Abstract
Proper repair of DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) is vital for the preservation of genomic integrity. There are two main pathways that repair DSBs, Homologous recombination (HR) and Non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ). HR is restricted to the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle due to the requirement for the sister chromatid as a template, while NHEJ is active throughout the cell cycle and does not rely on a template. The balance between both pathways is essential for genome stability and numerous assays have been developed to measure the efficiency of the two pathways. Several proteins are known to affect the balance between HR and NHEJ and the complexity of the break also plays a role. In this review we describe several repair assays to determine the efficiencies of both pathways. We discuss how disturbance of the balance between HR and NHEJ can lead to disease, but also how it can be exploited for cancer treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Genomic integrity and faithful replication are essential to prevent mutations and chromosomal rearrangements, which may otherwise lead to diseases and in some cases even death. DNA damage is generated by several different genotoxic agents such as reactive oxygen species, UV light from the sun and mutagenic chemicals [1]. These agents cause many types of DNA damage, ranging from base damage to double strand breaks (DSBs). To protect the genome from the deleterious effects of these lesions, several mechanisms have evolved that detect and repair DNA damage. Together with mechanisms that regulate cell cycle progression and cell death pathways this is known as the DNA damage response (DDR).
In this review we concentrate on DSBs, which are among the most cytotoxic types of DNA damage. The therapeutic effect of several commonly used cancer treatment modalities, such as ionizing radiation and the chemotherapeutic doxorubicin, are based on the cell-killing effect of DSBs. However, DSBs are also the initiating lesion of disease-causing chromosomal translocations in cancer. Therefore, it is important to understand the intricate regulation of the DDR upon DSB formation. We mainly concentrate on the two main DSB repair pathways, Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) and Homologous recombination (HR), with a special emphasis on the balance between both repair mechanisms in health and disease.
NHEJ
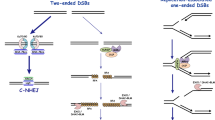
NHEJ is a relatively simple DSB repair pathway (Figure 1). Both ends of the break are first bound by the Ku70/Ku80 heterodimer, which then recruits the catalytic subunit of the DNA dependent protein kinase (DNA-PKcs) [2]. If necessary, the ends can be trimmed by nucleases (such as Artemis) or filled in by DNA polymerases (such as Polμ or Polλ) to create compatible ends [3]. Finally, the ligation complex, consisting of DNA ligase IV, X-ray cross-complementation group 4 (XRCC4) and Xrcc4 like factor (XLF)/Cernunnos ligates the ends [4, 5]. NHEJ can take place throughout the cell cycle. For an extensive review on NHEJ see [3].
HR and NHEJ. NHEJ) NHEJ starts with recognition of the DNA ends by the Ku70/80 heterodimer, which recruits DNA-PKcs. If the ends are incompatible, nucleases such as Artemis can trim the ends. The XRCC4-DNA Ligase IV-XLF ligation complex seals the break. HR) The MRN-CtIP-complex starts resection on the breaks to generate single stranded DNA (ssDNA). After resection the break can no longer be repaired by NHEJ. The ssDNA is first coated by RPA, which is subsequently replaced by Rad51 with the help of BRCA2. These Rad51 nucleoprotein filaments mediate strand invasion on the homologous template. Extension of the D-loop and capture of the second end lead to repair.
HR
HR uses a sequence similar or identical to the broken DNA as a template for accurate repair. The sister chromatid is used as an identical template in the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle, when the DNA has been replicated. HR is restricted to these cell cycle phases in higher eukaryotes to prevent recombination between (repetitive) non-identical sequences. Spurious HR can lead to loss of heterozygosity (when HR takes place between paternal and maternal chromosomes) or insertions/deletion (when repeats are not aligned properly).
The HR pathway starts with resection of the broken DNA ends (Figure 1) by the MRN-complex [6, 7], together with CtBP-interacting protein (CtIP) [8, 9] and other exonucleases, generating 3’-single stranded DNA (ssDNA) [9, 10]. The ssDNA tail is coated by Replication protein A (RPA) to remove secondary structure [11]. Subsequently, BRCA2 mediates the replacement of RPA by RAD51, to form a nucleoprotein filament that searches for the homologous sequence on the sister chromatid. After strand invasion, catalyzed by RAD51 and many other proteins, the DNA end is extended using the intact sequence as a template. After restoration of any lost sequence information, the second end of the broken DNA is captured and the junctions are resolved to give a precisely repaired DSB [12]. This resolution step can be accomplished via formation of two Holiday junctions, which are subsequently resolved to give crossover or non-crossover products (the double Holiday junction model). An alternative HR model, the synthesis dependent strand annealing (SDSA) model, does not involve Holiday junctions and results in non-crossover products only [13].
Foci
Microscopically, DSBs can be visualized as local spots of repair protein accumulation (also called foci) in the nucleus. For example, histone H2AX is phosphorylated locally around the DSB and 53BP1, RPA and RAD51 accumulate in foci after ionizing radiation. Changes in the number of foci per nucleus in time can be quantified to analyze the dynamics of DNA repair [14]. Not all repair proteins accumulate in sufficient numbers to form foci. For example Ku70/80 does not form foci, although it is recruited to DNA damage [15, 16].
Alternative DSB repair pathways
In addition to classical HR, several subpathways result in slightly different products. For example the single strand annealing (SSA) pathway uses directly repeated stretches of homology to repair DSBs. After resection of the break (as described above for HR) complementary stretches in the ssDNA anneal and the intervening sequence and one of the repeats is deleted [17]. Since HR and SSA use the same substrate, these pathways compete when repeats are present on both sides of the break and SSA should be suppressed to prevent its mutagenic effect.
Alternative end-joining pathways can also join DSBs in an error-prone manner, especially when classical NHEJ is impaired by deletion of essential components. The genetics of this pathway are not well defined and there may even be several alternative end-joining pathways. A dependence on DNA ligase III, Xrcc1 and PARP1 has been found in genetic assays [18, 19]. However, in another assay the repair of I-SceI induced DSBs in XRCC4-deficient pro-B cell lines did not require Xrcc1 [20]. Alternative pathways show increased DSB joining using microhomologies (stretches of 1–6 bp of direct repeat at the junction), possibly to stabilize the synapsed ends [3].
