Abstract
Background
Previous studies of human and simian immunodeficiency virus (HIV and SIV) have demonstrated that adaptive mutations selected during the course of infection alter viral replicative fitness, persistence, and pathogenicity. What is unclear from those studies is the impact of transmission on the replication and pathogenicity of the founding virus population. Using the SIV-macaque model, we examined whether the route of infection would affect the establishment and replication of two SIVmne variants of distinct in vitro and in vivo biological characteristics. For these studies, we performed dual-virus inoculations of pig-tailed macaques via intrarectal or intravenous routes with SIVmneCl8, a miminally pathogenic virus, and SIVmne027, a highly pathogenic variant that replicates more robustly in CD4+ T cells.
Results
The data demonstrate that SIVmne027 is the dominant virus regardless of the route of infection, indicating that the capacity to replicate efficiently in CD4+ T cells is important for fitness. Interestingly, in comparison to intravenous co-infection, intrarectal inoculation enabled greater relative replication of the less pathogenic virus, SIVmneCl8. Moreover, a higher level of SIVmneCl8 replication during primary infection of the intrarectally inoculated macaques was associated with lower overall plasma viral load and slower decline in CD4+ T cells, even though SIVmne027 eventually became the dominant virus.
Conclusions
These results suggest that the capacity to replicate in CD4+ T cells is a significant determinant of SIV fitness and pathogenicity. Furthermore, the data also suggest that mucosal transmission may support early replication of phenotypically diverse variants, while slowing the rate of CD4+ T cell decline during the initial stages of infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Human and simian immunodeficiency virus (HIV and SIV) undergo genetic and biological changes during the course of infection that correlate with increased viral load and disease progression. The evolution of the virus population results from direct competition of viral variants [1, 2], intense immune pressure [3], and target cell availability [4, 5]. Thus, viral fitness is a dynamic term and is dependent on the mutations and conditions under which viral replication is taking place. For example, CD8 epitope escape mutants may show increased fitness compared to wild type virus in context of a specific restricting HLA allele, but with a corresponding loss of replication capacity and, subsequently, lower levels of persistent replication [6, 7]. These types of mutations may revert during transmission to an unrestricted-HLA recipient, indicating that they impair fitness in vivo [8, 9]. Likewise, antiretroviral drug resistant mutants may show higher fitness compared to wild type virus in the presence of the inhibitor, but lower fitness when the drug is withdrawn [10–12]. Additionally, viral variants isolated during early and late stages of infection may differ in their phenotypic properties and pathogenicity, with late-stage variants demonstrating increases in replication capacity and virulence [13–16]. However, questions about HIV-1 fitness and pathogenicity have been incompletely addressed because of inadequate tissue culture assays and the absence of a suitable HIV-1 animal model of infection to confirm correlative observations by systematic examination of transmission and pathogenesis.
An alternative approach to address questions of HIV fitness and pathogenicity has been to use the simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV)-macaque model [17]. The advantage of the model is that the fitness and pathogenicity of a virus of known genotype and biological phenotype can be defined after experimental inoculation into multiple hosts. Studies have shown how immune pressure, by both the humoral and cellular immune responses of the macaque, affects replication and pathogenicity [18–22]. However, while cytotoxic T cell (CTL) escape mutations cause a loss of fitness, glycosylation changes in the envelope protein that reduce immunogenicity and neutralization enhance replication in the host. Other experiments have shown that enhancement of fitness and pathogenicity may involve more than selection due to immune pressure. SIV variants that evolve increased virulence compared to the parental virus have inherent gains in infectivity and replication capacity that result from mutations selected in various determinants within the viral genome, including, env gp41 [23], nef [22, 24–31] and gag ca [32], gag-pol [33], and rt [34].
Earlier studies primarily focused on defining how HIV and SIV adapt to the environment of the host in order to persistently replicate. What is less clear from those studies is the effect of transmission and the properties of the infecting viruses on the replicative fitness and pathogenicity of the founding virus population, which is commonly different from variants present at later stages of infection and disease [17, 35–37]. In the present study, we used the SIV-macaque model to examine whether the route of infection would affect the establishment and replication of two viral variants of distinct biological characteristics [22]. A comparison of dual-virus inoculation via intrarectal and intravenous routes demonstrates that a mucosal route of transmission allows greater relative replication capacity of a less pathogenic virus during co-infection with a more pathogenic virus, while limiting the rate of CD4+ T cell decline during the early stages of infection. However, the variant that replicates more robustly in CD4+ T cells eventually dominates. These results suggest that replication capacity in T cells is a significant determinant of SIV fitness, but that replication fitness of the dominant infecting virus may be reduced after mucosal transmission.
Results
Viral replication fitness in culture is host cell dependent
In vitro competitive replication fitness assays have been used to determine the fitness of both HIV-1 and SIV [38–40], but whether these types of assays predict viral fitness and pathogenicity in vivo has not been examined. In order to address the predictive value of a cell culture assay for SIV fitness, we first determined the relative in vitro competitive replicative fitness of two CCR5-using phenotypic variants: a minimally pathogenic, parental, virus (SIVmneCl8) and highly pathogenic, late-stage variant virus (SIVmne027). Both viruses used in this study have been characterized during in vitro and in vivo single infection/inoculation studies (Table 1). Three types of pig-tailed macaque primary cell cultures were used to examine competitive replication: activated peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBLs), dendritic cell/T cell (DC/T cell) co-cultures, and monocyte-derived macrophage cultures. To monitor the relative amounts of SIVmneCl8 and SIVmne027 in cell-free culture supernatants over time, we developed quantitative real-time PCR assays that measure the overall amount of viral RNA by detection of a conserved SIV gag sequence and the amount of SIVmneCl8 by detection of a unique env sequence. Using known quantities of SIVmneCl8 and SIVmne027 viral RNA targets, we determined that the assay is capable of accurately quantifying SIVmneCl8 even in the presence of 105 to 106-fold excess of SIVmne027 (data not shown). Furthermore, when activated pig-tail PBLs are infected with SIVmneCl8 alone, we observed a correlation between viral RNA measurements using the SIVmneCl8 env and SIV gag primer/probe sets (Figure 1a). As expected, SIVmneCl8 env was not detected in supernatants from SIVmne027 infected pig-tail (PBLs), even though there was about 3 × 109 viral RNA copies/ml of SIVmne027 as determined by total SIV RNA measurements (Figure 1b). This further indicated that there was insignificant detection of SIVmne027 by the SIVmneCl8 env specific real-time RT-PCR assay. Thus, the data show that SIVmneCl8 can be specifically detected by the allelic discriminating real-time PCR assay.
