Abstract
Background
Immunocytochemistry and RT-PCR have been widely used for the detection of circulating tumor cells in patients with breast cancer but their specificity is limited. Our purpose is to utilize a convenient and specific technology to detect circulating tumor cells in breast cancer patients.
Methods
To determine the sensitivity and specificity of our method, A431 cells were serially diluted with human peripheral blood leukocytes and stained with CK19. A total of 73 blood specimens including 25 healthy volunteers and 48 patients with breast carcinoma and benign tumor were tested by flow cytometry to quantify the expression of CK19.
Results
The detectable upper limit of A431 cells was 1 cancer cell among 104 human white blood cells. CK19 was detected in 27% of breast cancer patients but none control gives positive result. The number of cancer cells increased gradually along with the disease stages for it was the least in stage I (0%) and the most in stage IV (1.29%). Fifteen patients were observed during three month chemotherapy after surgery, and most of their CK19 expression levels declined after treatment.
Conclusion
Our research convinces that the detection of CK19 in peripheral blood by flow cytometry is also a specific and feasible method to monitor circulating tumor cells in breast cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Nowadays breast cancer is becoming the second leading cause of cancer deaths in females, almost 10% women have the risk of developing breast cancer [1]. Although great improvements have been made in curing breast cancer, the overall five-year survival rate remains < 50% and many patients relapse after surgical resection because of the dispersion of undetectable cancer cells [2, 3]. Therefore, it is necessary to establish sensitive and specific techniques for the detection of occult tumor cells. A better method for early diagnosis may help in predicting recurrence and planning appropriate therapies to improve survival [4, 5].
Many investigations have indicated that epithelial cells from the initial tumor can be recognized in peripheral blood or bone marrow aspirates of patients with breast cancer [6, 7]. The detection of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) in the peripheral blood of cancer patients has been associated with recurrence and metastasis of breast cancer [8–10]. Cytokeratins (CKs), characteristic intermediate filament of epithelial cells, especially CK19, are widely used to detect tumor cells derived from epithelial tissues [11, 12]. CK19 has been shown to correlate with poor clinical outcome for patients with breast cancer [13].
Flow cytometry is a technology which can not only give information of high statistical precision and subpopulation quantification but also analyze cells individually and rapidly, compared with immunocytochemistry [14, 15] and reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) [16, 17]. In this study, flow cytometry was used to detect occult tumor cells in peripheral blood of patients with breast cancer. The detection of CTCs in peripheral blood of 48 patients was intended to find the relationship of CK19+ cell percentage with disease progress. CK19 was positive in the peripheral white blood cells of breast cancer patients at stages II to IV, but not the patients at stage I and healthy controls. The percentage of CK19+ cells was increased following the severity of the disease and decreased after lumpectomy and chemotherapy.
Methods
Cell line
The A431 (human epithelial carcinoma) cell line obtained from the American Type Culture Collection was grown in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) supplemented with 15% fetal calf serum (both from GIBCO), 100 U/ml penicillin, and 100 μg/ml streptomycin at 37°C in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. Subculture was performed when confluence reached 70%.
Patients
Breast cancer patients were treated at the Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University. The cohort included 7 patients with benign tumor, 34 patients with primary breast cancer and 7 patients with metastatic breast cancer from October 2006 to April 2008. The patients underwent lumpectomy except those with distant metastases. And we detected CK19 expression of 15 patients with primary breast cancer during three month chemotherapy. Blood samples were obtained with informed consent after approval of the protocol by the Ethics Committee of the University of Science and Technology of China. Control blood samples were collected from 25 healthy female volunteers.
Blood sample preparation
The first 8 ml of blood was discarded to avoid epithelial contamination before the collection of 5 ml blood sample. Human white blood cells were isolated from adult peripheral blood using RBC lysis buffer (RX-2-1-2 U-gene China). Briefly, 3 ml blood and 15 ml RBC lysis buffer were mixed with vortex and kept on ice for 15 min until pellucid, then were centrifuged at 450 g for 10 min. Cells were suspended with 5 ml RBC lysis buffer and centrifuged at 450 g for 10 min again followed by twice rinse with PBS.
Immunofluorescence staining
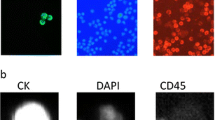
A431 cells were counted onto glass slides at a concentration of 5 × 105 cells per spot. Subsequently, the cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS for 15 min at room temperature, rinsed in PBS, and incubated with FITC-conjugated mouse anti-human CK19. Laser scanning confocal microscopy was performed and the data were processed with MetaMorph program.
