Abstract
Spinal cord α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors (AMPARs) mediate acute spinal processing of nociceptive and non-nociceptive information, but whether and how their activation contributes to the central sensitization that underlies persistent inflammatory pain are still unclear. Here, we examined the role of spinal AMPARs in the development and maintenance of complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA)-induced persistent inflammatory pain. Intrathecal application of two selective non-competitive AMPAR antagonists, CFM-2 (25 and 50 μg) and GYKI 52466 (50 μg), significantly attenuated mechanical and thermal hypersensitivities on the ipsilateral hind paw at 2 and 24 h post-CFA injection. Neither CFM-2 nor GYKI 52466 affected the contralateral basal responses to thermal and mechanical stimuli. Locomotor activity was not altered in any of the drug-treated animals. CFA-induced inflammation did not change total expression or distribution of AMPAR subunits GluR1 and GluR2 in dorsal horn but did alter their subcellular distribution. The amount of GluR2 was markedly increased in the crude cytosolic fraction and decreased in the crude membrane fraction from the ipsilateral L4–5 dorsal horn at 24 h (but not at 2 h) post-CFA injection. Conversely, the level of GluR1 was significantly decreased in the crude cytosolic fraction and increased in the crude membrane fraction from the ipsilateral L4–5 dorsal horn at 24 h (but not at 2 h) post-CFA injection. These findings suggest that spinal AMPARs might participate in the central spinal mechanism of persistent inflammatory pain.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA)-type ionotropic glutamate receptors (AMPARs) mediate most fast excitatory synaptic transmissions and play a critical role in synaptic plasticity in the mammalian central nervous system [1, 2]. AMPARs are tetramers that comprise a combination of four subunits termed GluR1-4 [3]. Changes in postsynaptic membrane trafficking or in synaptic targeting of these AMPAR subunits alter synaptic strength and have been recognized as a central mechanism underlying various forms of synaptic plasticity [1, 2].
Spinal central sensitization, a specific form of synaptic plasticity, is a mechanism that underlies the development and maintenance of pain hypersensitivity after peripheral inflammation [4, 5]. In addition to mediating acute spinal processing of nociceptive and non-nociceptive information, the activation of spinal AMPA/kainate receptors might contribute to spinal central sensitization under inflammation-induced persistent pain conditions. Intrathecal pretreatment with AMPA/kainate receptor antagonists was shown to markedly reduce thermal injury-induced mechanical tactile allodynia, second-phase formalin-induced nociceptive behaviors, and carrageenan-induced thermal and mechanical hypersensitivities [6, 7]. Because these antagonists are not highly selective for AMPARs, it is still unclear whether spinal AMPARs play a critical role in persistent inflammatory pain. In addition, these AMPA/kainate receptor antagonists also produce unwanted side effects [8], which limit their therapeutic potential in persistent pain.
Recent evidence suggests that peripheral inflammatory insults might regulate synaptic trafficking of AMPAR subunits in spinal cord. Capsaicin-induced acute visceral inflammatory insult rapidly increased the amount of GluR1 protein, but not GluR2 or GluR3 proteins, in the spinal cord membrane fraction and correspondingly decreased the level of GluR1 in the cytosolic fraction, without affecting total GluR1 or GluR2 protein expression in spinal cord [9]. The level of postsynaptic GluR1, but not GluR2 or GluR3, at lamina II nonpeptidergic C-fiber synapses was increased during capsaicin-induced acute inflammation [10]. Complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA)-induced persistent inflammation significantly elevates the amount of GluR1 in the postsynaptic density fraction from spinal cord [11]. This finding indicates that GluR1 could be recruited to the plasma membrane of spinal cord neurons by persistent noxious inflammation. A previous study reported that CFA-induced persistent inflammation increased expression of GluR1 and GluR2 mRNA and the density of total GluR1 and GluR2 immunohistochemical staining in dorsal horn [12], suggesting that the levels of GluR1 and GluR2 may be increased in both plasma membrane and cytosolic fractions of dorsal horn neurons after CFA injection. Thus, it is still unclear whether CFA-induced persistent inflammation, like capsaicin-induced acute inflammatory insult, leads to changes in synaptic trafficking of AMPAR subunits in dorsal horn neurons.
Here, we first characterized the role of AMPARs in CFA-induced persistent inflammatory pain in rats using two highly selective non-competitive AMPAR antagonists, 1-(4'-aminophenyl)-3,5-dihydro-7,8-dimethoxy-4H-2,3-benzodiazepin-4-one (CFM-2) and 4-(methyl-9H-1,3-dioxolo [4,5-h][2, 3]benzodiazepin-5-yl)-benzenamine hydrochloride (GYKI 52466) [13–15]. We then examined whether CFA-induced peripheral inflammation altered expression and distribution of total GluR1 and GluR2 proteins in dorsal horn. Finally, we determined whether the amounts of GluR1 and GluR2 proteins were changed in crude plasma membrane and cytosolic fractions from dorsal horn during CFA-induced inflammatory pain conditions.
Materials and methods
Animal preparation
Male Sprague-Dawley rats (250–300 g) were housed in cages on a standard 12:12 h light/dark cycle. Water and food were available ad libitum until rats were transported to the laboratory approximately 1 h before experiments. The animals were used in accordance with protocols that were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee at the Johns Hopkins University and were consistent with the ethical guidelines of the National Institutes of Health and the International Association for the Study of Pain. All efforts were made to minimize animal suffering and to reduce the number of animals used.