Quantitative real-time RT-PCR to measure relative levels of SIVmneCl8 and SIVmne027. The real-time RT-PCR assay was developed to detect two regions of the viral genome, a conserved gag sequence and an env V1 sequence specific to SIVmneCl8. The relative amount of SIVmneCl8 was determined from the amount of viral RNA detected by the SIVmneCl8 env V1 specific primer/probe set compared to the total amount of viral RNA detected by the primer/probe set recognizing the conserved gag sequence. Single-virus infections of activated pig-tail PBL with SIVmneCl8 (a) or SIVmne027 (b) shows that only SIVmneCl8 is recognized by the env V1 primer/probe, even when the overall viral RNA level is greater than 1 × 109 viral RNA copies/ml of SIVmne027.
When we analyzed activated PBLs or DC/T cell co-cultures that were co-infected with equal infectious doses of SIVmneCl8 and SIVmne027, we observed that SIVmneCl8 represented a minor fraction (0-30%) of total viral RNA by the end of each experiment (Figure 2a and 2b). This occurred even if SIVmneCl8 represented greater than 90% of the virus at early time points after infection. Similar results were obtained with DC-T-cell capture-transfer assays (data not shown). By contrast, in two of three infections of monocyte-derived macrophages, SIVmneCl8 represented 100% of total viral RNA during co-infection (Figure 2c). These data correlate with the abilities of the two viruses to replicate under the three culture conditions in single-virus infections. For example, SIVmne027 replicates efficiently in activated PBLs and in DC/T cell co-cultures but to low levels in monocyte-derived macrophages. In contrast, SIVmneCl8 replicates to lower levels than SIVmne027 in activated PBLs and in DC/T cell co-cultures but to moderate levels in macrophages (Figure 1 and Table 1). Together, the data demonstrate that SIVmne027 has greater competitive replication fitness than SIVmneCl8 in activated PBLs and DC/T cell co-cultures, but not in macrophage cultures.
Dual-virus competition assays in primary pig-tailed macaque cells. Activated PBLs (a), DC/T cell co-cultures (b), and macrophages (c) were infected with equal doses of SIVmneCl8 and SIVmne027. Total virus was determined by measuring consensus sequence gag RNA transcripts (--). SIVmneCl8 viral RNA levels were measures and are reported as percentages of total viral RNA (····). Three representative experiments (black circle/open circle, black triangle/open triangle, and black square/open square) are shown for each graph and viral RNA values represent the average reading for each time point. Each infection used cells from a different macaque blood donor.
SIVmne027 exhibits complete dominance over SIVmneCl8 following intravenous inoculation
Since in vitro infection assays are limited to analysis of viral replication without immune pressures, we co-inoculated pig-tailed macaques with equal infectious doses of SIVmneCl8 and SIVmne027 intravenously (IV) in order to determine relative replicative fitness of these two viruses within a host. Overall virus replication in the three macaques peaked at week 1 post-inoculation between 108-109 viral RNA copies/mL in plasma and stabilized around ~107 copies/mL (Figure 3a). Peak values and viral set-point levels in the co-infected animals are comparable to those seen during single-virus IV infections of pig-tailed macaques with SIVmne027 and about 30-1000-fold greater than infection with SIVmneCl8 [22, 41]. SIVmneCl8 was undetectable at all times tested post-infection, indicating that it was unable to persist at a measurable level during IV co-infection with SIVmne027. The identification of a recombinant env sequence in animal 29046 provided confirmation of SIVmneCl8 infection in these animals (Table 2). These results show that SIVmne027 is dominant over SIVmneCl8 during IV co-infections. Furthermore, in context of earlier studies with these viruses [22], the data also suggest that variants that emerge with increased ability to replicate in CD4+ T cells and which have increased pathogenicity are indeed more fit than viruses from which they evolved in the host.
Plasma viral loads from in vivo co-infections. Macaques were infected with equal doses of SIVmneCl8 and SIVmne027 using either an intravenous route of inoculation (a), animals 29046 (gray circle/open circle), 29047 (gray triangle/open triangle) and 29048 (gray square/open square) or an intrarectal route of inoculation (b), animals 28488 (black circle/open circle), 28489 (black triangle/open triangle) and 28490 (black square/open square). Total virus in plasma was determined by measuring consensus sequence gag RNA transcripts (--) by quantitative real-time PCR. SIVmneCl8 specific viral RNA levels were also measured by quantitative real-time PCR and are reported as percentages of total viral RNA (····). Viral RNA values represent the average reading for each time point.
SIVmneCl8 demonstrates higher relative replication levels after mucosal inoculation
We next examined what effect a mucosal route of infection would have on relative viral replication in the host. Pig-tailed macaques were co-infected intrarectally (IR) with equal doses of the same SIVmneCl8 and SIVmne027 stocks used to inoculate animals IV. We again found overall viral peak values in plasma ranged between 108-109 copies/mL (Figure 3b). Interestingly, post-acute plasma viral loads in IR-infected macaques varied considerably between individual macaques in comparison to those in IV-infected animals. Moreover, SIVmneCl8 was detectable throughout the acute stage of IR infection and peaked at 8 weeks post-infection. SIVmneCl8 plasma viral loads increased from undetectable to between 1 × 105 to 2 × 106 viral RNA copies/ml and represented between 10 and 50% of the virus population in plasma (Figure 3b and 4b). However, it eventually gave way to SIVmne027, which became completely dominant with time. Macaque 28490 had the highest levels of SIVmneCl8, which constituted as much as 50% of the total virus population at 8 weeks post-infection, and the lowest overall plasma viral load. The CD4+ T cell population in animal 28490 was also well preserved compared to the other animals (Figure 4c).
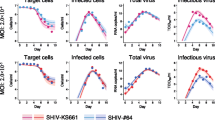
Comparison of IV vs IR viral loads and CD4+ T cell counts from SIVmneCl8/SIVmne027 co-inoculated macaques. Total plasma viral RNA transcripts (a), SIVmneCl8 env transcripts (b), and CD4+ T cell levels (c) from intravenously infected macaques (gray circles, triangles, and squares) and intrarectally infected macaques (black circles, triangles, and squares) are shown. Viral RNA measurements were determined as in Fig. 3. Values represent average readings for each time point ± the standard error. Levels of significance are denoted as follows: (**) p < 0.05, (*) p = 0.05. In panel (a) the p-value at peak plasma viral load is 0.0007. The p-value for differences in viral set-point at 20 and 24 weeks post-inoculation are 0.0544 and 0.0509, respectively. For panel (b) p-values at 2, 4, and 8 weeks post-inoculation are 0.049, 0.006, and 0.005, respectively. For panel (c) the p-value for period 0-8 weeks post-inoculation is 0.0013, and the p-value for period 8-24 weeks post-inoculation is 0.0006.
