Abstract
The discovery of CD117 mutation in almost all gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) marked a milestone. Other spindle cell neoplasms arising from the GI tract including lipoma, schwannoma, hemangioma, leiomyoma, and leiomyosarcoma are typically CD117-negative. GIST research and clinical care now represent a paradigm of translating discoveries in the molecular pathogenesis of cancer into highly effective targeted therapies that selectively inhibit etiologic “driver” pathways, leading to dramatically improved clinical outcomes. A series of investigations and trials are underway to develop novel and effective ways to treat patients with GIST. In this review, we discuss the highlights of recent advances and novel agents for GIST therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
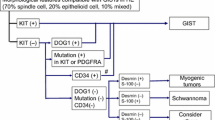
Remarkable developments have occurred in gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) research and clinical care in the past several years. GIST has served as a model for translational therapeutics in solid tumors. A major breakthrough occurred with the discovery of expression of the CD117 antigen by almost all GISTs. Other spindle cell neoplasms arising from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract including lipoma, schwannoma, hemangioma, leiomyoma, and leiomyosarcoma, are typically CD117-negative [1]. The CD117 molecule is part of the KIT (c-kit) receptor tyrosine kinase (KIT RTK) encoded by the KIT proto-oncogene (Figure 1). Since CD117 was found to be associated with GIST, the estimated incidence of GIST has been revised upward to approximately 5,000 new cases per year in the United States (US) [2, 3].
Molecular signature of GIST
In 1998, Hirota et al. defined the relationship between GIST and certain mutations in the KIT proto-oncogene that conferred uncontrolled activation to the KIT signaling enzyme [4]. Importantly, almost all GIST lesions with mutant KIT demonstrate only a single site of mutation in the KIT gene (Figure 2). Complex genetic changes are rare at initial diagnosis. Gain-of-function mutations have been recognized most commonly (up to 70% of cases) in exon 11 of KIT. Approximately 15% of GIST patients do not demonstrate activation and aberrant signaling of the KIT receptor. An additional 10% harbor mutations in the platelet-derived growth factor receptor – alpha (PDGFRA) [5, 6]. Very rare cases may have mutations in the BRAF kinase [7, 8]. Overall, about 5% of GISTs have no detectable kinase mutations (and are often referred to as wild type GIST). Janeway and colleagues have also shown that germline mutation in succinate dehydrogenase subunits B, C or D can cause KIT-/PDGFRA- wild type GIST [9].
National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines recommend KIT immunostaining for all cases of suspected GIST, and if negative, mutational analysis [10, 11]. Routine genotyping of KIT-positive GISTs is not recommended.
Imatinib for metastatic, unresectable or recurrent GIST
Imatinib was found to be able to potently inhibit the tyrosine kinase activity of KIT. The United States (US)–Finland trial enrolled 147 patients with metastatic GIST between July 2000 and April 2001 [12]. Nearly concurrently, a dose-finding study was also begun in Europe under the auspices of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Sarcoma Group to assess the tolerability and potential activity [13]. The two studies confirmed the unparalleled activity of imatinib in controlling metastatic GIST. The median overall survival (OS) of advanced GIST patients increased from 18 to 57 months with imatinib therapy [14]. Despite these excellent results complete responses (CR) are rare (less than 10 percent), and most patients who initially respond ultimately acquire resistance via additional mutations in KIT. The median time to progression is roughly two to three years [12, 15–17], although it is longer in some series [18]. Factors influencing the duration of disease control are still not well understood [17].
Correlative studies have reported differences in the activity of imatinib based on the genotype of the GIST lesion. The mutations in KIT and PDGFRA correlate with clinical response [19–22]. In a report of 127 patients with GISTs receiving imatinib, activating mutations in KIT and PDGFRA were found in 88 and 4.7 per cent, respectively [19]. All of the KIT mutant isoforms were associated with a response, however only a subset of PDGFRA mutants were imatinib-sensitive. Among patients with KIT mutations, those with an exon 11 mutation had a significantly greater response rate compared to patients with an exon 9 mutation or no detectable mutation in KIT or PDGFRA (84 versus 48 and 0 per cent, respectively). Exon 11 mutation patients also exhibited a longer time to treatment failure. A US Intergroup trial subsequently confirmed these results. This trial enrolled 324 patients and compared the two doses of imatinib [22]. Patients whose tumors who had an exon 11 mutant isoform were more likely to have an objective response to imatinib than those with an exon 9 isoform or those who had no mutations (72 versus 44 and 45 per cent, respectively). Patients with an exon 11 mutation also had a significantly longer time to disease progression (25 versus 17 and 13 months, respectively) and OS (median 60 versus 38 and 49 months, respectively). This also translated into more durable disease control over time with continuous dosing of imatinib. The results of this trial as well as subset analysis from the randomized EORTC dose–response trial suggest that high dose imatinib may preferentially benefit patients with an exon 9 mutation [22, 23]. In the EORTC trial, GISTs of 58 patients expressed an exon 9 mutant KIT protein. An initial daily imatinib dose of 800 mg resulted in a significantly superior progression-free survival (hazard ratio for progression 0.39) compared to 400 mg/day. In contrast, the time to progression was not affected by the initial dose in patients with an exon 11 mutation or wild-type KIT. No corresponding differences in overall survival between low-dose and high-dose initial therapy in patients with exon 9 mutations was seen. Similar conclusions were also reached in a meta-analysis that included patients treated on the EORTC and the US Intergroup trial [24]. Imatinib-sensitive PDGFRA mutations explain responses in certain GIST patients with wild-type KIT [19]. Thus, GIST lesion genotype is an important predictive tool and correlates with clinical efficacy of imatinib as a first-line therapy. In one large series of 289 GISTs with PDGFRA mutations, 181 (63 percent) had the imatinib-resistant substitution D842V. Because of the variability in response, patients with advanced GISTs should not be denied a trial of imatinib if they are KIT-negative. NCCN guidelines recommend initiating therapy for unresectable or metastatic disease with imatinib 400 mg daily [11]. However, if molecular diagnosis is available and the patient is exon 9-positive, they support the use of imatinib at 800 mg daily. In contrast, European Society for Medical Oncology recommends mutation testing for all patients and starting imatinib at 800 mg daily for exon 9 mutants [25].
