Abstract
Background
The aim of this double-blind randomized study is to test the efficacy of a radio electric stimulator device using an auricular reflex therapy protocol for stress-related symptoms.
Methods
The study has been carried out on 200 subjects (138 females, 62 males) that voluntarily came to our Institute declaring to "feel stressed".
The participants were randomly allocated with a computerized procedure: 150 were treated with auricular therapeutic protocol with radio electric stimulator device (REAC) and 50 were treated with an inactivated, placebo REAC. Psychological stress was evaluated trough the self-administered questionnaire Psychological Stress Measure (PSM). Assessment data were collected at 2 time points: before the treatment (T0) and immediately after the therapy cycle of 18 sessions about 4 weeks later (T1).
Results
In the group treated with REAC, the psychometric evaluation after the therapy's cycle showed a significant reduction of PSM total scores, from 107.8 ± 23,13 at T0 to 87.1 ± 16,21 at T1 (p < 0.5), while in the control group no significant variation in decreasing stress-related symptomatology has been noted (107.86 ± 25,80 at T0 and 106.32 ± 25,88 at T1 (p = NS).
Conclusions
The protocol of the auricular treatment with REAC seems to reduce the subjective perception of stress, as "psychometrically" demonstrated by the significant reduction in PSM test total score. This therapeutical procedure also provides a non invasive, not painful and very simple innovative approach to treat the widely diffused stress related disorders.
Trial Registration
This trial has been registered in the Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry (ANZCTR) with the number: ACTRN12607000529448
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Environmental stress produces important effects on the individual health. Chronic social stress is one of the most important factors [1–3] responsible for worsening stress related symptoms [4, 5] and for triggering previously undetected mood disorders [6, 7]. In recent years, the effects of social stress on psychopathologies development have been thoroughly investigated [4, 6, 8, 9]. It has been hypothesized that life stress alters the dynamic regulation of the autonomic, neuroendocrine [10] and immune systems [11].
The Central Nervous System (CNS), as the main biological target of stressful events [2, 7], has continuously to change to accommodate to rapid environmental development. This imperceptible adaptation process is detrimental to health and quality of life [12].
Allostasis represents the adaptation process of the complex physiological system to physical, psychosocial and environmental changes or social stress [13–15]. The term "allostatic load" was coined by McEwen and refers to physiological costs of chronic exposure to neural or neuroendocrine stress response [16, 17]. The allostatic state is unable to guarantee the good management of the physiological systems and consequently the health status and the individual's well-being, and this phenomena often leads to the development of psychological and psychiatric symptoms [18–32]. Among the several non-pharmacological strategies today available to reduce and/or to treat the symptomatic effects of the stress and to improve the allostatic response [33, 34], of particular interest appears the use of electrical and electromagnetic stimulation [35], also exploiting the "classical" acupuncture points [36, 37]. The REAC uses a new kind of non invasive and not painful electromagnetic stimulation that produces a weak radio frequency current (RFC) easily applied with a probe to specific somatic reflex points [38].
Aim of the Study
The purpose of this study is to verify if the use of REAC could reduce the subjective perception of stress and stress-related symptoms, evaluated by PSM at T0 and T1 [39–41]. PSM also allows the precise classification of the subject studied on a stress well-being scale, to accurately assess the effectiveness of the treatment.
Materials and methods
The study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, with the Societa di Ottimizzazione Neuro Psico Fisica e CRM Terapia institutional ethics committee approval, and all subjects provided written informed consent. A double-blind, randomized and placebo-controlled trial was performed to investigate the effectiveness of REAC auricular treatment in reducing of self perception of stress and stress-related symptoms and, consequently, the PSM total score.
Participants
The study has been carried out on 200 subjects (138 females, 62 males), that voluntarily came to our Institute suffering from a broad stress-related range of psychological symptoms such as affective-emotional reactions i.e. sadness, irritability, anger, depression, poor concentration and attention, insecurity, anxious and apprehensive condition, depression, sleep disorders, generalized muscle tension, gastro intestinal disorders, headaches. Participants were properly informed about significance and objectives of the study and then they completed, in association with the Project Director prior to enrolment, a written consent form. For all participants were properly collected and detailed: general demographic information, background characteristics, treatments history, drug history survey and medical examination.