Flow cytometric analysis
After fixation with 1% paraformaldehyde for 1 hour at room temperature, A431 cells or leukocytes were permeabilized with 0.01% Triton X-100 for 1 h at room temperature followed by mouse serum block (30 min, room temperature). Then the cells were incubated with FITC-conjugated CK19 antibody or FITC-mouse IgG1 isotype antibody (both from BD PharMingen) as negative control overnight. After washed twice with permeabilization buffer, samples were analyzed by FACSCalibur (Becton Dickinson).
Statistical analysis
K Related Samples Test was used for the analysis of CK19 expression in peripheral blood of patients before and after clinical treatment. Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare CK19 expression levels in peripheral blood between patients at stage III and stage IV. The statistical significance was defined as values of p < 0.05.
Results
CK19 expression in A431 cells
Immunofluorescence staining was used to detect the CK19 expression in A431 cells. The result showed that A431 cells were CK19-immunoreactive cells and CK19 was mainly located in the cytoplasm of A431 cells (Figure 1).
The specificity and sensitivity of flow cytometry
Intracellular flow cytometric analysis indicated that all the A431 cells expressed high level of CK19 (Figure 2A). However, healthy adult peripheral blood white blood cells had no CK19 expression (Figure 2B) (n = 25). A431 cells were mixed with healthy adult white blood cells at different ratios of 1:1, 1:10, 1:102, 1:103, and 1:104 to determine the sensitivity of flow cytometry. It showed that the percentages of CK19+ cells detected by flow cytometry were consistent with the ratios of A431/white blood cells. Flow cytometry could distinguish the very low percentage of CK19 expressing cells, even 1 A431 cell in 104 white blood cells. It suggested that flow cytometry had specificity and sensitivity to examine CK19 expression and possessed the potential to detect the few circulating breast cancer cells in the whole blood samples (Figure 3).
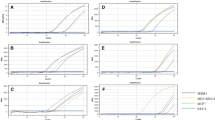
Expression of CK19 in A431 cells diluted with human white blood cells at different ratios. A431 cells were mixed with healthy adult white blood cells at different ratios of 1:1 (A), 1:10 (B), 1:102 (C), 1:103 (D), and 1:104 (E). The cell mixture was stained with FITC-anti-CK19 antibody and detected the expression of CK19.
Patient characteristics
The characteristics of 48 patients enrolled in the study are listed in Table 1. The age range of patients was from 28 to 82 years old and the median age was 46 years old. There were 41 patients with no evidence of metastasis in the liver and bone and 7 patients with metastatic breast cancer. All the patients with breast cancer were clinically classified as stages I to IV. The patients with primary breast cancer were performed lumpectomy followed by chemotherapy. Thirteen of the 48 patients (27%) were found to have CK19+ cells in peripheral blood including 7 patients with primary breast cancer and 6 with metastatic breast cancer (Table 2).
Detection of circulating breast cancer cells in peripheral blood of patients before surgery by flow cytometry
Flow cytometric analyses showed that no CK19 was expressed in peripheral blood of healthy control (n = 25), benign tumor patients (n = 7) and breast cancer patients at stage I (n = 4) (Figures 4A, B, C). But there existed CK19+ cells in the peripheral blood samples of patients at stages II, III, and IV (Figure 4D, E, F), with the median of each group of 0.15% (n = 2), 0.44% (n = 5) and 1.47% (n = 6) (Figure 5), respectively. There was significant difference in CK19 expression between patients at stage III and stage IV (p = 0.0043).
CK19 expression in peripheral blood of healthy controls and breast tumor patients. Peripheral white blood cells were isolated and stained with FITC-conjugated mouse anti-human CK19 antibody to examine CK19 expression. (A) Healthy volunteers; (B) Benign tumor patients; Breast cancer patients at stage I (C), stage II (D), stage III (E) and stage IV (F).
The expression level of CK19 in peripheral blood of breast cancer patients is correlated with the disease stage. CK19 from each peripheral blood sample was detected by flow cytometry as described in methods. All the negative results were shown as number undetected. All 4 patients at stage I were CK19 negative. The median is marked as "---" in each group. Where the frequency of negative cases is > 50%, the median cannot be shown. p < 0.05 was considered significant.
The change of CK19 expression in 15 patients with breast cancer during 3 month-chemotherapy
The dynamic expressions of CK19 in peripheral blood lymphocytes were observed in 15 patients with primary breast cancer during 3 month-chemotherapy after lumpectomy. The number of CK19+ cells among 105 leukocytes of each patient was presented in Figure 6. For the 7 metastatic patients, there was significant difference in CK19 expression level before and after clinical treatment (p = 0.001). The CK19+ cell numbers were obviously decreased after operation and chemotherapy, and there was almost none 3 months later (Figures 6A and 6C). For the 8 patients without CK19+ cells before surgery, no significant difference was seen after clinical treatment (p = 1). The numbers of CK19+ cells of 6 patients were always nearly zero during 3 month-chemotherapy, but increased in 2 patients after treatment (Figures 6B and 6D).
