Abstract
Background
Greater time spent screen-viewing (SV) has been linked to adverse health outcomes. The aim of this study was to examine whether parental SV time is associated with child SV time on week and weekend days.
Methods
Cross-sectional survey of 1078 children aged 5–6 and at least 1 parent. Child and parent SV was reported for weekday and weekend days. Logistic regression examined whether parental SV time was associated with child SV time, with separate analyses for mothers and fathers and interaction terms for child gender.
Results
12% of boys, 8% of girls and 30% of mothers and fathers watched ≥2 hours of TV each weekday. On a weekend day, 45% of boys, 43% of girls, 53% of mothers and 57% of fathers spent ≥2 hours watching TV. Where parents exceeded 2 hours TV-watching per weekday, children were 3.4 times more likely to spend ≥ 2 hours TV-watching if their father exceeded the threshold with odds of 3.7 for mothers. At weekends, daughters of fathers who exceeded 2 hours watching TV were over twice as likely as sons to exceed this level. Evidence that parent time spent using computers was associated with child computer use was also strongest between fathers and daughters (vs. sons) (OR 3.5 vs. 1.0, p interaction = 0.027).
Conclusions
Strong associations were observed between parent and child SV and patterns were different for weekdays versus weekend days. Results show that time spent SV for both parents is strongly associated with child SV, highlighting the need for interventions targeting both parents and children.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Greater time spent screen-viewing (watching television (TV), using computers, tablets and smartphones, and playing video games) has been associated with an increased risk for cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes and all-cause mortality among adults [1]. Among older children and adolescents greater time spent screen-viewing (SV) has been associated with increased risk of obesity, [2] psychological difficulties [3] and metabolic risk [4]. There is little information about levels of SV and associations with disease risk factors among younger children. Since there is evidence that SV behaviours track from childhood to adulthood [5], limiting SV behaviours during early childhood may be important for long-term disease prevention.
Parents exert considerable influence on the SV patterns of young children [6] and interventions to change the latter will therefore necessitate engaging with parents. Understanding the association between time spent in SV of parents and their children is important for designing interventions [6–12]. Previous studies have reported strong associations between the TV viewing behaviours of children and their parents, with some evidence of different associations for weekdays and weekend days [13]. In a sample of 210 children aged three- five and their parents, children with a parent who watched at least two hours of TV per day were over five times more likely to do the same [7]. However, with the exception of the study outlined above, a key feature of the current literature is the focus on older children and maternal TV viewing [7, 13, 14]. More information is needed about the associations between parent and child SV and whether associations differ by parent and/or child gender or day of the week, and also whether associations differ by SV devices other than television. This study addressed these limitations with a specific aim of examining whether parental SV time is associated with child SV time on week and weekend days.
Methods
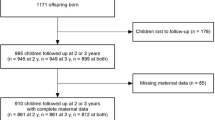
The current analyses used data from a cross-sectional study (B-ProAct1v) conducted at the University of Bristol which aimed to identify key factors associated with physical activity (PA) and SV among children in their second year of schooling (known as Year 1 in the UK - children aged five to six). Between January 2012 and July 2013, 250 primary schools within a 45 minute drive of the University were invited to participate in the study. Over half (138 - 55%) failed to respond, and a further 47 (19%) declined. Of the 65 schools which consented to participate, two withdrew (one due to issues with low English literacy of parents and one following a change in school management) before any children had been recruited. All children in Y1 (or Reception and Y1, or Y1 and Y2 in schools with combined classes) in the remaining 63 schools were eligible to take part. Written parental consent was obtained for both the parents’ and child’s participation, and data collection took place shortly after each individual school had been recruited. The study was approved by the School for Policy Studies Ethics committee at the University of Bristol. Overall, 1456 from a potential 2600 pupils (56%) were given consent for inclusion in the study. Results here are based on data for the 1078 families that provided SV data for at least one parent and the target child. Consistent with the STROBE guidelines, Figure 1 provides a detailed presentation of the participants [15].
Parents were asked to provide information about their SV time (TV, computer, games console and smartphone) on weekdays and weekend days. The parent designated as the ‘first’ parent (i.e. the parent who completed the main questionnaire) was also asked to provide the same information, with the exception of smartphone use, on behalf of their child. Separate questions were asked for the following SV items: TV, computer/laptop, games console, tablet and smartphone (except for time spent texting or talking, and assessed for parents only). For each item the parent was asked to report the time s/he spent and their child spent using it for (a) a normal weekday and (b) a normal weekend day, with response options: none; 1 minute- 30 minutes; 31 minutes-1 hour; 1–2 hours; 2–3 hours; 3–4 hours; 4 hours or more. If the second parent was participating, they self-reported SV time separately using the same items. The assessment of TV viewing using parental response to a single question has been shown to correlate moderately (r = 0.60) with 10 days’ of TV diaries among young children [16].