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy does not appear to cure patients with metastatic GIST. Rapid disease progression was seen within months after the imatinib is stopped [26, 27], this is considered a lifelong therapy. A French trial randomly assigned patients with advanced GIST and no disease progression after one year of imatinib to continuous treatment or interruption until disease progression [26]. The study was stopped prematurely after only 58 patients had been randomized when it became clear that the risk of progression was significantly higher if therapy was interrupted, even in completely responding patients.
At the 2011 annual meeting of American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), A Le Cesne et reported the effect of interruption of imatinib therapy in patients with GIST enrolled on the BFR 14 trial [28]. GIST patients were randomly assigned to either interrupt or continue therapy with imatinib after 1, 3, and 5 yrs. Progression free survival was significantly lower in the patients that interrupted therapy as compared to the patients who continued therapy. Imatinib re-introduction allowed tumor control in 94% patients with interrupted treatment. There was no significant difference in time to secondary resistance or OS between both arms. At the same meeting, Domont et al. reported the influence of imatinib interruption and re-introduction on tumor burden in patients with GIST on the BFR 14 trial [29]. They found that imatinib interruption in responding patients with advanced GIST results in tumor progression even in patients who were in complete remission at randomization. Among patients with imatinib interruption 49% experienced progressive disease while 51% had new lesions with concomitant progression of known lesions. Thus, continuous therapy until disease progression (or lifelong if disease does not progress) is currently standard of care. These clinical data support the hypothesis that continuous and chronic exposure to imatinib is necessary to maintain control over a population of GIST cells that may remain quiescent in the long term as long as aberrant KIT signaling is inhibited. Future studies are required to assess whether periodic pulse therapy might suppress emergence of multidrug-resistant GIST clones.
TKIs for imatinib-resistant GIST
Primary resistance was seen in 12 percent of 934 patients in the randomized European trial exploring two different doses of imatinib and was more likely in patients with lung but not liver metastases (41 percent) [16]. Alternatively, clonal evolution of resistant GIST may be detected after a durable objective response and disease control. Several mechanisms of resistance to imatinib in GIST have been explained [30, 31]. Pharmacokinetic variability may also contribute to acquired drug resistance [32]. Limited clonal progression appears as the first sign of resistance to imatinib [31, 33, 34]. The mechanism of resistance to imatinib most commonly observed is the emergence of new secondary mutations [30, 31]. Another likely mechanism is that pre-existing double-mutant tumor cells slowly grow out under the influence of chronic imatinib selection pressure, similar to the antibiotic-resistant strains of bacterial pathogens. Dose escalation of imatinib can also be considered in resistant patients started on imatinib 400 mg daily. The efficacy of this approach was shown in follow-up reports from both the American and European randomized dose-finding studies [14, 35].
Sunitinib is an anti-angiogenesis agent by virtue of targeting multiple tyrosine kinases, including the vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFR) in addition to PDGFR [22, 36–38]. An international phase III trial of sunitinib versus placebo in 312 patients with refractory disease definitively established the role of sunitinib in this setting [38] (Table 1). Patients demonstrating progression while on placebo crossed over to the active treatment arm. Despite a low objective response rate in the sunitinib group (7 percent partial response), median time to tumor progression, the primary endpoint, was fourfold longer as compared to the placebo group (27 versus 6 weeks). Despite the crossover, survival was also significantly better with initial sunitinib. Based on these data, this agent was approved for treatment of GIST following failure of imatinib in January 2006.
Clinical benefit (partial response or stable disease for longer than six months) was significantly higher for those with a primary KIT exon 9 (58 percent) or wild-type KIT/PDGFRA mutation (56 percent) than for those with a KIT exon 11 mutation (34 percent). The same pattern was seen for progression-free survival (PFS) and OS. Following progression on imatinib, patients with KIT exon 9 mutation or a PDGFRA mutation had a median time to progression of 19 months, while for those with exon 11 mutations, it was only 5 months. There was also a correlation between secondary mutations and response to sunitinib. Both progression-free and overall survival were significantly longer for patients with secondary KIT exon 13 or 14 mutations than for those with exon 17 or 18 mutations (7.8 versus 2.3 months). Resistance to sunitinib shares similar pathogenetic mechanisms to those identified in imatinib failure, with acquisition of secondary mutations after an extended initial response [43].