The CK19+ cell number in peripheral blood of 15 patients with primary cancer before surgery and after chemotherapy. All the patients underwent surgery followed immediately by chemotherapy. The CK19+ cell numbers were tested before surgery, 7 days after chemotherapy and 90 days after chemotherapy.(A and C) Patients with CK19 positive cells before surgery; (B and D) Patients without CK19 positive cells before surgery. Different symbols represent different breast cancer patients. The data were analyzed by the K Related Samples Test, **, p < 0.01 (A).
Discussion
The dispersion of tumor cells is one of the primary causes of recrudescence at distant sites and of death from cancer. So the detection of occult metastatic cells is important to predict recurrence and improve survival. In this study, we applied flow cytometry to examine the expression of CK19 in the peripheral blood of breast cancer patients to monitor CTCs.
Immunocytochemistry gives morphological detail of tumor cells but is not sensitive and lack of methodological standardization [18]. Although RT-PCR is able to find 1 cancer cell among 106 irrelevant cells [19], it cannot exactly quantify the number of tumor cells according to mRNA levels. Furthermore, its utility was limited for its low specificity because of the false positive results which may be explained by the phenomenon of "illegitimate expression" [20, 21].
In the present study, flow cytometry is utilized to examine the expression of CK19 to test CTCs in 48 breast cancer patients because most breast cancer cells but not blood cells express CK19. Although the sensitivity of our method is 1 cancer cell among 104 irrelevant cells, its specificity is very high. No CK19 expression was detected in healthy volunteers and patients with benign tumor. We consider high specificity is more important than high degree of sensitivity for clinical diagnoses because a wrong positive test will result in unnecessary treatments that may cause injury. Our data demonstrated that 86% of stage IV patients and 70% of stage III patients were detected CK19+ cells in the peripheral blood, which were a little higher than that reported by Aerts J [22]; but the percentage of patients at stages I and II was lower. This may be explained by that the detection of protein level is more precise than RNA level because of the false positive result of RT-PCR also reported by others [23]. In our study the percentages of CK19+ cells in the peripheral blood samples of patients were increased as the illness grew worse. This result was similar with that of Ivy Wong and his group that positive expression level of CK19 correlates strongly with disease stage in colorectal cancer [24]. Moreover, most patients positive for CK19 had a tumor size of more than 2 cm. It was also mentioned by Weihrauch that CK19 detection rate increased with tumor size [25]. However, Xenidis N and his colleagues found the presence of CK19 positive cells had nothing to do with clinicopathological prognostic factors [26].
After a follow-up period of three month-chemotherapy, the number of occult tumor cells in most metastatic patients was decreased rapidly, convincing the effect of adjuvant chemotherapy. In another hand, this can also be considered that most CTCs are apoptotic [27] so they vanished automatically. However, 2 patients with no metastasis before operation had CK19 positive cells after chemotherapy. It may be explained by that chemotherapy may evoke the exudation of proinflammatory cytokines which can regulate gene expression [28]. The tumor cells of one patient vanished after durative chemotherapy, but for the other patient they increased during this treatment. This phenomenon indicates that some tumor cells are sensitive to chemotherapy but others are resistant to it.
In conclusion, we have established a simple method for the test of CTCs in peripheral blood. Despite its sensitivity seems not as high as PCR, the specification and quantification accuracy is encouraging. Our technique can also be applied for bone marrow metastasis investigation. Many groups have reported the relationship of CK19+ cells with reduced overall survival and risk of distant relapse. The detection of CTCs by flow cytometry in breast cancer may monitor disease progression and be helpful in the selection of patients who have the risk of relapse after adjuvant treatment.
Conclusion
The presence of CTCs associates with clinicopathological factors such as tumor size and disease stage. The detection of CK19 in peripheral blood by flow cytometry is a specific and feasible method to monitor CTCs which relate to relapse and survival.
References
Howe HL, Wingo PA, Thun MJ, Ries LA, Rosenberg HM, Feigal EG, Edwards BK: Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer (1973 through 1998), featuring cancers with recent increasing trends. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001, 93: 824-842. 10.1093/jnci/93.11.824.
