Abstract
Background
Red wine (RW) is rich in antioxidant polyphenols that might protect from oxidative stress related diseases, such as cardiovascular disease and cancer. Antioxidant effects after single ingestion of RW or dealcoholized RW (DRW) have been observed in several studies, but results after regular consumption are contradictory. Thus, we examined if single or repeated consumption of moderate amounts of RW or DRW exert antioxidant activity in vivo.
Methods
Total phenolic content and concentration of other antioxidants in plasma/serum, total antioxidant capacity (TEAC) in plasma as well as DNA strand breaks in peripheral leukocytes were measured in healthy non-smokers A) before, 90 and 360 min after ingestion of one glass of RW, DRW or water; B) before and after consumption of one glass of RW or DRW daily for 6 weeks. DNA strand breaks (SB) were determined by single cell gel electrophoresis (Comet Assay) in untreated cells and after induction of oxidative stress ex vivo with H2O2 (300 μM, 20 min).
Results
Both RW and DRW transiently increased total phenolic content in plasma after single consumption, but only RW lead to a sustained increase if consumed regularly. Plasma antioxidant capacity was not affected by single or regular consumption of RW or DRW. Effects of RW and DRW on DNA SB were conflicting. DNA strand breaks in untreated cells increased after a single dose of RW and DRW, whereas H2O2 induced SB were reduced after DRW. In contrast, regular RW consumption reduced SB in untreated cells but did not affect H2O2 induced SB.
Conclusion
The results suggest that consumption of both RW and DRW leads to an accumulation of phenolic compounds in plasma without increasing plasma antioxidant capacity. Red wine and DRW seem to affect the occurrence of DNA strand breaks, but this cannot be referred to antioxidant effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Polyphenols show antioxidant activity in vitro and probably also in vivo and therefore might protect from oxidative stress related diseases such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, or chronic inflammatory processes [1, 2].
Red wine is rich in polyphenols [3, 4] and is one of the main polyphenol sources in western countries [5, 6]. Acute antioxidant effects after single ingestion of native and dealcoholized red wine as measured by increased antioxidant capacity in plasma or serum [7–12], reduced susceptibility of LDL to oxidation ex vivo [9], decreased plasma and urinary of F2-isoprostane concentrations [13] or protection from radiation-induced DNA damage [14] have been shown in several studies. Likewise, regular intake of red wine, dealcoholized red wine or red wine extract for 10 – 30 days induced antioxidant effects in some studies [15–20], but not in all [21–23]. Results of Cartron et al. [24] and van Golde et al. [25] even suggest prooxidant effects if red wine is consumed regularly. Hence it remains unclear if regular consumption of native or dealcoholized red wine can increase plasma antioxidant capacity and protects from oxidation in vivo. However, a sustained antioxidant response is necessary to achieve protection from oxidative stress related diseases. Hence, the aim of our study was to investigate if regular intake of moderate amounts of red wine could improve antioxidant parameters in healthy subjects, and if dealcoholized red wine could be an alternative source providing polyphenols without increasing the alcohol intake. We conducted two randomized, controlled intervention trials to examine the effects of single and repeated intake of native and dealcoholized red wine, respectively, on total phenolic content and antioxidant parameters in blood as well as on DNA strand breaks in peripheral leukocytes in healthy volunteers.
Methods
Subjects
Men and women, aged 18 – 50 y, free from any known diseases were included in the study. Smoking, excessive exercise (> 10 h/wk), pregnancy and lactation, present or former alcohol or drug abuse, medications interfering with antioxidants or intake of alcohol, supplementation of vitamins, minerals or probiotics (2 weeks before or during the study) were exclusion criteria. The study was performed according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the ethics committee of the University of Bonn. All subjects gave their informed written consent.
Study design
The study consisted of two parts, a single-dose analysis investigating the effects of a single ingestion of red wine (RW) versus dealcoholized red wine (DRW) and a long-term dietary intervention trial in which RW and DRW were consumed daily for 6 wk. Both trials were prospective, randomized and controlled studies.
Single-dose analysis
After an overnight fast, 27 healthy non-smokers (demographic data are shown in Table 1) were randomized to receive a single dose of 200 mL red wine (group RW; n = 9), 175 mL dealcoholized red wine (group DRW; n = 9), or 200 mL mineral water (controls; n = 9). Total phenolic content, total antioxidant capacity and concentrations of the major antioxidants (ascorbic acid, uric acid, albumin, bilirubin) in plasma, as well as DNA strand breaks in leukocytes (with and without ex vivo H2O2 treatment to induce oxidative stress) were measured before, 90 and 360 min after ingestion. Subjects were instructed to abstain from polyphenol rich foodstuff and from any alcoholic drinks 24 h before the first blood sampling until completion of the study. For this purpose they received a list of acceptable foods which are considered to be low in polyphenols. Compliance was controlled by a self-estimated 24-h dietary record. One hour after the first blood sampling, participants could choose from a breakfast buffet composed of foods low in polyphenols (white bread, butter, curd cheese, yogurt, cheese, honey, milk, fruit infusion, mineral water). All subjects were allowed to leave the study center at 90 min, when the initial blood samples had been drawn, and returned at 360 min for the follow-up blood samples. They were allowed to have lunch in between following the dietary restrictions concerning antioxidants.
