Abstract
Background
Prognosis of KRAS wild-type and mutant metastatic colorectal cancer (MCRC) patients (pts) treated with bevacizumab (BEV)-containing chemotherapy is not significantly different. Since specific KRAS mutations confer different aggressive behaviors, the prognostic role of prevalent KRAS mutations was retrospectively evaluated in MCRC pts treated with first line FIr-B/FOx, associating BEV to triplet chemotherapy.
Methods
Tumor samples were screened for KRAS codon 12, 13 and BRAF V600E mutations by SNaPshot and/or direct sequencing. MCRC pts <75-years-old were consecutively treated with FIr-B/FOx: weekly 12 hour-timed-flat-infusion/5-fluorouracil (900 mg/m2 on days 1,2, 8, 9, 15, 16,22, 23), irinotecan plus BEV (160 mg/m2 and 5 mg/kg, respectively, on days 1,15); and oxaliplatin (80 mg/m2, on days 8,22). Pts were classified as liver-limited (L-L) and other/multiple metastatic (O/MM). Progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were compared using the log-rank test.
Results
Fifty-nine pts were evaluated at a median follow-up of 21.5 months. KRAS mutant pts: c.35 G > A, 15 (25.4%); c.35 G > T, 7 (11.8%); c.38 G > A, 3 (5%); other, 3 (5%). KRAS wild-type, 31 pts (52.7%). The objective response rate (ORR), PFS and OS were, respectively: c.35 G > A mutant, 71%, 9 months, 14 months; other than c.35 G > A mutants, 61%, 12 months, 39 months. OS was significantly worse in c.35 G > A pts compared to KRAS wild-type (P = 0.002), KRAS/BRAF wild-type (P = 0.03), other MCRC patients (P = 0.002), other than c.35 G > A (P = 0.05), other codon 12 (P = 0.03) mutant pts. OS was not significantly different compared to c.35 G > T KRAS mutant (P = 0.142).
Conclusions
KRAS c.35 G > A mutant status may be significantly associated with a worse prognosis of MCRC pts treated with first line FIr-B/FOx intensive regimen compared to KRAS/BRAF wild type and other than c.35 G > A mutant pts.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
KRAS genotype, wild-type or mutant, addresses the medical treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer (MCRC) patients (pts), consisting of triplet regimens combining chemotherapeutic drugs, or doublets plus targeted agents [1]. The addition of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (anti-EGFR) treatment is not effective in KRAS mutant patients [2, 3]; anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) treatment added to doublet chemotherapy was effective in KRAS wild-type and mutant pts [4, 5]. In liver limited (L-L) MCRC, these first line options, integrated with secondary resection of liver metastases, may significantly increase survival [6–13].
The prognostic relevance of the KRAS genotype can be assessed by evaluation of clinical outcome (progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS)) in wild-type and mutant pts, depending on differential tumor biological aggressiveness and predictive effectiveness of treatment strategies. The median OS of KRAS wild-type and mutant MCRC pts treated with irinotecan, 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin (IFL) plus bevacizumab (BEV) was 27.7 and 19.9 months, respectively [4, 5]. The hazard ratio (HR) for risk of death was 0.51 and statistically significant only when KRAS and BRAF wild-type pts were compared with pts harboring mutations in one gene. In KRAS wild-type pts and in BRAF wild-type pts compared to mutant, HR was 0.64 and 0.38, respectively, but did not reach statistical significance [4]. Recently, phase II studies proposed by Masi et al. [8], and by our group [7], showed that intensive medical treatment consisting of triplet chemotherapy plus BEV, according to FOLFOXIRI plus BEV and FIr-B/FOx schedules, respectively, may increase the activity and efficacy of the treatment in MCRC pts with the KRAS wild-type and mutant genotypes [8, 13]. Median OS of pts treated with FIr-B/FOx was different in KRAS wild-type and mutant pts (38 months and 21 months, respectively), but not significantly [13]. L-L pts compared to other/multiple metastatic (O/MM) pts achieve significantly increased PFS and OS; in addition, KRAS wild-type pts with L-L disease may achieve a significantly greater benefit from integration with liver metastasectomies, with respect to KRAS mutant patients [11, 13].
The KRAS wild-type genotype predicts favorable clinical outcomes when anti-EGFR or anti-VEGF molecules are added to doublet chemotherapy [2, 5]. The KRAS mutant genotype significantly predicts prolonged PFS up to 9.3 months, while there was no increase in OS and activity [14, 5], in pts treated with BEV added to IFL compared to IFL.
