohan S: Nuclear factor-E2-related factor-1 mediates ascorbic acid induction of osterix expression via interaction with antioxidant-responsive element in bone cells. J Biol Chem 2007, 282: 22052-22061. 10.1074/jbc.M702614200
Zaher H: Comments on the evolution of the jaw adductor musculature of snakes. Zool J Linn Soc 1994, 111: 339-384. 10.1111/j.1096-3642.1994.tb01488.x
Zehr DR: Stages in the normal development of the common garter snake, Thamnophis sirtalis sirtalis . Copeia 1962, 2: 322-329.
Zhang C: Transcriptional regulation of bone formation by the osteoblast-specific transcription factor Osx. J Orthopaed Surg Res 2010, 5: 37. 10.1186/1749-799X-5-37
Zhang Z, Song Y, Zhang X, Tang J, Chen J, Chen Y: Msx1/Bmp4 genetic pathway regulates mammalian alveolar bone formation via induction of Dlx5 and Cbfa1. Mech Dev 2003, 120: 1469-1479. 10.1016/j.mod.2003.09.002
Acknowledgments
We appreciate Sriracha Crocodile Farm & Product Co., LTD. and the company staffs, especially Nussara Thongprasert in collection of fertilized eggs of Crocodiles. We also thank Manasaree Klomtun, Punnapa Pinweha, and Ekawit Threenet for their kind help in collection of Crocodile eggs. MT thanks Hiroshi Wada who allowed the use of facilities for experiments and analyses, Hiroki Ono who kindly gifted chick Msx1 probe, Matthew Brandley and Richard Schneider for critical reading and editing of a draft of the manuscript, and Johannes Müller for helpful comments to early version of the manuscript. This study was partially supported by Grants-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan to M.T. (22770077).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
MT conceived and designed the study. MT, WC, and JS contributed to collection and preparation of biological materials. MT performed experiments and analyses and wrote the paper. All authors read, discussed and approved the final manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
40064_2013_438_MOESM1_ESM.tiff
Additional file 1: Expression of musculoskeletal tissue marker genes in the head of crocodile embryos at stage 14. (A) Lateral view of the embryo. (B-D, and F) Frontal sections prepared around the plane indicated by the blue line in (A). (E) Frontal section prepared around the plane indicated by the red line in (A). (B) Expression of Runx2 is faintly detected at the mesenchymal cells above and below the eye, as well as in the mesenchyme distributed medial to the precursor of quadrate cartilage and in the mesenchyme surrounding the braincase (arrows). (C) Cranial muscular tissues are clearly labeled by MyoD probe. (D) Cartilaginous tissues, including the braincase and the quadrate (q), are labeled by Sox9 probe. (E) Scx is expressed in tendon precursor cells in close proximity of MyoD-positive jaw and eye muscle anlagen (arrowheads). (F) Six2 is expressed mainly in the mesenchyme around Sox9-positive cartilage precursors, including the quadrate and the braincase, as well as in the mesenchyme around MyoD-positive cranial muscle anlagen. The red outlined domains indicate the location of the anlagen of the jaw muscle complex. Scale bar in (A) is 1 mm. Scale bars in (B-F) are 0.5 mm. (TIFF 9 MB)
40064_2013_438_MOESM2_ESM.tiff
Additional file 1: Expression of musculoskeletal tissue marker genes in the head of turtle embryos at stage 14. (A) Lateral view of the embryo. (B-E) Frontal sections prepared around the plane indicated by the red line in (A). (B) Runx2-positive mesenchymal cells are distributed above and below the eye, as well as in the domain medial to the anlagen of jaw adductor muscle (black arrows). (C) Cranial muscular tissues are clearly labeled by MyoD probe. (D) Cartilaginous tissues, including the braincase and quadrate, are labeled by Sox9 probe. (E) Six2 is expressed mainly in the mesenchyme around Sox9-positive cartilage precursors and MyoD-positive cranial muscle anlagen. Scale bar in (A) is 1 mm. Scale bars in (B-E) are 0.5 mm. (TIFF 5 MB)
40064_2013_438_MOESM3_ESM.tiff
Additional file 1: A layer of fibrous connective tissue lateral to the external adductor muscle is found in late stage soft-shelled turtle embryo. (A) Lateral view of the head of a turtle embryo at stage 22. (B, C) Frontal sections of the head prepared in the planes indicated in (A). Note a clear layer of fibrous connective tissue lateral to the external adductor muscle (red arrowheads). (D) Lateral view of the head of a crocodile embryo at stage 20. (E, F) Frontal sections of the head prepared in the planes indicated in (D). (G) Lateral view of the head of a snake embryo at stage 31. (H, I) Frontal sections of the head prepared in the planes indicated in (G). A layer of fibrous connective tissue is not seen in the domain lateral to the external adductor muscle in crocodile and snake embryos. Rather, in crocodile and snake embryos, the domain is occupied by mesenchymal cells in low density or by acellular cavities. Scale bars are 1 mm. (TIFF 6 MB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Tokita, M., Chaeychomsri, W. & Siruntawineti, J. Skeletal gene expression in the temporal region of the reptilian embryos: implications for the evolution of reptilian skull morphology. SpringerPlus 2, 336 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-2-336
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-2-336