TV viewing behaviour in adults and children was dichotomized based on whether the participant met the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) guidance of under two hours of TV per day [17]. Information for weekend days was treated similarly. Parental computer use on weekdays and weekend days was divided into two categories (less than 31 minutes per day, 31 minutes or more per day). Children’s use of computers was dichotomized into ‘no use’ and ‘some use’. Games console use amongst children was similarly categorized, as was parental use of smartphones. Insufficient numbers of adults reported using games consoles to warrant creating categories for use in subsequent analyses.
Parents’ body mass index (BMI = kg/m2) was calculated using self-reported height and weight. Child height was measured to the nearest 0.1 cm using a SECA Leicester stadiometer (HAB International, Northampton). Weight was recorded to the nearest 0.1 kg using a SECA 899 digital scale (HAB International, Northampton). BMI was calculated and converted to a UK age and gender specific standard deviation score (BMI z-score) using the Stata ‘zanthro’ command [18, 19]. Weight categories of children were also derived using the same command. Participant postcodes were used to calculate index of multiple deprivation (IMD) scores where a higher score indicates a greater level of deprivation.
Statistical analysis
For the purpose of analysis a male adult was assumed to be a father and a female adult a mother. To be included in the analysis, participants had to provide information about their own and their child’s SV, as well as full information for the variables used in the fully adjusted analysis model. Student t-tests were used to investigate any differences in the characteristics of participants who were included in the analyses and those excluded due to incomplete questionnaire data.
Logistic regression models were used to investigate whether parental SV time for each screen type on weekdays and weekend days (the two analysed separately) were associated with child time spent on the same screen and also associations of total SV time between parents and children. As a very small proportion of parents used games consoles (95 fathers and 41 mothers; 11% overall) their use was not explored further. Each model was adjusted for child’s gender and BMI-z score, age and BMI of parent and household IMD. In addition, the model was adjusted for whichever parent (mother or father) had reported the child’s SV time in all analyses, as it is reasonable to assume that a parent who tends to underestimate their own SV time is likely to underestimate their child’s by a similar amount. Initial analyses used all participants, followed by subgroup analysis by child gender. We subjectively compared the magnitude of associations between child gender subgroups by examining the point estimates and we also tested statistically for evidence of heterogeneity (difference in magnitude of association between the subgroups) by including the interaction term of parent SV* child gender. Confidence intervals (CI) were based on robust standard errors which took account of the clustering of participants within schools. All analyses were performed in Stata version 12.0 [20].
Results
Data from both parents was obtained for 356 (36%) of the total of 990 children included in the analysis. Children excluded because of missing data had higher IMD scores, indicating greater levels of deprivation, than those included (Table 1). Similarly those who were excluded had higher BMI-z scores than those who were included and this was driven by a difference between the two groups of girls rather than between the two groups of boys. However, once the children’s weight was categorised, both excluded girls and boys were more likely to be overweight than children who were included in the analysis. Mothers and fathers who were excluded had higher IMD scores compared with those included. Excluded fathers were younger than those included in analyses.
TV viewing was similar for mothers and fathers, with just over two-thirds reporting that they watched less than two hours per weekday (Table 2). At the weekend, however, over half (57% of fathers, 53% of mothers) watched more than two hours per day. Similarly, a higher proportion of children watched more than two hours TV on each weekend day compared with weekdays, although for all days, children were more likely to meet the guidelines than adults. Reported computer use was similar for boys and girls on weekdays and weekend days, although a higher proportion of children had higher use at weekends. Boys’ use of games consoles was greater than that of girls on all days, although use was higher for both genders at weekends than on weekdays. Parental smartphone use was similar during the week and at weekends, but was consistently higher amongst fathers than in mothers.
There was strong statistical evidence that when fathers exceeded two hours of TV per weekday their children were 3.4 (95% CI: 1.8 to 6.7) times more likely to exceed the recommended amount of two hours per day compared with children whose fathers watched less than two hours per day. Results were similar using mothers’ TV viewing time and neither was markedly altered by adjustment for parental age and BMI, child’s gender and neighbourhood deprivation score (Table 3). There was no evidence that associations between either mothers’ or fathers’ TV viewing on weekdays with their child’s time spent TV viewing on weekdays differed between sons and daughters.
