Abstract
Every cell division in budding yeast is inherently asymmetric and counts on the correct positioning of the mitotic spindle along the mother-daughter polarity axis for faithful chromosome segregation. A surveillance mechanism named the spindle position checkpoint (SPOC), monitors the orientation of the mitotic spindle and prevents cells from exiting mitosis when the spindle fails to align along the mother-daughter axis. SPOC is essential for maintenance of ploidy in budding yeast and similar mechanisms might exist in higher eukaryotes to ensure faithful asymmetric cell division. Here, we review the current model of SPOC activation and highlight the importance of protein localization and phosphorylation for SPOC function.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Positioning of the mitotic spindle with respect to the polarity axis becomes important during asymmetric cell division. In many polarized cells that place the cleavage furrow in relation to the position of the mitotic spindle, orientation of the spindle determines the fate of the two daughter cells without affecting the accuracy of chromosome segregation (Figure 1A). However in S. cerevisiae, spindle alignment along the polarity axis is particularly crucial for fidelity of chromosome segregation. This is mainly because of the physical constrains that arise from the establishment of the site of cell division (bud neck) before entry into mitosis (Figure 1B).
Impact of spindle orientation on asymmetric cell division. Asymmetric cell division is depicted in a hypothetical polarized cell (A) and in budding yeast (B). Only two chromosomes are shown for simplicity. In the upper panels, spindle aligns along the polarity axis and asymmetric cell division ends successfully giving rise to two different cells which carry different cell fate determinants depicted in different colors. In the lower panels, spindle aligns perpendicular to the polarity axis which results in failure of the asymmetric cell division in A and aneuploidy in B. Note that, the site of cell division in budding yeast is determined at G1/S which is before spindle assembly and entry into mitosis. Hence, if budding yeast divides despite the failure of spindle alignment along the polarity axis, inheritance of the cell fate determinants is not affected but aneuploidy occurs.
In budding yeast, a faithful mitosis requires positioning of the mitotic spindle along the mother-bud axis to ensure that the expanding anaphase spindle leaves one set of chromosomes in the mother cell while the second set is dragged through the bud neck into the daughter cell (Figure 1B). Misalignment of the mitotic spindle eventually leads to aneuploidy. Therefore, yeast cells have developed several mechanisms to provide correct spindle alignment. Firstly, spindle positioning in budding yeast is achieved by two functionally redundant microtubule-associated pathways, one containing the Kar9 protein and the other containing the minus-end-directed motor protein dynein [1–8]. Impairment of either pathway brings about spindle misorientation in nearly 10-20% of the cells, while impairment of both is lethal [1, 7]. Secondly, to prevent cells exiting mitosis with misaligned spindles, budding yeast have evolved a surveillance mechanism known as the s pindle p osition c heckpoint (SPOC) [9–12]. Mutants affecting the function of either the KAR9 or DYN1 pathway genes frequently misalign their spindles and rely on SPOC for survival [10]. SPOC delays the exit from mitosis by inhibiting the m itotic e xit n etwork (MEN) in response to spindle orientation defects. SPOC inhibition of MEN involves phosphorylation events and alterations in the localization of proteins.
This review aims to assemble the recent advances in the SPOC field into a model. Starting from mitotic exit in budding yeast, we will focus on how SPOC inhibits MEN and how SPOC components are regulated.
Exit from mitosis in budding yeast
Mitosis in budding yeast is driven by the activity of the sole cyclin dependent kinase (Cdk) Cdc28 in complex with mitotic cyclins (Clb1-4) [13–15]. Consequently, mitotic exit requires inactivation of the mitotic cyclin-Cdk complex and reversal of the Cdk dependent phosphorylation of several Cdk substrates. In budding yeast, a conserved dual specificity protein phosphatase called Cdc14 is capable of performing both these functions [16–18]. Activation of Cdc14 occurs in two steps, each of which involves the alteration of Cdc14 localization and hence the availability of Cdc14 for its substrates. From G1 until anaphase Cdc14 is kept inactive and sequestered in the nucleolus in association with its inhibitor Net1 [19–21]. The first step of activation takes place in early anaphase by partial release of Cdc14 from the nucleolus into the nucleoplasm and to some extend into the cytoplasm. This process is driven by the cdc-f ourteen e arly a naphase r elease (FEAR) network which promotes Cdk dependent phosphorylation of Net1 [22–27]. FEAR dependent activation of Cdc14 is not essential for mitotic exit but it is crucial for the anaphase related tasks such as positioning of the anaphase nucleus, stabilization of the anaphase spindle, spindle midzone assembly and segregation of ribosomal DNA [28–35]. Full release of Cdc14 from nucleolus into the cytoplasm requires another step which is governed by the m itotic e xit n etwork (MEN) [19] (Figure 2). Unlike FEAR, MEN is essential for mitotic exit [36].
MEN was first proposed as an essential pathway for mitotic exit, by the analysis of temperature sensitive mutants that arrest in late anaphase with high mitotic cyclin levels [36]. Since then, it has been well established that the function of MEN in mitotic exit is to promote the full release of Cdc14 out of the nucleolus and retention of Cdc14 in the cytoplasm. MEN has also been reported to be important in regulation of cytokinesis [37–39]. However, our main focus in this section will be regulation of mitotic exit by the MEN.
MEN is a signal transduction pathway driven by the Ras-like GTPase Tem1 (Figure 2). GTP-bound Tem1 binds to the downstream kinase Cdc15 at the s pindle p ole b ody (SPB, centrosome equivalent in yeast) [40, 41]. This binding allows Cdc15 to activate the Dbf2-Mob1 kinase complex through phosphorylation of the Dbf2 kinase subunit [42–44]. Activated Dbf2-Mob1 translocates to the nucleus, promotes dissociation of Cdc14 from Net1 by a yet unknown mechanism and phosphorylates Cdc14 hindering its nuclear localization signal [45, 46]. Hence Cdc14 liberated from the nucleolus cannot return to the nucleus once phosphorylated by Dbf2-Mob1. Cdc14 in the cytoplasm is now free to dephosphorylate its targets to promote mitotic exit. Key Cdc14 substrates include the mitotic Cdk inhibitor Sic1, the transcription factor Swi5 and the a naphase p romoting c omplex (APC) activator Cdh1 [16, 47].
Tem1 is supposedly active in the GTP bound state by similarity to its fission yeast homologue Spg1 [48]. The two-component G TPase a ctivating p rotein (GAP) complex Bfa1-Bub2 inhibits Tem1 activity by promoting GTP hydrolysis [49]. The putative g uanine nucleotide e xchange f actor (GEF), Lte1, presumably promotes Tem1 activation in the daughter cell compartment, although the molecular basis of this activation is still unclear. Lte1 has a GEF domain homologous to that of Cdc25 [50]. In addition, lte1 Δ cells fail to exit mitosis at low temperatures. This mitotic exit defect is suppressed by a high copy number of TEM1 [41]. These observations led to the hypothesis that Lte1 is the GEF for Tem1. However, the fact that Lte1 is only essential at growth temperatures below 20°C suggests that Tem1 does not need a GEF at physiological temperatures. This could be explained by the high intrinsic GDP-to-GTP exchange activity of Tem1 [49]. Furthermore, the GEF domain of Lte1 is dispensable for mitotic exit activation at low temperatures, which also questions the GEF activity of Lte1 for Tem1 [51]. In fact, no Lte1 GEF activity was detected for Tem1 in vitro [52]. Instead, Lte1 appears to assist mitotic exit by an unknown mechanism, most likely via regulation of Bfa1 or Kin4 [52, 53].
How is MEN activated? Polarity factors such as Rho-like GTPase Cdc42 and its effectors Cla4, Ste20, Gic1 and Gic2 promote mitotic exit mainly through targeting of Lte1 to the bud cortex and by interfering with Bfa1-Bub2 GAP function [54–57]. In addition, Cdc14 released via FEAR contributes to the MEN activity by Cdc15 and Dbf2-Mob1 activation through dephosphorylation of Cdk phosphorylated Cdc15 and Mob1 respectively and by promoting Bfa1-Bub2 inactivation through an unknown mechanism [58–60].
On the other hand, Cdc14 released via MEN eventually inactivates the MEN forming a negative feedback loop. Firstly, Cdc14 activates APCCdh1 which in turn promotes Cdc5 degradation [61]. Secondly, once released by the MEN, Cdc14 dephosphorylates Bfa1 promoting its re-activation [58]. In addition, fully activated Cdc14 triggers dissociation of Lte1 from the bud cortex through dephosphorylation, which leads to Lte1 inactivation [56, 57]. Furthermore, Cdc14 induces transcription of the daughter-specific protein Amn1 which directly binds to Tem1 and prevents its interaction with Cdc15 [62]. This is achieved by activation of the transcription factors Swi5 and Ace2 through their dephosphorylation by Cdc14. Finally, Cdc14 returns into the nucleolus after it has dephosphorylated its targets, allowing the start of a new cell cycle [63].
Regulation of MEN by SPOC
The S. cerevisiae BUB2 (b udding u ninhibited by b enomyl) gene was originally identified in a genetic screen for mitotic checkpoint related genes required to delay cell cycle progression in response to microtubule defects (induced by microtubule depolymerizing drugs, benomyl and nocodazole) [64]. At that time, Bub2 was thought to be a part of the s pindle a ssembly c heckpoint (SAC; checkpoint that prevents metaphase to anaphase transition until all chromosomes accomplish bipolar attachment to the spindle microtubules) [64–67]. BFA1 (b yr-f our-a like-1) was discovered by homology to the fission yeast's Byr4 which together with Cdc16 (homologue of Bub2 in S. pombe) is involved in inhibition of the s eptation i nitiation n etwork (SIN, homolog of MEN in S. pombe; pathway essential for cytokinesis and its coordination with mitosis) [68–70]. In subsequent studies it became evident that Bfa1 and Bub2 belonged to a different branch of mitotic checkpoint than the SAC [66, 71–74]. It then became established that the Bfa1-Bub2 GAP complex constitutes a checkpoint that delays mitotic exit when the anaphase spindle fails to align in the mother-bud direction. This mechanism is now defined as the s pindle p osition c heckpoint (SPOC) [10, 11] (Figure 2).