Intrathecal catheters were implanted into animals under isoflurane anesthesia. A polyethylene (PE-10) tube was inserted into the subarachnoid space at the rostral level of the spinal cord lumbar enlargement segment through an incision at the atlanto-occipital membrane according to the method described previously [16, 17]. The animals were allowed to recover for 5–10 days before being used experimentally. Rats showing any neurologic deficits postoperatively were discarded from the study. The position of the PE-10 catheter was confirmed in each animal after behavioral testing.
Experimental drugs
CFA was purchased from Sigma Chemical Co. (St. Louis, MO). 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX, a competitive AMPA/kainate receptor antagonist), CFM-2 (a selective non-competitive AMPAR antagonist), and GYKI 52466 (a selective non-competitive AMPAR antagonist) were purchased from Tocris Bioscience (Ellisville, MO). CNQX was dissolved in 0.9% physiologic saline, whereas CFM-2 and GYKI 52466 were dissolved in 10% dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO).
CFA-induced persistent inflammatory pain model
To induce persistent inflammatory pain, the rats were placed under isoflurane anesthesia, and 100 μl of CFA (1 mg/ml Mycobacterium tuberculosis) solution was injected into the plantar side of one hind paw. Our previous studies showed that significant CFA-induced thermal and mechanical pain hypersensitivities appeared at 2 h, reached a peak level between 6 and 24 h, and were maintained for at least 72 h [17]. Therefore, we chose 2 h and 24 h post-CFA injection to represent the development and maintenance phases of CFA-induced persistent inflammatory pain for the pharmacologic and biochemical studies.
To examine the role of spinal cord AMPARs in persistent inflammatory pain, two selective competitive AMPAR antagonists, CFM-2 (5, 25, or 50 μg/10 μl) and GYKI 52466 (50 μg/10 μl) were injected intrathecally followed by 10 μl of saline to flush the catheter (total volume of the catheter: 10 μl) at 2 h or 24 h post-CFA injection. To compare the effects of selective and non-selective AMPAR antagonists on persistent inflammatory pain, a competitive AMPA/kainate receptor antagonist, CNQX (6.1 μg/10 μl), was given according to the same protocol. Saline and 10% DMSO were used as controls. The behavioral tests described below were performed 1 day before CFA injection (baseline) and at 20 min after drug administration. Separate groups of rats were used for the 2-h and 24-h behavioral tests. The antagonist doses used were based on data from previous studies [18–21] and our pilot work. The experimenters were blinded to the treatment groups.
Behavior testing
To measure paw withdrawal response to noxious heat stimuli, each animal was placed in a Plexiglas chamber on a glass plate located above a light box. Radiant heat from a Model 336 Analgesic Meter (IITC, Inc./Life Science Instruments, Woodland Hills, CA) was applied by aiming a beam of light through a hole in the light box through the glass plate to the middle of the plantar surface of each hind paw. When the animal lifted its foot, the light beam was turned off. The length of time between the start of the light beam and the foot lift was defined as the paw withdrawal latency. Each trial was repeated five times at 5-min intervals for each paw. A cut-off time of 20 s was used to avoid paw tissue damage.
To measure paw withdrawal response to repeated mechanical stimuli, each animal was placed in a Plexiglas chamber on an elevated mesh screen. A single trial of mechanical stimuli consisted of eight applications of a calibrated von Frey filament (8.01 mN, Stoelting Co., Wood Dale, IL) within a 2–3-s period. Each trial was repeated 10 times at 3-min intervals on each hind paw. The occurrence of hind paw withdrawal in each of these 10 trials was expressed as a percent response frequency, and this percentage was used as an indication of the amount of hind paw withdrawal.
Locomotor function testing
To examine whether the antagonists used in behavioral testing affected the locomotor function, three reflexes (placing, grasping, and righting) were tested as described previously [16, 22]. In brief, the naïve animals received a 10-μl intrathecal injection of vehicle (saline or 10% DMSO), CNQX (6.1 μg/10 μl), CFM-2 (50 μg/10 μl), or GYKI 52466 (50 μg/10 μl). Twenty minutes later, the following tests were performed with the experimenter blind to drug treatment: (1) Placing reflex: The experimenter held the rat with hind limbs slightly lower than the forelimbs and brought the dorsal surfaces of the hind paws into contact with the edge of a table. The experimenter recorded whether the hind paws were placed on the table surface reflexively; (2) Grasping reflex: The experimenter placed the rats on a wire grid and recorded whether the hind paws grasped the wire on contact; (3) Righting reflex: The experimenter placed the rat's back on a flat surface and noted whether it immediately assumed the normal upright position. Scores for placing, grasping, and righting reflexes were based on counts of each normal reflex exhibited in five trials. In addition, the rat's general behaviors, including spontaneous activity (e.g. walking and running), were observed.