Limited data are available on the efficacy of sorafenib and other TKIs (i.e., dasatinib, motesanib, nilotinib) in refractory GIST or after resistance to imatinib and/or sunitinib [44–49]. The efficacy of sorafenib was addressed in a multicenter phase II trial involving patients with refractory GIST [50]. In a report presented at the 2011 ASCO GI Cancers symposium, the disease control rate was 68 percent, and median PFS was 5.2 months. The most common grade 3 toxicities were hand-foot syndrome and hypertension. Kindler and co-workers reported the final results at the 2011 ASCO Annual Meeting [39]. Thirty eight patients were enrolled with baseline mutations in exon 11 (65%), exon 9 (15%), PDGFRA (4%). They reported partial responses in 13% and stable disease in 55%. The median PFS was 5.2 months and OS was 11.6 months. Grade 3 and 4 toxicities included hand-foot syndrome (45%), hypertension (21%), diarrhea (8%), hypophosphatemia (8%), GI bleed (5%), thrombosis (3%), GI perforation (3%) and intracranial hemorrhage (3%).
Korean GIST Study Group (KGSG) reported the results of a prospective, multicenter, phase II study evaluating the efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients with advanced GISTs who failed previous standard TKI’s [41]. Thirty-one patients with pathologically proven metastatic or unresectable GISTs who failed both imatinib and sunitinib were accrued. Ten patients received nilotinib as a third line treatment. With sorafenib, 3 patients (10%) achieved a partial response and 17 patients (55%) had stable disease. The median PFS was 4.9 months and the disease control rate was 37.6% at 6 months. Patients with prior use of 3rd line nilotinib and primary genotypes other than mutations at KIT exon 11 showed significantly worse PFS.
Guidelines from the NCCN suggest sorafenib as an option for patients with imatinib and sunitinib-resistant GIST [11]. Emerging results from in vitro studies suggest that the choice of salvage therapy in imatinib-refractory GISTs might depend, at least in part, on the specific mutation responsible for the acquisition of resistance [51]. However, these data require validation before they can be applied to clinical practice.
Nilotinib was studied in a randomized phase 3 clinical trial (ENEST g3) [40]. In this trial nilotinib was compared to a heterogeneous control arm in patients advanced/metastatic GIST who had failed imatinib and sunitinib. The control arm included best supportive care with physician choice to continue or stop imatinib or sunitinib. It failed to show significant benefit for nilotinib.
Dasatinib is an oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor of KIT, PDGFR, ABL and SRC with a distinct binding affinity for KIT and PDGFR. Trent and associates reported a phase II trial to assess antitumor activity of dasatinib in patients with advanced GIST who were refractory to imatinib and sunitinib [42]. They reported a partial response (PR) rate of 32% (15/47) by Choi criteria and 21% patients (10/47) were progression-free after 6 months. Median PFS and OS were 2.0 months and 19 months with median PFS for wild type GIST patients of 8.4 months. Dasatinib has significant activity but did not meet the predefined 6 month PFS rate of 30%.
Recent advances and meeting updates
Several clinical trials are already in progress using next-generation agents that target the KIT receptor via different mechanisms or that target the alternate pathways. We will now review the highlights on GIST from the 2011 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) meeting and the 2011 ASCO – Gastro-intestinal cancers symposium (Table 2).
New TKIs
Regorafenib is a novel oral multi-kinase inhibitor which has a broad spectrum of antitumor activity in preclinical and early phase trials. George et al. conducted a multi-center phase II trial of regorafenib in patients with advanced GIST after prior therapy with at least imatinib and sunitinib [52]. Thirty three patients received at least one dose of study drug. Most common grade 3 treatment related toxicities were hypertension, hand-foot skin reaction, and hypophosphatemia. There were two grade 4 events, one hyperuricemia and one thrombosis. Most eligible patients were without disease progression after 4 cycles of regorafenib. Benefit was seen in patients whose tumors had primary KIT exon 11 mutations, KIT exon 9 mutations or wild type kinase genotype. Thus, regorafenib demonstrated significant activity in patients with advanced GIST previously treated with imatinib and sunitinib. An international phase III trial is currently underway in patients with advanced GIST following treatment with at least imatinib and sunitinib.
Masitinib is a new tyrosine kinase inhibitor which has a greater activity and selectivity than imatinib. It is an oral inhibitor of both the KIT and PDGFRA receptors. It may have greater activity than imatinib against wild-type GIST and juxta-membrane KIT mutants. Blay et al. evaluated the safety and efficacy of masitinib as a first line therapy in patients with imatinib-naïve, inoperable, locally advanced or metastatic GIST [53, 55]. They reported a PFS of 41 months. OS was 72% at the end of 4 years. Main toxicities were rash (10%), neutropenia (7%) and abdominal pain (7%). A phase 3 trial is currently underway and actively recruiting participants (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00812240).
Crenolanib (formerly CP-868596) is an orally bioavailable, highly potent and selective PDGFR TKI for the D842V mutation encoded by exon 18. Currently approved TKIs have little to no in vitro activity against this mutation and are thus clinically ineffective. Phase I trials of Crenolanib have shown a favorable toxicity profile, and achievable serum concentrations as high as 2,000 nanomolar [56]. At the recommended phase II dosage (ie, 100 mg twice daily with food), the steady-state serum concentrations were more than 16 nanograms/milliliter. The half life was in the range of 12.3 to 18.5 hours. Heinrich and associates reported on the effect of crenolanib on phosphorylation of the imatinib-resistant D842V PDGFRA activating mutation [54]. Mutant PDGFRα isoforms were expressed by transient transfection of Chinese hamster ovary cells and these transfected cells were treated with various concentrations of crenolanib or imatinib. Crenolanib was effective in blocking the activity of single or compound PDGFRA D842V mutant kinases. In contrast, imatinib had no significant activity against these same mutant kinases. A phase II clinical study of crenolanib for treatment of GIST patients with primary or secondary PDGFRA D842V mutation is currently recruiting patients (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01243346).