Although these alternative DSB repair pathways can work in specific experimental settings, they probably do not play a major role in repair of most DSBs in wild type cells. Therefore this review will focus on the balance between the classical forms of HR and NHEJ.
Repair assays
To study the balance between HR and NHEJ, one would ideally measure both types of repair at the same time using a defined chromosomal site. Unfortunately such an assay is not yet available. There are, however, many assays to measure HR and NHEJ separately. A good understanding of these assays is indispensable for correct interpretation of the results obtained using these different approaches. We therefore review the major assay systems and discuss their merits and drawbacks.
Assays to measure NHEJ
NHEJ can be measured in many different ways. The simplest version is transfection of linearized DNA into wild type and mutant cells. Joining of the ends can be monitored by cloning out individual plasmids or PCR amplification followed by sequencing or digestion of the junction [21] (Figure 2a). Recircularization can also be monitored by following the restoration of expression of a reporter gene, such as an antibiotic resistance gene or a fluorescent marker (Figure 2b). A major disadvantage of these assays is that the linear DNA is extrachromosomal and NHEJ cannot be measured in the normal context of chromatin. However, it is a simple assay that can monitor decreased activity of the core NHEJ machinery as a shift towards microhomology use at the newly formed junctions.
NHEJ repair assays. a) Linear plasmid DNA with 6 bp repeats at the ends is joined after transfection. The joints are amplified by PCR and digested using BstXI to distinguish between direct repair and microhomology mediated repair [21]. b) Repair of linearized plasmid DNA results in restoration of GFP expression. c) Cleavage by I-SceI and subsequent repair lead to loss of the middle splice donor and acceptor sites (SD and SA) and the adenoviral exon (AD), resulting in the expression of active GFP [22]. d) H2Kd fused to CD8 is expressed from the intact substrate. Repair of the oppositely oriented I-SceI breaks results in loss of H2Kd-CD8 and allows expression of CD4 [23]. e) Similar to d), the intact substrate expresses GFP, while the repaired substrate allows expression of RFP and loses GFP expression [24]. f) Between the opposite I-SceI sites, a translation start site is located, preventing translation of the XHATM resistance gene. Repair of the I-SceI breaks and loss of the intervening ATG results in XHATM resistance. The sequence around the breaks can be sequenced to monitor loss of nucleotides [25]. g) V(D)J recombination assay. Cleavage by the Rag1/2 endonuclease at the recombination signal sequences induces inversion of the intervening sequence. Small arrows indicate location of PCR primers to amplify joints [21].
Another type of NHEJ assays uses two I-SceI restriction sites. These sites can be in the same or opposite orientation, generating compatible or incompatible ends, respectively. These constructs are generally integrated into the genome. The general theme of all these assays is restoration of expression of a marker gene, in some cases accompanied by inactivation of another gene. Mao et al. (Figure 2c) interrupted the GFP gene with an intron containing an adenoviral exon (AD) flanked by two I-SceI sites. Repair of the two I-SceI induced DSBs leads to loss of the intervening exon and expression of functional GFP [22]. Guirouilh-Barbat et al. developed a similar assay (Figure 2d) with compatible or incompatible I-SceI sites, but they used surface antigens as a read-out for repair [23]. Coleman and Greenberg also used a comparable assay (Figure 2e) with GFP between the I-SceI sites and RFP downstream, resulting in loss of GFP and expression of RFP after repair of the I-SceI induced DSBs [24]. In these assays with a double I-SceI site it is also possible to sequence the joints and to determine the loss of nucleotides around the breaks (Figure 2f) [25].
A disadvantage of these assays using I-SceI restriction sites is that the individual I-SceI break has compatible ends and can recreate an I-SceI site if it is repaired precisely by NHEJ. Therefore, several cycles of cleavage and repair can happen before the site is lost due to inaccurate repair and these assays cannot measure the NHEJ efficiency accurately. However, sequencing of the junctions can provide interesting information about imprecise end-joining events. To avoid the cut-and-paste cycle problem of the I-SceI sites, some assays use transposon excision to create a break. Repair of transposon-induced DSBs can reveal details of efficiency as well as precision of NHEJ [26, 27]. In principle, transposons would also be useful to study HR, although their DSB formation efficiency is generally lower than endonucleases.
The immune system depends on end-joining for V(D)J and class switch recombination (CSR). Pan-Hammarstrom and colleagues studied CSR by PCR amplification and sequencing of the junctions in normal individuals and patients. They found that patients with mutations in NHEJ components, such as DNA ligase IV, showed an increased dependence on longer microhomology stretches at the junctions [28]. An advantage of this assay is that repair is measured on endogenous substrates. However, it is not clear whether these loci are representative for other types of DSBs.
V(D)J recombination also depends on NHEJ factors to repair the breaks induced by the Rag1 and Rag2 proteins. This type of repair can be assayed using a specific repair substrate containing Recombination Signal Sequences, the recognition sites for Rag1 and Rag2 (Figure 2g) [21]. The V(D)J recombination assay gives a clear phenotype for defects in proteins involved in DNA end-processing, such as the Artemis nuclease [29]. The major disadvantage of these types of assays is the special nature of the DSBs formed by the RAG proteins, which may shuttle the breaks towards NHEJ [30].
Assays to measure HR
The most commonly used assay to measure HR is the DR-GFP assay developed by Pierce and Jasin [31] (Figure 3). The reporter construct can be inserted by gene targeting or random integration. It contains two GFP sequences separated by a selection marker. The 5’ GFP sequence is inactivated by an I-SceI site and internal stop codons, preventing GFP expression. The 3’ truncated GFP serves as a template for repair after DSB induction by I-SceI. Repair of the break by gene conversion using the downstream GFP sequence leads to restoration of the GFP gene and the percentage of GFP expressing cells can be determined by FACS analysis.
This HR assay has been used successfully to characterize defects in various (repair) mutant genetic backgrounds. An important advantage of this HR assay is that it measures repair using a chromatinized reporter construct in the chromosome. However, the template for repair is downstream of the break, whereas the normal template for HR is the equivalent position on the sister chromatid. Furthermore, the I-SceI site can be subject to several cycles of cleavage and repair by precise NHEJ or restoration of the sequence using the sister chromatid as a repair template, which leaves a high degree of uncertainty about the relative levels of HR and NHEJ.
