Abstract
For many diseases vaccines are lacking or only partly effective. Research on protective immunity and adjuvants that generate vigorous immune responses may help generate effective vaccines against such pathogens.
Similar content being viewed by others
The immune system is functionally diverse, able to make a refined response to hundreds of different types of infectious organisms. The initiation of an immune response to an infection requires collaboration between innate immune cells, which recognize general distinguishing features of pathogens, and the T lymphocytes of the adaptive immune system, whose highly variable antigen receptors are specific for a given pathogen. The activation of T lymphocytes depends on interactions with professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs), specialized cells of the innate immune system that are directly activated by the pathogens they engulf and regurgitate for presentation to, and activation of, T cells. The T cells then proliferate and are mobilized to protect the body by activating other immune cells or by killing infected cells. Among the immune cells activated by T lymphocytes, most importantly, are the B lymphocytes that produce antibodies. T lymphocytes direct the types of antibodies that B cells produce and the activity of other immune cells, thereby directing the immune response to optimally provide protection against different types of infections.
At the end of an immune response, the majority of activated B and T cells will undergo apoptosis, but a small number remain as memory cells, primed ready in case the host is exposed to the same infection [1, 2]. Vaccines must work in a similar way, priming antigen-specific T and B cells, some of which convert to the memory cells that will control subsequent infections by the invader targeted by the vaccine. Moreover, like the infection itself, the vaccine must generate the optimal type of immune response to protect against a particular pathogen.
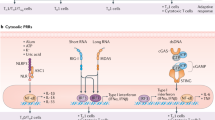
The different ways in which the immune system can respond to antigen are schematically summarized in Figure 1, which shows the two major classes of T lymphocyte, cytotoxic (or CD8) cells and helper (or CD4) cells, and their principal actions. For example, virus infections can be cleared by cytotoxic T cells (CTLs) or antibodies, whereas intracellular bacteria and parasites are most effectively controlled by T cells that produce cytokines specialized to activate particular groups of innate immune cells (Figure 1) [3–5].
Activation and differentiation of T lymphocytes. Dendritic cells (DCs) take up antigen delivered either by an infectious pathogen or by a vaccine (stage 1). DCs are activated by conserved components of pathogens binding to pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that induce the expression of co-stimulatory molecules and the release of inflammatory cytokines. Vaccines that do not contain intrinsic adjuvants are delivered with added adjuvants, such as aluminum salts, that also activate inflammatory pathways. DCs degrade the antigen into peptides that are returned to the cell surface on MHC molecules and presented to CD8 and CD4+ T cells - antigen being presented to CD8+ T cells by MHC class I molecules, and to CD4+ T cells on MHC class II molecules (stage 2). T cells also require signals provided by the co-stimulatory molecules and inflammatory cytokines to be fully activated. Activation results in cell proliferation (stage 3) and effector cell differentiation (stage 4). CD4+ T cells can make cytokines that activate innate immune cells (such as macrophages and neutrophils) to kill pathogens. Activated CD4+ T cells can also provide help to B cells, expressing the cell-surface and soluble mediators required for the production of high-affinity class switched antibody. Effector CD8+ T cells can kill infected cells by releasing cytotoxic granules or can activate other cell types by the release of inflammatory cytokines.
The immune system is thought to distinguish the different kinds of pathogens through recognition by innate immune cells of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) on microorganisms, which enables responding cells to direct the adaptive responses along the pathway that will best help to reject the invader. PAMPs include, for example, characteristic cell wall components of bacteria, double-stranded RNA, which is found in some viruses, and CpG-rich DNA, which can be present in bacteria and viruses. These microbial components are detected by innate signaling pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), among the best known and most versatile of which are the Toll-like receptors (TLRs). Different members of the TLR family of membrane-bound receptors are specialized for detection of different classes of pathogens. In addition, many cytoplasmic proteins have recently been recognized to be important in innate immunity as PRRs [6–9]. Recognition of PAMPs by responding cells promotes recruitment of innate immune cells and APCs and activates APCs, increasing uptake of antigen and inducing cell-surface molecules and soluble mediators that are required for T cell activation. Together, these effects influence the magnitude of T and B cell responses and the numbers of memory cells that are produced. Not only do they serve to warn and activate the cells of the adaptive immune response but, importantly, they also control the type of immune response that follows.
Currently, three main types of vaccine are used in humans: live attenuated vaccines composed of a virus or bacterium that is similar to but less pathogenic than the real pathogen; inactivated vaccines that are heat-inactivated or chemically inactivated particles of the pathogen; or subunit vaccines that are made from components of the pathogen. Vaccines contain not only the antigen that is the target of the adaptive immune response, but either PAMPs or other substances that amplify or influence the adaptive response: these are known as adjuvants. In the live attenuated vaccines, the antigens that are recognized by the cells of the adaptive immune system are coupled to the PAMPs that activate professional APCs, just as they are in the pathogen itself, and these thus provide a natural adjuvant. Subunit vaccines, by contrast, consist of the purified antigens that are specifically recognized by lymphocytes, and although they are safer than whole-organism vaccines, they are unable, on their own, to activate the immune system optimally because they lack intrinsic PAMPs. Such vaccines require the addition of adjuvants that enhance their immunogenicity and influence the magnitude and nature of the response.
Adjuvants may promote immune responses by recruiting professional APCs to the vaccination site, by increasing the delivery of antigens to APCs, or by activating APCs to produce cytokines and provide activating signals to T cells. One adjuvant that has a long historical use in human vaccines is aluminum salt (sometimes referred to as alum). Proteins from the pathogen are adsorbed onto the aluminum salt, creating a suspension that is injected intramuscularly. Despite its long-standing and widespread use in human vaccines, it is still not clear exactly how this adjuvant works. Although it was widely believed that aluminum adjuvants promote their effects by maintaining a slow-releasing depot of antigen to the immune system, it is now clear that they promote multiple effects on the innate immune system. In addition, excision of aluminum adjuvant nodules after immunization has no impact on the magnitude of the immune response, which has brought the role of the depot into question [10].
Adjuvants were first deliberately introduced into vaccines after it was shown that aluminum salts and other particles could enhance immune responses [11]. At present, there are very few licensed vaccine adjuvants for clinical use. In the USA, aluminum salts have been, for many years, the only adjuvants that could be added to human vaccines. Recently, monophosphoryl lipid A (MPL), a derivative of the highly immunogenic bacterial cell wall component lipopolysaccharide (LPS), has been approved for use in the GlaxoSmithKline vaccine for human papillomavirus in combination with aluminum hydroxide. In Europe several additional adjuvants are used, including the oil-in-water adjuvants MF59 and ASO3, made by Novartis and GlaxoSmithKline, respectively (Table 1). As well as these, a large number of novel vaccine adjuvants have been studied in the laboratory, and some of them have also been used in clinical trials in humans (Tables 1 and 2). Whether these adjuvants will pass the two major criteria required for general use (effectiveness and safety) remains to be determined.
