Abstract
Background
Lymphatic filariasis and onchocerciasis are debilitating diseases caused by filarial nematodes. Disease pathogenesis is induced by inflammatory responses following the death of the parasite. Wolbachia endosymbionts of filariae are potent inducers of innate and adaptive inflammation and bacterial lipoproteins have been identified as the ligands that bind toll-like receptors (TLR) 2 and TLR6. Lipoproteins are important structural and functional components of bacteria and therefore enzymes involved in Wolbachia lipoprotein biosynthesis are potential chemotherapeutic targets.
Results
Globomycin, a signal peptidase II (LspA) inhibitor, has activity against Gram-negative bacteria and a putative lspA gene has been identified from the Wolbachia genome of Brugia malayi (w Bm). The amino acids required for function are strictly conserved and functionality was verified by complementation tests in a temperature-sensitive Escherichia coli lspA mutant. Also, transformation of wild type E. coli with Wolbachia lspA conferred significant globomycin resistance. A cell-based screen has been developed utilizing a Wolbachia-containing Aedes albopictus cell line to assay novel compounds active against Wolbachia. Globomycin was screened using this assay, which resulted in a dose-dependent reduction in Wolbachia load. Furthermore, globomycin was also effective in reducing the motility and viability of adult B. malayi in vitro.
Conclusions
These studies validate lipoprotein biosynthesis as a target in an organism for which no genetic tools are available. Further studies to evaluate drugs targeting this pathway are underway as part of the A-WOL drug discovery and development program.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Lymphatic filariasis and onchocerciasis are leading causes of global morbidity, with 150 million people afflicted and 1.5 billion people at risk. The filarial nematodes responsible for these diseases; Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi (lymphatic filariasis) and Onchocerca volvulus (onchocerciasis), have a mutualistic association with a bacterial endosymbiont, Wolbachia pipientis. The symbiotic relationship is essential for parasite growth, development, fecundity and survival [1].
Wolbachia have emerged as a novel target for antibiotic therapy to treat filariasis. Antibiotic studies using ex vivo and in vivo animal model systems (reviewed by [1]) and extensive field trials have demonstrated the effectiveness of antibiotics such as doxycycline in the treatment of filariasis [2–14]. Depletion of Wolbachia leads to long-term sterility and ultimately to the death of adult worms. Furthermore, Wolbachia-targeted treatment has also been shown to lead to a reduction in the severity and improvement of lymphoedema and hydrocoele pathology in lymphatic filariasis [3, 5]. Despite these clear benefits of doxycycline therapy over conventional treatments, the extended period of treatment and contraindication in children under eight and pregnancy compromises their delivery through mass drug treatment programmes. This has driven the formation of the A-WOL (anti-Wolbachia) consortium to discover and develop new drugs active against Wolbachia for the treatment of filariasis that would be compatible with current control programme strategies.
Wolbachia lipoproteins have emerged as potent stimulators of the inflammatory pathogenesis of filarial disease [15]. Genomic analysis indicates that Wolbachia contain the lipoprotein biosynthesis genes lgt and lspA but not lnt, N-acyltransferase, which is required for the triacylation of apolipoproteins. This suggests that Wolbachia lipoproteins cannot be triacylated and accounts for the recognition by the diacyl-lipoprotein receptor complex TLR2/6 [15]. Bioinformatic and database searches consistently predicted the presence of only three lipoproteins in Wolbachia: Peptidoglycan-associated lipoprotein (PAL), a Type IV Secretion System protein (VirB6) and Small protein A [15].
Lipoproteins are important structural and functional components of bacteria and their biosynthesis is essential for bacterial viability. Globomycin, an inhibitor of lipoprotein signal peptidase, LspA [16], has previously been demonstrated to have potent anti-bacterial activity against Gram-negative bacteria [17–20]. We therefore sought to test whether globomycin was active against Wolbachia and to validate lipoprotein biosynthesis as a Wolbachia drug target.
Results
Identification and verification of a functional w Bm lspA gene
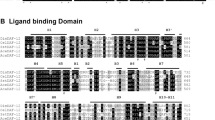
Putative lspA genes were identified from the available genome databases of w Bm and Wolbachia endosymbionts of Drosophila species. The deduced amino acid sequence of the putative Wolbachia (including w Bm) LspA proteins contain a predicted signal peptide with three transmembrane domains, which are evolutionarily conserved features in LspA proteins (Figure 1). High sequence identity (80-81%)/similarity (88%) was observed between B. malayi Wolbachia LspA and Drosophila Wolbachia LspA homologs, all containing the five conserved catalytic residues [21], although a low amino acid identity (25%)/similarity (49%) was revealed when compared to the Escherichia coli LspA homolog (Figure 1). The conservation of the amino acids required for function suggests that the w Bm LspA gene should be functional.