Western blot analysis
Expression of GluR1 and GluR2 proteins in the total soluble fraction, crude membrane fraction, and crude cytosolic fraction was examined. In brief, the animals were sacrificed by decapitation at 2 and 24 h after injection of saline (100 μl) or CFA into the plantar side of a hind paw. Naïve animals were used as controls. The L4–5 spinal cord ipsilateral and contralateral to CFA or saline injection was removed. The dorsal part of the spinal cord was separated from the ventral part and collected. Total soluble fraction, crude membrane fraction, and crude cytosolic fraction were prepared as described below. The samples were heated for 5 min at 99°C and then loaded onto 4% stacking/7.5% separating SDS-polyacrylamide gels. The proteins were electrophoretically transferred onto nitrocellulose membrane. The blotting membrane was blocked with 3% non-fat dry milk for 1 h and incubated overnight at 4°C with rabbit anti-GluR1 (1:200; Upstate/CHEMICON, Temecula, CA), rabbit anti-GluR2 (1:500; Upstate/CHEMICON), rabbit anti-N-cadherin (1:1,000; BD Biosciences, Palo Alto, CA), mouse anti-PSD-95 (1:1,000; Upstate/CHEMICON), or monoclonal mouse anti-β-actin (1:10,000; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA). N-cadherin and PSD-95 were used as loading controls and markers for crude membrane fraction, whereas β-actin was used as a loading control for total soluble fraction and cytosolic fraction. The proteins were detected with anti-rabbit or anti-mouse secondary antibody and visualized using the chemiluminescence reagents provided with the ECL kit (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, Piscataway, NJ) and exposure to film. The intensity of blots was quantified with densitometry. The blot density from naïve animals was set as 100%.
Subcellular fractionation of proteins
After tissues were homogenized in lysis buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, 250 mM sucrose, 5 mM MgCl2, 2 mM EGTA, 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 2 mM sodium orthovanadate, 1 mM NaF, 1 mM leupeptin, 2 mM pepstatin A, 1 mM dithiothreitol), the crude homogenates were centrifuged at 4°C for 15 min at 900 g. The supernatant was collected, and the pellet (nuclei and debris fraction) discarded. After the measurement of protein concentration, 20% of the supernatant was removed and considered to be the total soluble fraction. The remaining supernatant (80%) was centrifuged at 37,000 g for 1 h at 4°C. The supernatant was considered to be the crude cytosolic fraction, and the pellet, the crude plasma membrane fraction. The pellet was dissolved in buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 1.5% SDS, and 0.1% Triton X-100). Protein concentrations of the three fractions were measured, and samples were prepared for Western blotting, as described above.
Immunocytochemistry
The animals were deeply anesthetized with isoflurane and perfused with 4% paraformaldehyde in phosphate buffer (0.1 M, pH 7.4) at 2 or 24 h after saline or CFA injection. Naïve rats were used as controls. The L4–5 spinal cord segments were harvested, post-fixed in the same fixative solution for 2–4 h, cryoprotected by immersion in 30% sucrose overnight at 4°C, and frozen-sectioned at 25 μm. Every fourth section was collected (at least 30 sections/rat). The sections were blocked for 1 h at 37°C in 0.01 M phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) containing 10% normal goat serum plus 0.3% Triton X-100. Half of the sections (approximately 15 sections/rat) were incubated in primary rabbit antibody for GluR1 (1:500; Upstate/CHEMICON) and the remaining sections in primary mouse antibody for GluR2 (1:1,000; Upstate/CHEMICON) for 48 h at 4°C. The sections were finally incubated in biotinylated goat anti-rabbit or anti-mouse IgG (1:200; Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA) for 1 h at 37°C followed by avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (1:100; Vector) for 1 h at 37°C. The immune reaction product was visualized by catalysis of 3,3-diaminobenzidine by horseradish peroxidase in the presence of 0.01% H2O2.
Immunostained spinal cord sections were quantified with an Olympus microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) linked to a Toshiba 3CCD camera (Toshiba, Japan) and I-Cube computer image analysis system (I-Cube, Cambridge, MA). The entire superficial dorsal horn was delimited to quantify the optical density of GluR1 and GluR2 immunoreactivity. Five spinal cord sections randomly selected from a total of 15 sections from each animal were analyzed, and the relative optical densities of five sections were averaged to provide a mean for each animal.
Statistical Analysis
The results from the behavioral tests, Western blotting, and immunocytochemistry were statistically analyzed with a one-way or two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. When ANOVA showed significant difference, pairwise comparisons between means were tested by the post hoc Tukey method. Significance was set at p < 0.05. The statistical software package SigmaStat (Systat, Port Richard, CA) was used to perform all statistical analyses.
Results
Effects of intrathecal selective and nonselective AMPAR antagonists on CFA-induced mechanical and thermal hypersensitivities
The effect of intrathecal administration of CFM-2 on mechanical and thermal hypersensitivities in animals at 2 h or 24 h after CFA injection was first examined. Consistent with previous studies [17], CFA injection produced a significant increase in paw withdrawal frequency in response to mechanical stimulation (indicating mechanical hypersensitivity; Fig. 1A) and a remarkable decrease in paw withdrawal latency in response to thermal stimulation (indicating thermal hypersensitivity; Fig. 1C) on the ipsilateral side at both 2 h (n = 14, 7/test) and 24 h (n = 14, 7/test) post-CFA injection in the vehicle group. Intrathecal administration of CFM-2 dose-dependently attenuated CFA-induced mechanical hypersensitivity at 2 h and 24 h post-CFA injection (Fig. 1A). Compared with the corresponding vehicle-treated groups, the 25-μg dose of CFM-2 reduced paw withdrawal frequencies by 26% (p < 0.05) and 35% (p < 0.01) at 2 h and 24 h (n = 6/time point) post-CFA injection, respectively, and the 50-μg dose reduced paw withdrawal frequencies by 37% (p < 0.05) and 49% (p < 0.01) at these two time points (n = 6/time point). Paw withdrawal frequencies after administration of 5 μg of CFM-2 at 2 h (n = 6) and 24 h (n = 6) post-CFA injection were not significantly different from those of the vehicle group at those time points (p > 0.05). Interestingly, only the highest CFM-2 dose (50 μg) significantly reduced the CFA-induced thermal hypersensitivity (Fig. 1C). Compared with vehicle-treated rats, paw withdrawal latencies were increased by 31% at 2 h post-CFA injection (n = 6; p < 0.05) and by 70% at 24 h post-CFA injection (n = 6; p < 0.05). Neither the vehicle nor any of the three CFM-2 doses significantly altered basal paw withdrawal responses to mechanical and thermal stimuli applied to the contralateral hind paw at 2 h or 24 h post-CFA injection (Fig. 1B,D). Likewise, none of the doses of CFM-2 significantly affected basal paw withdrawal responses to mechanical and thermal stimuli in naïve rats (data not shown).
