Abstract
Background
Trichomoniasis is the most common sexually transmitted disease. However, limited data are available on an effective technique for the diagnosis of Trichomonas vaginalis.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted to evaluate the accuracy of wet mount microscopy, latex agglutination, Diamond’s media, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for detection of T. vaginalis among symptomatic women who attended the gynecological clinic at Khartoum, Sudan.
Results
Of the 297 women studied, 252 (84.8%) were positive for T. vaginalis by wet mount microscopy, 257 (86.5%) by latex agglutination, 253 (85.2%) by Diamond’s media, and 253 (85.2%) by PCR. The sensitivity and specificity of wet mount microscopy were 99.2% and 97.7%, respectively, compared with PCR. The sensitivity and specificity of latex agglutination and Diamond’s media were 99.6% and 88.6%, and 100.0% and 86.4%, respectively, compared with PCR.
Conclusions
In this study, wet mount microscopy, latex agglutination, and Diamond’s media were found to be highly sensitive and specific. However, the availability and cost effectiveness might limit the use of Diamond’s media and PCR in routine practice.
Virtual slides
The virtual slide(s) for this article can be found here: http://www.diagnosticpathology.diagnomx.eu/vs/7859723851211496
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Trichomonas vaginalis is a flagellated eukaryotic organism, which has caused a worldwide health problem, with an estimated 170 million people infected annually with T. vaginalis[1, 2]. Infection with Trichomonas is associated with a significant risk of morbidity in women, including pelvic inflammatory disease, adverse pregnancy outcomes (e.g., preterm labor and delivery), cervical dysplasia, infertility, increased risk of postoperative infection, and human immunodeficiency virus acquisition and transmission [3–5].
Therefore, accurate diagnosis of T. vaginalis infection is an important issue. T. vaginalis infection cannot be accurately diagnosed based on the clinical picture because clinical symptoms of trichomoniasis may be similar to those of other sexually transmitted diseases [6]. Different diagnostic methods that are usually used (wet mount method) for routine field diagnosis of T. vaginalis have low sensitivity [7, 8]. Other methods for diagnosis of T. vaginalis, such as culture and polymerase chain reaction (PCR), are time consuming and not available in all field laboratories [8]. Therefore, a simple and rapid diagnostic test with acceptable sensitivity and specificity is required. The latex agglutination test has a high sensitivity and specificity [8, 9]. However, there are few recently published data on the performance of different diagnostic methods for T. vaginalis and no data are available in Sudan.
The current study was conducted to evaluate the performance of wet mount microscopy, latex agglutination, Diamond’s media, and PCR for detection of T. vaginalis among symptomatic women who attended the gynecological clinic in Khartoum, Sudan. Findings from this study will be of great importance for care givers and researchers, and it will add to the diagnostic tools for different diseases among pregnant and non-pregnant Sudanese women [10–12].
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted during April to August 2012 at Khartoum, Sudan. After signing an informed consent and recording the socio-demographic characteristics and symptomatic history (vaginal discharge, itching, dysuria, dyspareunia, and foul odor) women who attended the gynecological clinic in Khartoum were approached to participate in the study.
Cotton-tipped applicators were used to obtain vaginal fluid swabs from each woman using a vaginal speculum. At least three swabs were collected in a sterile test tube that contained 0.2 ml of 5% glucose saline. This tube was maintained at body temperature for wet mount examination, which was performed within 10 minutes of collection of the specimen. The applicator was gently agitated in the saline, and a wet mount on a clean slide was prepared and observed under a microscope for motile trichomonads (400×) to confirm flagellar movement, morphological features, and the number of T. vaginalis.
The wet preparation was then inoculated into Diamond’s media, the latex agglutination test was applied, and T vaginalis DNA was detected by real-time PCR. An Amplicor swab (Roche Molecular) was used to collect specimens for PCR amplification, while Dacron-tipped swabs were used to collect materials for microscopic examination, the latex agglutination test, and culturing of the organism.