Dietary intervention trial
Seventy-eight healthy subjects were enrolled in the dietary intervention trial. They ingested 200 mL of red wine (group RW, 27 subjects) or 175 mL dealcoholized red wine (group DRW, 26 subjects) daily within one hour after dinner for 6 wk. The control group (25 subjects) did not receive any study drink. Subjects were instructed not to drink more than 2 cups (150 mL each) of coffee, black or green tea, and 2 glasses (200 mL each) of fruit juice per day, and to renounce from grape juice, multivitamin juices, and alcoholic beverages starting one week before the intervention throughout the whole study period.
Blood samples were drawn before and after intervention after an overnight fast (between 07.30 and 09.00 a.m.), and about 12 h after the last ingestion of RW or DRW. In addition to the laboratory parameters measured in the single-dose analysis, α-tocopherol concentration in serum was determined as changes are expected only in the long term [26]. To control compliance to dietary restrictions and assess possible changes of dietary patterns due to seasonal variations during the study period, self-estimated 7-day dietary records had to be completed in the week before and in the last week of intervention.
Study drinks
The red wine used in the present studies was Spätburgunder, 1999, Marienthaler Klostergarten, Ahr, Germany. Dealcoholized red wine was produced by vacuum extraction of alcohol from the same batch. The amounts of flavonoids and phenolic acids ingested from a single serving of RW (200 mL) and DRW (175 mL) are listed in Table 2. The application of 175 mL DRW based on the assumption that 12.5% of the volume (25 mL / 200 mL) would be lost due to alcohol extraction, which would increase polyphenol concentration in DRW. However, subsequent analysis revealed a lower polyphenol content in DRW due to the processing. Thus, intake of polyphenols, especially flavonoids, was slightly lower from 175 mL DRW compared to 200 mL RW. The water for the control group in the single-dose analysis was Markus Brunnen "Still" (Vereinte Mineral- und Heilquellen, Rosbach, Germany), a carbonated natural mineral water from which iron is removed.
Dietary intake of polyphenols
The subjects received a standardized dietary record which they completed for 24 h (single-dose analysis) or 7 days (dietary intervention trial), respectively. To determine polyphenol intake as exactly as possible, polyphenol rich foods were listed in detail. Calculation of the intake of flavonoids (kaempferol, quercetin, myricetin, catechin, epicatechin, epigallocatechin, gallocatechin, naringenin, cyanidin, peonidin, petunidin, and malvidin) and phenolic acids (salicylic, p-hydroxy benzoic, gallic, syringic, and ellagic acid) was based on data of Linseisen et al. [27] and Radtke et al. [28], which were completed by data for quercetin and kaempferol in tomato products [29] and catechin and epicatechin in apples, red grapes [30], and black tea [31].
Collection of samples
Peripheral venous blood was collected in Vacutainer® tubes (Becton Dickinson, Heidelberg, Germany) containing Li-heparin or no anticoagulant. Samples were protected from light and stored on ice until centrifugation (3000 × g, 20 min, 4°C). Plasma samples for determination of total phenolic content and antioxidant capacity were stored at -70°C, and for determination of albumin, uric acid and bilirubin at -20°C. For measurement of ascorbic acid, plasma was mixed with 5% trichloro acetic acid and centrifuged (3 min, 12000 × g). Supernatants were stored at -70°C. Serum was frozen at -20°C until measurement of α-tocopherol. For determination of DNA damage, heparinized blood was kept in the dark at room temperature until processing 60 – 120 min after sampling.
Antioxidants in plasma and serum
Total phenolic content in plasma (TPP) was determined by the Folin-Ciocalteu method modified by Serafini et al. [10] to avoid plasma protein interference. Unlike Serafini et al. [10], we centrifuged the thawed plasma samples at 12000 × g for 5 min. To remove plasma proteins completely, 2 mol/L metaphosphoric acid (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) was used for precipitation and an additional centrifugation step (2700 × g, 3 min) was introduced for the combined supernatants before adding Folin-Ciocalteu reagent (Fluka Chemie, Buchs, Switzerland). Experiments were performed in duplicate.
Plasma antioxidant capacity was determined by the Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC) assay as described previously [32]. The antioxidant capacity is given in comparison to a 1 mmol/L standard solution of 6-hydroxy-2,5,7,8-tetramethylchroman-2-carboxylic acid (Trolox) (Sigma, Deisenhofen, Germany). Experiments were performed in triplicate.
To control, if antioxidants other than polyphenols could have an impact on TEAC, the following major antioxidants in blood were also measured. Vitamin C concentration in plasma was determined colorimetrically according to Speitling et al. [33]. Experiments were performed in duplicate. Uric acid, albumin and bilirubin in plasma were determined by routine procedures at the Institute for Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine, University Duesseldorf, Germany. Concentration of α-tocopherol in serum was measured by High Performance Liquid Chromatography at the Research Centre for Diabetes, Duesseldorf, Germany.
DNA strand breaks in peripheral leukocytes
Single Cell Gelelectrophoresis (Comet Assay) was performed to assess DNA strand breaks in peripheral leukocytes. In this assay, cells are embedded in agarose on slides, incubated in PBS (control cells) or H2O2 (induction of oxidative stress), and lysed. During subsequent electrophoresis, DNA regions that are relaxed due to strand breaks migrate towards the anode forming a typical comet structure.