KRAS mutations occur in 35% to 45% of colorectal cancer (CRC), mostly in codon 12 (80%), c.35 G > A (G12D) and c.35 G > T (G12V) transversions, representing 32.5% [14, 15] and 22.5% [14, 16], respectively, and codon 13, predominantly c.38 G > A (G13D) mutations [17]. These mutations impair the intrinsic GTPase activity of KRAS, thus leading to constitutive, growth-factor-receptor independent activation of downstream signalling [18]. In the in vitro model proposed by Guerrero et al. [19], codon 12 mutations increase aggressiveness by the differential regulation of KRAS downstream pathways that lead to inhibition of apoptosis, enhanced loss of contact inhibition and increased predisposition to anchorage-independent growth [19]. Codon 13 mutations showed reduced transforming capacity compared to codon 12 mutations [20].
The biological aggressiveness of codon 12 KRAS mutant tumors seems to confer worse clinical behavior. A multivariate analysis suggested that the presence of KRAS mutation significantly increased the risk of recurrence and death; the codon 12 c.35 G > T (G12V) mutation retained an independent increased risk of recurrence and death [21], and significantly reduced disease-free survival and OS of Dukes C pts [16]. The poorer prognosis conferred by codon 12 KRAS mutations was not confirmed in other studies [22, 23].
We report a retrospective exploratory analysis evaluating the prognostic value of the prevalent codon 12 c.35 G > A (G12D) KRAS mutation in MCRC pts enrolled in a previously reported phase II study [7] and in an expanded clinical program proposing FIr-B/FOx intensive regimen as first line treatment.
Methods
Patient eligibility
MCRC pts were enrolled in a previously reported phase II study [7] and in the expanded clinical program proposing FIr-B/FOx association as first line treatment. The study was approved by the Local Ethical Committee (Comitato Etico, Azienda Sanitaria Locale n.4 L'Aquila, Regione Abruzzo, Italia) and conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All patients provided written, informed consent.
Schedule
FIr-B/FOx association consisted of 5-fluorouracil associated with alternating irinotecan/BEV or oxaliplatin, according to a previously reported weekly schedule [7].
Mutation analysis
KRAS and BRAF analyses were performed on paraffin-embedded tissue blocks from the primary tumor and/or metastatic site. Genotype status was analyzed for KRAS codon 12 and 13 mutations and BRAF c.1799 T > A (V600E) mutation by SNaPshot® multiplex [13, 24], for KRAS mutations and KRAS/BRAF mutations in 36 and 32 samples, respectively; direct sequencing of the KRAS gene was performed in 23 samples. After treatment with xylene thiocyanate and selection of tumor cell clusters, DNA was isolated using the RecoverAll™ Total Nucleic Acid Isolation Kit for FFPE Tissues (Applied Biosystems, Courtaboeuf, France) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
SNaPshot®assay
SNaPshot® multiplex assay was performed as previously reported [13, 25]. KRAS exon 2 and BRAF exon 15 were simultaneously PCR-amplified and analyzed for the presence of mutations at KRAS nucleotides c.34G, c.35G, c.37G, c.38G and BRAF mutation at nucleotide c.1799T using the ABI PRISM SNaPshot® Multiplex kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) [13, 25]. Labelled products were separated on 36 cm-long capillaries in POP7 polymer during a 25-minute run in an ABI Prism 3130xl Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems). Data were analyzed using the GeneMapper Analysis Software version 4.0 (Applied Biosystems).
Direct sequencing assay
KRAS exon 2 sequence reaction was performed from PCR-amplified tumor DNA, using the Big Dye V3.1 Terminator Kit (Applied Biosystems), and run on an automated sequencer (ABI 3130, Applied Biosystems).
Study design
A retrospective analysis has been planned to evaluate the prognostic relevance of the prevalent codon 12 c.35 G > A (G12D) KRAS mutant genotype on the clinical outcome of MCRC pts treated with first line FIr-B/FOx. Pts were classified as L-L and O/MM [13]. Clinical criteria of activity and efficacy were ORR, PFS and OS. ORR was evaluated according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) criteria [26]; pathological complete response was defined as absence of residual cancer cells in surgically resected specimens. Overall activity of integrated medical treatment and secondary liver surgery, consisting of the sum of clinical complete responses (cCR) and liver metastasectomies was also evaluated, as previously reported [11]. PFS and OS were evaluated using the Kaplan and Meier method [27]. The log-rank test was used to compare PFS and OS in different subgroups of pts [28]. PFS was defined as the length of time between the beginning of treatment and disease progression or death (resulting from any cause) or to last contact; OS, as the length of time between the beginning of treatment and death or to last contact. Clinical evaluation of response was made by computerized tomography (CT)-scan; positron emission tomography (PET) was added based on the investigators' assessment. Pts with L-L metastases were evaluated at baseline and every three cycles of treatment, by a multidisciplinary team (medical oncologist, liver surgeon, radiologist) to dynamically evaluate resectability, defined according to previously reported resectability categories [11]. The resection rate was evaluated in intent-to-treat population enrolled. Liver metastasectomies were defined as: R0, if radical surgery; R1, if radiofrequency was added.