Mucosal transmission decreases viral load and rate of CD4+T cell decline
To determine whether the route of transmission affected overall viral load, CD4+ T cell decline, and competitive replication fitness of SIVmneCl8 and SIVmne027, we compared the results from the IR and IV infections. Although there was no significant difference in the average peak plasma viral RNA measurements, we found peak viral replication significantly delayed (p = 0.0007) after IR inoculation. The viral set-point averages at weeks 20 and 24 were also reduced in IR-infected macaques as compared with IV-infected macaques but were marginally significant (p = 0.0544 and 0.0509, respectively) (Figure 4a). Secondly, a comparison of the level of SIVmneCl8 in plasma between IV and IR infected macaques revealed a significantly greater level of SIVmneCl8 at week 2, 4 and 8 (p = 0.049, 0.006 and 0.005, respectively) in IR-infected macaques, despite the presence of the more pathogenic variant, SIVmne027 (Figure 4b). This was verified by single-proviral cloning and sequencing of env from PBMC isolated at 8 weeks post-inoculation (Table 2).
An analysis of absolute values of CD4+ T cells showed a greater decrease in CD4+ T cell levels in IV-infected macaques than IR-infected macaques (week 0-8: p = 0.0013; week 8-24: p = 0.0006) (Figure 4c). These differences were also reflected in the population of central memory CD4+ T cells (Figure 5). Thus, although the more pathogenic and rapidly-replicating variant, SIVmne027, always dominated the co-infections, mucosal transmission enabled the slower-replicating SIVmneCl8 to replicate to relatively higher levels during the primary stage of infection. Interestingly, this was associated with lower viral loads and slower initial CD4+ T cell decline, suggesting the induction of protective immune responses by SIVmneCl8. Taken together, the data indicate that there may be greater control of SIV after IR infection compared to IV infection.
Comparison of central memory CD4+ T cells in intrarectally-infected and intravenously-infected pig-tailed macaques. Individual data points from intrarectally-infected animals (thin dotted lines with open symbols) with the predicted mean value (thick dotted line; Group 1) were compared with data from intravenously-infected animals (thin solid lines with closed symbols) with the predicted mean value (thick solid line; Group 2). Significant differences were found at all time points from week 1 through week 20. P-values for all time points (0, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24) are given here: 0.0528, <0.0001, <0.0001, <0.0001, <0.0001, <0.0001, 0.0003, 0.0009, 0.0585 and 0.9761 respectively.
Discussion
We examined the relative replicative fitness of phenotypic SIV variants using both in vitro and in vivo co-infections in order to examine the impact of competition and target cell availability on relative viral replication and CD4+ T cell decline during the early stages of infection. Our data demonstrate that a rapidly-replicating, highly pathogenic variant (SIVmne027) that evolved in vivo is indeed more fit than the slower-replicating parental virus (SIVmneCl8), regardless of whether co-inoculation was IV or IR. Furthermore, they confirm that in vitro competitive replication fitness experiments may predict replication fitness and pathogenicity in vivo [38–40]. The data support a model in which the predominant genotype established within a host is defined by how well a virus has adapted to replicating in CD4+ T cells. They also demonstrate that these viruses are likely to predominate in subsequent transmissions. This model is consistent with previous in situ studies, which show that the primary target cells during transmission and acute HIV-1 and SIV infection are primarily CD4+ T cells in lymphoid tissues [42–45].
Despite the dominance of the rapidly replicating variant, the slower replicating virus, SIVmneCl8, was able to expand exponentially during the acute stage after IR co-inoculation. It represented as much as 50% of the total virus population before giving way to SIVmne027. This was unexpected, given the nearly complete dominance of SIVmne027 that was observed after IV inoculation, the low competitive replication fitness of SIVmneCl8 in T cell and DC/T cell cocultures, and our previous observations that in single-virus infections, SIVmneCl8 demonstrates both lower initial spike and set-point plasma viral RNA copies/ml than SIVmne027 in pig-tailed macaques [22, 41]. However, the peak levels achieved by SIVmneCl8 are within range of what has been observed when it is inoculated alone. One potential explanation is that the viruses target different cell types after IR inoculation. For example, the dominant virus, SIVmne027, may spread in abundant memory CD4+ T cells. In contrast, the virus with greater relative replication fitness in macrophages, SIVmneCl8, may be mainly limited to replication in rectal macrophages, which are known to be susceptible target cells [14, 46]. While challenging, it would be of interest to examine the infection profile of a dual-virus inoculation and the cell types harboring virus in the rectum and gut-associated lymphoid tissue during acute infection. Alternatively, increased levels of the slower replicating virus, SIVmneCl8, could be due to immunosuppression induced by the dominant T-cell tropic variant, SIVmne027. However, this seems unlikely since higher levels of SIVmneCl8 were associated with greater preservation of the CD4+ T cell populations. Potentially, this association may indicate that SIVmneCl8 only replicates efficiently in a particular subpopulation of CD4+ T-cells that are available after IR inoculation but are depleted in the IV infected animals.
Some earlier studies have shown that multiple HIV-1 variants can be transmitted in both men and women, followed by purifying selection [47, 48]. On the other hand, more recent studies indicate that only single HIV-1 variants appear to be transmitted to new hosts from the index case [35, 36, 43]. Furthermore, a low dose SIV mucosal infection experiment with the SIV isolates SIVmac251 and SIVsmE660 also suggested single virus transmission was frequent [49]. However, a new study shows that multivariant transmission may occur more frequently in men having sex with men than during heterosexual transmission [50]. A second study demonstrates that multiple variants are commonly transmitted in low dose vaginal challenge of rhesus macaques with SIV [51]. The reasons for these contrasting results remain unclear. One explanation for the differences may be that bottlenecks in mucosal transmission appear to lessen only when transmission occurs with co-existing genital infections and inflammation [52]. Regardless, none of the studies distinguish between limited transmission of variants across the mucosal surface and competitive selection of variants during dissemination and establishment of infection as the cause for limited viral diversity.
The animals in this study did not have signs of anal inflammation. Also, they were not subjected to repeated low dose exposures to the SIV variants. Thus, we were not able to address the question of whether one virus is preferentially transmitted over the other. For the experiments, we used a minimal dose expected to allow 100% infection by both variants in order to address which variant was likely to establish a more robust persistent infection if both are given the opportunity to infect the animals. Our data agree with the potential for rapid purifying selection after transmission based on competitive replication fitness if more than one virus is transmitted [47, 48]. The data also raise the possibility that one variant may be highly dominant even if multiple variants get transmitted. In this regard, caution should be taken in considering a vaccine design that only targets what appears to be a commonly transmitted single genotype of HIV-1. Other variants may simply be hidden because of the high replication fitness of the predominant virus or because they are controlled by the host immune response [53].