Effect of intrathecal injection of CFM-2 (5, 25, and 50 μg) on the paw withdrawal responses to mechanical (A and B) and thermal (C and D) stimuli on the ipsilateral (A and C) and contralateral (B and D) sides at 2 and 24 h after intraplantar CFA injection. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. n = 6 rats/dose/test, except n = 7 for the vehicle-treated group. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 vs the corresponding vehicle-treated group.
To further confirm the effect of selective non-competitive AMPAR antagonists on persistent inflammatory pain, we intrathecally injected another selective non-competitive AMPAR antagonist, GYKI 52466 [15], at 2 h and 24 h post-CFA injection. A 50-μg injection of GYKI 52466 (n = 6/test/time point) attenuated both CFA-induced mechanical and thermal hypersensitivities on the ipsilateral hind paw (Fig. 2A,E). Paw withdrawal frequencies were 31% and 38% lower than those of the vehicle-treated group at 2 h (p < 0.05) and 24 h (p < 0.05) post-CFA injection, respectively (Fig. 2A). Paw withdrawal latencies were 38% and 92.5% higher than those of the vehicle-treated group at 2 h (p < 0.05) and 24 h (p < 0.05) post-CFA injection, respectively (Fig. 2E). Similar to CFM-2, 50 μg GYKI 52466 had no effect on paw withdrawal responses to thermal or mechanical stimuli applied to the contralateral hind paw at either time point (Fig. 2B,F) or in naïve rats (data not shown).
Effects of intrathecal injection of GYKI 52466 (50 μg, n = 6/test/time point, A, B, E, and F) and CNQX (6.1 μg, n = 5/test/time point, C, D, G, and H) on the paw withdrawal responses to mechanical (A–D) and thermal (E–H) stimuli on the ipsilateral (A, C, E, and G) and contralateral (B, D, F, and H) sides at 2 and 24 h after intraplantar CFA injection. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 vs the corresponding vehicle-treated group.
CNQX is a non-selective competitive AMPAR antagonist. Compared with the responses of the vehicle-treated group (n = 20; 5/test/time point), intrathecal CNQX (6.1 μg) significantly reduced CFA-induced mechanical and thermal hypersensitivities at 2 h (p < 0.01) and 24 h (p < 0.01) after CFA injection (Fig. 2C,G). However, the same dose of CNQX also significantly reduced basal paw withdrawal responses to mechanical stimulation on the contralateral hind paw at both time points (both p < 0.05; Fig. 2D), although it had no effect on basal paw withdrawal responses to thermal stimulation on the contralateral hind paw after CFA injection (Fig. 2H).
Effects of intrathecal selective and nonselective AMPAR antagonists on locomotor functions
To exclude the possibility that the behavioral effects described above were due to impaired motor functions caused by these antagonists, we then examined the effects of CFM-2, GYKI 52466, and CNQX on locomotor functions in naive animals. As indicated in Table 1, at the doses used, none of the antagonists significantly altered placing, grasping, or righting reflexes. In addition, no significant differences were observed in the rats' general behaviors (such as walking and running) between the vehicle-treated and the antagonist-treated groups.
Effect of CFA-induced peripheral inflammation on expression and distribution of total GluR1 and GluR2 proteins in dorsal horn
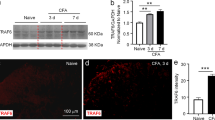
To further define the involvement of spinal cord AMPARs in persistent inflammatory pain, we examined whether CFA-induced inflammation produced the changes in expression of total GluR1 and GluR2 proteins in total soluble fraction derived from dorsal horn. In the ipsilateral and contralateral L4–5 dorsal horn, neither total GluR1 nor total GluR2 protein level was significantly different from that of naïve animals (n = 4) at 2 and 24 h post-saline (n = 4/time point) and post-CFA (n = 4/time point) injection (p > 0.05; Fig. 3A, B).
