Abstract
Background
The purpose of this study was to identify early features of lamin A/C gene mutation related dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) with cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR). We characterise myocardial and functional findings in carriers of lamin A/C mutation to facilitate the recognition of these patients using this method. We also investigated the connection between myocardial fibrosis and conduction abnormalities.
Methods
Seventeen lamin A/C mutation carriers underwent CMR. Late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) and cine images were performed to evaluate myocardial fibrosis, regional wall motion, longitudinal myocardial function, global function and volumetry of both ventricles. The location, pattern and extent of enhancement in the left ventricle (LV) myocardium were visually estimated.
Results
Patients had LV myocardial fibrosis in 88% of cases. Segmental wall motion abnormalities correlated strongly with the degree of enhancement. Myocardial enhancement was associated with conduction abnormalities. Sixty-nine percent of our asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic patients showed mild ventricular dilatation, systolic failure or both in global ventricular analysis. Decreased longitudinal systolic LV function was observed in 53% of patients.
Conclusions
Cardiac conduction abnormalities, mildly dilated LV and depressed systolic dysfunction are common in DCM caused by a lamin A/C gene mutation. However, other cardiac diseases may produce similar symptoms. CMR is an accurate tool to determine the typical cardiac involvement in lamin A/C cardiomyopathy and may help to initiate early treatment in this malignant familiar form of DCM.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Background
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a major cause of heart failure and sudden cardiac death. About one third of DCM cases are familial. During the past few decades, several DCM disease genes have been identified, many of them limited to individuals or families [1–3]. The lamin A/C gene (LMNA) is so far the most significant disease gene for DCM. It has been estimated that LMNA mutations cause up to 10% of familial DCM. The penetrance of the LMNA mutations causing cardiomyopathy is nearly complete [4]. The gene resides on chromosome 1q21.2-q21.3. By alternative splicing, it codes for lamins A and C, proteins found in the nuclear lamina. LMNA mutations may also cause a variety of other clinical entities such as neuromuscular syndromes, lipodystrophy or premature aging disease, i.e. progeria. We have previously described several LMNA mutations among Finnish DCM patients [2, 3].
Carriers of LMNA mutations causing cardiomyopathy should be recognised at an early stage so that regular cardiologic follow-up can be arranged; affected individuals have a high risk of sudden cardiac death or severe heart failure by middle age [5]. However, most of the patients are asymptomatic or only have mild symptoms for many years, and diagnosis is therefore difficult. Moreover, the serious nature of LMNA-related cardiomyopathy is easily overlooked at the early stage because the left ventricular (LV) dilatation is typically mild at the beginning, and it may remain so even later on although the LV ejection fraction may be very low. In other words, LMNA mutations may cause DCM, or cardiomyopathy with decreased systolic function, combined with LV dilatation that is too mild to fulfil the criteria of DCM. The earliest cardiac finding in cardiomyopathy caused by a LMNA mutation is usually conduction system disease, associated with atrial or ventricular arrhythmias, atrioventricular (AV) conduction abnormalities and myocardial dysfunction [6].
Echocardiography is regarded as the standard method to clinically study DCM; however, cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) plays an important role in the characterisation and risk stratification of patients with DCM. Late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) CMR with standard cine-imaging is an accurate and reproducible method both to demonstrate myocardial fibrosis and to measure wall thickness as well as global and regional function of both ventricles [7, 8].
The main purpose of this study was to characterise myocardial fibrosis, regional wall motion abnormalities, ventricular dilatation, longitudinal LV systolic function and global function with LGE CMR in asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic carriers of LMNA mutations causing DCM. In addition, we investigated the possible association between the localisation of myocardial fibrosis and the conduction abnormalities documented with electrocardiography (ECG).