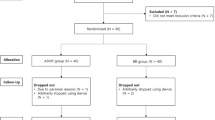
The participants, selected after a clinical screening, have been allocated randomly into 2 socially and demographically matched groups with a computerized procedure: Group A, treated with "active" REAC (N = 150, 46 males, age = 49.8 ± 13.7 yrs and 104 females, age = 48.3 ± 12.5 yrs), and Group B, treated with deactivated-placebo REAC (N = 50, 16 males, age = 52.7 ± 17.7 yrs, and 34 females, age = 50.6 ± 15.1 yrs). The 3:1 proportion between cases and controls has been selected only on the base of the main "typology" of the people who require a clinical treatment in our Institute: "stressed" subjects are more numerous than "non-stressed" subjects.
REAC protocol consists in 18 session each one lasting 3,5 seconds, administered in about 4 weeks.
All subjects were over 18 years old, declaring to suffer from stress-correlated psycho-physical conditions, as demonstrated by a clinical evaluation and the PSM total score >45. No history of drug abuse, nor severe mental illness or personality disorder according to DSM-IVTR criteria (as valuated by a psychiatrist, also trough the administration of SCL-90 scale in the "doubt" subjects) and no psychopharmacological-psychological interventions has been reported.
Exclusion criteria for both groups: diagnosis of axis I-II psychiatric disorders, organic CNS pathology, preceding skull traumas with loss of conscience longer than 5 minutes, dementia, alcohol dependence, current therapy with medications known to affect cognitive functioning.
Randomization
The study has been setted in 4 rooms. In 3 of the 4 rooms has been activate REAC and in the other 1 the placebo-REAC. The physicians that have participated in the treatment's administration turned in the different rooms, using both "active" and "inactive" REAC but they didn't know if they used an active or placebo REAC. The computerized randomization process, managed by an external operator to the study, foresaw the assignment of the subjects to each room. The target sample size 200, divided in the 4 rooms, has produced 4 subgroups, each composed by 50 people (n = 50 × 3 = 150 treated, n = 50 × 1 = 50 placebo).
Instruments and materials
Psychological Test
PSM, a standardized and validated self-reporting test for the measurement of psychological stress was administered to all subjects, before (T0) and after REAC treatment (T1) [39–41]. PSM consists of 49 items for the self-evaluation aimed at identifying different "clusters" of symptoms such as loss of control, irritability, psycho-physiological sensations, confusion, anxiety, depression, physical pain, hyperactivity and agitation. The patient must answer to the various items ranking the intensity of his psychological stress condition (very much = 4, much = 3, little = 2, none = 1). Although the clear risk of subjectivity of evaluation, this self-administered questionnaire was preferred with the aim to reduce the increasing of psychic and somatic anxiety levels and "arousal" inevitably due to a "direct" subject-physician interaction.
Description of the Radio Electric Asymmetric Conveyer REAC
The REAC is an innovative medical device [38] aimed to promote a reduction of the dysfunctional modifications in the Nervous System induced by stress and psychological factors [42]. REAC uses the radio electric effects produced by the interaction between the electromagnetic field of the human body (~30-300 GHz, of about 3 mW/m2) [43] and the field produced by the instrument (2.4 or 5.8 or 10.5 GHz, measurable from the emitter about 0.1 mW/m2) which lasts approximately a few milliseconds. This radio electric interaction is received by a probe (conveyer) placed on specific points of the auricular pinna giving a radio electric stimulation. The inactive REAC is the exact same machine, but has a modified probe. The instrument that we used is registered under the trademark Convogliatore di Radianza Modulante - CRM produced by ASMED, Italy.
Description of auricular therapy protocol
The auricular treatment protocol has been conceived by the authors and called Neuro Psycho Physical Optimization (NPPO). The REAC probe was applied to 7 specific points of the auricular pinna: "shen men", kidney, stomach, heart, occiput, ipotalamus, prefrontal cortex. Eighteen sessions of NPPO with REAC were administered on alternate days, in about four weeks, to each patient. Each therapeutic session lasted approximately 3 seconds. The protocol is painless, non-invasive, and without known side effects.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis were performed using Statistical Package for Social Science (version 13). The McNemar test is used to compare the relevant frequencies for data resulting from PSM test in patients belonging to group A and to group B before and after NPPO with REAC. Also Wilcoxon Signed Ranks Test and Sign test are used to evaluate the related samples of Total points resulting from PSM test of both groups. All results of p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
In both groups the total stress evaluation has been measured by PSM administered before (T0) and after a cycle of NPPO. In the group A, PSM total score progressively decreases from 107.8 ± 23.1 at T0 to 87.1 ± 16.2 at T1 (Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test Z = -9.854, p = 0.00; Sign Test Z = -10.132, p = 0.00). On the contrary, no significant difference has been noted in the group B: in fact, PSM total score ranged from 107.9 ± 25.8 at T0 to 106.3 ± 25.9 at T1 (Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test Z = -1.285, p = NS; Sign Test Z = 0.312, p = NS).