Expression of I-SceI is usually induced by transfection of an expression plasmid into an asynchronously growing cell population. This creates DSBs in the reporter substrate throughout the cell cycle, whereas HR only takes place in the S and G2 phases. To overcome this problem, Hartlerode et al. developed an I-SceI fusion protein that is drug-activatable. Enriching cells in a certain phase of the cell cycle then allows restricted activation of I-SceI [32].
HR can also be estimated by scoring sister chromatid exchanges (SCEs). In this assays a nucleotide analog is added in the first cell cycle to allow incorporation into the newly synthesized strand in S phase. After a second replication round, only one of the sister chromatids is labeled, which allows visualization of recombination between the sister chromatids in metaphase spreads by staining for the incorporated nucleotide analog. SCEs can be formed in S phase during the repair of collapsed replication forks as well as in G2 phase at two-ended DSBs [33].
A completely different method to assess the efficiency of DSB repair is monitoring the disappearance of γH2AX foci. These foci form within a few minutes after DSB formation and disappear slowly as repair takes place. By comparing the kinetics of several known HR and NHEJ mutants, the efficiency and likely repair pathway can be determined. For a review on the advantages and potential pitfalls of this assay, see [34].
As a more sophisticated approach, the formation and disappearance of 53BP1-YFP and Rad52-Cherry foci has been followed to estimate the use of HR and NHEJ in single cells throughout the cell cycle [35]. Karanam et al. found that there is a gradual increase in HR at the beginning of S phase. The number of Rad52 foci increases till mid S phase and then decreases towards the end of S phase. In G2, very few Rad52 foci were observed, showing that HR is not the predominant pathway in G2. This is consistent with data from Beucher et al., who demonstrated that NHEJ repairs approximately 85% of all IR-induced DSBs in G2, as measured by γH2AX foci kinetics [36].
Balancing HR and NHEJ
The presence of large numbers of highly repetitive sequences in the DNA of higher eukaryotes makes HR between sequences other than sister chromatids prone to misalignment of the homologous sequences. Therefore, HR generally dominates in organisms with a small genome (with low abundance of repetitive sequences), whereas mammals mainly rely on NHEJ for DSB repair [35, 37]. However, even in highly complex genomes, HR is used as the preferred DSB repair mechanism to deal with DSBs that are formed during replication. This necessitates intricate control mechanisms to prevent access of the wrong repair pathway to the DSB.
Resection & cell cycle
HR can only safely be used to repair breaks in the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle. The first mechanism to regulate this depends on S/G2 specific cyclin dependent kinases (CDKs). DNA end resection requires phosphorylation of CtIP on a CDK consensus sequence [9, 38, 39]. Proteasome-mediated degradation of the CtIP protein in G1 [40] adds an additional layer of regulation at the resection step.
CDK1/CyclinB also phosphorylates the NBS1 component of the MRN complex on Serine 432 during the S, G2 and M phases, which is required for resection and efficient HR. However, IR sensitivity was not affected in the Ser432Ala NBS1 mutant, consistent with the notion that NHEJ is the major DSB repair pathway in mammals [41].
Although activation of HR proteins in a cell cycle dependent manner helps to restrict their activity, it is insufficient to ensure safe use of HR. While replication is ongoing in the S phase, parts of the genome have not yet been replicated and recombination of these parts should be avoided to prevent loss of heterozygosity and non-allelic recombination. Therefore, another layer of regulation is provided by the structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) proteins such as Cohesin, Condensin and SMC5/6: they are able to confine repair to the sister chromatid and prevent HR between other sequences [42, 43].
Complexity of the break
Whether HR or NHEJ is used also depends on DSB complexity. This phenomenon has been studied in detail in the G2 phase of the cell cycle, when both HR and NHEJ contribute to DSB repair. Treatment of cells with the topoisomerase II inhibitor Etoposide results in breaks with a 4 bp 5’-overhang with covalently attached protein [44]. The large majority of these breaks are repaired rapidly by NHEJ. The remaining 10% of the Etoposide induced breaks is repaired with slow kinetics via HR [45]. High linear energy transfer (LET) carbon ions, on the other hand, induce highly complex clusters of DSBs and other types of DNA damage [46], because this type of radiation causes a high number of ionizations in a small volume. These breaks are frequently resected and their repair takes place via HR with slow kinetics [45]. From the breaks induced by low LET ionizing irradiation (IR), which causes less complex DSBs, only 20-30% is resected and their repair is much less dependent on HR [36, 45].
The chromatin structure around the DSB affects repair as well. Breaks in heterochromatin are repaired more slowly than breaks in euchromatin [47] probably because euchromatin is more easily accessible for repair and requires less or no remodeling. Repair of breaks in heterochromatin requires ATM [47]. ATM phosphorylates transcriptional corepressor Krüppel-associated box (KRAB)-associated protein (KAP)-1 [48], which disrupts the interaction between Kap-1 and CHD3 [49]. CHD3 is an ATP-dependent nucleosome remodeling enzyme and its dispersion allows chromatin relaxation, facilitating DSB repair in heterochromatin. Furthermore, the ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler SMARCAD1 can also be recruited to sites of DNA damage where it facilitates resection [50].
Genetic factors influencing pathway choice
The core HR and NHEJ machineries have been conserved from yeast to mammals [51]. However, several genes have been added to optimize or regulate both pathways in higher eukaryotes. For example, NHEJ has acquired DNA-PKCS and HR added several RAD51 paralogs. Furthermore, several additional genes in higher eukaryotes regulate DSB repair pathway choice without direct participation in the catalytic steps of the repair reaction.
53BP1
The p53 binding protein 1 (53BP1) is recruited to DSBs, where it has functions in cell cycle checkpoint maintenance and double strand break repair [52]. The fast phase in DSB repair is normal in the absence of 53BP1, but repair of breaks in heterochromatin is severely impaired, probably as a result of impaired Kap1 phosphorylation [49, 53].
A deeper understanding of the 53BP1 function has been gained from studies in the immune system. During class switch recombination, highly repetitive DNA segments are recombined to generate the different classes of antibodies. DSBs generated during this recombination reaction can be repaired via NHEJ or alternative end joining. In the absence of 53BP1, resection increases and microhomology mediated alternative end-joining takes over from classical NHEJ [54]. In V(D)J recombination, Variable (V), Diversity (D) and Joining (J) segments are recombined to create a large variety of functional coding sequences for immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors. DSBs created by Rag1/2 are repaired via NHEJ. 53BP1 prevents extensive degradation and it promotes synapsis of DNA ends and stabilizes long-range interactions, not only between breaks created during V(D)J recombination [55], but also between deprotected telomeres [56].