Bfa1 and Bub2 constitute a two-component GAP complex that activates GTP hydrolysis of Tem1. By doing so, it reduces the active form of Tem1 and inhibits mitotic exit. Despite the presence of a GAP homology domain (TBC), Bub2 alone does not affect the hydrolysis and dissociation of GTP from Tem1. However, Bub2 in the presence of Bfa1 increases the GTP dissociation and hydrolysis rate of Tem1 in vitro [49].
Bub2 and Bfa1 physically interact with each other and with Tem1 [10, 75]. Bfa1 protein levels seem to be important for cell survival because overexpression of Bfa1 arrests cells in anaphase [74]. Also, the transcription and the protein levels of Bfa1 and Bub2 are stable during the cell cycle [75–77]. In contrast, the phosphorylation status of Bfa1 changes in a cell cycle dependent manner. During anaphase, Bfa1 is hyperphosphorylated by the polo like kinase Cdc5 and this form of Bfa1 cannot bind to Tem1 [77]. Consequently, when Bfa1 is phosphorylated by Cdc5, Bfa1-Bub2 GAP activity for Tem1 is inhibited in vitro [78]. Cdc5 thus phosphorylates Bfa1 in an inhibitory manner, favoring mitotic exit. Bub2 and Tem1 also undergo cell cycle dependent phosphorylation although the functional significance of this regulation is largely unclear [79, 80].
Another kinase involved in Bfa1-Bub2 regulation is the Kin4 kinase. KIN4 was first identified as a genetic interactor of KAR9 in a large scale s ynthetic g enetic a rray (SGA) analysis where the deletion of KIN4 decreased the survival of kar9 Δ cells [81]. Following this, Kin4 was established as an essential component of the SPOC [82, 83]. As such, the phenotype of kin4 Δ is very similar to bfa1 Δ or bub2 Δ cells: all mutant cell types fail to arrest in response to spindle misalignment. Like Bfa1, high levels of Kin4 cause an anaphase arrest due to inactivation of the MEN that can be reverted by deletion of BUB2. However, unlike Bfa1 and Bub2, Kin4 is not required for the metaphase arrest induced upon microtubule depolymerization [82, 83].
Kin4 phosphorylates Bfa1 when the anaphase spindle is misplaced in the mother or when there are defective c ytoplasmic m icrot ubules (cMTs). By phosphorylating Bfa1, Kin4 inhibits Bfa1 phosphorylation by Cdc5 in vivo and hence promotes Bfa1-Bub2 GAP activity [82–84]. Interestingly, Bfa1 phosphorylated by Kin4 can still be phosphorylated by Cdc5 in vitro [84]. How Kin4 inhibits Cdc5 phosphorylation of Bfa1 in vivo could only be understood by protein localization studies which will be discussed in next sections (See: SPOC activation breaks the asymmetric protein localization).
Taken together, Bfa1-Bub2, Cdc5, and Kin4 constitute the SPOC. Activity of the GAP complex is regulated by two opposing kinases; Cdc5 and Kin4. If the spindle is correctly aligned, Cdc5 phosphorylates Bfa1 and inactivates the Bfa1-Bub2 GAP complex which leads to mitotic exit. However if the spindle is misaligned or the proper microtubule cortex interactions are interfered, Kin4 kinase activates the GAP complex by phosphorylating Bfa1 and preventing the inhibitory phosphorylation of Bfa1 by Cdc5. Eventually, GAP complex delays mitotic exit through inhibition of Tem1 until spindle re-aligns in the mother-bud direction (Figure 3).
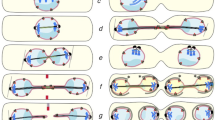
Localization of SPOC and MEN proteins. Localization of indicated SPOC and MEN proteins are shown in different phases of mitosis; metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Bfa1-Bub2 and Tem1 mainly localize at the dSPB (see the text for details) [10, 87, 88]. Cdc15 is recruited to both SPBs during late anaphase and relocates to the bud neck in late telophase [91, 92, 96, 160]. Dbf2-Mob1 localizes on both SPBs during anaphase and accumulates at the bud neck in telophase concomitant with a decrease in the SPB localization [44, 91, 93]. Dbf2-Mob1 was also shown to be localized in the nucleus at late anaphase [45, 46]. Cdc5 localizes to both SPBs and translocates to the bud neck in telophase [61, 90, 94, 95]. Lte1 localizes to the bud-cortex and -cytoplasm in S, G1 and M phases. However, in telophase, shortly before cytokinesis Lte1 dissociates from the bud cortex, diffusing into the cytoplasm of the daughter and mother cells equally [10, 88]. Kin4 localizes to the mother cell cortex throughout the cell cycle and to the mSPB in anaphase for a short time, and accumulates at the bud neck in telophase [53, 82, 83, 106]. Elm1 localizes to the bud neck in mitosis but dissociates from there during telophase [111, 117]. PP2A regulatory subunit Rts1 and Cdc14 are not depicted in the figure for simplicity. Rts1 localizes in the nucleus, bud neck and kinetochores [161]. Cdc14 is sequestered in the nucleolus, and released into the nucleus and cytoplasm in anaphase [19, 20]. Cdc14 also associates with the SPBs in early anaphase and with the bud neck in late anaphase [25, 58, 89, 162].
Protein localization in an unperturbed mitosis
Experiments based on fluorescence microscopy and immuno-electron microscopy have shown that most of the MEN and SPOC components associates with the cytoplasmic surface of the SPBs and many of them translocates to the bud neck in telophase to regulate cytokinesis (Figure 3) [10, 37, 38, 44, 61, 85–96]. Despite the transient SPB association of Kin4 during anaphase, localization of Kin4 and Lte1 differs remarkably from the others as they localize to the mother and daughter cell cortexes, respectively [10, 82, 83, 87, 88]. SPB localization of MEN proteins appears to be important for mitotic exit as their delocalization disturbs MEN [97]. Likewise, localization of SPOC proteins is essential for checkpoint function [3, 53, 98, 99]. Localization of proteins implemented in SPOC and its functional importance will be described in this section. However, details on localization of other MEN proteins can also be found in Figure 3.
Bfa1, Bub2 and Tem1 localize to the cytoplasmic face (outer plaque) of the SPBs, preferentially to the bud-ward directed SPB (dSPB, daughter-directed SPB) [10]. The term "asymmetric" is widely used to describe their localization pattern in an unperturbed mitosis because from metaphase onwards they are mainly concentrated at the dSPB rather than the mSPB (mother-directed SPB) [10, 88]. Bfa1-Bub2 binds to the SPB outer plaque via the SPB component Nud1, which links the γ-tubulin binder Spc72 to the central SPB protein Cnm67 [97, 100–102]. SPB localization of Bfa1 and Bub2 is dependent on each other but not on Tem1. However, Tem1 association with the SPBs relies on Bfa1-Bub2 during most of the cell cycle with the exception of late anaphase [10, 99]. In the absence of Bfa1-Bub2, Tem1 can bind to the SPBs only in late anaphase [10, 99]. This pool of Tem1 binds equally to both SPBs and more stably than in the presence of Bfa1-Bub2 as shown by the FRAP data, suggesting that at least two different docking sites (Bfa1-Bub2-dependent and -independent) exist for Tem1 SPB association [99].
SPB-bound Bfa1-Bub2 protein amounts increase in anaphase at the dSPB with a parallel decrease at the mSPB from which Bfa1-Bub2 eventually disappears [99]. Tem1 localization resembles the localization of Bfa1-Bub2. However, Tem1 never disappears from the mSPB [10, 87, 88]. At the end of mitosis Bfa1-Bub2 and Tem1 amounts decrease at the dSPB concomitantly increasing at the mSPB [99] (Figure 3). The physiological importance of asymmetrically localized Bfa1-Bub2 GAP complex and Tem1 is still not clear. Disappearance of Bfa1-Bub2 from the mSPB, however, might be important for a timely mitotic exit [52, 103].
How Bfa1-Bub2 and Tem1 asymmetry is established, is a question that still remains to be answered. So far, it has been shown that neither the forces generated during spindle elongation nor SPB inheritance nor passing from the bud neck affect Bfa1 asymmetry [104, 105]. Actin cytoskeleton is required to initiate Bfa1 asymmetry but it is not necessary for maintenance of the already established asymmetry [105]. This is most probably due to actin function in cell polarity because some cell polarity determinants (Cdc42 and Bni1) also contribute to Bfa1 asymmetry [105]. Alternatively, actin cytoskeleton might promote Bfa1 asymmetry by facilitating correct spindle orientation.
Kin4 localization is quite different than that of Bfa1-Bub2 and Tem1. During most of an unperturbed cell cycle Kin4 associates with the cortex of the mother cell body and accumulates at the bud neck in late anaphase. However, for a short time period during mid-anaphase, Kin4 also localizes to the mSPB [82, 83] (Figure 3). Accumulation of Kin4 at the bud neck is accompanied with a slight decrease in Kin4's mother specific localization. Kin4 stays at the bud neck during cytokinesis and afterwards translocates to the new bud site, where it appears only transiently [53, 106] (unpublished observation of Caydasi AK).
How Kin4 associates with the cortex and SPBs, what restricts Kin4 to the mother cell or what excludes it from the daughter cell is still unclear. However, data about Kin4 localization have been accumulating over the years. It has been shown that Kin4 binds to the SPBs via Spc72 which is the SPB outer plaque component that binds γ-tubulin [84]. In addition, Clb4 and to some extend Kar9 contribute to the exclusion of Kin4 from the daughter SPB during an unperturbed anaphase. It has also been shown that the C-terminal region of Kin4 is important for its localization to the mother cell cortex and SPB [53]. Cortex localization of Kin4 might be mediated by its interaction with ergosterol [107]. Importantly, SPB and mother-cortex localization of Kin4 require Rts1, B-type regulatory subunit of the p rotein p hosphatase 2A (PP2A) (See: Role of Kin4 localization in SPOC) [98, 106].
Cdc5 localizes to both SPBs in mitosis and to the bud neck during telophase [61, 90]. C-terminal polo box domain of Cdc5 is essential for both SPB and bud neck localization of Cdc5 [90]. SPB association of Cdc5 is important for MEN activation and requires the SPB outer plaque components Cnm67 and Nud1 [95]. Cdc5 phosphorylates not only Bfa1 but also Spc72 and Nud1 [84, 108, 109]. These phosphorylation events most likely take place at the SPBs in vivo because Cdc5 dependent phosphorylation of Bfa1, Nud1 and Spc72 is lost in the nud1-2 temperature sensitive mutant in which Bfa1, Nud1 and Spc72 are mislocalized at 37°C [84, 97].