Methods
Study patients
LMNA mutation carriers
The LMNA mutations had originally been identified in DCM patients who participated in an earlier molecular genetic study of DCM carried out in collaboration between the Helsinki University Hospital and the University of Kuopio [2, 3]. The subjects in the current study, recruited from the families of these DCM patients, were carriers of an LMNA mutation. The study group comprised seventeen subjects (eight men and nine women, mean age 36 ± 12, 39 ± 18 years, body surface area (BSA) 1.8 ± 0.2 m2) recruited for this study between 2004 and 2008. Each subject was a heterozygote for one mutation. A summary of the mutations, symptoms and ECG findings are presented in Table 1. The clinical evaluation of the subjects comprised hospital records, clinical examination, venous blood samples, 12-lead ECG, echocardiography and CMR. CMR was performed during the first visit.
All participants gave written informed consent. The project was approved by the local institutional ethics committee.
CMR
CMR was performed with a 1.5 T MR imager (Avanto; Siemens, Erlangen, Germany) using a multi-channel body-array coil as a receiver. Breath-hold cine CMR was performed using retrospectively electrocardiographically gated segmented true fast imaging with steady-state free precession (SSFP). Cine MR images were obtained in vertical and horizontal long-axis, and a stack of images in short-axis plane covering both ventricles was acquired. The imaging parameters were TR/TE 3.0/1.6 msec, flip angle 52 degrees, 256 × 256 matrix, 240 × 340 mm field of view. Slice thickness was 6 mm and interslice gap 20%. The temporal resolution was 42-49 msec.
Five to fifteen minutes after the injection of a contrast agent (gadoterate meglumine, Dotarem® 0.1 mmol/kg) LGE images were acquired in the same views as for cine images, using inversion recovery turbo fast-low angle shot (FLASH). The imaging parameters were TR/TE 2.58/2.3 msec, flip angle 50 degrees, 256 × 256 matrix, 240 × 340 mm field of view. Slice thickness was 8 mm and interslice gap 0%. Inversion time was optimised for each measurement to null the signal intensity of normal myocardium (240-360 msec).
Image analysis
The images were analysed in consensus by two experienced (> 10 years experience) cardiac radiologists (SK, MH). In each patient, the three LV short axis sections were divided into 17 segments according to American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines [9]. The planimetry of enhancing area was calculated within each segment. The segmental extent of enhancement on LGE images was graded using the following score: 0 = no enhancement, 1 = 1-25% enhancement, 2 = 26-50% enhancement, 3 = 51-75% enhancement, 4 = 76-100% enhancement. Right ventricle (RV) enhancement was also determined from the LGE images.
On the cine images, segmental wall motion was visually assessed and scored as 1 = normal, 2 = hypokinesia, 3 = akinesia and 4 = dyskinesia.
Measurement of volumes and ejection fraction of both ventricles were segmented semi-automatically by tracking the endocardial borders of both ventricles with a segmentation tool developed for this purpose [10].
To assess longitudinal LV systolic function, mitral annular displacement (MAD) was measured as the difference (between end-diastole and end-systole) of the distance from apex to the lateral and septal sites of the mitral annulus in the horizontal long-axis view, and apex to the anterior and inferior sites in the vertical long-axis view. The mean value of MAD at all four sites was then calculated.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using NCSS version 2007 software. Chi-Square test and Fisher's Exact test were used to calculate for correlation between the percentage of LGE and wall motion abnormalities. Volumetric results of both ventricles were compared to normal values published earlier by Maceira et al [11, 12] whose cine sequence technique (SSFP), protocol as well as volumetric analysis were comparable to those used in our study. Relationships between MAD and EF as well as MAD and percentage of LGE were assessed using Spearman Correlations test. Correlation between conduction defects and myocardial fibrosis was calculated using t-test.