BRCA1 and associated protein
In contrast to the NHEJ promoting effect of 53BP1, the tumor suppressor BRCA1 is required for efficient HR [57] and formation of Rad51 foci after DSB induction [58]. BRCA1 is an E3-ubiquitin ligase that forms a complex with the E2 enzyme BARD1 via its RING domain. This interaction is required for the ligase activity, as well as protein stability and nuclear localization [59]. Although several RING domain mutations have been found in patients, it is currently unknown how the HR defect is related to the E3-ligase function and BARD1 interaction. Drost et al. recently showed that the ring domain is necessary for tumor suppression, but not required for the development of resistance to chemotherapeutics. Tumors with a C61G mutation in the RING domain rapidly develop resistance to platinum drugs and the PARP inhibitor Olaparib, while retaining this mutation [60].
In addition to its function as a ubiquitin ligase, BRCA1 may also function as a scaffold protein that associates with many interaction partners, such as Abraxas, BACH1 and BRCA2/PALB2 [59]. For efficient resection of DNA ends, its interaction with CtIP and the MRN complex is probably important [39, 61]. BRCA1 also interacts with RAP80 and the BRCA1/RAP80 complex is recruited to ubiquitylated chromatin around DSBs [62–64]. In contrast to the BRCA1 interactions described above, the RAP80-BRCA1 interaction decreased HR: depletion of Rap80 stimulated recruitment of CtIP and Mre11 and thereby resection [24]. The BRCA1 interactions with CtIP and RAP80 are mutually exclusive, indicating that competition for this BRCA1 binding site affects resection and thereby pathway choice. For replication-associated breaks, BRCA1 clearly tips the balance towards HR.
Genetic interactions of BRCA1 and 53BP1
Recently, some unexpected genetic interactions between BRCA1 and 53BP1 shed new light on their function in balancing DSB repair pathways. Deletion of BRCA1 causes embryonic lethality, but this can be rescued by deletion of 53BP1 [65]. Unexpectedly, deletion of 53BP1 also restored HR and Rad51 foci formation in BRCA1 deficient cells [66, 67], implying that both factors influence HR in opposite directions and that inactivation of both genes largely restores the balance. Inactivation of 53BP1 in BRCA1−/− ES cells led to an increase in both nucleolytic DNA end processing and RPA phosphorylation [67]. ATM inhibition in BRCA1 −/− 53BP1−/− cells reduced RPA phosphorylation and Rad51 foci formation, indicating that ATM-dependent resection allows partial restoration of HR [67].
Figure 4 presents a plausible model to accommodate these findings. One-ended DSBs that are formed during replication require BRCA1 to stimulate resection. In BRCA1 deficient cells, 53BP1 prevents resection of DNA ends, leading to aberrant diversion of breaks to NHEJ. This creates dead-end products (if only one DNA end is present) or inappropriate joining to distant sequences causing chromosomal translocations (if a DNA end combines with an unrelated other DNA end). Two-ended DSBs, on the other hand, require 53BP1 to limit resection and allow efficient NHEJ. Overactive resection in 53BP1−/− cells may result in aberrant HR reactions (such as single-strand annealing) or alternative end-joining pathways, creating microhomology-mediated translocations and/or junctions with excessive deletions [68, 69].
BRCA1 and 53BP1 in DSB repair. a) Repair of replication associated breaks requires HR. 53BP1 blocks resection of the one-ended break in BRCA1 deficient cells, preventing repair via HR. The breaks are either left unrepaired or repaired via NHEJ using other random DNA ends, which leads to chromosomal rearrangements and genomic instability. In the absence of 53BP1, resection of the DNA ends can take place, allowing faithful repair via HR. b) IR induced two ended DSBs are mainly repaired via NHEJ, however part of the breaks is repaired via HR or alternative end-joining (alt-EJ). Repair via HR or alt-EJ increases when classical NHEJ is impaired by a mutation in one of the core NHEJ genes or 53BP1.
Further insight into the role of BRCA1 and 53BP1 in repair pathway choice was recently obtained using super resolution microscopy of IR induced foci (IRIF). The core of the focus contained mainly 53BP1 molecules in the G1 phase of the cell cycle, probably representing repair via NHEJ. In S phase, however, the core of the IRIF was filled with BRCA1 and 53BP1 formed a ring around this core, suggesting that BRCA1 physically excludes 53BP1 from the break to allow repair via HR [70].
BRCA1 deficient cells are exquisitely sensitive to PARP inhibitors, which inhibit single strand break repair [71, 72]. The rationale for this observation is that replication of DNA with single strand breaks results in formation of single DNA ends, which require HR for their repair (Figure 4). As described above, deletion of 53BP1 in BRCA1 deficient cells rescues embryonic lethality. However, loss of 53BP1 also leads to resistance to PARP inhibition [66, 73]. In the BRCA1-deficient cells that have also lost 53BP1, the number of chromosome and chromatid breaks is decreased and checkpoint activation is diminished compared to cells that are only BRCA1 deficient [66], suggesting that the regained HR capacity in these cells is largely sufficient to restore genomic stability. A subset BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutant tumors shows loss of 53BP1, indicating that therapy resistance via loss of 53BP1 may be clinically relevant [66].
Ubiquitylation and sumoylation
Ubiquitin and the small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) are small polypeptides that can be attached to proteins as a posttranslational modification. After activation of ubiquitin or SUMO by an E1 enzyme, they are transferred to an E2 conjugating enzyme. With the help of an ubiquitin (or SUMO) ligase (E3) the modification is attached to the substrate. Deubiquitylating enzymes (DUBs) can reverse the ubiquitin modification.