Our data suggest that the route of infection may have a significant effect on the level of viral replication in the host. Statistically significant lower plasma viral loads were observed following IR compared to IV inoculation. Thus, host-specific selective pressures exerted on the viral populations may play an important role in variant selection in addition to direct viral competition for resources. These results suggest that a mucosal route of infection exerts a modest selective pressure for viral variants with lower replicative fitness and pathogenicity compared to IV infection. Clearly, a shortcoming of our study is the limited number of animals used per group. Although the data are statistically significant, further experiments will be required to verify the results because of potential variability [54]. However, it is important to note that we have found in past experiments that significant differences are observable with limited numbers of pig-tailed macaques infected with SIVmne variant clones [22, 41]. Moreover, our data are in agreement with previous studies with uncloned SIVmac251, which also showed decreased viral fitness, lower viral loads, and pathogenicity after intrarectal inoculation or passage by intravaginal inoculation of rhesus macaques [55, 56]. Thus, unlike the gains in pathogenicity of SIV that occur with serial intravenous passage [22, 25], vaginal and rectal routes of infection may not lead to increased virulence and rate of progression to AIDS. It is unknown if these findings are particular to the viruses used for the studies. The use of molecular clones will allow us to compare the results of the current experiments with those using a different combination of cloned variant viruses.
Previous studies of recombination in SIVmac-infected rhesus macaques indicated rapid selection for recombinants with increased replication fitness [57, 58]. Recombination in the present study was rarely observed. One reason for the difference in results may be because the sequences analyzed in our study were primarily restricted to the env gene. However, we have also examined a limited number of complete proviral genomes (4 total) and env-nef-LTR sequences (approximately 40) PCR amplified from the IR-inoculated animals but have not found evidence for recombination (C. Gingaras and J.T. Kimata, unpublished observations). An alternative explanation may be a methodological difference. Both earlier studies on SIV recombination co-inoculated animals with two mutants with deletions in either vpr/vpx or nef. In that scenario, recombination may readily occur to form variants with wild type genomes that are more fit for persistent replication and are therefore dominant. In the current experiments, we co-inoculated two variants with different replicative and pathogenic phenotypes but no deletion mutations. Recombinants may not have had a clear advantage for persistence compared to the dominant SIVmne027 variant.
Whether the level of replication of the slower replicating SIVmneCl8 contributes to the decrease in plasma viral load that occurs after IR inoculation is unknown and will require further investigation. Although it is possible that SIVmneCl8 induces protective immune responses against SIVmne027, we previously demonstrated that a prime/boost vaccine based on SIVmneCl8 fails to protect or lower viral load in macaques challenged by another highly related variant SIVmne [41], suggesting the SIVmneCl8 infection may not prime an effective immune response against SIVmne027 either. However, we cannot rule out that a more robust immune response is induced during intrarectal infection preventing gains replic.
It will be of interest to determine whether continued mucosal passage of variants from SIVmneCl8/SIVmne027 infected macaques leads to additional reductions in viral fitness and lengthening of the time to disease, and to determine what immune responses contribute to the lower replication level of SIV after intrarectal inoculation. The results could provide important insights into host immune mechanisms that can contain infection and select for less pathogenic variants. As HIV-1 is primarily sexually transmitted, the reductions in viral load observed following mucosal infection and passage in the macaque may also provide an explain for why the overall rate of HIV disease progression in the general human population has remained relatively constant, or even decreased, despite the adaptations affecting pathogenicity that occur in the virus during the course of infection of an individual [59–61].
Conclusions
Previous studies demonstrated that HIV/SIV variants that evolve during an infection have increased competitive replication fitness compared to the infecting virus. We further those studies by showing in the macaque host that an SIV variant with increased pathogenicity, dominates infection when co-inoculated either IR or IV into a host along with the parent virus from which it evolved. We conclude that replication fitness evolves with pathogenicity and that variants that replicate most efficiently in CD4+ T cells are likely to dominate after subsequent infections. However, IR infection supported relatively higher replication of the less competitively fit virus despite replication of the more pathogenic variant, suggesting that the rectal environment provides greater target cell availability for replication of phenotypically diverse variants. Finally, our data agree with earlier studies suggesting that mucosal infections, unlike IV infections, may curtail increases in viral replication fitness and rate of CD4+ T cell decline, thereby preventing an increase in the rate of disease progression with passage of the virus to new hosts.
Materials and methods
Cell culture and Viruses
Primary pig-tailed macaque cells were cultured in RPMI1640 supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (HI-FBS), 2 mM L-glutamine, and 100 U/mL penicillin and 100 μg/mL streptomycin (P/S) (RPMI complete) with additional cytokines as required. sMAGI cells were maintained in DMEM, 10% HI-FBS, 2 mM L-glutamine, P/S (DMEM complete) with 0.20 mg/mL G418 and 50 U/mL hygromycin B. The cloning of the variant viruses, SIVmneCl8 and SIVmne027, were described previously [22, 62, 63]. Characteristics of each virus are summarized in Table 1[21, 22, 27, 34, 41, 62–67]. Infectious SIVmneCl8 and SIVmne027 stocks were prepared by transfection of plasmid DNA containing the respective provirus into 293T cells, and virus stocks (infectious units (IU)/ml) were quantified using the sMAGI assay as described [68].
In vitroviral infections
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated from pig-tailed macaque blood using Ficoll-hypaque isolation. Blood donor animals are different from those used for the in vivo inoculations described below. Monocytes were depleted by adherence and the remaining peripheral blood lymphocytes (105-106 cells/well) were seeded into a 24-well plate coated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 per well for co-stimulation and then used for viral replication assays as described [34]. Equal infectious doses of SIVmneCl8 and SIVmne027 (MOI = 0.001 for each virus) were added to each well in ~200 μl volume and incubated for 3 hours. Cells were washed twice with PBS to remove any unbound virus and resuspended in RPMI complete + 50 U/mL IL-2 (RPMI/IL-2). Supernatant samples were collected and media replaced with RPMI/IL-2 every 2-3 days. Viral RNA was isolated using QIAamp Viral RNA minikit (Qiagen). Samples were analyzed with real-time RT PCR as described below to quantify total SIV and SIVmneCl8 specific viral RNA.
Dendritic cell (DC)/T-cell co-cultures were prepared from monocytes and T-cells isolated from the blood of individual macaques as described [67]. Five days after isolation, monocyte-derived DCs and T-cells were mixed and equal doses of both SIVmneCl8 and SIVmne027 (2 × 103 IU; MOI = 0.01 relative to T cells) were added to the co-cultures, incubated for 3 hours, and washed twice with PBS to remove unbound virus. Co-cultures were resuspended in RPMI/IL-2. Alternatively, viruses were first captured by DCs and then transferred to T-cells (DC-T-cell capture-transfer assay) as described [67]. Supernatant samples were collected and media replaced every 2-3 days. Viral RNA was isolated using QIAamp Viral RNA minikit (Qiagen). Samples were analyzed with real-time RT PCR as described.