Diamond’s media
A total of 30 g of Diamond’s media was suspended in 900 ml of purified filtered water. This was then heated with frequent agitation, boiled for 1 minute, and then sterilized at 121°C for 15 minutes. After cooling to 45–50°C, 100 ml of horse serum and antibiotics were added and mixed thoroughly, and were dispensed into sterile culture tubes. The prepared media was stored at 2–8°C and protected from direct light, and dehydrated powder was stored in a dry place in tightly-sealed containers at 2–25°C. Prior to inoculation, the media was brought up to 35–37°C in an aerobic incubator for approximately 1–2 hours. Specimens were examined for T. vaginalis prior to inoculation into culture media. Tubes were incubated aerobically in a slanted position (45° angle) at 35–37°C. Cultures were examined by wet mount for motile trophozoites after 24 or 48 hours. Centrifugation of the culture was used to detect low-level growth, and then examined microscopically daily by adding one drop on a slide, and covering with a cover slip. Negative cultures were incubated for at least 96 hours and examined before reporting the culture.
Quality control of diamond’s media
An internal quality control for Diamond’s media was included by incubating one tube of Diamond’s media per batch to monitor the sterility of reagents. One tube of Diamond’s media was inoculated with a known culture of T. vaginalis. To check the quality of the batch of Diamond’s media, another tube of Diamond’s media was inoculated with a known culture.
Latex agglutination test
All reagents were brought to room temperature. The test latex was shaken well immediately before use. A volume of 50 μL of the vaginal swab suspension was eluted by agitation in phosphate-buffered saline. One drop of test latex was added. Both liquids were stirred to a completely homogenous mixture that covered the whole surface of the reaction zone. The glass slide was tilted with a rotating action continuously for 3 minutes. After 3 minutes, the degree of agglutination was obtained.
The degree of agglutination was recorded as follows. Latex that had agglutinated with a lot of accumulation around the edge of the reaction zone was recoded as positive+++. Agglutinated particles that were clearly seen against a background of granular latex were recorded as positive++. Agglutination that was just able to be discerned compared with a negative control was recorded as positive+. No agglutination compared with a negative control was negative.
A negative control was used in an adjacent reaction zone in parallel with a test sample to distinguish between a weak positive and negative result. A positive control was used to monitor the performance of the test latex. Running a positive control the first time the kit was used was recommended, as well as when removed from storage.
Positive and negative controls were run every time the latex agglutination test was performed. A negative test was repeated to ensure the results.
PCR
The target for the real-time PCR assay was a 67-base pair region of a repeated sequence of the T. vaginalis genome (Gene Bank Accession Number L23861). The primers and probes were designed using Primer Express (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). The PCR reaction contained 25 μl of 2× TaqMan1 Universal Master Mix (Applied Biosystems, manufactured by Roche, Branchburg, NJ, USA), with 5 ml each (final concentration of 900 nM) of TV forward primer (Tv3, 5′-ATTGTCGAACATTGGTCTTACCTC-3) and TV reverse primer (Tv7, 5′-TCTGTGCCGTCTTCAAGTATGC-3′), 5 ml (final concentration of 225 nM) of probe (5′FAM-TCA146 A.M. [13]. TTT CGG ATG GTC AAG CAG CCA-TAMRA-3′), and 5 μl of sample DNA. A volume of 5 μl of eluted DNA was used as a template in a final volume of 25 μl with PCR buffer (Hotstar Taq Mastermix; QIN gene), 25 μg of bovine serum albumin, 5 Mm Mg C12, and 2.0 pmol of each primer. The thermocycler used was set to provide amplification consisting of 15 minutes at 95°C followed by 50 cycles of 15 seconds at 95°C, and 1 minute at 60°C. Amplification detection and data analysis were performed with the Applied Biosystems 7500 Real Time PCR System. The PCR output from this system consisted of a cycle threshold (Ct) value, representing the amplification cycle in which the signal exceeded the background fluorescence, and indicating the parasite-specific DNA load in the sample tested.
A sample size of 295 subjects was calculated using the OpenEpi-Epidemiological calculator with 80% power and a confidence interval of 95% to detect a difference of 5% at α = 0.05, with 10% of non-respondents/incomplete data.
Ethical approval for the study was obtained from the Khartoum Hospital Ethical Board.
Statistics
Data were analyzed using SPSS software version 19.0. Sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values were determined as described previously [14].