Many proteins involved in the DDR can be ubiquitylated or sumoylated [2, 74–76]. For the sake of simplicity, we will focus on one part of the DDR signaling cascade as an example. Upon DSB formation, histone H2AX is phosphorylated by ATM or DNA-PK. MDC1 is recruited to this phosphorylated histone (γH2AX) and is in turn phosphorylated by ATM. This attracts the E3 ligase RNF8 which ubiquitylates H2A and H2AX. Subsequent action of the E3 ligase RNF168 leads to more extensive ubiquitylation of the chromatin around the break, creating a recruitment platform for many other repair proteins, including 53BP1 and BRCA1 [77]. These ubiquitylation events are also required for phospho-KAP-1 foci formation and thereby chromatin relaxation at sites of damage [53].
In addition to an effect on recruitment of repair proteins, ubiquitylation can also affect release of proteins from the lesion. The transient binding of Ku at DNA ends affects pathway choice. Ku binds in all phases of the cell cycle and must be removed to allow resection [78, 79]. This removal can be facilitated via ubiquitlyation of Ku by the E3 ligase RNF8 and an unknown E2 conjugating enzyme, leading to proteasome-dependent Ku degradation [80]. Since Ubiquitylation is a very abundant modification on DDR proteins, it is likely that more modifications affecting pathway choice will be discovered in the future.
Concluding remarks
A unifying model for DSB repair pathway choice should take into account that NHEJ is relatively fast, while resection is a slow process that probably creates a point of no return. Therefore, it is to be expected that NHEJ initially tries to repair all DSBs and only if this repair pathway fails to repair the lesion, the chance that resection takes place increases over time, necessitating repair via HR. This is consistent with the observation that the binding of the Ku heterodimer to DNA ends is a very fast process, but the assembly of end-joining complexes is dynamic and may in the long run give way to proteins mediating resection if they are active [16]. This means that initiation of HR will mainly be restricted to the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle, when CtIP is active. Indeed, a subfraction of DSBs in G2 requires BRCA2 for their repair, but knock-down of both CtIP and BRCA2 alleviates this repair defect [45], suggesting that avoiding resection prevents HR and allows repair of these DSBs by NHEJ. Replication associated breaks, on the other hand, should be channeled to HR, which is the only pathway that can restart a replication fork from a single broken DNA end.
The study of the balance between HR and NHEJ is important for the prediction of treatment responses upon inhibition of these pathways in various genetic backgrounds. Combined treatments might backfire when the balance is tipped the wrong way. For example, the treatment of BRCA1 and BRCA2 deficient cells is most effective when NHEJ is functional, whereas impaired NHEJ prevents lethal genomic instability and cytotoxicity, which counteracts the effect of PARP inhibitors in HR deficient cells [73, 81].
The balance between HR and NHEJ is heavily regulated, but the wiring and hierarchy of this regulatory network is still incompletely understood. Development of targeted therapies using DNA damage response defects requires a much more detailed knowledge of the precise network of the cellular responses to DNA damaging treatments. It is to be expected that new assay systems will be developed and that a flurry of novel combinations of chemical inhibitors and genetic defects will increase our understanding of these processes in the near future. This knowledge will then be an invaluable source for developing new targeted therapies for tumors with DNA damage response defects, which should yield more specific and effective therapeutic approaches to combat cancer. Novel tools to characterize tumor-specific (DNA repair gene) mutations, such as whole genome sequencing approaches, should then bring truly personalized medicine for cancer treatment within reach.
References
Friedberg ECW, Siede GC, Wood RD, Schultz RA, Ellenberger T: DNA repair and mutagenesis. 2006, Washington, USA: ASM press
Ciccia A, Elledge SJ: The DNA damage response: making it safe to play with knives. Mol Cell. 2010, 40: 179-204. 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.09.019.
Lieber MR: The mechanism of double-strand DNA break repair by the nonhomologous DNA end-joining pathway. Annu Rev Biochem. 2010, 79: 181-211. 10.1146/annurev.biochem.052308.093131.
Ahnesorg P, Smith P, Jackson SP: XLF interacts with the XRCC4-DNA ligase IV complex to promote DNA nonhomologous end-joining. Cell. 2006, 124: 301-313. 10.1016/j.cell.2005.12.031.
Buck D, Malivert L, de Chasseval R, Barraud A, Fondaneche MC, Sanal O, Plebani A, Stephan JL, Hufnagel M, le Deist F, et al: Cernunnos, a novel nonhomologous end-joining factor, is mutated in human immunodeficiency with microcephaly. Cell. 2006, 124: 287-299. 10.1016/j.cell.2005.12.030.
Heyer WD, Ehmsen KT, Liu J: Regulation of homologous recombination in eukaryotes. Annu Rev Genet. 2010, 44: 113-139. 10.1146/annurev-genet-051710-150955.
Stracker TH, Petrini JH: The MRE11 complex: starting from the ends. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011, 12: 90-103. 10.1038/nrm3047.
Limbo O, Chahwan C, Yamada Y, de Bruin RA, Wittenberg C, Russell P: Ctp1 is a cell-cycle-regulated protein that functions with Mre11 complex to control double-strand break repair by homologous recombination. Mol Cell. 2007, 28: 134-146. 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.09.009.
Sartori AA, Lukas C, Coates J, Mistrik M, Fu S, Bartek J, Baer R, Lukas J, Jackson SP: Human CtIP promotes DNA end resection. Nature. 2007, 450: 509-514. 10.1038/nature06337.
Wyman C, Kanaar R: DNA double-strand break repair: all's well that ends well. Annu Rev Genet. 2006, 40: 363-383. 10.1146/annurev.genet.40.110405.090451.
Sugiyama T, Zaitseva EM, Kowalczykowski SC: A single-stranded DNA-binding protein is needed for efficient presynaptic complex formation by the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rad51 protein. J Biol Chem. 1997, 272: 7940-7945. 10.1074/jbc.272.12.7940.
Pardo B, Gomez-Gonzalez B, Aguilera A: DNA repair in mammalian cells: DNA double-strand break repair: how to fix a broken relationship. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009, 66: 1039-1056. 10.1007/s00018-009-8740-3.
Maher RL, Branagan AM, Morrical SW: Coordination of DNA replication and recombination activities in the maintenance of genome stability. J Cell Biochem. 2011, 112: 2672-2682. 10.1002/jcb.23211.
Polo SE, Jackson SP: Dynamics of DNA damage response proteins at DNA breaks: a focus on protein modifications. Genes Dev. 2011, 25: 409-433. 10.1101/gad.2021311.
