Abstract
In this article, space shift keying (SSK) modulation is used to study a wireless communication system when multiple relays are placed between the transmitter and the receiver. In SSK, the indices of the transmit antennas form the constellation symbols and no other data symbol are transmitted. The transmitter and the receiver communicate through a direct link and the existing relays. In this study, two types of relays are considered. Conventional amplify and forward relays in which all relays amplify their received signal and forward it to the destination in a round-robin fashion. In addition, decode and forward relays in which the relays that correctly detect the source signal will forward the corresponding fading gain to the destination in pre-determined orthogonal time slots are studied. The optimum decoder for both communication systems is derived and performance analysis are conducted. The exact average bit error probability (ABEP) over Rayleigh fading channels is obtained in closed-form for a source equipped with two transmit antennas and arbitrary number of relays. Furthermore, simple and general asymptotic expression for the ABEP is derived and analyzed. Numerical results are also provided, sustained by simulations which corroborate the exactness of the theoretical analysis. It is shown that both schemes perform nearly the same and the advantages and disadvantages of each are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Cooperative communication creates collaboration through distributed transmission/processing by allowing different nodes in a wireless network to share resources. The information for each user is sent out not only by the user, but also by other collaborating users. This includes a family of configurations in which the information can be shared among transmitters and relayed to reach final destination in order to improve the system’s overall capacity and coverage [1, 2]. Recently, cooperative technologies have also made their way toward next generation wireless standards, such as IEEE 802.16 (WiMAX) [3] or LTE [4], and have been incorporated into many modern wireless applications, such as cognitive radio and secret communications.
Multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) technique is also one of the major contributions to the progress in wireless communications in recent years and has been considered in many recent standards such as LTE, WiMAX, WINNER [5], and others. Cooperative MIMO techniques promise a significant enhancement in spectral efficiency and network coverage for future wireless communication systems ([6], and references therein). The use of multiple antennas at the transmitter and the receiver in a MIMO system may not be feasible in all applications due to size, cost, and hardware considerations [7]. Therefore, multiple relays can be used as a virtual antenna array to emulate MIMO communications.
Space shift keying (SSK) is a MIMO technique which activates a single transmit-antenna during each time instant and uses the activated antenna index to implicitly convey information [8]. The fundamental idea of SSK is originally proposed in [9], which was further developed into spatial modulation (SM) in [10, 11]. Activating single transmit-antenna at a time eliminates inter-channel interference, avoids the need for inter-antenna synchronization, and creates a robust system to channel estimation errors since the probability of error is determined by the differences between channels associated with the different transmit antennas rather than the actual channel realization. Thereby, SSK is shown to have lower complexity and enhanced error performance with moderate number of transmit antennas as compared to other conventional MIMO techniques such as space–time coding [12] and vertical Bell laboratories layered space–time [13]. However, the diversity potential of MIMO systems is not fully exploited in conventional SSK where only receive diversity gain through the multiple receive antennas is achieved but no transmit diversity. Therefore, several recent attempts were made to develop systems based on the SSK concept that achieves both transmit and receive diversity [14–18].
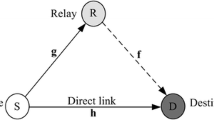
In this article, a source and a destination in a wireless communication system adopting SSK modulation communicates through a direct link and through a set of multiple relays. Conventional amplify and forward (AF) relays as well as decode and forward (DF) relays are considered. In conventional AF system, all existing relays amplify their received signals from the source and forward them to the destination in a round-robin fashion. While in DF system, only the relays that decode the source signals correctly participate in the retransmission process in a predetermined orthogonal time slots. The receiver, in turn, assumes full channel knowledge and estimates the activated transmit antenna to retrieve the transmitted information bits.
However, and though important, the use of SSK in cooperative MIMO is very limited. Recently, the application of SM in a dual-hop non-cooperative scenario is proposed in [19] and significant performance gains are reported as compared to non-cooperative DF system. Also, performance analyses of SSK with single AF relay are reported in [20]. In [15], a coherent versus non-coherent DF space–time shift keying system is proposed where a matrix dispersion approach is used to activate one of the relays similar to activating transmit antennas in SSK. In [21], a space–time SSK aided AF relaying is employed to avoid the need for a large number of transmit antennas and mitigate the effects of deep fading. Also, based on the concept of SSK, an information-guided transmission scheme is proposed in [22] for multi-relay channel and the achievable data rate is analyzed.