Results
Patient demographics
The KRAS/BRAF genotype was evaluated in 59 pts, among 64 consecutive, unselected MCRC pts recruited in the phase II study and expanded clinical enrollment of the FIr-B/FOx regimen as the first line treatment of MCRC [7, 13]: 31 pts (53%) were identified as KRAS wild-type and 28 (47%) as KRAS mutant [13]. The prevalence of KRAS mutations was: codon 12, 24 pts (40.6%), specifically c.35 G > A (G12D), 15 pts (25.4%), c.35 G > T (G12V), 7 pts (11.8%), c.34 G > A (G12S) and c.35 G > C (G12A), 1 patient each; codon 13, 4 pts (6.7%), c.38 G > A (G13D), 3 pts (5%) and c.37_39 dupl, 1 patient (Table 1).
Table 2 describes the demographic and baseline features of pts with the c.35 G > A KRAS mutation, other KRAS mutations, and KRAS wild-type: male/female ratio, 11/4, 5/8 and 21/10, respectively; liver metastases, 12 (80%), 8 (61.5%) and 19 pts (61%), respectively.
Pts' distribution according to extension of metastatic disease in c.35 G > A KRAS mutant, other KRAS mutant, and KRAS wild-type pts was, respectively: L-L 6 pts (40%), 7 pts (54%), and 12 pts (39%); O/MM 9 pts (60%), 6 pts (46%), 19 pts (61%).
Activity and efficacy according to specific KRASmutations
Activity and efficacy data in overall KRAS wild-type and mutant pts at a median follow-up of 21.5 months were previously reported [13]. Among 14 evaluable c.35 G > A KRAS mutant pts (Table 3), ORR was 71% (α 0.05, CI ± 26). We observed 10 objective responses: 9 partial responses (64%) and 1 complete response (CR) (7%) in a patient with single liver metastasis, who was progression-free at 60 months; 3 stable diseases (21%); 1 progressive disease (7%). Median PFS was 9 months (1+-60+ months): 10 events occurred and 5 pts (33%) were progression-free. Median OS was 14 months (1+-60+ months): 10 events occurred and 5 pts (33%) were alive. Liver metastasectomies were performed in 2 pts out of 15 (13%) and out of 6 pts with L-L metastases (33%); 1 R0 liver metastasectomy (17%). Clinical outcome according to extension of metastatic disease, L-L and O/MM [11, 13], was: median PFS 9 and 7 months, median OS 11 and 14 months, respectively.
Among 13 other than c.35 G > A KRAS mutant pts, ORR was 61% (α 0.05, CI ± 30). We observed 8 partial responses (61%), 2 stable diseases (15%), and 3 progressive diseases (23%). Median PFS was 12 months (3-37 months): 12 events occurred and 1 patient (8%) was progression-free >12 months. Median OS was 39 months (8-59+ months): 8 events occurred and 5 pts (38%) were alive. Liver metastasectomies were performed in 5 pts out of 13 (38%) and out of 7 (71%) with L-L metastases; 4 R0 liver resections (57%). Two pathologic CRs were obtained (15%) in pts with multiple L-L metastases, harboring codon 12 mutations, c.35 G > T and c.34 G > A: 1 patient progressed at 17 months, 1 patient was progression-free at 35 months. Clinical outcome according to extension of metastatic disease, L-L and O/MM [11, 13], was: median PFS 16 and 12 months and median OS 44 and 21 months, respectively.
Activity and efficacy among 30 evaluable KRAS wild-type pts was previously reported [13]: ORR was 90% (α 0.05, CI ± 11). Four cCR were obtained (13%): 1 patient progressed at 22 months; 3 pts were progression-free at 69, 40 and 4 months. Median PFS was 14 months (1+-69+ months). Median OS was 38 months (1+-69+ months). Liver metastasectomies were performed in 11 pts: 35% of wild-type MCRC pts and 10 out of 12 L-L pts (83%). Among 18 KRAS/BRAF wild-type pts [13], ORR was 83% (α 0.05, CI ± 14). Median PFS was 13 months (4-44 months), median OS was 31 months (8-66+ months).