Kim JS, Krasieva TB, Kurumizaka H, Chen DJ, Taylor AM, Yokomori K: Independent and sequential recruitment of NHEJ and HR factors to DNA damage sites in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 2005, 170: 341-347. 10.1083/jcb.200411083.
Mari PO, Florea BI, Persengiev SP, Verkaik NS, Bruggenwirth HT, Modesti M, Giglia-Mari G, Bezstarosti K, Demmers JA, Luider TM, et al: Dynamic assembly of end-joining complexes requires interaction between Ku70/80 and XRCC4. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006, 103: 18597-18602. 10.1073/pnas.0609061103.
Stark JM, Pierce AJ, Oh J, Pastink A, Jasin M: Genetic steps of mammalian homologous repair with distinct mutagenic consequences. Mol Cell Biol. 2004, 24: 9305-9316. 10.1128/MCB.24.21.9305-9316.2004.
Audebert M, Salles B, Calsou P: Involvement of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 and XRCC1/DNA ligase III in an alternative route for DNA double-strand breaks rejoining. J Biol Chem. 2004, 279: 55117-55126. 10.1074/jbc.M404524200.
Wang M, Wu W, Wu W, Rosidi B, Zhang L, Wang H, Iliakis G: PARP-1 and Ku compete for repair of DNA double strand breaks by distinct NHEJ pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34: 6170-6182. 10.1093/nar/gkl840.
Boboila C, Oksenych V, Gostissa M, Wang JH, Zha S, Zhang Y, Chai H, Lee CS, Jankovic M, Saez LM, et al: Robust chromosomal DNA repair via alternative end-joining in the absence of X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 1 (XRCC1). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012, 109: 2473-2478. 10.1073/pnas.1121470109.
Verkaik NS, Esveldt-van Lange RE, van Heemst D, Bruggenwirth HT, Hoeijmakers JH, Hoeijmakers MZ, van Gent DC: Different types of V(D)J recombination and end-joining defects in DNA double-strand break repair mutant mammalian cells. Eur J Immunol. 2002, 32: 701-709. 10.1002/1521-4141(200203)32:3<701::AID-IMMU701>3.0.CO;2-T.
Mao Z, Bozzella M, Seluanov A, Gorbunova V: Comparison of nonhomologous end joining and homologous recombination in human cells. DNA Repair (Amst). 2008, 7: 1765-1771. 10.1016/j.dnarep.2008.06.018.
Guirouilh-Barbat J, Huck S, Bertrand P, Pirzio L, Desmaze C, Sabatier L, Lopez BS: Impact of the KU80 pathway on NHEJ-induced genome rearrangements in mammalian cells. Mol Cell. 2004, 14: 611-623. 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.05.008.
Coleman KA, Greenberg RA: The BRCA1-RAP80 complex regulates DNA repair mechanism utilization by restricting end resection. J Biol Chem. 2011, 286: 13669-13680. 10.1074/jbc.M110.213728.
Schulte-Uentrop L, El-Awady RA, Schliecker L, Willers H, Dahm-Daphi J: Distinct roles of XRCC4 and Ku80 in non-homologous end-joining of endonuclease- and ionizing radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36: 2561-2569. 10.1093/nar/gkn094.
van Heemst D, Brugmans L, Verkaik NS, van Gent DC: End-joining of blunt DNA double-strand breaks in mammalian fibroblasts is precise and requires DNA-PK and XRCC4. DNA Repair (Amst). 2004, 3: 43-50. 10.1016/j.dnarep.2003.09.004.
Yant SR, Kay MA: Nonhomologous-end-joining factors regulate DNA repair fidelity during Sleeping Beauty element transposition in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2003, 23: 8505-8518. 10.1128/MCB.23.23.8505-8518.2003.
Pan-Hammarstrom Q, Jones AM, Lahdesmaki A, Zhou W, Gatti RA, Hammarstrom L, Gennery AR, Ehrenstein MR: Impact of DNA ligase IV on nonhomologous end joining pathways during class switch recombination in human cells. J Exp Med. 2005, 201: 189-194. 10.1084/jem.20040772.
van der Burg M, Verkaik NS, den Dekker AT, Barendregt BH, Pico-Knijnenburg I, Tezcan I, vanDongen JJ, van Gent DC: Defective Artemis nuclease is characterized by coding joints with microhomology in long palindromic-nucleotide stretches. Eur J Immunol. 2007, 37: 3522-3528. 10.1002/eji.200737624.
Lee GS, Neiditch MB, Salus SS, Roth DB: RAG proteins shepherd double-strand breaks to a specific pathway, suppressing error-prone repair, but RAG nicking initiates homologous recombination. Cell. 2004, 117: 171-184. 10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00301-0.
Pierce AJ, Johnson RD, Thompson LH, Jasin M: XRCC3 promotes homology-directed repair of DNA damage in mammalian cells. Genes Dev. 1999, 13: 2633-2638. 10.1101/gad.13.20.2633.
Hartlerode A, Odate S, Shim I, Brown J, Scully R: Cell cycle-dependent induction of homologous recombination by a tightly regulated I-SceI fusion protein. PLoS One. 2011, 6: e16501-10.1371/journal.pone.0016501.
Conrad S, Kunzel J, Lobrich M: Sister chromatid exchanges occur in G2-irradiated cells. Cell Cycle. 2011, 10: 222-228. 10.4161/cc.10.2.14639.
Lobrich M, Shibata A, Beucher A, Fisher A, Ensminger M, Goodarzi AA, Barton O, Jeggo PA: gammaH2AX foci analysis for monitoring DNA double-strand break repair: strengths, limitations and optimization. Cell Cycle. 2010, 9: 662-669. 10.4161/cc.9.4.10764.
Karanam K, Kafri R, Loewer A, Lahav G: Quantitative live cell imaging reveals a gradual shift between DNA repair mechanisms and a maximal Use of HR in Mid S phase. Mol Cell. 2012, 47: 320-329. 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.05.052.
Beucher A, Birraux J, Tchouandong L, Barton O, Shibata A, Conrad S, Goodarzi AA, Krempler A, Jeggo PA, Lobrich M: ATM and Artemis promote homologous recombination of radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks in G2. EMBO J. 2009, 28: 3413-3427. 10.1038/emboj.2009.276.