In the Group A, the greater improvement between T0 and T1 has been reported on PSM items loss of control, irritability, psycho-physiological sensations, confusion, anxiety, depression, physical pain, hyperactivity and agitation (table 1 and figure 1, 2).
PSM clusters pre-post NPPO-REAC real treatment, group A. The results show that a cycle of NPPO protocol with REAC reduces also the PSM symptomatic clusters related to loss of control, irritability, psycho physiological sensations, confusion, anxiety and depression, physical pain, hyperactivity and acceleration,
Discussion
The use of electricity and magnetic fields in the biomedical studies, and in particular in the treatment of disturbances of the nervous system, is not a new idea [44–47]. Nevertheless modern technology and advanced knowledge in the physical-medical field and in the neurosciences has allowed realizing the new biomedical instrument presented in this study.
In the present study we considered a group of patients treated with REAC and a group with placebo-REAC. The results suggest that a cycle of NPPO protocol with REAC reduces the total score of the PSM test (Figure 3, 4) in particular the clusters related to loss of control, irritability, psycho-physiological sensations, confusion, anxiety and depression, physical pain, hyperactivity and agitation (figure 1, 2), and this strictly correlates with a clinically significant improvement on the subjective perception of stress and stress related symptomatology. On the other hand, in the placebo-REAC, although the subjects have been submitted to the same "tactile" sensations on the ear of those with "active" REAC, no significant difference in PSM total score was highlighted between T0 and T1.
A growing number of studies suggests that the stress-related symptoms are the result of allostatic processes [12–15, 17–19, 21–23, 25–27, 29–31] and our data seems to indicate that NPPO protocol of REAC treatment is an effective instrument to ameliorate the responses to allostatic state and to environmental stressors.
Besides, this treatment has the advantage of being painless, non-invasive and free of side-effects not only in the patient groups, but also in the physicians that have applied this therapy.
The 3:1 proportion between case and controls certainly represent a bias of this study, mainly in terms of statistics. However, this has been simply due to the fact that our Institute is well-known with regard the treatment of psycho-physical stress-related dysfunctions and, paradoxically, it is been easier to enlist "stressed" than normal subjects. According to us, the physician's rotation in the different rooms and the fact that each one of them didn't known if were administering the "active" or "placebo" REAC, represent a attempt to achieve more "scientific" strictness.
Conclusions
We propose that NPPO treatment with REAC will help to improve the physiological capability of the organism's recovery, optimizing the adaptive response to environmental stressors.
Moreover, NPPO treatment with REAC is a non-pharmacological treatment and can represent an efficient support in many medical fields, because it does not interfere with the simultaneous use of other therapeutic approaches.
Obviously, though these observations on the effectiveness of NPPO - REAC treatment in the psychometric evaluation of stress related disorders are certainly important and suggestive, they are only preliminary and require further confirmation.
References
Selye H: The Significance of the Adrenals for Adaptation. Science 1937,85(2201):247–248. 10.1126/science.85.2201.247
Chrousos GP: Stress and disorders of the stress system. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2009,5(7):374–381. 10.1038/nrendo.2009.106
Sapolsky RM: Why stress is bad for your brain. Science 1996,273(5276):749–50. 10.1126/science.273.5276.749
Aubert A: Psychosocial stress, emotions and cytokine-related disorders. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov 2008,2(2):139–48. 10.2174/187221308784543647
Fink P, et al.: Symptoms and syndromes of bodily distress: an exploratory study of 978 internal medical, neurological, and primary care patients. Psychosom Med 2007,69(1):30–9. 10.1097/PSY.0b013e31802e46eb
Szubert S, Florkowski A, Bobinska K: [Impact of stress on plasticity of brain structures and development of chosen psychiatric disorders]. Pol Merkur Lekarski 2008,24(140):162–5.