Motesanib (AMG706) is an oral inhibitor of VEGF, PDGF, and Kit receptors. In a phase 2 multicenter study of AMG 706 in 102 advanced imatinib-resistant GISTs [48], the objective response rate was 3%. This included 59% patients who had stable disease. PET scans showed an objective response rate of 30% and per Choi criteria of 41%. The median PFS was 16 weeks. The most common motesanib treatment-related grade 3 adverse events were hypertension (23%), fatigue (9%), and diarrhea (5%).
PTK787/ZK222584 is another novel, oral selective inhibitor of receptor tyrosine kinases (KIT, PDGFRs, VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2). In a phase 2 open label study on PTK787 in GISTs resistant to imatinib [44], 13% patients achieved PR, 8 (53%) had SD for 3 months or longer. The clinical benefit rate (PR + SD) was 67%. The dose of 1,250 mg daily was generally well tolerated.
Novel agents
mTOR inhibitors
Novel approaches to overcome resistance to TKIs in GIST include targeting multiple levels of the signal transduction cascade intracellularly by combining agents (Table 3). This has been done by combining a kinase inhibitor such as imatinib with an mTOR inhibitor everolimus. [57]. In this phase 1/2 trial Schoffski et al. reported stable disease in 36%, PR in 2% and stable disease (SD) in 43% patients who had progressed after imatinib and sunitinib/other tyrosine kinase inhibitor. All these patients were treated with imatinib 600 mg/day plus everolimus 2.5 mg/day. Another phase 1/2 trial showed SD in 8 out of 31 patients in the trial [58].
Another mTOR inhibitor, sirolimus, as a single agent has also been reported [59, 60]. Richter and co-workers showed response efficacy (complete response, partial response or stable disease) in 27% refractory and heavily pre-treated patients [59]. Piovesan and colleagues reported anti-tumor activity of sirolimus in combination with TKIs in 3 patients with PDGFRA-D842V metastatic GIST. Of these 3 patients, two were progressing on imatinib, while the third patient was treated with imatinib and sirolimus upfront [60].
Hsp90 inhibitor
Other strategies that are being explored include the inhibition of other pathways involving KIT or PDGFRA oncoproteins, such as the heat shock protein-90 (Hsp90) chaperon system. By inhibiting Hsp90, preclinical and early clinical studies have already documented antineoplastic effects on resistant GIST both in vitro and in patients with progressive disease [64, 65].
Ganetespib (STA 9090) is a potent, synthetic inhibitor of Hsp90. It has an improved safety profile relative to 1st-generation Hsp90 inhibitors and has promising signals of antitumor activity in early clinical studies, including one patient with PDGFRA D842V mutant GIST. Demetri and co-workers [61] enrolled patients with advanced GIST who failed prior therapy to receive ganetespib (200 mg/m2) as a 1 hour IV infusion weekly for 3 weeks of a 28 day cycle. Toxicities reported in more than 20% patients were grade 1–2 and included diarrhea, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, increased alkaline phosphatase, headache, insomnia, and abdominal pain. Fifty two percent (12/23) evaluable patients had stable disease. However, analysis of client proteins in paired tumor biopsies (4 patients) did not show prolonged inhibition of activated KIT or its downstream pathways. The data suggest that once-weekly treatment schedule is not optimal for inhibition of KIT.
Retaspimycin hydrochloride (IPI504, a Hsp90 inhibitor) is another Hsp90 inhibitor [62]. A clinical study was terminated early due to a higher mortality rate in the IPI504 arm compared to the placebo arm. IPI504 was not well tolerated in this patient population. There was a higher rate of Grade 3 and 4 adverse events, including LFT abnormalities, in the IPI504 arm.
Perifosine
Other drugs that have been tried recently include perifosine [63]. The addition of perifosine to imatinib showed minimal activity in imatinib-refractory GIST.
Conclusion and future directions
In summary, it is clear that the deeper scientific understanding of GIST has led to the development of novel therapeutic tools such as imatinib and sunitinib to disable the malignant GIST cells. With improved technology and rational molecular targeting, this translation of science into applied therapeutics should continue to move forward at a very rapid pace. It is foreseeable that more agents with novel mechanisms of action and targeting different pathways will be studied for GIST therapy.
References
Rubin BP, Fletcher JA, Fletcher CD: Molecular Insights into the Histogenesis and Pathogenesis of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors. Int J Surg Pathol. 2000, 8 (1): 5-10. 10.1177/106689690000800105.
Fletcher CD, Berman JJ, Corless C, Gorstein F, Lasota J, Longley BJ, Miettinen M, O’Leary TJ, Remotti H, Rubin BP: Diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a consensus approach. Hum Pathol. 2002, 33 (5): 459-465. 10.1053/hupa.2002.123545.
Miettinen M, El-Rifai W, L HLS, Lasota J: Evaluation of malignancy and prognosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a review. Hum Pathol. 2002, 33 (5): 478-483. 10.1053/hupa.2002.124123.
Hirota S, Isozaki K, Moriyama Y, Hashimoto K, Nishida T, Ishiguro S, Kawano K, Hanada M, Kurata A, Takeda M: Gain-of-function mutations of c-kit in human gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science. 1998, 279 (5350): 577-580. 10.1126/science.279.5350.577.