Results
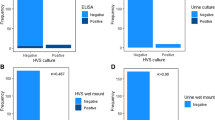
During the study period there were 542 admissions to the hospital. The majority of them (364, 67.2%) were obstetrical cases and the rest (178, 32.8%) were gynecological cases. There were 297 (35.1%) women with history suggestive of T. vaginalis and they were included in the study. There characteristics were shown in Table 1. Of the 297 women studied, 252 (84.8%) were positive for T. vaginalis by wet mount microscopy, 257 (86.5%) by latex agglutination, 253 (85.2%) by Diamond’s media, and 253 (85.2%) by PCR. The sensitivity and specificity of wet mount microscopy were 99.2% and 97.7%, respectively, compared with PCR. The sensitivity and specificity of the latex agglutination test and Diamond’s media were 99.6% and 88.6%, and 100.0% and 86.4%, respectively, compared with PCR (Table 2 and Figure 1).
While wet mount microscopy had the highest positive predictive value (99.6%, confidence interval = 98.1–100.0%), Diamond’s media had the highest negative predictive value (100.0%, confidence interval = 92.4–100.0) in the diagnosis of T. vaginalis (Table 2).
Discussion
The main findings of the current study were a high sensitivity and specificity of the investigated diagnostic tools (wet mount microscopy, latex agglutination test, and Diamond’s media). Additionally, wet mount microscopy had the highest positive predictive value and Diamond’s media had the highest negative predictive value in the diagnosis of T. vaginalis.
Recently, the sensitivity and specificity of wet mount microscopy were reported as 60% and 100%, respectively, whereas sensitivity and specificity of the culture (In-Pouch) system were 73.33% and 100%, respectively, when PCR was the gold standard in the diagnosis of T. vaginalis[15]. Moreover, Piperaki et al. [16] reported that PCR was the most sensitive method (100%), followed by culture (69.6%), wet mount (69.6%), and latex agglutination (54.6%) for detecting T. vaginalis. Likewise, Audo Sarkodie et al. [7] reported that the sensitivity of the latex agglutination test was 98.8% and specificity was 92.1% when an expanded gold standard based on the wet mount and culture results was used. In another study, Abraham and colleagues showed a high sensitivity (97.7%) [17], and Fernandez et al. showed a sensitivity of 86.7% and specificity of 95.1% for the latex agglutination test in detection of Trichomonas vaginalis in vaginal discharge [18]. However, inappropriate sensitivity and specificity (positive and negative predictive values were 6% and 100%, respectively) of the latex agglutination test were reported when culture was the gold standard [8].
One of the limitations of the current study was the selection criteria, where only symptomatic women were enrolled. This might be the reason behind the high rate of prevalence (approximately 85.0%) of T. vaginalis among these women, even different diagnostic tools were used. Another reason for the high rate of prevalence of T. vaginalis among the women in the current study might reflect the high sensitivity and specificity of the clinical diagnosis itself. Recently, a study showed that the sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values of the clinical diagnosis compared with those of the culture method for T. vaginalis were 75%, 95%, 28%, and 99%, respectively [19]. Interestingly a high prevalence of (40%) trichomoniasis was reported among women in [20] Zambia, even among women who had never had sex [19].
Conclusions
In this study, wet mount microscopy, the latex agglutination test, and Diamond’s media were found to be highly sensitive and specific. However, the availability and cost effectiveness might limit the use of Diamond’s media and PCR in routine practice.
References
World Health Organization: Global prevalence and incidence of selected curable sexually transmitted infections. 2001, Geneva, Switzerland: WHO
Johnston VJ, Mabey DC: Global epidemiology and control of Trichomonas vaginalis. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2008, 21: 56-64. 10.1097/QCO.0b013e3282f3d999.
Munson E, Napierala M, Olson R, Endes T, Block T, Hryciuk JE, Schell RF: Impact of Trichomonas vaginalis transcription-mediated amplification-based analyte-specific-reagent testing in a metropolitan setting of high sexually transmitted disease prevalence. J Clin Microbiol. 2008, 46: 3368-3374. 10.1128/JCM.00564-08.
Nye MB, Schwebke JR, Body BA: Comparison of APTIMA Trichomonas vaginalis transcription-mediated amplification to wet mount microscopy, culture, and polymerase chain reaction for diagnosis of trichomoniasis in men and women. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2009, 200: 188-e1188.e7
Verteramo R, Calzolari E, Degener AM, Masciangelo R, Patella A: Trichomonas vaginalis infection: risk indicators among women attending for routine gynecologic examination. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2008, 34: 233-237. 10.1111/j.1447-0756.2007.00692.x.
Sobngwi-Tambekou J, Taljaard D, Nieuwoudt M, Lissouba P, Puren A, Auvert B: Male circumcision and Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis and Trichomonas vaginalis: observations after a randomised controlled trial for HIV prevention. Sex Transm Infect. 2009, 85: 116-120.