Results
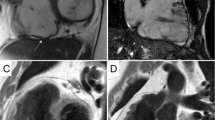
Out of 17 patients, 15 exhibited LGE. Among the total of 289 segments, LGE was observed in 47 (16%). The extent of LGE was less than 50% in 36/47 enhanced segments (Figure 1). In all patients, LGE occurred in the basal or mid-ventricular septal wall (Figure 2, 3). RV free wall enhancement was not observed. Thirty three of the 47 enhanced segments were in the septal area (segments 2-3, 8-9, 14). The typical pattern of LGE was linear and mid-myocardial (Figure 4). Diffuse enhancement of LV myocardium was observed in two advanced cases of the disease. LV wall thickness was normal in all patients. Abnormal motion was found in 27 segments (9%). The motion abnormalities were predominantly located in the basal regions of LV (segments 1-4). There was hypokinesia in 17 segments and akinesia in 10 segments. The correlation between the extent of enhancement and abnormal motion was significant (p < 0.001). Abnormal motion was found in 50% of segments enhancing 26-50% and in all segments if the enhancement was over 50% (Table 2).
The extent of enhancement (%) in abnormal myocardial segments. The percentage of late gadolinium enhancement in involved myocardial segments (n = 47). The extent of enhancement was under 25% in sixteen (6%) segments. Twenty (2%) of the segments showed enhancement of 26-50%. Eleven segments (4%) enhanced over 50% of the area.
Correlation between enhanced myocardial segments and wall motion abnormalities. Distribution of enhanced segments (a) and wall motion abnormalities (b) of the left ventricle are shown in bull's eye plots. Our data demonstrates predominant involvement of fibrosis and wall motion disturbances in the basal and anteroseptal segments.
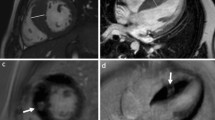
Myocardial late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) in the septal region evaluated with cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR). LGE CMR of a 32-year old male with lamin A/C mutation DCM. Four-chamber (a) and short axis (b) views of the heart show typical mid-myocardial and linear enhancement of the basal septum (arrows).
All patients with conduction abnormalities (11 with an AV conduction defect and two with a widened QRS complex) and two with atrial fibrillation showed enhancement of the basal and mid-ventricular septum. Conduction abnormalities correlated significantly with presence of LGE in the LV septum (p = 0.01). Four patients had a normal ECG recording, and two of them had enhancement of the basal septum. Table 3 summarises the ECG abnormalities in relation to the enhanced segments and regional wall motion abnormalities.
A volumetric analysis of one female subject was excluded because of poor cine image quality due to arrhythmia. When compared with the age, sex and BSA standardised normal values published earlier by Maceira et al [8, 9], ventricular volumes and systolic function were preserved in five patients. Minor systolic dysfunction without ventricular dilatation was observed in three patients (LV dysfunction in one patient and dysfunction of both ventricles in two patients). Mild LV dilatation without systolic dysfunction was observed in four patients, two of whom also had a slightly dilated RV. A dilated LV and systolic dysfunction was observed in four patients, three of whom also had RV dysfunction, and one female subject had RV dilatation without dysfunction. Table 4 summarises the global ventricular functions and ejection fractions for each of the 16 patients.
Longitudinal LV systolic function was decreased in nine patients when compared to normal values published by Nikitin et al [13]. Decreased MAD was observed in eight patients with decreased EF, three patients (18%) with normal EF showed longitudinal LV systolic dysfunction (Table 3).
MAD was significantly lowered when EF was decreased (p < 0.03) (Figure 5). MAD correlated significantly with percentage of myocardial LGE (p < 0.01) (Figure 6).
Relationship between mitral annular displacement (MAD) and Left ventricular ejection fraction (EF). Longitudinal LV systolic function measured using MAD showed correlation with decreased EF. Nine patients had decreased MAD (normal value 1.5-1.6 cm). Three lamin A/C DCM patients with normal EF had decreased MAD as an early marker of systolic dysfunction.
Relationship between mitral annular displacement (MAD) and late gadolinium enhancement (LGE). Longitudinal LV systolic function measured using MAD showed a significant correlation with a percentage of LGE (fibrosis) in the left ventricle myocardium. LGE scoring was calculated by summarizing enhanced LV segments of each patient. LV = left ventricle.