Heinrich MC, Corless CL, Duensing A, McGreevey L, Chen CJ, Joseph N, Singer S, Griffith DJ, Haley A, Town A: PDGFRA activating mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science. 2003, 299 (5607): 708-710. 10.1126/science.1079666.
Hirota S, Ohashi A, Nishida T, Isozaki K, Kinoshita K, Shinomura Y, Kitamura Y: Gain-of-function mutations of platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha gene in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Gastroenterology. 2003, 125 (3): 660-667. 10.1016/S0016-5085(03)01046-1.
Hostein I, Faur N, Primois C, Boury F, Denard J, Emile JF, Bringuier PP, Scoazec JY, Coindre JM: BRAF mutation status in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Am J Clin Pathol. 2010, 133 (1): 141-148. 10.1309/AJCPPCKGA2QGBJ1R.
Agaimy A, Terracciano LM, Dirnhofer S, Tornillo L, Foerster A, Hartmann A, Bihl MP: V600E BRAF mutations are alternative early molecular events in a subset of KIT/PDGFRA wild-type gastrointestinal stromal tumours. J Clin Pathol. 2009, 62 (7): 613-616. 10.1136/jcp.2009.064550.
Janeway KA, Kim SY, Lodish M, Nose V, Rustin P, Gaal J, Dahia PL, Liegl B, Ball ER, Raygada M: Defects in succinate dehydrogenase in gastrointestinal stromal tumors lacking KIT and PDGFRA mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011, 108 (1): 314-318. 10.1073/pnas.1009199108.
Demetri GD, von Mehren M, Antonescu CR, DeMatteo RP, Ganjoo KN, Maki RG, Pisters PW, Raut CP, Riedel RF, Schuetze S: NCCN Task Force report: update on the management of patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2010, 8 (Suppl 2): S1-41. quiz S42-44
NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network Guidelines. National Comprehensive Cancer Network Guidelines. 2012, 2012 (2): 2012-
Demetri GD, von Mehren M, Blanke CD, Van den Abbeele AD, Eisenberg B, Roberts PJ, Heinrich MC, Tuveson DA, Singer S, Janicek M: Efficacy and safety of imatinib mesylate in advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors. N Engl J Med. 2002, 347 (7): 472-480. 10.1056/NEJMoa020461.
van Oosterom AT, Judson I, Verweij J, Stroobants S, Donato-di-Paola E, Dimitrijevic S, Martens M, Webb A, Sciot R, Van Glabbeke M: Safety and efficacy of imatinib (STI571) in metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumours: a phase I study. Lancet. 2001, 358 (9291): 1421-1423. 10.1016/S0140-6736(01)06535-7.
Blanke CD, Rankin C, Demetri GD, Ryan CW, von Mehren M, Benjamin RS, Raymond AK, Bramwell VH, Baker LH, Maki RG: Phase III randomized, intergroup trial assessing imatinib mesylate at two dose levels in patients with unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors expressing the kit receptor tyrosine kinase: S0033. J Clin Oncol. 2008, 26 (4): 626-632. 10.1200/JCO.2007.13.4452.
Verweij J, Casali PG, Zalcberg J, LeCesne A, Reichardt P, Blay JY, Issels R, van Oosterom A, Hogendoorn PC, Van Glabbeke M: Progression-free survival in gastrointestinal stromal tumours with high-dose imatinib: randomised trial. Lancet. 2004, 364 (9440): 1127-1134. 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17098-0.
Van Glabbeke M, Verweij J, Casali PG, Le Cesne A, Hohenberger P, Ray-Coquard I, Schlemmer M, van Oosterom AT, Goldstein D, Sciot R: Initial and late resistance to imatinib in advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors are predicted by different prognostic factors: a European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer-Italian Sarcoma Group-Australasian Gastrointestinal Trials Group study. J Clin Oncol. 2005, 23 (24): 5795-5804. 10.1200/JCO.2005.11.601.
Rutkowski P, Nowecki ZI, Debiec-Rychter M, Grzesiakowska U, Michej W, Wozniak A, Siedlecki JA, Limon J, vel Dobosz AJ, Kakol M: Predictive factors for long-term effects of imatinib therapy in patients with inoperable/metastatic CD117(+) gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs). J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2007, 133 (9): 589-597. 10.1007/s00432-007-0202-4.
Armbrust T, Sobotta M, Gunawan B, Fuzesi L, Langer C, Cameron S, Ramadori G: Does imatinib turn recurrent and/or metastasized gastrointestinal stromal tumors into a chronic disease? - single center experience. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009, 21 (7): 819-823. 10.1097/MEG.0b013e32830b0f76.
Heinrich MC, Corless CL, Demetri GD, Blanke CD, von Mehren M, Joensuu H, McGreevey LS, Chen CJ, Van den Abbeele AD, Druker BJ: Kinase mutations and imatinib response in patients with metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor. J Clin Oncol. 2003, 21 (23): 4342-4349. 10.1200/JCO.2003.04.190.
Debiec-Rychter M, Dumez H, Judson I, Wasag B, Verweij J, Brown M, Dimitrijevic S, Sciot R, Stul M, Vranck H: Use of c-KIT/PDGFRA mutational analysis to predict the clinical response to imatinib in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours entered on phase I and II studies of the EORTC Soft Tissue and Bone Sarcoma Group. Eur J Cancer. 2004, 40 (5): 689-695. 10.1016/j.ejca.2003.11.025.