SPOC activation breaks the asymmetric protein localization
Upon spindle misalignment or microtubule defects (i.e. depolymerization by nocodazole) Bfa1-Bub2 and Tem1 localization changes from asymmetric to symmetric [10] (Figure 4). The term "symmetric", describes localization on both SPBs nearly equally. Similar to Bfa1-Bub2 and Tem1, SPOC activation also results in symmetric localization of Kin4 at the SPBs [82, 83]. In contrast, SPB localization of Cdc5 does not change in response to spindle misalignment [84].
Localization of SPOC proteins upon normal and misalignment of the anaphase spindle. Localization of SPOC components is illustrated in anaphase when the spindles are correctly aligned, along with the mother-daughter axis (left panel) and when the spindles are misaligned (right panel). Bfa1-Bub2, Tem1 and Kin4 localization turns to symmetric from asymmetric upon spindle misalignment while Cdc5, Lte1 and Elm1 localization is not affected. See the text for details.
Despite the lack of mechanistic understanding for the establishment of Bfa1-Bub2 and Tem1 asymmetry, more insight has been gained into how the asymmetry is broken. The order of the events most likely starts with the change in Kin4 localization which is triggered by SPOC activating conditions, like misaligned spindles or defective microtubules (see the section: Sensory mechanisms for SPOC activation). Thereby, Kin4 gets access to Bfa1 and phosphorylates it on at least two residues (S150 and S180) [84].
What is the functional consequence of Bfa1 phosphorylation by Kin4? Careful FRAP measurements have shown that Bfa1-Bub2 is stably associated with the dSPB during an unperturbed cell cycle (t1/2 > 200 s). However, phosphorylation of Bfa1 by Kin4 loosens Bfa1-Bub2 interaction with the dSPB and promotes rapid exchange (t1/2 ≈ 20 s) of the Bfa1-Bub2 GAP complex at both SPBs [99, 105]. This causes a decrease in SPB bound Bfa1-Bub2 amounts accompanied by an increase in the cytoplasmic pool of the GAP complex [99]. Cells, in which Bfa1-Bub2 is constitutively targeted on both SPBs symmetrically but "stably", are SPOC deficient; indicating that the change in Bfa1-Bub2 SPB binding dynamics is essential for SPOC activity [99].
How is Bfa1-Bub2 GAP complex kept so efficiently active during SPOC? Dissociation of Bfa1-Bub2 from the SPBs is most likely a way of keeping Bfa1 away from the inactivating action of the polo like kinase Cdc5, which phosphorylates Bfa1 at the SPBs [84, 99]. So far, it is unclear whether there is a phosphatase responsible for removing the phosphates from Cdc5 phosphorylated sites in Bfa1. Nevertheless, the rapid turnover of Bfa1 phosphorylated by Kin4 at SPBs might be sufficient to explain how Kin4 counteracts Cdc5 so efficiently in vivo but not in the in vitro system that lacks SPBs and any kind of compartmentalization [84, 99].
On the other hand, Tem1 association with the SPBs is highly dynamic in the presence of Bfa1-Bub2 (t1/2 ≈ 3 s) regardless of the cell cycle stage and the spindle alignment status [87, 99]. Tem1 amounts also decrease on the SPBs of misaligned spindles [87, 99]. Given that Tem1 association with the SPBs is via Bfa1-Bub2 except during late anaphase, the decrease in Tem1 SPB localization upon spindle misalignment likely follows the decrease in Bfa1-Bub2-SPB binding [10, 99]. Consequently, during spindle misalignment both the Bfa1-Bub2 GAP complex and the GTPase Tem1 is mostly found dispersed in the cytoplasm rather than at the SPBs. The mechanism by which cytoplasmic Bfa1 and Bub2 inhibit Tem1 is not clear. It is tempting to speculate that GAP activity of the cytoplasmic complex inhibits the GTPase mainly in the cytoplasm. The fact that Bfa1-Bub2 is able to promote GTP hydrolysis of Tem1 in vitro in the absence of SPBs further supports this notion. Rigorous biochemical analysis will be however necessary to clarify the molecular mechanism of Tem1 inhibition by Bfa1-Bub2 upon SPOC activation.
Role of Kin4 localization in SPOC
Role of Kin4 in SPOC function involves regulation of both its localization and its activity. SPB localization of Kin4 is essential for its role in activating Bfa1-Bub2, as preventing Kin4 SPB binding by targeting Kin4 constitutively to the cell cortex results in SPOC deficiency. In addition, constitutive targeting of Kin4 to the SPB outer plaque (via a Kin4-Spc72 chimera) is able to cause a 10 min delay in mitotic exit by promoting some Bfa1-Bub2 turnover (t1/2 ≈ 40 s) at the SPBs even when the anaphase spindle is correctly aligned [84, 99]. Yet, constitutive targeting of Kin4 to the SPBs is not adequate for SPOC proficiency, indicating that disruption of either SPB or cortex binding of Kin4 impairs proper Kin4 function when the spindle is misaligned [53, 98].
PP2A B-type regulatory subunit Rts1 is required for Kin4 SPB and cortex binding [98, 106]. Rts1 promotes dephosphorylation of Kin4, either directly or indirectly, and probably establishes Kin4 localization through this dephosphorylation. Besides, rts1Δ cells fail to arrest in response to spindle misalignment although Kin4 kinase activity is not affected, emphasizing the significance of Kin4 localization for checkpoint integrity [98, 106].
Chan and Amon (2010) recently demonstrated the importance of Kin4's C-terminal region for Kin4 localization and SPOC activity. Overexpression of the Kin4 kinase domain, which resides at the N-terminal region of Kin4, is enough to inhibit mitotic exit but its expression at endogenous levels is not sufficient to keep the anaphase arrest upon spindle misalignment. Furthermore, Kin4 lacking the C terminal 146 amino acids cannot localize to the mother cell cortex and the SPBs and thus it is unable to engage SPOC. Finally, a single amino acid substitution (F793A) at the C terminal region prevents cortical localization of Kin4 (as well as reducing the SPB localization) and results in SPOC deficiency [53]. All aforementioned data indicate that Kin4 localization relies on the C terminal region of Kin4 and SPOC proficiency is tightly coupled to proper Kin4 localization. Interestingly, mutation of a serine residing in the C-terminus of Kin4 to an alanine (S508A) results in Kin4 mislocalization on both mother and daughter cortexes suggesting that Kin4 C-terminal is also important for restriction of Kin4 to the mother cell cortex [53].
Elm1 regulation of Kin4 catalytic activity
Kin4 kinase activity is absolutely vital for SPOC function. Lately, we and others have shown that Kin4 kinase activity requires another kinase, namely Elm1 [106, 110]. Elm1 is a bud neck localized kinase which is responsible for regulation of many other kinases including Hsl1, Gin4, Snf1 and Cla4 [111–114]. Together with Hsl1, Gin4 and Kcc4, Elm1 is one of four bud neck kinases controlling proper septin ring assembly, cytokinesis and the morphogenesis checkpoint (a checkpoint that delays entry into mitosis in response to polarization defects) [111–114]. Deletion of ELM1, or replacement of the wild type ELM1 with a kinase dead allele rescues the toxicity of KIN4 overexpression. In addition, elm1 cells are deficient in keeping the SPOC arrest in response to spindle misalignment [106, 110]. This is because Kin4 is catalytically inactive in cells lacking ELM1 [106]. Elm1 is directly responsible for phosphorylation of a threonine (T209) residue within the Kin4 kinase activation loop (T-loop) which is essential for full activation of Kin4 [106].
Several protein kinases are regulated through T-loop phosphorylation. A dephosphorylated T-loop acts as an autoinhibitor by blocking substrate access to the active site or by blocking ATP binding [115]. Hence, T-loop phosphorylation is an excellent way of regulating kinase activity. Unexpectedly, Kin4 T-loop phosphorylation does not increase in response to SPOC activation, neither does Kin4 kinase activity [106] (unpublished observation of Caydasi AK). In this regard, it is important to keep in mind that Kin4 activity is also regulated by its localization in vivo. It is, therefore reasonable to hold Kin4 in an active state and change its localization as a response to spindle misalignment. Consequently, it is unlikely that Elm1 is either a sensor or a protein related with the sensor of the SPOC, but Elm1 phosphorylation of Kin4 at T209 residue is indispensable for Kin4 kinase activity and SPOC function [83, 84, 106, 110].
Kin4 T-loop phosphorylation by Elm1 persists throughout the cell cycle, with an increase in mitosis [106]. Kin4 kinase activity exhibits a similar pattern [83]. So far, no phosphatase is known to be removing the phosphate at the T209 residue. Thus, fluctuation in T209 phosphorylation might be a reflection of Elm1 protein levels that increase in mitosis and decrease at the end of mitosis likely by degradation through a mechanism dependent on its phosphorylation by Cdk [111, 114, 116]. At present, the physiological importance of down regulation of T209 phosphorylation at the end of mitosis is unclear. Kin4 mutants that permanently mimic the phosphorylation at T209 residue (Kin4-T209D) do not exhibit prolonged mitosis [110]. This suggests that reduction in T209 phosphorylation is not essential for timely exit from an unperturbed mitosis. One possibility is that, the decrease in ratio of T-loop phosphorylated Kin4 at the end of mitosis could be important for down regulation of Kin4 activity upon re-alignment of a previously misaligned spindle, and so it might be important for mitotic exit. Alternatively, basal levels of Kin4 activity might be important for phosphorylation of yet unknown targets of Kin4.
Elm1 localizes to the bud neck as soon as a bud neck forms and dissociates from there prior to cytokinesis. Elm1 bud neck localization depends on the septin Cdc12 and is mutually required for proper localization of the septins Cdc12 and Cdc11 [111, 117]. Bud neck localization of Elm1 has been shown to be important for Elm1 function in regulating the morphogenesis checkpoint but it is not required for activating the kinase Snf1 (a kinase involved in metabolic regulation under stress conditions, mainly during glucose starvation) [118]. The role of Elm1 bud neck localization is less clear in SPOC. Delocalized Elm1 can still activate Kin4 kinase via T209 phosphorylation [106]. However, cells carrying a C-terminally deleted ELM1 allele which cannot localize to the bud neck were reported to be SPOC deficient [110]. It is thus likely that Elm1 bud neck localization contributes to SPOC function via a mechanism different than T-loop phosphorylation.