Discussion
The present study demonstrates that 88% of asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic carriers of LMNA mutations causing cardiomyopathy had typical myocardial fibrosis, predominantly in the mid-myocardium of the basal septum. This was observed in all individuals with an AV conduction defect. The pattern of enhancement was typically linear and less than 50% of the area of the segment. Enhancement was associated with wall motion abnormalities at LV basal segments, where the degree of enhancement had a significant correlation with decreased motion. Minor systolic dysfunction without ventricular dilatation, preserved systolic function with mild LV dilatation or systolic dysfunction with mild dilatation of LV, or of both ventricles, was observed in 69% of LMNA mutation carriers. In our patients as an early marker of the disease longitudinal LV systolic function was decreased in nine patients when compared to normal values [13]. In addition, we found that LV EF as well as percentage of myocardial fibrosis correlated significantly with abnormal MAD.
Early studies show that even a very small amount of myocardial scar tissue is visible with routine LGE CMR sequences [14]. Myocardial diseases have typical enhancement patterns on the basis of their characteristic pathology [15]. In previous studies, about one third of DCM patients have demonstrated mid-myocardial linear enhancement on LGE CMR in a non-coronary distribution, predominantly in the LV basal and mid-ventricular septum [8, 16–19]. However, Ebeling Barbier et al have documented that 30% of elderly volunteers without or with minimal coronary artery disease showed myocardial LGE, but mostly inferolateral region of the LV. On the other hand, Breuckmann et al found that 12% of marathon runners had LGE. Subendocardial and transmural LGE pattern was found in five marathon runners, but also non-CAD pattern was documented in seven subjects [20]. A healthy control group of DCM patients in study by Zimmerman et al [18] showed no myocardial LGE. As LGE imaging is widely used as a gold standard in cardiac research, we did not collect any new data of healthy subjects [21]. In our study, 88% of LMNA mutation carriers had typical myocardial fibrosis, predominantly mid-myocardially in the basal septum. High degree of LGE in our patients may reflect the effect of these mutations alone and not the effects of Lamin A/C mutations in general.
Assomull et al reported that mid-wall myocardial fibrosis in DCM patients predicted both ventricular tachycardia and sudden cardiac death [17]. Cardiomyopathy caused by a LMNA mutation has a malignant course and affected individuals are at high risk of sudden cardiac death [6]. The earliest cardiac finding is usually conduction system disease [22]. Raman et al demonstrated mid-myocardial fibrosis and abnormal LV diastolic function with LGE CMR in patients with DCM caused by a LMNA mutation [23]. This is in line with our findings, the majority of our patients having myocardial scarring and regional motion abnormalities in corresponding areas.
Previous autopsy studies have shown the location of fibrosis near the region of the conduction system and this has been postulated to be the cause of the AV blocks in LMNA-related cardiomyopathies [24, 25]. In consensus, cardiac conduction defects such as a prolonged PR interval, a widened QRS complex and atrial fibrillation correlated with the presence of septal wall fibrosis and motion abnormalities in our study.
Zimmermann et al concluded that enhancement is a typical feature on CMR carried out in DCM patients but it did not correlate with myocardial biopsy findings [18]. Since a biopsy only yields information about the selected biopsy site the detection of fibrosis with biopsy can be unsatisfactory due to the mid-myocardial location of fibrosis. Whereas LGE imaging can be used to reliably detect the location and extent of fibrosis, and it can even be used to offer guidance in biopsy sampling [26]. Sixty-nine percent of our asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic patients also showed mild ventricular dilatation and systolic failure in global analysis. Twelve of our 17 patients were also participants in the study of Koikkalainen et al, which determined an amalgam of parameters calculated from cine images typical for LMNA mutation carriers [27]. The study also found a significant difference between the patient and control group in volumetric and function parameters even in the early and asymptomatic stage of the disease. Fifty-three percent of our patients had decreased longitudinal LV systolic function. LV myocardial contraction and relaxation are reported to impair first in longitudinal direction in patients with heart failure [28, 29].