Adjuvants and antibody production
Most current vaccines act by inducing long-lived plasma cells - terminally differentiated B cells - that continuously secrete antibody over a considerable period of time [5]. Antibodies act quickly by binding to and thus stopping the pathogen, or products of the pathogen, in their tracks before damage to the host occurs. They are thus ideal for control of many diseases, including infection by viruses and intoxication by a number of bacterial products, including tetanus and diphtheria toxins [5]. Many of the viral vaccines use attenuated viruses as agents and generate good, long-lasting antibody production [12]. However, this is not so true for the subunit vaccines. For example, the tetanus vaccine, which is composed of a toxoid (an inactivated toxin that retains its antigenic properties) adsorbed to aluminum adjuvant, leads to the generation of plasma cells that make anti-tetanus-toxin antibody. However, this vaccine is routinely given to individuals every 10 to 15 years as the specific plasma cells making the antibody eventually die off [13]. This is in contrast to the plasma cells that are generated following infection with live measles virus. These plasma cells are predicted to have a half-life of 3,014 years [12]. How the infection manages this and, therefore, how an adjuvant could achieve this are still unclear.
The type of antibody produced is also affected by the adjuvant. There are five major classes of antibody with different properties and, ideally, vaccines should be designed to induce the antibody class that would be most effective in dealing with the pathogen. Immunoglobulin A (IgA) is highly effective against agents that infect through mucosal surfaces (see, for example, [14]). This factor may be responsible for the overall greater effectiveness of the Sabin (live attenuated) than the Salk (heat killed) polio vaccine. This is because the oral, live vaccine induces IgA secretion in the gut and respiratory tract, whereas the inactivated intramuscular Salk vaccine does not [15]. It is possible that adjuvants can be selected to enhance secretory IgA production, probably through their effects on APCs and T cell differentiation (see below).
Antibodies are sometimes not enough
Influenza vaccines operate by inducing antibodies against the two main surface proteins from the virus, hemagglutinin and neuraminidase. In so doing they effectively protect against infection by influenza strains expressing versions of these proteins present in the vaccine. However, these two proteins change as a consequence of mutation and re-assortment and the vaccine must be reformulated each year to contain the hemagglutinin and neuraminidase of the expected strain. Moreover, the vaccine has historically been, and in the US is currently, administered in the absence of an adjuvant. This means that larger doses must be given and immunity has been difficult to induce against the proteins found in emerging strains, such as those in H5N1 viruses that cause avian flu [16]. This may be partly because individuals have memory cells that can recognize annual but not emerging strains of the virus. Memory cells can respond in the absence of high levels of co-stimulation [17] (Figure 1) and, therefore, can be activated in the absence of an adjuvant. A primary response is required, however, to protect against newly emerging virus strains as they are more antigenically distinct from annual influenza strains. This primary response cannot be activated in the absence of the inflammation induced by added adjuvant.
Addition of adjuvants (MF59, ASO3 or aluminum salts; Table 1) to influenza vaccines increases antibody titers and persistence [18–21]. However, these approaches do not provide cross-reactivity to distinct subtypes of the virus. The same is true for the attenuated influenza vaccine FluMist, which is also modified each year, although this vaccine may activate cross-reactive CD8+ T cells, at least in children [22]. CD8+ T cells recognize less variable parts of the virus - for example, in the core proteins [23–30] - and may provide a more cross-reactive response that could be induced by new vaccines.
Besides influenza there are clearly many other infections, HIV and malaria, for example, for which antibodies are not at all, or are insufficiently, protective. In these cases, both humoral immunity, mediated by antibodies, and cell-mediated immunity, which depends on cytotoxic T cells or T cells that activate immune cells by means of cytokines, may be required for effective protection.
Contribution of adjuvants to T cell priming
Dendritic cells (DCs) are key antigen-presenting cells in the initiation of T cell responses, and are thus likely to be a major target of adjuvant effects. In the absence of infection, DCs are distributed throughout the tissues as phagocytic cells. The presence of infection is signaled to these cells both directly, by pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs) for microbial constituents, and indirectly, by inflammatory cytokines released by other innate immune cells that recognize microbial constituents. These signals activate the DCs to undergo a process known as maturation and to migrate into secondary lymphoid organs where they activate naïve T cells. DC maturation involves increased processing of microbial proteins, portions of which are presented to T cells on major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules (discussed below). This serves as a required first activation signal. In addition, activation of DCs by PRRs results in expression on the surface of the DCs of so-called accessory and co-stimulatory molecules and the secretion of cytokines. Co-stimulatory signals are secondary signals required for DCs to activate naïve T cells, and cytokines offer a third signal to direct their differentiation along different pathways (Figure 1, stage 2). One way in which adjuvants such as aluminum salts and MF59 act is by promoting inflammation and infiltration of DCs into the site of inoculation and improving the uptake of associated antigens by DCs [31–34].
Adjuvant effects are relatively well understood for signals that induce T helper cell 1 (TH1) responses, which are characterized by T helper cells that produce high levels of IFNγ, and other cytokines that activate antimicrobial effects at the effector site. These TH1 driving signals are known to operate through TLRs to induce secretion of interleukin (IL)-12, which drives differentiation of TH1 cells [35–38]. Adjuvants such as QS21 or other saponins drive TH1 responses and are thought to work by the induction of IL-12 in DCs [39]. Aluminum salts, however, do not directly induce signaling through TLRs and do not stimulate IL-12 production by DCs. Instead, aluminum adjuvants drive TH2 responses [40], by mechanisms that are much less well understood.
The requirements for antigen presentation to CD8+ T cells, which give rise to cytotoxic cells, are distinct from those for the CD4 helper T cells. CD8+ T cells are specialized for detection of agents, such as viruses, that invade the cytoplasm, and the pathway by which antigen reaches the surface from the cytoplasm is distinct from the pathway followed by internalized antigen. Briefly, all antigens are carried to the cell surface by molecules encoded in the MHC. Internalized antigen is carried to the cell surface by one class of MHC molecules, MHC class II, which promotes activation of CD4 cells. In contrast, endogenous antigen reaches the cell surface on a different class, MHC class I, which activates CD8 cells. To activate cytotoxic T cells, antigen internalized by DCs must cross to the MHC class I pathway before reappearing on the cell surface, a process known as cross-presentation, for which specific subsets of DCs are specialized [41]. Adjuvant systems are likely to have important effects on antigen cross-presentation. For example, some TLR ligands, such as LPS, can promote delivery of essential parts of the MHC class I antigen-processing pathway to vesicles of the internalization pathway, presumably enhancing cross-presentation [42]. Other adjuvants, such as immunostimulatory complexes (ISCOM/ISCOMATRIX), particulate adjuvants made up of lipids, cholesterol and the saponin adjuvant Quil A, may promote cross-presentation and activation of CD8 cells by partly bypassing the normal antigen-processing pathway [43].