Sequence alignment of LspA proteins. Sequence alignment of LspA proteins from Wolbachia of Brugia malayi (w Bm, AAW71005), Wolbachia of Drosophila melanogaster (w Mel, AAS14450), Wolbachia of Drosophila willistoni (w Will, ZP_01314990), Ehrlichia canis (Eh. c, AAZ68883), Anaplasma marginale (A.m, AAV86940), and Escherichia coli (E.coli, NP_414568). Genbank accession numbers follow the abbreviations of each species indicated above. The conserved catalytic residues are indicated in bold font. The predicted signal peptides are labelled in pale colour and the predicted transmembrane domains are marked by black bars above the alignment. Asterisks (*) denote identical residues, double dots (:) denote conserved substitutions based on amino acid biochemical similarity and single dots (.) denote semi-conserved substitution. The similarity rate is derived from the overall amino acid biochemical similarity of the compared proteins.
w Bm LspA recombinant clone is active in a complementation test
To confirm activity of LspA, the recombinant clone was tested using a complementation assay in an E. coli strain with a ts LspA mutant. The point mutation in the lspA gene of E. coli Y815 strain confers temperature sensitivity to cell growth. At the non-permissive temperature (42°C), cell growth is hindered by the accumulation of prolipoproteins due to inactivation of LspA enzyme [22]. The plasmids pET21-Ec LspA.His (PC, positive control), pET21a-w BmLspA.His (T1: test 1), pGEX5.1-GST.w BmLspA.His (T2, test 2), pET21a (NC1, negative control 1) and pGEX5.1 (NC2, negative control 2) were transformed into E. coli strain Y815 for functional complementation tests of growth. NC1, NC2 and T2 transformants did not grow at 42°C, while both PC and T1 grew and formed visual colonies at the non-permissive temperature, confirming the w Bm lspA gene (T1) is a functional LspA enzyme (Table 1).
Globomycin resistance assays confirm w BmLspA activity
Globomycin resistance assays in E. coli were conducted to further test the function of the w Bm lspA gene. LspA inhibition by globomycin leads to the accumulation of unprocessed prolipoproteins in the inner cell membrane and thus hinders cell growth [16, 23, 24], while the inhibition can be overcome by over-expression of a functional lspA gene from other bacterial sources, which confers globomycin resistance [21, 25–27]. To confirm this with the w Bm lspA gene constructs, the plasmids NC1, PC, T1, NC2 and T2 in T7 Express E. coli were tested in globomycin resistance assays. With one exception, in the group without IPTG induction, all transformants grew well in the absence of globomycin and showed arrested growth when treated with 100 μg/ml globomycin. The exception was the PC transformant (E. coli transformed with pET21a-Ec LspA.His), which conferred globomycin resistance in the absence of induction by IPTG (Figure 2). The significant "leaky" expression of Ec LspA.His was also detected by western blot analysis (Figure 3). In the IPTG induction set, the cell growth in both PC and T2 transformants (E. coli transformed with pGEX5.1-GST.w BmLspA.His) was dramatically inhibited even without addition of globomycin, suggesting that a relatively high level of overexpression of Ec LspA.His and GST.w BmLspA.His proteins alone could hinder normal cell growth. w BmLspA.His (T1) was expressed when induced with IPTG, but did not lead to the significant growth inhibition observed for PC and T2 transformants. In the IPTG induction group, when treated with 100 μg/ml globomycin, E. coli cells with overexpressed Ec LspA.His (PC), w BmLspA.His (T1) or GST.w BmLspA.His (T2) conferred strong globomycin resistance compared to negative controls (NC1 and NC2) (Figure 3). A synthetic w Bm lspA gene was created for improving gene expression level in both E. coli Y815 and T7 Express E. coli. However, no detectable improvement was observed in both E. coli cell strains (data not shown).
Globomycin resistance assays of w Bm lspA -transformed T7 express E. coli cells. Cell growth was measured at 600 nm (OD600). NC1: pET21a vector only; PC: pET21a-Ec LspA.His; T1: pET21a-w BmLspA.His; NC2: pGEX5.1 vector only; T2: pGEX5.1-GST.w BmLspA.His. Starting OD is 0.1. Cells grow at 16°C for 16 hours.
Expression of recombinant LspA proteins in T7 express E. coli with and without IPTG induction. w BmLspA and EcLspA transformed E. coli cell lysates (~ 200 μg total protein/well) were loaded. The expressed recombinant LspA proteins were detected with Mouse anti-His monoclonal antibody (details in methods and materials). For each construct of samples without (w/o) and with (w/) IPTG induction are shown, Lane 1 & 2: E. coli cell/pET21a (NC1), Lane 3 & 4: E. coli cell/pET21a-Ec LspA.His (PC), Lane 5 & 6: E. coli cell/pET21a-w BmLspA.His (T1), Lane 7 & 8: E. coli cell/pGEX5.1 (NC2), Lane 9 & 10: E. coli cell/pGEX5.1-GST.w BmLspA.His (T2). The predicted molecular weights of recombinant w BmLspA.His, Ec LspA.His and GST.w BmLspA.His proteins are 19, 20 and 44 kDa, respectively.
Globomycin affects Wolbachia growth in a cell-based assay
We investigated whether globomycin affected Wolbachia growth in a cell-based assay using Wolbachia-infected insect cells (C6/36Wp; [28]). Cultures were treated with globomycin in a 96-well plate format and Wolbachia growth was determined by qPCR targeting the Wolbachia 16S rRNA gene. As shown in Figure 4A, Wolbachia 16S copy numbers were significantly reduced when compared to the DMSO (1%) control (P < 0.01). This reduction was dose-dependent and equated to log reductions of 1.33, 1.75 and 1.97 for 50, 80 and 100 μg/ml concentrations respectively at day 10 after initiation of treatment, which increased to between 1.88 and 2.48 by day 16. The reduction in 16S gene copy numbers achieved with globomycin at 20 μg/ml, although significant (P < 0.05), did not extend beyond a 0.55 log-drop throughout the test period. A. albopictus 18S rRNA gene copy numbers were also analyzed by qPCR in order to check for any effect of globomycin on cell growth (Figure 4B) and to normalize the 16S data by producing ratios of 16S to 18S gene copy numbers (Figure 4C). Globomycin had no significant effect on cell growth at concentrations up to and including 80 μg/ml (Figure 4B), although 100 μg/ml globomycin did have a small but significant effect on cell growth (P < 0.05). The normalization of 16S copy numbers to 18S copy numbers did not affect the overall results (Figure 4C).