Expression and distribution of total GluR1 and GluR2 in spinal cord dorsal horn. A and B: Top: representative Western blots showing GluR1 protein (A) and GluR2 protein (B) in total soluble fraction derived from the ipsilateral and contralateral L4–5 dorsal horns of naïve rats (n = 4) and the rats at 2 and 24 h post-saline (S; n = 4/time point) or post-CFA injection (C; n = 4/time point). Bottom: statistical summary of the densitometric analysis expressed relative to the corresponding loading control (β-actin). C: Representative photographs showing the distribution of GluR1 immunoreactive cells (arrow heads) in lamina V and of GluR2 immunoreactive cells (arrows) in laminae II-III. Scale bar: 20 μm. D and E: Representative photographs showing distribution of GluR1 (D) and GluR2 (E) immunoreactivity in the ipsilateral and contralateral L4 dorsal horns at 2 and 24 h post-CFA injection. Scale bar: 200 μm. F: Statistical summary of the optical density of GluR1 and GluR2 immunoreactivity in the ipsilateral and contralateral L4–5 dorsal horns at 2 and 24 h post-saline (n = 3/time point) or post-CFA (n = 3/time point) injection. N: naïve (n = 3). Data are presented as mean ± SEM.
We next examined whether peripheral inflammatory insult affected the distribution of total GluR1 and GluR2 immunoreactivities in the spinal dorsal horn at 2 and 24 h after CFA injection. Consistent with previous studies [12, 23, 24], GluR1 immunoreactivity was distributed mainly in laminae I and II, whereas GluR2 immunoreactivity was concentrated in inner lamina II and lamina III in naïve rats (n = 3). Under high magnification, some GluR1- and GluR2-positive cell bodies were observed in both superficial and deep dorsal horn (Fig. 3C). Neither intraplantar saline nor CFA produced significant changes in the distribution or optical density of GluR1 and GluR2 immunoreactivities in L4–5 spinal dorsal horn on the ipsilateral or contralateral side at 2 h (p > 0.05) or 24 h (p > 0.05) post-saline (n = 6, 3/time point) or post-CFA (n = 6, 3/time point) injection (Fig. 3D–F).
Effect of CFA-induced peripheral inflammation on the levels of GluR1 and GluR2 proteins in plasma membrane fraction and cytosolic fraction from dorsal horn
Finally, we examined whether CFA-induced peripheral inflammation affected the subcellular distribution of GluR1 and GluR2 proteins in dorsal horn neurons. Quantification of the protein levels revealed that, compared with the naïve animals (n = 4), the amount of GluR2 in the CFA-treated group was 90% higher in the cytosolic fraction (Fig. 4A; p < 0.01) and correspondingly 26% lower in the membrane fraction (Fig. 4B; p < 0.05) at 24 h post-CFA injection (n = 4). Conversely, the amount of GluR1 was decreased by 25% in the cytosolic fraction (Fig. 4C; p < 0.05) and correspondingly increased by 23% in the membrane fraction (Fig. 4D; p < 0.05) at 24 h post-CFA injection (n = 8) compared with the values of the naïve group (n = 8). Neither the GluR1 nor the GluR2 levels were significantly changed in either the cytosolic (Fig. 4A, C; p > 0.05) or membrane (Fig. 4B, D; p > 0.05) fraction at 2 h post-CFA injection (n = 4). As expected, no significant differences were observed between the saline-treated and naïve groups in either the cytosolic or membrane fractions at 2 or 24 h post-saline injection (Fig. 4; n = 4–8/time point).
The relative levels of GluR2 (A and B) and GluR1 (C and D) in the crude cytosolic (A and C) and plasma membrane fractions (B and D) from the ipsilateral L 4–5 dorsal horn at 2 and 24 h following saline or CFA injection. Naïve rats (n = 4–8) were used as a control group. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. n = 4–8 rats/treatment. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 vs the corresponding naïve group. E: The specificity of the fractionation procedure. Top: representative Western blots showing the expression of N-cadherin, PSD-95, and β-actin in total soluble fraction, plasma membrane fraction, and cytosolic fraction from L4–5 dorsal horns of naïve rats (n = 3). Bottom: statistical summary of the densitometric analysis expressed relative to the corresponding protein levels in the total soluble fraction.
To test the specificity of the fractionation procedure, the expression levels of a plasma membrane-specific protein (N-cadherin), a postsynaptic density protein (PSD-95), and an intracellular protein (β-actin) were assessed in both crude plasma membrane and cytosolic fractions from naïve rats (n = 3). Consistent with previous studies [9, 22], N-cadherin and PSD-95 were detected at high levels in the crude plasma membrane fraction but were barely detectable in the crude cytosolic fraction (Fig. 4E), whereas β-actin was expressed predominately in the crude cytosolic fraction (Fig. 4E), indicating that the fractionation procedure effectively separated cytosolic proteins from plasma membrane proteins.
Discussion
Peripheral tissue inflammation leads to persistent hyperalgesia in animals that mimics chronic inflammatory pain states in humans. Understanding the mechanisms that underlie persistent inflammatory pain may produce novel therapeutic strategies for prevention and/or treatment of clinical inflammatory pain. Although evidence documented over the last 30 years suggests that AMPARs might be involved in persistent inflammatory pain, the exact role of spinal cord AMPARs in this disorder is unclear. Our study provides pharmacologic evidence that blockade of spinal cord AMPARs produces marked reversal of mechanical and thermal hypersensitivities during the development and maintenance phases of CFA-induced persistent inflammatory pain. In addition, we show that CFA-induced peripheral inflammation leads to GluR2 internalization and GluR1 membrane insertion in dorsal horn neurons, without altering the expression and distribution of total GluR1 and GluR2 proteins in dorsal horn. These findings suggest that spinal cord AMPARs might play a critical role in the central mechanism of persistent inflammatory pain.