The role of adjuvant-induced inflammation in enhancing the initiation of T cell responses is an unresolved issue. For example, a crucial complex in the inflammatory pathway, the inflammasome, is suggested in some studies [44, 45], but not in others [46–48], to be required for recruitment of APCs and enhanced T and B cell responses following immunization with aluminum salt adjuvants, despite the use of similar methods in genetically identical mice. It is also not clear whether PRR-mediated pathways must be activated in DCs themselves, or whether inflammatory responses in local tissue cells can account for some adjuvant effects [49]. For example, inflammatory cytokines can recruit to the injection site monocytes that differentiate into DCs. These may subsequently be activated to migrate into the lymph node to present antigen to T cells. Such recruitment is one action of the MF59 adjuvant, an emulsion of oil (squalene) in water, and aluminum salt adjuvants [31, 34].
Establishment of T cell memory
Despite many years of research, immunologists still have little idea of which signals are required for the generation of memory T cells. This may be a stochastic process, in which a percentage of cells are randomly selected to survive, or a selective process, in which a subset of cells is designated early in the response to survive and generate the memory pool. Memory cells can be identified by characteristic markers [50–52] that may be useful in measuring the effectiveness of different antigen-adjuvant combinations. In some cases, the generation of memory cells that express lymphoid homing markers is associated with long-term survival and thus protection [53]. In contrast, other investigators argue that memory T cells that migrate into non-lymphoid organs, where re-infections are likely to occur, provide the most effective protection [54]. Therefore, measurements of protective capacity (for example, reduced viral titers or bacterial loads following challenge) are more useful indicators of a successful vaccine than the phenotype of the memory cells.
Many variables can affect the number and phenotype of memory cells. For example, a large dose of antigen can activate a larger number of cells, but a low dose may be preferable in a vaccine, if it activates only cells with high-affinity receptors, which may be more effective in some infections [55, 56]. This seems to be true in mouse models of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in which low-dose priming induces highly sensitive T cells that can make a broad cytokine response that is associated with protection [55].
Likewise, the amount of inflammation, which in the case of a vaccine can be influenced by the addition of an adjuvant, affects the phenotype and number of the memory cells generated, partly because inflammatory signals are required for the efficient expansion and survival of T cells [57]. The speed with which memory cells are generated, however, can be increased by reducing inflammation during priming, resulting in the more rapid generation of memory cells [58, 59]. It may be critical, therefore, to adjust the amount of antigen and adjuvant depending on how many and what type of memory cells are required to provide protection. This leads us to the question of how important the two major classes of T cells - CD4 cells and CD8 cells - are in providing protection.
CD4 T cell-mediated protection
It is clear that CD4+ T cells are critical directors of both cellular and humoral memory. It has been established for many years that CD4+ T cells provide help to B cells [60], but CD4+ T cells are also crucial for the generation of effective CD8 memory T cells [61]. Any vaccine, regardless of its intended action, must therefore activate helper CD4+ T cells. Perhaps the most important consideration for deciding what adjuvant to use in a vaccine is what type of CD4+ T cell response is required to direct the ensuing ideal immune response. At least five subsets of CD4+ T helper are now recognized: TH1 and TH2 cells, which activate macrophages in distinct ways and induce production of different classes of antibodies in B cells; TH17 cells, which are inflammatory; T follicular cells, which are specialized for activating B cells; and regulatory T cells, which are thought to prevent autoimmunity (Figure 2). These subsets have been reviewed extensively elsewhere [62, 63]; here we will mainly discuss TH1 cells as these have been most associated with protection following vaccination.
CD4+ T helper subsets. CD4+ T cells can differentiate into different subsets depending on the cytokine milieu present during T cell activation. TH1 cells, activated in the presence of IL-12 and IL-18 produced by activated DCs, make IFNγ, which is important in activating macrophages to kill intracellular bacteria, such as M. tuberculosis. IL-4 made by TH2 cells activates macrophages to expel parasites (the cellular source of the IL-4 that promotes TH2 development is currently poorly defined). T follicular (Tfh) cells can make the canonical cytokines that TH1 or TH2 cells produce, but they also make IL-21 and express cell-surface molecules, such as CD40 ligand and inducible T cell co-simulator (ICOS), that are required for effective B cell responses and production of high-affinity, class-switched antibodies. The more recently described TH17 cells can produce IL-17 and IL-22 and are generated in the presence of IL-6 and TGFβ. IL-17 and IL-22 are important for promoting the influx of neutrophils to inflamed sites and the production of antimicrobial peptides, respectively. TH17 cells are thought to be important in defense against extracellular bacteria and fungi. Activated T cells can also differentiate into regulatory T cells (Tregs) in the presence of TGFβ and/or retinoic acid (RA). These cells can inhibit and control immune responses to prevent excessive inflammation through cell-surface molecules (such as CTLA-4) or cytokines, such as IL-10.
Although it is clear that CD4+ T cells must be activated following vaccination, the importance of generating CD4 memory cells is less obvious. We have recently discussed the subject in some detail [64] and so will not go into specifics here, but a careful analysis of the available evidence suggests that relatively few protective immune responses depend on CD4+ T cell memory. Protection from M. tuberculosis is, however, a good example of how CD4 memory cells can act. CD4+ T cells producing the important cytokine interferon (IFN)γ provide protection to M. tuberculosis by activating macrophages in infected lungs [4]. The current M. tuberculosis vaccine, Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG), protects young children from the worse forms of the disease [65, 66], but it is of limited use in adults [4]. Therefore, much M. tuberculosis vaccine research is focused on a prime-boost approach, a series of two vaccines, with BCG as the primary vaccine and a second experimental vaccine designed to re-activate and increase the protective memory response. As the boost several substances have been tried. For example, a modified vaccinia virus (MVA) that expresses a protein from M. tuberculosis, 85A, has been tested in animals and humans. By using a vaccinia vector, a broad immune response, including IL-12 production by DCs and IFNγ production by CD4 cells, is induced [67, 68]. In mouse studies, boosting with MVA85A resulted in reduced levels of bacteria in challenged animals [69, 70]. The vaccine also successfully boosts antigen-specific cells in humans and the consequent memory cells produce a range of cytokines, including IFNγ and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)α [71–73]. Such multifunctional cells, which also make cytokines at higher levels, have been shown to provide protection against infections, including M. tuberculosis, in mouse models [55, 73, 74].
CD8 T cell-mediated protection
Although it has been difficult to demonstrate direct protective effects of CD4 memory T cells, the differentiation of CD8+ T cells into CTLs has long been a measure of their protective efficacy (Figure 1). Following activation and clonal expansion in lymphoid organs, CTLs migrate to sites of inflammation, where they kill infected cells by inducing apoptosis, thus limiting and eventually clearing the infection. CTLs have been shown to provide protection in various mouse infection models [3, 75–78], and CTL activity has been demonstrated in assays in vitro using human CD8+ T cells [23, 79, 80]. CTLs are also correlated with protection in humans infected with influenza [79, 81, 82].