Dynamics of Wolbachia and cell response to globomycin over 16 days. Wolbachia growth was measured by qPCR targeting the 16S rRNA gene (A), C6/36Wp cell growth was measured by targeting the 18S rRNA gene (B) and data was normalized by calculating the ratio of 16S copies to 18S copies (C). Error bars represent standard deviations from triplicate cultures.
Globomycin affects lipoprotein processing
As globomycin targets the enzyme signal peptidase II in the lipoprotein biosynthesis pathway [16], any inhibition that occurs should prevent the cleavage of the signal peptide and thus result in an accumulation of the prolipoprotein. Cells treated with globomycin were used to assess the effect of this drug on lipoprotein processing in Wolbachia. A western blot using antibody raised against recombinant w Bm PAL was conducted on lysates of cells treated with globomycin or vehicle-control for 24 hours. As shown in Figure 5, globomycin treatment inhibited processing of the precursor of the Wolbachia lipoprotein PAL in a dose-dependent manner. When compared to the vehicle control which shows a band of approximately 15 kDa representing the mature lipoprotein, the globomycin treated cells also showed an additional larger band of approximately 18 kDa. This suggests that the target of globomycin in Wolbachia is LspA and indicates that the resulting inhibition of growth and death of bacteria is due to the accumulation of prolipoprotein in the cytoplasmic membrane [16, 23, 24].
Inhibitory effect of globomycin on Wolbachia PAL processing. C6/36Wp cells were incubated with three concentrations of globomycin or DMSO control for 24 hours and extracts were subjected to Western blotting using antibodies to Wolbachia PAL. Cells treated with globomycin have 2 PAL proteins detectable, indicating inhibition of full lipoprotein processing.
The effect of globomycin on the motility and viability of B. malayi in vitro
The effect of this compound on nematode motility was examined by incubating B. malayi adult females with globomycin in vitro. Motility was assessed daily using a method described by Rao and Weil [29]. Over the test period of 10 days, globomycin reduced motility in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 6A). The highest concentration of globomycin (100 μg/ml) rendered the majority of worms inactive by day 3. Globomycin used at a concentration of 50 μg/ml was also found to render the majority of the nematodes immotile by day 7 (Figure 6A). A similar dose dependent reduction in motility was observed in male worms (data not shown).
The effect of globomycin on B. malayi motility and viability. The motility of worms cultured in the presence of globomycin was scored daily and is presented as percentages of the control (1% DMSO) motility (A). At the end of the test period worms were used in an MTT assay to assess effects on nematode viability (B). Remaining worms were used for qPCR analysis of Wolbachia numbers per worm (data not shown).
At the end of the motility test period, worms were collected for use in an MTT assay to assess viability. Figure 6B shows reduced viability of those exposed to the higher concentrations of globomycin, which at a concentration of 100 μg/ml globomycin was significantly reduced compared to vehicle-treated controls at 10 days post-treatment (P < 0.05). Furthermore, the MTT result for this treated group was not significantly different from that obtained from dead worm controls (P = 0.29) suggesting that globomycin at this concentration is able to kill adult B. malayi in vitro.
Discussion
One of the objectives of the A-WOL consortium is to identify and validate novel drug targets of Wolbachia to develop high throughput target based drug screening assays. Validating a potential drug target in Wolbachia, however, is problematic as these bacteria are not amenable to genetic manipulation. We have therefore used complementation assays of mutant E. coli to validate enzymatic function and a pharmacological inhibitor of lipoprotein biosynthesis, globomycin, to determine the effect of inhibition of lipoprotein biosynthesis on Wolbachia in a whole organism cell-based drug screening assay.
w Bm contains two genes encoding enzymes of the lipoprotein biosynthesis pathway [15, 30]: lgt, prolipoprotein diacylglyceryl transferase and lspA, lipoprotein signal peptidase. The third enzyme in the pathway responsible for triacylation, typically found in other bacteria, appears to be absent from Wolbachia. Although Wolbachia is intractable to genetic manipulation we were able to confirm that Wolbachia LspA is functional in E. coli, despite having only 25% identity and 49% amino acid similarity to its E. coli homolog. w Bm LspA has retained the conserved catalytic residues required for function and can genetically complement deficient growth of an lspA ts E. coli mutant. Globomycin is a known inhibitor of LspA and overexpression of Wolbachia LspA in wild-type E. coli conferred resistance to this compound allowing us to conclude that the expressed gene was functional.
We used a ts E. coli LspA mutant to confirm the functionality of the w BmLspA gene (Table 1). As expected, the N-terminal GST-fused full-length w BmLspA.His (T2) cannot rescue the ts mutant (Table 1); likely due to the loss of signal peptide at its N-terminus, indicating that proper subcellular localization of LspA is crucial for its functional activity. However, the misplaced GST.w BmLspA.His still conferred strong globomycin resistance, although its overexpression appeared to be toxic to the E. coli cell even without addition of globomycin (Figure 2). This may imply that the mis-localized GST.w BmLspA.His (T2) still maintains a structural specificity for globomycin binding. However, after removal of the signal peptide, GST-fused mature w BmLspA.His totally lost resistance to globomycin (data not shown).