Conclusions
In conclusion, in the early stage of DCM caused by a LMNA gene mutation, AV conduction defects are common with or without a minor depression in LV systolic function. Usually the suspicion of DCM caused by LMNA mutations is based on the presence of conduction system disturbances in an ECG and by clinical exclusion of other aetiologies. However, other inflammatory or infiltrative cardiomyopathies may resemble DCM caused by LMNA mutations. If the typical pattern and location of myocardial fibrosis, mild LV dilatation and systolic ventricular dysfunction can be accurately observed with LGE CMR in the early stage of the disease, the diagnosis can be confirmed by DNA analyses. Myocardial scarring is known to provide a substrate for ventricular dysfunction, conduction abnormalities and ventricular arrhythmias. The disease is known to have a malignant course, and the combination of ECG recordings and LGE CMR will help to recognise these patients. LGE CMR can also be used to differentiate between LMNA-related cardiomyopathy and cardiac sarcoidosis, both of which can cause AV conduction defects and arrhythmias. Although no specific medical treatment exits so far to prevent the development of LMNA-related cardiomyopathy, sudden cardiac death may be prevented by a timely placement of a pacemaker or an implantable cardioverter defibrillator.
LGE CMR is also a reproducible method to monitor the progression of the disease and therefore we have an ongoing follow-up study with DE-MRI to obtain further information about the progression of the familial form of DCM caused by a LMNA mutation.
Study limitations
We had a limited number of patients, all of them carriers of a rare familial form of DCM caused by a LMNA mutation (14 out of the 17 Lamin A/C mutations in the population are due to either a ser143pro mutation (n = 10) or an arg190trp mutation (n = 4)). Wall motion abnormalities were visually graded as well as the percentage of enhancement in LV segments. As both cine volumetry and LGE imaging are widely used as gold standards in cardiac research, we did not collect any new data of healthy subjects. Global volumetric CMR results and longitudinal systolic function were compared with previously published normal values obtained from healthy volunteers.
References
Arbustini E, Pilotto A, Repetto A, Grasso M, Negri A, Diegoli M, Campana C, Scelci L, Baldini E, Gavazzi A, Tavazzi L: Autosomal dominant dilated cardiomyopathy with atrioventricular block: a lamin A/C defect-related disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002, 39: 981-90. 10.1016/S0735-1097(02)01724-2.
Karkkainen S, Peuhkurinen K: Genetics of dilated cardiomyopathy. Ann Med. 2007, 39: 91-107. 10.1080/07853890601145821.
Karkkainen S, Helio T, Miettinen R, Tuomainen P, Peltola P, Rummukainen J, Ylitalo K, Kaartinen M, Kuusisto J, Toivonen M, Nieminen MS, Laakso M, Peuhkurinen : A novel mutation, Ser143Pro, in the lamin A/C gene is common in Finnish patients with familial dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J. 2004, 25: 885-93. 10.1016/j.ehj.2004.01.020.
Pasotti M, Klersy C, Pilotto A, Marziliano N, Rapezzi C, Serio A, Mannarino S, Gambarin F, Favalli V, Grasso M, Agozzino M, Campana C, Gavazzi A, Febo O, Marini M, Landolina M, Mortara A, Piccolo G, Viganò M, Tavazzi L, Arbustini E: Long-Term outcome and risk stratification in dilated cardiolaminopathies. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008, 52: 1250-61. 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.06.044.
Van Berlo JH, Duboc D, Pinto YM: Often seen but rarely recognized:cardiac complications of lamin A/C mutations. Eur Heart J. 2004, 25: 812-10.1016/j.ehj.2004.03.007.
Malhotra R, Mason PK: Lamin A/C deficiency as a cause of familial dilated cardiomyopathy. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2009, 24: 203-8. 10.1097/HCO.0b013e32832a11c6.
Pujadas S, Reddy GP, Weber O, Lee JJ, Higgins CB: MR imaging assessment of cardiac function. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2004, 19: 789-99. 10.1002/jmri.20079.