There has been a shift in the focus of influenza vaccine development towards generating memory CD8+ T cells that may be able to provide more cross-reactive protection; this is because, as mentioned above, the antigens that CD8+ T cells recognize are found in less variable portions of the virus [23–30]. Several approaches have been developed, and perhaps the most interesting are those that target the lung, generating memory cells in the correct location to provide the most rapid protection. For example, peptides recognized by CD8+ T cells have been combined with a lipid moiety, Pam-2-Cys, that activates a TLR on DCs to successfully prime protective CD8+ T cells [83]. When delivered intranasally, this vaccine generates CD8+ T cells that migrate to the lung to provide immediate protection.
The use of peptide fragments rather than whole antigens is a limitation for the outbred human population because different fragments are recognized by the T cells of different individuals, and a very large number of different fragments would need to be identified and included. As an alternative, whole detergent-inactivated influenza virus can be combined with ISCOMs, which can deliver enclosed antigen directly to DCs and activate a range of innate cells, generating a TH1 and CTL response [84]. ISCOMs containing inactivated influenza virus have been used to generate an intranasal vaccine that includes all the viral proteins and can induce cross-reactive protection [85]. This protection required both CTL and antibodies, indicating that the ISCOM vaccine induced an effective cell-mediated and humoral response.
The killing of infected cells by CTLs and TH1 cells is an effective way to clear an infection with an intracellular pathogen. However, in some cases, such as infection of the liver by the hepatitis B virus, IFNγ-producing CD8+ T cells offer more effective protection because the virus can be cleared without the death of a large number of host cells [86]. In a similar vein, IFNγ-producing CD8+ T cells are associated with protection in individuals vaccinated with the RTS, S malaria vaccine. This vaccine contains a protein from the parasite fused to a surface protein from the hepatitis B virus [87]. Although not enough is known about the mechanisms by which immune individuals resist infection, it is believed that both humoral and cell-mediated immunity directed against multiple antigens expressed at different stages of the parasite's lifecycle are required for protection during malarial infection [88]. The adjuvant system used in the most successful malarial vaccine is AS02, a preparation that contains both a saponin component and the TLR agonist MPL formulated in a particulate system. Notably, both saponin and MPL were required to induce a modest level of protection in immunized individuals [89]. In contrast, vaccines using the same antigen with aluminum hydroxide and MPL (AS04) or in an oil-in-water emulsion (AS03) induced high levels of antibody but failed to protect against infection. A greater understanding of the responses in protected individuals may help to efficiently identify more effective antigen-adjuvant combinations. For example, the successful adjuvant, AS02, promotes CD8 responses, TH1 differentiation and broad antibody responses [90]. This suggests that both antibody- and cell-mediated immunity have important roles in defense against this complex pathogen.
In pursuit of the ideal adjuvant
The immune system has a diverse range of mechanisms at its disposal to deal with infectious organisms (Figures 1 and 2). Successful vaccines should aim to activate several of these, creating a redundant protective response that can cope with mutations and pathogen escape strategies. Although live attenuated viral and bacterial vaccines can activate all arms of the immune system [67, 91, 92], adjuvants have so far not reached this goal. By combining adjuvants, such as aluminum salts with MPL, or using prime-boost strategies using DNA and then viral or bacterial vectors, both humoral and cell-mediated responses can be activated, and some successes, as discussed above, have been reported. Yellow fever and smallpox (vaccinia) viruses are highly effective live vaccines that promote B and T cell memory and promote lifelong protection [91, 93]. Recent work from the groups of Rafi Ahmed and Bali Pulendran into why the yellow fever and vaccinia vaccines work so well may provide markers of both innate activation and early adaptive responses, providing biomarkers to evaluate the success of new vaccine and adjuvant strategies [91, 92].
References
Sprent J, Surh CD: T cell memory. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002, 20: 551-579. 10.1146/annurev.immunol.20.100101.151926.
Ahmed R, Gray D: Immunological memory and protective immunity: understanding their relation. Science. 1996, 272: 54-60. 10.1126/science.272.5258.54.
Harty JT, Tvinnereim AR, White DW: CD8+ T cell effector mechanisms in resistance to infection. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000, 18: 275-308. 10.1146/annurev.immunol.18.1.275.
Hoft DF: Tuberculosis vaccine development: goals, immunological design, and evaluation. Lancet. 2008, 372: 164-175. 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61036-3.
Plotkin SA: Vaccines: correlates of vaccine-induced immunity. Clin Infect Dis. 2008, 47: 401-409. 10.1086/589862.
Kawai T, Akira S: Toll-like receptor and RIG-I-like receptor signaling. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008, 1143: 1-20. 10.1196/annals.1443.020.
Pedra JH, Cassel SL, Sutterwala FS: Sensing pathogens and danger signals by the inflammasome. Curr Opin Immunol. 2009, 21: 10-16. 10.1016/j.coi.2009.01.006.
Takeuchi O, Akira S: MDA5/RIG-I and virus recognition. Curr Opin Immunol. 2008, 20: 17-22. 10.1016/j.coi.2008.01.002.
Geijtenbeek TB, Gringhuis SI: Signalling through C-type lectin receptors: shaping immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009, 9: 465-479. 10.1038/nri2569.
Holt LB: Developments in Diphtheria Prophylaxis. 1950, London: Wm Heinemann
Glenny AT, Pope CG, Waddington H, Wallace U: The antigenic value of toxoid precipitated by potassium alum. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1926, 29: 38-45.
Amanna IJ, Carlson NE, Slifka MK: Duration of humoral immunity to common viral and vaccine antigens. N Engl J Med. 2007, 357: 1903-1915. 10.1056/NEJMoa066092.
Simonsen O, Kjeldsen K, Heron I: Immunity against tetanus and effect of revaccination 25-30 years after primary vaccination. Lancet. 1984, 2: 1240-1242. 10.1016/S0140-6736(84)92796-X.
Sanchez J, Holmgren J: Virulence factors, pathogenesis and vaccine protection in cholera and ETEC diarrhea. Curr Opin Immunol. 2005, 17: 388-398. 10.1016/j.coi.2005.06.007.
Ogra PlK DT, Righthand F, MacGillivray M: Immunoglobulin response in serum and secretions after immunization of live and inactivated polio vaccine and natural infection. N Engl J Med. 1968, 279: 893-899.
Ellebedy AH, Webby RJ: Influenza vaccines. Vaccine. 2009, 27 Suppl 4: D65-D68. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.08.038.
Berard M, Tough DF: Qualitative differences between naive and memory T cells. Immunology. 2002, 106: 127-138. 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2002.01447.x.
Vesikari T, Groth N, Karvonen A, Borkowski A, Pellegrini M: MF59-adjuvanted influenza vaccine (FLUAD) in children: safety and immunogenicity following a second year seasonal vaccination. Vaccine. 2009, 27: 6291-6295. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.02.004.
Nicholson KG, Thompson CI, Klap JM, Wood JM, Batham S, Newman RW, Mischler R, Zambon MC, Stephenson I: Safety and immunogenicity of whole-virus, alum-adjuvanted whole-virus, virosomal, and whole-virus intradermal influenza A/H9N2 vaccine formulations. Vaccine. 2009, 28: 171-178. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.09.103.