Wiedswang G, Borgen E, Schirmer C, Karesen R, Kvalheim G, Nesland JM, Naume B: Comparison of the clinical significance of occult tumor cells in blood and bone marrow in breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 2006, 118: 2013-2019. 10.1002/ijc.21576.
Souglakos J, Vamvakas L, Apostolaki S, Perraki M, Saridaki Z, Kazakou I, Pallis A, Kouroussis C, Androulakis N, Kalbakis K, Millaki G, Mavroudis D, Georgoulias V: Central nervous system relapse in patients with breast cancer is associated with advanced stages, with the presence of circulating occult tumor cells and with the HER2/neu status. Breast Cancer Res. 2006, 8: R36-10.1186/bcr1516.
Stathopoulou A, Vlachonikolis I, Mavroudis D, Perraki M, Kouroussis C, Apostolaki S, Malamos N, Kakolyris S, Kotsakis A, Xenidis N, Reppa D, Georgoulias V: Molecular detection of cytokeratin-19-positive cells in the peripheral blood of patients with operable breast cancer: evaluation of their prognostic significance. J Clin Oncol. 2002, 20: 3404-3412. 10.1200/JCO.2002.08.135.
Masuda TA, Kataoka A, Ohno S, Murakami S, Mimori K, Utsunomiya T, Inoue H, Tsutsui S, Kinoshita J, Masuda N, Moriyama N, Mori M: Detection of occult cancer cells in peripheral blood and bone marrow by quantitative RT-PCR assay for cytokeratin-7 in breast cancer patients. Int J Oncol. 2005, 26: 721-730.
Kwon S, Kang SH, Ro J, Jeon CH, Park JW, Lee ES: The melanoma antigen gene as a surveillance marker for the detection of circulating tumor cells in patients with breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2005, 104: 251-256. 10.1002/cncr.21162.
Benoy IH, Elst H, Auwera Van der I, Van Laere S, van Dam P, Van Marck E, Scharpe S, Vermeulen PB, Dirix LY: Real-time RT-PCR correlates with immunocytochemistry for the detection of disseminated epithelial cells in bone marrow aspirates of patients with breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2004, 91: 1813-1820. 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602189.
Hayes DF, Walker TM, Singh B, Vitetta ES, Uhr JW, Gross S, Rao C, Doyle GV, Terstappen LW: Monitoring expression of HER-2 on circulating epithelial cells in patients with advanced breast cancer. Int J Oncol. 2002, 21: 1111-1117.
Hauch S, Zimmermann S, Lankiewicz S, Zieglschmid V, Bocher O, Albert WH: The clinical significance of circulating tumour cells in breast cancer and colorectal cancer patients. Anticancer Res. 2007, 27: 1337-1341.
Cristofanilli M, Hayes DF, Budd GT, Ellis MJ, Stopeck A, Reuben JM, Doyle GV, Matera J, Allard WJ, Miller MC, Fritsche HA, Hortobagyi GN, Terstappen LW: Circulating tumor cells: a novel prognostic factor for newly diagnosed metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005, 23: 1420-1430. 10.1200/JCO.2005.08.140.
Ge M, Shi D, Wu Q, Wang M, Li L: Fluctuation of circulating tumor cells in patients with lung cancer by real-time fluorescent quantitative-PCR approach before and after radiotherapy. J Cancer Res Ther. 2005, 1: 221-226.
Zhong LP, Zhao SF, Chen GF, Ping FY, Xu ZF, Hu JA: Increased levels of CK19 mRNA in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue detected by relative quantification with real-time polymerase chain reaction. Arch Oral Biol. 2006, 51: 1112-1119. 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2006.05.005.
Xenidis N, Markos V, Apostolaki S, Perraki M, Pallis A, Sfakiotaki G, Papadatos-Pastos D, Kalmanti L, Kafousi M, Stathopoulos E, Kakolyris S, Mavroudis D, Georgoulias V: Clinical relevance of circulating CK-19 mRNA-positive cells detected during the adjuvant tamoxifen treatment in patients with early breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2007, 18: 1623-1631. 10.1093/annonc/mdm208.
Loo WT, Fong JH, Zhu L, Cheung MN, Chow LW: The value of bone marrow aspirates culture for the detection of bone marrow micrometastasis in breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2005, 59 (Suppl 2): S384-386. 10.1016/S0753-3322(05)80084-8.
Weinschenker P, Soares HP, Clark O, Del Giglio A: Immunocytochemical detection of epithelial cells in the bone marrow of primary breast cancer patients: a meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2004, 87: 215-224. 10.1007/s10549-004-8691-1.