The therapeutic potential of AMPAR antagonists in persistent pain has been largely overlooked because it is generally thought that AMPARs are involved primarily in fast synaptic transmission and acute spinal processing of nociceptive and non-nociceptive inputs in the dorsal horn [4]. For example, some earlier studies showed that intrathecal injection of competitive AMPA/kainate receptor antagonists produced dose-dependent antinociception in the tail flick test and hot plate test [25] in rats. Moreover, systemic administration of a competitive AMPA/kainate receptor antagonist, NBQX, reduced chronic allodynia-like response in spinally injured rats; however, it also reduced muscle tone and caused sedation at the dose studied [8]. In our study, intrathecal CNQX, another competitive AMPA/kainate receptor antagonist, markedly attenuated CFA-induced mechanical and thermal hypersensitivities ipsilaterally, but it also significantly reduced basal paw withdrawal response to mechanical stimulation on the contralateral hind paw after peripheral inflammation. These unwanted side effects associated with AMPA/kainate receptor antagonists may prevent them from providing therapeutic potential in persistent pain.
The present study demonstrates that intrathecally administered CFM-2 and GYKI 52466, two highly selective non-competitive AMPAR antagonists [13–15], significantly reverse CFA-induced mechanical and thermal hypersensitivities on the ipsilateral side, without affecting basal nociceptive responses on the contralateral side. Neither CFM-2 nor GYKI 52466 at the doses used affected normal nociceptive responses or locomotor function in naïve animals. These data indicate that CFM-2 and GYKI 52466 at the doses used affect peripheral inflammation-induced behavioral reflex sensitization rather than basal behavioral reflex, suggesting a role of spinal cord AMPARs in mediating the sensitized nociceptive transmission that occurs under persistent inflammatory pain conditions.
Among the four AMPAR subunits, GluR1 and GluR2 are the most abundant in dorsal horn, particularly in the superficial dorsal horn [24, 26], where they are highly concentrated on the postsynaptic neuronal membranes [27, 28]. We found that CFA injection did not affect the distribution or optical density of GluR1 and GluR2 immunoreactivity in dorsal horn. This finding is inconsistent with a previous report that showed that CFA-induced peripheral inflammation increased the density of GluR1 and GluR2 immunoreactivity in dorsal horn [12]. The reason for the discrepancy between the previous and present results is unclear but might be related to different primary antibody and immunostaining duration. Quantitative Western blot analyses from the present study and those of others [29, 30] further demonstrated that the expression levels of total GluR1 and GluR2 proteins were not significantly changed in dorsal horn under CFA-induced inflammatory pain conditions. It is very likely that peripheral inflammatory insult does not alter translation of GluR1 and GluR2 genes and/or degradation of their proteins in dorsal horn neurons.
One important observation that we made is that peripheral persistent inflammation produces distinct changes in the levels of GluR1 and GluR2 in plasma membrane and cytosolic fractions from dorsal horn. Consistent with a recent study [11], the present study showed that CFA injection produced GluR1 membrane insertion in dorsal horn neurons at 24 h post-CFA injection. We also found that GluR2 was markedly internalized in dorsal horn neurons at 24 h post-CFA injection. Moreover, the number of internalized GluR2 subunits is likely greater than the number of GluR1 subunits inserted in the membrane. Electrophysiological studies from our laboratory and those of others demonstrated that Ca2+-permeable AMPARs were significantly increased in the superficial dorsal horn neurons at 24 and 72 h post-CFA injection [31, 32]. Because only GluR2 determines the properties of synaptic AMPAR function, particularly Ca2+ permeability [3], GluR2 internalization might be a major player in AMPAR subunit trafficking in dorsal horn neurons during the maintenance of persistent inflammatory pain syndromes.
An unexpected observation in the current study was that CFA injection did not produce a marked change in the levels of GluR1 and GluR2 in subcellular fractions from dorsal horn at 2 h post-CFA injection. The reason for the discrepancy in AMPAR trafficking at 2 h and 24 h post-CFA injection is unclear, but it may be related to the limited sensitivity of Western blotting. It is possible that GluR1 membrane insertion and GluR2 internalization in dorsal horn neurons are too minimal at 2 h post-CFA injection to be detected by this approach. In addition, synaptic AMPAR exchange for intracellular receptors in dorsal horn neurons may have a long timescale because synaptic AMPAR trafficking events in vitro and in intact brains have a slow rate time constant of ~15–18 h [33, 34].
The molecular mechanisms by which GluR1 is inserted into plasma membrane and GluR2 is internalized into cytoplasm in dorsal horn neurons during the maintenance phase of persistent inflammatory pain are unclear, but they might be related to inflammation-induced spinal cord GluR1 and GluR2 phosphorylation. Protein kinase A phosphorylation of GluR1 Ser845 promotes the surface-expression of GluR1 in cultured hippocampal neurons during activity-dependent long-term potentiation [35] and might also be responsible for spinal GluR1 membrane insertion in vivo following CFA-induced inflammation. Similarly, Protein kinase C phosphorylation of GluR2 at Ser880 disrupts GluR2 binding to its synaptic anchoring protein ABP/GRIP and promotes GluR2 internalization in cultured hippocampal neurons [36, 37]. Such a mechanism might also contribute to CFA-induced internalization of GluR2 subunits in vivo. It will be very important to further elucidate these mechanisms to fully understand the role of spinal AMPAR trafficking in the spinal central sensitization that underlies persistent inflammatory pain.