McEwen BS: Physiology and neurobiology of stress and adaptation central role of the brain. Physiol Rev 2007,87(3):873–904. 10.1152/physrev.00041.2006
Ruggiero GM, et al.: The influence of stress on the relationship between cognitive variables and measures of eating disorders (in healthy female university students): a quasi-experimental study. Eat Weight Disord 2008,13(3):142–8.
Rygula R, et al.: Pharmacological validation of a chronic social stress model of depression in rats: effects of reboxetine, haloperidol and diazepam. Behav Pharmacol 2008,19(3):183–96. 10.1097/FBP.0b013e3282fe8871
Ulrich-Lai YM, Herman JP: Neural regulation of endocrine and autonomic stress responses. Nat Rev Neurosci 2009,10(6):397–409. 10.1038/nrn2647
Pike JL, et al.: Chronic life stress alters sympathetic, neuroendocrine, and immune responsivity to an acute psychological stressor in humans. Psychosom Med 1997,59(4):447–57.
McEwen BS: Stress, adaptation, and disease. Allostasis and allostatic load. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1998, 840: 33–44. 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb09546.x
Sterling P, E J: Allostasis: a new paradigm to explain arousal pathology. In Handbook of Life Stress, Cognition, and Health. Edited by: RJ Fisher S. Wiley: NY; 1998.
Goldstein DS, McEwen B: Allostasis, homeostats, and the nature of stress. Stress 2002,5(1):55–8. 10.1080/102538902900012345
Seeman TE, et al.: Price of adaptation--allostatic load and its health consequences. MacArthur studies of successful aging. Arch Intern Med 1997,157(19):2259–68. 10.1001/archinte.157.19.2259
McEwen BS, Wingfield JC: The concept of allostasis in biology and biomedicine. Horm Behav 2003,43(1):2–15. 10.1016/S0018-506X(02)00024-7
McEwen BS, Seeman T: Protective and damaging effects of mediators of stress. Elaborating and testing the concepts of allostasis and allostatic load. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1999, 896: 30–47. 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb08103.x
Stewart JA: The detrimental effects of allostasis: allostatic load as a measure of cumulative stress. J Physiol Anthropol 2006,25(1):133–45. 10.2114/jpa2.25.133
McEwen BS: Protection and damage from acute and chronic stress: allostasis and allostatic overload and relevance to the pathophysiology of psychiatric disorders. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2004, 1032: 1–7. 10.1196/annals.1314.001
Kapczinski F, et al.: Allostatic load in bipolar disorder: implications for pathophysiology and treatment. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2008,32(4):675–92. 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2007.10.005
van Dijk G, Buwalda B: Neurobiology of the metabolic syndrome: an allostatic perspective. Eur J Pharmacol 2008,585(1):137–46. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.11.079
Glei DA, et al.: Do chronic stressors lead to physiological dysregulation? Testing the theory of allostatic load. Psychosom Med 2007,69(8):769–76. 10.1097/PSY.0b013e318157cba6
Langelaan S, et al.: Is burnout related to allostatic load? Int J Behav Med 2007,14(4):213–21. 10.1007/BF03002995
Li W, Zhang JQ, Wang S: [Research progress on allostatic load as a measurement of the effects of chronic stress]. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 2007,25(8):500–2.
Nelson KM, et al.: Peripheral arterial disease in a multiethnic national sample: the role of conventional risk factors and allostatic load. Ethn Dis 2007,17(4):669–75.
Anderson GC: Allostatic load and failure to progress. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs 2008,37(1):2–3.
Logan JG, Barksdale DJ: Allostasis and allostatic load: expanding the discourse on stress and cardiovascular disease. J Clin Nurs 2008,17(7B):201–8. 10.1111/j.1365-2702.2008.02347.x
Sabbah W, et al.: Effects of allostatic load on the social gradient in ischaemic heart disease and periodontal disease: evidence from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J Epidemiol Community Health 2008,62(5):415–20. 10.1136/jech.2007.064188
Maloney EM, et al.: Chronic fatigue syndrome and high allostatic load: results from a population-based case-control study in Georgia. Psychosom Med 2009,71(5):549–56. 10.1097/PSY.0b013e3181a4fea8
Szanton SL, et al.: Allostatic load and frailty in the women's health and aging studies. Biol Res Nurs 2009,10(3):248–56. 10.1177/1099800408323452
Von Korff M, et al.: Childhood psychosocial stressors and adult onset arthritis: broad spectrum risk factors and allostatic load. Pain 2009,143(1–2):76–83. 10.1016/j.pain.2009.01.034
McEwen BS: Mood disorders and allostatic load. Biol Psychiatry 2003,54(3):200–7. 10.1016/S0006-3223(03)00177-X
Galvin JA, et al.: The relaxation response: reducing stress and improving cognition in healthy aging adults. Complement Ther Clin Pract 2006,12(3):186–91. 10.1016/j.ctcp.2006.02.004
Angevaren M, et al.: Physical activity and enhanced fitness to improve cognitive function in older people without known cognitive impairment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2008(2):CD005381.
