Abstract
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP) is an inheritable predisposition for the occurrence of numerous polyps in the large intestine. In about 50% of all patients, the occurrence of the disease is conditioned by heterozygotic mutations of the APC gene. Screening for genetic factors in persons without mutations in the APC gene led to the identification of homozygotic mutations of the MYH gene as the cause of the appearance of the polyposis form which is characterized by recessive heritability and a milder course than in the case of the classic form of the disease. The authors examined 90 persons from the DNA bank of patients with FAP from the Institute of Human Genetics of the Polish Academy of Sciences in Poznań in whom no mutations in the APC gene were detected. Two of the most frequent mutations of the MYH gene (Y165C and G382D) were found to be heterozygous in 13% of patients and no other mutations in this gene coding sequence were observed. In the group with heterozygotic occurrence of the mutation in the MYH gene, the disease phenotype was not milder in comparison with the entire examined group and the mean age of the disease manifestation was even lower. This observation allows one to conclude that the employed methods of mutation screening were correct and, in the case of the examined group, the mutation ratio of the MYH gene does not precondition the occurrence of the disease, but it cannot be excluded that it may modify its phenotype. The obtained results indicate that the criteria applied during the process of FAP qualification are more rigorous than those applied in other countries.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Familial adenomatous polyposis is characterized by the appearance of numerous polyps in the large intestine. Untreated polyps lead to the development of colorectal cancer before age 50 years. The correlation between mutations of the APC gene and the occurrence of familial adenomatous polyposis was described in 1991 [1, 2] and since then mutations of the APC gene have been investigated in many research centres identifying various types of mutations. In the case of the largest group, comprising 1,164 families from Germany, mutations were identified in 54% of families [3].
The latest investigations point to a correlation between homozygotic mutations of the MYH gene alleles and the occurrence of the recessive form of polyposis of the large intestine. The product of the MYH gene is an endonuclease of the DNA repair system by way of base excision and recognises non-pairings of the A/G, A/GO and A/C types [4]. The defect of both gene alleles gives a status of somatic mutations of the APC gene in the form of G:C > T:A pairs which change GAA codons into TAA. The APC gene is particularly sensitive to the appearance of mutations developing as a result of the lack of functions in the MYH locus because 216 GAA codons occur in it [5]. The MYH gene is located on chromosome 1p32-34, consists of 16 exons and encompasses 7,100 base pairs [5]. The two most common mutations, Y165C and G382D, which occur in the European population with a frequency of 1%, are observed in 80% patients with mutations of both alleles of the MYH gene [6–8]. Data concerning the phenotype of mutation carriers in the MYH gene are not very extensive. In the majority, the described mutation carriers in the MYH gene are characterized by a milder course of the disease and a smaller number of polyps than is the case in the classic FAP. The phenotype is similar to attenuated adenomatous polyposis of the colon (AAPC) and the number of polyps does not exceed 1,000. Homozygous mutations of the MYH gene are associated with the occurrence of the disease in 8% of patients in whom mutations in the APC gene have not been discovered [6].
In samples collected in our DNA bank of families with FAP, mutations were identified in 50% of families [9]. In the course of this study, 90 FAP patients with no mutation identified in the APC gene were examined with regard to the occurrence of mutations in the MYH gene using the PCR-HD and PCR-SSCP methods to investigate the coding sequence of the APC gene. We determined the frequency occurrence of the G382M and Y165C mutations as well as the V22M polymorphism described earlier.
Patients and methods
The examined group comprised patients with diagnosed large intestine polyposis derived from the DNA bank of patients with familial polyposis from the Institute of Human Genetics, Polish Academy of Sciences in Poznań. The group of 90 patients with no mutation identified in the APC gene derived from different parts of Poland. The age when the first disease symptoms occurred ranged from 10 to 50 years with an average age of 29.5 at symptom appearance. In the examined group, 12 cases occurred in the studied families de novo (typical FAP phenotype), 16 patients represented cases of the attenuated form of the disease with a small number of polyps, and the remainding were cases of the classical form of familial polyposis with the number of polyps exceeding 1,000.