This assay was performed according to the standard protocol of Bauch et al. [34] adapted to the use of hydrogen peroxide as a stressor. To simulate the in vivo situation as far as possible and to avoid artifacts by density centrifugation, whole blood was used instead of isolated mononuclear cells. Ten μL heparinized whole blood were diluted with 90 μL PBS (10 mmol/L, pH 7.4, without Ca2+/Mg2+) (Sigma) to obtain a single cell suspension. After preparation of the slides, they were incubated for 20 min at 4°C with either 300 μmol/L H2O2 (Sigma) in PBS to induce DNA strand breaks or in pure PBS (controls). Electrophoresis was performed at 4°C and 1 V/cm for 4 min on a flat-bed electrophoresis apparatus with electrode spacing of 39 cm (Mega Horizontal Gelbox Safety; Molecular Bio-Products, San Diego, USA). Experiments were performed in duplicate.
For analysis, gels were rehydrated in aqua bidest. (10 min, room temperature) and DNA was dyed with 150 μL propidium iodide (Sigma) (25 μmol/L, solved in 125 mmol/L Tris with 123 mmol/L NaCl in aqua bidest., pH 7.5). Measurements were performed with the image analysis software package Comet Assay II (Perceptive Instruments, Suffolk, UK) coupled to a fluorescence microscope (Leitz DM RB, Leica, Bensheim, Germany) with a CCD camera (Cohu, San Diego, USA). Fifty cells were measured on each slide and Tail Intensity (TI) and Tail Moment (TM) were calculated to quantify DNA strand breaks.
DNA strand breaks in untreated cells reflect the steady state between DNA damage and repair in vivo [35–37] and are therefore referred to as "endogenous" DNA damage in this paper. "Exogenous" DNA strand breaks are those induced by treatment with H2O2 ex vivo and were calculated as the difference between treated and untreated cells.
Sample size calculation
The sample size calculation was based on plasma antioxidant capacity (TEAC), which was considered as main outcome and based on data from a previous study with healthy subjects who ingested polyphenol rich fruit-juices or a fruit-vegetable concentrate [32]. With 6 subjects in each group (RW, ERW, controls) the single-dose analysis has a power of 90% to detect TEAC changes >0.033 mmol/L, which was the mean difference between two measurements in the previous study. To account for possible drop-outs, we included 9 subjects in each group, adding up to a total of 27 participants.
Mean TEAC difference in the previous long-term study was 0.075 mmol/L. To detect changes ≥ 0.075 mmol/L and differences between the groups with a power of 90%, a sample size of 25 subjects in each group (RW, DRW, controls) was calculated. Level of significance was 5% for all tests.
Statistical analysis
Values given are means ± SD unless indicated otherwise. Differences between the groups were examined using the Mann-Whitney U-test. The effects of the study drinks on the investigated parameters were evaluated by comparing the values obtained at different time intervals with baseline for each group using the Wilcoxon signed rank test. Differences indicated by p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Statistical tests were performed with SPSS 10.0 for Windows (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
Results
Single-dose analysis
The day before the study the subjects ingested 22.9 ± 47.4 mg polyphenols (Flavonoids: 2.1 ± 5.3 mg; Phenolic acids: 20.8 ± 46.2 mg). This corresponds to 8 – 16% of the average intake observed in another German cohort [27, 28] and in our dietary intervention trial (see below) indicating good compliance to the dietary restrictions.
Results for the antioxidant parameters in plasma are presented in Table 3. Total phenolic content in plasma increased 90 min after ingestion of RW (p = 0.008) or DRW (p = 0.008). After 360 min values were higher than at baseline in groups RW (p = 0.02) and DRW (p = 0.008), but also in control subjects (p = 0.01). Vitamin C concentration in plasma decreased 360 min after RW consumption (p = 0.008), but increased in group DRW (p = 0.02). Significant changes of endogenous antioxidants, i.e. uric acid, albumin or bilirubin, have been observed after consumption of RW and DRW, and also in the control group, but TEAC was not altered significantly in any group.
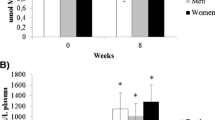
Endogenous DNA strand breaks increased 360 min after consumption of either RW or DRW compared to baseline values. In group DRW an increase could be observed after 90 min, but only with borderline significance (p = 0.05). Hydrogen peroxide-induced DNA strand breaks decreased in group DRW at 360 min, whereas no alterations could be observed after RW consumption or in controls. Statistical analysis provides the same results for TI (Figure 1) and TM (Table 3).
DNA strand breaks in peripheral leukocytes after single ingestion of native or dealcoholized red wine. A) Tail Intensity in untreated cells (endogenous DNA strand breaks) B) Tail Intensity in cells treated with 300 μM H2O2 for 20 min (exogenous DNA strand breaks)Amounts of study drinks ingested were 200 mL red wine (RW), 175 mL dealcoholized red wine (DRW) or 200 mL water (Controls) The box represents the distribution falling between the 25th and 75th percentiles, with the median as the horizontal line within the box. The whiskers connect the largest and smallest values not categorized as outliers or extreme values, which are represented by single data points. *, ** Values different from baseline, *P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01 by Wilcoxon signed rank test a,bValues marked with identical letters differ between groups, P < 0.01 by Mann-Whitney U-test
Dietary intervention trial
Four subjects were lost during the study. One woman in group DRW did not tolerate the study drink. The other subjects were allocated to group RW. Of those, one woman fell ill, which was not related to the intervention. One man started smoking during the study and the other one was lost to follow-up. Demographic data of the 74 subjects who completed the study are summarized in Table 1.