Audo Sarkodie Y, Opoku BK, Danso KA, Weiss HA, Mabey D: Comparison of latex agglutination, wet preparation and culture for the detection of Trichomonas vaginalis. Sex Transm Infect. 2004, 80: 201-203. 10.1136/sti.2003.007864.
Darani HY, Ahmadi F, Zabardast N, Yousefi HA, Shirzad H: Development of a latex agglutination test as a simple and rapid method for diagnosis of Trichomonas vaginalis infection. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2010, 2: 63-66.
Martens GM, Faro S, Soper D: Infectious disease in women. 2001, Philadelphia: Saunders, 1
Kashif AH, Adam GK, Mohmmed AA, Elzaki SE, AbdelHalim AM, Adam I: Reliability of rapid diagnostic test for diagnosing peripheral and placental malaria in an area of unstable malaria transmission in Eastern Sudan. Diagn Pathol. 2013, 8: 59-10.1186/1746-1596-8-59.
Abdelrahman EG, Gasim GI, Musa IR, Elbashir LM, Adam I: Red blood cell distribution width and iron deficiency anemia among pregnant Sudanese women. Diagn Pathol. 2012, 7: 168-10.1186/1746-1596-7-168.
Adam I, Ahmed S, Mahmoud MH, Yassin MI: Comparison of HemoCue® hemoglobin-meter and automated hematology analyzer in measurement of hemoglobin levels in pregnant women at Khartoum hospital, Sudan. Diagn Pathol. 2012, 7: 30-10.1186/1746-1596-7-30.
Caliendo AM, Jordan JA, Green AM, Ingersoll J, Diclemente RJ, Wingood GM: Real-time PCR improves detection of Trichomonas vaginalis infection compared with culture using self-collected vaginal swabs. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol. 2005, 13: 145-150. 10.1080/10647440500068248.
Harper R, Reeves B: Reporting of precision of estimates for diagnostic accuracy: a review. BMJ. 1999, 318: 1322-1323.
Patil MJ, Nagamoti JM, Metgud SC: Diagnosis of Trichomonas vaginalis from vaginal specimens by wet mount microscopy, in pouch TV culture system, and PCR. J Glob Infect Dis. 2012, 4 (1): 22-25. 10.4103/0974-777X.93756.
Piperaki ET, Theodora M, Mendris M, Barbitsa L, Pitiriga V, Antsaklis A, Tsakris A: Prevalence of Trichomonas vaginalis infection in women attending a major gynaecological hospital in Greece: a cross-sectional study. J Clin Pathol. 2010, 63: 249-5323. 10.1136/jcp.2009.070920.
Lopez Abraham AM, Artiles Mde L, Ferandez Masso JR, San Martin DG, Alonso M, Alvarez RE: Evaluation of an agglutination method with latex particles sensitized for diagnosis of vaginal trichomoniasis. Rev Cubana Med Trop. 2005, 57: 133-136.
Fernandez Limia O, Lantero MI, Betancourt A, de Armas E, Villoch A: Prevalence of Candida albicans and Trichomonas vaginalis in pregnant women in Havana city by an immunologic latex agglutination test. MedGenMed. 2004, 6: 50-
Buvé A, Weiss HA, Laga M, Van Dyck E, Musonda R, Zekeng L, Kahindo M, Anagonou S, Morison L, Robinson NJ, Hayes RJ: Study group on heterogeneity of HIV epidemics in African cities: the epidemiology of trichomoniasis in women in four African cities. AIDS. 2001, 15 (Suppl 4): S89-S96.
Vijaya Mn D, Umashankar K, Sudha , Nagure AG, Kavitha G: Prevalence of the trichomonas vaginalis infection in a tertiary care hospital in rural bangalore, southern India. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013, 7: 1401-1403.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
AMS, GIG and IA designed the study. HSA, SMB and GIG conducted the clinical work. AMS and ABS conducted the laboratory work. IA, ABS and SMB performed the statistical analyses. All of the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Saleh, A.M., Abdalla, H.S., Satti, A.B. et al. Diagnosis of Trichomonous vaginalis by microscopy, latex agglutination, diamond’s media, and PCR in symptomatic women, Khartoum, Sudan. Diagn Pathol 9, 49 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-1596-9-49
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-1596-9-49