In addition to T209 phosphorylation, Elm1 phosphorylates other residues in the C-terminal region of Kin4 in vitro. Mutation of these phosphorylation sites to alanine results in mild SPOC deficiency without affecting Kin4 kinase activity and localization [106]. At present, the reason behind this SPOC deficiency is unclear. It could be via subtle modulations of Kin4 SPB and cortex binding dynamics which were not resolved by the still image analysis. Alternatively, it could be via alteration of Kin4 binding to the bud neck, although the significance of Kin4 bud neck localization is not yet clear. Indeed, in elm1Δ cells, Kin4 localizes to the SPBs as in wild type cells and to the mother cell cortex only with slightly reduced efficiency, whereas bud neck localization of Kin4 is significantly reduced [106, 110].
Kin4 kinase activity appears to be dispensable for Kin4 SPB and cortex localization because a kinase dead mutant of Kin4 and Kin4 of elm1Δ cells can still localize on both sub-cellular positions [84, 106]. Hence, Kin4, which is not activated by Elm1, can still be targeted to the SPBs and to the cell cortex possibly in an Rts1 dependent manner. However, the appearance of hyperphosphorylated forms of Kin4 in rts1Δ cells requires Elm1, which supports another notion that Rts1 can act downstream and/or parallel of Elm1 in Kin4 regulation [106].
Current Model of SPOC Activation
Figure 5 represents an overview of the current model of SPOC activation. In every cell cycle, Kin4 is activated by Elm1 mainly during mitosis regardless of the spindle alignment status. In addition, Rts1 mediates the cortex and mSPB binding of Kin4. Once the spindle is misaligned, Kin4 kinase localizes on both SPBs likely in an Rts1 dependent manner and thereby phosphorylates Bfa1 [82, 83, 119].
Current model of SPOC activation. A simple molecular network of our current understanding of SPOC function. Details of the model can be found in the text. To which structural SPB component the proteins bind is not depicted in the figure and will be explained here: Bfa1-Bub2 associates with the SPBs through Nud1 [97]. Tem1 binding to the SPBs is via Bfa1-Bub2 except for during late anaphase [10]. Kin4 binds to Spc72 [84]. Cdc5 SPB localization largely depends on Cnm67 and Nud1 although it also interacts with Spc72 [95, 108]. How Cdc15 localizes to the SPBs is not clear; however it depends on Tem1 and Cnm67 and to some extend Nud1 [91, 96, 97]. For simplicity only one SPB (outer plaque) has been depicted and all reactions are shown in one direction except for the highly dynamic SPB binding of Tem1 and Bfa1-Bub2 which is indicated by the two-sided arrows. However, Bfa1-Bub2 independent SPB binding of Tem1 in late anaphase was not depicted as a two-sided arrow for being a relatively more stable binding than the Bfa1-Bub2 dependent pool. Dashed-lines represent the potential reactions which are not known at the moment. Double-lines refer to the reactions that favor MEN activation. Hypothetical autophosphorylation of Kin4 is indicated by a question mark.
Phosphorylation of Bfa1 by Kin4 increases the turn-over rate of Bfa1-Bub2 at the SPBs accompanied by a decrease in the levels of SPB associated Bfa1-Bub2. Kin4 phosphorylated Bfa1 is protected from the GAP inhibition action of the polo-like kinase Cdc5, simply because Bfa1-Bub2 dissociates from the SPBs and therefore it is kept away from Cdc5 which phosphorylates Bfa1 at the SPBs [84, 99].
Together with Bfa1-Bub2; Tem1 is also released into the cytoplasm because Tem1 binds to the SPBs mainly via Bfa1-Bub2 [10, 99]. Hence, the GAP complex is released into the cytoplasm, probably where it inhibits the Tem1 GTPase. Given that a pool of Tem1 (likely the active form) associates with the SPBs independently of Bfa1-Bub2 in late anaphase [10, 99] and mitotic exit occurs without any delay in BUB2 and/or BFA1 deleted cells [10, 73], we can assume that it is the Bfa1-Bub2 independent pool of Tem1 that recruits Cdc15 to the SPBs in late anaphase when the spindle is correctly aligned, triggering downstream events in MEN. Thus, it is tempting to speculate that upon SPOC activation Tem1 which is kept away from the SPB and inhibited in the cytoplasm cannot bind to the Bfa1-Bub2-independent docking site at the SPBs where it is supposed to meet with its target, Cdc15. Hence, mitotic exit is inhibited until spindle misalignment is corrected. When the spindle re-aligns in the mother-bud direction, this process is most likely reversed because the mitotic exit activator Lte1 resides in the daughter cell compartment and Kin4 is excluded from there.
Sensory mechanisms for SPOC activation
SPOC gets activated when the mitotic spindle misaligns in the mother cell. This could be due to defects in cMT nucleation or in spindle positioning pathways. Observations indicate that loss of cMT-daughter cell cortex interactions is the main activator of Bfa1 symmetry rather than loss of mitotic spindle integrity or cMT-mother cortex interactions [105]. Treatment of the cells with nocodazole like drugs also activates SPOC, mainly because they depolymerize the microtubules diminishing cMT-cortex interactions. It is not known how the information is transferred from the cMT-cortex interaction to Kin4, but apparently Kin4 localization on both SPBs is triggered in response to loss of contact between cMTs and bud cell cortex.
It is also worth mentioning that, cMT-bud neck contact was also reported to be important in SPOC arrest in a way that persistent loss of cMT-bud neck interaction causes SPOC failure [120, 121]. Therefore, SPOC might monitor the presence of cMTs in the bud neck. However, this has likely a small contribution to SPOC activation, if at all, because of the low penetrance of the phenotype [120, 121]. It may still be possible that the presence of cMTs at the bud neck and loss of cMT-daughter cell cortex interactions might additively promote SPOC arrest.
Moreover, SPB itself might be a part of the SPOC sensory mechanism. Kin4 binds to the SPBs via the γ-tubulin receptor Spc72 [84]. Nevertheless, Spc72-7 mutants that are able to recruit Kin4 to the SPBs are still SPOC deficient, indicating that Spc72 might have a function in SPOC other than providing a docking site for Kin4 [84].
What is the molecular mechanism sensing cMT-cortex interaction? We could learn from the sensory machinery of other mitotic checkpoints like s pindle a ssembly c heckpoint (SAC). SAC senses the occupancy of the kinetochores by the microtubules and the lack of tension between the sister kinetochores [122]. It has been well established that the kinetochores which are not yet attached to the spindle microtubules recruit the SAC components keeping the SAC active. Whereas, microtubules attached to the kinetochores promote the removal of these proteins, inhibiting the SAC machinery (i.e. Mad1-Mad2 complex) [123–125]. On the other hand, kinetochores attached to the microtubules in a syntelic or monotelic manner are occupied but not under tension. In this case, the conserved protein kinase Aurora B (Ipl1 in budding yeast) promotes the detachment of the microtubules from the kinetochores by phosphorylating key substrates including Dam1 and Ndc80 complexes [126–132]. Aurora B, localizing to the innercentromeric region, has access to its substrates at the kinetochore only in the absence of an intrakinetochore tension, likely due to spatial separation [133–138].
It would be interesting to understand if any similarity exists between SPOC and SAC sensory mechanisms. The fact that disruption of the spindle microtubules per se does not activate SPOC, indicates that tension created on SPBs by the spindle forces are not involved in SPOC activation [105]. However, we cannot exclude the possibility that the tension created on the SPB outer plaque through cMTs might trigger SPOC activation. Alternatively, loss of cMT-daughter cortex interactions might be transmitted to the SPOC components by a mechanism similar to sensing of an unattached kinetochore. It is possible that some factors transferred along the cMT from the bud cortex to the dSPB might inhibit Kin4 binding to the dSPB when the cMTs are attached to the bud cortex. Likewise, absence of cMT-cortex interactions could generate a signal that modifies Kin4 allowing for its SPB binding. These are only hypothesis at the moment and more research is needed for elucidation of the true sensor for SPOC.
SPOC like mechanisms in higher eukaryotes
Spindle orientation along the polarity axis is vital in asymmetric cell divisions to assure the outcome of the division is asymmetric. Therefore it is likely that checkpoints ensuring correct spindle positioning exist in higher eukaryotes too. Interestingly, studies from Yamashita and colleagues indicate the presence of a checkpoint, monitoring centrosome orientation in Drosophila male germ line stem cells [139, 140]. Centrosome orientation checkpoint monitors the position of the centrosomes with respect to the position of the hub and delays entry into mitosis when centrosomes fail to align perpendicularly to the hub. The frequency of centrosome misalignment increases with the age of the fly. Therefore the number of stem cells that can undergo mitosis decreases as the organism ages. Thus, spermatogenesis declines in elderly flies without a need for reduction in the stem cell number [139, 140]. Many other studies established the existence of a preferred direction of spindle orientation in asymmetric cell divisions of other cell types including basal epidermal cells, intestinal stem cells, and neuronal stem cells [139, 141–146]. It would be interesting to ask whether SPOC or centrosome alignment checkpoint like mechanisms exist in those systems too.
Functional higher eukaryotic equivalents of Tem1, Bfa1-Bub2 and Kin4 have not been identified so far. Nevertheless, homologues of the downstream MEN components Cdc15 and Dbf2-Mob1 exist in S alvador-W arts-H ippo pathway (SWH, pathway that controls organ size) of Drosophila and human [147]. In addition, Elm1 is known to be involved in a pathway the homologue of which exists in mammals. Elm1 together with Sak1 and Tos3 activates Snf1 (yeast homologue of mammalian AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase) [148–150] (Figure 6). AMPK is activated by mammalian LKB1, CaMKK and TAK1 kinases. Interestingly, Elm1/Sak1/Tos3 function in regulating Snf1 in budding yeast can also be fulfilled by human LKB1/CaMKK/TAK1 kinases indicating that they are highly conserved [151]. Budding yeast's Snf1 is important for metabolic control, especially in response to stress conditions [151, 152]. On the other hand, in fruit fly and mammals, AMPK is implemented in many cellular pathways involving cell cycle, cell polarity, metabolic control and stress response [153, 154]. Given the analogy between the yeast Snf1 pathway and mammalian AMPK pathway (Figure 6), what fulfills the cell cycle and polarity functions in Snf1 pathway? Kin4 appears to be a good candidate as it acts by coordinating mitosis with spindle alignment along the polarity axis. Besides, Kin4 has been categorized in Snf1/AMPK family kinases belonging to the major group CaMK (Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase) upon amino acid sequence similarity [155–157]. Consequently, further molecular studies of SPOC and functional identification of mammalian counterparts of yeast homologues might help to shed light onto related pathways contributing to accuracy of asymmetric cell divisions in higher eukaryotes.