Among 44 evaluable other than c.35 G > A KRAS mutant plus KRAS wild-type pts, ORR was 81% (α 0.05, CI ± 12), median PFS was 13 months (1+-69+ months) and median OS was 34 months (1+-69+ months) (Table 4). Among 21 evaluable codon 12 KRAS mutant pts, ORR was 71% (α 0.05, CI ± 20), median PFS was 12 months (1+-60+ months) and median OS was 20 months (1+-60+ months). Among 7 c.35 G > T KRAS mutant pts, ORR was 57% (α 0.05, CI ± 40), median PFS was 12 months (3-5 months) and median OS was 21 months (11-46+ months). Among 4 codon 13 KRAS mutant pts, ORR was 75% (α 0.05, CI ± 49), median PFS was 12 months (7-37 months) and median OS was 44 months (8-59+ months). Among 3 c.38 G > A KRAS mutant pts, ORR was 67% (α 0.05, CI ± 65), median PFS was 12 months (7-37 months) and median OS was not reached (8-59+ months).
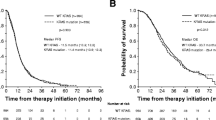
Figure 1 shows that PFS of c.35 G > A KRAS mutant pts compared to KRAS wild-type pts was not significantly different while OS was significantly worse (P = 0.002). In addition, c.35 G > A KRAS mutant pts compared to other than c.35 G > A KRAS mutant pts showed significantly worse OS (P = 0.05); other than c.35 G > A KRAS mutant pts compared to KRAS wild-type pts did not have different OS (Figure 2). KRAS c.35 G > A mutant pts also had significantly worse OS compared to: other than c.35 G > A KRAS mutant pts plus KRAS wild-type pts (P = 0.002); KRAS/BRAF wild-type pts (P = 0.03); and other codon 12 mutant pts (P = 0.03) (Figure 3). The prognostic relevance was not significantly different compared to c.35 G > T KRAS mutant pts (P = 0.142) (Figure 3).
Overall survival, Kaplan-Meier survival estimate. A, c.35 G > A KRAS mutant patients versus other KRAS mutant plus KRAS wild-type patients; B, c.35 G > A KRAS mutant patients versus KRAS/BRAF wild-type patients; C, c.35 G > A KRAS mutant patients versus other codon 12 KRAS mutant patients; D, c.35 G > A KRAS mutant patients versus c.35 G > T KRAS mutant patients.
Discussion
The prognostic relevance of KRAS status, wild-type or mutant, is not significantly different in MCRC pts treated with BEV-containing chemotherapy. Reported median OS ranges from 29.9 to 38 months in KRAS wild-type and 19.9 to 21 months in KRAS mutant pts [4, 5, 8, 13]. The addition of anti-EGFR or anti-VEGF molecules to doublet chemotherapy predicts a favorable clinical outcome in KRAS wild-type pts [2, 5]. BEV addition to IFL compared to IFL significantly predicts prolonged PFS up to 9.3 months, but not increased OS and activity, in KRAS mutant pts [5, 14]. BEV addition to triplet chemotherapy, according to FIr-B/FOx or FOLFOXIRI/BEV schedules, resulted in high activity and efficacy in KRAS wild-type and mutant MCRC pts [8, 13]. In particular, KRAS mutant pts had an ORR of 67% and 71%, median PFS of 11 and 12.6 months, and median OS 20 months, respectively [8, 13]. We recently reported a significantly favorable prognosis (PFS and OS) in KRAS wild-type L-L compared to O/MM pts [11, 13]. Conversely, in KRAS mutant MCRC pts, median PFS and OS were not significantly affected by the extension of metastatic disease (L-L compared to O/MM) [11, 13].
The prevalent c.35 G > A (G12D) KRAS mutation characterizes 10.3% of CRC and represents up to 30% of KRAS mutations [16]. In the present evaluation, 25.4% of MCRC pts harbored the c.35 G > A KRAS mutation and exhibited a high activity of the FIr-B/FOx intensive regimen (ORR 71%). Liver metastasectomies were performed in 13% of pts (33% of L-L disease), median PFS and OS were 9 and 14 months, respectively. In pts with the KRAS c.35 G > A mutation, activity and PFS were not significantly different, while OS was significantly worse compared to KRAS wild-type, KRAS/BRAF wild-type, and other codon 12 and 13 mutant pts. Median OS was not significantly different in other KRAS mutant compared to wild-type pts. This is the first report of a worse prognosis in KRAS c.35 G > A (G12D) mutant MCRC pts, treated with intensive triplet chemotherapy plus BEV.