Macrophages were differentiated from monocytes isolated by plastic adherence from pig-tailed macaque PBMCs as described previously [62, 66]. Cultures were inoculated with equal doses of SIVmneCl8 and SIVmne027 (MOI 0.01), washed twice with PBS to removed unbound virus after 4 hours, and cultured in RPMI complete media. Supernatant samples were collected every 2-3 days and media replaced with fresh media. Viral RNA was isolated from samples using QIAamp Viral RNA minikit (Qiagen). Samples were analyzed with real-time RT PCR as described.
In vivoinoculations of macaques
Six pig-tailed macaques (three per group) were infected either intravenously or by atraumatic intrarectal inoculation with 1 × 104 IU each of SIVmneCl8 and SIVmne027 using previously described methods [22, 69, 70]. This dose was experimentally determined to be the minimum required to inoculate 100% of pig-tailed macaques with an uncloned infectious stock of SIVmne by the rectal route [71]. Animal care and usage were performed in accordance with protocols approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Southwest Foundation for Biomedical Research and were conducted in accordance with Animal Welfare Act guidelines.
PCR cloning
Env fragments were cloned from DNA of PBMCs harvested eight weeks post infection by nested PCR using previously described methods [72]. Individual clones were amplified from PBMC DNA after limiting dilution of each specimen determined the minimal amount of DNA required to amplify a proviral env sequence. Env fragments were cloned into pCR2.1-TOPO vector using the TOPO TA Cloning Kit (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Sequences were analyzed for identity to the parental viruses, SIVmneCl8 or SIVmne027, or for possible recombination.
Real-time RT PCR Assay
RNA standards for detecting gag and SIVmneCl8 env V1 sequences were prepared from plasmid stocks pKS+-BamHI-KpaI (pKS+ plasmid containing BamHI-KpaI fragment of SIVmneCl8 gag) and pSK+-Cl8.Env (pSK+ plasmid containing the fragment 219-570 of SIVmneCl8 env) by in vitro transcription. RNA sample and standard dilutions were prepared in DEPC-H2O + 50 U/mL RNase Inhibitor (Invitrogen) and 0.1 μg/μL yeast tRNA (Sigma). Plates were prepared with 40 μL of an RT PCR master mix (25 μL 2× RT PCR master mix, 1.25 μL 40× RNase inhibitor mix, 12.92 μL DEPC-H2O and 0.83 μL 60× GAG primer/probe mix [forward primer: TGTCAGGGAAGAAAGCAGATGAATT; reverse primer: TGCCCATACTACATGCTTCAACAT; dye, probe sequence and quencher: FAM-CCGGGTCGTAGCCTAA-MGB NFQ] for gag detection and for specific detection of the SIVmneCl8 Env 12.5 μL DEPC-H2O plus [0.25 μL 200× forward primer CAACAGCACCAACAGCAATACC, 0.25 μL 200× reverse primer ACAAGGACTATTCTCATTGACCACTTT and 1.25 μL 40× Env Probe VIC-ACAAAAGCAGAGGCAAT-MGB NFQ] (Applied Biosystems). 10 μL of standard or sample was then added and plates were analyzed with a standard cycling procedure on a 7500 Real Time PCR System with SDS 1.0 software (Applied Biosystems). Non-templated and no RT controls were prepared as above, but substituting DEPC-H2O for template RNA or a 2× DNA Master Mix (Applied Biosystems) for the 2× RT PCR Master Mix, respectively. Validation assays were performed to demonstrate accuracy and specificity of the primer/probe sets.
Flow Cytometry Analysis
CD4+ T cell counts were determined by multiplying the total lymphocytes counts by the fractional amount of CD4+CD3+ T cells. Central memory CD4+ T cells were determined by multiplying the number of CD4+ T cells by the fractional amount of CD95+CD28+ cells in the CD4+ T cell gate. Percentages of CD4+ T cells were determined by 5-color flow cytometry using antibodies from Becton Dickinson: anti-CD3-Alexa 700 (SP34-2), anti-CD4-APC, anti-CD95-FITC (DX2), anti-CD8-PerCP, and anti-CD28-APC (28.2).
Statistical Methods
For comparative analysis of total SIV virion RNA and that of SIVmneCl8 between IV and IR infected macaques a mixed model was used with fixed effects using SP (POW) for variance-covariance structure. This approach was also used for comparing memory CD4+ T cells. To meet the normality assumption for the model, natural logarithm transferred variable (Ln_CMCD4) were used in the analysis. The analysis of total CD4+ T cell counts used one-way ANOVA for repeated measures.
References
Ball CL, Gilchrist MA, Coombs D: Modeling within-host evolution of HIV: mutation, competition and strain replacement. Bull Math Biol. 2007, 69: 2361-2385. 10.1007/s11538-007-9223-z.
Tsui R, Herring BL, Barbour JD, Grant RM, Bacchetti P, Kral A, Edlin BR, Delwart EL: Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 superinfection was not detected following 215 years of injection drug user exposure. J Virol. 2004, 78: 94-103. 10.1128/JVI.78.1.94-103.2004.
Althaus CL, De Boer RJ: Dynamics of immune escape during HIV/SIV infection. PLoS Comput Biol. 2008, 4: e1000103-10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000103.
Arien KK, Gali Y, El-Abdellati A, Heyndrickx L, Janssens W, Vanham G: Replicative fitness of CCR5-using and CXCR4-using human immunodeficiency virus type 1 biological clones. Virology. 2006, 347: 65-74. 10.1016/j.virol.2005.11.045.
Clapham PR, McKnight A: HIV-1 receptors and cell tropism. Br Med Bull. 2001, 58: 43-59. 10.1093/bmb/58.1.43.
Miura T, Brockman MA, Schneidewind A, Lobritz M, Pereyra F, Rathod A, Block BL, Brumme ZL, Brumme CJ, Baker B, et al: HLA-B57/B*5801 human immunodeficiency virus type 1 elite controllers select for rare gag variants associated with reduced viral replication capacity and strong cytotoxic T-lymphocyte [corrected] recognition. J Virol. 2009, 83: 2743-2755. 10.1128/JVI.02265-08.
Troyer RM, McNevin J, Liu Y, Zhang SC, Krizan RW, Abraha A, Tebit DM, Zhao H, Avila S, Lobritz MA, et al: Variable fitness impact of HIV-1 escape mutations to cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) response. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5: e1000365-10.1371/journal.ppat.1000365.
Allen TM, Altfeld M, Yu XG, O'Sullivan KM, Lichterfeld M, Le Gall S, John M, Mothe BR, Lee PK, Kalife ET, et al: Selection, transmission, and reversion of an antigen-processing cytotoxic T-lymphocyte escape mutation in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J Virol. 2004, 78: 7069-7078. 10.1128/JVI.78.13.7069-7078.2004.
Goepfert PA, Lumm W, Farmer P, Matthews P, Prendergast A, Carlson JM, Derdeyn CA, Tang J, Kaslow RA, Bansal A, et al: Transmission of HIV-1 Gag immune escape mutations is associated with reduced viral load in linked recipients. J Exp Med. 2008, 205: 1009-1017. 10.1084/jem.20072457.