The leaky expression of Ec LspA.His (PC) conferred strong resistance to globomycin without significantly reducing E. coli cell growth, while its excessive overexpression, induced by IPTG, although still conferring globomycin resistance, led to striking cell growth inhibition (Figure 2). This might suggest that the expression of LspA is required and at the same time strictly regulated for achieving normal cell growth, which is in line with the fact that codon-optimized w Bm LspA gene did not improve its expression in E. coli.
Lipoproteins perform multiple essential structural and functional roles in bacteria. For example, the lipoprotein PAL is not only involved in the maintenance of outer membrane integrity [31] but has also been demonstrated to be involved in the uptake of nutrients across the membrane of Pseudomonas putida[32] and required for virulence in Haemophilus ducreyi infection of humans [33]. Therefore the inhibition of lipoprotein biosynthesis is likely to affect multiple functions in bacteria. Globomycin is a 19-membered depsipeptide antibiotic isolated from actinomycetes strains [18–20], which targets LspA. Although not commercially available for use as an antibiotic, it has been widely used as a research tool to determine the requirement of lipoprotein biosynthesis for a range of biological features of bacteria [34, 35]. In addition to using globomycin to assess the functionality of the Wolbachia LspA enzyme in transformed E. coli, we used this compound to assess the importance of the lipoprotein biosynthesis pathway in a Wolbachia cell line (C6/36Wp) and in B. malayi adult nematodes cultured in vitro.
The C6/36Wp system is currently the primary screen used in the A-WOL drug discovery program for Wolbachiahttp://www.a-wol.com, and aims to discover novel compounds with anti-Wolbachia activity. In this study, globomycin was shown to have a dose-dependent anti-Wolbachia effect on the C6/36Wp cell line, demonstrating a new class of antibiotic active against Wolbachia.
Globomycin acts by an inhibition of a prolipoprotein processing enzyme, resulting in an accumulation of the prolipoprotein in the cell envelope [16, 23, 24] and this inhibition occurs through the non-competitive binding of globomycin to the lipoprotein signal peptidase and not by binding to the substrate [16]. Treatment of Wolbachia cell cultures with globomycin resulted in the accumulation of prolipoprotein suggesting a similar mode of action occurs in Wolbachia. Furthermore, globomycin affected both the processing of OmpA in Ehrlichia chaffeensis, an obligate intracellular bacterium closely related to Wolbachia pipientis, and its ability to infect HL-60 cells [35].
Globomycin was also shown to have adverse effects on the motility and viability of adult female and male B. malayi nematodes in vitro. QPCR analysis did not, however, demonstrate any differences in Wolbachia load between treated groups (data not shown) suggesting that the Wolbachia qPCR assay may not have sufficient sensitivity to detect effects on Wolbachia load over this time frame in nematodes, perhaps due to the slower growth rate of nematode Wolbachia compared to insect Wolbachia in cell culture. Notably doxycycline also fails to produce a reduction in Wolbachia load over this time frame. An alternative explanation is that inhibition of Wolbachia lipoprotein biosynthesis is sufficient to affect nematode motility and viability independent of or prior to any effect on Wolbachia load. We also cannot rule out a direct effect of globomycin on nematode motility and viability and alternative mechanisms of action have been suggested in Mycobacterium tuberculosis[36], where globomycin was found to be active against this bacterium independently of its effect on LspA.
Conclusions
In summary, in the search for new anti-wolbachial drugs, we have identified and validated the lipoprotein biosynthesis pathway as a target for Wolbachia drug discovery and development and shown that globomycin, a drug targeting lipoprotein signal peptidase, is active against Wolbachia.
Methods
Globomycin
Globomycin was obtained as a kind gift from Professor Masatoshi Inukai of International University of Health and Welfare, Tochigi, Japan. A stock solution of 10 mg/ml was made in dimethylsulphoxide (DMSO) and stored in single-use aliquots at -80°C. Before use, the stock solution was diluted in the appropriate culture medium to the appropriate concentrations.
LspA gene cloning
B. malayi DNA (including Wolbachia DNA) was extracted with DNeasy extraction kit (Qiagen) from live adult worms purchased from TRS Labs, Athens, GA. Primers were designed with restriction endonuclease sites (Additional File 1; Table S1), based on the available w Bm and E. coli lspA gene sequences (Genbank accession numbers AE017321 and NC_000913, respectively). The full-length lspA genes from B. malayi Wolbachia (w Bm) and E. coli were amplified by PCR using Phusion polymerase (New England Biolabs, NEB), and were cloned into the expression vector pET21a+ with a C-terminal 6XHis tag (Novagen) after digestion with corresponding restriction endonucleases (NEB). The generated plasmids were named as pET21a-w BmLspA.His and pET21a-Ec LspA.His, respectively. w BmlspA gene with an added C-terminal 6XHis tag was also cloned into the expression vector pGEX5.1 (GE Healthcare) with a N-terminal GST fusion, named as pGEX5.1-GST.w BmLspA.His. A codon-optimized version of w BmlspA was designed by DNAworks oligonucleotide designing software [37], synthesized using USER cloning methods [38] and cloned into pET21a+ vector for improvement of gene expression. The T7 Express competent E. coli strain 2566 (NEB) was used as a host for plasmid recipients. The sequences of the lspA gene inserts were verified by DNA sequencing.