Corless CL, Schroeder A, Griffith D, Town A, McGreevey L, Harrell P, Shiraga S, Bainbridge T, Morich J, Heinrich MC: PDGFRA mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors: frequency, spectrum and in vitro sensitivity to imatinib. J Clin Oncol. 2005, 23 (23): 5357-5364. 10.1200/JCO.2005.14.068.
Heinrich MC, Owzar K, Corless CL, Hollis D, Borden EC, Fletcher CD, Ryan CW, von Mehren M, Blanke CD, Rankin C: Correlation of kinase genotype and clinical outcome in the North American Intergroup Phase III Trial of imatinib mesylate for treatment of advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor: CALGB 150105 Study by Cancer and Leukemia Group B and Southwest Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol. 2008, 26 (33): 5360-5367. 10.1200/JCO.2008.17.4284.
Debiec-Rychter M, Sciot R, Le Cesne A, Schlemmer M, Hohenberger P, van Oosterom AT, Blay JY, Leyvraz S, Stul M, Casali PG: KIT mutations and dose selection for imatinib in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Eur J Cancer. 2006, 42 (8): 1093-1103. 10.1016/j.ejca.2006.01.030.
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Meta-Analysis G: Comparison of two doses of imatinib for the treatment of unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a meta-analysis of 1,640 patients. J Clin Oncol. 2010, 28 (7): 1247-1253.
Casali PG, Jost L, Reichardt P, Schlemmer M, Blay JY, Group EGW: Gastrointestinal stromal tumours: ESMO clinical recommendations for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Annals of oncology : official journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology/ESMO. 2009, 20 (Suppl 4): 64-67.
Blay JY, Le Cesne A, Ray-Coquard I, Bui B, Duffaud F, Delbaldo C, Adenis A, Viens P, Rios M, Bompas E: Prospective multicentric randomized phase III study of imatinib in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors comparing interruption versus continuation of treatment beyond 1 year: the French Sarcoma Group. J Clin Oncol. 2007, 25 (9): 1107-1113. 10.1200/JCO.2006.09.0183.
Le Cesne A, Ray-Coquard I, Bui BN, Adenis A, Rios M, Bertucci F, Duffaud F, Chevreau C, Cupissol D, Cioffi A: Discontinuation of imatinib in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours after 3 years of treatment: an open-label multicentre randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11 (10): 942-949. 10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70222-9.
Le Cesne A, Ray-Coquard IL, Bui-Nguyen B, Adenis A, Rios M, Bertucci F, Duffaud F, Cupissol D, Chevreau C, Bompas E: Time to secondary resistance (TSR) after interruption of imatinib (IM) in advanced GIST: updated results of the prospective French Sarcoma Group randomized phase III trial on long-term survival. ASCO Meeting Abstracts. 2011, 29 (15 _uppl): 10015-
Domont J, Blay J, Ray-Coquard IL, Bui-Nguyen B, Adenis A, Rios M, Bertucci F, Duffaud F, Cupissol D, Chevreau C: Influence of imatinib interruption and imatinib rechallenge on the residual tumor volume in patients with advanced GIST: results of the BFR14 prospective French Sarcoma Group randomized phase III trial. ASCO Meeting Abstracts. 2011, 29 (15_suppl): 10054-
Heinrich MC, Corless CL, Blanke CD, Demetri GD, Joensuu H, Roberts PJ, Eisenberg BL, von Mehren M, Fletcher CD, Sandau K: Molecular correlates of imatinib resistance in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2006, 24 (29): 4764-4774. 10.1200/JCO.2006.06.2265.
Desai J, Shankar S, Heinrich MC, Fletcher JA, Fletcher CD, Manola J, Morgan JA, Corless CL, George S, Tuncali K: Clonal evolution of resistance to imatinib in patients with metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2007, 13 (18 Pt 1): 5398-5405.
Eechoute K, Sparreboom A, Burger H, Franke RM, Schiavon G, Verweij J, Loos WJ, Wiemer EA, Mathijssen RH: Drug transporters and imatinib treatment: implications for clinical practice. Clin Cancer Res. 2011, 17 (3): 406-415. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2250.
Raut CP, Posner M, Desai J, Morgan JA, George S, Zahrieh D, Fletcher CD, Demetri GD, Bertagnolli MM: Surgical management of advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors after treatment with targeted systemic therapy using kinase inhibitors. J Clin Oncol. 2006, 24 (15): 2325-2331. 10.1200/JCO.2005.05.3439.
Shankar S, vanSonnenberg E, Desai J, Dipiro PJ, Van Den Abbeele A, Demetri GD: Gastrointestinal stromal tumor: new nodule-within-a-mass pattern of recurrence after partial response to imatinib mesylate. Radiology. 2005, 235 (3): 892-898. 10.1148/radiol.2353040332.
Zalcberg JR, Verweij J, Casali PG, Le Cesne A, Reichardt P, Blay JY, Schlemmer M, Van Glabbeke M, Brown M, Judson IR: Outcome of patients with advanced gastro-intestinal stromal tumours crossing over to a daily imatinib dose of 800 mg after progression on 400 mg. Eur J Cancer. 2005, 41 (12): 1751-1757. 10.1016/j.ejca.2005.04.034.
Debiec-Rychter M, Cools J, Dumez H, Sciot R, Stul M, Mentens N, Vranckx H, Wasag B, Prenen H, Roesel J: Mechanisms of resistance to imatinib mesylate in gastrointestinal stromal tumors and activity of the PKC412 inhibitor against imatinib-resistant mutants. Gastroenterology. 2005, 128 (2): 270-279. 10.1053/j.gastro.2004.11.020.