Snf1 and AMPK pathways. Analogy between budding yeast's Snf1 and mammalian AMPK pathways is illustrated. Elm1/Sak1/Tos3 redundantly activates Snf1 which is involved in metabolic control and stress response. LKB1/CaMKK/TAK1 activates AMPK which is implicated in metabolic control, stress response, cell division cycle and cell polarity. Kin4 is activated by Elm1 and mediates coordination of mitotic exit with spindle alignment along the polarity axis. Elm1 is also involved in regulation of other proteins related with polarity and cell division. Solid lines indicate direct activation of the protein catalytic activity. Dashed lines represent involvement of the indicated proteins in the regulation of the corresponding proteins or pathways directly or indirectly.
Conclusion
Every cell division is inherently asymmetric in S. cerevisiae and relies on correct positioning of the mitotic spindle along the polarity axis for maintenance of ploidy. This makes budding yeast an excellent model organism to study coordination of asymmetric cell division with correct spindle orientation. SPOC was discovered in budding yeast as a mechanism monitoring the spindle direction and halting cell cycle progression in response to spindle misalignment. Since then, our knowledge about SPOC is growing, but we are far from fully understanding the molecular mechanisms behind.
At the moment the main mystery is how the positional cue (likely from cMT-bud cortex) is transmitted to the SPOC activating kinase Kin4. Elm1 and Rts1 are upstream elements controlling Kin4 activity and localization. However, Elm1 activates Kin4 regardless of the spindle direction and we lack information about how exactly Rts1 contributes to Kin4 localization. Analysis of how Kin4 is localized to the cell cortex and to the SPBs might lead us to understand Rts1's role in Kin4 regulation and might help us to find other regulators of Kin4.
Another ambiguity is how the MEN gets activated, and especially how SPOC is inactivated after re-alignment of a previously misaligned spindle. Polarized localization of the SPOC activator Kin4 to the mother and MEN activator Lte1 to the daughter cell could be an explanation for this. However, what happens in reality is probably more complex than that, because Lte1 is not essential for mitotic exit at physiological temperatures and the role of Lte1 in MEN activation is so far uncertain.
Is Kin4 pathway the only way of GAP activation? Analysis of protein binding dynamics shows that Kin4 is the major factor promoting Bfa1-Bub2 turnover at the SPBs. However, even in cells lacking Kin4, Bfa1-Bub2 binding to the SPBs becomes slightly dynamic upon misorientation of the anaphase spindle. This observation suggests that yet unidentified pathways might also regulate Bfa1-Bub2 in parallel to Kin4 as a response to spindle misalignment. Indeed, Bfa1-Bub2 is also required for metaphase and G2/M arrests due to spindle or DNA damage respectively. In addition, the phosphorylation status of Bfa1 and Bub2 changes as a response to SAC and DNA damage checkpoint activation [12, 77, 79, 158, 159]. Thus, there are other means of regulating Bfa1-Bub2, but if any of those also contribute to the SPOC arrest is still not known.
In conclusion, more work has to be done to illuminate the SPOC field. Like in every concept, the more insight we gain, it is likely that the more unknowns we will face. We believe that elucidation of the mechanisms by which SPOC works will progress faster in this era of molecular and systems biology.
Authors' information
GP is the group leader of the Helmholtz junior research group M olecular B iology of C entrosomes and C ilia (MBCC) at German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) in Heidelberg/Germany. AKC is a PhD student and BI is a postdoctoral fellow. We are interested in understanding how spindle orientation and cytokinesis are coordinated with chromosome segregation in budding yeast and how ciliogenesis occurs in mammalian cells.
References
Miller RK, Rose MD: Kar9p is a novel cortical protein required for cytoplasmic microtubule orientation in yeast. J Cell Biol 1998, 140: 377–390. 10.1083/jcb.140.2.377
Siller KH, Doe CQ: Spindle orientation during asymmetric cell division. Nat Cell Biol 2009, 11: 365–374. 10.1038/ncb0409-365
Moore JK, Cooper JA: Coordinating mitosis with cell polarity: Molecular motors at the cell cortex. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2010, 21: 283–289. 10.1016/j.semcdb.2010.01.020
Lee L, Tirnauer JS, Li J, Schuyler SC, Liu JY, Pellman D: Positioning of the mitotic spindle by a cortical-microtubule capture mechanism. Science 2000, 287: 2260–2262. 10.1126/science.287.5461.2260
Miller RK, Cheng SC, Rose MD: Bim1p/Yeb1p mediates the Kar9p-dependent cortical attachment of cytoplasmic microtubules. Mol Biol Cell 2000, 11: 2949–2959.
Moore JK, Stuchell-Brereton MD, Cooper JA: Function of dynein in budding yeast: mitotic spindle positioning in a polarized cell. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 2009, 66: 546–555. 10.1002/cm.20364
Li YY, Yeh E, Hays T, Bloom K: Disruption of mitotic spindle orientation in a yeast dynein mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993, 90: 10096–10100. 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10096
Eshel D, Urrestarazu LA, Vissers S, Jauniaux JC, van Vliet-Reedijk JC, Planta RJ, Gibbons IR: Cytoplasmic dynein is required for normal nuclear segregation in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993, 90: 11172–11176. 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11172
Yeh E, Skibbens RV, Cheng JW, Salmon ED, Bloom K: Spindle dynamics and cell cycle regulation of dynein in the budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol 1995, 130: 687–700. 10.1083/jcb.130.3.687
Pereira G, Hofken T, Grindlay J, Manson C, Schiebel E: The Bub2p spindle checkpoint links nuclear migration with mitotic exit. Mol Cell 2000, 6: 1–10. 10.1016/S1097-2765(00)00002-2
Bloecher A, Venturi GM, Tatchell K: Anaphase spindle position is monitored by the BUB2 checkpoint. Nat Cell Biol 2000, 2: 556–558. 10.1038/35019601
Wang Y, Hu F, Elledge SJ: The Bfa1/Bub2 GAP complex comprises a universal checkpoint required to prevent mitotic exit. Curr Biol 2000, 10: 1379–1382. 10.1016/S0960-9822(00)00779-X
Morgan DO: The Cell Cycle-Principles of Control. New Science Press Ltd; 2007.
Hartwell LH, Culotti J, Pringle JR, Reid BJ: Genetic control of the cell division cycle in yeast. Science 1974, 183: 46–51. 10.1126/science.183.4120.46
Nasmyth K: Control of the yeast cell cycle by the Cdc28 protein kinase. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1993, 5: 166–179. 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90099-C
Visintin R, Craig K, Hwang ES, Prinz S, Tyers M, Amon A: The phosphatase Cdc14 triggers mitotic exit by reversal of Cdk-dependent phosphorylation. Mol Cell 1998, 2: 709–718. 10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80286-5
Stegmeier F, Amon A: Closing mitosis: the functions of the Cdc14 phosphatase and its regulation. Annu Rev Genet 2004, 38: 203–232. 10.1146/annurev.genet.38.072902.093051
Mocciaro A, Schiebel E: Cdc14: a highly conserved family of phosphatases with non-conserved functions? J Cell Sci 2010, 123: 2867–2876. 10.1242/jcs.074815
Shou W, Seol JH, Shevchenko A, Baskerville C, Moazed D, Chen ZW, Jang J, Charbonneau H, Deshaies RJ: Exit from mitosis is triggered by Tem1-dependent release of the protein phosphatase Cdc14 from nucleolar RENT complex. Cell 1999, 97: 233–244. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80733-3
Visintin R, Hwang ES, Amon A: Cfi1 prevents premature exit from mitosis by anchoring Cdc14 phosphatase in the nucleolus. Nature 1999, 398: 818–823. 10.1038/19775
Traverso EE, Baskerville C, Liu Y, Shou W, James P, Deshaies RJ, Charbonneau H: Characterization of the Net1 cell cycle-dependent regulator of the Cdc14 phosphatase from budding yeast. J Biol Chem 2001, 276: 21924–21931. 10.1074/jbc.M011689200
Visintin R, Stegmeier F, Amon A: The role of the polo kinase Cdc5 in controlling Cdc14 localization. Mol Biol Cell 2003, 14: 4486–4498. 10.1091/mbc.E03-02-0095
Queralt E, Lehane C, Novak B, Uhlmann F: Downregulation of PP2A(Cdc55) phosphatase by separase initiates mitotic exit in budding yeast. Cell 2006, 125: 719–732. 10.1016/j.cell.2006.03.038
Amon A: A decade of Cdc14--a personal perspective. Delivered on 9 July 2007 at the 32nd FEBS Congress in Vienna, Austria. FEBS J 2008, 275: 5774–5784. 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06693.x
Yoshida S, Asakawa K, Toh-e A: Mitotic exit network controls the localization of Cdc14 to the spindle pole body in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Biol 2002, 12: 944–950. 10.1016/S0960-9822(02)00870-9
Stegmeier F, Visintin R, Amon A: Separase, polo kinase, the kinetochore protein Slk19, and Spo12 function in a network that controls Cdc14 localization during early anaphase. Cell 2002, 108: 207–220. 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00618-9
Yoshida S, Toh-e A: Budding yeast Cdc5 phosphorylates Net1 and assists Cdc14 release from the nucleolus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2002, 294: 687–691. 10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00544-2
Khmelinskii A, Lawrence C, Roostalu J, Schiebel E: Cdc14-regulated midzone assembly controls anaphase B. J Cell Biol 2007, 177: 981–993. 10.1083/jcb.200702145
Khmelinskii A, Roostalu J, Roque H, Antony C, Schiebel E: Phosphorylation-dependent protein interactions at the spindle midzone mediate cell cycle regulation of spindle elongation. Dev Cell 2009, 17: 244–256. 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.06.011
Ross KE, Cohen-Fix O: A role for the FEAR pathway in nuclear positioning during anaphase. Dev Cell 2004, 6: 729–735. 10.1016/S1534-5807(04)00128-5
Sullivan M, Morgan DO: Finishing mitosis, one step at a time. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2007, 8: 894–903. 10.1038/nrm2276
Rock JM, Amon A: The FEAR network. Curr Biol 2009, 19: R1063–1068. 10.1016/j.cub.2009.10.002
Sullivan M, Higuchi T, Katis VL, Uhlmann F: Cdc14 phosphatase induces rDNA condensation and resolves cohesin-independent cohesion during budding yeast anaphase. Cell 2004, 117: 471–482. 10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00415-5
D'Amours D, Stegmeier F, Amon A: Cdc14 and condensin control the dissolution of cohesin-independent chromosome linkages at repeated DNA. Cell 2004, 117: 455–469.