McCrohon JA, Moon JCC, Prasad SK, McKenna WJ, Lorenz CH, Coats AJS, Pennell DJ: Differentiation of heart failure related to dilated cardiomyopathy and coronary artery disease using gadolinium-enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance. Circulation. 2003, 108: 54-9. 10.1161/01.CIR.0000078641.19365.4C.
Cerqueira MD, Weissman NJ, Dilsizian V, Jacobs AK, kaul S, Laskey WK, Pennell DJ, Rumberger JA, Ryan T, Verani MS: Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for tomographic imaging of the heart. A tatement for healthcare professionals from the cardiac imaging committee of the council on clinical cardiology of the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2002, 105: 539-542. 10.1161/hc0402.102975.
Lötjönen J, Kivistö S, Koikkalainen J, Smutek D, Lauerma K: Statistical shape model of atria, ventricles, and epicardium from short- and long-axis MR images. Med Image Anal. 2004, 8: 371-386. 10.1016/j.media.2004.06.013.
Maceira AM, Prasad SK, Khan M, Pennell DJ: Normalized left ventricular systolic and diastolic function by steady state free precession cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson Imaging. 2006, 8: 417-426.
Maceira AM, Prasad SK, Khan M, Pennell DJ: Reference right ventricular systolic and diastolic function normalized to age, gender and body surface area from steady-state free precession cardiovascular magnetic resonance. Eur Heart J. 2006, 27: 2879-88. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehl336.
Nikitin NP, Loh PH, de Silva R, Witte KKA, Lukaschuk EI, Parker A, Farnsworth A, Alamgir FM, Clark AL, Cleland JGF: Left ventricular morphology, global and longitudinal function in normal older individuals: A cardiac magnetic resonance study. Int J Cardiol. 2006, 108: 76-83. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2005.04.009.
Wagner A, Mahrholdt H, Holly TA, Regenfus M, Parker M, Klocke FJ, Bonow RO, Kim RJ, Judd RM: Contrast-enhanced MRI and routine single proton emission computed tomography (SPECT) perfusion imaging for detection of subendocardial myocardial infarcts: an imaging study. Lancet. 2003, 361: 374-79. 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12389-6.
Mahrholdt H, Wagner A, Judd RM, Sechtem U, Raymond JK: Delayed enhancement cardiovascular magnetic resonance assessment of non-ischaemic cardiomyopathies. Eur Heart J. 2005, 26: 1461-74. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehi258.
Hunold P, Vogt FM, Eggebrecht H, Schmermud A, Bruder O, Schuler WO, Barkhausen J: Myocardial late enhancement in contrast-enhanced cardiac MRI: Distinction between infarction scar and non-infarction-related disease. Am J Roentgenol. 2005, 184: 1420-26.
Assomul RG, Prasad AK, Lyne J, Smith G, Burman ED, Khan M, Sheppard MN, Poole-Wilson PA, Pennell DJ: Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, fibrosis, and prognosis in dilated cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006, 48: 1977-85. 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.07.049.
Zimmermann O, Grebe O, Mercle N, Nusser T, Kochs M, Bienek-Ziolkowski M, Hombach V, Torzewski J: Myocardial biopsy findings and gadolinium enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance in dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur J Heart Fail. 2006, 8: 162-66. 10.1016/j.ejheart.2005.06.001.
Nanjo S, Yoshikawa K, Harada M, Inoue Y, Namiki A, Nakano H, Yamazaki J: Correlation between left ventricular diastolic function and ejection fraction in dilated cardiomyopathy using magnetic resonance imaging with late gadolinium enhancement. Circ J. 2009, 73: 1939-44. 10.1253/circj.CJ-08-0965.
Ebeling Barbier C, Bjerner T, Hansen T, Andersson J, Lind L, Hulthe J, Johansson L, Ahlström H: Clinically unrecognized myocardial infarction detected at MR imaging may not be associated with atherosclerosis. Radiology. 2007, 245: 103-10. 10.1148/radiol.2451061664.