Chu DW, Hwang SJ, Lim FS, Oh HM, Thongcharoen P, Yang PC, Bock HL, Drame M, Gillard P, Hutagalung Y, Tang H, Teoh YL, Ballou RW, H5N1 Flu Study Group for Hong Kong, Singapore, Taiwan and Thailand: Immunogenicity and tolerability of an AS03(A)-adjuvanted prepandemic influenza vaccine: a phase III study in a large population of Asian adults. Vaccine. 2009, 27: 7428-7435. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.07.102.
Schwarz TF, Horacek T, Knuf M, Damman HG, Roman F, Drame M, Gillard P, Jilg W: Single dose vaccination with AS03-adjuvanted H5N1 vaccines in a randomized trial induces strong and broad immune responsiveness to booster vaccination in adults. Vaccine. 2009, 27: 6284-6290. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.01.040.
He XS, Holmes TH, Zhang C, Mahmood K, Kemble GW, Lewis DB, Dekker CL, Greenberg HB, Arvin AM: Cellular immune responses in children and adults receiving inactivated or live attenuated influenza vaccines. J Virol. 2006, 80: 11756-11766. 10.1128/JVI.01460-06.
Kreijtz JH, de Mutsert G, van Baalen CA, Fouchier RA, Osterhaus AD, Rimmelzwaan GF: Cross-recognition of avian H5N1 influenza virus by human cytotoxic T-lymphocyte populations directed to human influenza A virus. J Virol. 2008, 82: 5161-5166. 10.1128/JVI.02694-07.
Lee LY, Ha do LA, Simmons C, de Jong MD, Chau NV, Schumacher R, Peng YC, McMichael AJ, Farrar JJ, Smith GL, Townsend AR, Askonas BA, Rowland-Jones S, Dong T: Memory T cells established by seasonal human influenza A infection cross-react with avian influenza A (H5N1) in healthy individuals. J Clin Invest. 2008, 118: 3478-3490.
Wang M, Lamberth K, Harndahl M, Roder G, Stryhn A, Larsen MV, Nielsen M, Lundegaard C, Tang ST, Dziegiel MH, Rosenkvist J, Pedersen AE, Buus S, Claesson MH, Lund O: CTL epitopes for influenza A including the H5N1 bird flu; genome-, pathogen-, and HLA-wide screening. Vaccine. 2007, 25: 2823-2831. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2006.12.038.
Boon AC, de Mutsert G, van Baarle D, Smith DJ, Lapedes AS, Fouchier RA, Sintnicolaas K, Osterhaus AD, Rimmelzwaan GF: Recognition of homo- and heterosubtypic variants of influenza A viruses by human CD8+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 2004, 172: 2453-2460.
Braciale TJ: Immunologic recognition of influenza virus-infected cells. II. Expression of influenza A matrix protein on the infected cell surface and its role in recognition by cross-reactive cytotoxic T cells. J Exp Med. 1977, 146: 673-689. 10.1084/jem.146.3.673.
Jameson J, Cruz J, Terajima M, Ennis FA: Human CD8+ and CD4+ T lymphocyte memory to influenza A viruses of swine and avian species. J Immunol. 1999, 162: 7578-7583.
Kees U, Krammer PH: Most influenza A virus-specific memory cytotoxic T lymphocytes react with antigenic epitopes associated with internal virus determinants. J Exp Med. 1984, 159: 365-377. 10.1084/jem.159.2.365.
Yewdell JW, Bennink JR, Smith GL, Moss B: Influenza A virus nucleoprotein is a major target antigen for cross-reactive anti-influenza A virus cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1985, 82: 1785-1789. 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1785.
Kool M, Soullie T, van Nimwegen M, Willart MA, Muskens F, Jung S, Hoogsteden HC, Hammad H, Lambrecht BN: Alum adjuvant boosts adaptive immunity by inducing uric acid and activating inflammatory dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 2008, 205: 869-882. 10.1084/jem.20071087.
Dupuis M, Murphy TJ, Higgins D, Ugozzoli M, van Nest G, Ott G, McDonald DM: Dendritic cells internalize vaccine adjuvant after intramuscular injection. Cell Immunol. 1998, 186: 18-27. 10.1006/cimm.1998.1283.
Mosca F, Tritto E, Muzzi A, Monaci E, Bagnoli F, Iavarone C, O'Hagan D, Rappuoli R, De Gregorio E: Molecular and cellular signatures of human vaccine adjuvants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008, 105: 10501-10506. 10.1073/pnas.0804699105.
Seubert A, Monaci E, Pizza M, O'Hagan DT, Wack A: The adjuvants aluminum hydroxide and MF59 induce monocyte and granulocyte chemoattractants and enhance monocyte differentiation toward dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2008, 180: 5402-5412.
Vyas JM, Veen Van der AG, Ploegh HL: The known unknowns of antigen processing and presentation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008, 8: 607-618. 10.1038/nri2368.
Trinchieri G: Interleukin-12 and the regulation of innate resistance and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003, 3: 133-146. 10.1038/nri1001.
Jakob T, Walker PS, Krieg AM, Udey MC, Vogel JC: Activation of cutaneous dendritic cells by CpG-containing oligodeoxynucleotides: a role for dendritic cells in the augmentation of TH 1 responses by immunostimulatory DNA. J Immunol. 1998, 161: 3042-3049.
Martin M, Michalek SM, Katz J: Role of innate immune factors in the adjuvant activity of monophosphoryl lipid A. Infect Immun. 2003, 71: 2498-2507. 10.1128/IAI.71.5.2498-2507.2003.
Robson NC, Beacock-Sharp H, Donachie AM, Mowat AM: The role of antigen-presenting cells and interleukin-12 in the priming of antigen-specific CD4+ T cells by immune stimulating complexes. Immunology. 2003, 110: 95-104. 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2003.01705.x.
De Gregorio E, D'Oro U, Wack A: Immunology of TLR-independent vaccine adjuvants. Curr Opin Immunol. 2009, 21: 339-345. 10.1016/j.coi.2009.05.003.
Schnorrer P, Behrens GM, Wilson NS, Pooley JL, Smith CM, El-Sukkari D, Davey G, Kupresanin F, Li M, Maraskovsky E, Belz GT, Carbone FR, Shortman K, Heath WR, Villadangos JA: The dominant role of CD8+ dendritic cells in cross-presentation is not dictated by antigen capture. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006, 103: 10729-10734. 10.1073/pnas.0601956103.
Burgdorf S, Scholz C, Kautz A, Tampe R, Kurts C: Spatial and mechanistic separation of cross-presentation and endogenous antigen presentation. Nat Immunol. 2008, 9: 558-566. 10.1038/ni.1601.