The associations between parent and child TV viewing were different for weekdays and weekend days. For a weekday the children were 3.4 (95% CI: 1.8 to 6.7) times more likely to exceed the two hour threshold if their father watched TV for at least two hours per day while for a weekend day the odds were 4.8 (95% CI: 3.2 to 7.3). There were similar differences for mothers (3.7 vs. 4.7). For fathers only there was evidence that the association of time spent watching TV at weekends was more strongly associated with time spent watching TV by daughters rather than sons (OR 7.9 vs. 3.8; pinteraction = 0.049).
Evidence suggested that time spent using computers by fathers and mothers during the week was positively associated with child time spent using a computer during the week, but with fathers only at weekends (Table 4). During the week, there was no difference in associations between either parent for sons and daughters, whereas at weekends daughters of fathers who spent more than 30 minutes per day using a computer were 3.5 times as likely to engage in some computer use compared with daughters of fathers who spent less than half an hour per day using a computer. This was in contrast to the relationship between fathers and sons where there was no evidence of any association for computer use at weekends and an interaction term suggested that there was evidence that these associations were different for girls and boys (pinteraction = 0.027).
Discussion
The study results show that 12% of boys and 8% of girls aged five to six watched more than two hours of TV on a weekday while 30% of fathers and mothers exceeded this threshold. On a weekend day 45% of boys and 42% of girls spent more than two hours watching TV, with 57% of fathers and 53% of mothers exceeding this threshold. A greater proportion of parents used a computer for more than 31 minutes on a weekend day than a weekday and a greater proportion of children used a games console on the weekend than a weekday, indicating differences in both parent and child SV on weekdays versus weekend days. If either mothers or fathers spent more than two hours per day watching a TV on a weekday, children were at least 3.4 times more likely to spend more than two hours watching TV. Estimates for mothers and fathers were similar. For weekend TV viewing there was an interaction between child gender and male parent TV viewing with boys 3.8 times more likely to exceed the two hour recommendation, rising to 7.9 times for girls. There was some evidence that parental weekend computer use was associated with child computer use but only in relation to girls and fathers. Collectively, these findings provide evidence of positive associations between parent and child SV time but suggest that patterns differ for weekend and weekend days. Associations are stronger for parental use at weekends than weekdays and fathers’ weekend TV and computer use may be more strongly associated with daughters’ than sons’ use.
The data reported here extends previous literature in this area which has largely focussed on mothers, young children and TV viewing. A study in Greece reported that 32% of children aged three to five spent more than two hours per weekday watching TV with both maternal (r = 0.27) and paternal (r = 0.20) hours of weekday TV correlated with child viewing time, with similar patterns for weekend days [21]. In a sample of 750 UK families with a six to eight year old child, the child was 7.8 times more likely to watch more than two hours of TV per weekday if the parent did the same; this paper did not report separately for weekend days [14]. The findings reported here are therefore comparable to previous literature but greatly extend the evidence by highlighting how patterns may differ for weekend versus weekdays. Interestingly, recent qualitative data from six European countries indicated that parents of children aged four to six reported that their children enjoyed watching TV and that most parents were not concerned about their child’s TV viewing [22]. Efforts to change behaviour are therefore likely to require improving parental understanding of why high SV is a concern and how parents’ own SV behaviour may affect their child’s. Based on the results of this study it is not possible to determine whether strategies that focus on both children and the parents are needed to change children’s SV habits. However, intuitively it seems that integrated interventions which work with both children and parents have greater potential to change behaviour than parent only focussed interventions.
The results presented here show that SV levels are higher among children at the weekend, and children with parents who engage in high levels of SV at the weekend are more likely to engage in this behaviour. Stronger associations have also been found between fathers and their daughters, compared with sons, for weekend TV and computer use. In general, time spent in SV by both parents was positively and strongly associated with their child’s SV and the magnitudes of association with both genders combined were similar. This highlights the importance of engaging both parents in the development of any interventions to reduce child SV. Many studies have struggled to engage fathers in child-focussed research [23–25] and we are not aware of any study that has specifically attempted to engage fathers in reducing child SV.
The AAP guidance on youth SV was based on expert opinion in 2001 [17] and at that time applied only to TV viewing. Although this guidance was amended in 2011 to take account of changes in technology and viewing patterns, it does not distinguish between weekday and weekend SV [26]. Although the evidence presented might suggest that greater effects could be obtained by intervening on weekend days, there are more weekdays. Thus, a child with 5 hours SV each weekend day and 2 hours each weekday spends the same amount of time in total SV during the week as at the weekend (10 hours). If the time spent each day at the weekend was double that of weekdays (e.g. 6 vs. 3 or 5 vs. 2.5 hours), for most plausible examples the total time spent SV at weekends would be less than on weekdays. Furthermore, there is no evidence that interventions to reduce SV in parents (and consequently in children) would be more effective if they solely or largely targeted weekend SV. It should also be stressed that the evidence base for greater SV in children or adults being causally related to adverse health outcomes is weak and there is currently no evidence for risk increasing at any particular threshold [27]. This is why the UK’s four Chief Medical Officers recently issued public health guidance that children and young people should limit SV but did not recommend a specific threshold [28]. Thus, consistent strategies to reduce SV in children across the whole week are likely to be needed.