Demetri GD, Heinrich MC, Fletcher JA, Fletcher CD, Van den Abbeele AD, Corless CL, Antonescu CR, George S, Morgan JA, Chen MH: Molecular target modulation, imaging, and clinical evaluation of gastrointestinal stromal tumor patients treated with sunitinib malate after imatinib failure. Clin Cancer Res. 2009, 15 (18): 5902-5909. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0482.
Demetri GD, van Oosterom AT, Garrett CR, Blackstein ME, Shah MH, Verweij J, McArthur G, Judson IR, Heinrich MC, Morgan JA: Efficacy and safety of sunitinib in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumour after failure of imatinib: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2006, 368 (9544): 1329-1338. 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69446-4.
Kindler HL, Campbell NP, Wroblewski K, Maki RG, D’Adamo DR, Chow WA, Gandara DR, Antonescu C, Stadler WM, Vokes EE: Sorafenib (SOR) in patients (pts) with imatinib (IM) and sunitinib (SU)-resistant (RES) gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST): Final results of a University of Chicago Phase II Consortium trial. ASCO Meeting Abstracts. 2011, 29 (15_suppl): 10009-
Reichardt P, Blay JY, Gelderblom H, Schlemmer M, Demetri GD, Bui-Nguyen B, McArthur GA, Yazji S, Hsu Y, Galetic I: Phase III study of nilotinib versus best supportive care with or without a TKI in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors resistant to or intolerant of imatinib and sunitinib. Ann Oncol. 2012, 23: -
Park SH, Ryu MH, Ryoo BY, Im SA, Kwon HC, Lee SS, Park SR, Kang BY, Kang YK: Sorafenib in patients with metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors who failed two or more prior tyrosine kinase inhibitors: a phase II study of Korean gastrointestinal stromal tumors study group. Invest New Drugs. 2012, 30: -
Trent JC, Wathen K, von Mehren M, Samuels BL, Staddon AP, Choy E, Butrynski JE, Chugh R, Chow WA, Rushing DA: A phase II study of dasatinib for patients with imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST). ASCO Meeting Abstracts. 2011, 29 (15_suppl): 10006-
Guo T, Hajdu M, Agaram NP, Shinoda H, Veach D, Clarkson BD, Maki RG, Singer S, Dematteo RP, Besmer P: Mechanisms of sunitinib resistance in gastrointestinal stromal tumors harboring KITAY502-3ins mutation: an in vitro mutagenesis screen for drug resistance. Clin Cancer Res. 2009, 15 (22): 6862-6870. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1315.
Joensuu H, De Braud F, Coco P, De Pas T, Putzu C, Spreafico C, Bono P, Bosselli S, Jalava T, Laurent D: Phase II, open-label study of PTK787/ZK222584 for the treatment of metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors resistant to imatinib mesylate. Annals of oncology : official journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology/ESMO. 2008, 19 (1): 173-177.
Montemurro M, Schoffski P, Reichardt P, Gelderblom H, Schutte J, Hartmann JT, von Moos R, Seddon B, Joensuu H, Wendtner CM: Nilotinib in the treatment of advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours resistant to both imatinib and sunitinib. Eur J Cancer. 2009, 45 (13): 2293-2297. 10.1016/j.ejca.2009.04.030.
Dewaele B, Wasag B, Cools J, Sciot R, Prenen H, Vandenberghe P, Wozniak A, Schoffski P, Marynen P, Debiec-Rychter M: Activity of dasatinib, a dual SRC/ABL kinase inhibitor, and IPI-504, a heat shock protein 90 inhibitor, against gastrointestinal stromal tumor-associated PDGFRAD842V mutation. Clin Cancer Res. 2008, 14 (18): 5749-5758. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0533.
Demetri GD, Casali PG, Blay JY, von Mehren M, Morgan JA, Bertulli R, Ray-Coquard I, Cassier P, Davey M, Borghaei H: A phase I study of single-agent nilotinib or in combination with imatinib in patients with imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2009, 15 (18): 5910-5916. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0542.
Benjamin RS, Schoffski P, Hartmann JT, Van Oosterom A, Bui BN, Duyster J, Schuetze S, Blay JY, Reichardt P, Rosen LS: Efficacy and safety of motesanib, an oral inhibitor of VEGF, PDGF, and Kit receptors, in patients with imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011, 68 (1): 69-77. 10.1007/s00280-010-1431-9.
Wiebe L, Kasza KE, Maki RG, D’Adamo DR, Chow WA, Wade JL, Agamah E, Stadler WM, Vokes EE, Kindler HL: Activity of sorafenib (SOR) in patients (pts) with imatinib (IM) and sunitinib (SU)-resistant (RES) gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST): A phase II trial of the University of Chicago Phase II Consortium. ASCO Meeting Abstracts. 2008, 26 (15_suppl): 10502-
Campbell NP, Wroblewski K, Maki RG, D’Adamo DR, Chow WA, Gandara DR, Antonescu C, Stadler WM, Vokes EE, Kindler HL: Final results of a University of Chicago phase II consortium trial of sorafenib (SOR) in patients (pts) with imatinib (IM)- and sunitinib (SU)-resistant (RES) gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST). ASCO Meeting Abstracts. 2011, 29 (4_suppl): 4-
Guo T, Agaram NP, Wong GC, Hom G, D’Adamo D, Maki RG, Schwartz GK, Veach D, Clarkson BD, Singer S: Sorafenib inhibits the imatinib-resistant KITT670I gatekeeper mutation in gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Clin Cancer Res. 2007, 13 (16): 4874-4881. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0484.