Pereira G, Schiebel E: Cdc14 phosphatase resolves the rDNA segregation delay. Nat Cell Biol 2004, 6: 473–475. 10.1038/ncb0604-473
Jaspersen SL, Charles JF, Tinker-Kulberg RL, Morgan DO: A late mitotic regulatory network controlling cyclin destruction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Cell 1998, 9: 2803–2817.
Meitinger F, Petrova B, Lombardi IM, Bertazzi DT, Hub B, Zentgraf H, Pereira G: Targeted localization of Inn1, Cyk3 and Chs2 by the mitotic-exit network regulates cytokinesis in budding yeast. J Cell Sci 2010, 123: 1851–1861. 10.1242/jcs.063891
Yeong FM, Lim HH, Surana U: MEN, destruction and separation: mechanistic links between mitotic exit and cytokinesis in budding yeast. Bioessays 2002, 24: 659–666. 10.1002/bies.10106
Surana U, Amon A, Dowzer C, McGrew J, Byers B, Nasmyth K: Destruction of the CDC28/CLB mitotic kinase is not required for the metaphase to anaphase transition in budding yeast. Embo J 1993, 12: 1969–1978.
Asakawa K, Yoshida S, Otake F, Toh-e A: A novel functional domain of Cdc15 kinase is required for its interaction with Tem1 GTPase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 2001, 157: 1437–1450.
Shirayama M, Matsui Y, Toh EA: The yeast TEM1 gene, which encodes a GTP-binding protein, is involved in termination of M phase. Mol Cell Biol 1994, 14: 7476–7482.
Toyn JH, Johnston LH: The Dbf2 and Dbf20 protein kinases of budding yeast are activated after the metaphase to anaphase cell cycle transition. EMBO J 1994, 13: 1103–1113.
Mah AS, Jang J, Deshaies RJ: Protein kinase Cdc15 activates the Dbf2-Mob1 kinase complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001, 98: 7325–7330. 10.1073/pnas.141098998
Luca FC, Mody M, Kurischko C, Roof DM, Giddings TH, Winey M: Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mob1p is required for cytokinesis and mitotic exit. Mol Cell Biol 2001, 21: 6972–6983. 10.1128/MCB.21.20.6972-6983.2001
Stoepel J, Ottey MA, Kurischko C, Hieter P, Luca FC: The mitotic exit network Mob1p-Dbf2p kinase complex localizes to the nucleus and regulates passenger protein localization. Mol Biol Cell 2005, 16: 5465–5479. 10.1091/mbc.E05-04-0337
Mohl DA, Huddleston MJ, Collingwood TS, Annan RS, Deshaies RJ: Dbf2-Mob1 drives relocalization of protein phosphatase Cdc14 to the cytoplasm during exit from mitosis. J Cell Biol 2009, 184: 527–539. 10.1083/jcb.200812022
Jaspersen SL, Charles JF, Morgan DO: Inhibitory phosphorylation of the APC regulator Hct1 is controlled by the kinase Cdc28 and the phosphatase Cdc14. Curr Biol 1999, 9: 227–236. 10.1016/S0960-9822(99)80111-0
Sohrmann M, Schmidt S, Hagan I, Simanis V: Asymmetric segregation on spindle poles of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe septum-inducing protein kinase Cdc7p. Genes Dev 1998, 12: 84–94. 10.1101/gad.12.1.84
Geymonat M, Spanos A, Smith SJ, Wheatley E, Rittinger K, Johnston LH, Sedgwick SG: Control of mitotic exit in budding yeast. In vitro regulation of Tem1 GTPase by Bub2 and Bfa1. J Biol Chem 2002, 277: 28439–28445. 10.1074/jbc.M202540200
Shirayama M, Matsui Y, Tanaka K, Toh-e A: Isolation of a CDC25 family gene, MSI2/LTE1, as a multicopy suppressor of ira1. Yeast 1994, 10: 451–461. 10.1002/yea.320100404
Yoshida S, Ichihashi R, Toh-e A: Ras recruits mitotic exit regulator Lte1 to the bud cortex in budding yeast. J Cell Biol 2003, 161: 889–897. 10.1083/jcb.200301128
Geymonat M, Spanos A, de Bettignies G, Sedgwick SG: Lte1 contributes to Bfa1 localization rather than stimulating nucleotide exchange by Tem1. J Cell Biol 2009, 187: 497–511. 10.1083/jcb.200905114
Chan LY, Amon A: Spindle position is coordinated with cell-cycle progression through establishment of mitotic exit-activating and -inhibitory zones. Mol Cell 2010, 39: 444–454. 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.07.032
Hofken T, Schiebel E: A role for cell polarity proteins in mitotic exit. EMBO J 2002, 21: 4851–4862. 10.1093/emboj/cdf481
Hofken T, Schiebel E: Novel regulation of mitotic exit by the Cdc42 effectors Gic1 and Gic2. J Cell Biol 2004, 164: 219–231. 10.1083/jcb.200309080
Jensen S, Geymonat M, Johnson AL, Segal M, Johnston LH: Spatial regulation of the guanine nucleotide exchange factor Lte1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Sci 2002, 115: 4977–4991. 10.1242/jcs.00189
Seshan A, Bardin AJ, Amon A: Control of Lte1 localization by cell polarity determinants and Cdc14. Curr Biol 2002, 12: 2098–2110. 10.1016/S0960-9822(02)01388-X
Pereira G, Manson C, Grindlay J, Schiebel E: Regulation of the Bfa1p-Bub2p complex at spindle pole bodies by the cell cycle phosphatase Cdc14p. J Cell Biol 2002, 157: 367–379. 10.1083/jcb.200112085
Jaspersen SL, Morgan DO: Cdc14 activates cdc15 to promote mitotic exit in budding yeast. Curr Biol 2000, 10: 615–618. 10.1016/S0960-9822(00)00491-7
Konig C, Maekawa H, Schiebel E: Mutual regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase and the mitotic exit network. J Cell Biol 2010, 188: 351–368. 10.1083/jcb.200911128
Shirayama M, Zachariae W, Ciosk R, Nasmyth K: The Polo-like kinase Cdc5p and the WD-repeat protein Cdc20p/fizzy are regulators and substrates of the anaphase promoting complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Embo J 1998, 17: 1336–1349. 10.1093/emboj/17.5.1336
Wang Y, Shirogane T, Liu D, Harper JW, Elledge SJ: Exit from exit: resetting the cell cycle through Amn1 inhibition of G protein signaling. Cell 2003, 112: 697–709. 10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00121-1
Visintin C, Tomson BN, Rahal R, Paulson J, Cohen M, Taunton J, Amon A, Visintin R: APC/C-Cdh1-mediated degradation of the Polo kinase Cdc5 promotes the return of Cdc14 into the nucleolus. Genes Dev 2008, 22: 79–90. 10.1101/gad.1601308
Hoyt MA, Totis L, Roberts BT: S. cerevisiae genes required for cell cycle arrest in response to loss of microtubule function. Cell 1991, 66: 507–517. 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90014-3
Li R, Murray AW: Feedback control of mitosis in budding yeast. Cell 1991, 66: 519–531. 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90015-5
Wang Y, Burke DJ: Checkpoint genes required to delay cell division in response to nocodazole respond to impaired kinetochore function in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 1995, 15: 6838–6844.
Pangilinan F, Spencer F: Abnormal kinetochore structure activates the spindle assembly checkpoint in budding yeast. Mol Biol Cell 1996, 7: 1195–1208.
Krapp A, Simanis V: An overview of the fission yeast septation initiation network (SIN). Biochem Soc Trans 2008, 36: 411–415. 10.1042/BST0360411
Song K, Mach KE, Chen CY, Reynolds T, Albright CF: A novel suppressor of ras1 in fission yeast, byr4, is a dosage-dependent inhibitor of cytokinesis. J Cell Biol 1996, 133: 1307–1319. 10.1083/jcb.133.6.1307
Bardin AJ, Amon A: Men and sin: what's the difference? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2001, 2: 815–826. 10.1038/35099020
Alexandru G, Zachariae W, Schleiffer A, Nasmyth K: Sister chromatid separation and chromosome re-duplication are regulated by different mechanisms in response to spindle damage. EMBO J 1999, 18: 2707–2721. 10.1093/emboj/18.10.2707
Fesquet D, Fitzpatrick PJ, Johnson AL, Kramer KM, Toyn JH, Johnston LH: A Bub2p-dependent spindle checkpoint pathway regulates the Dbf2p kinase in budding yeast. EMBO J 1999, 18: 2424–2434. 10.1093/emboj/18.9.2424
Fraschini R, Formenti E, Lucchini G, Piatti S: Budding yeast Bub2 is localized at spindle pole bodies and activates the mitotic checkpoint via a different pathway from Mad2. J Cell Biol 1999, 145: 979–991. 10.1083/jcb.145.5.979
Li R: Bifurcation of the mitotic checkpoint pathway in budding yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999, 96: 4989–4994. 10.1073/pnas.96.9.4989
Lee SE, Jensen S, Frenz LM, Johnson AL, Fesquet D, Johnston LH: The Bub2-dependent mitotic pathway in yeast acts every cell cycle and regulates cytokinesis. J Cell Sci 2001, 114: 2345–2354.
Spellman PT, Sherlock G, Zhang MQ, Iyer VR, Anders K, Eisen MB, Brown PO, Botstein D, Futcher B: Comprehensive identification of cell cycle-regulated genes of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae by microarray hybridization. Mol Biol Cell 1998, 9: 3273–3297.