Strengths and limitations
The major strength of this study is the assessment of SV-time for both mothers and fathers, which has facilitated the examination of both maternal and paternal associations with child SV. The availability of information directly reported by fathers is a unique and important addition to the literature and addresses the current over-reliance on maternal reports of SV behaviour. Information on a key age group, for both weekdays and weekend days on a range of SV behaviours will also greatly inform the future development of targeted interventions. There are, however, limitations that should also be acknowledged. Firstly, the data is reliant on parental report of child SV. Although we are not aware of any alternative, reliable means of collecting this data, as the children are too young to self-report, a degree of error is likely in the parental reports. Of particular importance is the potential correlation of errors between the parent’s self-reported SV and their reported estimate of their child’s SV. An attempt was made to address this by adjusting for whichever parent had reported their child’s SV and it is somewhat reassuring that associations are similar for both parents. Secondly, we did not assess multi-SV in which children or parents simultaneously use multiple screen devices, which limits our ability to capture this modern pattern of viewing [10]. Finally, the cross-sectional nature of our data precludes any interpretation of the direction of association between parent and child SV. However, due to the age of the children it seems unlikely that children are influencing parent behaviour.
Conclusions
This study shows that SV patterns of children aged five to six and their parents are different for weekdays and weekend days, with higher levels of SV on an average weekend day than an average weekday for both children and their parents. Results show that time spent SV of both fathers and mothers is strongly associated with child time spent SV, highlighting the need for interventions targeting both parents and children.
References
Grontved A, Hu FB: Television viewing and risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and all-cause mortality: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2011, 305 (23): 2448-2455. 10.1001/jama.2011.812.
Jago R, Baranowski T, Baranowski JC, Thompson D, Greaves KA: BMI from 3–6 y of age is predicted by TV viewing and physical activity, not diet. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2005, 29 (6): 557-564. 10.1038/sj.ijo.0802969.
Page AS, Cooper AR, Griew P, Jago R: Children’s screen viewing is related to psychological difficulties irrespective of physical activity. Pediatrics. 2010, 126 (5): e1011-e1017. 10.1542/peds.2010-1154.
Ekelund U, Brage S, Froberg K, Harro M, Anderssen SA, Sardinha LB, Riddoch C, Andersen LB: TV viewing and physical activity are independently associated with metabolic risk in children: the European Youth Heart Study. PLoS Med. 2006, 3 (12): e488-10.1371/journal.pmed.0030488.
Biddle SJ, Pearson N, Ross GM, Braithwaite R: Tracking of sedentary behaviours of young people: a systematic review. Prev Med. 2010, 51: 345-351. 10.1016/j.ypmed.2010.07.018.
Jago R, Edwards MJ, Urbanski CR, Sebire SJ: General and specific approaches to media parenting: a systematic review of current measures, associations with screen-viewing, and measurement implications. Child Obes. 2013, 9 (Suppl): S51-S72.
Jago R, Sebire SJ, Edwards MJ, Thompson JL: Parental TV viewing, parental self-efficacy, media equipment and TV viewing among preschool children. Eur J Pediatr. 2013, 172: 1543-1555. 10.1007/s00431-013-2077-5.
Biddle SJ, Gorely T, Marshall SJ, Murdey I, Cameron N: Physical activity and sedentary behaviors in youth: issues and controversies. J R Soc Health. 2004, 124 (1): 29-33.
Gorely T, Marshall SJ, Biddle SJ, Cameron N: Patterns of sedentary behaviour and physical activity among adolescents in the United Kingdom: Project STIL. J Behav Med. 2007, 30 (6): 521-531. 10.1007/s10865-007-9126-3.
Jago R, Sebire SJ, Gorely T, Cillero IH, Biddle SJ: “I’m on it 24/7 at the moment”: a qualitative examination of multi-screen viewing behaviours among UK 10–11 year olds. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2011, 8: 85-10.1186/1479-5868-8-85.
Pearson N, Biddle SJH: Sedentary behavior and dietary intake in children, adolescents, and adults: a systematic review. Am J Prev Med. 2011, 41 (2): 178-188. 10.1016/j.amepre.2011.05.002.
