Abstract
Introduction
Early cholecystectomy within 72 hours has been shown to be superior to late or delayed cholecystectomy with regard to outcome and cost of treatment. Recently, immediate cholecystectomy within 24 hours of onset of symptom was proposed as standard procedure for the management of fit patients presenting with acute cholecystitis. We sort to find out if there are any differences in surgical outcomes between patients managed within 24 h and those managed 25-72 h following symptom begin for acute cholecystitis.
Patients and methods
A retrospective analysis was performed. The outcomes of patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy within 24 h were compared to those of patients managed 25-72 h following symptom onset for acute cholecystitis.
Results
35 patients managed 25-72 h following begin of symptoms were matched with 35 patients with similar baseline features, medical comorbidities and disease severity managed within 24 hours of symptom onset. There were no significant differences in the duration of surgery, postoperative complications, rate of conversion and length of hospital stay.
Conclusion
Immediate laparoscopic cholecystectomy for acute cholecystitis within 24 hour of symptom onset is not superior to surgery 25–72 hour after symptoms begin. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy for acute cholecystitis therefore can be safely performed anytime within the golden 72 h.
Similar content being viewed by others

Introduction
Acute cholecystitis (AC) is a common diagnosis in the surgical practice with a clear indication for surgery. Although widely discussed in the past, unequivocal evidence exists supporting the superiority of early laparoscopic cholecystectomy within 72 hours over delayed LC with respect to outcome and cost of treatment [1–8]. This trend was confirmed in a recently published randomized study in patients managed within 24 hours of admission [9]. Cholecystectomy however, may not always be possible within 24 hours of admission for many different reasons. In such cases, surgery should be performed within 72 hours as recommended in several guidelines [10–12]. The aim of this study was to compare the outcomes of patients undergoing LC within 24 h of symptom begin on one hand to those of patients managed 25 to 72 h after symptom begin for AC on the other hand.
Patients and methods
A retrospective review of the charts of patients undergoing cholecystectomy for AC from January 2009 to December 2013 in the department of surgery of a primary care hospital in Germany was performed. Baseline characteristics including age, sex, body mass index (BMI) and medical comorbidities as defined by the American Society of Anesthesiology (ASA) were retrieved for each patient.
Acute cholecystitis was diagnosed as outlined in the Tokyo guidelines [13, 14]. The diagnosis was confirmed during surgery and following histopathology. Only patients managed within 72 hours of symptom begin were included for analysis. All patients were placed on intravenous antibiotics upon admission which was continued after surgery. Perioperative data including the duration of anesthesia, the duration of surgery, conversion to open surgery, postoperative complications and the length of postoperative hospital stay were retrieved from surgical documentation sheets, surgeon’s notes and discharge records.
All surgeries in this study were performed by experienced attending surgeons. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy [15] was carried out using four incisions with pneumoperitoneum installed via a sub-umbilical mini-laparotomy with the maximum intraabdominal pressure kept at 12 mmHg.
The data collected was analyzed using the Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS®), IBM, version 22. The study population was statistically described using absolute case numbers, percentages, medians and interquartile ranges. Significances were calculated using the Fisher' s exact test with levels of significance set at p < 0.05.
Patients operated upon 25 to 72 h after symptom begin (study group) were matched with regard to baseline and clinical features (same gender, similar ages, disease severity, BMI, ASA and APACHE II Scores) as well as disease severity grade (as outlined in the Tokyo guidelines) with patients operated upon within 24 h following symptom begin (control group). Both groups were comparable with regard to demographic and clinical characteristics.
Primary endpoints included the duration of anesthesia, the duration of surgery and postoperative complications. Secondary endpoints included the length postoperative of hospital stay and hospital mortality.
Results
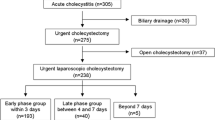
Within the period of investigation 152 cases of AC were managed surgically. The distribution of study population is represented in Figure 1. Thirty-five patients were managed within 25-72 h following symptom begin (study group). Thirty-five patients with similar characteristics to those of the study group were selected from the 105 patients managed within 24 h of symptom begin, Table 1. The demographic characteristics of the study population are summarized in Table 2. Both groups were comparable in all cases.
There was no significant difference in the duration of anesthesia, the duration of surgery and the length of postoperative hospital stay amongst both groups. Five cases (14.2%) were converted to open cholecystectomy in the group managed within 24 h, while 3 cases (8.6%) were converted in the group operated upon within 25-72 h of symptom onset. This difference was not statistically significant, p = 0.23.