Gao Y, Paxinos E, Galovich J, Troyer R, Baird H, Abreha M, Kityo C, Mugyenyi P, Petropoulos C, Arts EJ: Characterization of a subtype D human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolate that was obtained from an untreated individual and that is highly resistant to nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. J Virol. 2004, 78: 5390-5401. 10.1128/JVI.78.10.5390-5401.2004.
Harrigan PR, Bloor S, Larder BA: Relative replicative fitness of zidovudine-resistant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates in vitro. J Virol. 1998, 72: 3773-3778.
Weber J, Rangel HR, Chakraborty B, Tadele M, Martinez MA, Martinez-Picado J, Marotta ML, Mirza M, Ruiz L, Clotet B, et al: A novel TaqMan real-time PCR assay to estimate ex vivo human immunodeficiency virus type 1 fitness in the era of multi-target (pol and env) antiretroviral therapy. J Gen Virol. 2003, 84: 2217-2228. 10.1099/vir.0.19123-0.
Nielsen C, Pedersen C, Lundgren JD, Gerstoft J: Biological properties of HIV isolates in primary HIV infection: consequences for the subsequent course of infection. AIDS. 1993, 7: 1035-1040. 10.1097/00002030-199308000-00002.
Phillips AN, McLean AR, Loveday C, Tyrer M, Bofill M, Devereux H, Madge S, Dykoff A, Drinkwater A, Burke A, et al: In vivo HIV-1 replicative capacity in early and advanced infection. AIDS. 1999, 13: 67-73. 10.1097/00002030-199901140-00009.
Tuttle DL, Anders CB, Aquino-De Jesus MJ, Poole PP, Lamers SL, Briggs DR, Pomeroy SM, Alexander L, Peden KW, Andiman WA, et al: Increased replication of non-syncytium-inducing HIV type 1 isolates in monocyte-derived macrophages is linked to advanced disease in infected children. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2002, 18: 353-362. 10.1089/088922202753519133.
Zhu T, Mo H, Wang N, Nam DS, Cao Y, Koup RA, Ho DD: Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of HIV-1 patients with primary infection. Science. 1993, 261: 1179-1181. 10.1126/science.8356453.
Kimata JT: HIV-1 fitness and disease progression: insights from the SIV-macaque model. Curr HIV Res. 2006, 4: 65-77. 10.2174/157016206775197628.
Chackerian B, Rudensey LM, Overbaugh J: Specific N-linked and O-linked glycosylation modifications in the envelope V1 domain of simian immunodeficiency virus variants that evolve in the host alter recognition by neutralizing antibodies. J Virol. 1997, 71: 7719-7727.
Friedrich TC, Dodds EJ, Yant LJ, Vojnov L, Rudersdorf R, Cullen C, Evans DT, Desrosiers RC, Mothe BR, Sidney J, et al: Reversion of CTL escape-variant immunodeficiency viruses in vivo. Nat Med. 2004, 10: 275-281. 10.1038/nm998.
Loh L, Reece JC, Fernandez CS, Alcantara S, Center R, Howard J, Purcell DF, Balamurali M, Petravic J, Davenport MP, Kent SJ: Complexity of the inoculum determines the rate of reversion of SIV Gag CD8 T cell mutant virus and outcome of infection. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5: e1000378-10.1371/journal.ppat.1000378.
Rudensey LM, Kimata JT, Long EM, Chackerian B, Overbaugh J: Changes in the extracellular envelope glycoprotein of variants that evolve during the course of simian immunodeficiency virus SIVMne infection affect neutralizing antibody recognition, syncytium formation, and macrophage tropism but not replication, cytopathicity, or CCR-5 coreceptor recognition. J Virol. 1998, 72: 209-217.
Kimata JT, Kuller L, Anderson DB, Dailey P, Overbaugh J: Emerging cytopathic and antigenic simian immunodeficiency virus variants influence AIDS progression. Nat Med. 1999, 5: 535-541. 10.1038/8414.
Alexander L, Illyinskii PO, Lang SM, Means RE, Lifson J, Mansfield K, Desrosiers RC: Determinants of increased replicative capacity of serially passaged simian immunodeficiency virus with nef deleted in rhesus monkeys. J Virol. 2003, 77: 6823-6835. 10.1128/JVI.77.12.6823-6835.2003.
Du Z, Lang SM, Sasseville VG, Lackner AA, Ilyinskii PO, Daniel MD, Jung JU, Desrosiers RC: Identification of a nef allele that causes lymphocyte activation and acute disease in macaque monkeys. Cell. 1995, 82: 665-674. 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90038-1.
Edmonson P, Murphey-Corb M, Martin LN, Delahunty C, Heeney J, Kornfeld H, Donahue PR, Learn GH, Hood L, Mullins JI: Evolution of a simian immunodeficiency virus pathogen. J Virol. 1998, 72: 405-414.
Fultz PN: Replication of an acutely lethal simian immunodeficiency virus activates and induces proliferation of lymphocytes. J Virol. 1991, 65: 4902-4909.
Patel PG, Yu Kimata MT, Biggins JE, Wilson JM, Kimata JT: Highly pathogenic simian immunodeficiency virus mne variants that emerge during the course of infection evolve enhanced infectivity and the ability to downregulate CD4 but not class I major histocompatibility complex antigens. J Virol. 2002, 76: 6425-6434. 10.1128/JVI.76.13.6425-6434.2002.
Heidecker G, Munoz H, Lloyd P, Hodge D, Ruscetti FW, Morton WR, Hu S, Benveniste RE: Macaques infected with cloned simian immunodeficiency virus show recurring nef gene alterations. Virology. 1998, 249: 260-274. 10.1006/viro.1998.9325.
Iafrate AJ, Carl S, Bronson S, Stahl-Hennig C, Swigut T, Skowronski J, Kirchhoff F: Disrupting surfaces of nef required for downregulation of CD4 and for enhancement of virion infectivity attenuates simian immunodeficiency virus replication in vivo. J Virol. 2000, 74: 9836-9844. 10.1128/JVI.74.21.9836-9844.2000.
Sugimoto C, Tadakuma K, Otani I, Moritoyo T, Akari H, Ono F, Yoshikawa Y, Sata T, Izumo S, Mori K: nef gene is required for robust productive infection by simian immunodeficiency virus of T-cell-rich paracortex in lymph nodes. J Virol. 2003, 77: 4169-4180. 10.1128/JVI.77.7.4169-4180.2003.
Schindler M, Munch J, Brenner M, Stahl-Hennig C, Skowronski J, Kirchhoff F: Comprehensive analysis of nef functions selected in simian immunodeficiency virus-infected macaques. J Virol. 2004, 78: 10588-10597. 10.1128/JVI.78.19.10588-10597.2004.