Flavonoid intake increased significantly in group RW (28.9 ± 16.6 vs. 76.7 ± 24.5 mg/d; p < 0.001) and DRW (39.1 ± 20.5 vs. 64.2 ± 27.6 mg/d; p < 0.001), but not in controls (37.7 ± 21.3 vs. 41.0 ± 24.8 mg/d). During intervention, the flavonoid intake in group RW exceeded that in group DRW (p = 0.005), and it was higher in group RW (p < 0.001) and DRW (p = 0.005) than in controls. Intake of phenolic acids increased during supplementation of RW (107.8 ± 75.5 vs. 135.1 ± 82.5 mg/d; p = 0.01) and DRW (123.5 ± 83.2 vs. 158.3 ± 102.7 mg/d; p = 0.02), but also in controls (87.2 ± 69.7 vs. 135.6 ± 100.3 mg/d; p = 0.03). The amounts did not differ between the groups before or during intervention.
The difference to the average intake of 54 mg/d flavonoids [27] and 222 mg/d phenolic acids [28] reported by others could be explained by the restriction of polyphenol rich foods, especially coffee, which is a major source of phenolic acids in Germany [28].
Total phenolic content in plasma (Table 4) increased after 6 wk regular consumption of RW (p = 0.002), but did not change in group DRW or controls. A significant increase of plasma uric acid concentration was observed in controls (p = 0.04), and a decrease of bilirubin in group DRW (p = 0.02) (Table 4). In contrast, vitamin C and albumin in plasma, α-tocopherol in serum, and plasma antioxidant capacity did not change significantly in any group (Table 4). There was no significant difference between the groups before and after 6 wk of intervention considering the antioxidant parameters.
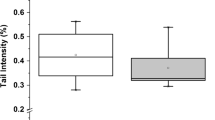
Endogenous DNA strand breaks (Figure 2, Table 4) decreased only after regular consumption of RW (TI: p = 0.03; TM: p = 0.04), but not in group DRW and controls. Susceptibility of leukocytes towards H2O2-induced DNA damage was not altered in any group. Differences in endogenous or ex vivo induced DNA strand breaks could not be observed between the groups, neither before nor after 6 wk intervention (Figure 2, Table 4).
DNA strand breaks in peripheral leukocytes after regular consumption of native or dealcoholized red wine. Amounts ingested daily for 6 weeks were 200 mL red wine (RW) or 175 mL dealcoholized red wine (DRW). Control subjects did not receive any study drink. TI0: Tail Intensity in untreated cells (endogenous DNA strand breaks); TI300: Tail Intensity in cells treated with 300 μM H2O2 for 20 min (exogenous DNA strand breaks)Boxes represent the distribution falling between the 25th and 75th percentiles, with the median as the horizontal line within the box. The whiskers connect the largest and smallest values not categorized as outliers or extreme values, which are represented by single data points. *Value different from baseline, P < 0.05 by Wilcoxon signed rank test.
Discussion
The present studies demonstrate that polyphenols from RW and DRW are bioavailable and accumulate in plasma after regular consumption. Even though total antioxidant capacity in plasma did not change after RW or DRW consumption, both drinks affected DNA strand breaks in peripheral leukocytes. Results are contradictory, as DNA damaging effects of RW and DRW occur after single ingestion, whereas regular RW consumption seems to protect from endogenous DNA strand breaks. Further investigations are required to clarify whether interactions of red wine polyphenols with cellular DNA result in genotoxic or anticarcinogenic effects.
The results of the single-dose analysis confirm that polyphenols are bioavailable from both RW and DRW [8, 10, 11], and that alcohol does not significantly affect polyphenol absorption in humans [38–40]. Accumulation of phenolic compounds in plasma could be measured after regular consumption of RW corresponding to previous findings [16, 19] but not in group DRW. We assume that this is rather due to the slightly lower intake of polyphenols from DRW than to different alcohol content [38–40].
The impact of phenolic compounds from RW and DRW on the pro-/antioxidant balance in plasma seems to be low, as plasma antioxidant capacity was neither altered significantly in the short nor in the long term as also reported by others [7, 20, 22, 23]. There was no effect of RW or DRW consumption on antioxidant vitamins in the dietary intervention trial corresponding to the findings of previous studies [17, 20]. Interestingly, the concentration of vitamin C in plasma increased 360 min after consumption of one single dose of DRW whereas it decreased after RW suggesting that the polyphenols might act as antioxidants in vivo but this is counteracted by prooxidant effects of alcohol in native RW [13, 23]. Changes in vitamin C levels did not have a significant impact on plasma antioxidant capacity but might have protected cellular DNA from oxidation ex vivo, which will be discussed later on.
Uric acid, one of the main antioxidants contributing to plasma antioxidant capacity [13, 32], increased after single RW consumption as expected [13, 41]. However, the increase of 15% in TEAC observed after 90 min, even in combination with a 17% increase of total phenolic content did not lead to a significant rise of plasma TEAC. This supports the observations of Cao et al. [7] implying that the TEAC method is not sensitive enough to measure small changes in the pro-antioxidant balance after ingestion of foods rich in polyphenols.
Further changes of albumin, uric acid and bilirubin concentrations occurred in both trials, probably due to normal biological variance, but they were not associated with changes of plasma TEAC.