George S, von Mehren M, Heinrich MC, Wang Q, Corless CL, Butrynski JE, Morgan JA, Wagner AJ, Choy E, Tap WD: A multicenter phase II study of regorafenib in patients (pts) with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST), after therapy with imatinib (IM) and sunitinib (SU). ASCO Meeting Abstracts. 2011, 29 (15_suppl): 10007-
Blay J, Le Cesne A, Bin-Bui N, Bouche O, Adenis A, Julien D, Cioffi A, Moussy A, Hermine O: Overall survival benefit with masitinib mesylate in imatinib-naive, locally advanced, or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST): 4-years follow-up of the French Sarcoma Group phase II trial. ASCO Meeting Abstracts. 2011, 29 (4_suppl): 85-
Heinrich MC, Griffith D, McKinley A, Presnell A, Ramachandran A: The effect of crenolanib (CP-868596) on phosphorylation of the imatinib-resistant D842V PDGFRA activating mutation associated with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors. ASCO Meeting Abstracts. 2011, 29 (15_suppl): 10012-
Le Cesne A, Blay JY, Bui BN, Bouche O, Adenis A, Domont J, Cioffi A, Ray-Coquard I, Lassau N, Bonvalot S: Phase II study of oral masitinib mesilate in imatinib-naive patients with locally advanced or metastatic gastro-intestinal stromal tumour (GIST). Eur J Cancer. 2010, 46 (8): 1344-1351. 10.1016/j.ejca.2010.02.014.
Lewis NL, Lewis LD, Eder JP, Reddy NJ, Guo F, Pierce KJ, Olszanski AJ, Cohen RB: Phase I study of the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of oral CP-868,596, a highly specific platelet-derived growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor in patients with advanced cancers. J Clin Oncol. 2009, 27 (31): 5262-5269. 10.1200/JCO.2009.21.8487.
Schoffski P, Reichardt P, Blay JY, Dumez H, Morgan JA, Ray-Coquard I, Hollaender N, Jappe A, Demetri GD: A phase I-II study of everolimus (RAD001) in combination with imatinib in patients with imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Annals of oncology : official journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology/ESMO. 2010, 21 (10): 1990-1998. 10.1093/annonc/mdq076.
van Oosterom A, Reichardt P, Blay J-Y, Dumez H, Fletcher J, Debiec-Rychter M, Shand N, Drimitrijevic S, Yap A, Demetri G: A phase I/II trial of the oral mTOR-inhibitor everolimus (E) and imatinib mesylate (IM) in patients (pts) with gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) refractory to IM: Study update. ASCO Meeting Abstracts. 2005, 23 (16_suppl): 9033-
Richter S, Pink D, Hohenberger P, Schuette H, Casali PG, Pustowka A, Reichardt P: Multicenter, triple-arm, single-stage, phase II trial to determine the efficacy and safety of everolimus (RAD001) in patients with refractory bone or soft tissue sarcomas including GIST. ASCO Meeting Abstracts. 2010, 28 (15_suppl): 10038-
Piovesan C, Fumagalli E, Coco P, Palassini E, Dileo P, Morosi C, Gronchi A, Casali P: Response to sirolimus in combination to tirosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) in three cases of PDGFRA-D842V metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST). ASCO Meeting Abstracts. 2009, 27 (15S): 10565-
Demetri GD, Heinrich MC, Chmielowski B, Morgan JA, George S, Bradley R, Blackman RK, Teofilovici F, Fletcher JA, Tap WD: An open-label phase II study of the Hsp90 inhibitor ganetespib (STA-9090) in patients (pts) with metastatic and/or unresectable GIST. ASCO Meeting Abstracts. 2011, 29 (15_suppl): 10011-
Demetri G, Le Cesne A, von Mehren M: Final results from a Phase III study of IPI‒504 retaspimycin hydrochloride) versus placebo in patients (pts) with gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) following failure of tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapies. ASCO Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium Meeting abstracts. 2010, 28 (15_suppl): 64-
Conley AP, Araujo D, Ludwig J, Ravi V, Samuels BL, Choi H, Thall PF, Patel S, Benjamin R, Trent J: A randomized phase II study of perifosine (P) plus imatinib for patients with imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST). ASCO Meeting Abstracts. 2009, 27 (15S): 10563-
Bauer S, Yu LK, Demetri GD, Fletcher JA: Heat shock protein 90 inhibition in imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Cancer Res. 2006, 66 (18): 9153-9161. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0165.
Demetri GD, George S, Morgan JA, Wagner A, Quigley MT, Polson K, Pokela J, van den Abbeele A, Adams J, Grayzel D: Inhibition of the Heat Shock Protein 90 (Hsp90) chaperone with the novel agent IPI-504 to overcome resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in metastatic GIST: Updated results of a phase I trial. ASCO Meeting Abstracts. 2007, 25 (18_suppl): 10024-
Acknowledgements
This study was partly supported by the NYMC Blood Diseases fund (DL).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors have no conflicts of interests.
Author’s contributions
SA, RG, BL contributed to data preparation. GL and DL were involved in concept design, data collection, and manuscript preparation. All authors reviewed and assisted in revising the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Lamba, G., Ambrale, S., Lee, B. et al. Recent advances and novel agents for gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST). J Hematol Oncol 5, 21 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-8722-5-21
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-8722-5-21