With respect to current literature, our contributions are threefold: (i) the optimum receiver ML detectors for the signal received via single or multiple relays and through a direct link in AF and DF systems are derived, (ii) the end-to-end average error probability for the systems under study are computed in closed-form without resorting to Monte Carlo numerical simulations, and (iii) approximate and accurate expressions for the average error probability are also obtained to illustrate the impact of fading parameters on the systems under study.
The remainder of this article is organized as follows: AF and DF systems with optimum receiver detector are discussed in “System model and optimum receiver design” section. Performance analysis for conventional AF relaying is given in “Performance analysis of conventional AF relaying system” section and for DF system in “DF system performance analysis” section. Numerical and analytical results are discussed in “Numerical analysis and discussion” section and a conclusion at the last section.
System model and optimum receiver design
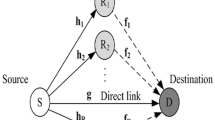
A MIMO system consisting of N t transmit antennas, single receive antenna, N r =1, and M DF relays is depicted in Figure 1.
The transmission is conducted in two phases. In the first phase, each log2 (N t ) bits are mapped into the index of one of the transmitting antennas. At each time instant, only one transmit antenna (ℓ) is active and it transmits an energy E s . The other transmit antenna remains silent during this instant. The transmitted information bits at this particular time instance are incorporated in the location of the active transmit antenna and no other data symbol is transmitted. The received signal at the m th relay input over the MIMO channel can be written as
where x(t) is a unit energy deterministic signal,is a unit energy deterministic signal, n s − r m (t) is the additive white gaussian noise (AWGN) at the m th relay input with both real and imaginary parts having a double-sided power spectral density equal to N0/2, and is the channel complex path gain between transmit antenna ℓ and the relay m with |hm,ℓ| and being the amplitude and the phase of the said channel, respectively. Similarly, the received signal through the direct link at the receiver can be written as
where is the channel complex path gain between transmit antenna ℓ and the receive antenna with |f ℓ | and being the amplitude and the phase of the channel; and ns−dis the AWGN at the receiver input with similar characteristics as .
In the second transmission phase, the relays participate in retransmitting the source message to the destination. Based on the relays type, two systems are discussed in what follows.
Conventional AF relaying
In conventional AF relaying, all the relays participate in re-sending the source signal to the destination in pre-determined time slots. Therefore, M + 1 time slots are needed for each symbol transmission. The received signal at the destination can be written as
where denotes the channel complex path gain between the relay m and the receiver, is the amplification factor at the relay m, and is the AWGN with both real and imaginary parts having a double-sided power spectral density equal to N0/2.
It is assumed that the receiver has full channel state information (CSI). Therefore, the received signal can be simplified to
where .
The optimum ML detector, assuming N t transmit antennas and perfect time synchronization, is then given by [23]
where D ℓ is the decision metric defined as [23]
where Re(·) denotes the real part of complex number, T s is the symbol time, (·)∗ is the complex conjugate, and .
DF relaying
In the DF relaying system, only the relays that correctly detect the active transmit antenna index will forward the channel path gain multiplied by the unit energy deterministic signal to the destination. To simplify the analysis, a genie-aided receiver at each relay is assumed. This receiver is able to determine exactly which symbols in the transmitted data frame are erroneously detected at the relay. At each symbol position, only those relays that correctly detect the symbol are allowed to forward a message in the second phase. In other words, with this genie-aided system, the decoding set C, i.e., the set of forwarding relays, actually changes from symbol to symbol. This is different from a practical DF system involving an error-detecting code, where the decoding set is fixed and comprises only those relays that correctly decode the entire data frame. Nonetheless, this assumption of the relays’ knowledge of erroneous symbol after detection facilitates the error probability derivations. Such an approach is commonly used in the literature (see [24–27]). Furthermore, this can be used as bench mark for all practical systems. Hence, the received C signals at d can be rewritten as
Again, the receiver is assumed to have full CSI. Therefore, the optimum ML detector, assuming perfect time synchronization, is similar to Equations (5) and (6) except that the summation considers only the relays that belong to set C.
Performance analysis of conventional AF relaying system
Conditional error probability
A closed-form expressions are derived in what follows for the case of N t =2 transmit antennas. A generalization to any number of transmit antennas can be obtained by using the union bounding technique as in ([20], Section III-B). Let us assume that at a particular time instant the active antenna index is ν. Then, the decision metrics can be rewritten as
where , , , and .