Breuckmann F, Möhlenkamp S, nassenstein K, Lehmann N, Ladd S, Schmermund A, Sievers B, Schlosser T, Jöckel KH, Heusch G, Erbel R, Barkhausen J: Myokardial late gadolinium enhancement: Prevalence, pattern and prognostiv relevance in marathon runners. Radiology. 2009, 251: 50-57. 10.1148/radiol.2511081118.
Becane HM, Bonne G, Varnous S, Muchir A, Ortega V, Hammouda EH, Urtizberea JA, Lavergne T, Fardeau M, Eymard B, Weber S, Schwartz K, Duboc D: High incidence of sudden death with conduction system and myocardial disease due to lamins A and C gene mutation. Pacing Clin Electrofysiol. 2000, 23: 1661-66. 10.1046/j.1460-9592.2000.01661.x.
Raman SV, Sparks EA, Baker PM, McCarthy B, Wooley CF: Mid-myocardial fibrosis by cardiac magnetic resonance in patients with lamin A/C cardiomyopathy: Possible substrate for diastolic function. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2007, 9: 907-13. 10.1080/10976640701693733.
Graber H, Unverferth D, Baker P, Ryan J, Baba N, Wooley C: Evolution of a hereditary cardiac conduction and muscle disorder: a study involving a family with six generations affected. Circulation. 1986, 74: 21-35. 10.1161/01.CIR.74.1.21.
Sueyoshi E, Sakamoto I, Uetani M: Myocardial delayed contrast-enhanced MRI: relationships between various enhancing patterns and myocardial diseases. Brit J Radiol. 2009, 82: 691-97. 10.1259/bjr/23291589.
Jerosch-Herold M, Sheridan DC, Kushner JD, Nauman D, Burgess D, Dutton D, Alharethi R, Li D, Hershberger RE: Replacement and reactive myocardial fibrosis in idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy: comparison of magnetic resonance imaging with right ventricular biopsy. Eur J Heart Fail. 2010, 12: 227-231. 10.1093/eurjhf/hfq004.
Koikkalainen JR, Antila M, Lötjönen JMP, Heliö T, Lauerma K, Kivistö SM, Sipola P, Kaartinen MA, Kärkkäinen STJ, Reissell E, Kuusisto J, Laakso M, Oresic M, Nieminen MS, Peuhkurinen KJ: Early familiar dilated cardiomyopathy: Identification with determination of disease state parameters from cine MR image data. Radiology. 2008, 249: 88-96. 10.1148/radiol.2491071584.
Mizuguchi Y, Oishi Y, Miyoshi H, Iuchi A, Nagase N, Oki T: The functional role of longitudinal, circumferential, and radial myocardial deformation for regulating the early impairment of left ventricular contraction and relaxation in patients with cardiovascular risk factors: A study with two-dimensional strain imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2008, 21: 1138-44. 10.1016/j.echo.2008.07.016.
Carlsson M, Ugander M, Mosen H, Buhre T, Arheden H: Atrioventricular plane displacement is the major contributor to left ventricular pumping in healthy adults, athletes, and patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007, 292: 452-59.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank technicians Aki Syrjälä, Timo Päivärinta and Ilkka Jussila for their expertise in acquiring MRI images, Timo Pessi for his help in statistical analysis and Sini Weckström for excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
MH, SK, KL have carried out cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging studies, performed image analysis and participated drafting the manuscript. MA have been involved in cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging and analyzing images. TH have participated in the study design and coordination, performed clinical examinations and echocardiography's of the patients and have been involved in drafting the manuscript. RJ, MK, ER, JK, SK and KP have participated in the design of the study, performed clinical examinations and echocardiography's of the patients and the control group. They have been involved in revising the manuscript. JK and JT have participated in analyzing magnetic resonance images. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Holmström, M., Kivistö, S., Heliö, T. et al. Late gadolinium enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance of lamin A/C gene mutation related dilated cardiomyopathy. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 13, 30 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1186/1532-429X-13-30
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1532-429X-13-30