Schnurr M, Orban M, Robson NC, Shin A, Braley H, Airey D, Cebon J, Maraskovsky E, Endres S: ISCOMATRIX adjuvant induces efficient cross-presentation of tumor antigen by dendritic cells via rapid cytosolic antigen delivery and processing via tripeptidyl peptidase II. J Immunol. 2009, 182: 1253-1259. 10.4049/jimmunol.0990022.
Li H, Willingham SB, Ting JP, Re F: Cutting edge: inflammasome activation by alum and alum's adjuvant effect are mediated by NLRP3. J Immunol. 2008, 181: 17-21.
Eisenbarth SC, Colegio OR, O'Connor W, Sutterwala FS, Flavell RA: Crucial role for the Nalp3 inflammasome in the immunostimulatory properties of aluminium adjuvants. Nature. 2008, 453: 1122-1126. 10.1038/nature06939.
McKee AS, Munks MW, MacLeod MK, Fleenor CJ, Van Rooijen N, Kappler JW, Marrack P: Alum induces innate immune responses through macrophage and mast cell sensors, but these sensors are not required for alum to act as an adjuvant for specific immunity. J Immunol. 2009, 183: 4403-4414. 10.4049/jimmunol.0900164.
Kool M, Petrilli V, De Smedt T, Rolaz A, Hammad H, van Nimwegen M, Bergen IM, Castillo R, Lambrecht BN, Tschopp J: Cutting edge: alum adjuvant stimulates inflammatory dendritic cells through activation of the NALP3 inflammasome. J Immunol. 2008, 181: 3755-3759.
Franchi L, Nunez G: The Nlrp3 inflammasome is critical for aluminium hydroxide-mediated IL-1beta secretion but dispensable for adjuvant activity. Eur J Immunol. 2008, 38: 2085-2089. 10.1002/eji.200838549.
Nolte MA, Leibundgut-Landmann S, Joffre O, Reis e Sousa C: Dendritic cell quiescence during systemic inflammation driven by LPS stimulation of radioresistant cells in vivo. J Exp Med. 2007, 204: 1487-1501. 10.1084/jem.20070325.
Joshi NS, Cui W, Chandele A, Lee HK, Urso DR, Hagman J, Gapin L, Kaech SM: Inflammation directs memory precursor and short-lived effector CD8(+) T cell fates via the graded expression of T-bet transcription factor. Immunity. 2007, 27: 281-295. 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.07.010.
Kondrack RM, Harbertson J, Tan JT, McBreen ME, Surh CD, Bradley LM: Interleukin 7 regulates the survival and generation of memory CD4 cells. J Exp Med. 2003, 198: 1797-1806. 10.1084/jem.20030735.
Li J, Huston G, Swain SL: IL-7 promotes the transition of CD4 effectors to persistent memory cells. J Exp Med. 2003, 198: 1807-1815. 10.1084/jem.20030725.
Wherry EJ, Teichgraber V, Becker TC, Masopust D, Kaech SM, Antia R, von Andrian UH, Ahmed R: Lineage relationship and protective immunity of memory CD8+ T cell subsets. Nat Immunol. 2003, 4: 225-234. 10.1038/ni889.
Zinkernagel RM, Hengartner H: Protective 'immunity' by pre-existent neutralizing antibody titers and preactivated T cells but not by so-called 'immunological memory'. Immunol Rev. 2006, 211: 310-319. 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2006.00402.x.
Aagaard C, Hoang TT, Izzo A, Billeskov R, Troudt J, Arnett K, Keyser A, Elvang T, Andersen P, Dietrich J: Protection and polyfunctional T cells induced by Ag85B-TB10.4/IC31 against Mycobacterium tuberculosis is highly dependent on the antigen dose. PLoS One. 2009, 4: e5930-10.1371/journal.pone.0005930.
Appay V, Douek DC, Price DA: CD8+ T cell efficacy in vaccination and disease. Nat Med. 2008, 14: 623-628. 10.1038/nm.f.1774.
Marrack P, Kappler J, Mitchell T: Type I interferons keep activated T cells alive. J Exp Med. 1999, 189: 521-530. 10.1084/jem.189.3.521.
Badovinac VP, Harty JT: Manipulating the rate of memory CD8+ T cell generation after acute infection. J Immunol. 2007, 179: 53-63.
Badovinac VP, Porter BB, Harty JT: CD8+ T cell contraction is controlled by early inflammation. Nat Immunol. 2004, 5: 809-817. 10.1038/ni1098.
MacLennan IC, Gulbranson-Judge A, Toellner KM, Casamayor-Palleja M, Chan E, Sze DM, Luther SA, Orbea HA: The changing preference of T and B cells for partners as T-dependent antibody responses develop. Immunol Rev. 1997, 156: 53-66. 10.1111/j.1600-065X.1997.tb00958.x.
Khanolkar A, Badovinac VP, Harty JT: CD8+ T cell memory development: CD4+ T cell help is appreciated. Immunol Res. 2007, 39: 94-104. 10.1007/s12026-007-0081-4.
Locksley RM: Nine lives: plasticity among T helper cell subsets. J Exp Med. 2009, 206: 1643-1646. 10.1084/jem.20091442.
Zhou L, Chong MM, Littman DR: Plasticity of CD4+ T cell lineage differentiation. Immunity. 2009, 30: 646-655. 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.05.001.
MacLeod MK, Clambey ET, Kappler JW, Marrack P: CD4 memory T cells: what are they and what can they do?. Semin Immunol. 2009, 21: 53-61. 10.1016/j.smim.2009.02.006.
Rodrigues LC, Diwan VK, Wheeler JG: Protective effect of BCG against tuberculous meningitis and miliary tuberculosis: a meta-analysis. Int J Epidemiol. 1993, 22: 1154-1158. 10.1093/ije/22.6.1154.
Trunz BB, Fine P, Dye C: Effect of BCG vaccination on childhood tuberculous meningitis and miliary tuberculosis worldwide: a meta-analysis and assessment of cost-effectiveness. Lancet. 2006, 367: 1173-1180. 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)68507-3.
Xu R, Johnson AJ, Liggitt D, Bevan MJ: Cellular and humoral immunity against vaccinia virus infection of mice. J Immunol. 2004, 172: 6265-6271.
Yammani RD, Pejawar-Gaddy S, Gurley TC, Weimer ET, Hiltbold EM, Alexander-Miller MA: Regulation of maturation and activating potential in CD8+ versus CD8- dendritic cells following in vivo infection with vaccinia virus. Virology. 2008, 378: 142-150. 10.1016/j.virol.2008.05.031.
Goonetilleke NP, McShane H, Hannan CM, Anderson RJ, Brookes RH, Hill AV: Enhanced immunogenicity and protective efficacy against Mycobacterium tuberculosis of bacille Calmette-Guerin vaccine using mucosal administration and boosting with a recombinant modified vaccinia virus Ankara. J Immunol. 2003, 171: 1602-1609.
Williams A, Goonetilleke NP, McShane H, Clark SO, Hatch G, Gilbert SC, Hill AV: Boosting with poxviruses enhances Mycobacterium bovis BCG efficacy against tuberculosis in guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 2005, 73: 3814-3816. 10.1128/IAI.73.6.3814-3816.2005.