Codon 12 KRAS mutations may increase aggressiveness by the differential regulation of KRAS downstream pathways associated with higher AKT/protein kinase B activation, bcl-2, E-catherin, β-catenin, and focal adhesion kinase overexpression, and RhoA underexpression, whereas codon 13 KRAS mutant cells show increased sensitivity associated with increased activation of the c-Jun-NH2-terminal kinase I pathway [19]. Several studies compared the prognostic roles of KRAS codon 12 with codon 13 mutations in CRC. RASCAL (Kirsten Ras in CRC) studies showed that the presence of the KRAS mutation significantly increased the risk of death by 26% [16, 21]; the c.35 G > T (G12V) mutation, but not c.35 G > A (G12D) or c.35 G > C (G12A), represented an independent risk factor for recurrence and death and significantly increased the risk of death by 44% [21]. It also had a significantly worse impact on failure-free survival and OS, increasing the risk of recurrence or death by 30% [16], and up to 50% in Dukes' C cancers [16]. KRAS codon 12 mutations (in particular, c.35 G > T) were associated with inferior survival in patients with KRAS-wild-type/BRAF-wild-type cancers [29].
In MCRC pts, specific BRAF and KRAS mutations can confer different biological aggressiveness and effectiveness of treatment strategies; the balance between aggressiveness and effectiveness can differentiate prognosis, that is, median OS. Comparison of median OS in pts with different genotypes can discriminate this net prognostic effect. Thus, specific mutations and treatment strategies (medical regimens and secondary liver surgery, further lines of treatment) could be major parameters determining different prognoses in MCRC. The prevalent BRAF c.1799 T > A (V600E) mutation, characterizing 4.7% to 8.7% of CRC, demonstrated a negative prognostic effect compared to BRAF wild-type pts in MCRC pts treated with doublet chemotherapy alone or added to cetuximab, BEV and cetuximab plus BEV, with a median PFS of 5.6 to 8 months and median OS of 10.3 to 15.9 months [4, 30, 31]. The favorable predictive effect of cetuximab or BEV addition to chemotherapy was not significantly demonstrated in BRAF mutant MCRC pts [4, 31, 32]. Patients with tumors harbouring the KRAS c.35 G > T mutation and other mutations were associated with a worse outcome when receiving chemotherapy plus cetuximab, compared with chemotherapy alone [33].
In MCRC pts pre-treated with chemotherapy alone, the KRAS c.38 G > A mutation (G13D) confers a significantly worse prognosis [34]. Cetuximab or cetuximab plus chemotherapy significantly predicted increased OS (median 7.6 and 10.6 months, respectively) and PFS (median 4.0 and 4.1 months, respectively) compared to other KRAS mutations [34], and no different outcome was found compared to KRAS wild-type pts [34]. Recently, a retrospective pooled analysis confirmed the favorable predictive effect of c.38 G > A KRAS mutation in first line cetuximab-containing chemotherapy [33]: significantly improved PFS (median, 7.4 versus 6.0 months) and tumor response (40.5% versus 22.0) but not survival (median, 15.4 versus 14.7 months). Moreover, systematic reviews and meta analyses confirmed that KRAS c.38 G > A (G13D) mutant pts demonstrated a significantly favorable predictive effect of cetuximab-containing associations compared to other KRAS mutant MCRC, and significantly lower ORR, with no significantly different PFS and OS compared to KRAS wild-type pts [35, 36]. In patients with MCRC treated with panitumumab or control therapy in first-or second-line chemorefractory settings, no consistent associations were found between tumors with specific KRAS mutations and patient outcome. Opposite findings were reported when panitumumab was combined with first line oxaliplatin, whereas similar data were reported when it was combined with second-line FOLFIRI [37].
Prospective studies should be developed to confirm the differential prognosis and predictive effect of chemotherapeutics and/or targeted agents in MCRC pts harboring KRAS/BRAF mutations, specifically KRAS c.35 G > A (G12D), c.35 G > T (G12V), c.38 G > A (G13D) mutations and BRAF c.1799 T > A (V600E).
Conclusions
The prevalent KRAS c.35 G > A (G12D) mutant genotype has a significantly worse effect on the OS of MCRC pts treated with the first line FIr-B/FOx intensive regimen compared to wild-type pts or to pts harboring different other KRAS mutations, due to heterogeneous biological aggressiveness and the effectiveness of treatment strategies. The present findings should be verified in prospective trials of multidisciplinary strategies comparing clinical outcome in MCRC pts harboring specific mutations that differentially activate the downstream RAS-MAPK or PI3K pathways.
Abbreviations
- Anti-EGFR:
-
anti-epidermal growth factor receptor
- anti-VEGF:
-
anti-vascular endothelial growth factor
- BEV:
-
bevacizumab
- cCR:
-
clinical complete responses
- CR:
-
complete response
- CRC:
-
colorectal cancer
- CT:
-
computed tomography
- HR:
-
hazard ratio
- IFL:
-
irinotecan, 5-fluorouracil, and leucovorin
- L-L:
-
liver-limited
- MCRC:
-
metastatic colorectal cancer
- O/MM:
-
other/multiple metastatic
- ORR:
-
objective response rate
- OS:
-
overall survival
- PET:
-
positron emission tomography
- PFS:
-
progression-free survival
- pts:
-
patients
- RECIST:
-
Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors.