Kirmaier A, Wu F, Newman RM, Hall LR, Morgan JS, O'Connor S, Marx PA, Meythaler M, Goldstein S, Buckler-White A, et al: TRIM5 suppresses cross-species transmission of a primate immunodeficiency virus and selects for emergence of resistant variants in the new species. PLoS Biol. 8:
Jesus da Costa L, Lopes Dos Santos A, Mandic R, Shaw K, Santana de Aguiar R, Tanuri A, Luciw PA, Peterlin BM: Interactions between SIVNef, SIVGagPol and Alix correlate with viral replication and progression to AIDS in rhesus macaques. Virology. 2009, 394: 47-56. 10.1016/j.virol.2009.08.024.
Biesinger T, Yu Kimata MT, Kimata JT: Changes in simian immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase alleles that appear during infection of macaques enhance infectivity and replication in CD4+ T cells. Virology. 2008, 370: 184-193. 10.1016/j.virol.2007.08.011.
Derdeyn CA, Decker JM, Bibollet-Ruche F, Mokili JL, Muldoon M, Denham SA, Heil ML, Kasolo F, Musonda R, Hahn BH, et al: Envelope-constrained neutralization-sensitive HIV-1 after heterosexual transmission. Science. 2004, 303: 2019-2022. 10.1126/science.1093137.
Keele BF, Giorgi EE, Salazar-Gonzalez JF, Decker JM, Pham KT, Salazar MG, Sun C, Grayson T, Wang S, Li H, et al: Identification and characterization of transmitted and early founder virus envelopes in primary HIV-1 infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008, 105: 7552-7557. 10.1073/pnas.0802203105.
Zhu T, Wang N, Carr A, Nam DS, Moor-Jankowski R, Cooper DA, Ho DD: Genetic characterization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in blood and genital secretions: evidence for viral compartmentalization and selection during sexual transmission. J Virol. 1996, 70: 3098-3107.
Quinones-Mateu ME, Ball SC, Marozsan AJ, Torre VS, Albright JL, Vanham G, van Der Groen G, Colebunders RL, Arts EJ: A dual infection/competition assay shows a correlation between ex vivo human immunodeficiency virus type 1 fitness and disease progression. J Virol. 2000, 74: 9222-9233. 10.1128/JVI.74.19.9222-9233.2000.
Troyer RM, Collins KR, Abraha A, Fraundorf E, Moore DM, Krizan RW, Toossi Z, Colebunders RL, Jensen MA, Mullins JI, et al: Changes in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 fitness and genetic diversity during disease progression. J Virol. 2005, 79: 9006-9018. 10.1128/JVI.79.14.9006-9018.2005.
Voronin Y, Overbaugh J, Emerman M: Simian immunodeficiency virus variants that differ in pathogenicity differ in fitness under rapid cell turnover conditions. J Virol. 2005, 79: 15091-15098. 10.1128/JVI.79.24.15091-15098.2005.
Polacino P, Cleveland B, Zhu Y, Kimata JT, Overbaugh J, Anderson D, Hu SL: Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of Gag/Pol/Env vaccines derived from temporal isolates of SIVmne against cognate virus challenge. J Med Primatol. 2007, 36: 254-265. 10.1111/j.1600-0684.2007.00243.x.
Mattapallil JJ, Douek DC, Hill B, Nishimura Y, Martin M, Roederer M: Massive infection and loss of memory CD4+ T cells in multiple tissues during acute SIV infection. Nature. 2005, 434: 1093-1097. 10.1038/nature03501.
Salazar-Gonzalez JF, Salazar MG, Keele BF, Learn GH, Giorgi EE, Li H, Decker JM, Wang S, Baalwa J, Kraus MH, et al: Genetic identity, biological phenotype, and evolutionary pathways of transmitted/founder viruses in acute and early HIV-1 infection. J Exp Med. 2009, 206: 1273-1289. 10.1084/jem.20090378.
Schacker T, Little S, Connick E, Gebhard K, Zhang ZQ, Krieger J, Pryor J, Havlir D, Wong JK, Schooley RT, et al: Productive infection of T cells in lymphoid tissues during primary and early human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Infect Dis. 2001, 183: 555-562. 10.1086/318524.
Zhang Z, Schuler T, Zupancic M, Wietgrefe S, Staskus KA, Reimann KA, Reinhart TA, Rogan M, Cavert W, Miller CJ, et al: Sexual transmission and propagation of SIV and HIV in resting and activated CD4+ T cells. Science. 1999, 286: 1353-1357. 10.1126/science.286.5443.1353.
Mestecky J, Moldoveanu Z, Smith PD, Hel Z, Alexander RC: Mucosal immunology of the genital and gastrointestinal tracts and HIV-1 infection. J Reprod Immunol. 2009, 83: 196-200. 10.1016/j.jri.2009.07.005.
Learn GH, Muthui D, Brodie SJ, Zhu T, Diem K, Mullins JI, Corey L: Virus population homogenization following acute human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J Virol. 2002, 76: 11953-11959. 10.1128/JVI.76.23.11953-11959.2002.
Long EM, Martin HL, Kreiss JK, Rainwater SM, Lavreys L, Jackson DJ, Rakwar J, Mandaliya K, Overbaugh J: Gender differences in HIV-1 diversity at time of infection. Nat Med. 2000, 6: 71-75. 10.1038/71563.
Keele BF, Li H, Learn GH, Hraber P, Giorgi EE, Grayson T, Sun C, Chen Y, Yeh WW, Letvin NL, et al: Low-dose rectal inoculation of rhesus macaques by SIVsmE660 or SIVmac251 recapitulates human mucosal infection by HIV-1. J Exp Med. 2009, 206: 1117-1134. 10.1084/jem.20082831.
Li H, Bar KJ, Wang S, Decker JM, Chen Y, Sun C, Salazar-Gonzalez JF, Salazar MG, Learn GH, Morgan CJ, et al: High Multiplicity Infection by HIV-1 in Men Who Have Sex with Men. PLoS Pathog. 6: e1000890-10.1371/journal.ppat.1000890.
Stone M, Keele BF, Ma ZM, Bailes E, Dutra J, Hahn BH, Shaw GM, Miller CJ: A limited number of simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) env variants are transmitted to rhesus macaques vaginally inoculated with SIVmac251. J Virol. 84: 7083-7095. 10.1128/JVI.00481-10.
Haaland RE, Hawkins PA, Salazar-Gonzalez J, Johnson A, Tichacek A, Karita E, Manigart O, Mulenga J, Keele BF, Shaw GM, et al: Inflammatory genital infections mitigate a severe genetic bottleneck in heterosexual transmission of subtype A and C HIV-1. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5: e1000274-10.1371/journal.ppat.1000274.