Two complications, including one patient with pneumonia and one with wound infection, were recorded in the group operated upon within 24 hours (5.7%). Five complications, including three patients with bile leak, one patient with wound infection and one patient with acute renal failure, were recorded in the group managed between 25-72 h of symptom begin (14.2%). This difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.42), Table 3. There was no mortality in both groups.
Discussion
The optimal timing of surgery for patients with AC has been a topic of controversy in the past. Initially, patients were managed conservatively with the aim of “cooling down” the inflammation, and then perform cholecystectomy weeks later. The heterogeneity of patients suffering from AC and their medical co-morbidities it difficult to standardize treatment [16]. Acute cholecystitis was once considered a relative contraindication for LC at the beginning of the laparoscopic era, mainly due to high rates of complications and conversion. This trend however changed following growing expertise in laparoscopy. Nowadays, laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the gold standard for the management of benign gallbladder disorders and belongs to one of the most commonly performed procedures in surgery [17, 18]. Current data suggest that early LC for acute cholecystitis is superior to late or delayed LC with regard to outcome and cost of treatment [2, 19].
The term „early“ is rather vaguely defined in the literature [20, 21]. In some series, „early“ defines the begin of symptoms while the same term is used with regard to the time of admission in other series. In this study, “early” was defined with respect to symptom begin. Generally speaking, early cholecystectomy is performed within a time interval of 72 h, the so called golden 72 h [22].
In a recently published multi-center randomized study by Gutt et. al., laparoscopic cholecystectomy performed within 24 h of admission was shown to be superior to delayed LC with regard to outcome. The authors concluded that immediate LC should become the treatment of choice for operable patients with AC [9]. This conclusion however, cannot be generally applied at all levels of patient care. Furthermore, immediate LC may not always be possible for different reasons. A number of patients presenting with AC may require special consultations and correction of co-morbidities (e.g. those on oral anticoagulation treatment) before undergoing surgery. Besides, experienced laparoscopic surgeons may not be available within 24 h, as may be the case in quiet a number of primary care hospitals. In such cases, LC should be performed within 72 h.
The aim of this study was to compare the outcomes of patients with AC managed within 24 h of symptom begin to those of patients managed 25-72 h following symptom onset. Data of patients undergoing LC in a primary care hospital in Germany was retrospectively analyzed. Thirty-five patients with AC managed within 24 h were matched (similar baseline characteristics, comorbidities and disease severity) with 35 patients managed 25 - 72 h after symptom onset. All surgeries were performed laparoscopically by surgical attendings with expertise in laparoscopy.
Surgery for acute cholecystitis could be time critical. According to Zhu et. al., gallbladder inflammation during the first 72 h of onset of symptoms may not involve structures within the triangle of Calot [23]. Surgical dissection within this critical period therefore appears easiest due to lack of organized adhesions. Cholecystectomy within this time frame reduces the risk of injury to the structures within the triangle of Calot. This is reflected in the low rates of complication and conversation.
There was no significant difference amongst both groups with respect to the duration of anesthesia and the duration of surgery. Equally, there was no significant difference in the rates of conversion and morbidity between both groups. All cases of conversion were due to the inability to clearly identify the structures within the space of calot.
Interestingly, three cases of bile leak were recorded in the study group. These complications occurred in patients with severity grade III and histopathologic evidence of necrotizing cholecystitis.
We could not prove any difference in outcome between the group managed within 24 h and that managed 25 - 72 h of onset of symptoms. Our results therefore suggest that it is not necessary to perform LC for AC within 24 h following symptom onset.
Taken together, a division of the critical time frame, i.e. the so called “golden 72 h” for the surgical management of acute cholecystitis into a more favorable “golden 24 h” and a less favorable “silver 25-72 h” could not be justified in this series.
This study is limited by the relatively small size of the cohorts and the retrospective study design. Since the study did not include consecutive patients, there might have been some degree of bias in the selection of the patients for the matching group. Therefore the trend shown in this study must be validated in prospective studies with larger case numbers.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy for acute cholecystitis must not be performed within 24 h of admission. The golden 72 h time frame however should be maintained where possible.
References
Gurusamy K, Samraj K, Gluud C, Wilson E, Davidson BR: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials on the safety and effectiveness of early versus delayed laparoscopic cholecystectomy for acute cholecystitis. Br J Surg. 2010, 97 (2): 141-150. 10.1002/bjs.6870.
Gurusamy KS, Koti R, Fusai G, Davidson BR: Early versus delayed laparoscopic cholecystectomy for uncomplicated biliary colic. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013, 6: CD007196-
Lau B, DiFronzo LA: An acute care surgery model improves timeliness of care and reduces hospital stay for patients with acute cholecystitis. Am Surg. 2011, 77 (10): 1318-1321.