The instantaneous probability of error, P e (f1,f2,hm,1,hm,2,g m ) conditioned upon the channel impulse responses (f1,f2,hm,1,hm,2, and g m ), can explicitly be written as follows
After a few algebraic manipulations, the instantaneous probability of error, given that transmit antenna one was active, is reduced to
where , which when conditioned upon the fading channels is a random variable with zero-mean and a variance of .
Accordingly, P e can readily be computed in closed form as follows [23, 28, 29]
Using similar analytical steps, can be obtained and is equivalent to (11). Substituting |P e |ℓ=1 and |P e |ℓ=2 in (9), the conditional error probability can be written as
where , , and with being the m th relay output energy.
Average error probability using moment generation function-based approach
In what follows, the average error probability will be computed by exploiting the moment-generation function (MGF)-based approach for performance analysis of digital communication systems over fading channels.
Let us define and , γ s =P s |hm,2−hm,1|2/2 with , and . Note that γ r and γ s are random variables following exponential distribution given by and , respectively. The MGF of γs−dis [23]
The cumulative distribution function of is computed as follows [30, 31]
The integration in (14) can be evaluated to yield
where K ν (·) is the ν th-order modified Bessel function of the second kind. The probability density function (PDF) of can be computed from (15) and is given by,
The MGF of can be computed from the PDF in (16) and is given by [20, 30, 31]
where E1(·) is the exponential integral function.
Using the MGF, an exact closed form expression for the average error probability in a finite single integral can be computed as follows [32],
To avoid numerical integration, this integral can be approximated as
Asymptotic analysis at high SNR analysis
A simpler form for the expression in (18), which offer insight into the effect of the system parameters, is derived in what follows. According to [28, 29], the asymptotic error and outage probabilities can be derived based on the behavior of γ m around the origin. By using Taylor’s series, can be written as
where H.O.T stands for higher-order terms. Therefore, the average error probability can be simplified to
A diversity gain of M is clearly seen in the above equation.
Arbitrary number of transmit antennas
So far, exact closed-form expressions for the average error probability when the source is equipped with two transmit antennas are provided. The framework is generalized in what follows to account for an arbitrary number of transmit antennas. The error performance is derived using the well-known union bounding technique. The average error probability for the system with N t transmit antennas is union bounded as ([23], pp. 261–262)
where is the number of error bits when choosing instead of ℓ as the transmitting antenna index and is the pairwise error probability (PEP) of deciding on given that x ℓ was transmitted. The PEP for two transmit antennas can be computed as in (18) and substituted in (22) to obtain the error probability for an arbitrary number of transmit antennas.
DF system performance analysis
Conditional error probability
Let us assume that antenna number i is used to send the bit at a particular time instance. Then, the decision metrics, can be rewritten as
Following similar analytical steps as discussed in previous section, the conditional error probability can be written as
Average error probability
In DF system, the transmitted message is received via a direct link and through all relays that were able to detect the transmitted signal correctly. The average probability that the relay detects the signal incorrectly Poff is given by
where |H m |2 is an exponential random variable with PDF . Hence, Poffcan be written as
where P s =E s /N0.
The probability that all relays will be off and only direct link communication exist is (Poff)M and the average error probability in this case can be written as
with and the term can be computed as
In the second scenario, m out of M relays detect the signal correctly and in that case the destination will combine the direct link with the m indirect links to estimate the transmitted signal. The probability that this scenario occurs is , where the summation from m=1 to M is to consider all possible values of m. The average error probability for the second scenario is then given by
with , where and .
The exact equation for (29) is calculated in what follows. Let X1 and X2 be two exponential distributed random variables with PDFs and . The PDF of X=X1X2is then given by [32]
where K κ (·) denotes the modified Bessel function of the second kind of order κ. The MGF of X is then written as
where Γ(0,·) is the incomplete Gamma function. Therefore, the MGF of can be written as
with P r =E r /N0. Using similar steps, the MGF of γs−dis written as
Collecting all formulas, the term is given by
The above expression can be approximated as (by substituting φ=Π/2)
By collecting all terms, the exact expression for the average error probability can be obtained and given by
Asymptotic analysis: high SNR approximation
Although the expression for the average error probability in (36) enables numerical evaluation of the system performance and may not be computationally intensive, it does not offer insight into the effect of the system parameters. We now aim at expressing in a simpler form to ease the analysis of the optimization problems. At high SNR, all relays will be on and the error probability can be written as
The initial value theorem [33] states that . Therefore, can be written as
where ψ(1) denotes the digamma function.