In conclusion, we demonstrated that selective blockade of spinal AMPAR activity significantly reduces mechanical and thermal hypersensitivities during the development and maintenance of persistent inflammatory pain. We also showed that GluR2 is likely transported away from the plasma membrane and GluR1 inserted into plasma membrane of dorsal horn neurons during the maintenance (but not the development) of persistent inflammatory pain. These findings imply that spinal cord AMPARs are involved in the central mechanism of persistent inflammatory pain.
Abbreviations
- AMPA:
-
α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid
- AMPAR:
-
AMPA receptor
- ANOVA:
-
analysis of variance
- CFA:
-
complete Freund's adjuvant
- DMSO:
-
dimethylsulfoxide
- GluR1:
-
glutamate receptor subunit 1
- GluR2:
-
glutamate receptor subunit 2
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline.
References
Derkach VA, Oh MC, Guire ES, Soderling TR: Regulatory mechanisms of AMPA receptors in synaptic plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci 2007, 8: 101–13. 10.1038/nrn2055
Greger IH, Esteban JA: AMPA receptor biogenesis and trafficking. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2007, 17: 289–97. 10.1016/j.conb.2007.04.007
Dingledine R, Borges K, Bowie D, Traynelis SF: The glutamate receptor ion channels. Pharmacol Rev 1999, 51: 7–61.
Dubner R, Basbaum AI: The Textbook of Pain. Edited by: Wall PD, Melzack R. Churchill-Livingstone, London; 1994:225–241.
Ji RR, Kohno T, Moore KA, Woolf CJ: Central sensitization and LTP: do pain and memory share similar mechanisms? Trends Neurosci 2003, 26: 696–705. 10.1016/j.tins.2003.09.017
Nozaki-Taguchi N, Yaksh TL: Pharmacology of spinal glutamatergic receptors in post-thermal injury-evoked tactile allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia. Anesthesiology 2002, 96: 617–26. 10.1097/00000542-200203000-00018
Sorkin LS, Yaksh TL, Doom CM: Pain models display differential sensitivity to Ca2+-permeable non-NMDA glutamate receptor antagonists. Anesthesiology 2001, 95: 965–73. 10.1097/00000542-200110000-00028
Hao JX, Xu XJ: Treatment of a chronic allodynia-like response in spinally injured rats: effects of systemically administered excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists. Pain 1996, 66: 279–85. 10.1016/0304-3959(96)03039-4
Galan A, Laird JM, Cervero F: In vivo recruitment by painful stimuli of AMPA receptor subunits to the plasma membrane of spinal cord neurons. Pain 2004, 112: 315–23. 10.1016/j.pain.2004.09.011
Larsson M, Broman J: Translocation of GluR1-containing AMPA receptors to a spinal nociceptive synapse during acute noxious stimulation. J Neurosci 2008, 28: 7084–90. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5749-07.2008
Katano T, Furue H, Okuda-Ashitaka E, Tagaya M, Watanabe M, Yoshimura M, Ito S: N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein (NSF) is involved in central sensitization in the spinal cord through GluR2 subunit composition switch after inflammation. Eur J Neurosci 2008, 27: 3161–70. 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06293.x
Zhou QQ, Imbe H, Zou S, Dubner R, Ren K: Selective upregulation of the flip-flop splice variants of AMPA receptor subunits in the rat spinal cord after hind paw inflammation. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 2001, 88: 186–93. 10.1016/S0169-328X(01)00041-9
Chimirri A, De Sarro G, De Sarro A, Gitto R, Grasso S, Quartarone S, Zappalà M, Giusti P, Libri V, Constanti A, Chapman AG: 1-Aryl-3,5-dihydro-4H-2,3-benzodiazepin-4-ones: novel AMPA receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 1997, 40: 1258–69. 10.1021/jm960506l
Monnerie H, Le Roux PD: Glutamate receptor agonist kainite enhances primary dendrite number and length from immature mouse cortical neurons in vitro. J of Neurosci Res 2006, 83: 944–56. 10.1002/jnr.20805
Ouardouz M, Durand J: GYKI 52466 antagonizes glutamate responses but not NMDA and kainate responses in rat abducens motoneurones. Neurosci Lett 1991, 125: 5–8. 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90115-A
Liaw WJ, Stephens RL Jr, Binns BC, Chu Y, Sepkuty JP, Johns RA, Rothstein JD, Tao YX: Spinal glutamate uptake is critical for maintaining normal sensory transmission in rat spinal cord. Pain 2005, 115: 60–70. 10.1016/j.pain.2005.02.006
Zhang B, Tao F, Liaw WJ, Bredt DS, Johns RA, Tao YX: Effect of knock down of spinal cord PSD-93/chapsin-110 on persistent pain induced by complete Freund's adjuvant and peripheral nerve injury. Pain 2003, 106: 187–96. 10.1016/j.pain.2003.08.003
Mao J, Price DD, Hayes RL, Lu J, Mayer DJ: Differential roles of NMDA and non-NMDA receptor activation in induction and maintenance of thermal hyperalgesia in rats with painful peripheral mononeuropathy. Brain Res 1992, 598: 271–8. 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90193-D
Jones TL, Sorkin LS: Calcium-permeable α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid/kainate receptors mediate development, but not maintenance, of secondary allodynia evoked by first-degree burn in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2004, 310: 223–9. 10.1124/jpet.103.064741
Minami T, Matsumura S, Nishizawa M, Sasaguri Y, Hamanaka N, Ito S: Acute and late effects on induction of allodynia by acromelic acid, a mushroom poison related structurally to kainic acid. Br J Pharmacol 2004, 42: 679–88. 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705834
Sluka KA, Jordan HH, Westlund KN: Reduction in joint swelling and hyperalgesia following post-treatment with a non-NMDA glutamate receptor antagonist. Pain 1994, 59: 95–100. 10.1016/0304-3959(94)90052-3
Tao Y-X, Huang YZ, Mei L, Johns RA: Expression of PSD-95/SAP90 is critical for N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-mediated thermal hyperalgesia in the spinal cord. Neuroscience 2000, 98: 201–6. 10.1016/S0306-4522(00)00193-7
Harris JA, Corsi M, Quartaroli M, Arban R, Bentivoglio M: Upregulation of spinal glutamate receptors in chronic pain. Neuroscience 1996, 74: 7–12. 10.1016/0306-4522(96)00196-0
Engelman HS, Allen TB, MacDermott AB: The distribution of neurons expressing calcium-permeable AMPA receptors in the superficial laminae of the spinal cord dorsal horn. J Neurosci 1999, 19: 2081–9.