Jung YS, Lee KJ, Kim HJ, Yim HE, Park JS, Soh EY, Kim MW, Park HB: Clinical significance of bone marrow micrometastasis detected by nested rt-PCR for keratin-19 in breast cancer patients. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2003, 33: 167-172. 10.1093/jjco/hyg038.
Fabisiewicz A, Kulik J, Kober P, Brewczynska E, Pienkowski T, Siedlecki JA: Detection of circulating breast cancer cells in peripheral blood by a two-marker reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction assay. Acta Biochim Pol. 2004, 51: 747-755.
Pierga JY, Bonneton C, Vincent-Salomon A, de Cremoux P, Nos C, Blin N, Pouillart P, Thiery JP, Magdelenat H: Clinical significance of immunocytochemical detection of tumor cells using digital microscopy in peripheral blood and bone marrow of breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2004, 10: 1392-1400. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-0102-03.
Felton T, Harris GC, Pinder SE, Snead DR, Carter GI, Bell JA, Haines A, Kollias J, Robertson JF, Elston CW, Ellis IO: Identification of carcinoma cells in peripheral blood samples of patients with advanced breast carcinoma using RT-PCR amplification of CK7 and MUC1. Breast. 2004, 13: 35-41. 10.1016/S0960-9776(03)00126-7.
Bostick PJ, Chatterjee S, Chi DD, Huynh KT, Giuliano AE, Cote R, Hoon DS: Limitations of specific reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction markers in the detection of metastases in the lymph nodes and blood of breast cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 1998, 16: 2632-2640.
Gilbey AM, Burnett D, Coleman RE, Holen I: The detection of circulating breast cancer cells in blood. J Clin Pathol. 2004, 57: 903-911. 10.1136/jcp.2003.013755.
Aerts J, Wynendaele W, Paridaens R, Christiaens MR, Bogaert van den W, van Oosterom AT, Vandekerckhove F: A real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) to detect breast carcinoma cells in peripheral blood. Ann Oncol. 2001, 12: 39-46. 10.1023/A:1008317512253.
Ji XQ, Sato H, Tanaka H, Konishi Y, Fujimoto T, Takahashi O, Tanaka T: Real-time quantitative RT-PCR detection of disseminated endometrial tumor cells in peripheral blood and lymph nodes using the LightCycler System. Gynecol Oncol. 2006, 100: 355-360. 10.1016/j.ygyno.2005.08.041.
Wong IH, Yeo W, Chan AT, Johnson PJ: Quantitative relationship of the circulating tumor burden assessed by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction for cytokeratin 19 mRNA in peripheral blood of colorectal cancer patients with Dukes' stage, serum carcinoembryonic antigen level and tumor progression. Cancer Lett. 2001, 162: 65-73. 10.1016/S0304-3835(00)00630-3.
Weihrauch MR, Skibowski E, Koslowsky TC, Voiss W, Re D, Kuhn-Regnier F, Bannwarth C, Siedek M, Diehl V, Bohlen H: Immunomagnetic enrichment and detection of micrometastases in colorectal cancer: correlation with established clinical parameters. J Clin Oncol. 2002, 20: 4338-4343. 10.1200/JCO.2002.02.152.
Xenidis N, Vlachonikolis I, Mavroudis D, Perraki M, Stathopoulou A, Malamos N, Kouroussis C, Kakolyris S, Apostolaki S, Vardakis N, Lianidou E, Georgoulias V: Peripheral blood circulating cytokeratin-19 mRNA-positive cells after the completion of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with operable breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2003, 14: 849-855. 10.1093/annonc/mdg259.
Mehes G, Witt A, Kubista E, Ambros PF: Circulating breast cancer cells are frequently apoptotic. Am J Pathol. 2001, 159: 17-20.
Jung R, Kruger W, Hosch S, Holweg M, Kroger N, Gutensohn K, Wagener C, Neumaier M, Zander AR: Specificity of reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction assays designed for the detection of circulating cancer cells is influenced by cytokines in vivo and in vitro. Br J Cancer. 1998, 78: 1194-1198.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Ministry of Science & Technology of China (863 Hi-Tech Project #2006AA02A245). We would like to thank the Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medial University for providing us clinical samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
LW performed the laboratory assays and drafted the manuscript. YW carried out the statistical analysis and revised the manuscript. MC conceived of the study and participated in its coordination. YL contributed to cell culture, image treatment and manuscript revision. XW participated in the use of LSCM. HW was the principal investigator of the study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Wang, Y., Liu, Y. et al. Flow cytometric analysis of CK19 expression in the peripheral blood of breast carcinoma patients: relevance for circulating tumor cell detection. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 28, 57 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-9966-28-57
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-9966-28-57