Hu F, Wang Y, Liu D, Li Y, Qin J, Elledge SJ: Regulation of the Bub2/Bfa1 GAP complex by Cdc5 and cell cycle checkpoints. Cell 2001, 107: 655–665. 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00580-3
Geymonat M, Spanos A, Walker PA, Johnston LH, Sedgwick SG: In vitro regulation of budding yeast Bfa1/Bub2 GAP activity by Cdc5. J Biol Chem 2003, 278: 14591–14594. 10.1074/jbc.C300059200
Hu F, Elledge SJ: Bub2 is a cell cycle regulated phospho-protein controlled by multiple checkpoints. Cell Cycle 2002, 1: 351–355. 10.4161/cc.1.5.154
Wang Y, Ng TY: Phosphatase 2A negatively regulates mitotic exit in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Cell 2006, 17: 80–89. 10.1091/mbc.E04-12-1109
Tong AH, Lesage G, Bader GD, Ding H, Xu H, Xin X, Young J, Berriz GF, Brost RL, Chang M, et al.: Global mapping of the yeast genetic interaction network. Science 2004, 303: 808–813. 10.1126/science.1091317
Pereira G, Schiebel E: Kin4 kinase delays mitotic exit in response to spindle alignment defects. Mol Cell 2005, 19: 209–221. 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.05.030
D'Aquino KE, Monje-Casas F, Paulson J, Reiser V, Charles GM, Lai L, Shokat KM, Amon A: The protein kinase Kin4 inhibits exit from mitosis in response to spindle position defects. Mol Cell 2005, 19: 223–234.
Maekawa H, Priest C, Lechner J, Pereira G, Schiebel E: The yeast centrosome translates the positional information of the anaphase spindle into a cell cycle signal. J Cell Biol 2007, 179: 423–436. 10.1083/jcb.200705197
Hwa Lim H, Yeong FM, Surana U: Inactivation of mitotic kinase triggers translocation of MEN components to mother-daughter neck in yeast. Mol Biol Cell 2003, 14: 4734–4743. 10.1091/mbc.E03-04-0238
Frenz LM, Lee SE, Fesquet D, Johnston LH: The budding yeast Dbf2 protein kinase localises to the centrosome and moves to the bud neck in late mitosis. J Cell Sci 2000,113(Pt 19):3399–3408.
Molk JN, Schuyler SC, Liu JY, Evans JG, Salmon ED, Pellman D, Bloom K: The differential roles of budding yeast Tem1p, Cdc15p, and Bub2p protein dynamics in mitotic exit. Mol Biol Cell 2004, 15: 1519–1532. 10.1091/mbc.E03-09-0708
Bardin AJ, Visintin R, Amon A: A mechanism for coupling exit from mitosis to partitioning of the nucleus. Cell 2000, 102: 21–31. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00007-6
Adames NR, Cooper JA: Microtubule interactions with the cell cortex causing nuclear movements in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol 2000, 149: 863–874. 10.1083/jcb.149.4.863
Song S, Grenfell TZ, Garfield S, Erikson RL, Lee KS: Essential function of the polo box of Cdc5 in subcellular localization and induction of cytokinetic structures. Mol Cell Biol 2000, 20: 286–298. 10.1128/MCB.20.1.286-298.2000
Visintin R, Amon A: Regulation of the mitotic exit protein kinases Cdc15 and Dbf2. Mol Biol Cell 2001, 12: 2961–2974.
Xu S, Huang HK, Kaiser P, Latterich M, Hunter T: Phosphorylation and spindle pole body localization of the Cdc15p mitotic regulatory protein kinase in budding yeast. Curr Biol 2000, 10: 329–332. 10.1016/S0960-9822(00)00382-1
Yoshida S, Toh-e A: Regulation of the localization of Dbf2 and mob1 during cell division of saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Genet Syst 2001, 76: 141–147. 10.1266/ggs.76.141
Liang F, Jin F, Liu H, Wang Y: The molecular function of the yeast polo-like kinase Cdc5 in Cdc14 release during early anaphase. Mol Biol Cell 2009, 20: 3671–3679. 10.1091/mbc.E08-10-1049
Park JE, Park CJ, Sakchaisri K, Karpova T, Asano S, McNally J, Sunwoo Y, Leem SH, Lee KS: Novel functional dissection of the localization-specific roles of budding yeast polo kinase Cdc5p. Mol Cell Biol 2004, 24: 9873–9886. 10.1128/MCB.24.22.9873-9886.2004
Cenamor R, Jimenez J, Cid VJ, Nombela C, Sanchez M: The budding yeast Cdc15 localizes to the spindle pole body in a cell-cycle-dependent manner. Mol Cell Biol Res Commun 1999, 2: 178–184. 10.1006/mcbr.1999.0173
Gruneberg U, Campbell K, Simpson C, Grindlay J, Schiebel E: Nud1p links astral microtubule organization and the control of exit from mitosis. EMBO J 2000, 19: 6475–6488. 10.1093/emboj/19.23.6475
Chan LY, Amon A: The protein phosphatase 2A functions in the spindle position checkpoint by regulating the checkpoint kinase Kin4. Genes Dev 2009, 23: 1639–1649. 10.1101/gad.1804609
Caydasi AK, Pereira G: Spindle alignment regulates the dynamic association of checkpoint proteins with yeast spindle pole bodies. Dev Cell 2009, 16: 146–156. 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.10.013
Knop M, Schiebel E: Spc98p and Spc97p of the yeast gamma-tubulin complex mediate binding to the spindle pole body via their interaction with Spc110p. EMBO J 1997, 16: 6985–6995. 10.1093/emboj/16.23.6985
Jaspersen SL, Winey M: The budding yeast spindle pole body: structure, duplication, and function. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2004, 20: 1–28. 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.20.022003.114106
Knop M, Schiebel E: Receptors determine the cellular localization of a gamma-tubulin complex and thereby the site of microtubule formation. EMBO J 1998, 17: 3952–3967. 10.1093/emboj/17.14.3952
Fraschini R, D'Ambrosio C, Venturetti M, Lucchini G, Piatti S: Disappearance of the budding yeast Bub2-Bfa1 complex from the mother-bound spindle pole contributes to mitotic exit. J Cell Biol 2006, 172: 335–346. 10.1083/jcb.200507162
Pereira G, Tanaka TU, Nasmyth K, Schiebel E: Modes of spindle pole body inheritance and segregation of the Bfa1p-Bub2p checkpoint protein complex. EMBO J 2001, 20: 6359–6370. 10.1093/emboj/20.22.6359
Monje-Casas F, Amon A: Cell polarity determinants establish asymmetry in MEN signaling. Dev Cell 2009, 16: 132–145. 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.11.002
Caydasi AK, Kurtulmus B, Orrico MI, Hofmann A, Ibrahim B, Pereira G: Elm1 kinase activates the spindle position checkpoint kinase Kin4. J Cell Biol 2010, 190: 975–989. 10.1083/jcb.201006151
Li X, Gianoulis TA, Yip KY, Gerstein M, Snyder M: Extensive in vivo metabolite-protein interactions revealed by large-scale systematic analyses. Cell 2010, 143: 639–650. 10.1016/j.cell.2010.09.048
Snead JL, Sullivan M, Lowery DM, Cohen MS, Zhang C, Randle DH, Taunton J, Yaffe MB, Morgan DO, Shokat KM: A coupled chemical-genetic and bioinformatic approach to Polo-like kinase pathway exploration. Chem Biol 2007, 14: 1261–1272. 10.1016/j.chembiol.2007.09.011
Park CJ, Park JE, Karpova TS, Soung NK, Yu LR, Song S, Lee KH, Xia X, Kang E, Dabanoglu I, et al.: Requirement for the budding yeast polo kinase Cdc5 in proper microtubule growth and dynamics. Eukaryot Cell 2008, 7: 444–453. 10.1128/EC.00283-07
Moore JK, Chudalayandi P, Heil-Chapdelaine RA, Cooper JA: The spindle position checkpoint is coordinated by the Elm1 kinase. J Cell Biol 2010, 191: 493–503. 10.1083/jcb.201006092
Bouquin N, Barral Y, Courbeyrette R, Blondel M, Snyder M, Mann C: Regulation of cytokinesis by the Elm1 protein kinase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Sci 2000,113(Pt 8):1435–1445.
Barral Y, Parra M, Bidlingmaier S, Snyder M: Nim1-related kinases coordinate cell cycle progression with the organization of the peripheral cytoskeleton in yeast. Genes Dev 1999, 13: 176–187. 10.1101/gad.13.2.176
Edgington NP, Blacketer MJ, Bierwagen TA, Myers AM: Control of Saccharomyces cerevisiae filamentous growth by cyclin-dependent kinase Cdc28. Mol Cell Biol 1999, 19: 1369–1380.
Sreenivasan A, Kellogg D: The elm1 kinase functions in a mitotic signaling network in budding yeast. Mol Cell Biol 1999, 19: 7983–7994.