Molecular methods
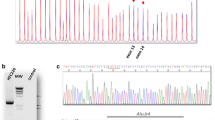
DNA was extracted from peripheral blood cells by the classical phenol purification method. The MYH gene fragments were amplified using primers and PCR reaction condition as previously described by Al-Tassan [10]. The amplified fragments of the MYH gene were screened for mutations using heteroduplex analysis (HD) and single strand conformational polymorphism (SSCP) methods [11]. DNA fragments showing heteroduplex in HD analysis or additional pattern in SSCP analysis were subjected to direct PCR product sequencing and analysed using the Perking Elmer ABI 377 DNA sequencer according to the manufacturer's specifications. For V22M screening, the PCR product of exon 2 of the MYH gene was digested with -Nco I endonuclease. Exons 7 and 13 were screened for Y165C and G382D variants using the DHPLC method. The amplified fragments were denatured at 95°C for 5 min. and slowly annealed from 95°C to 65°C over 30 min. to promote heteroduplex formation. The PCR products were injected into the column and eluted using an increasing acetonitryle gradient. The conditions distinguishing the Y165C (exon 7) and the G382D (exon 13) variants were established, Figure 1. The DHPLC parameters for those separations are presented in Table 1.
Results and discussion
96 probands without mutation in the APC gene were examined for the occurrence of mutation in the MYH gene. The main emphasis in the performed studies was placed on the frequency of occurrence of the already described pathogenic substitutions Y165C and G382D. For easy variant identification, conditions of the DHPLC examination were optimized for the above two mutations. The third variant, V22M, which is not considered pathogenic, was examined using restriction analysis. In the examined group, 9 cases of G382C substitution, 4 cases of Y165C and 5 cases of V22M were recorded.
Examination of the MYH gene coding sequence using PCR-HD and PCR-SSCP methods led to the conclusion that the MYH gene did not contain polymorphic variants in the remaining part of the coding sequence. The above-mentioned frequent mutations failed to occur as homozygous (Table 2). One of the carriers of the Y165C mutation with the classical form of familial polyposis was also the carrier of the G169D mutation in the second allele of the MYH gene. G169D is a novel change in the MYH gene not described before. A change in amino acid sequence can lead to a phenotypic effect but the pathogenicity of this variant cannot be determined at this stage. This mutation is also observed in the patient's brother with clinical symptoms and phenotype of classical form of FAP. In the case of both affected brothers, numerous polyps were observed to appear in the fourth decade of their lives. In 12 persons in whom one of the pathogenic mutations occurred, the mild form of the disease was diagnosed in 3 cases, whereas in 9 cases the diagnosed form was that of classical FAP. The age of appearance of the disease in this group was quite low and the youngest patients were only 12 years old when the first symptoms of the disease were identified. The percentage of the mild form of the polyposis did not differ significantly from the frequency observed in the entire examined group. The phenotype of the classical form of the disease observed in this group failed to correlate with the earlier observations about the milder course of the disease in the carriers of homozygotic mutation in the MYH gene [10, 12]. This observation reveals the absence of predisposition to the disease by mutations in the MYH gene in the homozygotic system as confirmed by screening for the mutation using PCR-HD and PCR-SSCP methods. In addition, the average age of occurrence of the disease in the group in which one of the pathogenic mutations or the V22M polymorphism occur is by 10 years lower than in the entire examined population. It is true that the size of the examined group is not big, but it cannot be excluded that these mutations may have a modifying effect on other genetic factors predisposing to the disease. The results indicate that in our group of patients with diagnosed FAP without mutation in the APC gene, the proportion of the mutation in the MYH gene exerts a very small effect on preconditioning the disease.
This situation may be associated with the fact that our physicians may use more stringent criteria in the course of qualifications for examinations than doctors in other groups. The stringent criteria used in the qualification of patients as having FAP syndrome may be one explanation of the above observations.
This work was supported by grant 2PO5A10728 from the Ministry of Science and Information Society Technologies awarded to AP.