Lamarche BJ, Orazio NI, Weitzman MD: The MRN complex in double-strand break repair and telomere maintenance. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584: 3682-3695. 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.07.029.
Huertas P, Jackson SP: Human CtIP mediates cell cycle control of DNA end resection and double strand break repair. J Biol Chem. 2009, 284: 9558-9565. 10.1074/jbc.M808906200.
Yun MH, Hiom K: CtIP-BRCA1 modulates the choice of DNA double-strand-break repair pathway throughout the cell cycle. Nature. 2009, 459: 460-463. 10.1038/nature07955.
Germani A, Prabel A, Mourah S, Podgorniak MP, Di Carlo A, Ehrlich R, Gisselbrecht S, Varin-Blank N, Calvo F, Bruzzoni-Giovanelli H: SIAH-1 interacts with CtIP and promotes its degradation by the proteasome pathway. Oncogene. 2003, 22: 8845-8851. 10.1038/sj.onc.1206994.
Falck J, Forment JV, Coates J, Mistrik M, Lukas J, Bartek J, Jackson SP: CDK targeting of NBS1 promotes DNA-end resection, replication restart and homologous recombination. EMBO Rep. 2012, 13: 561-568. 10.1038/embor.2012.58.
Cortes-Ledesma F, de Piccoli G, Haber JE, Aragon L, Aguilera A: SMC proteins, new players in the maintenance of genomic stability. Cell Cycle. 2007, 6: 914-918. 10.4161/cc.6.8.4107.
Covo S, Westmoreland JW, Gordenin DA, Resnick MA: Cohesin Is limiting for the suppression of DNA damage-induced recombination between homologous chromosomes. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6: e1001006-10.1371/journal.pgen.1001006.
Spitzner JR, Chung IK, Gootz TD, McGuirk PR, Muller MT: Analysis of eukaryotic topoisomerase II cleavage sites in the presence of the quinolone CP-115,953 reveals drug-dependent and -independent recognition elements. Mol Pharmacol. 1995, 48: 238-249.
Shibata A, Conrad S, Birraux J, Geuting V, Barton O, Ismail A, Kakarougkas A, Meek K, Taucher-Scholz G, Lobrich M, Jeggo PA: Factors determining DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice in G2 phase. EMBO J. 2011, 30: 1079-1092. 10.1038/emboj.2011.27.
Hada M, Georgakilas AG: Formation of clustered DNA damage after high-LET irradiation: a review. J Radiat Res. 2008, 49: 203-210. 10.1269/jrr.07123.
Goodarzi AA, Noon AT, Deckbar D, Ziv Y, Shiloh Y, Lobrich M, Jeggo PA: ATM signaling facilitates repair of DNA double-strand breaks associated with heterochromatin. Mol Cell. 2008, 31: 167-177. 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.05.017.
Ziv Y, Bielopolski D, Galanty Y, Lukas C, Taya Y, Schultz DC, Lukas J, Bekker-Jensen S, Bartek J, Shiloh Y: Chromatin relaxation in response to DNA double-strand breaks is modulated by a novel ATM- and KAP-1 dependent pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 2006, 8: 870-876. 10.1038/ncb1446.
Goodarzi AA, Kurka T, Jeggo PA: KAP-1 phosphorylation regulates CHD3 nucleosome remodeling during the DNA double-strand break response. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011, 18: 831-839. 10.1038/nsmb.2077.
Costelloe T, Louge R, Tomimatsu N, Mukherjee B, Martini E, Khadaroo B, Dubois K, Wiegant WW, Thierry A, Burma S, et al: The yeast Fun30 and human SMARCAD1 chromatin remodellers promote DNA end resection. Nature. 2012, 489 (7417): 581-584. 10.1038/nature11353.
Sonoda E, Hochegger H, Saberi A, Taniguchi Y, Takeda S: Differential usage of non-homologous end-joining and homologous recombination in double strand break repair. DNA Repair (Amst). 2006, 5: 1021-1029. 10.1016/j.dnarep.2006.05.022.
Rappold I, Iwabuchi K, Date T, Chen J: Tumor suppressor p53 binding protein 1 (53BP1) is involved in DNA damage-signaling pathways. J Cell Biol. 2001, 153: 613-620. 10.1083/jcb.153.3.613.
Noon AT, Shibata A, Rief N, Lobrich M, Stewart GS, Jeggo PA, Goodarzi AA: 53BP1-dependent robust localized KAP-1 phosphorylation is essential for heterochromatic DNA double-strand break repair. Nat Cell Biol. 2010, 12: 177-184. 10.1038/ncb2017.
Bothmer A, Robbiani DF, Feldhahn N, Gazumyan A, Nussenzweig A, Nussenzweig MC: 53BP1 regulates DNA resection and the choice between classical and alternative end joining during class switch recombination. J Exp Med. 2010, 207: 855-865. 10.1084/jem.20100244.
Difilippantonio S, Gapud E, Wong N, Huang CY, Mahowald G, Chen HT, Kruhlak MJ, Callen E, Livak F, Nussenzweig MC, et al: 53BP1 facilitates long-range DNA end-joining during V(D)J recombination. Nature. 2008, 456: 529-533. 10.1038/nature07476.
Dimitrova N, Chen YC, Spector DL, de Lange T: 53BP1 promotes non-homologous end joining of telomeres by increasing chromatin mobility. Nature. 2008, 456: 524-528. 10.1038/nature07433.
Moynahan ME, Chiu JW, Koller BH, Jasin M: Brca1 controls homology-directed DNA repair. Mol Cell. 1999, 4: 511-518. 10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80202-6.
Chen JJ, Silver D, Cantor S, Livingston DM, Scully R: BRCA1, BRCA2, and Rad51 operate in a common DNA damage response pathway. Cancer Res. 1999, 59: 1752s-1756s.
Ohta T, Sato K, Wu W: The BRCA1 ubiquitin ligase and homologous recombination repair. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585: 2836-2844. 10.1016/j.febslet.2011.05.005.
Drost R, Bouwman P, Rottenberg S, Boon U, Schut E, Klarenbeek S, Klijn C, van der Heijden I, van der Gulden H, Wientjens E, et al: BRCA1 RING function is essential for tumor suppression but dispensable for therapy resistance. Cancer Cell. 2011, 20: 797-809. 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.11.014.