In contrast to antioxidant capacity, there was a significant effect of RW and DRW on DNA strand breaks in peripheral leukocytes suggesting interactions of red wine polyphenols with cellular DNA. Regular consumption of RW protects cellular DNA from strand breaks in vivo, which corresponds to findings of previous studies [18, 42], probably due to DNA stabilizing and/or antioxidant effects of RW polyphenols [43]. In contrast, single ingestion of RW or DRW increased endogenous DNA strand breaks. This was not expected as DNA damaging effects of RW polyphenols have been observed only in vitro and for concentrations of 25–1000 μM [44–46], whereas in human plasma polyphenols occur mainly as metabolites and in concentrations below 1 μM [6]. As the same outcome was found in groups RW and DRW, genotoxic effects of alcohol [47] can also be excluded. Since strand breaks occur during DNA repair via base or nucleotide excision [35], increased DNA strand breaks as observed in our study might also result from activation of DNA repair enzymes by polyphenols [48]. To clarify the mechanisms, a modified protocol for the single cell gel electrophoresis allowing to separately assessing oxidation of purine and pyrimidin bases [35] as well as DNA repair kinetics [49] should be used in future studies.
The discrepancy between increased DNA strand breaks after single and reduced DNA strand breaks after repeated consumption of RW might be due to different polyphenols which might have been present in plasma or leukocytes after single or regular consumption, respectively. This would be plausible regarding the different elimination half lives of the various RW polyphenols and their metabolites [6, 39, 50, 51], but quantitative analysis of single polyphenolic compounds in plasma/cells would be necessary to confirm this. Furthermore, the different mode of RW consumption in the short- and the long-term study (after an overnight fast vs. regularly after dinner) could also provide an explanation. Since consumption of RW with meals reduces prooxidative effects occurring post-prandially [24, 52, 53], the DNA protective effects of RW in our dietary intervention trial might have resulted from reduced prooxidative effects of the meals, which were lacking in the single-dose analysis.
Exogenous DNA strand breaks, which reflect the activity of non-enzymatic antioxidants [35, 37], have only been reduced after single consumption of DRW, which corresponds to the results of a recent study showing that consumption of 300 mL DRW protected lymphocytes from radiation-induced DNA damage ex vivo [14]. As in our study the plasma phenolic content was not different between groups RW and DRW, the increased vitaminC concentration in plasma observed in group DRW might have protected leukocyte DNA against oxidative stress ex vivo. Indeed, DNA protecting effects of vitamin C have been described in vitro [54, 55] and are also supposed to occur in vivo [36, 56, 57]. This is also supported by Greenrod et al. [14] who observed that the contribution of catechin to DNA protecting effects or DRW is quite small, and that other factors seem to play an important role.
It has to be noted that in the dietary intervention trial consumption of RW and DRW lead to an increase in flavonoid intake compared to baseline and to controls, whereas phenolic acid consumption increased in RW, DRW and controls after 6 weeks compared to baseline without any differences between the groups. This is probably due to seasonal variations of the food pattern as our study period was between May and July, when consumption of fresh fruit rich in phenolic acids increased (data not shown). Hence, the observed effects of RW on DNA strand breaks in peripheral leukocytes can be attributed to the additional intake of flavonoids rather than to phenolic acids.
The major advantage of our study compared to others is the investigation of both single and regular consumption of RW and DRW which has only been done so far by Cartron et al. [24]. In both studies substantial differences between short- and long-term effects occurred implying that single-dose analysis alone are not appropriate to investigate potential health effects of red wine consumption.
However, our study has some constraints, regarding the different polyphenol intake with RW and DRW, which does not allow a direct comparison of both study drinks. In future studies, drinks with equal polyphenol composition should be applied. Moreover, in the single dose analysis TPP increased 360 min after intervention in groups RW and DRW, but also in controls. This could be due to 1) unknown amounts of polyphenols in "permitted" foods (e.g. white bread or pasta). These foods are generally considered to be low in polyphenols and thus, are not listed in the polyphenol database [27, 28]. Nevertheless, they may have provided considerable amounts of polyphenols, especially phenolic acids [50] leading to an increase of TPP in the control group. 2) As food intake at lunchtime was not recorded, we cannot exclude that the volunteers failed to comply with the polyphenol poor diet in the time interval between blood sampling at 90 and 360 min. To avoid these confounding factors in future short-term studies we strongly recommend to provide the subjects with standardized amounts of polyphenol free formula diets instead of foods low in polyphenols ad libitum.
It is unlikely that random inhomogeneities of the groups (Table 1) would have influenced our results. In the single-dose analysis, control subjects were only slightly older (≈ 5 years) than those in group RW and DRW and therefore metabolic alterations are not expected. In the dietary intervention trial, the higher body weight and BMI in group RW could have reduced the response to RW, as the intake of polyphenols / kg body weight was lower in that group. However, effects on plasma phenolic content and DNA strand breaks occurred only with RW, and even more pronounced effects might have been observed in subjects with a lower body weight.
Conclusion
One glass of RW or DRW is sufficient to transiently increase concentration of phenolic compounds in plasma, but accumulation after regular consumption could only be shown for RW. Polyphenols from RW and DRW seem to affect DNA damage in leukocytes, but antioxidant effects probably play only a minor role. Endogenous DNA strand breaks increased after a single dose of RW or DRW but could be reduced after 6 wk daily consumption of RW. As DNA damage is involved in cancer initiation, the mechanisms and the physiological relevance of these findings are worth being considered in future studies.