Harouse JM, Buckner C, Gettie A, Fuller R, Bohm R, Blanchard J, Cheng-Mayer C: CD8+ T cell-mediated CXC chemokine receptor 4-simian/human immunodeficiency virus suppression in dually infected rhesus macaques. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003, 100: 10977-10982. 10.1073/pnas.1933268100.
Parker RA, Regan MM, Reimann KA: Variability of viral load in plasma of rhesus monkeys inoculated with simian immunodeficiency virus or simian-human immunodeficiency virus: implications for using nonhuman primate AIDS models to test vaccines and therapeutics. J Virol. 2001, 75: 11234-11238. 10.1128/JVI.75.22.11234-11238.2001.
Greenier JL, Miller CJ, Lu D, Dailey PJ, Lu FX, Kunstman KJ, Wolinsky SM, Marthas ML: Route of simian immunodeficiency virus inoculation determines the complexity but not the identity of viral variant populations that infect rhesus macaques. J Virol. 2001, 75: 3753-3765. 10.1128/JVI.75.8.3753-3765.2001.
Trivedi P, Horejsh D, Hinds SB, Hinds PW, Wu MS, Salvato MS, Pauza CD: Intrarectal transmission of simian immunodeficiency virus in rhesus macaques: selective amplification and host responses to transient or persistent viremia. J Virol. 1996, 70: 6876-6883.
Kim EY, Busch M, Abel K, Fritts L, Bustamante P, Stanton J, Lu D, Wu S, Glowczwskie J, Rourke T, et al: Retroviral recombination in vivo: viral replication patterns and genetic structure of simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) populations in rhesus macaques after simultaneous or sequential intravaginal inoculation with SIVmac239Deltavpx/Deltavpr and SIVmac239Deltanef. J Virol. 2005, 79: 4886-4895. 10.1128/JVI.79.8.4886-4895.2005.
Wooley DP, Smith RA, Czajak S, Desrosiers RC: Direct demonstration of retroviral recombination in a rhesus monkey. J Virol. 1997, 71: 9650-9653.
Arien KK, Troyer RM, Gali Y, Colebunders RL, Arts EJ, Vanham G: Replicative fitness of historical and recent HIV-1 isolates suggests HIV-1 attenuation over time. AIDS. 2005, 19: 1555-1564. 10.1097/01.aids.0000185989.16477.91.
Gali Y, Berkhout B, Vanham G, Bakker M, Back NK, Arien KK: Survey of the temporal changes in HIV-1 replicative fitness in the Amsterdam Cohort. Virology. 2007, 364: 140-146. 10.1016/j.virol.2007.02.021.
Muller V, Ledergerber B, Perrin L, Klimkait T, Furrer H, Telenti A, Bernasconi E, Vernazza P, Gunthard HF, Bonhoeffer S: Stable virulence levels in the HIV epidemic of Switzerland over two decades. AIDS. 2006, 20: 889-894. 10.1097/01.aids.0000218553.51908.6b.
Kimata JT, Mozaffarian A, Overbaugh J: A lymph node-derived cytopathic simian immunodeficiency virus Mne variant replicates in nonstimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Virol. 1998, 72: 245-256.
Rudensey LM, Kimata JT, Benveniste RE, Overbaugh J: Progression to AIDS in macaques is associated with changes in the replication, tropism, and cytopathic properties of the simian immunodeficiency virus variant population. Virology. 1995, 207: 528-542. 10.1006/viro.1995.1113.
Forte S, Harmon ME, Pineda MJ, Overbaugh J: Early- and intermediate-stage variants of simian immunodeficiency virus replicate efficiently in cells lacking CCR5. J Virol. 2003, 77: 9723-9727. 10.1128/JVI.77.17.9723-9727.2003.
Kimata JT, Overbaugh J: The cytopathicity of a simian immunodeficiency virus Mne variant is determined by mutations in Gag and Env. J Virol. 1997, 71: 7629-7639.
Kimata JT, Wilson JM, Patel PG: The increased replicative capacity of a late-stage simian immunodeficiency virus mne variant is evident in macrophage- or dendritic cell-T-cell cocultures. Virology. 2004, 327: 307-317. 10.1016/j.virol.2004.07.010.
Yu Kimata MT, Cella M, Biggins JE, Rorex C, White R, Hicks S, Wilson JM, Patel PG, Allan JS, Colonna M, Kimata JT: Capture and transfer of simian immunodeficiency virus by macaque dendritic cells is enhanced by DC-SIGN. J Virol. 2002, 76: 11827-11836. 10.1128/JVI.76.23.11827-11836.2002.
Chackerian B, Haigwood NL, Overbaugh J: Characterization of a CD4-expressing macaque cell line that can detect virus after a single replication cycle and can be infected by diverse simian immunodeficiency virus isolates. Virology. 1995, 213: 386-394. 10.1006/viro.1995.0011.
Kuller L, Thompson J, Watanabe R, Iskandriati D, Alpers CE, Morton WR, Agy MB: Mucosal antibody expression following rapid SIV(Mne) dissemination in intrarectally infected Macaca nemestrina. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1998, 14: 1345-1356. 10.1089/aid.1998.14.1345.
Polacino P, Stallard V, Montefiori DC, Brown CR, Richardson BA, Morton WR, Benveniste RE, Hu SL: Protection of macaques against intrarectal infection by a combination immunization regimen with recombinant simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmne gp160 vaccines. J Virol. 1999, 73: 3134-3146.
Kuller L, Benveniste RE, Tsai CC, Clark EA, Polacino P, Watanabe R, Overbaugh J, Katze MG, Morton WR: Intrarectal inoculation of macaques by the simian immunodeficiency virus, SIVmne E11S: CD4+ depletion and AIDS. J Med Primatol. 1994, 23: 397-409.
Overbaugh J, Rudensey LM, Papenhausen MD, Benveniste RE, Morton WR: Variation in simian immunodeficiency virus env is confined to V1 and V4 during progression to simian AIDS. J Virol. 1991, 65: 7025-7031.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to dedicate this manuscript to the memory of Jonathan Allan. We thank Claudia Kozinetz and Xiaoying Yu of the Baylor-UT Houston CFAR design and analysis core for help with statistical analyses of the data and the veterinary staff at the SNPRC for assistance with the animal studies. Support was provided by NIH grant R01 AI047725, and in part by the Baylor-UT Houston CFAR (P30 AI036211), the Southwest National Primate Research Center (P51 RR13986), the Washington National Primate Research Center (P51 RR000166), and NIH training grant in Molecular Virology (T32 AI07471).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
JSA, JTK, and TB designed the experiments. TB performed most of the experiments, and analyzed the data. JSA, RW, and BKW assisted with the macaque infections and the flow cytometry analyses. MTY performed the PCR cloning. TB and JTK wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Biesinger, T., White, R., Yu Kimata, M.T. et al. Relative replication capacity of phenotypic SIV variants during primary infections differs with route of inoculation. Retrovirology 7, 88 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-4690-7-88
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-4690-7-88