Beveridge NE, Price DA, Casazza JP, Pathan AA, Sander CR, Asher TE, Ambrozak DR, Precopio ML, Scheinberg P, Alder NC, Roederer M, Koup RA, Douek DC, Hill AV, McShane H: Immunisation with BCG and recombinant MVA85A induces long-lasting, polyfunctional Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific CD4+ memory T lymphocyte populations. Eur J Immunol. 2007, 37: 3089-3100. 10.1002/eji.200737504.
Brookes RH, Hill PC, Owiafe PK, Ibanga HB, Jeffries DJ, Donkor SA, Fletcher HA, Hammond AS, Lienhardt C, Adegbola RA, Hill AV: Safety and immunogenicity of the candidate tuberculosis vaccine MVA85A in West Africa. PLoS One. 2008, 3: e2921-10.1371/journal.pone.0002921.
Hawkridge T, Scriba TJ, Gelderbloem S, Smit E, Tameris M, Moyo S, Lang T, Veldsman A, Hatherill M, Merwe L, Fletcher HA, Mahomed H, Hill AV, Hanekom WA, Hussey GD, McShane H: Safety and immunogenicity of a new tuberculosis vaccine, MVA85A, in healthy adults in South Africa. J Infect Dis. 2008, 198: 544-552. 10.1086/590185.
Darrah PA, Patel DT, De Luca PM, Lindsay RW, Davey DF, Flynn BJ, Hoff ST, Andersen P, Reed SG, Morris SL, Roederer M, Seder RA: Multifunctional TH1 cells define a correlate of vaccine-mediated protection against Leishmania major. Nat Med. 2007, 13: 843-850. 10.1038/nm1592.
Kagi D, Ledermann B, Burki K, Seiler P, Odermatt B, Olsen KJ, Podack ER, Zinkernagel RM, Hengartner H: Cytotoxicity mediated by T cells and natural killer cells is greatly impaired in perforin-deficient mice. Nature. 1994, 369: 31-37. 10.1038/369031a0.
Kagi D, Seiler P, Pavlovic J, Ledermann B, Burki K, Zinkernagel RM, Hengartner H: The roles of perforin- and Fas-dependent cytotoxicity in protection against cytopathic and noncytopathic viruses. Eur J Immunol. 1995, 25: 3256-3262. 10.1002/eji.1830251209.
Topham DJ, Tripp RA, Doherty PC: CD8+ T cells clear influenza virus by perforin or Fas-dependent processes. J Immunol. 1997, 159: 5197-5200.
Walsh CM, Matloubian M, Liu CC, Ueda R, Kurahara CG, Christensen JL, Huang MT, Young JD, Ahmed R, Clark WR: Immune function in mice lacking the perforin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994, 91: 10854-10858. 10.1073/pnas.91.23.10854.
McMichael AJ, Gotch FM, Noble GR, Beare PA: Cytotoxic T-cell immunity to influenza. N Engl J Med. 1983, 309: 13-17.
Malik A, Egan JE, Houghten RA, Sadoff JC, Hoffman SL: Human cytotoxic T lymphocytes against the Plasmodium falciparum circumsporozoite protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1991, 88: 3300-3304. 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3300.
McElhaney JE, Ewen C, Zhou X, Kane KP, Xie D, Hager WD, Barry MB, Kleppinger A, Wang Y, Bleackley RC, Granzyme B: Correlates with protection and enhanced CTL response to influenza vaccination in older adults. Vaccine. 2009, 27: 2418-2425. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.01.136.
McElhaney JE, Xie D, Hager WD, Barry MB, Wang Y, Kleppinger A, Ewen C, Kane KP, Bleackley RC: T cell responses are better correlates of vaccine protection in the elderly. J Immunol. 2006, 176: 6333-6339.
Jackson DC, Lau YF, Le T, Suhrbier A, Deliyannis G, Cheers C, Smith C, Zeng W, Brown LE: A totally synthetic vaccine of generic structure that targets Toll-like receptor 2 on dendritic cells and promotes antibody or cytotoxic T cell responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004, 101: 15440-15445. 10.1073/pnas.0406740101.
Smith RE, Donachie AM, Grdic D, Lycke N, Mowat AM: Immune-stimulating complexes induce an IL-12-dependent cascade of innate immune responses. J Immunol. 1999, 162: 5536-5546.
Sambhara S, Kurichh A, Miranda R, Tumpey T, Rowe T, Renshaw M, Arpino R, Tamane A, Kandil A, James O, Underdown B, Klein M, Katz J, Burt D: Heterosubtypic immunity against human influenza A viruses, including recently emerged avian H5 and H9 viruses, induced by FLU-ISCOM vaccine in mice requires both cytotoxic T-lymphocyte and macrophage function. Cell Immunol. 2001, 211: 143-153. 10.1006/cimm.2001.1835.
Guidotti LG, Ishikawa T, Hobbs MV, Matzke B, Schreiber R, Chisari FV: Intracellular inactivation of the hepatitis B virus by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Immunity. 1996, 4: 25-36. 10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80295-2.
Sun P, Schwenk R, White K, Stoute JA, Cohen J, Ballou WR, Voss G, Kester KE, Heppner DG, Krzych U: Protective immunity induced with malaria vaccine, RTS, S, is linked to Plasmodium falciparum circumsporozoite protein-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells producing IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 2003, 171: 6961-6967.
Richie T: High road, low road? Choices and challenges on the pathway to a malaria vaccine. Parasitology. 2006, 133 Suppl: S113-S144. 10.1017/S0031182006001843.
Stoute JA, Slaoui M, Heppner DG, Momin P, Kester KE, Desmons P, Wellde BT, Garcon N, Krzych U, Marchand M: A preliminary evaluation of a recombinant circumsporozoite protein vaccine against Plasmodium falciparum malaria. RTS, S Malaria Vaccine Evaluation Group. N Engl J Med. 1997, 336: 86-91. 10.1056/NEJM199701093360202.
Schofield L, Villaquiran J, Ferreira A, Schellekens H, Nussenzweig R, Nussenzweig V: Gamma interferon, CD8+ T cells and antibodies required for immunity to malaria sporozoites. Nature. 1987, 330: 664-666. 10.1038/330664a0.
Miller JD, Most van der RG, Akondy RS, Glidewell JT, Albott S, Masopust D, Murali-Krishna K, Mahar PL, Edupuganti S, Lalor S, Germon S, Del Rio C, Mulligan MJ, Staprans SI, Altman JD, Feinberg MB, Ahmed R: Human effector and memory CD8+ T cell responses to smallpox and yellow fever vaccines. Immunity. 2008, 28: 710-722. 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.02.020.
Querec TD, Akondy RS, Lee EK, Cao W, Nakaya HI, Teuwen D, Pirani A, Gernert K, Deng J, Marzolf B, Kennedy K, Wu H, Bennouna S, Oluoch H, Miller J, Vencio RZ, Mulligan M, Aderem A, Ahmed R, Pulendran B: Systems biology approach predicts immunogenicity of the yellow fever vaccine in humans. Nat Immunol. 2009, 10: 116-125. 10.1038/ni.1688.