Nishiyama T, Yaksh TL, Weber E: Effects of intrathecal NMDA and non-NMDA antagonists on acute thermal nociception and their interaction with morphine. Anesthesiology 1998, 89: 715–22. 10.1097/00000542-199809000-00023
Furuyama T, Kiyama H, Sato K, Park HT, Maeno H, Takagi H, Tohyama M: Region-specific expression of subunits of ionotropic glutamate receptors (AMPA-type, KA-type and NMDA receptors) in the rat spinal cord with special reference to nociception. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 1993, 18: 141–51. 10.1016/0169-328X(93)90183-P
Morrison BM, Janssen WG, Gordon JW, Morrison JH: Light and electron microscopic distribution of the AMPA receptor subunit, GluR2, in the spinal cord of control and G86R mutant superoxide dismutase transgenic mice. J Comp Neurol 1998, 395: 523–34. 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19980615)395:4<523::AID-CNE8>3.0.CO;2-3
Lu CR, Hwang SJ, Phend KD, Rustioni A, Valtschanoff JG: Primary afferent terminals in spinal cord express presynaptic AMPA receptors. J Neurosci 2002, 22: 9522–9.
Katano T, Mabuchi T, Tagaya M, Ito S: Proteomic analysis of functional molecules in the spinal cord after inflammation. Soc Neurosci Abstr 2006. Program No. 51.5
Lu Y, Sun YN, Wu X, Sun Q, Liu FY, Xing GG, Wan Y: Role of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionate (AMPA) receptor subunit GluR1 in spinal dorsal horn in inflammatory nociception and neuropathic nociception in rat. Brain Res 2008, 1200: 19–26. 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.01.012
Vikman KS, Rycroft BK, Christie MJ: Switch to Ca2+permeable AMPA and reduced NR2B NMDA receptor mediated neurotransmission at dorsal horn nociceptive synapses during inflammatory pain in the rat. J Physiol 2008, 586: 515–527. 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.145581
Voitenko NV, Shang X, Kopach O, Sotnik A, Isaev D, Belan , Tao Y-X: A switch of Ca2+-impermeable AMPA receptors expressed on spinal dorsal horn neurons into Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors after peripheral inflammation. Soc Neurosci Abstr 2007. Program No. 284.12
Adesnik H, Nicoll RA, England PM: Photoinactivation of native AMPA receptors reveals their real-time trafficking. Neuron 2005, 48: 977–85. 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.11.030
McCormack SG, Stornetta RL, Zhu JJ: Synaptic AMPA receptor exchange maintains bidirectional plasticity. Neuron 2006, 50: 75–88. 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.02.027
Oh MC, Derkach VA, Guire ES, Soderling TR: Extrasynaptic membrane trafficking regulated by GluR1 serine 845 phosphorylation primes AMPA receptors for long-term potentiation. J Biol Chem 2006, 281: 752–758. 10.1074/jbc.M509677200
Chung HJ, Xia J, Scannevin RH, Zhang X, Huganir RL: Phosphorylation of the AMPA receptor subunit GluR2 differentially regulates its interaction with PDZ domain-containing proteins. J Neurosci 2000, 20: 7258–67.
Perez JL, Khatri L, Chang C, Srivastava S, Osten P, Ziff EB: PICK1 targets activated protein kinase Calpha to AMPA receptor clusters in spines of hippocampal neurons and reduces surface levels of the AMPA-type glutamate receptor subunit 2. J Neurosci 2001, 21: 5417–28.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grants NS 058886 and NS 057343, the Blaustein Pain Research Fund, and the Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care Medicine at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine (Y.X.T.). The authors thank Claire Levine, MS, and Tzipora Sofare, MA, for their editorial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
JSP carried out all behavioral experiments and most biochemical experiments. MY, XG, JTX, and MHS assisted with immunocytochemical experiments and the data analysis. YG and SNR participated in the data interpretation and critical review manuscript. YXT contributed to the design of the study, some biochemical experiments, the data analysis and interpretation, and drafting and critical review the manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Park, JS., Yaster, M., Guan, X. et al. Role of spinal cord alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors in complete Freund's adjuvant-induced inflammatory pain. Mol Pain 4, 67 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-8069-4-67
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-8069-4-67