References
Bruera G, Ricevuto E: Intensive chemotherapy of metastatic colorectal cancer: weighing between safety and clinical efficacy. Evaluation of Masi G, Loupakis F, Salvatore L, et al. Bevacizumab with FOLFOXIRI (irinotecan, oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and folinate) as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: a phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 2010;11:845-52. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2011, 11: 821-824. 10.1517/14712598.2011.582462.
Van Cutsem E, Kohne CH, Hitre E, Zaluski J, Chang Chien CR, Makhson A, D'Haens G, Pinter T, Lim R, Bodoky G, Roh JK, Folprecht G, Ruff P, Stroh C, Tejpar S, Schlichting M, Nippgen J, Rougier P: Cetuximab and chemotherapy as initial treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009, 351: 1408-1417.
Bokemeyer C, Bondarenko I, Makhson A, Hartmann JT, Aparicio J, de Braud F, Donea S, Ludwig H, Schuch G, Stroh C, Loos AH, Zubel A, Koralewski P: Fluorouracil, leucoverin, and oxaliplatin with or without cetuximab in the first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009, 27: 663-671. 10.1200/JCO.2008.20.8397.
Ince WL, Jubb AM, Holden SN, Holmgren EB, Tobin P, Sridhar M, Hurwitz HI, Kabbinavar F, Novotny WF, Hillan KJ, Koeppen H: Association of k-ras, b-raf, and p53 status with the treatment effect of Bevacizumab. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005, 97: 981-989. 10.1093/jnci/dji174.
Hurwitz HI, Yi J, Ince W, Novotny WF, Rosen O: The clinical benefit of bevacizumab in metastatic colorectal cancer is independent of K-ras mutation status: analysis of a phase III study of bevacizumab with chemotherapy in previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncologist. 2009, 14: 22-28.
Folprecht G, Gruenberger T, Bechstein WO, Raab HR, Lordick F, Hartmann JT, Lang H, Frilling A, Stoehlmacher J, Weitz J, Konopke R, Stroszczynski C, Liersch T, Ockert D, Herrmann T, Goekkurt E, Parisi F, Kohne CH: Tumour response and secondary resectability of colorectal liver metastases following neoadjuvant chemotherapy with Cetuximab: the CELIM randomized phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11: 38-47. 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70330-4.
Bruera G, Santomaggio A, Cannita K, Lanfiuti Baldi P, Tudini M, De Galitiis F, Mancini M, Marchetti P, Antonucci A, Ficorella C, Ricevuto E: "Poker" association of weekly alternating 5-fluorouracil, irinotecan, bevacizumab and oxaliplatin (FIr-B/FOx) in first line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: a phase II study. BMC Cancer. 2010, 10: 567-10.1186/1471-2407-10-567.
Masi G, Loupakis F, Salvatore L, Fornaro L, Cremolini C, Cupini S, Ciarlo A, Del Monte F, Cortesi E, Amoroso D, Granetto C, Fontanini G, Sensi E, Lupi C, Andreuccetti M, Falcone A: Bevacizumab with FOLFOXIRI (irinotecan, oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and folinate) as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: a phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11: 845-852. 10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70175-3.
Garufi C, Torsello A, Tumolo S, Ettorre GM, Zeuli M, Campanella C, Vennarecci G, Mottolese M, Sperduti I, Cognetti F: Cetuximab plus chronomodulated irinotecan, 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin and oxaliplatin as neoadiuvant chemotherapy in colorectal liver metastases: POCHER trial. Br J Cancer. 2010, 103: 1542-1547. 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605940.
Masi G, Vasile E, Loupakis F, Cupini S, Fornaro L, Baldi G, Salvatore L, Cremolini C, Stasi I, Brunetti I, Fabbri MA, Pugliesi M, Trenta P, Granetto C, Chiara S, Fioretto L, Allegrini G, Crinò L, Andreuccetti M, Falcone A: Randomized trial of two induction chemotherapy regimens in metastatic colorectal cancer: an updated analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011, 103: 21-30. 10.1093/jnci/djq456.
Bruera G, Cannita K, Giuliante F, Lanfiuti Baldi P, Vicentini R, Marchetti P, Nuzzo G, Antonucci A, Ficorella C, Ricevuto E: Effectiveness of liver metastasectomies in metastatic colorectal cancer (MCRC) patients treated with triplet chemotherapy plus bevacizumab (FIr-B/FOx). Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2012, 11: 119-126. 10.1016/j.clcc.2011.11.002.