Chen L, Nievera CJ, Lee AY, Wu AY: Cell cycle-dependent complex formation of BRCA1.CtIP.MRN is important for DNA double-strand break repair. J Biol Chem. 2008, 283: 7713-7720. 10.1074/jbc.M710245200.
Kim H, Chen J, Yu X: Ubiquitin-binding protein RAP80 mediates BRCA1-dependent DNA damage response. Science. 2007, 316: 1202-1205. 10.1126/science.1139621.
Sobhian B, Shao G, Lilli DR, Culhane AC, Moreau LA, Xia B, Livingston DM, Greenberg RA: RAP80 targets BRCA1 to specific ubiquitin structures at DNA damage sites. Science. 2007, 316: 1198-1202. 10.1126/science.1139516.
Wang B, Matsuoka S, Ballif BA, Zhang D, Smogorzewska A, Gygi SP, Elledge SJ: Abraxas and RAP80 form a BRCA1 protein complex required for the DNA damage response. Science. 2007, 316: 1194-1198. 10.1126/science.1139476.
Cao L, Xu X, Bunting SF, Liu J, Wang RH, Cao LL, Wu JJ, Peng TN, Chen J, Nussenzweig A, et al: A selective requirement for 53BP1 in the biological response to genomic instability induced by Brca1 deficiency. Mol Cell. 2009, 35: 534-541. 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.06.037.
Bouwman P, Aly A, Escandell JM, Pieterse M, Bartkova J, van der Gulden H, Hiddingh S, Thanasoula M, Kulkarni A, Yang Q, et al: 53BP1 loss rescues BRCA1 deficiency and is associated with triple-negative and BRCA-mutated breast cancers. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010, 17: 688-695. 10.1038/nsmb.1831.
Bunting SF, Callen E, Wong N, Chen HT, Polato F, Gunn A, Bothmer A, Feldhahn N, Fernandez-Capetillo O, Cao L, et al: 53BP1 inhibits homologous recombination in Brca1-deficient cells by blocking resection of DNA breaks. Cell. 2010, 141: 243-254. 10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.012.
Nik-Zainal S, Alexandrov LB, Wedge DC, Van Loo P, Greenman CD, Raine K, Jones D, Hinton J, Marshall J, Stebbings LA, et al: Mutational processes molding the genomes of 21 breast cancers. Cell. 2012, 149: 979-993. 10.1016/j.cell.2012.04.024.
Morales JC, Franco S, Murphy MM, Bassing CH, Mills KD, Adams MM, Walsh NC, Manis JP, Rassidakis GZ, Alt FW, Carpenter PB: 53BP1 and p53 synergize to suppress genomic instability and lymphomagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006, 103: 3310-3315. 10.1073/pnas.0511259103.
Chapman JR, Sossick AJ, Boulton SJ, Jackson SP: BRCA1-associated exclusion of 53BP1 from DNA damage sites underlies temporal control of DNA repair. J Cell Sci. 2012, 125: 3529-3534. 10.1242/jcs.105353.
Bryant HE, Schultz N, Thomas HD, Parker KM, Flower D, Lopez E, Kyle S, Meuth M, Curtin NJ, Helleday T: Specific killing of BRCA2-deficient tumours with inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Nature. 2005, 434: 913-917. 10.1038/nature03443.
Farmer H, McCabe N, Lord CJ, Tutt AN, Johnson DA, Richardson TB, Santarosa M, Dillon KJ, Hickson I, Knights C, et al: Targeting the DNA repair defect in BRCA mutant cells as a therapeutic strategy. Nature. 2005, 434: 917-921. 10.1038/nature03445.
Bunting SF, Callen E, Kozak ML, Kim JM, Wong N, Lopez-Contreras AJ, Ludwig T, Baer R, Faryabi RB, Malhowski A, et al: BRCA1 functions independently of homologous recombination in DNA interstrand crosslink repair. Mol Cell. 2012, 46: 125-135. 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.02.015.
Dou H, Huang C, Van Nguyen T, Lu LS, Yeh ET: SUMOylation and de-SUMOylation in response to DNA damage. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585: 2891-2896. 10.1016/j.febslet.2011.04.002.
Selvarajah J, Moumen A: Role of ubiquitination in the DNA damage response: proteomic analysis to identify new DNA-damage-induced ubiquitinated proteins. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010, 38: 87-91. 10.1042/BST0380087.
Al-Hakim A, Escribano-Diaz C, Landry MC, O'Donnell L, Panier S, Szilard RK, Durocher D: The ubiquitous role of ubiquitin in the DNA damage response. DNA Repair (Amst). 2010, 9: 1229-1240. 10.1016/j.dnarep.2010.09.011.
Stewart GS, Panier S, Townsend K, Al-Hakim AK, Kolas NK, Miller ES, Nakada S, Ylanko J, Olivarius S, Mendez M, et al: The RIDDLE syndrome protein mediates a ubiquitin-dependent signaling cascade at sites of DNA damage. Cell. 2009, 136: 420-434. 10.1016/j.cell.2008.12.042.
Shao Z, Davis AJ, Fattah KR, So S, Sun J, Lee KJ, Harrison L, Yang J, Chen DJ: Persistently bound Ku at DNA ends attenuates DNA end resection and homologous recombination. DNA Repair (Amst). 2012, 11: 310-316. 10.1016/j.dnarep.2011.12.007.
Postow L, Ghenoiu C, Woo EM, Krutchinsky AN, Chait BT, Funabiki H: Ku80 removal from DNA through double strand break-induced ubiquitylation. J Cell Biol. 2008, 182: 467-479. 10.1083/jcb.200802146.
Feng L, Chen J: The E3 ligase RNF8 regulates KU80 removal and NHEJ repair. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012, 19: 201-206. 10.1038/nsmb.2211.
Patel AG, Sarkaria JN, Kaufmann SH: Nonhomologous end joining drives poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor lethality in homologous recombination-deficient cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011, 108: 3406-3411. 10.1073/pnas.1013715108.
Acknowledgement
The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Community’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under grant agreement No. HEALTH-F2-2010-259893.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that hey have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
IB wrote the first draft. IB and DvG wrote the final text. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Brandsma, I., van Gent, D.C. Pathway choice in DNA double strand break repair: observations of a balancing act. Genome Integrity 3, 9 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1186/2041-9414-3-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/2041-9414-3-9