Lau H, Lo CY, Patil NG, Yuen WK: Early versus delayed-interval laparoscopic cholecystectomy for acute cholecystitis: a metaanalysis. Surg Endosc. 2006, 20 (1): 82-87. 10.1007/s00464-005-0100-2.
Lee AY, Carter JJ, Hochberg MS, Stone AM, Cohen SL, Pachter HL: The timing of surgery for cholecystitis: a review of 202 consecutive patients at a large municipal hospital. Am J Surg. 2008, 195 (4): 467-470. 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2007.04.015.
Overby DW, Apelgren KN, Richardson W, Fanelli R: Society of American G, Endoscopic S: SAGES guidelines for the clinical application of laparoscopic biliary tract surgery. Surg Endosc. 2010, 24 (10): 2368-2386. 10.1007/s00464-010-1268-7.
Papi C, Catarci M, D'Ambrosio L, Gili L, Koch M, Grassi GB, Capurso L: Timing of cholecystectomy for acute calculous cholecystitis: a meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004, 99 (1): 147-155. 10.1046/j.1572-0241.2003.04002.x.
Wilson E, Gurusamy K, Gluud C, Davidson BR: Cost-utility and value-of-information analysis of early versus delayed laparoscopic cholecystectomy for acute cholecystitis. Br J Surg. 2010, 97 (2): 210-219. 10.1002/bjs.6872.
Gutt CN, Encke J, Köninger J, Harnoss JC, Weigand K, Kipfmüller K, Schunter O, Götze T, Golling MT, Menges M, Klar E, Feilhauer K, Zoller WG, Ridwelski K, Ackmann S, Baron A, Schön MR, Seitz HK, Daniel D, Stremmel W, Büchler MW: Acute cholecystitis: Early versus delayed cholecystectomy, a multicenter randomized trial (ACDC Study, NCT00447304). Ann Surg. 2013, 258 (3): 385-393. 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3182a1599b.
Mayumi T, Takada T, Kawarada Y, Nimura Y, Yoshida M, Sekimoto M, Miura F, Wada K, Hirota M, Yamashita Y, Nagino M, Tsuyuguchi T, Tanaka A, Gomi H, Pitt HA: Results of the Tokyo Consensus Meeting Tokyo Guidelines. J Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat Surg. 2007, 14 (1): 114-121. 10.1007/s00534-006-1163-8.
Miura F, Takada T, Strasberg SM, Solomkin JS, Pitt HA, Gouma DJ, Garden OJ, Buchler MW, Yoshida M, Mayumi T, Okamoto K, Gomi H, Kusachi S, Kiriyama S, Yokoe M, Kimura Y, Higuchi R, Yamashita Y, Windsor JA, Tsuyuguchi T, Gabata T, Itoi T, Hata J, Liau KH, Tokyo Guidelines Revision Comittee: TG13 flowchart for the management of acute cholangitis and cholecystitis. J Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat Sci. 2013, 20 (1): 47-54. 10.1007/s00534-012-0563-1.
Takada T, Strasberg SM, Solomkin JS, Pitt HA, Gomi H, Yoshida M, Mayumi T, Miura F, Gouma DJ, Garden OJ, Büchler MW, Kiriyama S, Yokoe M, Kimura Y, Tsuyuguchi T, Itoi T, Gabata T, Higuchi R, Okamoto K, Hata J, Murata A, Kusachi S, Windsor JA, Supe AN, Lee S, Chen XP, Yamashita Y, Hirata K, Inui K, Sumiyama Y, et al: TG13: Updated Tokyo Guidelines for the management of acute cholangitis and cholecystitis. J Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat Sci. 2013, 20 (1): 1-7. 10.1007/s00534-012-0566-y.
Sekimoto M, Takada T, Kawarada Y, Nimura Y, Yoshida M, Mayumi T, Miura F, Wada K, Hirota M, Yamashita Y, Strasberg S, Pitt HA, Belghiti J, de Santibanes E, Gadacz TR, Hilvano SC, Kim SW, Liau KH, Fan ST, Belli G, Sachakul V: Need for criteria for the diagnosis and severity assessment of acute cholangitis and cholecystitis: Tokyo Guidelines. J Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat Surg. 2007, 14 (1): 11-14. 10.1007/s00534-006-1151-z.