Recombinant LspA protein expression in E. coli
Expression of C-terminally 6XHis tagged w BmLspA, Ec LspA, and GST.w BmLspA recombinant proteins in T7 Express E. coli strain with and without isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) inductions was detected by Mouse anti-His tag monoclonal antibody and subsequent secondary horseradish peroxidase (HRP) conjugated Rabbit anti-Mouse IgG antibody (Novagen) in combination with the use of LumiGLO(r) chemiluminescent reagent and peroxide (Cell Signaling Technology, CST).
ts E. coli lspA mutant
E. coli strain Y815 is a type II lipoprotein signal peptidase [21] temperature sensitive (ts) mutant, containing a pHY001 vector, which carries a tetracycline resistance gene (tetR ) and a lpp gene encoding a major outer membrane lipoprotein inducible by IPTG [22].
Complementation assays in E. coli
The constructs pET21a-w BmLspA.His, pET21a-Ec LspA.His, and pGEX5.1-GST.w BmLspA.His, along with the vector only controls, pET21a and pGEX5.1, were transformed into E. coli Y815 cells with appropriate antibiotic selection. The E. coli Y815 ts lspA mutant grows normally at 30°C, but not at 42°C for colony formation. The detailed protocol is described in [21].
Sequence analysis of Wolbachia lspA genes
The LspA protein sequences from different Wolbachia strains and other reference species (shown in Figure 1) were retrieved from NCBI Genbank database [39] via protein-protein BLAST similarity searches and were aligned using CLUSTALX 1.83 [40]. The sequences in the alignment were further analyzed by Genedoc 2.6 [41] for calculating percentage of amino acid identity/similarity, TMHMM 2.0 [42] for prediction of transmembrane domains, and SignalP 3.0 [43] for predicting signal peptide.
Globomycin resistance assays in E. coli
The experiments were devised and developed from a previous strategy [21]. T7 Express E. coli were transformed with plasmids pET21a-w BmLspA.His, pET21a-Ec LspA.His, and pGEX5.1-GST.w BmLspA.His, along with the vector only controls pET21a and pGEX5.1. Transformants were grown to 0.6 ~ 1.0 OD600 at 37°C in Luria-Bertani (LB) medium containing 100 μg/ml ampicillin before being diluted to 0.1 OD600. The diluted samples were equally divided into IPTG (0.1 mM) induced and non-induced groups. In each group, the samples were further divided into globomycin treatment (100 μg/ml) and non-treatment subgroups. All samples were grown at 16°C for 16 hours with shaking. The samples with high cell density were diluted before measurement by spectrophotometer at 600 nm for accuracy. The samples had two replicates in each experiment and three independent experiments were carried out in total.
Wolbachia cell-based drug screening assay
An Aedes albopictus cell line C6/36 (ATCC number CRL-1660) stably infected with Wolbachia pipientis w AlbB (C6/36Wp) was routinely cultured in Leibovitz-15 medium containing 2 mM L-glutamine, 5% foetal bovine serum, 1% non-essential amino acids and 2% tryptose phosphate broth at 26°C [28]. For drug assays, C6/36Wp cells were cultured in 96-well microtitre plates at a concentration of 10,000 cells per well overnight. Globomycin and vehicle (DMSO) controls were added in triplicate at the appropriate concentration, based on previous publications [17, 19, 21], the following day and replaced every 4 days. Samples were collected at appropriate timepoints by washing once in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) then adding 150 μl Wizard® SV Lysis Buffer (Promega) to each well. Lysates were stored at -80°C for processing at a later date.
Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
Genomic DNA was prepared from cell lysates using the Wizard(r) SV 96 Genomic DNA Purification System (Promega) according to the manufacturer's instructions and eluted in 100 μl water. qPCR targeting the 16S rRNA gene of Wolbachia and the 18S rRNA gene of the cell was conducted according to that described by [44] with minor modifications. Briefly, reaction mixtures consisted of a pair of primers (5'-TTGCTATTAGATGAGCCTATATTAG-3' and 5'-GTGTGGCTGATCATCCTCT-3' for 16S ribosomal DNA qPCR and 5'-CCGTGATGCCCTTAGATGTT-3' and 5'-ATGCGCATTTAAGCGATTTC-3' for 18S ribosomal qPCR) at 200 nM each, 1 × SYBR Green reaction mix (Qiagen) and 2 μl DNA in the case of 16S qPCR or 1 μl DNA for 18S qPCR. Quantitative DNA standards were prepared as serial dilutions from stock single-stranded oligonucleotides representing the full-length amplicons (Sigma Genosys) and used at 5 × 106 to 5 × 100 copies [44], in duplicate reactions. Assays were performed on a DNA Engine PTC-200 thermocycler (MJ Research, GRI) with Chromo4 real-time PCR detection system (Bio-Rad) using the following conditions: denaturation at 95°C for 15 min followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 15 sec, 55°C for 30 sec and 72°C for 15 sec. Melting curve analysis was performed between 50°C and 95°C to confirm specificity. Copy number was calculated from the standard curve by standard methods.