Theiler M, Smith HH: The use of Yellow Fever virus modified by in vitro cultivation for human immunization. J Exp Med. 1937, 65: 787-800. 10.1084/jem.65.6.787.
Clements CJ, Griffiths E: The global impact of vaccines containing aluminium adjuvants. Vaccine. 2002, 20 Suppl 3: S24-S33. 10.1016/S0264-410X(02)00168-8.
Ott G, Barchfeld GL, Van Nest G: Enhancement of humoral response against human influenza vaccine with the simple submicron oil/water emulsion adjuvant MF59. Vaccine. 1995, 13: 1557-1562. 10.1016/0264-410X(95)00089-J.
Durando P, Fenoglio D, Boschini A, Ansaldi F, Icardi G, Sticchi L, Renzoni A, Fabbri P, Ferrera A, Parodi A, Bruzzone B, Gabutti G, Podda A, Del Giudice G, Fragapane E, Indiveri F, Crovari P, Gasparini R: Safety and immunogenicity of two influenza virus subunit vaccines, with or without MF59 adjuvant, administered to human immunodeficiency virus type 1-seropositive and - seronegative adults. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2008, 15: 253-259. 10.1128/CVI.00316-07.
Coler RN, Carter D, Friede M, Reed SG: Adjuvants for malaria vaccines. Parasite Immunol. 2009, 31: 520-528. 10.1111/j.1365-3024.2009.01142.x.
Heineman TC, Clements-Mann ML, Poland GA, Jacobson RM, Izu AE, Sakamoto D, Eiden J, Van Nest GA, Hsu HH: A randomized, controlled study in adults of the immunogenicity of a novel hepatitis B vaccine containing MF59 adjuvant. Vaccine. 1999, 17: 2769-2778. 10.1016/S0264-410X(99)00088-2.
McFarland EJ, Borkowsky W, Fenton T, Wara D, McNamara J, Samson P, Kang M, Mofenson L, Cunningham C, Duliege AM, Sinangil F, Spector SA, Jimenez E, Bryson Y, Burchett S, Frenkel LM, Yogev R, Gigliotti F, Luzuriaga K, Livingston RA, AIDS Clinical Trials Group 230 Collaborators: Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120-specific antibodies in neonates receiving an HIV-1 recombinant gp120 vaccine. J Infect Dis. 2001, 184: 1331-1335. 10.1086/323994.
Vélez ID, Gilchrist K, Martínez S, Ramírez-Pineda JR, Ashman JA, Alves FP, Coler RN, Bogatzki LY, Kahn SJ, Beckmann AM, Cowgill KD, Reed SG, Piazza FM: Safety and immunogenicity of a defined vaccine for the prevention of cutaneous leishmaniasis. Vaccine. 2009, 28: 329-337. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.10.045.
Sun HX, Xie Y, Ye YP: ISCOMs and ISCOMATRIX. Vaccine. 2009, 27: 4388-4401. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.05.032.
Ennis FA, Cruz J, Jameson J, Klein M, Burt D, Thipphawong J: Augmentation of human influenza A virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte memory by influenza vaccine and adjuvanted carriers (ISCOMS). Virology. 1999, 259: 256-261. 10.1006/viro.1999.9765.
Lell B, Agnandji S, von Glasenapp I, Haertle S, Oyakhiromen S, Issifou S, Vekemans J, Leach A, Lievens M, Dubois MC, Demoitie MA, Carter T, Villafana T, Ballou WR, Cohen J, Kremsner PG: A randomized trial assessing the safety and immunogenicity of AS01 and AS02 adjuvanted RTS, S malaria vaccine candidates in children in Gabon. PLoS One. 2009, 4: e7611-10.1371/journal.pone.0007611.
Boland G, Beran J, Lievens M, Sasadeusz J, Dentico P, Nothdurft H, Zuckerman JN, Genton B, Steffen R, Loutan L, Van Hattum J, Stoffel M: Safety and immunogenicity profile of an experimental hepatitis B vaccine adjuvanted with AS04. Vaccine. 2004, 23: 316-320. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2004.06.006.
Giannini SL, Hanon E, Moris P, Van Mechelen M, Morel S, Dessy F, Fourneau MA, Colau B, Suzich J, Losonksy G, Martin MT, Dubin G, Wettendorff MA: Enhanced humoral and memory B cellular immunity using HPV16/18 L1 VLP vaccine formulated with the MPL/aluminium salt combination (AS04) compared to aluminium salt only. Vaccine. 2006, 24: 5937-5949. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2006.06.005.
Morefield GL, Sokolovska A, Jiang D, HogenEsch H, Robinson JP, Hem SL: Role of aluminum-containing adjuvants in antigen internalization by dendritic cells in vitro. Vaccine. 2005, 23: 1588-1595. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2004.07.050.
Rimaniol AC, Gras G, Verdier F, Capel F, Grigoriev VB, Porcheray F, Sauzeat E, Fournier JG, Clayette P, Siegrist CA, Dormont D: Aluminum hydroxide adjuvant induces macrophage differentiation towards a specialized antigen-presenting cell type. Vaccine. 2004, 22: 3127-3135. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2004.01.061.
Del Giudice G, Hilbert AK, Bugarini R, Minutello A, Popova O, Toneatto D, Schoendorf I, Borkowski A, Rappuoli R, Podda A: An MF59-adjuvanted inactivated influenza vaccine containing A/Panama/1999 (H3N2) induced broader serological protection against heterovariant influenza virus strain A/Fujian/2002 than a subunit and a split influenza vaccine. Vaccine. 2006, 24: 3063-3065. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2006.01.015.
Atmar RL, Keitel WA, Patel SM, Katz JM, She D, El Sahly H, Pompey J, Cate TR, Couch RB: Safety and immunogenicity of nonadjuvanted and MF59-adjuvanted influenza A/H9N2 vaccine preparations. Clin Infect Dis. 2006, 43: 1135-1142. 10.1086/508174.
Stephenson I, Bugarini R, Nicholson KG, Podda A, Wood JM, Zambon MC, Katz JM: Cross-reactivity to highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 viruses after vaccination with nonadjuvanted and MF59-adjuvanted influenza A/Duck/Singapore/97 (H5N3) vaccine: a potential priming strategy. J Infect Dis. 2005, 191: 1210-1215. 10.1086/428948.
Lahiri A, Das P, Chakravortty D: Engagement of TLR signaling as adjuvant: towards smarter vaccine and beyond. Vaccine. 2008, 26: 6777-6783. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.09.045.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Amy S McKee, Megan KL MacLeod contributed equally to this work.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
McKee, A.S., MacLeod, M.K., Kappler, J.W. et al. Immune mechanisms of protection: can adjuvants rise to the challenge?. BMC Biol 8, 37 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7007-8-37
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7007-8-37