Abbreviations
- (RW):
-
Red wine
- (DRW):
-
dealcoholized red wine
- (TEAC):
-
total antioxidant capacity
- (TPP):
-
total phenolic content in plasma.
References
Hollman PCH: Evidence for health benefits of plant phenols: local or systemic effects?. J Sci Food Agr. 2001, 81: 842-852. 10.1002/jsfa.900.
Nijveldt RJ, van Nood E, van Hoorn DEC, Boelens PG, van Norren K, van Leeuwen PAM: Flavonoids: a review of probable mechanisms of action and potential applications. Am J Clin Nutr. 2001, 74: 418-425.
Soleas GJ, Diamandis EP, Goldberg DM: Wine as a biological fluid: history, production, and role in disease prevention. J Clin Lab Analysis. 1997, 11: 287-313. 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2825(1997)11:5<287::AID-JCLA6>3.0.CO;2-4.
Mattivi U, Zulian C, Nicolini G, Valenti L: Wine, biodiversity, technology, and antioxidants. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002, 957: 37-56.
Hertog MGL, Kromhout D, Aravanis C, Blackburn H, Buzina R, Fidanza F, Giampaoli S, Jansen A, Menotti A, Nedeljkovc S, et al: Flavonoid intake and long-term risk of coronary heart disease and cancer in the Seven Countries Study. Arch Intern Med. 1995, 155: 381-386. 10.1001/archinte.155.4.381.
Scalbert A, Williamson G: Dietary intake and bioavailability of polyphenols. J Nutr. 2000, 130 (Suppl 8S): 2073S-2085S.
Cao G, Russel RM, Lischner N, Prior RL: Serum antioxidant capacity is increased by consumption of strawberries, spinach, red wine or vitamin C in elderly women. J Nutr. 1998, 128: 2383-2390.
Duthie GG, Pedersen MW, Gardner PT, Morrice PC, McJenkinson A, McPhail DB, Steele GM: The effect of whisky and wine consumption on total phenol content and antioxidant capacity of plasma from healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1998, 52: 733-736. 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600635.
Serafini M, Laranjinha JAN, Almeida LM, Maiani G: Inhibition of human LDL lipid peroxidation by phenol-rich beverages and their impact on plasma total antioxidant capacity in humans. J Nutr Biochem. 2000, 11: 585-590. 10.1016/S0955-2863(00)00124-8.
Serafini M, Maiani G, Ferro-Luzzi A: Alcohol-free red wine enhances plasma antioxidant capacity in humans. J Nutr. 1998, 128: 1003-1007.
Simonetti P, Gardana C, Pietta P: Plasma levels of caffeic acid and antioxidant status after red wine intake. J Agric Food Chem. 2001, 49: 5964-5968. 10.1021/jf010546k.
Whitehead TP, Robinson D, Allaway S, Syms J, Hale A: Effect of red wine ingestion on the antioxidant capacity of serum. Clin Chem. 1995, 41: 32-35.
Abu-Amsha Caccetta R, Burke V, Mori TA, Beilin LJ, Puddey IB, Kroft KD: Red wine polyphenols, in the absence of alcohol, reduce lipid peroxidative stress in smoking subjects. Free Rad Biol Med. 2001, 30: 636-642. 10.1016/S0891-5849(00)00497-4.
Greenrod W, Stockley CS, Burcham P, Abbey M, Fenech M: Moderate acute intake of de-alcoholised red wine, but not alcohol, is protective against radiation-induced DNA damage ex vivo – Results of a comparative in vivo intervention study in younger men. Mutat Res. 2005, 591: 290-301.
Carbonneau MA, Leger CL, Monnier L, Bonnet C, Michel F, Fouret G, Dedeieu F, Descomps B: Supplementation with wine phenolic compounds increases the antioxidant capacity of plasma and vitamin E of low-density lipoprotein without changing the lipoprotein Cu(2+)-oxidizability: possible explanation by phenolic location. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1997, 51: 682-690. 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600464.
Fuhrman B, Lavy A, Aviram M: Consumption of red wine with meals reduces the susceptibility of human plasma and low-density lipoprotein to lipid-peroxidation. Am J Clin Nutr. 1995, 61: 549-554.
Chopra M, Fitzsimons PEE, Strain JJ, Thurnham DI, Howard AN: Nonalcoholic red wine extract and quercetin inhibit LDL oxidation without affecting plasma antioxidant vitamin and carotenoid concentrations. Clin Chem. 2000, 46: 1162-1170.
Leighton F, Cuevas A, Guasch V, Pérez DD, Strobel P, San Martín A, Urzua U, Díez MS, Foncea R, Castillo O, et al: Plasma polyphenols and antioxidants, oxidative DNA damage and endothelial function in a diet and wine intervention study in humans. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1999, XXV: 133-141.
Nigdikar SV, Williams NR, Griffin BA, Howard AN: Consumption of red wine polyphenols reduces the susceptibility of low-density lipoproteins to oxidation in vivo. Am J Clin Nutr. 1998, 68: 258-265.
Tsang C, Higgins S, Duthie GG, Duthie SJ, Howie M, Mullen W, Lean MEJ, Crozier A: The influence of moderate red wine consumption on antioxidant status and indices of oxidative stress associated with CHD in healthy volunteers. Br J Nutr. 2005, 93: 233-240. 10.1079/BJN20041311.
de Rijke YB, Demacker PN, Assen NA, Sloots LM, Katan MB, Stalenhoef AF: Red wine consumption does not affect oxidizability of low-density lipoproteins in volunteers. Am J Clin Nutr. 1996, 63: 329-334.