Fedotchev AI: [Stress, the consequences of its influence on humans and modern non-drug methods of its correction]. UspFiziol Nauk 2009,40(1):77–91.
Lysenyuk VP, et al.: Experimental study on the low-intensity millimeter-wave electro-magnetic stimulation of acupuncture points. Acupunct Electrother Res 2000,25(2):91–9.
Usichenko TI, Ivashkivsky OI, Gizhko VV: Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with electromagnetic millimeter waves applied to acupuncture points--a randomized double blind clinical study. Acupunct Electrother Res 2003,28(1–2):11–8.
Rinaldi S, Fontani V: Radioelectric Asymmetric Conveyer for therapeutic use. In European Patent Office - World Intellectual Property Organization, EP Office Edited by: Rinaldi S, Fontani V. 2000.
Lemyre L, Tessier R: Mesure de Stress Psychologique (MSP): Se sentir stressé-e. Canadian Journal of Behavioural Science 1988, 20: 302–321.
Lemyre L, Tessier R: Measuring psychological stress. Concept, model, and measurement instrument in primary care research. Can Fam Physician 2003, 49: 1159–60.
Trovato GM, et al.: Psychological stress measure in type 2 diabetes. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2006,10(2):69–74.
Collodel G, et al.: Effect of emotional stress on sperm quality. Indian J Med Res 2008,128(3):254–61.
Valberg PA, van Deventer TE, Repacholi MH: Workgroup report: base stations and wireless networks-radiofrequency (RF) exposures and health consequences. Environ Health Perspect 2007,115(3):416–24. 10.1289/ehp.9633
Bystritsky A, Kerwin L, Feusner J: A pilot study of cranial electrotherapy stimulation for generalized anxiety disorder. J Clin Psychiatry 2008,69(3):412–7. 10.4088/JCP.v69n0311
Childs A, Price L: Cranial electrotherapy stimulation reduces aggression in violent neuropsychiatric patients. Primary Psychiatry 2007,14(3):50–56. [http://www.depressiontreatmentnow.com/pp_childs_07.pdf]
Kirsch D, Smith R: Cranial electrotherapy stimulation for anxiety, depression, insomnia, cognitive dysfunction, and pain. In Bioelectromagnetic Medicine Edited by: aMSM Paul J Rosch. Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York; 2004, 727–740. [http://www.depressiontreatmentnow.com/bioelectric_medicine.pdf]
Marshall FG, Kirsch DL: Cranial Electrotherapy Stimulation Review: A Safer Alternative to Psychopharmaceuticals in the Treatment of Depression. Journal of Neurotherapy 2005,9(2):7–26. [http://www.depressiontreatmentnow.com/CES_Review.pdf] 10.1300/J184v09n02_02
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their gratitude to Matteo Lotti Margotti Eng. for randomization process and data analysis. Thanks to Giorgio Saragò M.D., and Stefania Bini M.D. for help in administering the NPPO-REAC treatment and Alessandro Castagna M.D. for his helpful support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
SR and VF are the inventors of the Radio electric Asymmetric Conveyer.
Authors' contributions
SR and VF conceived of the study, participated in its design and coordination and in drafting of the manuscript. LA has critically revised the manuscript and PM has done the psychiatric evaluation. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Salvatore Rinaldi, Vania Fontani, Lucia Aravagli contributed equally to this work.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Rinaldi, S., Fontani, V., Aravagli, L. et al. Psychometric evaluation of a radio electric auricular treatment for stress related disorders: a double-blinded, placebo-controlled controlled pilot study. Health Qual Life Outcomes 8, 31 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7525-8-31
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7525-8-31