Ficorella C, Bruera G, Cannita K, Porzio G, Lanfiuti Baldi P, Tinari N, Natoli C, Ricevuto E: Triplet chemotherapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: toward the best way to safely administer a highly active regimen in clinical practice. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2012, 11: 229-237. 10.1016/j.clcc.2012.05.001.
Bruera G, Cannita K, Di Giacomo D, Lamy A, Troncone G, Dal Mas A, Coletti G, Frébourg T, Sabourin JC, Tosi M, Ficorella C, Ricevuto E: Prognostic value of KRAS genotype in metastatic colorectal cancer (MCRC) patients treated with intensive triplet chemotherapy plus bevacizumab (FIr-B/FOx) according to extension of metastatic disease. BMC Medicine. 2012, 10: 135-10.1186/1741-7015-10-135.
Forbes S, Clements J, Dawson E, Bamford S, Webb T, Dogan A, Flanagan A, Teague J, Wooster R, Futreal PA, Stratton MR: Cosmic 2005. Br J Cancer. 2006, 94: 318-322. 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602928.
Bos JL: ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res. 1989, 49: 4682-4689.
Andreyev HJ, Norman AR, Cunningham D, Oates J, Dix BR, Iacopetta BJ, Young Y, Walsh T, Ward R, Hawkins N, Beranek M, Jandik P, Benamouzig R, Jullian E, Laurent-Puig P, Olschwang S, Muller O, Hoffmann I, Rabes HM, Zietz C, Troungos C, Valavanis C, Yuen ST, Ho JWC, Croke CT, O'Donoghue DP, Giaretti W, Rapallo A, Russo A, Bazan V, et al: Kirsten ras mutations in patients with colorectal cancer: the 'RASCAL II' study. Br J Cancer. 2001, 85: 692-696. 10.1054/bjoc.2001.1964.
Normanno N, Tejpar S, Morbillo F, De Luca A, Van Cutsem E, Ciardiello F: Implication of KRAS status and EGFR-targeted therapies in metastatic CRC. Nat Rev Clin Onc. 2009, 6: 519-527. 10.1038/nrclinonc.2009.111.
Schubbert S, Shannon K, Bollag G: Hyperactive ras in developmental disorders and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007, 7: 295-308. 10.1038/nrc2109.
Guerrero S, Casanova I, Farrè L, Mazo A, Capellà G, Mangues R: K-ras codon 12 mutation induces higher level of resistance to apoptosis and predisposition to anchorage-independent growth than codon 13 mutation or proto-oncogene overexpression. Cancer Res. 2000, 60: 6750-6756.
Bos JL, Toksoz D, Marshall CJ, Verlaan-de Vries M, Veeneman GH, van der Eb AJ, van Boom JH, Janssen JW, Steenvoorden AC: Amino-acid substitutions at codon 13 of the N-ras oncogene in human acute myeloid leukaemia. Nature. 1985, 315: 726-730. 10.1038/315726a0.
Andreyev HJN, Norman AR, Cunningham D, Oates JR, Clarke PA: Kirsten ras mutations in patients with colorectal cancer: the multicenter 'RASCAL' study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998, 90: 675-684. 10.1093/jnci/90.9.675.
Samowitz WS, Curtin K, Schaffer D, Robertson M, Leppert M, Slattery ML: Relationship of Ki-ras mutations in colon cancers to tumor location, stage, and survival: a population-based study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2000, 9: 1193-1197.
Westra JL, Schaapveld M, Hollema H, de Boer JP, Kraak MMJ, de Jong D, ter Elst A, Mulder NH, Buys CHCM, Hofstra RMW, Plukker JTM: Determination of TP53 mutation is more relevant than microsatellite instability status for the prediction of disease-free survival in adjuvant-treated stage III colon cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 2005, 23: 5635-5643. 10.1200/JCO.2005.04.096.
Di Fiore F, Blanchard F, Charbonnier F, Le Pessot F, Lamy A, Galais MP, Bastit L, Killian A, Sesboué R, Tuech JJ, Queniet AM, Paillot B, Sabouirin JC, Michot F, Michel P, Frebourg T: Clinical relevance of KRAS mutation detection in metastatic colorectal cancer treated by cetuximab plus chemotherapy. Br J Cancer. 2007, 96: 1166-1169. 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603685.
Lamy A, Blanchard F, Le Pessot F, Sesboué R, Di Fiore F, Bossut J, Fiant E, Frébourg T, Sabourin JC: Metastatic colorectal cancer KRAS genotyping in routine practice: results and pitfalls. Mod Pathol. 2011, 24: 1090-1100. 10.1038/modpathol.2011.60.
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, Verweij J, Glabbeke MV, van Oosterom AT, Christian MC, Gwyther SG: New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors: European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000, 92: 205-216. 10.1093/jnci/92.3.205.