Sharpe PC, McGrath LT, McClean E, Young IS, Archbold GPR: Effect of red wine consumption on lipoprotein (a) and other risk factors for atherosclerosis. Q J Med. 1995, 88: 101-108.
van der Gaag MS, van den Berg R, van den Berg H, Schaafsma G, Hendriks HF: Moderate consumption of beer, red wine and spirits has counteracting effects on plasma antioxidants in middle-aged men. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2000, 54: 586-591. 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601061.
Cartron E, Fouret G, Carbonneau MA, Lauret C, Michel F, Monnier L, Descomps B, Léger CL: Red-wine beneficial long-term effect on lipids but not on antioxidant characteristics in plasma in a study comparing three types of wine – Description of two O-methylated derivatives of gallic acid in humans. Free Radic Res. 2003, 37: 1021-1035. 10.1080/10715760310001598097.
van Golde PHM, Sloots LM, Vermeulen WP, Wielders JPM, Hart HC, Bouma BN, van de Weil A: The role of alcohol in the anti low density lipoprotein oxidation activity of red wine. Atherosclerosis. 1999, 147: 365-370. 10.1016/S0021-9150(99)00206-3.
Pietta P, Simonetti P, Gardana C, Brusamolino A, Morazzoni P, Bombardelli E: Relationship between rate and extent of catechin absorption and plasma antioxidant status. Biochem Mol Biol Int. 1998, 46: 895-903.
Linseisen J, Radtke J, Wolfram G: Flavonoidzufuhr Erwachsener in einem bayerischen Teilkollektiv der Nationalen Verzehrsstudie. Z Ernährungswiss. 1997, 36: 403-412. 10.1007/BF01617836.
Radtke J, Linseisen J, Wolfram G: Phenolsäurezufuhr Erwachsener in einem bayerischen Teilkollektiv der Nationalen Verzehrsstudie. Z Ernährungswissen. 1998, 37: 190-197. 10.1007/s003940050016.
Stewart AJ, Bozonnet S, Mullen W, Jenkins GI, Lean ME, Crozier A: Occurrence of flavonols in tomatoes and tomato-based products. J Agric Food Chem. 2000, 48: 2663-2669. 10.1021/jf000070p.
Arts ICW, van den Putte B, Hollman PCH: Catechin content of foods commonly consumed in the Netherlands. 1. Fruits, vegetables, staple foods, and processed foods. J Agric Food Chem. 2000, 48: 1746-1751. 10.1021/jf000025h.
Arts ICW, Van den Putte B, Hollman PCH: Catechin content of foods commonly consumed in the Netherlands. 2. Tea, wine, fruit juices, and chocolate milk. J Agric Food Chem. 2000, 48: 1752-1757. 10.1021/jf000026+.
Arendt BM, Boetzer AM, Winkler P, Lemoch H, Rockstroh JK, Berthold HK, Spengler U, Goerlich R: Plasma antioxidant capacity of HIV-seropositive and healthy subjects during long-term ingestion of fruit juices or a fruit-vegetable-concentrate containing antioxidant polyphenols. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2001, 55: 786-792. 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601227.
Speitling A, Hüppe R, Kohlmeier M, Matiaske B, Stelte W, Thefeld W, Wetzel S: VERA-Schriftenreihe. 1992, Niederkleen: Wiss. Fachverlag Dr. Fleck
Bauch T, Böcker W, Mallek U, Müller W-U, Streffer C: Optimization and standardization of the "Comet Assay" for analyzing the repair of DNA damage in cells. Strahlenther Onkol. 1999, 175: 333-340. 10.1007/s000660050020.
Duthie SJ, Ma A, Ross MA, Collins AR: Antioxidant supplementation decreases oxidative DNA damage in human lymphocytes. Cancer Res. 1996, 56: 1291-1295.
Møller P, Loft S: Oxidative DNA damage in human white blood cells in dietary antioxidant intervention studies. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002, 76: 303-310.
Riso P, Santangelo A, Porrini M: The comet assay for the evaluation of cell resistance to oxidative stress. Nutr Res. 1999, 19: 325-333. 10.1016/S0271-5317(99)00002-0.
Bell JRC, Donovan JL, Wong R, Waterhouse AL, German JB, Walzem RL, Kasim-Karakas SE: (+)-Catechin in human plasma after ingestion of a single serving of reconstituted red wine. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000, 71: 103-108.
Donovan JL, Bell JRC, Kasim-Karakas SE, German JB, Walzem RL, Hansen RJ, Waterhouse AL: Catechin is present as metabolites in human plasma after consumption of red wine. J of Nutrition. 1999, 129: 1662-1668.
Bub A, Watzl B, Heeb D, Rechkemmer G, Briviba K: Malvidin-3-glucoside bioavailability in humans after ingestion of red wine, dealcoholized red wine and red grape juice. Eur J Nutr. 2001, 40: 113-120. 10.1007/s003940170011.
Abu-Amsha Caccetta R, Croft KD, Beilin LJ, Puddey IB: Ingestion of red wine significantly increases plasma phenolic acid concentrations but does not acutely affect ex vivo lipoprotein oxidizability. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000, 71: 67-74.