Western blot analysis
C6/36Wp cells were cultured in duplicate as described for the cell-based drug assays. Following 24 hours of globomycin treatment, cells were washed once in PBS then lysed by adding 25 μl of ice-cold RIPA buffer (Pierce) containing freshly added protease inhibitor solution (GE Healthcare) and incubating at room temperature for 5 min. Duplicate cultures were pooled and centrifuged at 16,000 × g for 15 min and the lysates were collected. Cell lysates were diluted in 2 × Laemmli sample buffer containing reducing agents (Sigma Aldrich) and incubated at 96°C for 10 min. 25 μl of samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE using 15% Tris-HCl gels (Bio-Rad) and protein bands were transferred onto a 0.45 μm PVDF membrane. After blocking for 2 h in 4% milk diluted in Tris-buffered saline (TBS) containing 0.1% Tween, membranes were incubated overnight at 4°C in affinity-purified anti-B. malayi Wolbachia PAL (w BmPAL) antibody [15] diluted 1 in 5,000 in blocking buffer. Membranes were washed at least four times in TBS 0.1% Tween then incubated with secondary antibody (goat-anti-rabbit-HRP, Perkin Elmer) diluted 1 in 5,000 for one hour at room temperature. Following washing, the blots were developed using the Supersignal West system (Pierce).
In vitro B. malayi assays
Adult B. malayi were obtained from TRS Laboratories, Athens, Georgia. Female and male adult worms were cultured in 12-well plates, five worms per well, three wells per group in 2.5 ml RPMI containing 10% foetal bovine serum and penicillin-streptomycin (Invitrogen, 200 U/ml/200 μg/ml final concentration). Globomycin and vehicle controls were added the following day and motility was scored daily in a blinded manner using the scoring system described by [29]. The assay was terminated at day 10 and worms were used in an MTT assay to assess viability [45]. Worms were added singly to wells of a 96 well plate and washed with 200 μl PBS. 200 μl MTT was added at a final concentration of 0.5 mg/ml in PBS and the plate was incubated for two hours at 37°C with 5% CO2. MTT solution was removed and worms were washed twice with PBS then incubated in 200 μl of DMSO for one hour at 37°C, 5% CO2 in order to solubilise the formazan product. The plate was read at 490 nm using DMSO alone as a blank. Frozen B. malayi were used as non-viable controls. Remaining worms were stored at -80°C for DNA extraction at a later date.
Statistical analysis
Differences between groups were assessed using Student's T test.
References
Taylor MJ, Bandi C, Hoerauf A: Wolbachia bacterial endosymbionts of filarial nematodes. Adv Parasitol. 2005, 60: 245-284. 10.1016/S0065-308X(05)60004-8.
Debrah AY, Mand S, Marfo-Debrekyei Y, Batsa L, Pfarr K, Buttner M, Adjei O, Buttner D, Hoerauf A: Macrofilaricidal effect of 4 weeks of treatment with doxycycline on Wuchereria bancrofti. Trop Med Int Health. 2007, 12: 1433-1441. 10.1111/j.1365-3156.2007.01949.x.
Debrah AY, Mand S, Marfo-Debrekyei Y, Batsa L, Pfarr K, Lawson B, Taylor M, Adjei O, Hoerauf A: Reduction in levels of plasma vascular endothelial growth factor-A and improvement in hydrocele patients by targeting endosymbiotic Wolbachia sp. in Wuchereria bancrofti with doxycycline. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2009, 80: 956-963.
Debrah AY, Mand S, Marfo-Debrekyei Y, Larbi J, Adjei O, Hoerauf A: Assessment of microfilarial loads in the skin of onchocerciasis patients after treatment with different regimens of doxycycline plus ivermectin. Filaria J. 2006, 5: 1-10.1186/1475-2883-5-1.
Debrah AY, Mand S, Specht S, Marfo-Debrekyei Y, Batsa L, Pfarr K, Larbi J, Lawson B, Taylor M, Adjei O, Hoerauf A: Doxycycline reduces plasma VEGF-C/sVEGFR-3 and improves pathology in lymphatic filariasis. PLoS Pathog. 2006, 2: e92-10.1371/journal.ppat.0020092.
Hoerauf A, Mand S, Fischer K, Kruppa T, Marfo-Debrekyei Y, Debrah AY, Pfarr KM, Adjei O, Buttner DW: Doxycycline as a novel strategy against bancroftian filariasis-depletion of Wolbachia endosymbionts from Wuchereria bancrofti and stop of microfilaria production. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2003, 192: 211-216. 10.1007/s00430-002-0174-6.
Hoerauf A, Mand S, Volkmann L, Buttner M, Marfo-Debrekyei Y, Taylor M, Adjei O, Buttner DW: Doxycycline in the treatment of human onchocerciasis: Kinetics of Wolbachia endobacteria reduction and of inhibition of embryogenesis in female Onchocerca worms. Microbes Infect. 2003, 5: 261-273. 10.1016/S1286-4579(03)00026-1.
Hoerauf A, Specht S, Buttner M, Pfarr K, Mand S, Fimmers R, Marfo-Debrekyei Y, Konadu P, Debrah AY, Bandi C: Wolbachia endobacteria depletion by doxycycline as antifilarial therapy has macrofilaricidal activity in onchocerciasis: a randomized placebo-controlled study. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2008, 197: 295-311. 10.1007/s00430-007-0062-1.
Hoerauf A, Specht S, Marfo-Debrekyei Y, Buttner M, Debrah AY, Mand S, Batsa L, Brattig N, Konadu P, Bandi C: Efficacy of 5-week doxycycline treatment on adult Onchocerca volvulus. Parasitol Res. 2009, 104: 437-447. 10.1007/s00436-008-1217-8.