Adams JA: Activation loop phosphorylation and catalysis in protein kinases: is there functional evidence for the autoinhibitor model? Biochemistry 2003, 42: 601–607. 10.1021/bi020617o
Manderson EN, Malleshaiah M, Michnick SW: A novel genetic screen implicates Elm1 in the inactivation of the yeast transcription factor SBF. PLoS One 2008, 3: e1500. 10.1371/journal.pone.0001500
Thomas CL, Blacketer MJ, Edgington NP, Myers AM: Assembly interdependence among the S. cerevisiae bud neck ring proteins Elm1p, Hsl1p and Cdc12p. Yeast 2003, 20: 813–826. 10.1002/yea.1003
Rubenstein EM, McCartney RR, Schmidt MC: Regulatory domains of Snf1-activating kinases determine pathway specificity. Eukaryot Cell 2006, 5: 620–627. 10.1128/EC.5.4.620-627.2006
Nelson SA, Cooper JA: A novel pathway that coordinates mitotic exit with spindle position. Mol Biol Cell 2007, 18: 3440–3450. 10.1091/mbc.E07-03-0242
Moore JK, Magidson V, Khodjakov A, Cooper JA: The spindle position checkpoint requires positional feedback from cytoplasmic microtubules. Curr Biol 2009, 19: 2026–2030. 10.1016/j.cub.2009.10.020
Adames NR, Oberle JR, Cooper JA: The surveillance mechanism of the spindle position checkpoint in yeast. J Cell Biol 2001, 153: 159–168. 10.1083/jcb.153.1.159
Musacchio A, Salmon ED: The spindle-assembly checkpoint in space and time. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2007, 8: 379–393. 10.1038/nrm2163
Howell BJ, McEwen BF, Canman JC, Hoffman DB, Farrar EM, Rieder CL, Salmon ED: Cytoplasmic dynein/dynactin drives kinetochore protein transport to the spindle poles and has a role in mitotic spindle checkpoint inactivation. J Cell Biol 2001, 155: 1159–1172. 10.1083/jcb.200105093
De Antoni A, Pearson CG, Cimini D, Canman JC, Sala V, Nezi L, Mapelli M, Sironi L, Faretta M, Salmon ED, Musacchio A: The Mad1/Mad2 complex as a template for Mad2 activation in the spindle assembly checkpoint. Curr Biol 2005, 15: 214–225. 10.1016/j.cub.2005.01.038
Wojcik E, Basto R, Serr M, Scaerou F, Karess R, Hays T: Kinetochore dynein: its dynamics and role in the transport of the Rough deal checkpoint protein. Nat Cell Biol 2001, 3: 1001–1007. 10.1038/ncb1101-1001
Biggins S, Murray AW: The budding yeast protein kinase Ipl1/Aurora allows the absence of tension to activate the spindle checkpoint. Genes Dev 2001, 15: 3118–3129. 10.1101/gad.934801
Ciferri C, Pasqualato S, Screpanti E, Varetti G, Santaguida S, Dos Reis G, Maiolica A, Polka J, De Luca JG, De Wulf P, et al.: Implications for kinetochore-microtubule attachment from the structure of an engineered Ndc80 complex. Cell 2008, 133: 427–439. 10.1016/j.cell.2008.03.020
DeLuca JG, Gall WE, Ciferri C, Cimini D, Musacchio A, Salmon ED: Kinetochore microtubule dynamics and attachment stability are regulated by Hec1. Cell 2006, 127: 969–982. 10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.047
Cheeseman IM, Chappie JS, Wilson-Kubalek EM, Desai A: The conserved KMN network constitutes the core microtubule-binding site of the kinetochore. Cell 2006, 127: 983–997. 10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.039
Tanaka TU, Rachidi N, Janke C, Pereira G, Galova M, Schiebel E, Stark MJ, Nasmyth K: Evidence that the Ipl1-Sli15 (Aurora kinase-INCENP) complex promotes chromosome bi-orientation by altering kinetochore-spindle pole connections. Cell 2002, 108: 317–329. 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00633-5
Biggins S, Severin FF, Bhalla N, Sassoon I, Hyman AA, Murray AW: The conserved protein kinase Ipl1 regulates microtubule binding to kinetochores in budding yeast. Genes Dev 1999, 13: 532–544. 10.1101/gad.13.5.532
Cheeseman IM, Anderson S, Jwa M, Green EM, Kang J, Yates JR, Chan CS, Drubin DG, Barnes G: Phospho-regulation of kinetochore-microtubule attachments by the Aurora kinase Ipl1p. Cell 2002, 111: 163–172. 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00973-X
Francisco L, Wang W, Chan CS: Type 1 protein phosphatase acts in opposition to IpL1 protein kinase in regulating yeast chromosome segregation. Mol Cell Biol 1994, 14: 4731–4740.
Liu D, Vleugel M, Backer CB, Hori T, Fukagawa T, Cheeseman IM, Lampson MA: Regulated targeting of protein phosphatase 1 to the outer kinetochore by KNL1 opposes Aurora B kinase. J Cell Biol 2010, 188: 809–820. 10.1083/jcb.201001006
Liu D, Vader G, Vromans MJ, Lampson MA, Lens SM: Sensing chromosome bi-orientation by spatial separation of aurora B kinase from kinetochore substrates. Science 2009, 323: 1350–1353. 10.1126/science.1167000
Maresca TJ, Salmon ED: Welcome to a new kind of tension: translating kinetochore mechanics into a wait-anaphase signal. J Cell Sci 2010, 123: 825–835. 10.1242/jcs.064790
Nezi L, Musacchio A: Sister chromatid tension and the spindle assembly checkpoint. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2009, 21: 785–795. 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.09.007
Khodjakov A, Pines J: Centromere tension: a divisive issue. Nat Cell Biol 2010, 12: 919–923. 10.1038/ncb1010-919
Cheng J, Turkel N, Hemati N, Fuller MT, Hunt AJ, Yamashita YM: Centrosome misorientation reduces stem cell division during ageing. Nature 2008, 456: 599–604. 10.1038/nature07386
Inaba M, Yuan H, Salzmann V, Fuller MT, Yamashita YM: E-cadherin is required for centrosome and spindle orientation in Drosophila male germline stem cells. PLoS One 2010, 5: e12473. 10.1371/journal.pone.0012473
Estivill-Torrus G, Pearson H, van Heyningen V, Price DJ, Rashbass P: Pax6 is required to regulate the cell cycle and the rate of progression from symmetrical to asymmetrical division in mammalian cortical progenitors. Development 2002, 129: 455–466.
Yamashita YM, Fuller MT: Asymmetric centrosome behavior and the mechanisms of stem cell division. J Cell Biol 2008, 180: 261–266. 10.1083/jcb.200707083
Lechler T, Fuchs E: Asymmetric cell divisions promote stratification and differentiation of mammalian skin. Nature 2005, 437: 275–280. 10.1038/nature03922
Quyn AJ, Appleton PL, Carey FA, Steele RJ, Barker N, Clevers H, Ridgway RA, Sansom OJ, Nathke IS: Spindle orientation bias in gut epithelial stem cell compartments is lost in precancerous tissue. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 6: 175–181. 10.1016/j.stem.2009.12.007
Kaltschmidt JA, Davidson CM, Brown NH, Brand AH: Rotation and asymmetry of the mitotic spindle direct asymmetric cell division in the developing central nervous system. Nat Cell Biol 2000, 2: 7–12. 10.1038/71323
Adams RJ: Metaphase spindles rotate in the neuroepithelium of rat cerebral cortex. J Neurosci 1996, 16: 7610–7618.
Harvey K, Tapon N: The Salvador-Warts-Hippo pathway - an emerging tumour-suppressor network. Nat Rev Cancer 2007, 7: 182–191. 10.1038/nrc2070
Hong SP, Leiper FC, Woods A, Carling D, Carlson M: Activation of yeast Snf1 and mammalian AMP-activated protein kinase by upstream kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003, 100: 8839–8843. 10.1073/pnas.1533136100
Nath N, McCartney RR, Schmidt MC: Yeast Pak1 kinase associates with and activates Snf1. Mol Cell Biol 2003, 23: 3909–3917. 10.1128/MCB.23.11.3909-3917.2003
Sutherland CM, Hawley SA, McCartney RR, Leech A, Stark MJ, Schmidt MC, Hardie DG: Elm1p is one of three upstream kinases for the Saccharomyces cerevisiae SNF1 complex. Curr Biol 2003, 13: 1299–1305. 10.1016/S0960-9822(03)00459-7
Hedbacker K, Carlson M: SNF1/AMPK pathways in yeast. Front Biosci 2008, 13: 2408–2420. 10.2741/2854
Hardie DG: AMP-activated/SNF1 protein kinases: conserved guardians of cellular energy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2007, 8: 774–785. 10.1038/nrm2249
Williams T, Brenman JE: LKB1 and AMPK in cell polarity and division. Trends Cell Biol 2008, 18: 193–198. 10.1016/j.tcb.2008.01.008
Brenman JE: AMPK/LKB1 signaling in epithelial cell polarity and cell division. Cell Cycle 2007, 6: 2755–2759. 10.4161/cc.6.22.4927
Manning G, Plowman GD, Hunter T, Sudarsanam S: Evolution of protein kinase signaling from yeast to man. Trends Biochem Sci 2002, 27: 514–520. 10.1016/S0968-0004(02)02179-5
Hunter T, Plowman GD: The protein kinases of budding yeast: six score and more. Trends Biochem Sci 1997, 22: 18–22. 10.1016/S0968-0004(96)10068-2
Miranda-Saavedra D, Stark MJ, Packer JC, Vivares CP, Doerig C, Barton GJ: The complement of protein kinases of the microsporidium Encephalitozoon cuniculi in relation to those of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe. BMC Genomics 2007, 8: 309. 10.1186/1471-2164-8-309
Kim J, Song K: The study of Bfa1p(E438K) suggests that Bfa1 control the mitotic exit network in different mechanisms depending on different checkpoint-activating signals. Mol Cells 2006, 21: 251–260.
Kim J, Jang SS, Song K: Different levels of Bfa1/Bub2 GAP activity are required to prevent mitotic exit of budding yeast depending on the type of perturbations. Mol Biol Cell 2008, 19: 4328–4340. 10.1091/mbc.E08-02-0149
Bardin AJ, Boselli MG, Amon A: Mitotic exit regulation through distinct domains within the protein kinase Cdc15. Mol Cell Biol 2003, 23: 5018–5030. 10.1128/MCB.23.14.5018-5030.2003
Gentry MS, Hallberg RL: Localization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein phosphatase 2A subunits throughout mitotic cell cycle. Mol Biol Cell 2002, 13: 3477–3492. 10.1091/mbc.02-05-0065
Bembenek J, Kang J, Kurischko C, Li B, Raab JR, Belanger KD, Luca FC, Yu H: Crm1-mediated nuclear export of Cdc14 is required for the completion of cytokinesis in budding yeast. Cell Cycle 2005, 4: 961–971.
Acknowledgements and Funding
We are grateful to Elmar Schiebel and Fouzia Ahmad for critically reading the manuscript and to Saravanan Palani for comments. We thank to all MBCC lab members for discussions. We apologize from those whose work was not cited because of the scope of the paper.
The work of GP is supported by the Helmholtz association grant (HZ-NG-111) and Marie Curie fellowship (MEXT-CT-2006-042544). BI and AKC are funded by the Helmholtz and DKFZ international PhD Program respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
AKC wrote the manuscript with help of BI and the critical input of GP. AKC and BI designed and prepared the figures. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Caydasi, A.K., Ibrahim, B. & Pereira, G. Monitoring spindle orientation: Spindle position checkpoint in charge. Cell Div 5, 28 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1186/1747-1028-5-28
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1747-1028-5-28