Sebire SJ, Jago R, Gorely T, Hoyos Cillero I, Biddle SJ: “If there wasn’t the technology then I would probably be out everyday”: a qualitative study of children’s strategies to reduce their screen viewing. Prev Med. 2011, 53: 303-308. 10.1016/j.ypmed.2011.08.019.
Jago R, Stamatakis E, Gama A, Marques V, Noqueira H, Mourao I, Padez C: Parental and child screen-viewing time and home media environment. Am J Prev Med. 2012, 43 (2): 150-158. 10.1016/j.amepre.2012.04.012.
Jago R, Sebire SJ, Lucas PJ, Turner KM, Bentley GF, Goodred JK, Stewart-Brown S, Fox KR: Parental modelling, media equipment and screen-viewing among young children: cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2013, 3 (4): e002593.
Von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gotzsche PC, Vandenbroucke JP, Initiative S: The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet. 2007, 370 (9596): 1453-1457. 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61602-X.
Anderson DR, Field DE, Collins PA, Lorch EP, Nathan JG: Estimates of young children’s time with television: a methodological comparison of parent reports with time-lapse video home observation. Child Dev. 1985, 56 (5): 1345-1357. 10.2307/1130249.
American Academy of Pediatrics - Committee on Public Education: Children, Adolescents and Television. Pediatrics. 2001, 107 (2): 423-426.
Cole TJ, Freeman JV, Preece MA: Body mass index reference curves for the UK, 1990. Arch Dis Child. 1995, 73 (1): 25-29. 10.1136/adc.73.1.25.
Vidmar S, Carlin J, Hesketh K, Cole T: Standardizing anthropometric measures in children and adolescents with new functions for egen. Stata J. 2004, 4 (1): 50-55.
Statacorp: Stata, Version 12.0. 2011, TX: Statacorp: College Station, 120
Kourlaba G, Kondaki K, Liarigkovinos T, Manios Y: Factors associated with television viewing time in toddlers and preschoolers in Greece: the GENESIS study. J Public Health (Oxf). 2009, 31 (2): 222-230. 10.1093/pubmed/fdp011.
De Decker E, De Craemer M, De Bourdeaudhuij I, Wijndaele K, Duvinage K, Koletzo B, Grammatikaki E, Iotova V, Usheva N, Fernandez-Alvira JM, Zych K, Manios Y, Cardon G, ToyBox Study Group: Influencing factors of screen time in preschool children: an exploration of parents’ perceptions through focus groups in six European countries. Obes Rev. 2012, 13 (Suppl 1): 75-84.
Phares V, Lopez E, Fields S, Kamboukos D, Duhig AM: Are fathers involved in pediatric psychology research and treatment?. J Pediatr Psychol. 2005, 30 (8): 631-643. 10.1093/jpepsy/jsi050.
Phares V, Fields S, Kamboukos D, Lopez D: Still looking for Poppa. Am Psychol. 2005, 60 (7): 735-736.
McLean N, Griffin S, Toney K, Hardeman W: Family involvement in weight control, weight maintenance and weight-loss interventions: a systematic review of randomised trials. Int J Obes (Lond). 2003, 27 (9): 987-1005. 10.1038/sj.ijo.0802383.
American Academy of Pediatrics: Children, adolescents, obesity, and the media. Pediatrics. 2011, 128 (1): 201-208.
Ekelund U, Luan J, Sherar LB, Esliger DW, Griew P, Cooper A, International Children’s Accelerometry Database C: Moderate to vigorous physical activity and sedentary time and cardiometabolic risk factors in children and adolescents. JAMA. 2012, 307 (7): 704-712. 10.1001/jama.2012.156.
Department of Health (UK): Start Active, Stay Active: A report on physical activity from the four home countries’ Chief Medical Officers. 2011, London: Department of Health, 1-59.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by a project grant from the British Heart Foundation (ref PG/11/51/28986). The funder had no involvement in data analysis, data interpretation or writing of the paper. We would like to thank all the children, parents and schools that participated in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
RJ, SJS, JLT and DAL were involved in the design of this study and in seeking funding for it. RJ, LP and JZ were responsible for the study conduct with LP managing data collection. LW performed all analyses. RJ wrote the first draft of the paper and coordinated contributions from other co-authors. All authors made critical comments on drafts of the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Jago, R., Thompson, J.L., Sebire, S.J. et al. Cross-sectional associations between the screen-time of parents and young children: differences by parent and child gender and day of the week. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 11, 54 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5868-11-54
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5868-11-54