Mand S, Pfarr K, Sahoo PK, Satapathy AK, Specht S, Klarmann U, Debrah AY, Ravindran B, Hoerauf A: Macrofilaricidal activity and amelioration of lymphatic pathology in bancroftian filariasis after 3 weeks of doxycycline followed by single-dose diethylcarbamazine. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2009, 81: 702-711. 10.4269/ajtmh.2009.09-0155.
Supali T, Djuardi Y, Pfarr KM, Wibowo H, Taylor MJ, Hoerauf A, Houwing-Duistermaat JJ, Yazdanbakhsh M, Sartono E: Doxycycline treatment of Brugia malayi-infected persons reduces microfilaremia and adverse reactions after diethylcarbamazine and albendazole treatment. Clin Infect Dis. 2008, 46: 1385-1393. 10.1086/586753.
Taylor MJ, Makunde WH, McGarry HF, Turner JD, Mand S, Hoerauf A: Macrofilaricidal activity after doxycycline treatment of Wuchereria bancrofti: a double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2005, 365: 2116-2121. 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)66591-9.
Turner JD, Mand S, Debrah AY, Muehlfeld J, Pfarr K, McGarry HF, Adjei O, Taylor MJ, Hoerauf A: A randomized, double-blind clinical trial of a 3-week course of doxycycline plus albendazole and ivermectin for the treatment of Wuchereria bancrofti infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2006, 42: 1081-1089. 10.1086/501351.
Turner JD, Tendongfor N, Esum M, Johnston KL, Langley RS, Ford L, Faragher B, Specht S, Mand S, Hoerauf A: Macrofilaricidal activity after doxycycline only treatment of Onchocerca volvulus in an area of Loa loa co-endemicity: a randomized controlled trial. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2010, 4: e660-10.1371/journal.pntd.0000660.
Turner JD, Langley RS, Johnston KL, Gentil K, Ford L, Wu B, Graham M, Sharpley F, Slatko B, Pearlman E, Taylor MJ: Wolbachia lipoprotein stimulates innate and adaptive immunity through Toll-like receptors 2 and 6 to induce disease manifestations of filariasis. J Biol Chem. 2009, 284: 22364-22378. 10.1074/jbc.M901528200.
Dev IK, Harvey RJ, Ray PH: Inhibition of prolipoprotein signal peptidase by globomycin. J Biol Chem. 1985, 260: 5891-5894.
Lai JS, Philbrick WM, Hayashi S, Inukai M, Arai M, Hirota Y, Wu HC: Globomycin sensitivity of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: effects of mutations affecting structures of murein lipoprotein. J Bacteriol. 1981, 145: 657-660.
Inukai M, Enokita R, Torikata A, Nakahara M, Iwado S, Arai M: Globomycin, a new peptide antibiotic with spheroplast-forming activity. I. Taxonomy of producing organisms and fermentation. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 1978, 31: 410-420.
Inukai M, Nakajima M, Osawa M, Haneishi T, Arai M: Globomycin, a new peptide antibiotic with spheroplast-forming activity. II. Isolation and physico-chemical and biological characterization. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 1978, 31: 421-425.
Nakajima M, Inukai M, Haneishi T, Terahara A, Arai M, Kinoshita T, Tamura C: Globomycin, a new peptide antibiotic with spheroplast-forming activity. III. Structural determination of globomycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 1978, 31: 426-432.
Rahman MS, Ceraul SM, Dreher-Lesnick SM, Beier MS, Azad AF: The lspA gene, encoding the type II signal peptidase of Rickettsia typhi: transcriptional and functional analysis. J Bacteriol. 2007, 189: 336-341. 10.1128/JB.01397-06.
Yamagata H, Ippolito C, Inukai M, Inouye M: Temperature-sensitive processing of outer membrane lipoprotein in an Escherichia coli mutant. J Bacteriol. 1982, 152: 1163-1168.
Hussain M, Ichihara S, Mizushima S: Accumulation of glyceride-containing precursor of the outer membrane lipoprotein in the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli treated with globomycin. J Biol Chem. 1980, 255: 3707-3712.
Inukai M, Takeuchi M, Shimizu K, Arai M: Mechanism of action of globomycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 1978, 31: 1203-1205.
De Greeff A, Hamilton A, Sutcliffe IC, Buys H, Van Alphen L, Smith HE: Lipoprotein signal peptidase of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Microbiology. 2003, 149: 1399-1407. 10.1099/mic.0.26329-0.
Paitan Y, Orr E, Ron EZ, Rosenberg E: A nonessential signal peptidase II (Lsp) of Myxococcus xanthus might be involved in biosynthesis of the polyketide antibiotic TA. J Bacteriol. 1999, 181: 5644-5651.
Pragai Z, Tjalsma H, Bolhuis A, van Dijl JM, Venema G, Bron S: The signal peptidase II (Isp) gene of Bacillus subtilis. Microbiology. 1997, 143 (Pt 4): 1327-1333. 10.1099/00221287-143-4-1327.
Turner JD, Langley RS, Johnston KL, Egerton G, Wanji S, Taylor MJ: Wolbachia endosymbiotic bacteria of Brugia malayi mediate macrophage tolerance to TLR- and CD40-specific stimuli in a MyD88/TLR2-dependent manner. J Immunol. 2006, 177: 1240-1249.