References
Groden J, Thliveris A, Samowitz W, Carlson M, Gelbert L, Albertsen H, Joslyn G, Stevens J, Spirio L, Robertson M, Sargeant L, Krapcho K, Wolff E, Burt R, Hughes JP, Warrington J, McPherson J, Wasmuth J, Le Paslier D, Abderrahim H, Cohen D, Leppert M, White R: Identification and characterization of the familial adenomatous polyposis coli gene. Cell 1991, 66: 589–600. 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90021-0
Kinzler KW, Nilbert MC, Vogelstein B, Bryan TM, Levy DB, Smith KJ, Preisinger AC, Hamilton SR, Hedge P, Markham A, Carlson M, Joslyn G, Groden J, White R, Miki Y, Miyoshi Y, Nishisho I, Nakamura Y: Identification of a gene located at chromosome 5q21 that is mutated in colorectal cancers. Science 1991, 251: 1366–1370. 10.1126/science.1848370
Friedl W, Aretz S: Familial Adenomatous Polyposis: Experience from a Study of 1164 Urelated German Plyposis Patients. Hereditary Cancer in Clinical Practice 2005, 3: 87–114.
McGoldrick JP, Yeh YC, Solomon M, Essigmann JM, Lu AL: Characterization of a mammalian homolog of the Escherichia coli MutY mismatch repair protein. Mol Cell Biol 1995, 15: 989–996.
Cheadle JP, Sampson JR: Exposing the MYtH about base excision repair and human inherited disease. Hum Mol Genet 2003, 12: R159–165. 10.1093/hmg/ddg259
Sieber OM, Lipton L, Crabtree M, Heinimann K, Fidalgo P, Phillips RK, Bisgaard ML, Orntoft TF, Aaltonen LA, Hodgson SV, Thomas HJ, Tomlinson IP: Multiple colorectal adenomas, classic adenomatous polyposis, and germ-line mutations in MYH. N Engl J Med 2003, 348: 791–799. 10.1056/NEJMoa025283
Al-Tassan N, Eisen T, Maynard J, Bridle H, Shah B, Fleischmann C, Sampson JR, Cheadle JP, Houlston RS: Inherited variants in MYH are unlikely to contribute to the risk of lung carcinoma. Hum Genet 2004, 114: 207–210. 10.1007/s00439-003-1033-2
Jones S, Emmerson P, Maynard J, Best JM, Jordan S, Williams GT, Sampson JR, Cheadle JP: Biallelic germline mutations in MYH predispose to multiple colorectal adenoma and somatic G:C--> T:A mutations. Hum Mol Genet 2002, 11: 2961–2967. 10.1093/hmg/11.23.2961
Plawski A, Lubinski J, Banasiewicz T, Paszkowski J, Lipinski D, Strembalska A, Kurzawski G, Byrski T, Zajaczek S, Hodorowicz-Zaniewska D, Gach T, Brozek I, Nowakowska D, Czkwaniec E, Krokowicz P, Drews M, Zeyland J, Juzwa W, Slomski R: Novel germline mutations in the adenomatous polyposis coli gene in Polish families with familial adenomatous polyposis. J Med Genet 2004, 41: e11. 10.1136/jmg.2003.010215
Al-Tassan N, Chmiel NH, Maynard J, Fleming N, Livingston AL, Williams GT, Hodges AK, Davies DR, David SS, Sampson JR, Cheadle JP: Inherited variants of MYH associated with somatic G:C--> T:A mutations in colorectal tumors. Nat Genet 2002, 30: 227–232. 10.1038/ng828
Plawski A, Jura J, Slomski R: Wykrywanie mutacji punktowych w genie supresorowym APC człowieka metodą heterodupleksów. In Przykłady analiz DNA. Edited by: Słomski R. Wydawnictwo Akademii Rolniczej w Poznaniu; 2004:100–106.
Kairupan CF, Meldrum CJ, Crooks R, Milward EA, Spigelman AD, Burgess B, Groombridge C, Kirk J, Tucker K, Ward R, Williams R, Scott RJ: Mutation analysis of the MYH gene in an Australian series of colorectal polyposis patients with or without germline APC mutations. Int J Cancer 2005, 116: 73–77. 10.1002/ijc.20983
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Skrzypczak, M., Podralska, M., Heinritz, W. et al. MYH Gene Status in Polish FAP Patients without APC Gene Mutations. Hered Cancer Clin Pract 4, 43 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1186/1897-4287-4-1-43
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1897-4287-4-1-43