Using the theorem in [34], the PDF of λ is written as
Finally, the asymptotic error probability is written as
Numerical analysis and discussion
Simulation and analytical results along with asymptotic results for SSK system with two transmit antennas, different number of relays, and single receive antenna are shown in Figure 2 using AF conventional relays and in Figure 3 using DF relays. Results are plotted as a function of E t /N0, where E t =E s + E r . Numerical and analytical results demonstrate an identical match for a wide range of SNR values. While, asymptotic results show close performance for pragmatic SNR values. The achieved diversity gain increases with increasing the number of relays and this is obvious in the figure. The performances of both systems are nearly the same. However, the spectral efficiency of the conventional AF relays is less than that of DF relays since all relays participate in the retransmission process. While, system complexity of DF relays is higher than that of AF relays since the relays decode the received signal, use error detection techniques, and then cooperate in the retransmission process.
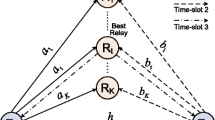
Simulation results for three systems with four and eight transmit antennas and different number of relays are shown in Figure 4 and compared to analytical results using the bound in (22). The bound demonstrates good matching with the simulation results for E t /N0values greater than 10 dB. However, for DF system, the analysis with an arbitrary number of transmit antennas is not straightforward. In fact, the selection of the optimum relay when the source is equipped with more than two transmit antennas is a complicated process. The selection criteria should be designed such that the selected relays maximizes the euclidian distances between the channel paths form all transmit antennas to the selected relay. This is different than conventional systems where the relay that maximizes the SNR is the best relay. The analysis of SSK with more than two transmit antennas and DF relaying is left for future investigations. Nevertheless, simulation results for N t =4 SSK system with 2 and 4 DF relays are shown in Figure 5. In the simulation, only the relays that correctly detect the active transmit antenna participate in the retransmission process. It is shown that the performance with four transmit antennas degrades the performance by about 1 dB as compared to two transmit antennas. However, it is significant to mention that the spectral efficiency with four transmit antennas is double the spectral efficiency with two transmit antennas.
Conclusion
We have introduced an accurate analysis of the performance of SSK modulation over Rayleigh fading channels with arbitrary number of relays. Conventional AF relays as well as DF relays are considered in the study. A simple asymptotic expression for the error probability has been derived as well. Numerical results have validated the accuracy of the proposed analytical derivations. Also, it is shown that the complexity and the spectral efficiency of the two proposed schemes can be traded off while maintaining almost identical performance. Optimizing the transmitted power and the relays positions as well as comparing to other cooperative MIMO techniques will be considered in future works.
References
Renk T, Kloeck C, Burgkhardt C, Jondral FK: Cooperative communications in wireless networks—a requested relaying protocol. In 16th IST Mobile and Wireless Communications Summit. Budapest, Hungary; 1.
Wang C-X, Hong X, Ge X, Cheng X, Zhang G, Thompson J: Cooperative MIMO channel models: a survey. IEEE Commun. Mag 2010, 48(2):80-87.
Genc V, Murphy S, Yu Y, Murphy J: IEEE 802.16J relay-based wireless access networks: an overview. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2008, 15(5):56-63.
Nokia: E-UTRA Link adaption: consideration on MIMO. 3GPP LTE Std. R1-051 415, 2005
IST-4-027756 WINNER II D3 4 1: The WINNER II Air Interface: Refined Spatial Temporal Processing Solutions. Retrieved 08 March 2010 [https://www.ist-winner.org/WINNER2-Deliverables/]
Ng CTK, Huang H: Linear precoding in cooperative MIMO cellular networks with limited coordination clusters. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun. 2010, 28(9):1146-1454.
He X, Luo T, Yue T: Optimized distributed MIMO for cooperative relay networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2010, 14(1):9-11.
Jeganathan J, Ghrayeb A, Szczecinski L, Ceron A: Space shift keying modulation for MIMO channels. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2009, 8(7):3692-3703.
Chau YA, Yu S-H: Space modulation on wireless fading channels. In Proc. IEEE VTC 2001 Fall Vehicular Technology Conference, vol. 3. (Atlantic City, New Jersey, USA; 7–11 October 2001), pp. 1668–1671
Mesleh R, Haas H, Sinanović S, Ahn CW, Yun S: Spatial modulation. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol 2008, 57(4):2228-2241.
Jeganathan J, Ghrayeb A, Szczecinski L: Spatial modulation: optimal detection and performance analysis. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2008, 12(8):545-547.