Rao R, Weil GJ: In vitro effects of antibiotics on Brugia malayi worm survival and reproduction. J Parasitol. 2002, 88: 605-611.
Foster J, Ganatra M, Kamal I, Ware J, Makarova K, Ivanova N, Bhattacharyya A, Kapatral V, Kumar S, Posfai J: The Wolbachia genome of Brugia malayi: endosymbiont evolution within a human pathogenic nematode. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3: e121-10.1371/journal.pbio.0030121.
Cascales E, Bernadac A, Gavioli M, Lazzaroni JC, Lloubes R: Pal lipoprotein of Escherichia coli plays a major role in outer membrane integrity. J Bacteriol. 2002, 184: 754-759. 10.1128/JB.184.3.754-759.2002.
Llamas MA, Rodriguez-Herva JJ, Hancock RE, Bitter W, Tommassen J, Ramos JL: Role of Pseudomonas putida tol-oprL gene products in uptake of solutes through the cytoplasmic membrane. J Bacteriol. 2003, 185: 4707-4716. 10.1128/JB.185.16.4707-4716.2003.
Fortney KR, Young RS, Bauer ME, Katz BP, Hood AF, Munson RS, Spinola SM: Expression of peptidoglycan-associated lipoprotein is required for virulence in the human model of Haemophilus ducreyi infection. Infect Immun. 2000, 68: 6441-6448. 10.1128/IAI.68.11.6441-6448.2000.
Lundemose AG, Rouch DA, Penn CW, Pearce JH: The Chlamydia trachomatis Mip-like protein is a lipoprotein. J Bacteriol. 1993, 175: 3669-3671.
Huang H, Lin M, Wang X, Kikuchi T, Mottaz H, Norbeck A, Rikihisa Y: Proteomic analysis of and immune responses to Ehrlichia chaffeensis lipoproteins. Infect Immun. 2008, 76: 3405-3414. 10.1128/IAI.00056-08.
Banaiee N, Jacobs WR, Ernst JD: LspA-independent action of globomycin on Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007, 60: 414-416. 10.1093/jac/dkm223.
Hoover DM, Lubkowski J: DNAWorks: an automated method for designing oligonucleotides for PCR-based gene synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30: e43-10.1093/nar/30.10.e43.
Bitinaite J, Rubino M, Varma KH, Schildkraut I, Vaisvila R, Vaiskunaite R: USER friendly DNA engineering and cloning method by uracil excision. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35: 1992-2002. 10.1093/nar/gkm041.
NCBI Genbank Database. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov]
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG: The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25: 4876-4882. 10.1093/nar/25.24.4876.
Genedoc 2.6. [http://www.nrbsc.org/gfx/genedoc/]
TMHMM 2.0. [http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/]
Emanuelsson O, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H: Locating proteins in the cell using TargetP, SignalP and related tools. Nat Protoc. 2007, 2: 953-971. 10.1038/nprot.2007.131.
Makepeace BL, Rodgers L, Trees AJ: Rate of elimination of Wolbachia pipientis by doxycycline in vitro increases following drug withdrawal. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006, 50: 922-927. 10.1128/AAC.50.3.922-927.2006.
Townson S, Tagboto S, McGarry HF, Egerton GL, Taylor MJ: Onchocerca parasites and Wolbachia endosymbionts: evaluation of a spectrum of antibiotic types for activity against Onchocerca gutturosa in vitro. Filaria J. 2006, 5: 4-10.1186/1475-2883-5-4.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Professor Masatoshi Inukai of International University of Health and Welfare, Tochigi, Japan for providing globomycin. We are also grateful to Drs. M. Sayeedur Rahman and Abdu F. Azad (University of Maryland, School of Medicine) for sending us E. coli strain Y815. We also appreciate Drs. Donald Comb, Bill Jack, and Tilde Carlow for scientific encouragement and Dr. Jeremy Foster for discussions and critical proofreading of the manuscript. This work was supported by a grant awarded to Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (the A-WOL consortium).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
KLJ participated in the design of the study, conducted the cell-based assays and qPCR analysis, western blot analysis and drafted the manuscript. BW participated in the design of the study, conducted the cloning and E. coli experiments and helped to draft the manuscript. AG performed the B. malayi assays and assisted with data analysis. LF participated in the design of the study and assisted with data analysis and interpretation. BES co-designed the study and helped to draft the manuscript. MJT designed and co-ordinated the study and helped to draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Kelly L Johnston, Bo Wu contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
13071_2010_227_MOESM1_ESM.PPT
Additional file 1: Table S1 - Wolbachia ( w Bm) and E. coli LspA gene specific primers used. Wolbachia (w Bm) and E. coli LspA gene specific primers were used for PCR amplification of the full-length coding sequences for cloning into pET21a+ vector and pGEX5.1 vector. Primers were designed based on sequence information available in Genbank http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Restriction enzyme sites in primers are underlined. Abbreviations used: w Bm: Wolbachia endosymbiont of Brugia malayi, Ec: E. coli, f: forward primer, r: reverse primer, LspA: type II lipoprotein signal peptidase. (PPT 102 KB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Johnston, K.L., Wu, B., Guimarães, A. et al. Lipoprotein biosynthesis as a target for anti-Wolbachia treatment of filarial nematodes. Parasites Vectors 3, 99 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-3-99
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-3-99