Fenech M, Stockley C, Aitken C: Moderate wine consumption protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced DNA damage. Mutagenesis. 1997, 12: 289-296.
Duthie SJ, Dobson VL: Dietary flavonoids protect human colonocyte DNA from oxidative attack in vitro. Eur J Nutr. 1999, 38: 28-34. 10.1007/s003940050043.
Duthie SJ, Johnson W, Dobson VL: The effect of dietary flavonoids on DNA damage (strand breaks and oxidised pyrimidines) and growth in human cells. Mutat Res. 1997, 390: 141-151.
Johnson MK, Loo G: Effects of epigallocatechin gallate and quercetin on oxidative damage to cellular DNA. Mutat Res. 2000, 459: 211-218.
Szeto YT, Benzie IF: Effects of dietary antioxidants on human DNA ex vivo. Free Radic Res. 2002, 36: 113-118. 10.1080/10715760210161.
Greenrod W, Fenech M: The principal phenolic and alcoholic components of wine protect human lymphocytes against hydrogen peroxide- and ionizing radiation-iduced DNA damage in vitro. Mutagenesis. 2003, 18: 119-126. 10.1093/mutage/18.2.119.
Ferguson LR: Role of plant polyphenols in genomic stability. Mutat Res. 2001, 475: 89-111.
Collins AR, MA AG, Duthie SJ: The kinetics of repair of oxidative DNA damage (strand breaks and oxidized pyrimidines) in human cells. Mutat Res. 1995, 336: 69-77.
Rechner AR, Kuhnle G, Bremner P, Hubbard GP, Moore KP, Rice-Evans CA: The metabolic fate of dietary polyphenols in humans. Free Radic Biol Med. 2002, 33: 220-235. 10.1016/S0891-5849(02)00877-8.
Boyle SP, Dobson VL, Duthie SJ, Hinselwood DC, Kyle JA, Collins AR: Bioavailability and efficiency of rutin as an antioxidant: a human supplementation study. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2000, 54: 774-782. 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601090.
Natella F, Ghiselli A, Guidi A, Ursini F, Scaccini C: Red wine mitigates the postprandial increase of LDL susceptibility to oxidation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2001, 30: 1036-1044. 10.1016/S0891-5849(01)00504-4.
Ursini F, Zamburlini A, Cazzolato G, Maiorino M, Bittolo Bon G, Sevanian A: Postprandial plasma lipid hydroperoxides: a possible link between diet and atherosclerosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 1998, 25: 250-252. 10.1016/S0891-5849(98)00044-6.
Fabiani R, De Bartolomeo A, Rosignoli P, Morozzi G: Antioxidants prevent the lymphocyte DNA damage induced by PMA-stimulated monocytes. Nutr Cancer. 2001, 39: 284-291. 10.1207/S15327914nc392_19.
Noroozi M, Burns J, Crozier A, Kelly IE, Lean MEJ: Prediction of dietary flavonol consumption from fasting plasma concentration or urinary excretion. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2000, 54: 143-149. 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600908.
Lenton KJ, Therriault H, Fulop T, Payette H, Wagner JR: Glutathione and ascorbate are negatively correlated with oxidative DNA damage in human lymphocytes. Carcinogenesis. 1999, 20: 607-613. 10.1093/carcin/20.4.607.
Cadenas S, Barja G, Poulsen HE, Loft S: Oxidative DNA damage estimated by oxo8dG in the liver of guinea-pigs supplemented with graded dietary doses of ascorbic acid and alpha-tocopherol. Carcinogenesis. 1997, 18: 2373-2377. 10.1093/carcin/18.12.2373.
Acknowledgements
We thank the State Winery Marienthal, Germany, for providing the wine, Carl Jung GmbH, Ruedesheim, Germany, for dealcoholization of the wine, Prof. Dr. Dietrich, Department of Wine Analysis and Beverage Research, Geisenheim, Germany, for polyphenol analysis of the study drinks, Dr. Susanto, Research Centre for Diabetes, Duesseldorf, Germany, for analysis of α-tocopherol in serum, and the Institute for Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine, University Duesseldorf, Germany, for analysis of uric acid in plasma. We thank Dr. Thomas Bauch, Institute for Medical Radiobiology, University Clinics of Essen, Germany, for introducing us to the comet assay and are grateful to the volunteers participating in these studies. The work was supported by scholarships from the Friedrich-Ebert-Foundation (BMA) and the Landesgraduiertenfoerderung North-Rhine-Westphalia (SE) and by a grant from the German Wine Academy Mainz, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
BMA participated in study design and coordination, carried out the trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity assay and the single cell gel electrophoresis, did the statistical analysis and drafted the article. SE was involved in study design and realization and helped to draft the manuscript. KK measured total phenolic content and vitamin C concentration in plasma, and analysed the dietary records together with LG. RF did the sample size calculation and contributed to the statistical analysis. US supervised the clinical part of the study. W-UM supported the implementation, data analysis and interpretation of the single cell gel electrophoresis. RG had the initial idea and supervised the study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Arendt, B.M., Ellinger, S., Kekic, K. et al. Single and repeated moderate consumption of native or dealcoholized red wine show different effects on antioxidant parameters in blood and DNA strand breaks in peripheral leukocytes in healthy volunteers: a randomized controlled trial [ISRCTN68505294]. Nutr J 4, 33 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-4-33
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-4-33