Kaplan EL, Meier P: Nonparametric estimation of incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc. 1958, 53: 457-481. 10.1080/01621459.1958.10501452.
Peto R, Peto J: Asymptomatically efficient rank invariant test procedures. J R Stat Soc A. 1972, 135: 185-206. 10.2307/2344317.
Imamura Y, Morikawa T, Liao X, Lochhead P, Kuchiba A, Yamauchi M, Qian ZR, Nishihara R, Meyerhardt JA, Haigis KM, Fuchs CS, Ogino S: Specific mutations in KRAS codons 12 and 13, and patient prognosis in 1075 BRAF-wild-type colorectal cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2012, 18: 4753-4763. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-3210.
Di Nicolantonio F, Martini M, Molinari F, Sartore-Bianchi A, Arena S, Saletti P, de Dosso S, Mazzucchelli L, Frattini M, Siena S, Bardelli A: Wild-type BRAF is required for response to panitumumab and cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008, 26: 5705-5712. 10.1200/JCO.2008.18.0786.
Van Cutsem E, Köhne CH, Làng I, Folprecht G, Nowacki MP, Cascinu S, Shchepotin I, Maurel J, Cunningham D, Tejpar S, Schlichting M, Zubel A, Celik I, Rougier P, Ciardiello F: Cetuximab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: updated analysis of overall survival according to tumor KRAS and BRAF mutation status. J Clin Oncol. 2011, 29: 2011-2019. 10.1200/JCO.2010.33.5091.
Bokemeyer C, Bondarenko I, Hartmann JT, de Braud F, Schuch G, Zubel A, Celik I, Schlichting M, Koralewski P: Efficacy according to biomarker status of cetuximab plus FOLFOX-4 as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: the OPUS study. Ann Oncol. 2011, 22: 1535-1546. 10.1093/annonc/mdq632.
Tejpar S, Celik I, Schlichting M, Sartorius U, Bokemeyer C, Van Cutsem E: Association of KRAS G13D tumor mutations with outcome in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer treated with first-line chemotherapy with or without cetuximab. J Clin Oncol. 2012, 30: 3570-3577. 10.1200/JCO.2012.42.2592.
De Roock W, Jonker DJ, Di Nicolantonio F, Sartore-Bianchi A, Tu D, Siena S, Lamba S, Arena S, Frattini M, Piessevaux H, Van Cutsem E, O'Callaghan CO, Khambata-Ford S, Zalcberg JR, Simes J, Karapetis CS, Bardelli A, Tejpar S: Association of KRAS p.G13D mutation with outcome in patients with chemotherapy-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer treated with cetuximab. JAMA. 2010, 304: 1812-1820. 10.1001/jama.2010.1535.
Mao C, Huang YF, Yang ZY, Zheng DY, Chen JZ, Tang JL: KRAS p.G13D mutation and codon 12 mutations are not created equal in predicting clinical outcomes of cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer. 2013, 119: 714-721. 10.1002/cncr.27804.
Chen J, Ye Y, Sun H, Shi G: Association between KRAS codon 13 mutations and clinical response to anti-EGFR treatment in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: results from a meta-analysis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013, 71: 265-272. 10.1007/s00280-012-2005-9.
Peeters M, Douillard JY, Van Cutsem E, Siena S, Zhang K, Williams R, Wiezorek J: Mutant KRAS codon 12 and 13 alleles in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: assessment as prognostic and predictive biomarkers of response to panitumumab. J Clin Oncol. 2013, 31: 759-765. 10.1200/JCO.2012.45.1492.
Pre-publication history
The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1741-7015/11/59/prepub
Acknowledgements
Gino Coletti and Antonella Dal Mas, Pathology Department, S. Salvatore Hospital, L'Aquila, Italy, for collection and assembly of biological materials. They declare no competing interests or funding source. GB is a PhD student in Biotechnology, Department of Biotechnological and Applied Clinical Sciences, University of L'Aquila, funded by the University of L'Aquila, Italy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
GB contributed to the conception and design of the study, in the provision of study materials of patients, in data analysis and interpretation and in the manuscript writing. ER contributed to the conception and design of the study, in data analysis and interpretation and in the manuscript writing. KC, TF, MT, EA participated in data analysis and interpretation. GB, KC, CF and ER provided clinical management and data on patients. DDG, AL, JCS provided molecular genetic analysis. All authors participated in the collection and/or assembly of data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Bruera, G., Cannita, K., Di Giacomo, D. et al. Worse prognosis of KRASc.35 G > A mutant metastatic colorectal cancer (MCRC) patients treated with intensive triplet chemotherapy plus bevacizumab (FIr-B/FOx). BMC Med 11, 59 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-11-59
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-11-59