Yokoe M, Takada T, Strasberg SM, Solomkin JS, Mayumi T, Gomi H, Pitt HA, Garden OJ, Kiriyama S, Hata J, Gabata T, Yoshida M, Miura F, Okamoto K, Tsuyuguchi T, Itoi T, Yamashita Y, Dervenis C, Chan AC, Lau WY, Supe AN, Belli G, Hilvano SC, Liau KH, Kim MH, Kim SW, Ker CG, Tokyo Guidelines Revision Committee: TG13 diagnostic criteria and severity grading of acute cholecystitis (with videos). J Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat Sci. 2013, 20 (1): 35-46. 10.1007/s00534-012-0568-9.
Ferrarese AG, Solej M, Enrico S, Falcone A, Catalano S, Pozzi G, Marola S, Martino V: Elective and emergency laparoscopic cholecystectomy in the elderly: our experience. BMC Surg. 2013, 13 (Suppl 2): S21-10.1186/1471-2482-13-S2-S21.
Campanile FC, Catena F, Coccolini F, Lotti M, Piazzalunga D, Pisano M, Ansaloni L: The need for new "patient-related" guidelines for the treatment of acute cholecystitis. World J Emerg Surg : WJES. 2011, 6 (1): 44-10.1186/1749-7922-6-44.
Agresta F, Ansaloni L, Baiocchi GL, Bergamini C, Campanile FC, Carlucci M, Cocorullo G, Corradi A, Franzato B, Lupo M, Mandalà V, Mirabella A, Pernazza G, Piccoli M, Staudacher C, Vettoretto N, Zago M, Lettieri E, Levati A, Pietrini D, Scaglione M, De Masi S, De Placido G, Francucci M, Rasi M, Fingerhut A, Uranüs S, Garattini S: Laparoscopic approach to acute abdomen from the Consensus Development Conference of the Societa Italiana di Chirurgia Endoscopica e nuove tecnologie (SICE), Associazione Chirurghi Ospedalieri Italiani (ACOI), Societa Italiana di Chirurgia (SIC), Societa Italiana di Chirurgia d'Urgenza e del Trauma (SICUT), Societa Italiana di Chirurgia nell'Ospedalita Privata (SICOP), and the European Association for Endoscopic Surgery (EAES). Surg Endosc. 2012, 26 (8): 2134-2164. 10.1007/s00464-012-2331-3.
Campanile F, Carrara A, Motter M, Ansaloni L, Agresta F: Laparoscopy and Acute Cholecystitis: The Evidence. Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy. Edited by: Agresta F, Campanile FC, Vettoretto N. 2014, Springer International Publishing, 59-72.
Johner A, Raymakers A, Wiseman SM: Cost utility of early versus delayed laparoscopic cholecystectomy for acute cholecystitis. Surg Endosc. 2013, 27 (1): 256-262. 10.1007/s00464-012-2430-1.
Degrate L, Ciravegna AL, Luperto M, Guaglio M, Garancini M, Maternini M, Giordano L, Romano F, Gianotti L, Uggeri F: Acute cholecystitis: The golden 72-h period is not a strict limit to perform early cholecystectomy. Results from 316 consecutive patients. Langenbeck's Arch Surg. 2013, 398 (8): 1129-1136. 10.1007/s00423-013-1131-0.
Gomes RM, Mehta NT, Varik V, Doctor NH: No 72-hour pathological boundary for safe early laparoscopic cholecystectomy in acute cholecystitis: A clinicopathological study. Ann Gastroenterol. 2013, 26 (4): 340-345.
Ambe P, Esfahani BJ, Tasci I, Christ H, Köhler L: Is laparoscopic cholecystectomy more challenging in male patients?. Surg Endosc Interv Tech. 2011, 25 (7): 2236-2240. 10.1007/s00464-010-1539-3.
Zhu B, Zhang Z, Wang Y, Gong K, Lu Y, Zhang N: Comparison of laparoscopic cholecystectomy for acute cholecystitis within and beyond 72 h of symptom onset during emergency admissions. World J Surg. 2012, 36 (11): 2654-2658. 10.1007/s00268-012-1709-7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contribution
Study concept and design: PA, SW. Data collection: PA, DW. Statistical analysis: PA, HD. Interpretation: PA;SW;CH;DW. Drafting the manuscript: PA. Critical review and approval: PA; SW; HC; DW. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Ambe, P., Weber, S.A., Christ, H. et al. Cholecystectomy for acute cholecystitis. How time-critical are the so called “golden 72 hours”? Or better “golden 24 hours” and “silver 25–72 hour”? A case control study. World J Emerg Surg 9, 60 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1749-7922-9-60
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1749-7922-9-60