Tarokh V, Jafarkhani H, Calderbank AR: Space-time block coding for wireless communications: performance results. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 1999, 17(3):451-460. 10.1109/49.753730
Wolniansky P, Foschini G, Golden G, Valenzuela R: V-BLAST: an architecture for realizing very high data rates over the rich-scattering wireless channel. In Unino Radio-Scientifique Internationale (URSI) International Symposium on Signals, Systems, and Electronics (ISSSE). (Pisa, Italy; September 29–October 2, 1998), pp. 295–300
Yang Y, Aissa S: Information-guided transmission in decode-and-forward relaying systems: spatial exploitation and throughput enhancement. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2011, 10(7):2341-2351.
Sugiura S, Chen S, Haas H, grant PM, Hanzo L: Coherent versus non-ciherent decode-and-forward relaying aided cooperative space-time shift keying. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2011, 59(6):1707-1719.
Di Renzo M, Haas H, Grant PM: Spatial modulation for multiple-antenna wireless systems: a survey. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2011, 49(12):182-191.
Yang L-L: Signal detection in antenna-hopping space-division multiple-access systems with space-shift keying modulation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2012, 60(1):351-366.
Di Renzo M, Haas H: A general framework for performance analysis of space shift keying (SSK) modulation for MISO correlated Nakagami-m fading channels. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2010, 58(9):2590-2603.
Serafimovski N, Sinanovic S, Di Renzo M, Haas H: Dual-hop spatial modulation (Dh-SM). In IEEE 73rd Vehicular Technology Conference: VTC2011-Spring. (Budapest, Hungary; May 2011).
Mesleh R, Ikki S, Alwakeel M: Performance analysis of space shift keying with amplify and forward relaying. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2011, 15(99):1-3.
Yang D, Xu C, Yang LL, Hanzo L: Transmit-diversity-assisted space-shift keying for colocated and distributed/cooperative MIMO elements. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2011, 60(6):2864-2869.
Yang Y, Bonello N, Aissa S: An information-guided channel-hopping scheme for block-fading channels with estimation errors. In Proc. IEEE Global Telecommunications Conf. (GLOBECOM 2010). (Miami, USA, July 2010); pp. 1–5
Proakis JG: Digital Communications. (McGraw-Hill New York, 1995);
Beaulieu NC, Hu J: A closed-form expression for the outage probability of decode-and-forward relaying in dissimilar Rayleigh fading channels. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2006, 10(12):813-815.
Ikki SS, Ahmed MH: Performance analysis of adaptive decode-and-forward cooperative diversity networks with best-relay selection. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2010, 58(1):68-72.
Lee I-H, Kim D: BER analysis for decode-and-forward relaying in dissimilar Rayleigh fading channels. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2007, 11(1):52-54.
Chen H, Liu J, Zheng L, Zhai C, Zhou Y: An improved selection cooperation scheme for decode-and-forward relaying. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2010, 14(12):1143-1145.
Wang Z, Giannakis GB: A simple general parameterization quantifying performance in fading channels. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2003, 51(8):1389-1398. 10.1109/TCOMM.2003.815053
Ribeiro A, Cai X, Giannakis GB: Symbol error probabilities for general cooperative links. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2005, 4(3):1264-1273.
Hasna MO, Alouini M-S: A performance study of dual-hop transmissions with fixed gain relays. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2004, 3(6):1963-1968. 10.1109/TWC.2004.837470
Hasna MO, Alouini M-S: End-to-end performance of transmission systems with relays over Rayleigh-fading channels. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2003, 2(6):1126-1131. 10.1109/TWC.2003.819030
Simon MK, Alouini M-S: Digital Communication Over Fading Channels: A Unified Approach to Performance Analysis. (John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York); 2000.
Papoulis A: Probability, Random Variables, and Stochastic Processes,. McGraw-Hill, New York; 1991.
Ikki SS, Aissa S: Performance analysis of amplify-and-forward relaying over weibull-fading channels with multiple antennas. IET Commun. 2012, 6: 165-171. 10.1049/iet-com.2011.0264
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support for this study from SNCS Research center at University of Tabuk under the grant from the Ministry of Higher Education in Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Mesleh, R., Ikki, S.S., Aggoune, EH.M. et al. Performance analysis of space shift keying (SSK) modulation with multiple cooperative relays. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2012, 201 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1186/1687-6180-2012-201
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1687-6180-2012-201